Abstract
The discharge of dye waste by industries has caused environmental impacts on water properties, aquatic species, and human life. The production of eco-friendly materials for dye removal from wastewater has gained increasing interest, particularly through adsorption, as it is an efficient method for removing pollutants. However, the selectivity and limited adsorption capacity of materials for simultaneously adsorbing cationic and anionic dyes make it challenging to address the prevailing dye effluent issue. In this work, a poly(glycerol citrate) polyester was prepared without a solvent, using microwave heating, and was combined with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) to modulate the simultaneous adsorption of cationic (Rhodamine B, RB) and anionic dyes (acid blue 113, AB and acid red 27, AR). The formation of the polyester was successfully confirmed by ATR-FTIR and the thermal properties were evaluated by TGA and DCS. In the presence of CTAB 5 mM, the material removes almost 100% of the dyes, reaching the kinetics equilibrium in 30 min following the Pseudo-second order model. Additionally, dye adsorption on the polyester in the presence of CTAB was described by the Freundlich isotherm model, indicating a heterogeneous polyester surface that promotes a multi-layer adsorption driven by electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonds. The material showed an adsorption capacity of 73.7 ± 3.2, 82.1 ± 4.4, and 21.2 ± 0.6 mg/g for RB, AB, and AR, respectively. Our results provide evidence that the poly(glycerol citrate)/CTAB has a higher potential for application in wastewater treatment to remove both anionic and cationic dyes.
1. Introduction
Organic and synthetic dyes play a crucial role in several industries, including textiles, food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical industries, among others. Currently, there are over 1000 different dyes and pigments used in countless industrial formulations, with the market projected to reach approximately $15 billion by 2026 [1]. However, the extensive use of dyes and pigments contributes to environmental contamination, particularly in water sources. The textile and dyeing industries are the major contributors to dye contamination in effluents, accounting for approximately 54% and 21% of the presence of dyes in wastewater, respectively [2,3,4]. For instance, in the textile industry, about 10–15% of the synthetic dyes used are lost and discharged into water sources, such as rivers and lakes, without adequate treatment [5,6]. Even low concentrations of dyes in water (1 mg/L) can have a significant impact on the aquatic environment, as these pigments can absorb and reflect sunlight, affecting the development of aquatic species and plants. Additionally, dyes are resistant to thermal degradation and light in natural conditions, making them persistent pollutants in wastewater [2,7]. Typically, dyes contain aromatic, azo, carboxyl, and sulphonated groups, which are highly toxic to human health and can cause skin issues, cardiovascular diseases, and mutations, among other adverse effects [8,9]. Therefore, efficient methods for the removal of dyes from contaminated water are necessary before their release into the environment.
Several methods have been explored for the removal and/or reduction of dye concentrations in contaminated water, including photocatalysis [10], electrochemical treatments [11], bacteria treatment [12], oxidation [13], and solvent extraction [14]. Among these methods, the adsorption process is considered an efficient strategy for removing contaminants from water sources. It is often preferred due to its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and energy-saving properties, compared to other removal methods [15,16]. However, the use of hazardous and toxic solvents, such as aromatic solvents, chlorinated solvents, and organic solvents, in the production of adsorbent materials is considered problematic due to the increased environmental pollution. In the adsorption process, the functional groups (–NH2, –SO3H, –COOH, –OH) of the dyes chemically and/or physically interact with the surface of the adsorbents through hydrogen bonding, electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions, and π–π stacking [17]. Therefore, various materials, such as carbon nanotubes, metallic nanoparticles, hydrogels, and metallic composites with functional groups, have been explored for the removal of dye pollutants from water sources [18,19]. However, many of these materials have high production costs and require multiple preparation steps, which limit their application in industrial processes. For example, carbon-based materials have demonstrated the ability to retain larger quantities of dyes, but their preparation methods involve pyrolysis steps and long retention times [20]. Polyesters are inexpensive alternative materials for adsorbing cationic dyes, with higher removal efficiency, and can be formed by the reaction of polyfunctional acids and alcohols, such as citric acid (CA) and glycerol [21]. CA is an affordable material found in several natural sources, such as vegetables and citrus fruits like lemons, oranges, and limes [22]. When combined with glycerol under heat, it forms a three-dimensional poly(glycerol citrate) material, which is considered a benign and biodegradable material [21,23]. Poly(glycerol citrate) has a higher content of unreacted carboxylate and hydroxyl groups, providing the material with anionic sites to interact with cationic dyes in wastewater. However, to our knowledge, there are no reported applications of this material in the removal of cationic and/or anionic dyes. Similar materials, such as hydrogels formed with glycerol, CA, and acrylic acid, have been explored for the adsorption of methylene blue (a cationic dye). The results showed that the hydrogel had an adsorption capacity ranging from 202 to 245 mg/g, which could be attributed to electrostatic interactions and electron exchange between the dye and the material [24]. However, due to the anionic surface, the material is limited to adsorbing anionic dyes.
Cationic surfactants, such as cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), have been demonstrated to interact and adsorb on surfaces with an opposite charge to the surfactant’s cationic head, forming monolayers and hemimicelles [25]. The saturation of the surface by the surfactant promotes hydrophobic interactions between the surfactant coils, forming bilayers where the outer surface is composed of the cationic head of the surfactant [25,26]. Therefore, the surfactant bilayer can interact with anionic contaminates such as dyes to remove them from wastewater. The use of CTAB bilayers as a strategy to remove cationic dyes has been explored with TiO2 nanoparticles for the removal of alizarin red and indigo carmine, but the adsorption capacity of the materials is limited [27]. Based on the fact that CTAB can adsorb and interact with the anionic dyes, this work aimed to obtain solvent-free poly(glycerol citrate) material through microwave heating, to form an environmentally friendly and cost-effective material and evaluate its dye removal capability, with and without CTAB. Rhodamine B (RB), acid blue 113 (AB), and acid red 27 (AR) were used as model dyes to assess the removal efficiency of the material (Figure 1). Furthermore, to understand the adsorption mechanism, the sorbent–sorbate equilibrium and kinetic adsorption were evaluated using isotherm and kinetics models, respectively.
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of model dyes tested in this study: rhodamine B, acid blue 113, and Acid red 27.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Citric acid (CA, 98%), cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 99%), rhodamine B (RB, 99%), acid blue 113 (AB, 99%), and acid red 27 (AR, 99%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Burlington, MA, USA. Industrial grade glycerol was obtained from a local market. All the chemicals were used without further purification. Distilled water was used throughout all the experiments.
2.2. Preparation of Poly(Glycerol Citrate) Material
Biodegradable poly(glycerol citrate) was obtained from CA and glycerol without solvent, using microwave heating. To form the material, 96.8 g of glycerol and 240.0 g of CA were mixed, resulting in a molar ratio of 1.0:1.0 of CA to glycerol. The mixture was stirred manually until a homogeneous material was obtained. Next, the mixture was placed in a microwave oven and heated for 15 min at a power of 360 W. Finally, the obtained polyester was milled and sieved through a 2.0 mm diameter.
2.3. Physiochemical Characterization of Poly(Glycerol Citrate) Material
The poly(glycerol citrate) material was characterized using various techniques. Fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy with attenuated total reflectance (ATR-FTIR) was performed using an IR-Affinity-1 instrument (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) to verify the esterification reaction. The data were acquired from 4000 to 700 cm−1 at a scanning rate of 2 cm−1 per point, and each sample underwent 20 scans. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was carried out using TA Instrument SDT-Q600 (TA instrument, New Castle, DE, USA). The poly(glycerol citrate) weighed between 5 and 10 mg and was heated from room temperature to 800 °C at a constant heating rate of 10 °C/min, under a nitrogen flow of 20 mL/min. The results were evaluated by analyzing the first-order derivative of the weight loss thermogram. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was performed using a TA Instrument DSC25 (TA instrument, Delaware, USA). Prior to analysis, any thermal memory of the material was eliminated by heating from room temperature to 170 °C, at a ramp rate of 15 °C/min, followed by isothermal heating at 170 °C for 3 min. Subsequently, the material was cooled from 180 °C to −30 °C at a cooling ramp rate of 25 °C/min. Finally, the DSC was carried out by heating the material from −30 °C to 170 °C at a ramp rate of 15 °C/min. In addition to spectroscopy and thermal analysis, digital photographs were taken of the materials before and after immersion in water distilled water. These photographs were captured using a flexible digital electronic microscope (Suzhou Jingtong Instrument Co., Ltd., Suzhou, China) to visually assess any changes in the samples upon water exposure.
2.4. Dye Adsorption Studies
2.4.1. Dye Removal Efficiency
To evaluate the adsorption capacity of poly(glycerol citrate), AB, RB, and AR were used. Approximately 0.3 g of adsorbed poly(glycerol citrate) was added to 5.0 mL of a dye solution (500 mg/L), then shaken at 100 rpm in a water bath for 24 h until equilibrium was achieved. Afterward, the samples were centrifuged at 5000 rpm to separate the poly(glycerol citrate)/dye material. The concentration of the dye solutions in the supernatant was determined using an ultraviolet visible spectrophotometer (Drawell DU-8800DS, Chongqing Drawell Instrument Co., Ltd, Chongqing, China), with a linear calibration curve specific to each dye used. The linear calibration curve ranged from 0.5 to 4.0 mg/L for AB, from 3.0 to 20.0 mg/L for RB, and from 2.0 to 50.0 mg/L for AR (Figure S1, Supplementary Materials). The concentrations of AB, RB, and AR were measured at equilibrium at wavelengths of 566 nm, 554 nm, and 520 nm, respectively. These values correspond to the absorbance maxima according to literature data [28,29,30]. The percentage removal efficiency (%RE) was calculated using Equation (1):
where C1 and C2 are the concentrations of the dye solution in mg/L before and after the adsorption process, respectively [31]. The %RE was also determined in the presence of different concentrations of CTAB (1–40 mM) to evaluate the effectiveness of the surfactant in promoting dye removal. Additionally, the materials were recovered after dye adsorption (with and without CTAB 5 mM) and dispersed in water (10 mg/mL) to conduct zeta potential measurements (DLS, Malvern Panalytical, Zetasizer LAB, Malvern, UK), performed in triplicate.
2.4.2. Adsorption Capacity
To study the adsorption process in the absence and presence of CTAB, the same methodology described in Section 2.4.1 was employed at 298 K. However, the adsorption capacity at equilibrium (qe, mg/g) for different initial dye concentrations (0–5000 mg/L) was calculated using Equation (2):
where Co (mg/L) and Ce (mg/L) are the initial and equilibrium concentrations of the dye, respectively. V (L) is the volume of dye solution used and m (g) is the weight of the dried poly(glycerol citrate) material. The Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin adsorption isotherms, described by Equations (3)–(5), were evaluated to understand the interaction mechanism between the dye and the polyester [6,31].
where qm and qe (mg/g) are the maximum adsorption capacity and adsorption capacity at equilibrium, respectively. Ce (mg/L) is the equilibrium dye solution concentration. In the Langmuir model, KL (L/mg) is the Langmuir constant, which relates to both the free energy and adsorption affinity. The Freundlich constants KF (L/ mg) and n pertain to adsorption capacity and intensity, respectively. Lastly, KT is the binding constant of the Temkin isotherm, and BT is the Temkin constant, which is influenced by the adjusted uptake temperature (J mol−1).
2.4.3. Adsorption kinetics
The effect of the CTAB surfactant on the dye adsorption was also evaluated at various times (30–1440 min), allowing the calculation of the adsorption capacity at each time interval (qt), using Equation (6).
where the dye concentrations at time t and the initial dye concentration are represented by Ct and C0 (mg/L), respectively. V (mL) is the volume of the dye solution and m (g) is the mass of the adsorbent. To evaluate the adsorption kinetics mechanism, the experimental data were fitted to the pseudo-first-order model, pseudo-second-order model, and Boyd liquid-film diffusion model, which follow Equations (7)–(9).
where qe (mg/g) and qt (mg/g) are the adsorption capacities at equilibrium time and time t (min), respectively. k1 (/min) represents the pseudo-first-order rate constant, k2 (g (mg/min)) the pseudo-second-order rate constant, and kFD (1/min) represents the adsorption constant corresponding to the Boyd liquid-film diffusion model [17,31].
2.4.4. Selectivity and Remotion Mix of Dyes
The adsorption selectivity of the poly(glycerol citrate) for the dyes was investigated using the methodology described in Section 2.4.1. The %RE was evaluated for three combinations of dyes: RB and AR, RB and AB, AB and AR. The %RE was calculated using Equation (1) for each system. Additionally, digital photographs were taken of the systems and the solid residue after centrifugation, using a flexible digital electronic microscope. The mass ratio was evaluated for adsorption with and without CTAB 5 mM.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(Glycerol Citrate)
Figure 2 shows the ATR-FTIR spectra of glycerol, CA, and the poly(glycerol citrate) material. Figure 2A shows the principal bands of the glycerol, highlighting the bands in the fingerprint at 845 cm−1, attributed to the stretching of the C–C bonds. Additionally, bands at 993 cm−1, 1036 cm−1, and 1109 cm−1 correspond to the C–O stretching of the three C–O bonds in the glycerol structure. The O–H deformation and stretching bands are observed in the range of 1400 cm−1 to 1100 cm−1 and at 3320 cm−1, respectively [32,33]. However, at 1640 cm−1, there is a band due to the presence of water, as the glycerol used is of industrial grade and not reactive grade, making it an economical material with easy application in the industry. On the other hand, the ATR-FTIR spectra of CA (Figure 2B) exhibit three bands between 1700 cm−1 and 1600 cm−1, which are attributed to the stretching of the carboxylic (C=O) groups in CA [21,33].
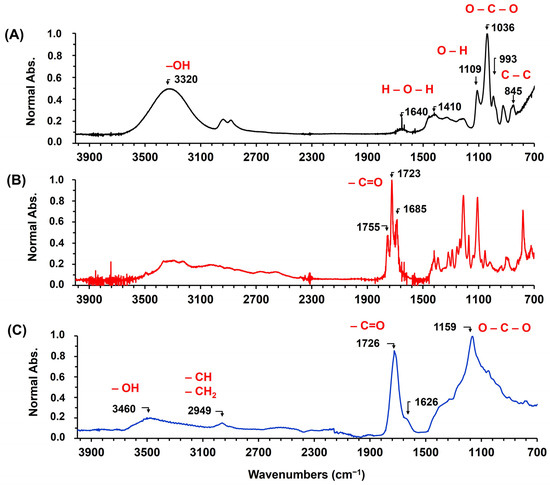
Figure 2.
ATR-FTIR spectra of (A) glycerin, (B) citric acid, and (C) poly(glycerol citrate).
The ATR-FTIR spectra of the poly(glycerol citrate) material (Figure 2C) show a band at 1726 cm−1, indicating the presence of the ester group and confirming the successful reaction between glycerol and CA [21,33]. However, there is also a band at 1626 cm−1, suggesting the presence of carboxylate groups from CA and indicating the incomplete reaction of acid groups. Similar bands were observed by [33] in the polycondensation reaction between glycerol and CA. This characteristic of the material is interesting, because it suggests that the carboxylate groups with a negative charge can interact with cationic dyes through electrostatic interactions, providing active sites on the polyester for the chemisorption of the dyes. Additionally, a band at 1159 cm−1 is observed, which is attributed to the O–C–O stretching in the polyester. These results confirm the polycondensation reaction achieved by microwave heating, demonstrating that the produced polyester is a low-cost material that follows the principles of green chemistry, as it utilizes economical reactants, does not require organic solvents, and has low energy demand.
The TGA analysis of the poly(glycerol citrate) material revealed a weight loss as the temperature increased. The first significant weight loss occurred at 123.1 °C, which can be attributed to the loss of water through a condensation reaction within the material (Figure 3A). DTA analysis indicated two degradation events at higher temperatures (346.1 and 400.5 °C), suggesting that the poly(glycerol citrate) can withstand higher temperature degradation, compared to the boiling points of CA (175 °C) and glycerol (290 °C) compounds [21]. Additionally, the glass transition of the material was found at 88.9 °C (Figure 3B). Furthermore, the material displayed a rigid structure (Figure 4) and even after immersion in distilled water for 24 h, the structure remained intact, without dispersion. However, a gelatinization appearance, resembling a hydrogel, was observed, likely due to the absorption and/or entrapment of water within the material. The insolubility of the material is an important characteristic that enables its application in the adsorption of pollutants.
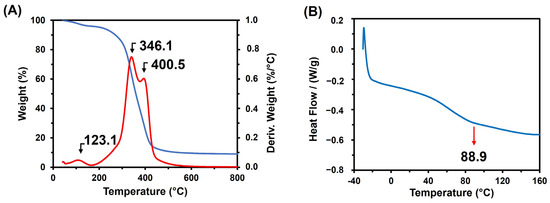
Figure 3.
(A) TGA (─) and DTA (─), (B) DSC of poly(glycerol citrate).

Figure 4.
Digital photographs of the poly(glycerol citrate) synthetized: (A,C) dried, (B) immersed in water, and (D) after immersion in water.
3.2. Adsorption Studies
The poly(glycerol citrate) material exhibits a high density of unreacted carboxyl groups, which enables strong interactions with cationic dyes. This is evident in Figure 5A, where the cationic dye RB dye (Figure 1) is effectively removed by the poly(glycerol citrate), with an efficiency of almost 100% (98.5 ± 0.1%). This demonstrates the efficient capacity of the polyester to interact with RB and adsorb it at its interface. However, for anionic dyes such as AB and AR (Figure 5B,C), the removal efficiency is lower, with values of 67.9 ± 2.5% and 11.6 ± 6.4%, respectively. This can be attributed to the chemical repulsion between the dyes and the carboxylate groups in the poly(glycerol citrate). AB contains two sulfate groups and AR contains three sulfate groups in their chemical structures, leading to electrostatic repulsion with the polyester, reducing the adsorption capacity.
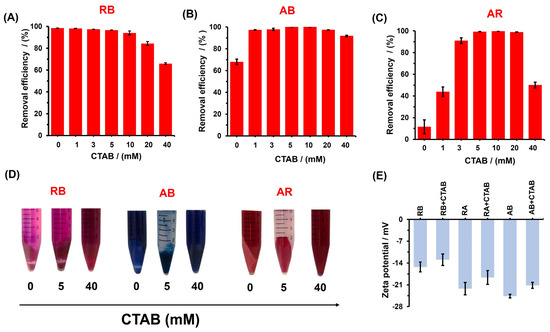
Figure 5.
Effect of CTAB in the dye %RE of the poly(glycerol citrate) of (A) RB, (B) AB, and (C) AR. A dye concentration of 500 mg/L was used in each assay. (D) Digital photographs of the effect of CTAB (0, 5, and 40 mM) on dyes (RB, AB, and AR) remotion by poly(glycerol citrate) synthetized. (E) Zeta potential of poly(glycerol citrate) with dyes (500 mg/L) tested without and without CTAB 5 mM.
To explore the potential application of the polyester, the dye removal efficiency was evaluated at different concentrations of CTAB (1–40 mM). In the case of RB, the removal efficiency decreases as the CTAB concentration increases, with a lower value of 50.1 ± 2.6% observed at CTAB 40 mM. However, for the anionic dyes AB and AR, the results exhibit the opposite behavior. As the CTAB concentration increases (Figure 5B,C), the removal efficiency also increases, reaching values of up to 99.1%. This indicates that the CTAB surfactant promotes efficient dye removal for these colorants, within the range of 5–10 mM. Beyond that concentration, the removal efficiency decreases with increasing CTAB concentration. These findings are further supported by the digital photographs of dye removal at 0, 5, and 40 mM CTAB concentrations (Figure 5D), highlighting the efficient removal of RB and AR in 5 mM of CTAB.
CTAB, as a cationic surfactant, exhibits a critical micelle concentration (CMC) of around 1 mM in pure water [34]. In the presence of CTAB at 5 mM, the formation of CTAB micelles and aggregates significantly affects the adsorption behavior of the dyes. It is likely that at low CTAB concentrations, interaction occurs between the CTAB aggregates (with positive charge) and the poly(glycerol citrate) material. This was corroborated by zeta potential measurement, where the CTAB 5 mM adsorbed on the material surface, increasing the zeta potential value from −16.8 ± 2.7 mV to −13.2 ± 1.1 mV, facilitating the removal of the dyes. The negative charge of the polyester particles indicates that CTAB does not interact with all of the particle surface, leaving carboxylate and/or acid carboxylic functional groups disponible to interact with the cationic dye, thus explaining the higher adsorption of RB with CTAB at 5 mM. Additionally, the adsorption of RB on the material surface with and without CTAB 5 mM increases the zeta potential to −15.3 ± 1.6 mV and −12.9 ± 1.8 mV, indicating the adsorption of the RB dye and CTAB on the polyester surface (Figure 5E).
In the case of AB and AR, the removal of the dyes may involve favorable electrostatic interactions between the negative sulfate groups on the dyes and positive ammonium groups on the surfactant head, as well as hydrophobic interactions between the organic chain of CTAB and hydrophobic functional groups of the dyes. When calculating the molar proportion between the AB and AR dyes with CTAB at 5 mM, it was found that the removal was more effective at the proportions of 3.6:25 and 4.9:25, respectively. This indicates that the same amount of CTAB could remove a larger amount of AR dye than AB. This is likely because the AR dye has three negative charges in its chemical structure, whereas AB contains only two negative charges, thus favoring the electrostatic interaction with the CTAB adsorber in the material. Consequently, it can be hypothesized that CTAB acts as a vehicle or mediator to trap the dyes and interact with the surface of the poly(glycerol citrate) material for their removal. This hypothesis is supported by the zeta potential values of the poly(glycerol citrate) after dye adsorption with and without CTAB at 5 mM (Figure 5E). In the cases of RA and RB (anionic dyes), the zeta potential was −22.2 ± 1.9 mV and −24.6 ± 0.6 mV, respectively, and both systems increased the zeta potential in CTAB 5 M, indicating that the cationic surfactant can enhance the retention of the dyes by increasing the particle charge. However, at higher CTAB concentrations, efficient dye removal is not observed, even for RB dyes. This may be attributed to two reasons: (i) the higher density of surfactant micelles, leading to the favorable encapsulation of the dyes, inhibiting their adsorption on the polyester; (ii) the saturation of the polyester surface by CTAB, resulting in repulsive interactions between the cationic RB dye and the cationic surfactant head. To validate these hypotheses, further investigations were conducted, including adsorption kinetics and isotherm studies.
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
To investigate the adsorption kinetics of the dyes on the polyester, the adsorption capacity of the dyes was evaluated at various time intervals, ranging from 30 to 1440 min at 500 ppm at 298 K (Figure 6). For the RB dye, the adsorption capacity reaches approximately 8 mg/g after 30 min of contact, and remains nearly constant as the contact time increases, regardless of the presence of CTAB. In the case of the AB and AR dyes, in the absence of CTAB, the adsorption capacity reaches values of 6.8 ± 0.2 mg/g and 1.4 ± 0.1 mg/g, respectively, after 720 min. However, the addition of CTAB at 5 mM significantly enhances the adsorption capacity of both dyes, reaching approximately 8 mg/g. Furthermore, the presence of CTAB reduces the time required to achieve the adsorption equilibrium to 30 min for the systems.
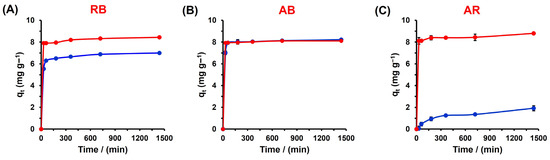
Figure 6.
Effect of time on the dye adsorption of RB (A), AB (B), and AR (C) in distilled water (•) and CTAB 5 mM (•) at 298 K.
The kinetics data were analyzed using the pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, and Boyd liquid-film diffusion models, to gain insight into the adsorption mechanisms on the polyester surface. Table 1 presents the kinetics parameters for each dye, revealing that the pseudo-second order model exhibits the highest R2 values. The adsorption process involves several steps, including the transportation of the dye from the aqueous solution to the surface of the polyester, diffusion of the dye from the outer surface to active adsorption sites on the material, and the physical and/or chemical interaction between the dye and the active functional groups present [35,36].

Table 1.
Kinetic model parameters for dyes on poly(glycerol citrate) material at 298 K.
The pseudo-second-order model suggests that the adsorption rate is primarily driven by the chemical adsorption mechanisms involving chemical bounding, electrostatic interaction, hydrogen bonds, and other interactions [31,37]. Therefore, the kinetics model confirms the hypothesis that the adsorption of the dyes occurs through electrostatic interactions between the negative carboxylate functional groups on the polyester surface and the tested dyes. In the case of RB dye, the cationic NH4+ groups can interact with the carboxylate groups through electrostatic interactions, facilitating the adsorption of the RB dye (Figure 7A). The presence of CTAB alters this behavior, as CTAB can exist in both liquid solid phases. In the aqueous solution, CTAB can exist as monomers and micelles aggregates, which are in equilibrium with the monomers and aggregates (hemimicelle, bilayers, and micelles) formed on the polyester surface through Coulombic attractive forces (Figure 7B,C) [38]. This suggests the hypothesis that the CTAB aggregates adsorbed on the polyester surface may induce repulsive interactions with the RB dye, reducing the adsorption capacity. However, no significant difference was observed in the presence of CTAB, indicating that the polyester possesses sufficient active sites to interact with the dye at the tested CTAB concentration.
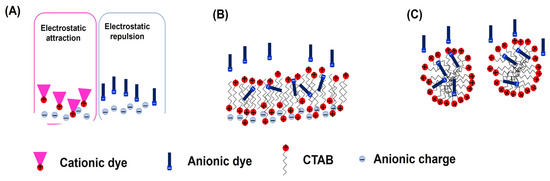
Figure 7.
Representation of possible interactions between cationic and anionic dyes with the polyester surface without (A) and with CTAB surfactant (B,C) at 298 K.
On the other hand, for the anionic dyes (AB and AR), without CTAB, the presence of negative charges on the sulfate groups prolongs the time required to reach the kinetic equilibrium. This effect is more pronounced in the case of AR dye, due to its higher negative charge, which increases the electrostatic repulsion with the negative charge on the polyester surface. In contrast, in the presence of CTAB, the anionic dyes likely strongly interact with the positive charge on the external surface of the CTAB aggregates on the polyester surface. This interaction reduces the time required to reach kinetics equilibrium and increases the adsorption capacity of the material for the anionic dyes under the tested conditions. Additionally, the anionic dyes may be hosted inside the CTAB aggregates through favorable hydrophobic interactions between the CTAB coils and the dyes, providing protection for the dyes. Similar behavior was observed by [27], in the adsorption of indigo carmine (anionic dye) on CTAB-modified TiO2 nanoparticles, where CTAB acted as a bridge through bilayer aggregation between the negatively charged surface of the TiO2 nanoparticles and the dye, reaching adsorption equilibrium within 100 min.
3.4. Adsorption Isotherm Study
The constructed adsorption isotherms in water and CTAB 5 mM at different initial dye concentrations from 50 to 5000 mg/L provide further insights into the characteristics of the adsorption processes (Figure 8). All the systems tested showed an increase in the qe as the Ce concentration increased (Tables S1–S3, Supplementary Materials). However, a saturation profile of the polyester surface with the tested dye concentrations was not observed. Comparing the adsorption results at the maximum initial concentration point, it was found that CTAB decreased the qe capacity for the RB dye from 75.7 ± 3.9 mg/g to 73.7 ± 3.2 mg/g. In contrast, for the AB and AR dyes, the qe increased significantly from 72.9 ± 3.3 to 82.1 ± 4.4 mg/g for the AB, and from 18.3 ± 1.6 to 21.2 ± 0.6 mg/g for the AR. These are particularly interesting results, as the presence of the CTAB surfactant enhanced the removal efficiency of the AR dye. This demonstrates that the poly(glycerol citrate) material is efficient in removing both anionic and cationic dyes from water sources, especially with CTAB, which has a notable affinity for dyes with a higher negative charge density in their molecular structure. The experimental results obtained in this study were compared with various adsorbent materials reported in the literature for RB, AB, and AR adsorption (Table 2). The adsorption capacity values obtained in this work for RB were found to be higher than those reported for RB retention in other materials, except for the graphene oxide/Poly(NIPAM-co-AA) hydrogel [39] and chitosan/electrospun sodium alginate nanofiber [40], which showed three and ten times higher adsorption capacity for RB, respectively. In the cases of AB and AR, the materials reported in the literature also exhibited higher values compared to those reported in this work, especially for the materials in the nanometric scale. However, the high cost of production for the nanomaterial is a disadvantage when considering their application. Therefore, considering the successful dye removal results, the low cost, and ease of production of poly(glycerol citrate), this material has great potential for application in the wastewater treatment industry.
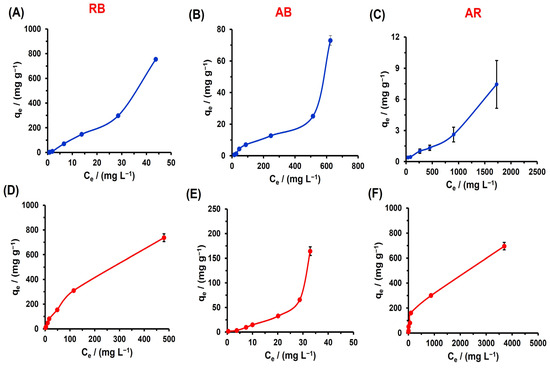
Figure 8.
Dye adsorption isotherm of RB (A,D), AB (B,E), and AR (C,F) in deionized water (•) and CTAB 5 mM (•) at 298 K.

Table 2.
Comparing poly(glycerol citrate) with various adsorbents to remove RB in water, and AB and AR dyes in CTAB 5 mM.
On the other hand, to better understand the adsorption process of cationic and anionic dyes tested with and without CTAB, adsorption isotherm models such as Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin were fitted to the dye adsorption isotherm data, allowing the determination of the adsorption isotherm parameters for each model tested (Table 3). Based on the R2 values, the Freundlich isotherm showed the best correlation compared to the other models. The Freundlich isotherm has been applied to dye adsorption on the materials, as it is not limited by a number of specific adsorption sites and does not saturate the material surface [49]. This is in agreement with the adsorption behavior observed in Figure 8, where the material surface it is not saturated, describing an IUPAC isotherm classification type II with and without CTAB, except for the system AR with CTAB which shows type I behavior, indicating surface saturation. In general, the KF parameters, which are related to the adsorption capacity, were found to be higher in the presence of CTAB 5 mM than in water for the tested AB and AR dyes, indicating that the surfactant increases the adsorption capacity.

Table 3.
Adsorption isotherm parameters for dyes on poly(glycerol citrate) material at 298 K.
The Freundlich adsorption model is an empirical equation that assumes a heterogeneous adsorbent surface, promoting multilayer coverage over the surface with different energy values [50,51]. It suggests that the adsorbate interacts with the active adsorption center with maximum energy first, followed by adsorption on centers with lower energy. Thus, the poly(glycerol citrate) material has a heterogeneous surface, with different active centers, to interact with the tested dyes, indicating incomplete reaction of the acid groups. This is in accordance with the FTIR-ATR results (Figure 2C), as previously described. Additionally, the Freundlich adsorption model has been used to describe multilayer adsorption, suggesting the deposition of the dye on the material surface at higher dye concentrations (3000 mg/L of dye), producing a multilayer adsorption profile. This behavior was also observed in the adsorption of acid blue 80 (anionic dye) on white mud when higher dye concentrations were used [52]. On the other hand, the parameter n in this model provides information about the intensity of interaction between the adsorbent and adsorbate. When n < 1, the adsorption process occurs through chemical interaction, involving the sharing of electrons to form covalent or ionic bonds. When n > 1, the process occurs through physical adsorption. In general, the n values obtained show that the adsorption of the dye-CTAB systems occurs through physical adsorption on the polyester surface [31,39]. Additionally, the 1/n values found in the range of 0–1 reflect the favorable adsorption of the dyes in the presence of CTAB, compared to the AB and AR dyes, although this favorability decreases in the absence of the surfactant. These results are consistent with the kinetics results, where CTAB influences the adsorption process and reduces the time required to reach equilibrium, due to the highly favorable electrostatic interactions between the CTAB micelle, the dye, and the polyester surface with carboxylate groups. Despite the low R2 values obtained for the Langmuir and Temkin isotherms, the KL and KT parameters show a similar trend to the Freundlich, as they also exhibit higher values in the presence of CTAB for all the dyes tested.
3.5. Selectivity, Separation, and Dye Remotion Studies
According to adsorption isotherms, the adsorption capacity increases with the dye concentration, however, in order to know the amount of dye removed by the polyester materials, the %RE versus the dye concentration was plotted to evaluate the applicability of the material (Figure 9). The RB showed a higher affinity for the polyester material in the absence of the cationic surfactant, resulting in nearly 100% removal for all RB concentrations. However, in the presence of CTAB, the %RE slightly decreases as the dye concentration increases, likely due to competitive interactions between the cationic dye and the CTAB on the anionic surface, and/or the entrapment of the dye in the aqueous phase by the CTAB micelles. A different behavior was observed for the AB and AR dyes. Without CTAB, for the AR dye, the %RE did not exceed 30%. In the presence of CTAB, there were two distinct trends: for concentrations ranging from 0 to 1000 mg/L, the polyester material removed almost 100% of the dye, but after 1000 mg/L, the %RE decreased as the dye concentration increased. This suggests that the CTAB aggregate phase adsorbed on the polyester material starts to saturate with the dye at 1000 mg/L, leading to a decrease in the %RE.
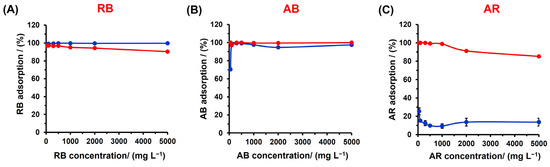
Figure 9.
Dye remotion by the poly(glycerol citrate) material of (A) RB, (B) AB, and (C) AR in distilled water (•) and CTAB 5 mM (•).
Since the adoption capacity of the RB was higher than that of AR in the absence of CTAB, it can be inferred that RB and AR can be selectively absorbed and separated by the polyester material. To evaluate the selectivity of the material, adsorption experiments were conducted using dye mixtures with and without CTAB, as shown in Figure 10. In the mixture of RB and AR dyes without CTAB, the %RE for AR increased compared to the results in Figure 10A, and the dye removal increased as the mass ratio of RB increased. RB dye has a positive charge, making it favorably adsorb onto the anionic surface. Additionally, according to the zeta potential results reported in Section 3.2, the adsorption of RB increases the zeta potential of the material surface, facilitating the adsorption of AR dye, which has three negative charges in its structure. Thus, the AR adsorption possibly occurs through electrostatic interaction between the AR and RB dyes, allowing AR to approach the polyester surface. However, the material exhibited greater adsorption capacity for the cationic dye, as corroborated by the pink color of the polyester after adsorption (Figure 10D). When analyzing the structure of RB and AR, it can be inferred that favorable electrostatic interactions occur between the cationic charge of RB and the negatively charged sulfate groups. Additionally, both dyes contain aromatic rings that promote favorable π–π stacking interactions [37]. In the presence of CTAB 5 mM, both dyes exhibited a higher adsorption capacity, with %RE values ranging between 89 and 90% for both dyes. The color of the aqueous phase confirmed that under these conditions, complete removal of the dyes did not occur where dye mixtures were used (Figure 10D).
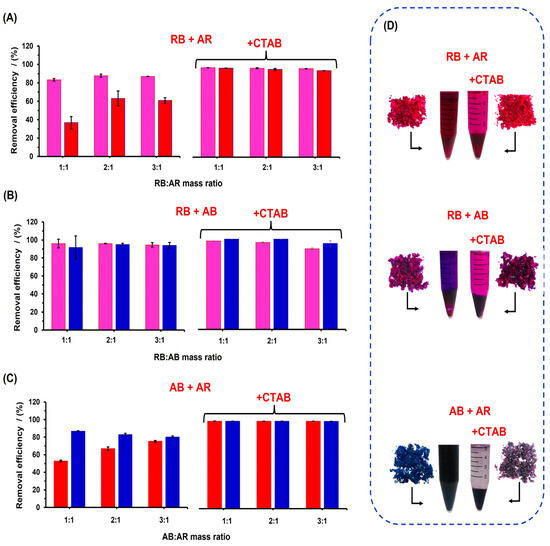
Figure 10.
%RE on poly(glycerol citrate) material, with and without CTAB, of mixture dyes at different mass ratios of: (A) RB:AR, (B) RB:AB, and (C) AB:AR. (D) Digital photography of adsorption systems and polyester material after adsorption at 3:1 mass ratio, with and without CTAB. The pink, red, and blue bars represent the RB, AR, and AB dyes, respectively. Mass ratio indicates the dye mass (mg) in the system: 1:1 (1.2 mg:1.2 mg), 2:1 (2.4 mg:1.2 mg), and 3:1 (3.6 mg:1.2 mg).
In the RB + AB system (Figure 10B), higher %RE values were obtained for both dyes, with and without CTAB, at different mass ratios. Without CTAB, RB promoted the removal of AB because AB dye has two negative charges in its structure, decreasing the repulsive interaction with the polyester surface. This indicates the more selective retention of AB than AR, when mixed with RB dye. However, complete removal of the dyes was not achieved, indicating that interactions between RB and AB negatively affected the adsorption process. Similar behavior was observed for the adsorption of AB + AR dyes without CTAB (Figure 10C), where the %RE for AR increased to approximately 80% as the AB mass ratio increased. These results can be explained by the repulsive electrostatic interaction of the negatively charged surface of the material with anionic dyes, where the repulsion interaction is higher for AR (three negative charges) than AB (two negative charges), indicating a more selective interaction with AB than with AR (supported by the visual observation of the solid phase). In the presence of CTAB, both dyes showed almost 100% removal, resulting in a purple coloration of the solid phase after adsorption. Additionally, the material showed an uncolored region, indicating that the material was not completely saturated. These results demonstrate that the polyester material exhibits a more selective adsorption capability for RB and AB dyes, compared to AR dye. However, in the presence of CTAB, all dyes showed a higher %RE, indicating that CTAB is an effective solute for promoting the simultaneous adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. Therefore, poly(glycerol citrate) has the potential to be used as an adsorbent for wastewater treatment.
4. Conclusions
A poly(glycerol citrate) material was formed by microwave heating of glycerol and citric acid, without the use of solvents. ATR-FTIR and TGA results confirmed the successful formation of the ester with high temperature resistance, making the material stable at temperatures below 300 °C. The presence of anionic groups on the material facilitated a selective interaction with the cationic dye RB, resulting in the removal of nearly 100% of the tested dye concentrations. In the case of anionic dyes, the adsorption capacity increased significantly in the presence of CTAB. This can be attributed to the ability of the surfactant to adsorb on the polyester surface in the form of hemimicelles and bilayers, imparting a positive charge to the polyester surface, which promotes favorable interactions with the anionic dyes. This was supported by the zeta potential results, indicating that CTAB increases the surface charge of the polyester. The kinetics results indicated that the adsorption of both cationic and anionic dyes followed a Pseudo-second-order model, suggesting that electrostatic interactions played a crucial role in the adsorption process. Furthermore, the Freundlich isotherm model showed the best fit with the adsorption data, except in the adsorption of RA with CTAB. The Freundlich isotherm model indicates a heterogeneous adsorption process, involving the formation of multilayers on the polyester surface. In the presence of CTAB, the poly(glycerol citrate) material demonstrated an efficient capacity (>95%) to remove both cationic and anionic dyes. Overall, this low-cost and environmentally-friendly poly(glycerol citrate)/CTAB system holds promise for the development of robust methods of wastewater treatment.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16131860/s1, Figure S1: Calibration curve of: (A) rhodamine B (RB), (B) acid blue 113 (AB), and (C) acid red 27 (AR); Table S1: Equilibrium data of the adsorption of rhodamine B on poly(glycerol citrate) with and without CTAB; Table S2: Equilibrium data of the adsorption of acid blue 113 on poly(glycerol citrate) with and without CTAB; Table S3: Equilibrium data of the adsorption of acid red 27 on poly(glycerol citrate) with and without CTAB.
Author Contributions
T.A.L. Investigation, Formal analysis, writing—review and editing: A.F.C. Investigation, Formal analysis, writing—review and editing. M.P. Conceptualization, Investigation, Formal analysis, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been funded by Dirección General de Investigaciones of Universidad Santiago de Cali under call No. DGI-01-2024 and grant number No. 939-621122-030.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article (and Supplementary Materials).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Benkhaya, S.; M’rabet, S.; El Harfi, A. Classifications, properties, recent synthesis, and applications of azo dyes. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rápó, E.; Tonk, S. Factors affecting synthetic dye adsorption—Desorption studies: A review of results from the last five years (2017–2021). Molecules 2021, 26, 5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gisi, S.; Lofrano, G.; Grassi, M.; Notarnicola, M. Characteristics and Adsorption Capacities of Low-Cost Sorbents for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2016, 9, 10–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouabidi, Z.B.; El-Naas, M.H.; Cortes, D.; McKay, G. Steel-Making Dust as a Potential Adsorbent for the Removal of Lead (II) from an Aqueous Solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.C.; Wang, J.J.; Xuan, X.P.; Fan, J.; Fan, M. Factors affecting ionic liquids-based removal of anionic dyes from water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5090–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Niu, J.; Yang, H.; Tian, S.; Lu, M. Highly efficient, rapid, and simultaneous removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution using monodispersed mesoporous silica nanoparticles as the adsorbent. Nanomaterials 2017, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C. The Strengthening Role of the Amino Group in Metal-Organic Framework MIL-53 (Al) for Methylene Blue and Malachite Green Dye Adsorption. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 3414–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, S.; Mahmoudi, F.; Amini, M.M.; Dusek, M.; Jarosova, M. Synthesis and characterization of a series of novel perov-skite-type LaMnO3/Keggin-type polyoxometalate hybrid nanomaterials for fast and selective removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions. Dalton. Trans. 2017, 46, 3252–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardila-Leal, L.D.; Poutou-Piñales, R.A.; Pedroza-Rodríguez, A.M.; Quevedo-Hidalgo, B.E. A Brief History of Colour, the Environmental Impact of Synthetic Dyes and Removal by Using Laccases. Molecules 2021, 26, 3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahar, D.; Kumar, D.; Thakur, P.; Thakur, A. Visible light induced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye by using Mg doped Co-Zn nanoferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 2023, 162, 112205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belal, R.M.; Zayed, M.A.; El-Sherif, R.M.; Ghany, N.A. Electrochemical Degradation and Degree of Mineralization of the BY28 Dye in a Supporting Electrolyte Mixture Using an Expanded Dimensionally Stable Anode. Electrocatalysis 2022, 13, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Navariya, J.K.; Bhojiya, A.A.; Singh, A.; Mohanty, S.R.; Upadhyay, S.K. Bioprospecting of novel ligninolytic bacteria for effective bioremediation of agricultural by-product and synthetic pollutant dyes. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 270, 127330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamrock, W.; Abdelhamid, H.N. Fenton-like Cerium Metal–Organic Frameworks (Ce-MOFs) for Catalytic Oxidation of Olefins, Alcohol, and Dyes Degradation. J. Clust. Sci. 2023, 34, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar]
- Karma, V.; Gande, V.V.; Pushpavanam, S. Simultaneous extraction and enrichment of sunset yellow dye in an aqueous two-phase system. Dyes. Pigm. 2023, 212, 111100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Wang, A. Adsorption of dyes onto palygorskite and its composites: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1274–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, M.A. Low-Cost Adsorbents for Environmental Pollution Control: A Concise Systematic Review from the Prospective of Principles, Mechanism and Their Applications. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2022, 43, 1612–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunkhe, B.; Schuman, T.P. Super-Adsorbent Hydrogels for Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution: Dye Ad-sorption Isotherms, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Properties. Macromoleclues 2021, 1, 256–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, A.; Nabizadeh, R.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nasseri, S. Magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes-loaded alginate for treatment of industrial dye manufacturing effluent: Adsorption modelling and process optimisation by central composite face-central design. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 103, 1509–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourens, A.; Falch, A.; Malgas-Enus, R. Magnetite immobilized metal nanoparticles in the treatment and removal of pollutants from wastewater: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 2951–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Shi, Q.; Feng, J.; Yao, J.; Huang, H.; Xie, X. Adsorption Behaviors of Cationic Methylene Blue and Anionic Reactive Blue 19 Dyes onto Nano-Carbon Adsorbent Carbonized from Small Precursors. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisserat, B.; O’kuru, R.H.; Hwang, H.; Mohamed, A.A.; Holser, R. Glycerol citrate polyesters produced through heating without catalysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 3429–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Md Tahir, P.; Lum, W.C.; Tan, L.P.; Bawon, P.; Park, B.-D.; Osman Al Edrus, S.S.; Abdullah, U.H. A Review on Citric Acid as Green Modifying Agent and Binder for Wood. Polymers 2020, 12, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berube, M.A.; Schorr, D.; Ball, R.J.; Landry, V.; Blanchet, P. Determination of in situ esterification parameters of citric acid-glycerol based polymers for wood impregnation. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, D.S.; Guhanathan, S. Investigation of citric acid–glycerol-based pH-sensitive biopolymeric hydrogels for dye removal applications: A green approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 121, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Pan, D.; Ding, L.; Tang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Yao, S. Mixed hemimicelles SPE based on CTAB-coated Fe3O4/SiO2 NPs for the determination of herbal bioactive constituents from biological samples. Talanta 2010, 80, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejaoui, B.; Nefzi, K.; Bouchmila, I.; Koumba, S.; Joly, N.; M’Hamdi, N.; Martin, P. Solid phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water samples using CTAB-TIO2 modified nanotubes. Microchemistry J. 2023, 193, 109027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolgharnein, J.; Rajabalipour, F.; Dermanaki Farahani, S. Indigo Carmine Dye Adsorptive Removal by Polyethylene Glycol-Modified Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles as an Efficient Adsorbent. Water. Air. Soil. Pollut. 2023, 234, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaif-Allah, M.A.; Taqui, S.N.; Syed, U.T.; Syed, A.A. Kinetic and isotherm modeling for acid blue 113 dye adsorption onto low-cost nutraceutical industrial fenugreek seed spent. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Garba, Z.N.; Sun, S.; Lawan, I.; Wang, L.; Lin, M.; Yuan, Z. Preparation and evaluation of an effective activated carbon from white sugar for the adsorption of rhodamine B dye. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Santana, J.E.; de Andrade, F.G.S.; Ferreira, A.F.; Ghislandi, M.G.; da Motta Sobrinho, M.A. Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics of industrial dye acid red 27 adsorption on Sugarcane Bagasse Ash. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, R.A.; Alminderej, F.M.; Al-Harby, N.F.; Elmehbad, N.Y.; Mohamed, N.A. Preparation and Characterization of a New Bis-Uracil Chitosan-Based Hydrogel as Efficient Adsorbent for Removal of Anionic Congo Red Dye. Polymers 2023, 15, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razali, N.A.; Conte, M.; McGregor, J. The role of impurities in the La2O3 catalysed carboxylation of crude glycerol. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahlan, H.; Saeed, W.S.; Alrasheed, R.; Alandes, N.M.; Aouak, T. Synthesis of poly (citric acid-co-glycerol) and its application as an inhibitor of CaCO3 deposition. Materials 2019, 12, 3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahrooee, T.R.; Moud, A.A.; Danesh, M.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. Rheological characterization of CNC-CTAB network below and above critical micelle concentration (CMC). Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Chang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Song, G.; Sun, Y.; Ding, G. A review on selective dye adsorption by different mechanisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.B.; Vakili, M.; Horri, B.A.; Poh, P.E.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Salamatinia, B. Adsorption of dyes by nanomaterials: Recent developments and adsorption mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 150, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Shen, X. Preparation of Chitosan-Diatomite/Calcium Alginate Composite Hydrogel Beads for the Adsorption of Congo Red Dye. Water 2023, 15, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnomo, A.S.; Prasetyoko, D.; Bahruji, H. Single-step synthesis and modification of CTAB-hectorite for efficient adsorption of methyl orange dye. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 291, 126749. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, G.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, H. Dual-responsive graphene oxide/poly (NIPAM-co-AA) hydrogel as an adsorbent for rhodamine B and imidacloprid. J. Chem. Amp. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 4054–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Lou, T. Simultaneous adsorption for cationic and anionic dyes using chitosan/electrospun sodium alginate nanofiber composite sponges. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 276, 118728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Dahiya, S.; Ali, I. Use of kaolinite as adsorbent: Equilibrium, dynamics and thermodynamic studies on the adsorption of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 69, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, R.J.; Pereira, K.R.A.; Avelino, F. Parametric and modeling studies of Rhodamine-B adsorption using coconut coir-based materials as eco-friendly adsorbents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Gupta, B.; Rastogi, A.; Agarwal, S.; Nayak, A. A comparative investigation on adsorption performances of mesoporous activated carbon prepared from waste rubber tire and activated carbon for a hazardous azo dye—Acid Blue 113. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, T.J.; Mengelizadeh, N.; Al Rawi, O.; Balarak, D. Capacity and modeling of acid blue 113 dye adsorption onto chitosan magnetized by Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhani, H.; Hedaoo, S.; Murugesan, G.; Pai, S.; Vinayagam, R.; Varadavenkatesan, T.; Selvaraj, R. Adsorptive removal of Acid Blue 113 using hydroxyapatite nanoadsorbents synthesized using Peltophorum pterocarpum pod extract. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Lo, I.M. Removal of ionizable aromatic pollutants from contaminated water using nano γ-Fe2O3 based magnetic cationic hydrogel: Sorptive performance, magnetic separation, and reusability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.H.; Foo, K.Y.; Wilson, L.D.; Hameed, B.H.; Hussin, M.H.; Sabar, S. Microwave-assisted synthesis of polyeth-yleneimine grafted chitosan beads for the adsorption of acid red 27. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimpoor, S.; Kiarostami, V.; Khosravi, M.; Davallo, M.; Ghaedi, A. Bees metaheuristic algorithm with the aid of artificial neural networks for optimization of acid red 27 dye adsorption onto novel polypyrrole/SrFe12O19/graphene oxide nano-composite. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 6529–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, R.L.; Wu, F.C. Inferring the favorable adsorption level and the concurrent multi-stage process with the Freundlich constant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Das, R. Strong adsorption of CV dye by Ni ferrite nanoparticles for wastewater purification: Fits well the pseudo second order kinetic and Freundlich isotherm model. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 16199–16215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.C.M.; Dos Santos, T.C.; dos Reis Coimbra, J.S.; de Oliveira, E.B. Chitosan/carboxymethylcellulose polyelectrolyte complexes (PECs) are an effective material for dye and heavy metal adsorption from water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 315, 120977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.X.; Lee, L.; Wang, H.H.; Wang, Z. Removal of an anionic dye by adsorption/precipitation processes using alkaline white mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).