The Recycling Characteristics of Different Silicon Forms and Biogenic Silicon in the Surface Sediments of Dianchi Lake, Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
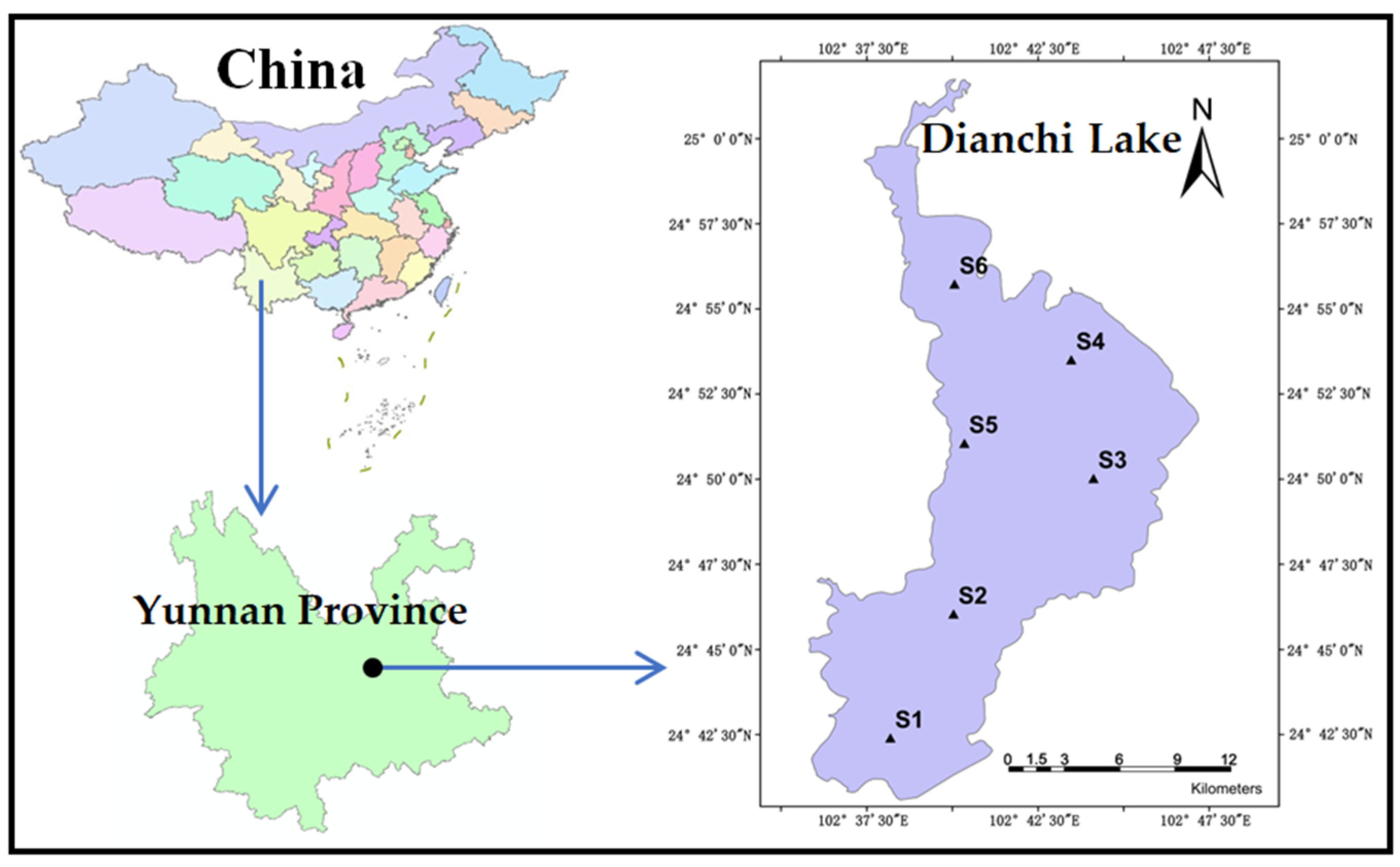
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Sequential Extraction of Different Si Forms in Sediments
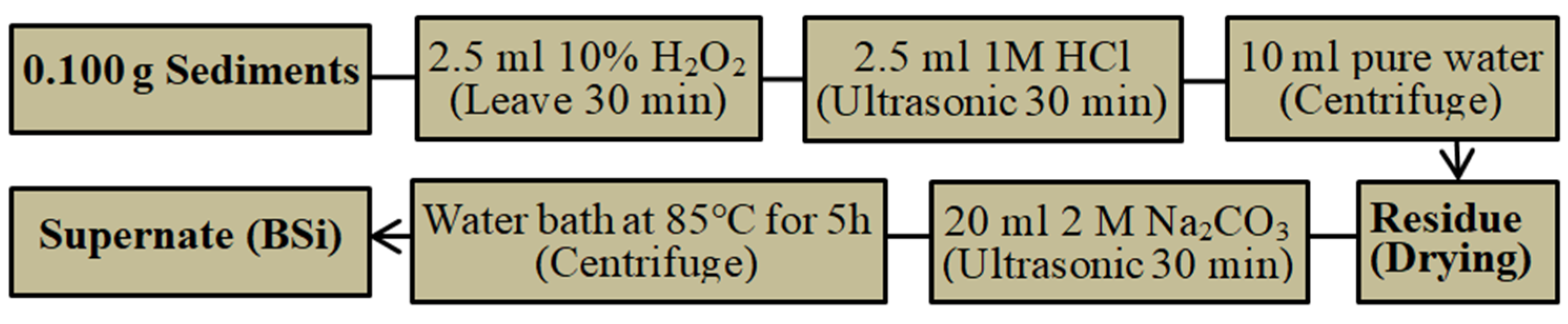
2.3. Extraction of BSi in Sediments
2.4. Determination of Chlorophyll a in Sediments
2.5. Data Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
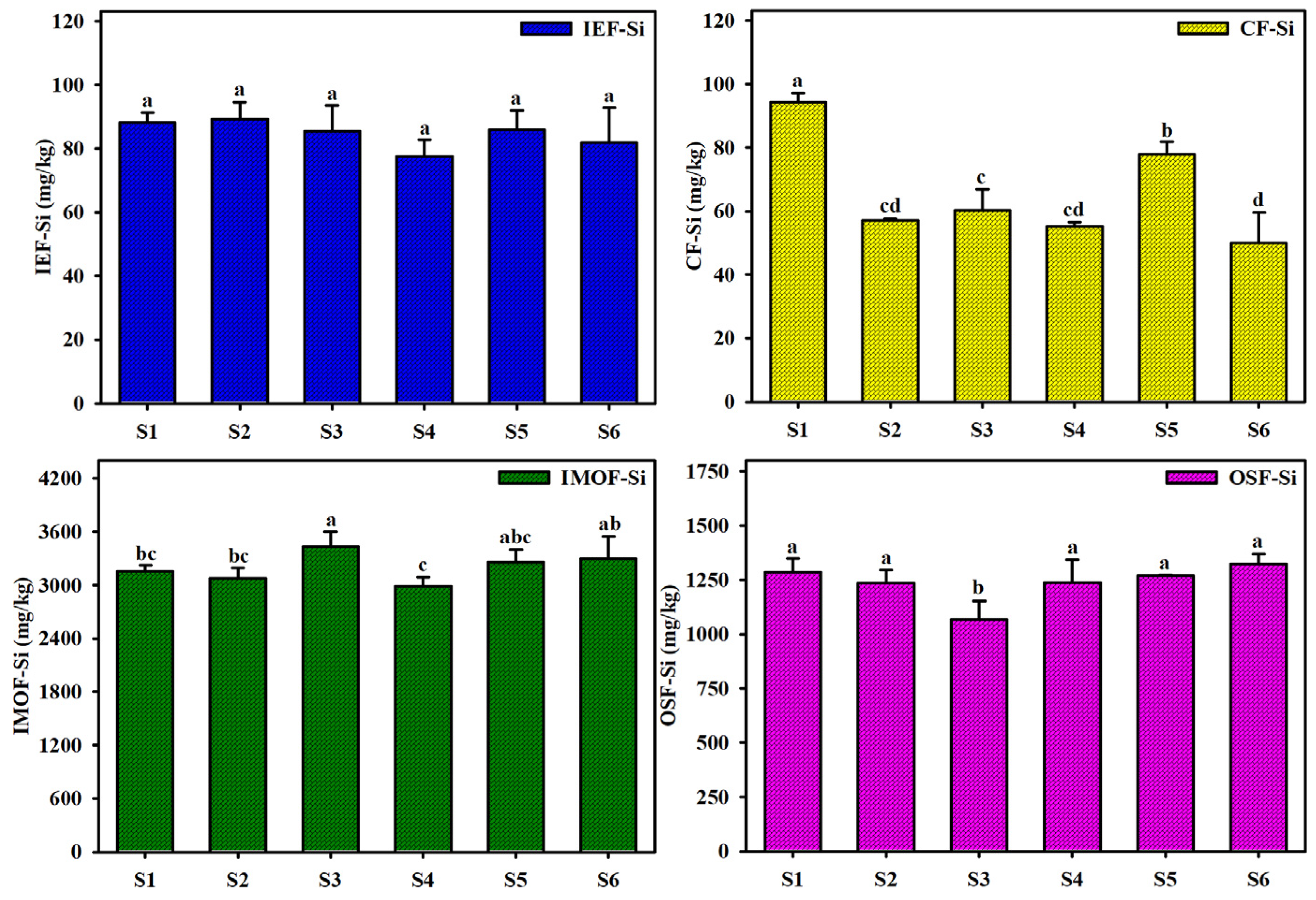
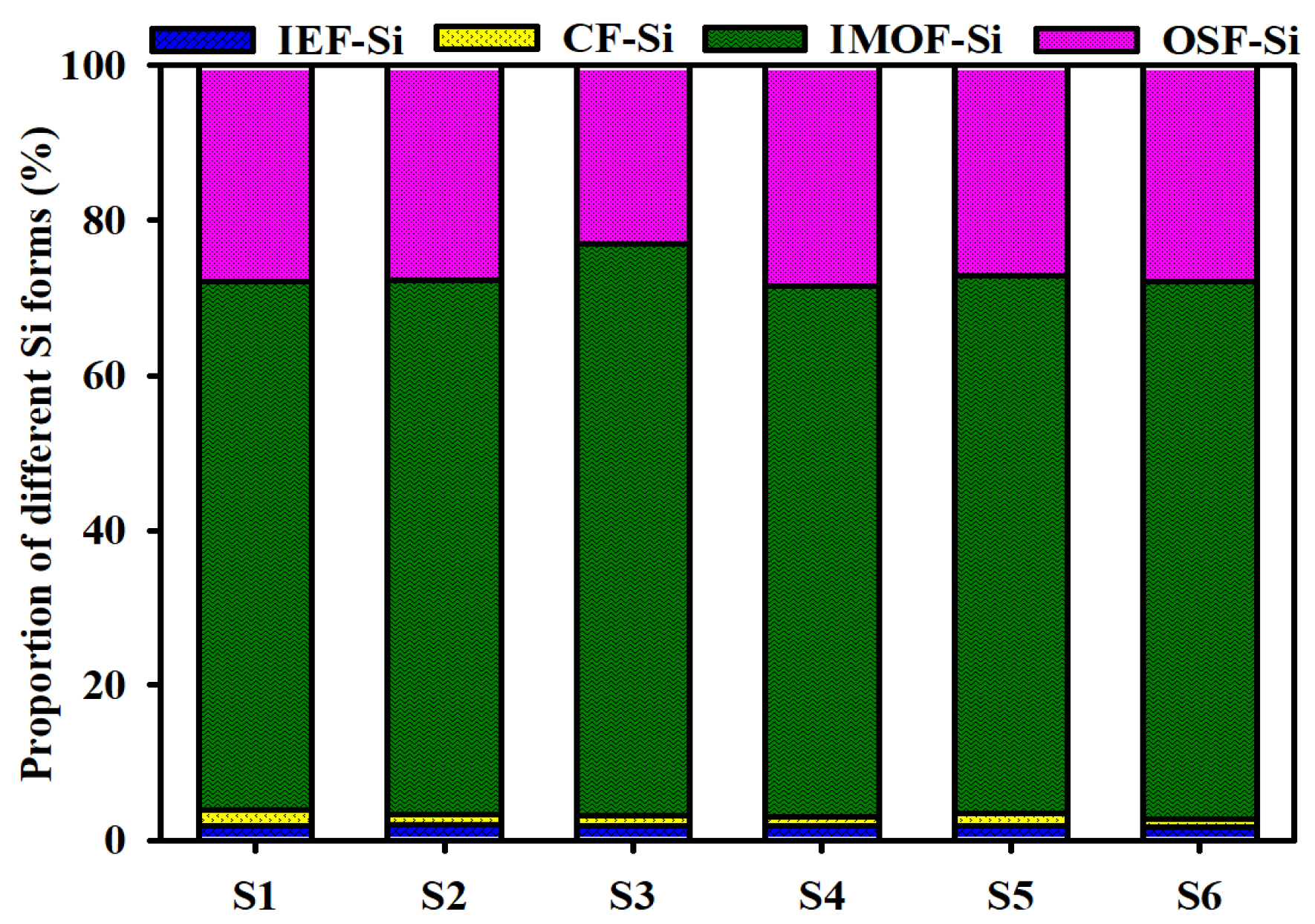
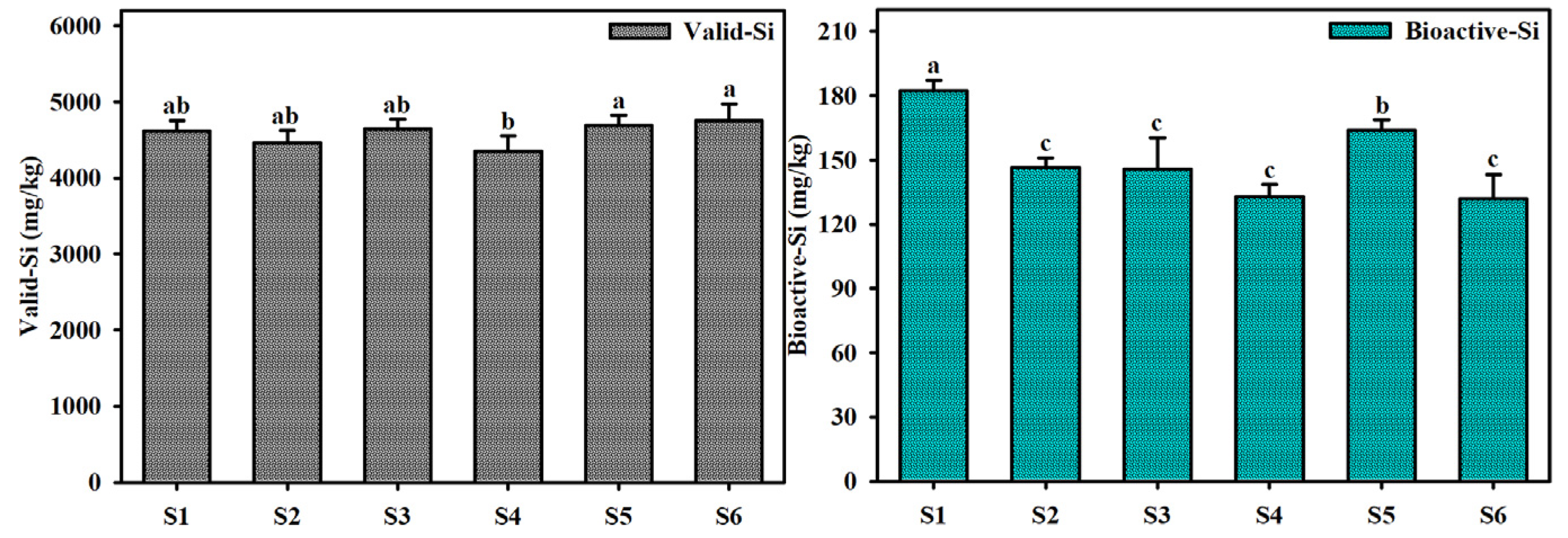
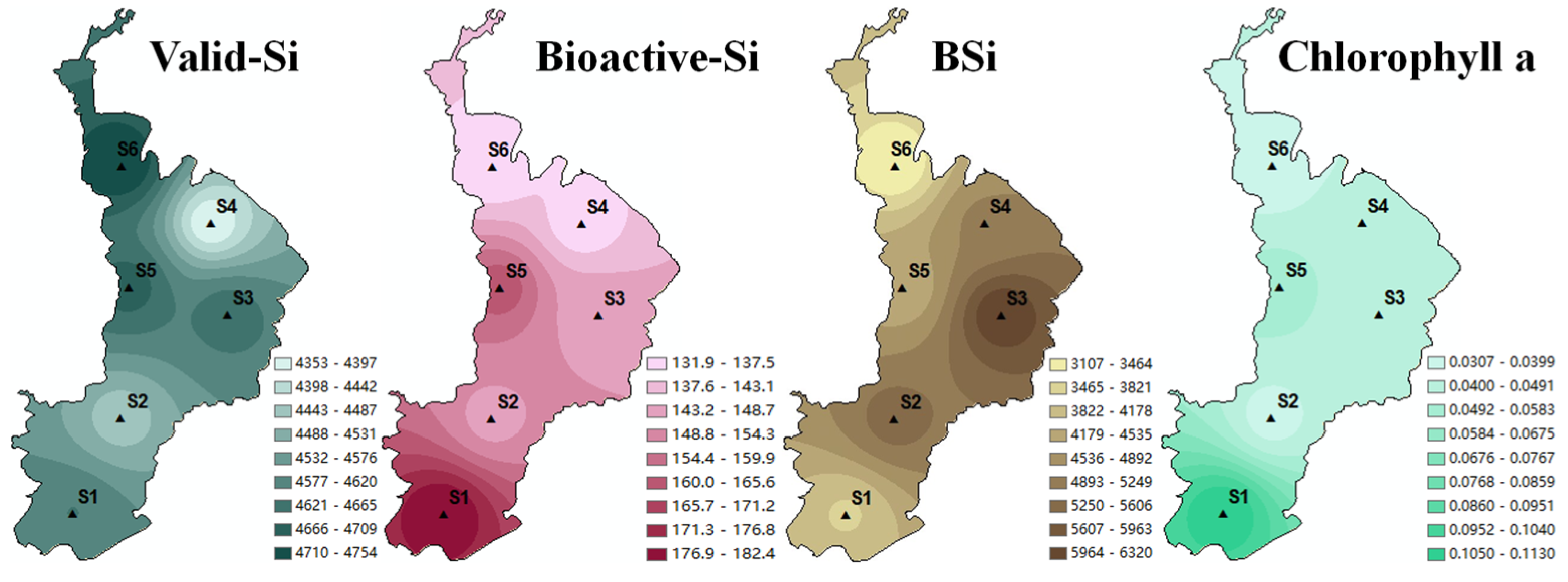
3.1. Content and Environmental Significance of Different Si Forms in Sediments
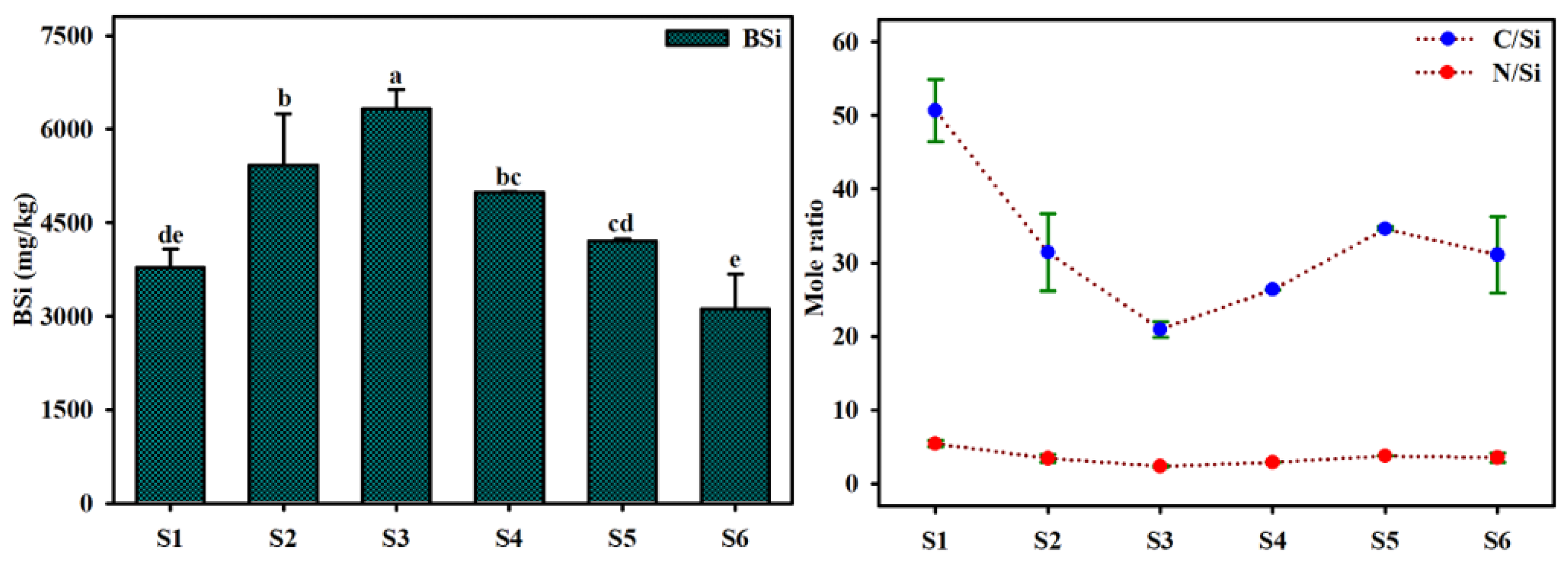
3.2. Indicator of BSi Contents, TOC/BSi (C/Si) and TN/BSi (N/Si) in Sediments
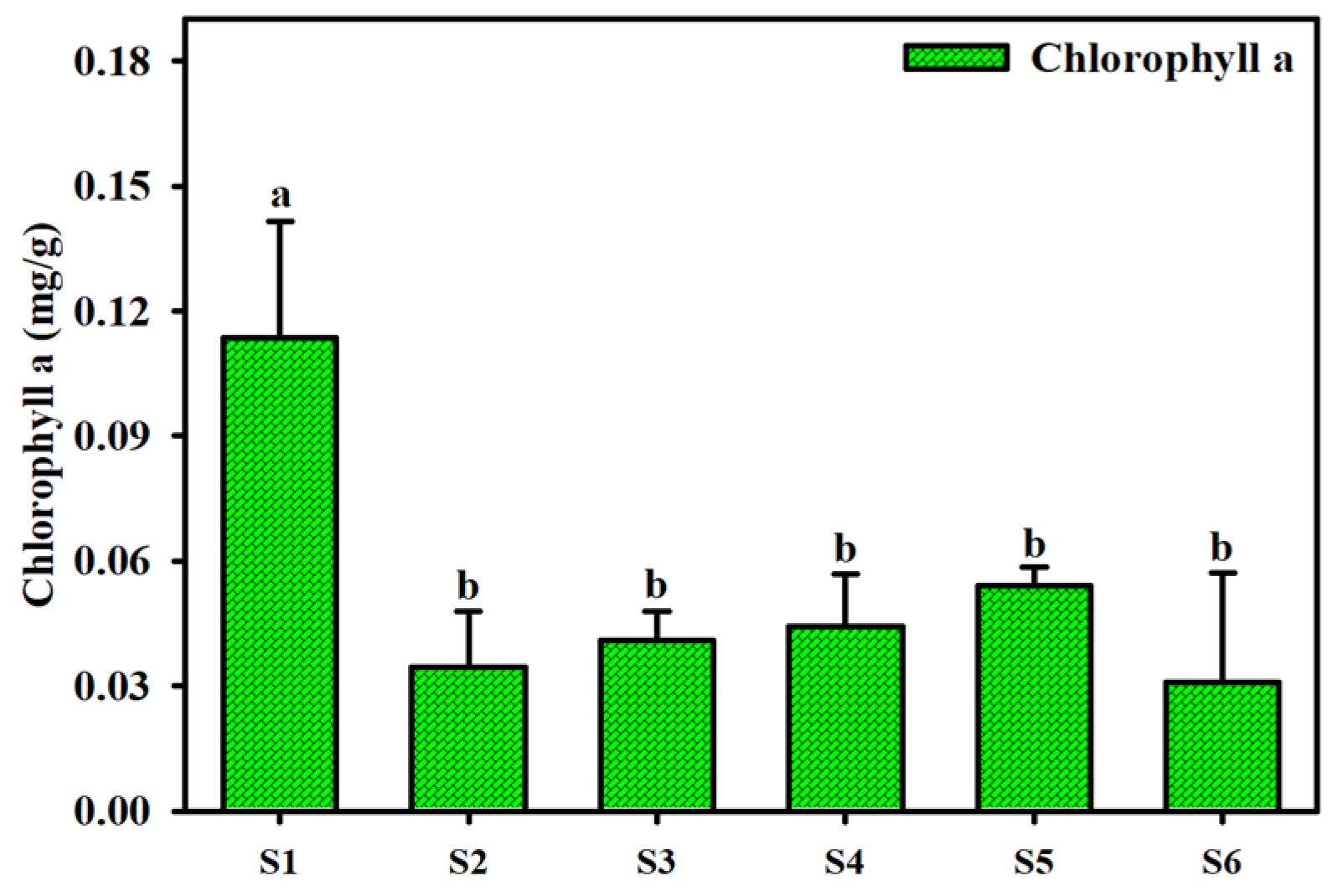
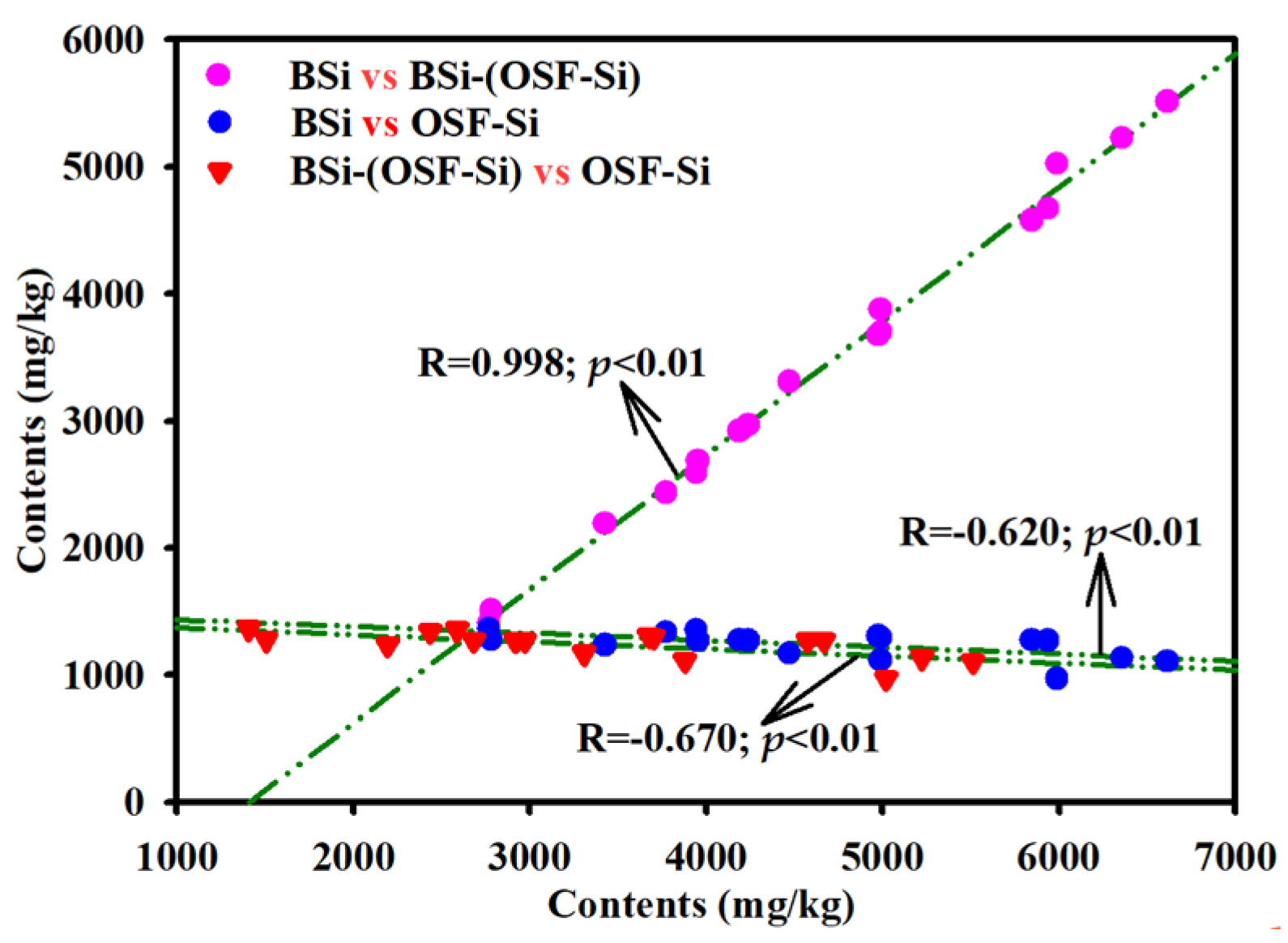
3.3. Correlation between Different Si Forms, BSi, TOC, TN and Chlorophyll a in Sediments
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The coupling relationship between the four different Si forms in the surface sediments of Dianchi Lake was poor (p > 0.05), indicating that their sources were relatively independent and that their formation was more likely to be influenced by the adsorption, fixation and redistribution of dissolved silicon by different lake substances. Moreover, the influence of direct input and transport settlement of terrigenous silicon might be very small. The order of the relationship between the content of different Si forms in the surface sediments was IMF-Si > OSF-Si > IEF-Si > CF-Si.
- (2)
- IMOF-Si (2983.7~3434.7 mg/kg) and CF-Si (50.1~94.2 mg/kg) in the surface sediments of Dianchi Lake had decisive effects on Valid-Si and Bioactive-Si, respectively. Furthermore, the release and recycling of sediment Si may be more sensitive to the redox conditions or pH changes at the sediment–water interface. In particular, the change of sediment redox conditions was the main method of silicon recycling in the surface sediments of Dianchi Lake. In addition, the slow degradation of OSF-Si-rich organosilicones may lead to long-term and continuous internal silicon recycling.
- (3)
- The low proportion (0.3~0.6%) and large spatial difference of BSi in the surface sediments of Dianchi Lake, as well as the poor correlation between BSi and TOC, TN and chlorophyll a, indicated that the primary productivity of Dianchi Lake was still dominated by bloom algae, such as cyanobacteria, while the relative abundance of siliceous organisms such as diatoms was low and closer to the lake center. However, BSi may have a faster dissolution and release ability than TOC to participate in silicon recycling within lake water ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bokor, B.; Santos, C.S.; Kostoláni, D.; Machado, J.; Silva, M.N.; Carvalho, S.M.P.; Vaculík, M.; Vasconcelos, M.W. Mitigation of climate change and environmental hazards in plants: Potential role of the beneficial metalloid silicon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Singh, S.K.; Bhushan, R.; Rai, V.K. Dissolved silicon and its isotopes in the water column of the Bay of Bengal: Internal cycling versus lateral transport. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 151, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, X.; Gao, Y.; Jia, J.; Lu, Y.; Sun, K.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Deng, W. The role of phytoplankton communities on coupled carbon-silicon cycling in a large floodplain lake system. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2022, 22, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wei, G.; Gao, Q.; Tao, Z. Impacts of damming on the biogeochemical cycles of dissolved silicon in a tributary of the Pearl Rriver in South China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2023, 250, 105654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienel, U.; Kirillin, G.; Brademann, B.; Plessen, B.; Lampe, R.; Brauer, A. Effects of spring warming and mixing duration on diatom deposition in deep Tiefer See, NE Germany. J. Paleolimnol. 2016, 57, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Yang, H. Distribution characteristics and forms of sediment silicon in the Inner Mongolia stretch of Yellow River. Environ. Pollut. Control 2020, 42, 432–436. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.H.; Sun, X.; Somelar, P.; Kirsimäe, K.; Pickering, R.A.; Kim, J.H.; Kielman-Schmitt, M.; Hong, W.L. Separating Si phases from diagenetically-modified sediments through sequential leaching. Chem. Geol. 2023, 637, 121681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Song, Z.; Zwieten, L.V.; Wang, Y.; Ran, X.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Wei, Y.; et al. Silicon fractionations in coastal wetland sediments: Implications for biogeochemical silicon cycling. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Schelske, C.L. Potential role of sponge spicules in influencing the silicon biogeochemistry of Florida Lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallberg, P.; Opfergelt, S.; Cornelis, J.T.; Liljendahl, A.; Weckström, J. High concentrations of amorphous, biogenic Si (BSi) in the sediment of a small high-latitude lake: Implications for biogeochemical Si cycling and for the use of BSi as a paleoproxy. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 77, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, K.; Guo, H.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Y. Assessment of the spatial-temporal eutrophic character in the Lake Dianchi. J. Geogr. Sci. 2005, 15, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lin, Z.; Liu, M.; Jiang, F.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, S. Effect of ferric chloride on phosphorus immobilization and speciation in Dianchi Lake sediments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Dan, S.F.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Zhu, D.; Jiao, L. Importance of ammonia nitrogen potentially released from sediments to the development of eutrophication in a plateau lake. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 305, 119275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, L.K.; Hendy, C.H.; Hamilton, D.P. Dynamics of silicon in lakes of the Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand, and implications for diatom growth. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gong, X.; Xie, F.; Liao, H.; Wu, D.; Wu, F. Sedimentary records of accelerated eutrophication in Dianchi Lake over the recent decades. Res. Environ. Sci. 2012, 25, 1236–1242. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheeru, K.A.; Okoro, H.K.; Adekola, F.A.; Abdus-Salam, N. Mobility and sequential Extraction of potentially toxic elements in sediment of Lagos Lagoon. Chem. Afr. 2021, 4, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortlock, R.A.; Froelich, P.N. A simple method for the rapid determination of biogenic opal in pelagic marine sediments. Deep Sea Res. Part A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1989, 36, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, Q. Exploration on the determination method of biosilicon in reservoir bottom mud. J. Neijiang Teach. Coll. 2006, 21, 226–229. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.J.; Zhou, Y.F. Silicate sorption and desorption by a Si-deficient soil—Effects of pH and period of contact. Geoderma 2020, 365, 114204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisawapipat, W.; Christl, I.; Bouchet, S.; Fang, X.; Chareonpanich, M.; Kretzschmar, R. Temporal development of arsenic speciation and extractability in acidified and non-acidified paddy soil amended with silicon-rich fly ash and manganese- or zinc-oxides under flooded and drainage conditions. Chemosphere 2024, 351, 141140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z. Bioavailability of Sediment Phosphorus in Dianchi Lake, Southwest China: Evidence from Enzyme Hydrolysis and Phosphate Oxygen Isotopes. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yang, W.; He, H.; Guo, Y.; Xie, G.; Wang, T. Mixed mineralization of carbonate type and silicate type phosphorite in Dianchi area. Phosphate Compd. Fertil. 2023, 38, 11–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B. Status and developing potentiality of the phosphorite resource around Dianchi Lake of Kunming. Geol. Chem. Miner. 2008, 30, 149–154. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, C.; Hou, J.; Miao, L.; Yao, Y. A simulation study on the effect of redox change on the Si in the estuarine sediment. Environ. Chem. 2018, 37, 974–983. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Guo, P.; Lu, D.; Chen, J.; Teng, C.; Wang, Y. Distribution characteristics and environmental significance of different silicon forms in surface sediments of Shanmei Reservoir. China Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 211–217. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/ChlQZXJpb2RpY2FsQ0hJTmV3UzIwMjMxMjI2Eg96Z2hqa3gyMDE1MDEwMjgaCDV1Mjhucndw (accessed on 15 May 2024). (In Chinese).
- Lei, Y.; Wang, F.; Lu, D.; Mei, H.; Yin, R. Determination of biogenic silica in sediments of reservoirs in the Wujiang River and its environment significance. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2011, 31, 30–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, J.; Salimova, A.; Li, A.; Li, L.; Li, D. Phytoplankton distribution characteristics and its relationship with bacterioplankton in Dianchi Lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 40592–40603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Future directions for management and treatment of algal blooms: A case study of filamentous—Cyanobacteria in Dianchi Lake. Theor. Nat. Sci. 2023, 6, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, J.A.; Lehman, J.T. Interannual variation in diatom bloom dynamics:roles of hydrology, nutrient limitation, sinking, and whole lake manipulation. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2551–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, F.; Wu, M.; Yin, R. Distributions of total phosphorus, phosphorus fractions, and biogenic silica in Dianchi Lake and Hongfeng Lake sediments. Chin. J. Ecol. 2009, 28, 88–94. Available online: https://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/STXZ200901014.htm (accessed on 20 May 2024). (In Chinese).
- Michalopoulos, P.; Aller, R.C. Early diagenesis of biogenic silica in the Amazon delta: Alteration, authigenic clay formation, and storage. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, C.W.; He, J.; Liang, Y.; Mao, H.F.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, F.J. Temporal and spatial distribution of biogenic silica and its significance in the Wuliangsuhai Lake and Daihai Lake. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Yan, H.; Xu, S.; Ou, D.; Lin, X. Distribution of biogenic silica in tidal flat sediments of Yangtze Estuary and its influence factors. China Environ. Sci. 2007, 27, 665–669. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B. Distribution, Dissolution and Influencing Factors of Biogenic Silica in Sediments of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2015. (In Chinese). Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/thesis/ChJUaGVzaXNOZXdTMjAyNDAxMDkSCFkyODg0MjYzGghmaTZ2aWlzbg%3D%3D (accessed on 18 May 2024).
- Gallinari, M.; Ragueneau, O.; Corrin, L.; DeMaster, D.J.; Treguer, P. The importance of water column processes on the dissolution properties of biogenic silica in deep-sea sediments I. Solubility. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 2701–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucaide, S.; Cappelle, P.V.; Behrends, T. Dissolution of biogenic silica from land to ocean: Role of salinity and pH. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, P.A.; Ishiwatari, R. Lacustrine organic geochemistry—An overview of indicators of organic matter sources and diagenesis in lake sediments. Org. Geochem. 1993, 20, 867–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller WE, G.; Schröder, H.C.; Wang, X. The Understanding of the Metazoan Skeletal System, Based on the Initial Discoveries with Siliceous and Calcareous Sponges. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, M.; López-Acosta, M.; Sitjà, C.; García-Puig, M.; Galobart, C.; Ercilla, G.; Leynaert, A. Sponge skeletons as an important sink of silicon in the global oceans. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| IEF-Si | CF-Si | IMOF-Si | OSF-Si | Valid-Si | Bioactive-Si | BSi | Chlorophyll a | TN | TOC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IEF-Si | 1 | |||||||||
| CF-Si | 0.287 | 1 | ||||||||
| IMOF-Si | 0.137 | −0.083 | 1 | |||||||
| OSF-Si | −0.115 | 0.175 | −0.269 | 1 | ||||||
| Valid-Si | 0.138 | 0.098 | 0.860 ** | 0.251 | 1 | |||||
| Bioactive-Si | 0.601 | 0.938 ** | −0.020 | 0.105 | 0.132 | 1 | ||||
| BSi | −0.024 | −0.193 | 0.088 | −0.620 ** | −0.245 | −0.170 | 1 | |||
| Chlorophyll a | 0.102 | 0.850 ** | −0.263 | 0.133 | −0.131 | 0.746 ** | −0.254 | 1 | ||
| TN | 0.402 | 0.722 ** | −0.265 | −0.026 | −0.204 | 0.748 ** | 0.168 | 0.644 ** | 1 | |
| TOC | 0.394 | 0.733 ** | −0.280 | 0.001 | −0.206 | 0.754 ** | 0.140 | 0.654 ** | 0.999 ** | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, G.; Wang, J.; Xu, K.; Jin, Z.; Huang, G. The Recycling Characteristics of Different Silicon Forms and Biogenic Silicon in the Surface Sediments of Dianchi Lake, Southwest China. Water 2024, 16, 1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131824
Liu Y, Liu J, Xu G, Wang J, Xu K, Jin Z, Huang G. The Recycling Characteristics of Different Silicon Forms and Biogenic Silicon in the Surface Sediments of Dianchi Lake, Southwest China. Water. 2024; 16(13):1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131824
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yong, Jv Liu, Guoli Xu, Jingfu Wang, Kai Xu, Zuxue Jin, and Guojia Huang. 2024. "The Recycling Characteristics of Different Silicon Forms and Biogenic Silicon in the Surface Sediments of Dianchi Lake, Southwest China" Water 16, no. 13: 1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131824
APA StyleLiu, Y., Liu, J., Xu, G., Wang, J., Xu, K., Jin, Z., & Huang, G. (2024). The Recycling Characteristics of Different Silicon Forms and Biogenic Silicon in the Surface Sediments of Dianchi Lake, Southwest China. Water, 16(13), 1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131824







