Enhanced Remediation of Lead and Cadmium by the Co-System of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Immobilized on Goethite-Modified Biochar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Performance of Strain L1
2.3. Synthesis of Goethite-Modified Biochar and Immobilization of PSB
2.4. Aqueous Solution Adsorption Experiment
2.5. Soil Incubation Experiment
2.6. Characterization
2.7. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Strain L1
3.1.1. Identification of Strain L1
3.1.2. Phosphate-Solubilizing Ability of Strain L1
3.1.3. The Growth Curve of Strain L1
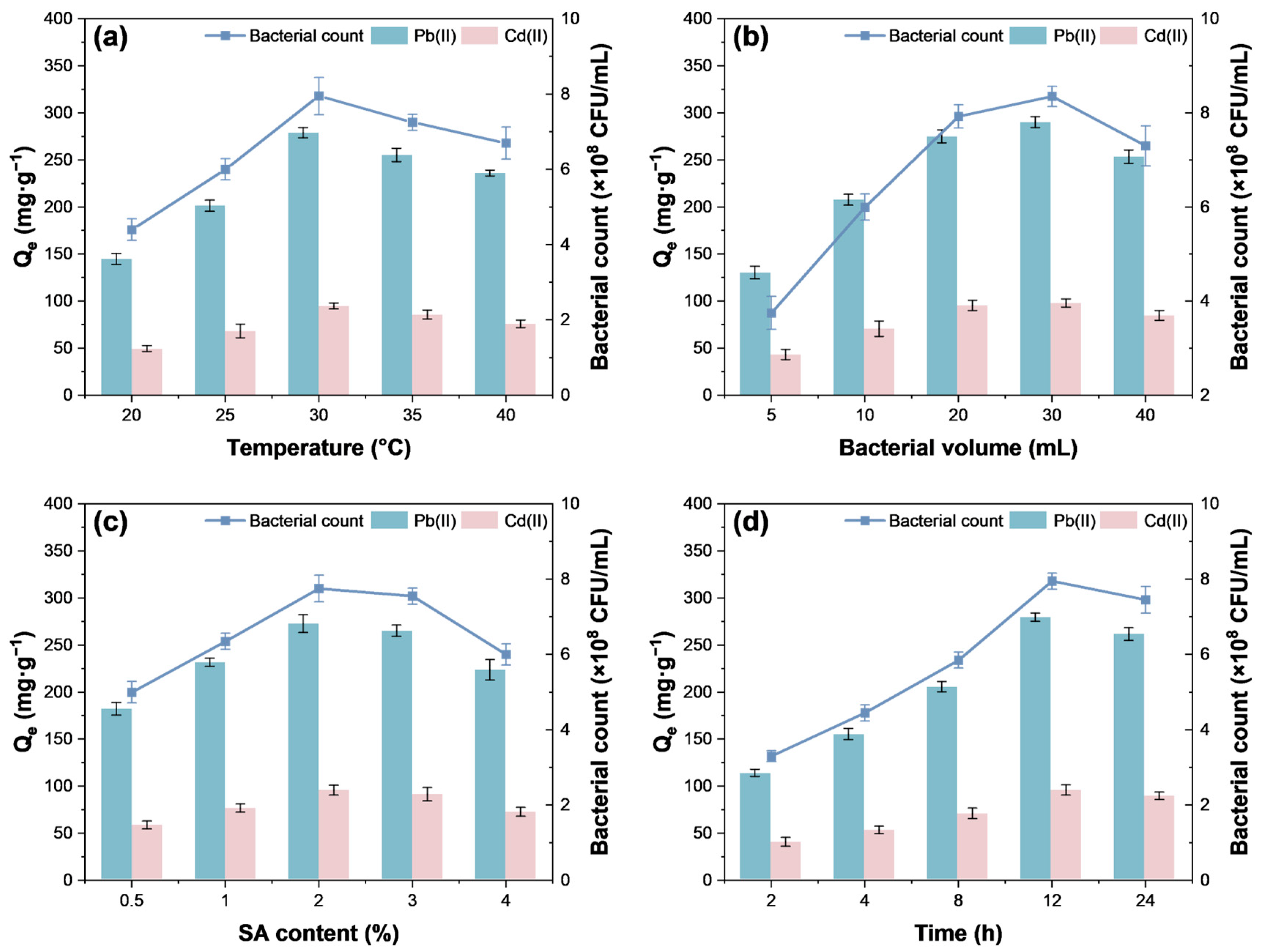
3.2. Optimization of Immobilization Conditions
3.2.1. Temperature
3.2.2. Bacterial Volume
3.2.3. SA Content
3.2.4. Cross-Linking Time
3.3. Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solution
3.3.1. Removal of Heavy Metals in Different Treatments
3.3.2. Effect of Different Factors on Heavy Metal Removal
3.3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
3.3.4. Adsorption Isotherm
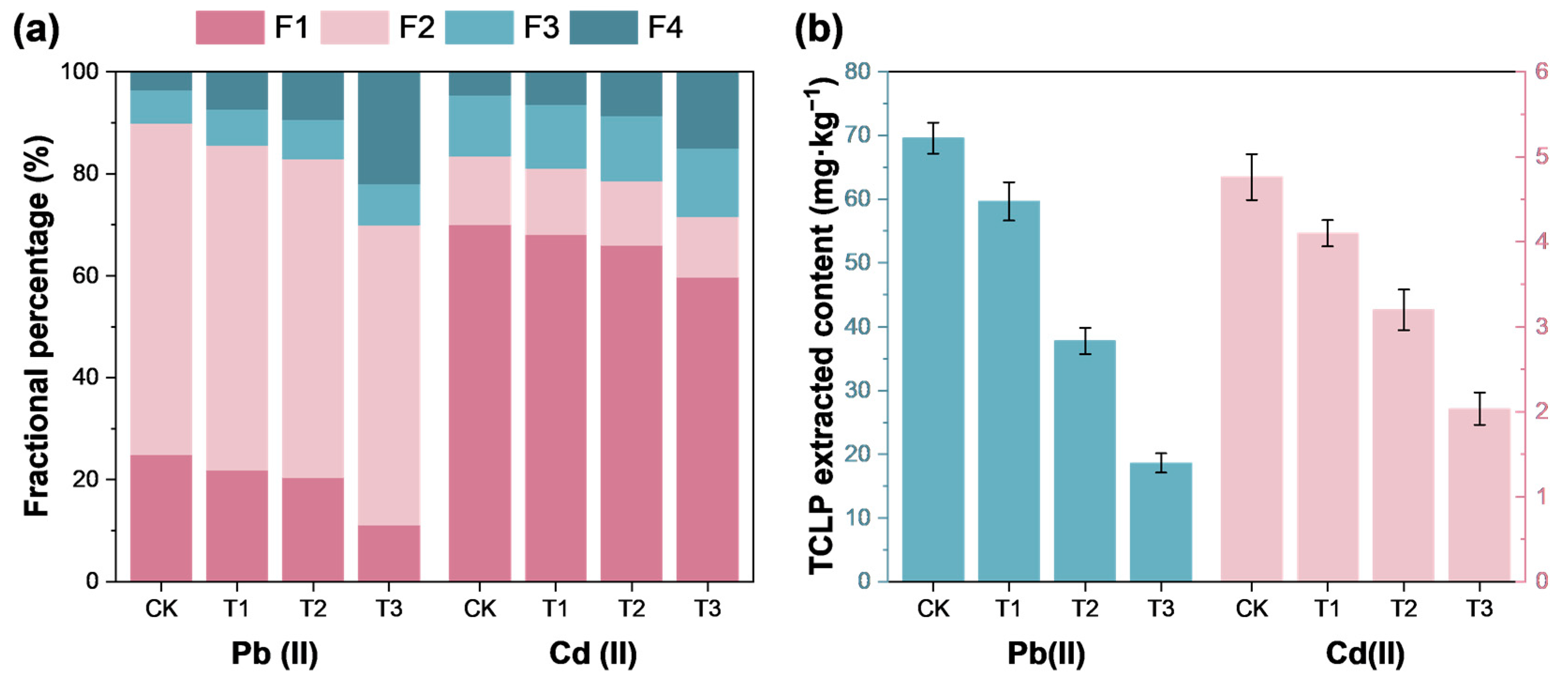
3.4. Immobilization of Heavy Metals in Soil
3.4.1. Fractions of Heavy Metals in Soil
3.4.2. TCLP-Extracted Heavy Metals and Ecological Risk Assessment
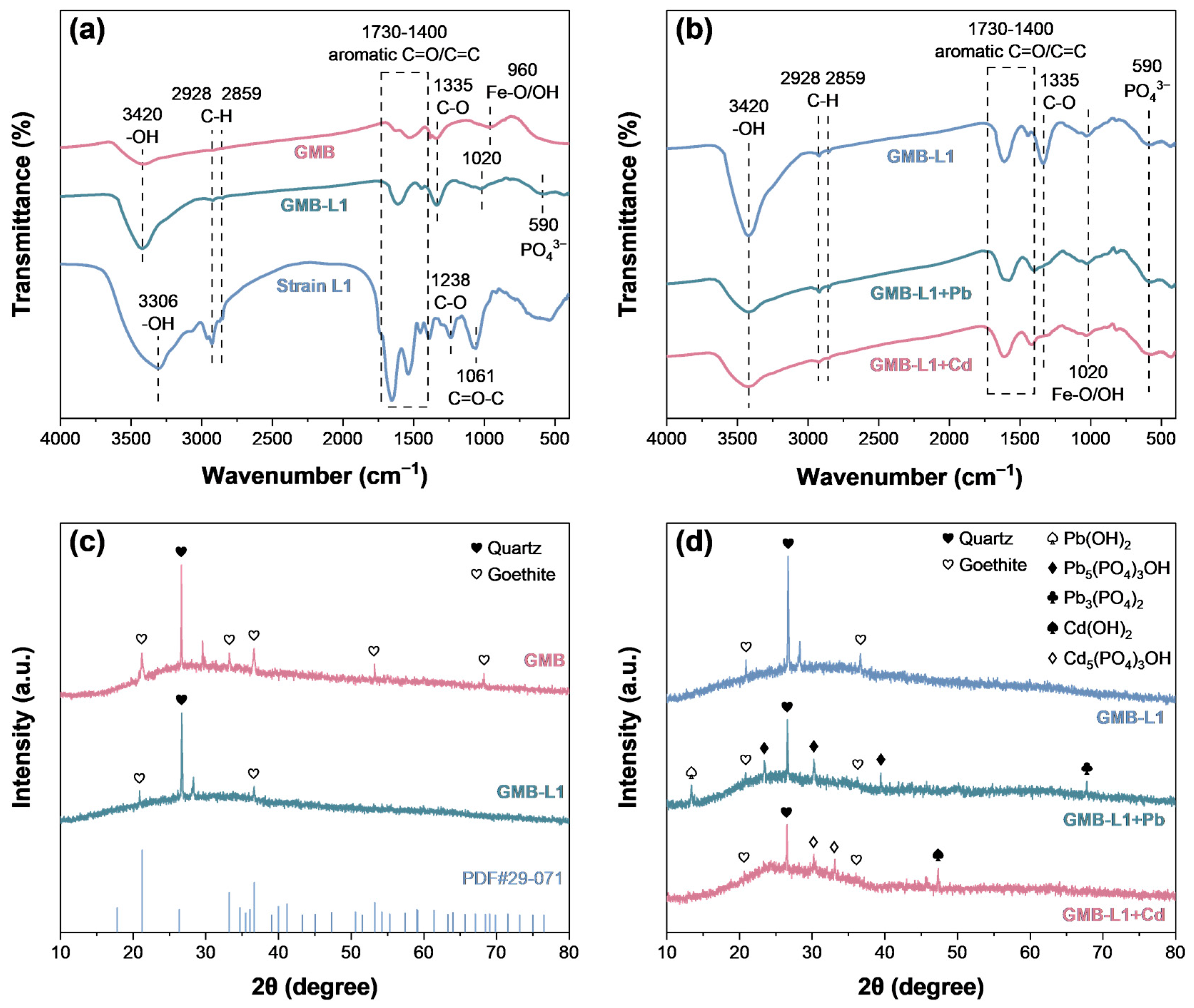
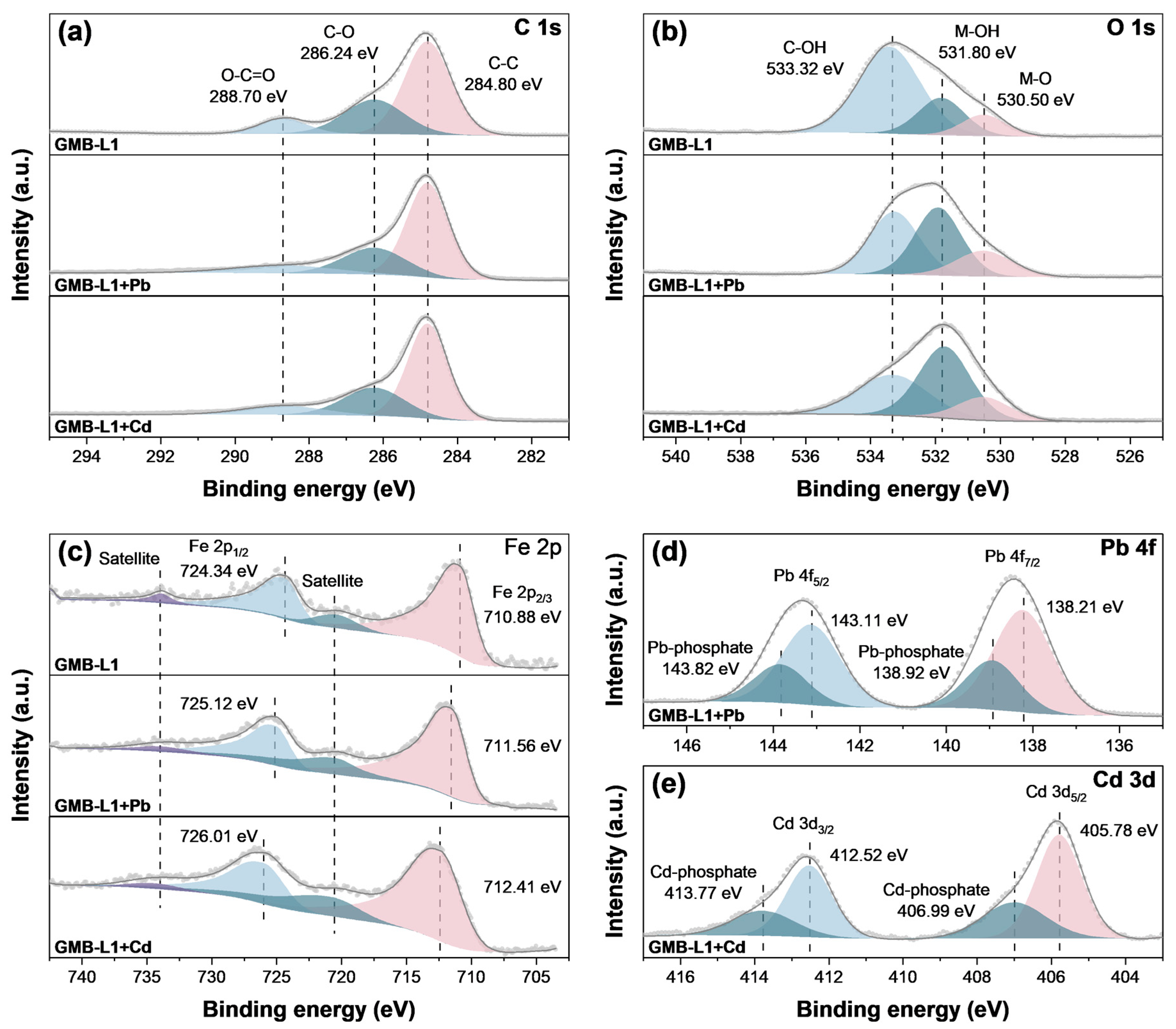
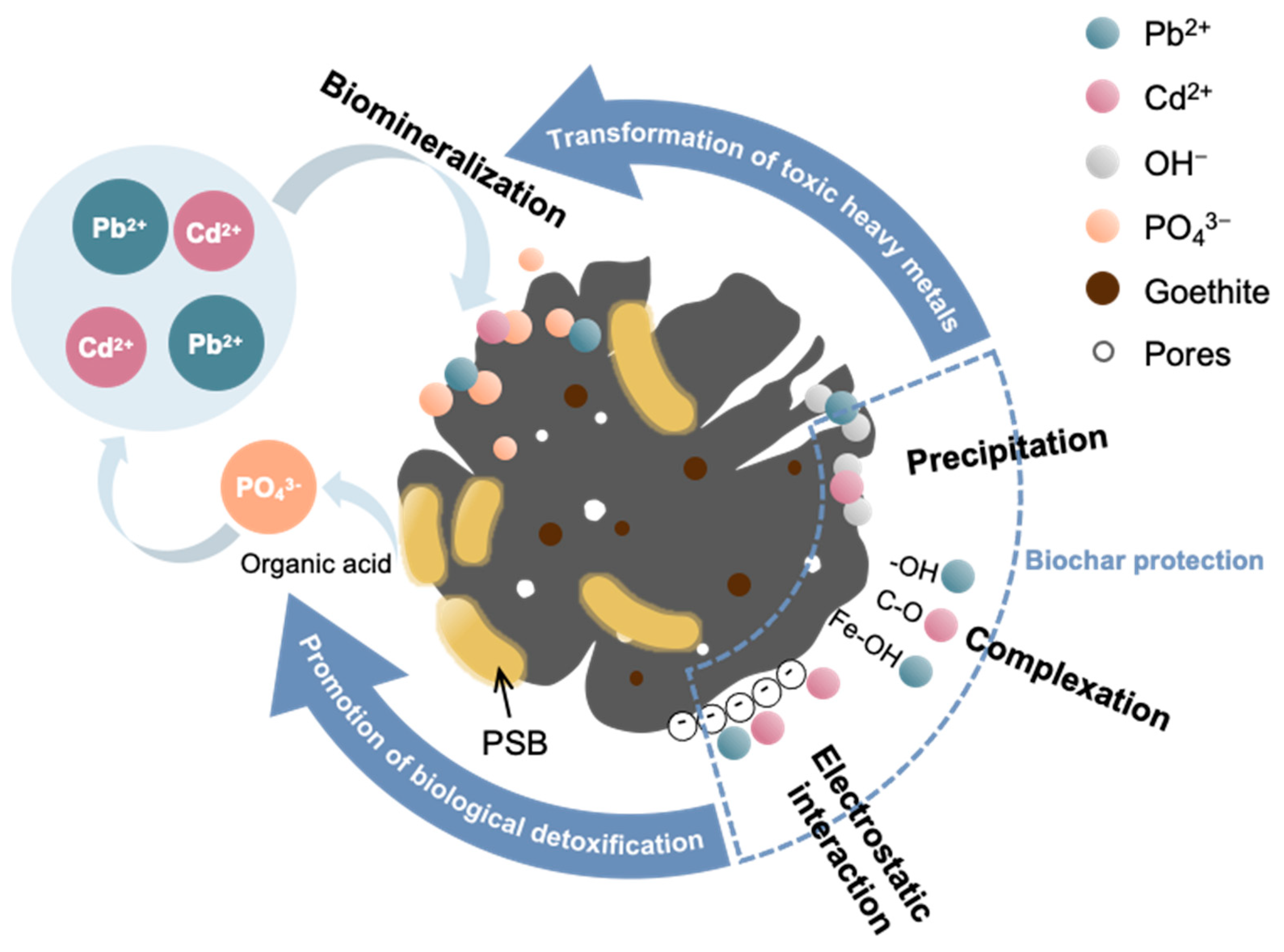
3.5. Remediation Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saha, R.; Nandi, R.; Saha, B. Sources and toxicity of hexavalent chromium. J. Coord. Chem. 2011, 64, 1782–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, W.; Rai, S.; Banerjee, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Mondal, M.H.; Bhattarai, A.; Saha, B. A comprehensive review on the sources, essentiality and toxicological profile of nickel. Rsc Adv. 2022, 12, 9139–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; O’Connor, D.; Igalavithana, A.D.; Alessi, D.S.; Luo, J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Sparks, D.L.; Yamauchi, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Metal contamination and bioremediation of agricultural soils for food safety and sustainability. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Peng, C.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, X. Heavy metals in soils around non-ferrous smelteries in China: Status, health risks and control measures. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 282, 117038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Li, K.; Wu, R.-R.; Yan, Y.-J.; Xiao, R.-B. Insight into the Cd2+ biosorption by viable Bacillus cereus RC-1 immobilized on different biochars: Roles of bacterial cell and biochar matrix. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Saha, R.; Ghosh, A.; Nandi, R.; Saha, B. A review on toxic cadmium biosorption from contaminated wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 53, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Kang, H.; Zhang, X.; Shao, H.; Chu, L.; Ruan, C. A critical review on the bio-removal of hazardous heavy metals from contaminated soils: Issues, progress, eco-environmental concerns and opportunities. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-Y.; Seo, Y.-D.; Kim, B.; Kim, I.Y.; Cha, D.K. Microbial reduction of nitrate in the presence of zero-valent iron and biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, R.; Laskar, S.; Saha, B. Surfactant-promoted enhancement in bioremediation of hexavalent chromium to trivalent chromium by naturally occurring wall algae. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 1619–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Min, F.; Hu, X.; Ma, D.; Huo, Z. Biochar assists phosphate solubilizing bacteria to resist combined Pb and Cd stress by promoting acid secretion and extracellular electron transfer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Wei, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Effective lead passivation in soil by bone char/CMC-stabilized FeS composite loading with phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampieri, B.D.B.; Pinto, A.B.; Schultz, L.; de Oliveira, M.A.; de Oliveira, A.J.F.C. Diversity and Distribution of Heavy Metal-Resistant Bacteria in Polluted Sediments of the Araça Bay, São Sebastião (SP), and the Relationship Between Heavy Metals and Organic Matter Concentrations. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Li, M.; Teng, Z.; Qiu, B.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, K. Effects of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) Stress on Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria (Bacillus sp. Strain MRP-3): Oxidative Stress and Bioaccumulation Potential. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Han, X. Preparation of metal-resistant immobilized sulfate reducing bacteria beads for acid mine drainage treatment. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Singh, A.P.; Khan, N.; Chowdhary, P.; Giri, B.S.; Varjani, S.; Chaturvedi, P. Bio-composite of Fe-sludge biochar immobilized with Bacillus Sp. in packed column for bio-adsorption of Methylene blue in a hybrid treatment system: Isotherm and kinetic evaluation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, X.P.; Liu, X.Y.; Hu, X.X.; Yuan, X.Y. Response of soil bacterial community to bioaugmentation with a plant residue-immobilized bacterial consortium for crude oil removal. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.C.; Niu, X.G.; Zhang, N.W.; Li, T.J. Effect of biochar-immobilized Sphingomonas sp. PJ2 on bioremediation of PAHs and bacterial community composition in saline soil. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Niu, L.L.; Su, A.X.; Li, M.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Xu, Y. Sustained and efficient remediation of biochar immobilized with Sphingobium abikonense on phenanthrene-copper co-contaminated soil and microbial preferences of the bacteria colonized in biochar. Biochar 2023, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Guo, B.; Yang, J.; Shen, Z.; Hou, D.; Ok, Y.S.; Poon, C.S. Biochar as green additives in cement-based composites with carbon dioxide curing. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Fan, G.; Zhou, J.; Lin, R.; Cao, X.; Song, Y.; Luo, J.; Zou, J.; Hong, Z.; Xu, K.-Q.; et al. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by P-Doped Cow Manure Biochar for Enhancing Degradation of 17β-Estradiol. Water 2024, 16, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tang, L.; Wang, Z.; Su, M.; Tian, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z. Evaluating the protection of bacteria from extreme Cd (II) stress by P-enriched biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harindintwali, J.D.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W.; Gu, Q.; Yu, X. Biochar-bacteria-plant partnerships: Eco-solutions for tackling heavy metal pollution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 204, 111020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Ye, F.; Jin, C.; Ma, X.; Huang, C.; Sheng, G.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y. The enhancement roles of layered double hydroxide on the reductive immobilization of selenate by nanoscale zero valent iron: Macroscopic and microscopic approaches. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Johir, M.A.H.; Sornalingam, K.; Belhaj, D.; Kallel, M. Nano-Fe0 immobilized onto functionalized biochar gaining excellent stability during sorption and reduction of chloramphenicol via transforming to reusable magnetic composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, Q.; Yue, T.; Zhang, F.; Liu, L. Facile preparation of activated carbon supported nano zero-valent iron for Cd(II) removal in aqueous environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irshad, M.K.; Chen, C.; Noman, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Adeel, M.; Shang, J. Goethite-modified biochar restricts the mobility and transfer of cadmium in soil-rice system. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Ma, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H. β-FeOOH Nanorods/Carbon Foam-Based Hierarchically Porous Monolith for Highly Effective Arsenic Removal. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 13480–13490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, N.; Yang, X.; Chen, C.; Shang, J. Goethite modified biochar as a multifunctional amendment for cationic Cd(II), anionic As(III), roxarsone, and phosphorus in soil and water. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, W.; Liu, J.; Xue, Q. Geo-environmental and mechanical behaviors of As(V) and Cd(II) co-contaminated soils stabilized by goethite nanoparticles modified biochar. Biochar 2023, 5, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. Citation-Classic—A Modified Single Solution Method for the Determination of Phosphate in Natural-Waters. Curr. Contents/Agric. Biol. Environ. Sci. 1986, 12, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Nemati, K.; Abu Bakar, N.K.; Abas, M.R.; Sobhanzadeh, E. Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Shih, K.; Liu, C.; Liao, C. Cubic and tetragonal ferrite crystal structures for copper ion immobilization in an iron-rich ceramic matrix. RSC. Adv. 2016, 6, 28579–28585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemerow, N. Scientific Stream Pollution Analysis. 1974. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/48447669_Scientific_Stream_Pollution_Analysis (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Sarma, S.J.; Pakshirajan, K. Surfactant aided biodegradation of pyrene using immobilized cells of Mycobacterium frederiksbergense. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Z.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Immobilized enzyme reactors in proteomics. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, S.; Ke, Y.; Xue, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, X. Immobilized sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) enhanced passivation performance of biochar for Zn. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Oshiki, M.; Rathnayake, L.; Ishii, S.; Satoh, H.; Okabe, S. Rapid and successful start-up of anammox process by immobilizing the minimal quantity of biomass in PVA-SA gel beads. Water. Res. 2015, 79, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Leng, S. Effective removal of chlortetracycline and treatment of simulated sewage by Bacillus cereus LZ01 immobilized on erding medicine residues biochar. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 14, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Ran, B.; Deng, S.; Jin, N.; Zhao, B.; Song, J.; Fu, S. Peanut shell biochar immobilized Pseudomonas hibiscicola strain L1 to remove electroplating mixed-wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Wu, X.; Tao, Y.; Xia, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Luo, J.; Zou, J.; Hong, Z.; Xu, K. Enhanced inactivation of Microcystis aeruginosa by heterogeneous interfacial Ag2MoO4/TACN under visible light. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.-S. Removal of lead from water using biochars prepared from hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, S.K.; Nair, V. Pseudomonas stutzeri Immobilized Sawdust Biochar for Nickel Ion Removal. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Fan, G.; Li, X.; Cao, X.; Du, B.; Li, H.; Luo, J.; Hong, Z.; Xu, K.-Q. Recyclable magnetic AgBr/BiOBr/Fe3O4 photocatalytic activation peroxymonosulfate for carbamazepine degradation: Synergistic effect and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Zhang, L.; Lin, X.; Cao, X.; Li, H.; Luo, J.; Zou, J.; Hong, Z.; Xu, K.-Q. Fabrication of heterostructured T-BaTiO3/Ag3PO4 for efficient piezophotocatalytic inactivation of M. aeruginosa under visible light with ultrasound. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 338, 126522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Fan, G.; Yang, S.; Luo, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, K.-Q. Mechanistic insight into humic acid-enhanced sonophotocatalytic removal of 17β-estradiol: Formation and contribution of reactive intermediates. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Lin, Q.; Yao, X.; Yin, G. Removal of Cd from aqueous solution by chitosan coated MgO-biochar and its in-situ remediation of Cd-contaminated soil. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Tian, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, S.; Cao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S. Effective removal of tetracycline antibiotics from water by magnetic functionalized biochar derived from rice waste. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 330, 121681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Yuan, X.; Xiong, T.; Tan, Y.Z.; Wang, H. Physicochemical properties, metal availability and bacterial community structure in heavy metal-polluted soil remediated by montmorillonite-based amendments. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 128010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, L.; Su, M.; Tian, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Hu, S. Enhanced Pb immobilization via the combination of biochar and phosphate solubilizing bacteria. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Gou, J.; Chen, X.; Xiao, S.; Ali, I.; Shang, R.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Han, M.; Luo, X. Application of mixed bacteria-loaded biochar to enhance uranium and cadmium immobilization in a co-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.G.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, W.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Heavy metal stabilization in municipal solid waste incineration flyash using heavy metal chelating agents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 113, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, S.T.; Arslan, S.; Alp, T.; Arslan, D.; Akar, T. Biosorption potential of the waste biomaterial obtained from Cucumis melo for the removal of Pb2+ ions from aqueous media: Equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic and mechanism analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 185, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Adsorption behavior of ammonium by a bioadsorbent—Boston ivy leaf powder. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, L.; Zhou, F.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Burkholderia cepacia immobilized on eucalyptus leaves used to simultaneously remove malachite green (MG) and Cr(VI). Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2018, 172, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, F.; Tang, B. Adsorption and redox conversion behaviors of Cr(VI) on goethite/carbon microspheres and akaganeite/carbon microspheres composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, H.; Sun, G.; Kumar, A.; Yu, Z. Enhancing arsenic adsorptions by optimizing Fe-loaded biochar and preliminary application in paddy soil under different water management strategies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 101616–101626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Tian, D.; Zhang, X.; Tang, L.; Su, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Hu, S.; Hou, D. Mechanisms of biochar assisted immobilization of Pb2+ by bioapatite in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Han, L. Characteristics of tetracycline adsorption by cow manure biochar prepared at different pyrolysis temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 285, 121348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, N.; Ran, M.; Hu, L.; Jiang, C.; Liu, Y. Periplasmic space is the key location for Pb(II) biomineralization by Burkholderia cepacia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Wan, J.; Wang, X.; Peng, C.; Wang, G.; Liang, W.; Zhang, W. Mixed bacteria-loaded biochar for the immobilization of arsenic, lead, and cadmium in a polluted soil system: Effects and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 152112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, G.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Z.; Qian, Y.; Wu, H. Amorphous MnO2 Modified Biochar Derived from Aerobically Composted Swine Manure for Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5049–5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, J.; Ma, R.; Xue, Y.; Ma, Q.; Yuan, S.; Teng, W. Enhanced removal of heavy metals by α-FeOOH incorporated carboxylated cellulose nanocrystal: Synergistic effect and removal mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 19427–19438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wen, J.; Yang, L.; Cui, H.; Zeng, T.; Huang, J. Exploration on the role of different iron species in the remediation of As and Cd co-contamination by sewage sludge biochar. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 39154–39168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.; Chang, S.X.; Cai, Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.-L.; Ryu, C.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Mechanistic insights into the (im)mobilization of arsenic, cadmium, lead, and zinc in a multi-contaminated soil treated with different biochars. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Meng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Brookes, P. Zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: New findings on simultaneous adsorption of Cd(II), Pb(II), and As(III) in aqueous solution and soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Li, Q.; Liao, L.; Wu, Z.; Yin, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, T. Simultaneous and efficient removal of multiple heavy metal(loid)s from aqueous solutions using Fe/Mn (hydr)oxide and phosphate mineral composites synthesized by regulating the proportion of Fe(II), Fe(III), Mn (II) and PO43−. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Bolan, N.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Isolation of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their potential for lead immobilization in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Jiang, Z.; Deng, F.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. KOH-activated porous biochar with high specific surface area for adsorptive removal of chromium (VI) and naphthalene from water: Affecting factors, mechanisms and reusability exploration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.M.; Trinh, V.T.; Doan, D.P.; Van, H.T.; Nguyen, T.V.; Vigneswaran, S.; Ngo, H.H. Removing ammonium from water using modified corncob-biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, G.; Zhou, J.; Cao, X.; You, W.; Lin, C.; Luo, J.; Zou, J.; Xu, K.-Q.; Luo, Q. Enhanced Remediation of Lead and Cadmium by the Co-System of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Immobilized on Goethite-Modified Biochar. Water 2024, 16, 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131917
Fan G, Zhou J, Cao X, You W, Lin C, Luo J, Zou J, Xu K-Q, Luo Q. Enhanced Remediation of Lead and Cadmium by the Co-System of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Immobilized on Goethite-Modified Biochar. Water. 2024; 16(13):1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131917
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Gongduan, Junhou Zhou, Xingfeng Cao, Wu You, Chen Lin, Jing Luo, Jianyong Zou, Kai-Qin Xu, and Quanda Luo. 2024. "Enhanced Remediation of Lead and Cadmium by the Co-System of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Immobilized on Goethite-Modified Biochar" Water 16, no. 13: 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131917
APA StyleFan, G., Zhou, J., Cao, X., You, W., Lin, C., Luo, J., Zou, J., Xu, K.-Q., & Luo, Q. (2024). Enhanced Remediation of Lead and Cadmium by the Co-System of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Immobilized on Goethite-Modified Biochar. Water, 16(13), 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131917







