Abstract
The development and utilization of unconventional water resources has become a strategy to alleviate the agricultural water crisis in many countries and regions. To understand the research progress, hot spots, and future trends in the field of unconventional water agricultural irrigation (UWAI), this paper systematically analyzes 6738 publications based on the core database of Web of Science 1990–2023 using the scientific bibliometric analysis software CiteSpace, VOSviewer, and Scimago Graphica. The results showed that the research on UWAI is always rapidly developing. Soil science, crop science, and bioengineering are the main disciplines involved. Most research on WUAI has occurred in China and the United States. Countries with higher levels of development tend to have more influence. Collaboration among authors is fragmented, and collaboration between authors and states needs to be strengthened. Through keyword analysis, the research hotspots are summarized as follows: (1) The effects of traditional and emerging pollutants brought by unconventional water irrigation on soil physicochemical properties, crop growth, and groundwater quality; (2) the health threats caused by pollutants entering the food chain and groundwater; (3) unconventional water utilization technologies, including rainwater harvesting agriculture, precision agriculture, and urban agriculture. Future research hotspots will focus on the mechanisms of pollutant solute transport and transformation in the water–soil–crop system under non-conventional water irrigation conditions and crop physiological responses. We suggest that the research on traditional and emerging pollutants in unconventional water should be strengthened in the future, and the risk control system of unconventional water irrigation should be improved. International cooperation should be strengthened, especially with poor countries in arid regions, to promote the formation of unified international standards and guidelines for non-conventional water irrigation in agriculture.
1. Introduction
According to the United Nations World Water Development Report, agriculture is the largest consumer of water resources, with irrigation accounting for over 70% of global freshwater use [1]. Most crops depend on irrigation, and the rapid development of irrigated agriculture has played a huge role in increasing yields [2]. However, all countries in the world are faced with problems such as increasing demand for freshwater resources and uneven distribution of water resources, resulting in a prominent contradiction between the supply of and the demand for water resources [3,4]. Especially in countries located in arid and semi-arid areas, it is difficult for freshwater resources to meet the demand for agricultural water, and the cost of agricultural irrigation is gradually increasing [5,6,7]. About 61% of the population of the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region lives in areas of extreme water scarcity and faces extreme water stress [8,9]. Precipitation is the main source of freshwater resources, and agricultural irrigation is almost dependent on rainfall, which greatly limits agricultural development in the region and causes climate and food crises. Even countries located in the eastern Mediterranean, such as Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Jordan, Iraq, and Iran, have a relatively mild and humid climate, but the region as a whole has only a few perennial rivers and has mainly ephemeral rivers that flow only during the rainy season [10,11,12]. In the case of the increasing water resources shortage and the increasing demand for agricultural water, it is urgent to find alternative water sources for agricultural irrigation, and the development and comprehensive utilization of unconventional water resources has become an important way. Unconventional water resources include reclaimed water, brackish water, rainwater, seawater, and mine water. As a widely distributed and renewable water source, the exploitation and utilization of unconventional water resources has become a strategy to alleviate the agricultural water crisis in many countries and regions [13,14]. Seventy percent of the world’s desalination plants are located in the Middle East, and Israel mixes desalinated water with groundwater to develop efficient agriculture. Saudi Arabia uses desalinated water to grow wheat, greatly alleviating the food crisis [15]. Brackish water has been used for agricultural irrigation for many years. Through extensive research and practice, safe and efficient technologies for its utilization have gradually developed and matured. Israel was the first country to carry out the research on brackish water agricultural irrigation, which provided a lot of theories and experience for the comprehensive utilization of brackish water agriculture in the world [16]. Rainwater harvesting irrigation techniques involve the engineered collection and storage of stormwater runoff to increase water availability and reduce evaporation, enabling active irrigation during periods of crop water demand. Combining it with water-saving measures is crucial for improving the utilization rate of rainwater resources, especially in arid regions [17]. In Rome, rooftop rainwater harvesting can meet 22–40% of the irrigation needs of urban agriculture, saving freshwater resources to a large extent [18]. In the context of seasonal lack of surface water and groundwater resources, Pakistan’s rain-fed agriculture area is as high as 25%. Reclaimed water refers to industrial sewage or domestic sewage after reasonable treatment, to meet certain water quality standards and to meet certain requirements of the use of water sources. The total amount of reclaimed water is large, the distribution is wide, and the influence of season and climate is small. The use of reclaimed water to irrigate farmland has been widely promoted and practiced. Reclaimed water for large-scale farmland irrigation began in California, the United States, in the early 20th century. The California government formulated the world’s first water quality standard for reclaimed water irrigation in 1918 to regulate the healthy development of reclaimed water irrigation. At the beginning of the 21st century, the amount of reclaimed water for agricultural and urban green belt irrigation in California accounted for about 70% of the total recycled water reuse [19]. In the 1960s, the reuse of all sewage was listed as a basic national policy in Israel, and by 1987, Israel had achieved 100% of domestic sewage and 72% of municipal sewage reuse, and nearly 50% of Israel’s recycled water was directly used for farmland irrigation [20]. In relatively water-scarce areas of southern Europe, more than 45% of reclaimed water is used for agricultural irrigation.
Bibliometrics is the in-depth exploration of the information contained in the literature. Through qualitative and quantitative analysis of the literature, we can understand the research progress, research hotspots, and research trends in related fields [21]. Bibliometrics technology has been widely used in the fields of engineering, agriculture, medicine, and management science. With the development of bibliometrics, a variety of visualization tools for different literature analysis methods have emerged in recent years, such as VOSviewer, CoPalRed, CiteSpace, Bibliometrix, Scimago Graphica, etc. Scholars can carry out literature visualization analysis according to the characteristics of these tools. In recent years, many scholars have conducted bibliometrics research on various topics by using visual tools. However, to the best of our knowledge, it is almost unprecedented for scholars to conduct a comprehensive and systematic analysis of the application of unconventional water in agricultural irrigation from a scientometrical perspective. Therefore, this paper integrates the advantages of various visualization software platforms and chooses VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and Scimago Graphica to conduct scientometrics research on the UWAI literature. VOSviewer has clear and simple characteristics, and it can draw a visual network that fits the timeline. In this paper, it is used for publication visual network analysis. CiteSpace has the advantages of simple operation and comprehensive analysis results [22]. In this paper, CiteSpace is used to analyze research hotspots and trends. Scimago Graphica can combine the number of publications and the curve of the cooperation relationship with the map, which is used in the analysis of country/region cooperation in this paper. Based on this, this study adopts bibliometrics to systematically analyze and interpret the publications in the field of UWAI and to identify the research progress, research hotspots, and popular trends. This paper is divided into the following parts. The first part analyzes the general nature of the publications from the perspective of the overall output of the publications (the number of publications, the number of citations, and the categories of subjects involved). The second part, through the publication visualization network analysis, comprehensively analyzes the core authors, institutions, countries, and journals of UWAI publications, and the cooperation among them, and reveals the disciplinary evolution direction of UWAI. The third part, through keyword co-occurrence, clustering, and emergent analysis, reveals the main progress and popular trend in the UWAI field.
This paper combined the advantages of the three bibliometrics analysis tools to carry out a visual analysis of UWAI-related publications. The necessity of such an analysis lies in its ability to systematically organize and synthesize the existing research within the UWAI domain, ensuring that the derived results are both comprehensive and scientifically valid. Our objective is to synthesize the findings of bibliometric analyses with the specific content of pertinent literature to gauge the overall development level of UWAI-related research (including the number of publications, the number of citations, the range of disciplines involved, etc.) and obtain the core authors, institutions, countries, and journals in this field, as well as to uncover the cooperation situation. The aim is to grasp the research progress, hot spots, and trends in this field. Finally, based on the insights derived from our analysis, we intend to propose recommendations concerning future research directions, risk control, and policy formulation. This paper will provide guidance for scholars and policymakers in the UWAI field.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
In this paper, on 9 April 2024, we selected the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) of the Web of Science Core Collection (WSCC) from the digital library of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) as the paper retrieval source. The search scope of WoS was set as “topic”, and the search string was as follows: TS = (salt water OR brackish water OR desalinated seawater OR harvested rainwater OR rainwater collecting OR rainfall storage OR rainwater catchment and utilization OR reclaimed water OR unconventional water OR seawater OR sewage OR wastewater OR Pit water) AND TS = (agricultural irrigation OR field irrigation). The document types selected were “article” and “review”. From 1 January 1990 to 31 December 2023 was set as the time span. A total of 6899 publications were retrieved. After excluding irrelevant research fields, a total of 6738 valid publications were selected as the scientometrics database for this paper. The selected publications were exported in pure text files containing information such as the number of publications, keywords, and references.
2.2. Research Methods
Scientometrics of publications is a method used to conduct qualitative and quantitative analyses of a database of publications based on statistics and computational techniques. It can clearly and succinctly summarize the development process, hot spots, and future trends of a certain field [23]. The flow chart of the research design for this review is shown in Figure 1. First, the research theme of this paper was defined: a scientometric analysis of the research trends and knowledge structure of CEI from 1993 to 2022. Next, preliminary literature databases were searched based on the topic, and after excluding publications from unrelated research areas, the relevant data were exported through publication selection. Finally, data analysis and data visualization were carried out through visualization software. The visualization software used in this article includes CiteSpace, VOSviewer, and Scimago Graphica. Among them, VOSviewer (Version 1.6.20) is a software tool for constructing and visualizing bibliometric networks; it is used in this paper for institutional cooperative network analysis, and journal co-citation analysis. Scimago Graphica (Version 1.0.42) is a powerful and easy-to-use graphical tool that can be used for bibliometric analysis. In this study, it is used to produce a country/region collaboration map with the number of publications. CiteSpace (Version 6.2.R7) is citation visualization analysis software that was gradually developed against the background of scientometrics and data visualization. In this paper, it is used for author cooperative network analysis, keyword co-occurrence analysis, keyword cluster analysis, and keyword bursts analysis.

Figure 1.
Study design flow chart of UWAI.
3. Results
3.1. General Analysis
3.1.1. Overall Trend of Publications and Citations
Through the analysis of the annual cumulative number of published documents, we can grasp the overall development level and development speed of the UWAI field and predict the future development trend. In addition, it can also show the degree of the scholars’ attention to this field in different time periods. From 1990 to 2023, a total of 6738 publications were published, with an overall increasing trend year by year, as shown in Figure 2. In the past three decades, the average annual growth rate of the number of papers was 18%, and the overall annual publication trend was exponential. Based on the annual publication trend of the published papers, the development of the UWAI field can be divided into three stages. The first stage, from 1990 to 2000, was the initial stage of related research. Only 473 academic studies were published, accounting for 7.02% of the total number of papers, and the scholars lacked direction and experience in exploring theoretical knowledge in the UWAI field. The period from 2001 to 2010 was the second stage; it was a slow development stage, with a total of 1199 publications, accounting for 17.79% of the total number of publications. The number of published papers and citations increased compared with the previous period, indicating that the UWAI field began to be widely considered and belonged to the “growth stage” of the UEAI field. Since 2011, the UWAI field has entered a stage of rapid development, and the number of papers cited and published has increased rapidly, with a total of 5072 papers published, accounting for 75.27% of the total number of papers published. The cumulative citations in this stage reached 164,767, accounting for 91.4% of the total citations. To sum up, research on UWAI is gradually gaining popularity and has entered a stage of flourishing development, and this trend will continue in the future as society and government pay more and more attention to unconventional water resources.
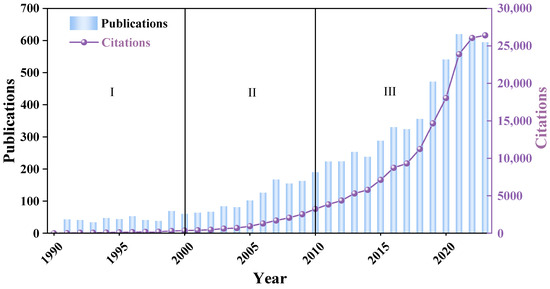
Figure 2.
The annual distribution of the UWAI publications and citations from 1990 to 2023.
3.1.2. Subject Category Analysis of Publications
Subject category analysis can reflect the scope of the disciplines involved in the UWAI field, help scholars understand the direction of discipline development, and judge whether the field tends towards specialization or integration [24]. Based on a statistical analysis of 6738 publications, the top ten subject categories in the field were derived, as shown in Table 1. On the whole, the number of publications on various subjects showed an increasing trend; soil science, crop science, and bioengineering were the three main subject categories. Based on the annual distribution of publications and citations, the publications were analyzed by subject category in three time periods (1990–2000, 2001–2010, and 2011–2023). From the first stage to the second stage, the publications on soil science, crop science, bioengineering, contamination and phytoremediation, and water resources have grown rapidly. In contrast, the publications on other subjects exhibited slower growth rates. Transitioning from the second period to the third, there was a significant increase in the number of publications across these top ten subject categories, signaling an expansion in the scope of subjects within the UWAI field. This expansion suggests a growing trend towards interdisciplinary collaboration among researchers and an overall diversification of scientific research in the UWAI field.

Table 1.
The publications output of the top ten subject categories.
A dual-map overlay is designed to show the broad disciplinary relationship of the combination of citing publications and cited publications (Figure 3). The dual-map design enables the publication’s disciplinary links and citation path to be visually represented. The map on the left is the map of the citing journal, and the map on the right is the map of the cited journal. Therefore, we can analyze the origin of journal citations according to the double graph. The curve is the citation path of the publication, which can indirectly reflect the disciplinary connection between the citing publication and the cited publication. The diagram mainly consists of five main paths. The yellow line represents the subject link from “veterinary, animal, science” to “plant, ecology, zoology”, “environmental, toxicology, nutrition”, “molecular, biology, genetics”, and “earth, geology, geophysics”. The blue line indicates subject associations from “ecology, earth, marine” to “plant, ecology, zoology”. The relevant publications indicating the UWAI field are mainly concentrated in the fields of “veterinary, animal, science” and “ecology, earth, marine”. The publications cited are mainly in the fields of “plant, ecology, zoology”, “environmental, toxicology, nutrition”, “molecular, biology, genetics”, and “earth, geology, geophysics”. The path from the left to the right (from citing publications to cited publications) in the figure becomes significantly more fragmented, indicating a broader range of disciplines in the cited literature. The fact that UWAI publications cite publications from a wider range of disciplines further illustrates the trend towards diversification in UWAI research.
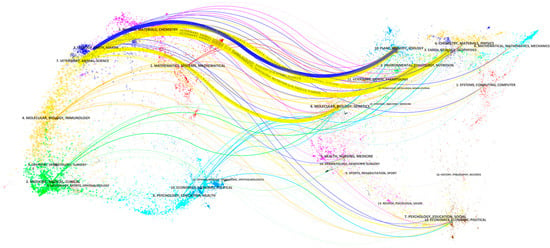
Figure 3.
The dual-map overlay for publications related to UWAI using CiteSpace.
3.2. Academic Impacts and Cooperation Analysis
3.2.1. Country Influence and Cooperation Analysis
Figure 4 shows the global distribution of country/regional collaborations, with the number of publications per country represented by nodes. The more publications a country has, the larger its nodes on the map. A total of 135 countries worldwide have published publications related to UWAI research. Only 22 countries published more than 100 publications, accounting for only 16.30% of the total, and 88 countries published fewer than 30 publications, accounting for 65.19% of the total. Notably, China and the United States stand out as the top contributors, displaying significantly higher publication numbers compared to other countries (Table 2). The initial pioneers in UWAI research include the United States, Israel, India, Iran, Australia, and Germany. In terms of international collaboration, China and the US showcase the strongest partnership (Figure 5), followed by Egypt and Saudi Arabia, as well as China and Pakistan. Only 24 countries cooperate more frequently than 20; so, most countries cooperate less. Disparities in publication output are evident, with economically disadvantaged countries, particularly in Africa, producing fewer publications. Centrality can reflect the influence of a country in a certain field of research. The countries with the largest centrality are the USA (1.22), Spain (0.15), Germany (0.18), and the United Kingdom (0.23), indicating that these countries have greater influence and a leading role in this field, and these countries are all developed countries. Therefore, there is a positive relationship between a country’s degree of development and its influence in the UWAI field. The more developed a country is, the greater its influence. Developed countries tend to have more influence in the UWAI field. China leads in the number of published papers and citations in UWAI research, suggesting its prominence in scientific research in this field. However, China’s centrality is low at 0.09, possibly due to the later initiation of UWAI-related research in the country. Furthermore, countries like Australia, Israel, Pakistan, and Egypt exhibit significant research output, which is possibly driven by their geographic characteristics. Nations with vast land areas tend to focus on water resource management, while those facing water scarcity prioritize conservation efforts, thereby intensifying their UWAI research endeavors.
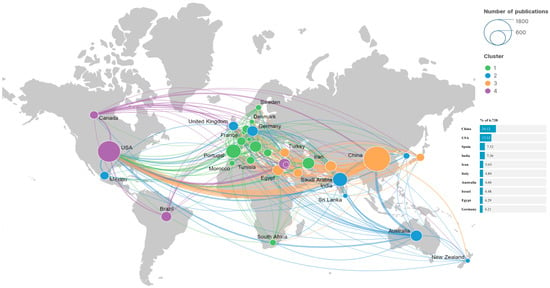
Figure 4.
Country/region collaboration map of UWAI using Scimago Graphica.

Table 2.
Top 15 contributing countries.
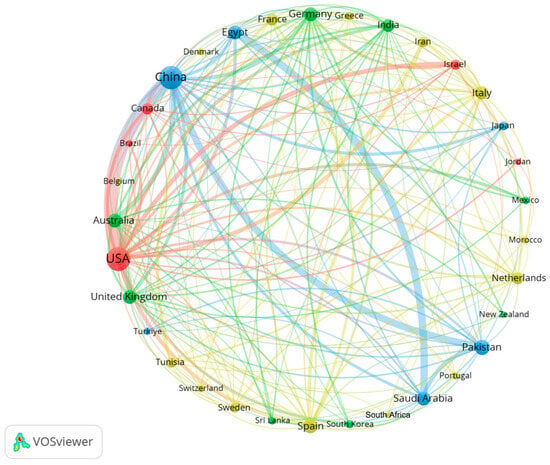
Figure 5.
Country/region collaboration map of UWAI using VOSviewer.
3.2.2. Institutional Cooperation Network Analysis
Through the analysis of the institutional cooperation network, we can reveal the contribution degree of each institution in the field of UWAI research and also reflect the cooperation among institutions [25]. To better understand the research and analyze potential future trends, Figure 6 shows the timeline of the institute’s collaborative network by VOSviewer. Of the 619 institutions in the field, 17 are eligible for ≥50 published publications. For further precise analysis, Table 3 lists the top 15 institutions in this field by number of publications. The top five institutions with the highest number of published publications are the Chinese Academy of Sciences (364), China Agricultural University (148), University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (129), Spanish National Research Council (87), and Agricultural Research organization (84). They are major contributors to scientific research in the UWAI field. Most of these top institutions are from China (6/15), followed by the United States and Israel (3/15), indicating China’s prominent position in UWAI research. Centrality, which reflects an institution’s influence in the research field, is vital for understanding collaboration dynamics. The Chinese Academy of Sciences stands out with the highest centrality score of 0.22, indicating its strong influence and extensive collaboration with other institutions. Additionally, the Chinese Academy of Sciences has the highest total link strength (457), underscoring its role as a core research institution in UWAI. Early contributors to UWAI research include USDA ARS (1990), CSIC (1996), Agr Res Org (1997), Ben Gurion Univ Negev (1999), and Hebrew Univ Jerusalem (1999). Emerging institutions, such as Univ Chinese Acad Sci, Northwest A&F Univ, and Hohai Univ, are gaining influence in the field but require stronger inter-institutional cooperation to maximize their impact. The findings illustrate the diverse landscape of institutional partnerships and emphasize the need for continued collaboration in UWAI research.
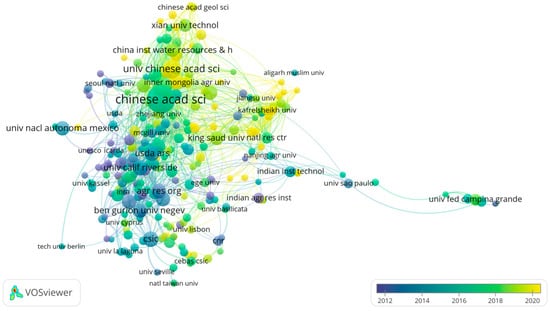
Figure 6.
Network visualization of cooperation among academic institutes using VOSviewer.

Table 3.
Top 15 contributing institutions.
3.2.3. Author Cooperation Network Analysis
The author cooperation network can directly reflect the authors’ publications and cooperation in the UWAI field. Figure 7 is the visual network of author collaboration from CiteSpace, in which the larger the nodes, the more the publications published by the authors, the thicker the connection lines, and the more frequent the collaboration between the authors. A total of 56 authors have published more than 10 publications, among which Kang Yaohu (count = 33) has the most publications, followed by Gheyi, Hans Raj and Wan, Shuqin (count = 31) and Huo, Zailin and Li, Xiaobin (count = 27). They are major contributors to the UWAI field of references. However, most authors publish fewer than five articles. There are 21 pairs of authors with 10 or more collaborations between them, and the close partnership is in the dotted line in Figure 7. The most active collaboration is that of Kang, Yaohu, Wan, Shuqin and Li, Xiaobin. Overall, the clusters formed between the nodes of the collaborative network are fragmented, suggesting that most researchers in the UWAI field are limited to collaborative research with familiar scholars. Strengthening collaborative relationships among scholars is crucial, and researchers should look beyond familiar groups to explore new avenues for research breakthroughs.
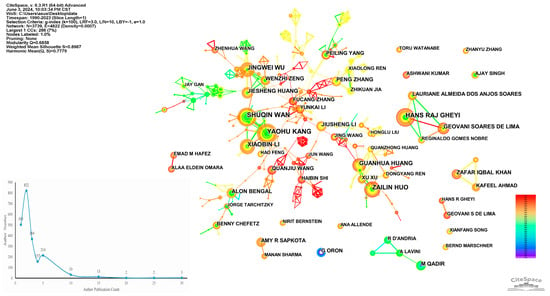
Figure 7.
Network visualization of cooperation among authors using CiteSpace.
3.2.4. Journal Co-Citation Analysis
The co-citation frequency of a journal is positively correlated with its influence, and the co-citation of a journal can reflect the academic influence of a journal in the UWAI field [26]. Figure 8 is a collaborative diagram of the cited journal using VOSviewer. Each node represents a journal, and the size of the node indicates how many times the journal has been cited. The co-citation between journals is represented by the connecting line, and the thickness of the connecting line indicates the co-citation degree between two journals. Of the 22,759 journals, 91 were cited more than 500 times. In addition, in order to further analyze the co-citations of the journals in detail, the top 10 journals in the UWAI field were statistically analyzed, as shown in Table 4. According to the association strength, the relevant journals in the UWAI field are divided into four groups. These groups are red, blue, yellow, and green. Their representative journals are Agricultural Water Management (13,837 times), Science of the Total Environment (7931 times), Water Research (4490), Environmental Science & Technology (4301), Plant Soil (2503 times), and Journal of Hydrology (4211 times). The JCR quartile of the journals is in Q1. It shows that they are the leading journals in the UWAI field. Agricultural Water Management has the highest number of publications and is undoubtedly the core journal in the UWAI field. However, despite its leading position, Agricultural Water Management has a relatively low impact factor of 6.7. This lower impact factor is likely influenced by the journal’s subject category. Therefore, when searching authoritative journals in a certain research field, in order to grasp the research frontier, researchers should take into account the number of citations, JCR quartile, impact factor, and association strength of the journal to ensure the comprehensiveness of the study. Authors should discuss the results and how they can be interpreted from the perspective of previous studies and of the working hypotheses. The findings and their implications should be discussed in the broadest context possible.
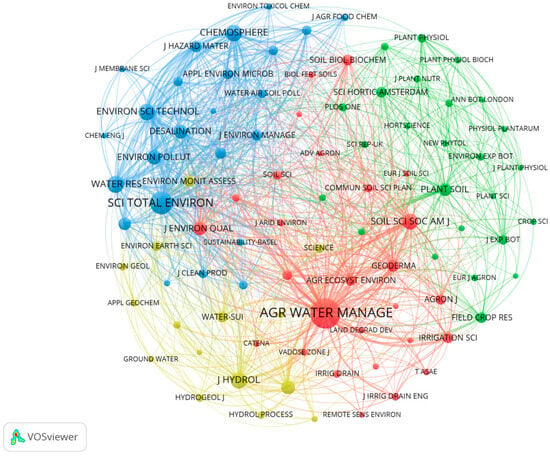
Figure 8.
The cooperation relation graph of cited journals using VOSviewer.

Table 4.
The top 10 most published journals.
3.3. Research Hotspots and Emerging Trends
3.3.1. Keyword Co-Occurrence Analysis
The key words of the literature summarize the core content of the literature and reflect a large amount of information. Analyzing the key words in the research field is helpful to understand the research hotspots in the field [27]. Figure 9 shows the keyword co-occurrence network, in which the nodes represent the keywords, and the size of the nodes represents the frequency of the keyword occurrence. It is evident that keywords such as “growth”, “quality”, “soil”, “management”, and “yield” have a higher frequency of occurrence, in addition to those closely related to the search terms. This indicates that the research objects of the publications in the field of UWAI generally focus on crops and soils. The color of the nodes changes from dark blue to light green, indicating that the year in which the keyword appears in the article is getting closer and closer. The line between the two nodes indicates that the keywords represented by the nodes have co-appeared in the same article, and the color change in the line indicates the time change in the keyword co-occurrence; the closer the color is to light green, the earlier the two keywords co-appeared in the article. The purple circle around the node indicates that the intermediate centrality of the keyword is greater than 0.1. Keywords such as “salinity”, “quality”, “heavy metal”, “field”, and “plant” exhibit the highest intermediate centrality in the network. This suggests that these keywords serve as bridges within the network, indicating that numerous publications on unconventional water agricultural irrigation incorporate these keywords in their content. Table 5 shows the top 30 most frequent keywords. These keywords are reflective of the shared themes present in the research content of the publications. Salinity is a key research direction of unconventional water irrigation. Brackish water, seawater, and part of reclaimed water all contain soluble salt, which can lead to soil salinization, crop salt stress, groundwater pollution, etc., covering a wide range of research directions. The quality of crops irrigated with unconventional water is the most direct influencing factor of unconventional water irrigation. For example, brackish water irrigation will lead to the reduction in the production and quality of some crops, and wastewater irrigation will lead to the enrichment of heavy metals in crops. The quality of unconventional water is also a key factor in determining whether it can be used for agricultural irrigation. The term “heavy metals” indicates that heavy metals are common pollutants in unconventional water sources. The accumulation of heavy metals in soil and crops is a primary focus of the research on unconventional water irrigation pollution.
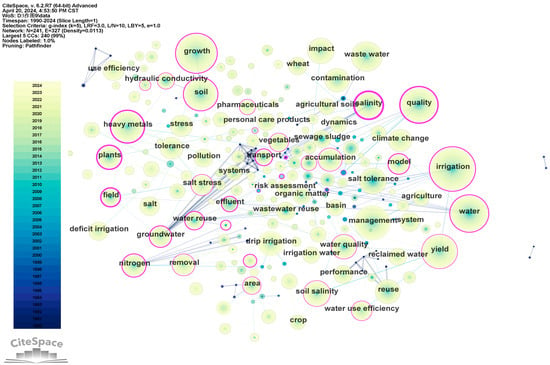
Figure 9.
The keyword co-occurring network using CiteSpace.

Table 5.
Top 30 most frequent keywords.
3.3.2. Keyword Clustering Analysis
Figure 10 demonstrates the keyword clustering analysis, which can scientifically divide a large field into several small fields according to the research content. This refines the research hotspots and facilitates scholars’ overall understanding of the research hotspots. Keyword cluster analysis uses a statistical cluster algorithm to simplify a complex co-occurrence network into relatively simple inter-group relations [28]. Each cluster also reflects the main research advances in the research area, which amounts to a generalization of the main elements of the research area. Figure 10 includes a total of 12 different clusters, and the main keyword information contained in the clusters is shown in Table 6. The parameter silhouette in the table is used to evaluate the clustering effect [29]. When the value is greater than 0.7, the clustering results will be highly reliable. The closer the value is to 1, the better the clustering effect is.
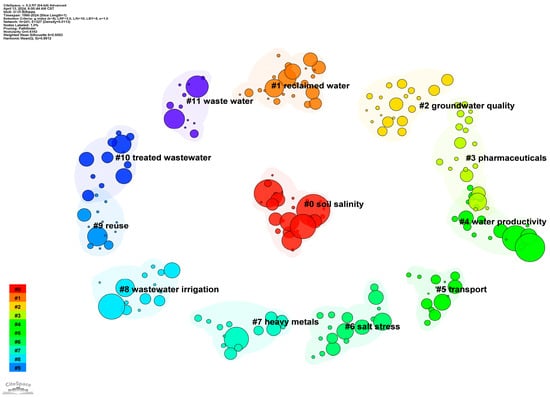
Figure 10.
Keyword cluster analysis.

Table 6.
Top 12 clusters and the main keywords within the clusters.
The first and sixth clusters are related to salt. Brackish water, seawater, and some reclaimed water contain salt ions, and unreasonable irrigation methods applied to farmland will cause adverse effects on soil and crops. Brackish water is a kind of unconventional water source that is widely existing in arid and semi-arid areas, and it is also the earliest unconventional water source used for agricultural irrigation. The biggest problem of brackish water irrigation is that it easily causes soil salt accumulation; so, various brackish water irrigation methods came into being, such as brackish water drip irrigation technology, brackish water and freshwater alternating irrigation, mixed irrigation, etc., and strive to minimize the negative impact on soil. Drip irrigation technology originated in Israel in the 1960s and was applied to 80% of the farmland in Israel by 1999. Since drip irrigation belongs to point source infiltration, it can save water and suppress salt when combined with brackish water [30]. Drip irrigation technology under a brackish water film is also widely used in Xinjiang, China. Salt stress has always been a key research content in plant physiology. A salt stress environment will affect the growth and development of crops, mainly causing ion balance imbalance in plants, ion toxicity, photosynthetic efficiency reduction, and other phenomena that adversely affect crop growth and development. Studies have shown that the slow growth rate of new leaves of plants is the most salt stress-sensitive physiological manifestation [31,32,33,34,35]. Therefore, the research contents of the studies on brackish water and seawater irrigation mainly include two aspects: soil salt accumulation and crop salt stress.
The eighth, tenth, and eleventh clusters focus on wastewater irrigation, which has long been used for agricultural irrigation in countries around the world. As early as the early 20th century, the United States began to promote wastewater for urban green irrigation (urban agriculture). In 1912, Golden Park in San Francisco sprayed its lawn with wastewater treated with a corruptor [36,37,38]. The wastewater used for agricultural irrigation mainly includes domestic wastewater, industrial wastewater, aquaculture wastewater, and so on. In order to avoid damage to humans, crops, and soil, sewage should be treated before it is used for irrigation. The treatment process includes precipitation, filtration, sterilization, etc. At the same time, large-scale flood irrigation with a large quota should be avoided to prevent underground seepage from polluting groundwater. When wastewater is used for irrigation, attention should be paid to the types of crops, soil conditions, irrigation methods, and so on [39,40,41]. The main factors that have the greatest impact on crop growth in wastewater are heavy metal ions and toxic organic matter, and the removal technology of these components has been the main research direction of various countries. In the future, wastewater treatment technology will be further optimized for agricultural irrigation [42,43,44].
The third and seventh clusters show that the two main pollutants in wastewater and some reclaimed water are heavy metals and some harmful chemicals. The practice of wastewater irrigation in countries around the world shows that urban and industrial wastewater is considered to be the main source of heavy metals in farmland soil, and improper treatment of farmland irrigation with this water source will lead to heavy metal enrichment in soil [45,46,47,48]. Rattan et al. [49] found that Zn, Cu, Fe, Ni, and Pb in soil under sewage irrigation increased by 208%, 170%, 170%, 63%, and 29%, respectively, compared with that under water irrigation, and Zn exceeded the tolerance limit of plant toxicity. Wastewater irrigation also affects heavy metal content in crops due to crop absorption. A multi-year study in Egypt found that the use of marginal water irrigation increased the concentration of elements (Pb, B, Ni, Co) in all crops [50]. Xue, Zhan-Jun et al. [51] found that the concentrations of the elements Cd, Zn, and Ni in vegetables collected from wastewater-irrigated soil exceeded the maximum allowable limits, which increased the daily intake of metals in food. Therefore, the concentration of heavy metals in vegetables grown in soil under wastewater irrigation conditions should be regularly monitored, and effective soil remediation techniques should be implemented to reduce the negative impact on human health. The harm to crops and soil and the ecological risks of harmful chemicals such as those in pharmaceutical and personal care products in reclaimed water have been extensively studied in recent years. Studies have shown that wastewater irrigation may increase antibiotic residues in the soil, and the accumulation of antibiotics in the soil will lead to microbial disorders, reduce soil quality, reduce crop yield, and enter the food chain to harm human health [52,53,54,55,56]. Triclosan (TCN) is a common personal care product. Wastewater irrigation will lead to the increase in TCN in soil, reduce the types of soil microorganisms, and then affect the physical and chemical properties of soil, especially soil permeability [57,58].
The second cluster and the fifth cluster are concerned with groundwater quality and the transport of unconventional water to groundwater. One of the key ways of testing whether the use of unconventional water resources is safe is to determine whether the unconventional water irrigation has caused damage to the quality of the groundwater. Reclaimed water and brackish water may contain soluble salts, heavy metals, pathogenic microorganisms, harmful chemical components, and emerging pollutants. After they enter the soil with irrigation water and cause damage to the soil environment, they may enter the groundwater with soil water to further damage the quality of the groundwater and pose a threat to human health [59,60,61]. Therefore, the research of unconventional water treatment technology should be strengthened to realize the source control of pollutants. At the same time, groundwater quality should be monitored over time in areas irrigated with unconventional water.
The ninth cluster involves the rainwater harvesting and reuse technology, and “seasonal allocations” and “agricultural reuse” appear. In arid and semi-arid areas, due to the lack and uneven distribution of water resources, there is a time–space mismatch between rainfall and crop water demand, which seriously restricts the sustainable development of food production and the agricultural economy. Rainwater harvesting agriculture uses rainwater harvesting projects to control rainwater resources, increase storage, or reduce evaporation to collect and store rainwater and to carry out active irrigation in the critical period of crop water demand, which is an important way to solve the problem of drought. Rainwater harvesting systems were established in the Middle East, in the dry river valleys of Libya, and in northern Egypt as early as 2000 BC [62,63,64,65]. At the end of last century, many countries widely used rainwater harvesting technology in farmland irrigation, saline–alkali land transformation, and other aspects. With the development of rainwater harvesting agriculture, many countries have obtained technical experience and scientific research results. The main research directions include the design of rainwater collection engineering, seepage prevention and evaporation of water storage engineering, water transfer and distribution engineering and water-saving irrigation technology, selection of suitable crops, and selection of rainwater collection sites. In Pakistan, the rain-fed agriculture covers 25% of the land area. The scholars used mathematical models to optimize the size and spatial distribution of rainwater underground cisterns to reduce the loss by leakage and evaporation as much as possible, so that the water storage in the rainy season can meet the irrigation demand in the dry season [66,67,68]. The United States developed the Geographic Information System Mapping Tool based on rainfall and evapotranspiration combined with a geographic information system to obtain the potential location of rainwater collection [69,70]. But rainwater used in agricultural irrigation has not yet formed a standardized technology; there is still a series of problems related to rainwater collection technology, water storage facility design, irrigation mode, crop matching, and so on.
3.3.3. Keyword Bursts Analysis
The burst analysis of keywords helps to explore the change in research hotspots in a certain field and predict the future research trend in the field [71]. Figure 11 shows the top 25 keywords with high burst strength. The light blue line indicates that the keyword has not yet appeared; when the dark blue or red line begins to appear, it indicates that the keyword has begun to appear, and the entire red line represents the burst cycle of the keyword. With the passage of time, the research hotspots in the UWAI field have changed. The results show that the keyword with the earliest burst time is “water”, and its burst strength is also the largest, which is 37.61. Its bursts lasted 16 years, from 1991 to 2006. This is related to the inclusion of this keyword in the search string and also indicates that the researchers began their research on agricultural irrigation with unconventional water very early on. Salt tolerance (24.64), the keyword with the second largest burst strength, also has a long burst duration of 20 years. It shows that researchers always focused on the study of crop salt tolerance from 1993 to 2012, which is related to the salt in brackish water, partially reclaimed water, and seawater. How to use unconventional water for farmland irrigation to ensure that crops are not subjected to salt stress to maintain yield or even increase production is a major research direction in the field of UWAI. The keyword with the longest burst duration is effluent, which has lasted for 22 years. Sewage sludge also has a long burst duration, which has lasted for 16 years. It shows that wastewater, as a major unconventional water resource, has been the main research direction of researchers, who have applied it to agricultural irrigation. Hydraulic conductivity as a keyword describing the physical properties of soil has been emergent for 18 years, which indicates that the effect of unconventional water used in agricultural irrigation on farmland soil has been given attention by researchers. The physical and chemical properties of farmland soil are not only related to the growth and yield of crops, but are also closely related to the sustainable utilization of farmland soil. Improper unconventional water irrigation may cause secondary salinization of soil and a decline in soil quality. The keywords “spatial distribution”, “mechanisms”, “drought stress”, and “trace elements” continue to pop up in the recent period, indicating that they are future research hotspots in the field of UWAI. The relevant studies related to these keywords were searched, and their contents were summarized. The key words “spatial distribution” and “trace elements” relate to the spatial distribution of pollutants in soil under unconventional water irrigation conditions and the migration and transformation of solutes contained in pollutants in the water–soil–crop system. In recent years, solute inversion using digital models at a field scale and a regional scale has been a hot research direction. The key word “mechanisms” relates to the migration and transformation of solutes in soil under unconventional irrigation conditions, the growth and regulation mechanism of crops, and the evolution mechanism of the farmland soil environment. The key word “drought stress” refers to the physiological phenomenon of crops under the condition of unconventional water irrigation. Drought stress is caused by crops that have difficulty with water absorption, which is caused by salt and other solutes and the low soil moisture. Severe drought stress will reduce crop yield and quality. To sum up, the above analysis is helpful for scholars to grasp current research hotspots, predict future research directions, and improve research efficiency.
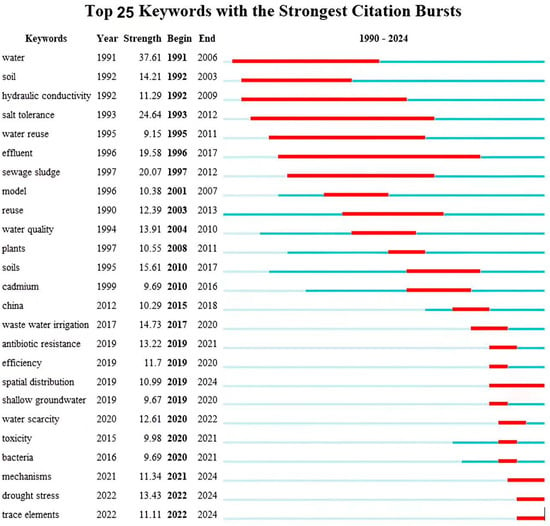
Figure 11.
Keyword bursts analysis.
4. Discussion
Unconventional water resources are widely distributed, and many countries have obtained advanced research results after many years of research. Unconventional water has a more complex composition compared to conventional fresh water, as it contains a variety of substances, such as soluble salts, heavy metals, pharmaceuticals, personal care products, pathogens, and emerging contaminants. In order to ensure the sustainable use of unconventional water resources for agricultural irrigation, the following aspects must be comprehensively considered: (1) soil salinization and crop salt stress; (2) accumulation of heavy metals in soil and plant enrichment; (3) pollution of groundwater by salt, chemical pollutants, and emerging pollutants; and (4) pollutants and pathogens that enter the food chain through crops to harm the human body. Therefore, the research of unconventional water security utilization technology is still in progress.
The main risks of brackish water irrigation are soil salinization, groundwater pollution, and the effects of brackish water irrigation on crop yield and quality. Many researchers have made a series of achievements with regard to the safe utilization of brackish water. Brackish water desalination technology reduces the salinity of irrigation water at the source and thus reduces the irrigation risk [72]. Currently, distillation and membrane separation technology are the primary methods utilized in brackish water desalination. Distillation, the earliest technique employed in this context, has a well-established development history. Its primary strength lies in its simplicity and relatively straightforward operational procedures. The various forms of distillation include multi-effect evaporation, multi-stage flash distillation, and pressure steam distillation. However, the inherent drawbacks of distillation are its inability to completely separate water from salt ions, low separation efficiency, and high costs for large-scale implementations [73]. At present, membrane separation technology is widely recognized as a crucial technological process that effectively separates solute or particles from brackish water using a diaphragm. This technology encompasses various methods, such as electrodialysis, forward osmosis, reverse osmosis, and microfiltration. Membrane separation technology stands out for its ability to achieve high water flux and desalination rates, coupled with the benefits of good stability, long service life, and low energy consumption. Consequently, it has emerged as the predominant brackish water desalination technology in current practice [74]. The optimization of irrigation methods can also reduce the negative effects of brackish water irrigation to a certain extent. The technique of alternating brackish water and freshwater irrigation is based on the characteristics of crops with different salt-tolerance abilities at different growth stages, and by adjusting the time and sequence of alternating brackish water and freshwater irrigation and by irrigating fresh water during the salt-sensitive period of the crop, the soil desalination rate can be improved, the permeability of the soil regulated, and the quality of the farmland soil ensured [75]. Mixed brackish and freshwater irrigation involves the use of a reasonable ratio of brackish water to fresh water for irrigation or the use of brackish and freshwater double-drip irrigation systems for water supply, with the aim of reducing the salinity of the irrigation water or changing its salt composition. Mixed brackish and freshwater irrigation can increase the total amount of water that can be irrigated while improving the quality of irrigation water [76,77]. Similar brackish water safety utilization technology also includes brackish water drip irrigation technology. Drip irrigation of brackish water is the frequent irrigation of brackish water from the ground in the form of point source infiltration into the soil in the range of crop root distribution. This method facilitates the leaching of salts, which are carried by the water to the outer regions of the root system. Consequently, this process helps maintain low salt levels within the soil layer where the roots are actively growing [78,79,80].
Reclaimed water refers to the water resources that can be reused within a certain range after being recovered from non-traditional water sources, such as municipal sewage, industrial drainage, and domestic sewage, and reaches certain water quality standards after proper treatment. Three common techniques for reclaimed water irrigation are the mixing method, soil dilution method, and rotation irrigation method. The mixing method involves utilizing the water supply network to blend water of different qualities, enabling the quality of the mixed water to be tailored to the specific needs of the irrigated soil and crops. This method is often employed in conjunction with drip irrigation practices [81,82,83,84]. The soil dilution method entails strategically timing irrigation to first use reclaimed water followed by fresh water, or vice versa, in order to effectively enhance soil water content while preserving soil quality. The rotation irrigation method involves alternating between reclaimed water and freshwater irrigation based on factors such as reclaimed water quality characteristics and the growth stages of the crops. By optimizing the irrigation approach between reclaimed and fresh water in accordance with the specific needs of the crops, this method ensures a judicious use of resources and minimizes the potential risks associated with reclaimed water irrigation [85,86]. In addition, reclaimed water safe application technology also includes plant type identification and risk assessment technology [87]. Risk assessment technology can quantitatively characterize the current risks of renewable water resources development and utilization and predict the environmental evolution trend after the target irrigation years [88]. The plant type identification technology generally divides the crops irrigated by reclaimed water into three categories. The first category consists of industrial raw material plants, garden green spaces, and forest trees. The second category includes field food crops, peeled vegetables, melons, fruit trees, forage, feed, etc. The third category encompasses raw vegetables, herbs, and fruits [89]. Based on the type of irrigated crops and the results of the risk assessment, different levels of water treatment projects are selected. Irrigation is then carried out in combination with scientific and reasonably safe irrigation technology to form a scientific integrated application model [90,91]. This model effectively guarantees the safe irrigation of recycled water. Although reclaimed water meets certain water quality standards after undergoing various levels of water treatment processes, its composition remains complex compared to conventional water. Current water treatment technologies are still unable to completely and effectively remove the various pollutants present in reclaimed water. Therefore, many scholars are focusing their research on pollution under reclaimed water irrigation conditions. Martinez-Piernas et al. [92,93] conducted targeted and suspicious screening of organic micropollutants in soils irrigated with reclaimed water, and the results showed that 11 kinds of organic micropollutants were detected in soil samples, and organic micropollutants that had never been reported before were found. Wastewater treatment processes are not fully effective in removing all contaminants, such as antimicrobial-resistant bacteria (ARBs) and antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs). Irrigation with wastewater that is not fully treated can increase antimicrobial resistance in soil. Studies have shown that pathogens and bacteria in wastewater pose a threat to public health, and the National Institutes of Health has investigated the health of wastewater irrigation workers in different areas and found that wastewater can increase the risk of potentially infectious diseases [94]. It has been proved that the use of reclaimed water for farmland irrigation increases the content of PPCPs in soil, which are absorbed by crops [95,96,97]. For example, carbamazepine, diclofenac, and triclosan accumulate in the stems and leaves of leafy vegetables. Heavy metals are also major pollutants in soil under reclaimed water irrigation. Kyushu Univ investigated the accumulation of heavy metals in crops in the irrigation area of industrial wastewater in Bangladesh, and the results showed that many heavy metals, such as Zn and Pb, in the crops exceeded the allowable levels [98,99]. The pollution of shallow and deep groundwater by reclaimed water is one of the most concerning problems. Heavy metals, soluble salts, organic pollutants, viruses, heterotrophic bacteria, polyethylene, and polypropylene contained in untreated or poorly treated reclaimed water increase the risk of groundwater contamination and pose a health threat to local populations that use these waters [100,101,102,103,104].
Seawater irrigated agriculture is of great significance for expanding agricultural development space and alleviating the shortage of freshwater resources in coastal areas. However, scholars have been concerned about whether seawater irrigation has adverse effects on soil and, in particular, whether the degree of soil salinization is intensified. There are several approaches to seawater irrigation, including utilizing seawater directly to irrigate salt-tolerant crops, employing varying ratios of seawater and fresh water for irrigating salt-tolerant crops, and applying seawater desalination techniques to decrease seawater salinity for crop irrigation. Thus, the critical technological challenges in seawater irrigation involve the cultivation of salt-tolerant crops, the optimization of seawater mixed irrigation methods, and the advancement of seawater desalination technologies [105,106,107,108]. Cultivating salt-tolerant plants typically involves two strategies: one is genetically modifying freshwater plants by introducing salt-resistant genes through biotechnology to enhance their salt and alkali resistance, while the other method involves identifying salt-tolerant wild plants and domesticating them into conventional crops through artificial breeding and selection processes [109,110,111,112]. The damage of seawater irrigation to farmland is huge, and it is particularly important to control the risk of seawater irrigation. On the one hand, the use of seawater desalination technology to reduce seawater salinity at the source is a necessary measure to solve the shortage of agricultural water supply in coastal areas. At present, seawater desalination technology mainly includes distillation, reverse osmosis, electrodialysis, freezing crystallization, and so on [113,114,115,116,117]. On the other hand, because the salinity of seawater is very high, direct irrigation can easily cause soil salinization; so, it is necessary to increase the research of seawater irrigation methods, such as long-term monitoring of seawater irrigation soil and adopting modern irrigation technology.
The safe utilization of unconventional water agriculture irrigation technology is a key issue that the international community should focus on. However, there is no unified international standard and guideline for the reuse of unconventional water agriculture at present. All countries formulate relevant standards and technical specifications based on existing water resources management policies and in combination with the local water resources supply and demand situation and utilization ways. [118,119]. These standards are mainly to protect the farmland environment and the safety of agricultural products. International water quality standards and policies for unconventional water agricultural irrigation would be beneficial. Previously, the World Health Organization proposed strict guidelines for sewage agricultural reuse, involving sewage treatment technology, the irrigation mode, exposed population and crop types, etc.; countries with sewage agricultural reuse issues are given a unified template, no doubt to promote the attention and development of countries in this area. Of course, there are some differences in the standards and policies of unconventional water agricultural irrigation in different countries and regions with different geographical and climatic characteristics and development levels. The United States Environmental Protection Agency’s reclaimed water reuse guidelines include reclaimed water planning and management, which contain regional differences in reclaimed water reuse by states and provide targeted standards, which greatly promote the efficiency of reclaimed water reuse in states [120]. Agricultural reuse of unconventional water is high on Israel’s list of national priorities, and the extreme water scarcity has led to the establishment of a committee to review existing regulations and propose new ones to address issues arising from unconventional water reuse. Israel’s gradually updated policies and regulations are undoubtedly a good example for other Middle Eastern countries with similar climates [121,122]. The policies of developed European countries on water resources management are mostly economic and environmental. France has applied integrated economic technology models to water resource management and assessment and has suggested that the recycling of unconventional water and agricultural irrigation are the most cost-effective options and has adapted them in conjunction with public attitudes and environmental policies [123]. However, the formulation of relevant policies and regulations in many countries with relatively backward development is still in its infancy, especially in poor countries in arid and semi-arid areas, where unconventional water sources are the only water source for people’s living and agricultural irrigation, and the use of unconventional water is often unplanned; so, the policy impact is also complicated. On the one hand, the benefits of unconventional water to farmers cannot be ignored, especially those living downstream from the discharge of industrial wastewater, which is used to irrigate their fields to solve the food crisis and provide a stable source of income. In contrast to these benefits, farmers and consumers will face health risks and the sustainable use of farmland soils will be threatened. In order to solve this problem, international exchanges should be increased, especially in countries with similar geographical and climatic conditions, and the latest research results and theories in the field of UWAI should be exchanged and guided. To ensure effective implementation of policies and regulations, it is essential for government departments to establish a solid theoretical foundation. Once this basis is established, relevant policies should be formulated and submitted to local management authorities. Subsequently, local management departments should engage in consultations with key stakeholders to solicit their input and address their concerns. Additionally, it is important to provide alternative solutions and incentives to key stakeholders for execution to ensure compliance and efficacy. Moreover, raising awareness about the associated health risks among all stakeholders is crucial to foster informed decision making and proactive engagement.
5. Conclusions
This study conducted a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of the field of UWAI and scientifically and objectively analyzed the academic development process of UWAI. The analysis identifies the most influential authors, institutions, countries, and journals contributing to UWAI research. Additionally, the major advancements in the field are summarized, and future research trends are explored. The findings of this study provide valuable reference material for scholars and policymakers engaged in UWAI, enhancing their understanding and facilitating decision making.
The publication and citations of UWAI-related publications have shown an exponential growth trend in recent years, indicating that more and more countries and regions have begun to pay attention to the agricultural use of unconventional water resources. This trend is expected to continue, and it also reflects that this study has strong guide significance. With the rapid development of this field, the main disciplines involved are becoming more and more diversified, and the cross-links between the disciplines are becoming closer and closer, indicating that the research scope of UWAI is gradually expanding, mainly due to the accelerated modernization process of more and more countries and regions, the emergence of new pollutants, the continuous compression of agricultural water, and the increase in health risks. Changing public attitudes toward unconventional water and the increasing cost of water treatment have prompted researchers to seek new directions and breakthroughs to address these issues. Another serious problem is the growing gap between countries in the level of research, attitudes, and policy development on the use of unconventional water agriculture. Countries with a high level of development began to study UWAI very early, and after years of development, their research level, risk management and control mode, policy standards, and public attitudes have reached a mature level, and they have begun to comprehensively consider economic costs, environmental impacts, and other factors to further expand the research direction of UWAI. However, poor countries in arid and semi-arid regions lag behind in this area. Agriculture in these areas is basically completely dependent on unconventional water; so, it is more urgent for them to master unconventional water security agricultural irrigation technology because it will affect food security and people’s survival. Irrational unconventional water use poses a great threat to crop yield, the cultivated land environment, and people’s health, and this phenomenon needs attention. The cooperation among authors is scattered; most authors are reluctant to break through familiar groups to seek breakthroughs, and the cooperation between countries is also limited; cooperation between scholars from different countries should be promoted in the future. Through keyword analysis, the main research progress in the UWAI field is identified. The main contents include: (1) Effects of salinity on soil physicochemical properties, crops, and groundwater quality under brackish water, partially reclaimed water, and seawater irrigation conditions; (2) effects of pollutants on soil and crops under wastewater irrigation conditions and optimization of wastewater treatment technology; (3) the main pollutants in unconventional water (including heavy metals, pharmaceuticals, personal care products, emerging pollutants, etc.); (4) contaminants in unconventional water pose a threat to human health by contaminating groundwater or entering the food chain; (5) the impact of unconventional water irrigation on groundwater quality; (6) migration and transformation of soil water, salt, and solute under unconventional water irrigation; and (7) rainwater harvesting agriculture; (8) precision agriculture and urban agriculture. The above content is conducive to the overall understanding of UWAI by scholars and policymakers. Through keyword burst analysis, we consider the way that future research hotspots will focus on the mechanism of pollutant solute transport transformation and crop physiological response in soil–soil–crop systems under unconventional irrigation conditions.
Based on the above research, I think the future research and development of UWAI field should be carried out according to the following aspects:
- (1)
- According to the keyword analysis results, the research on the migration and transformation of traditional pollutants, such as soluble salt and heavy metals, in soil, crops, and groundwater under unconventional water irrigation and their impacts has achieved a lot after years of continuous development, but its mechanism needs to be further explored.
- (2)
- Most research in the field of UWAI focuses on traditional contaminants (e.g., salt, heavy metals, pharmaceuticals, etc.), and the research on emerging contaminants (e.g., microplastics) and pathogenic microorganisms is not sufficiently comprehensive and should be enhanced.
- (3)
- Inappropriate unconventional water irrigation extends the negative impacts of water environment risks further, increases human health and food safety risks, and increases the complexity of risk control. Risk control of unconventional water irrigation should be strengthened in the future, especially the identification and control of risk factors. Interdisciplinary and holistic research on unconventional water irrigation should be further strengthened. Water quality control, irrigation management, and risk monitoring should be combined to form an integrated risk control system.
- (4)
- There is an imbalance in the development of the UWAI field, and the more influential countries are mostly developed countries, which benefit from superior cooperation, exchanges, and opportunities for scientific advancement, thereby widening the gap between them and poorer countries. This disparity is particularly problematic for impoverished regions in arid areas, where the need for safe agricultural utilization technology of unconventional water resources is more urgent. To address this issue, it is recommended that relevant international organizations strengthen their cooperation and exchanges with these less advantaged countries in future initiatives.
- (5)
- At present, there is no unified international standard for unconventional water agricultural irrigation, and the policies of various countries are greatly influenced by their national conditions and geographical landforms, while developing countries and less developed areas lack relevant policy support [124,125,126,127,128]. In the future, cooperation and exchanges between countries should be promoted to facilitate the formation of unified international standards and guidelines.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.X.; data curation, P.X.; formal analysis, Z.J. and H.N.; supervision, H.N. and J.W.; writing—original draft, P.X.; writing—review and editing, J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China: (2022YFD1900502).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- UN-Water. Water and climate change. In The United Nations World Water Development Report; UN-Water: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Özerol, G.; Bressers, H.; Coenen, F. Irrigated agriculture and environmental sustainability: An alignment perspective. Environ. Sci. Policy 2012, 23, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koech, R.; Langat, P. Improving irrigation water use efficiency: A review of advances, challenges and opportunities in the Australian context. Water 2018, 10, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Water saving irrigation in China. Irrig. Drain. J. Int. Comm. Irrig. Drain. 2006, 55, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.-P.; Shan, L.; Zhang, H.; Turner, N.C. Improving agricultural water use efficiency in arid and semiarid areas of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzayev, M.A. Problems of water protection against adverse impact of irrigated agriculture and approaches to their solution in arid zones. Water Resour. 2017, 44, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; He, B. Research and Application of Water Resources Carrying Capacity in Arid Area. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 14, 341–342. [Google Scholar]
- Sowers, J.; Vengosh, A.; Weinthal, E. Climate change, water resources, and the politics of adaptation in the Middle East and North Africa. Clim. Chang. 2011, 104, 599–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, H.; Mohsen, M.S. Overview of sustainable water management in the MENA green industries. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 79, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salem, S.S. Overview of the water and wastewater reuse crisis in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Eastern Mediterr. Health J. 2001, 76, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti Suman, A.; García-Herrero, L.; Lavrnić, S.; Sole, M.C.; Toscano, A.; Vittuari, M. The advent of EU water reuse regulation in the Mediterranean region: Policy and legislative adaptation to address non-conventional water resources utilization in agriculture. Water Int. 2023, 48, 839–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, A.; Abu-Zeid, M.; Lacirignola, C. Water Crisis in the Mediterranean: Agricultural Water Demand Management. Water Int. 1995, 20, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, W. Review and Development Strategy of Irrigation with Unconventional Water Resources in China. Chin. J. Eng. Sci. 2018, 20, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Da-fub, W. Some studies on unconventional water resources utilization in agriculture. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2008, 19, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Haq, M.A.; Khan, M.Y. Crop Water Requirements with Changing Climate in an Arid Region of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaritz, M.; Nadler, A.; Kafri, U.; Arad, A. Hydrogeochemistry of continental brackish waters in the southern Coastal Plain, Israel. Chem. Geol. 1984, 42, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C. Modeling surface water-groundwater interaction in arid and semi-arid regions with intensive agriculture. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 63, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannopoulos, S.; Antoniou, G.; Kaiafa-Saropoulou, M.; Angelakis, A.N. Historical development of rainwater harvesting and use in Hellas: A preliminary review. Water Supply 2016, 17, 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, L.; York, D.; Sheikh, B.; Holden, R. Reclaimed Water as an Alternative Water Source for Crop Irrigation. HortScience 2010, 45, 1626–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icekson-Tal, N.; Avraham, O.; Sack, J.; Cikurel, H. Water reuse in Israel—The Dan Region Project: Evaluation of water quality and reliability of plant’s operation. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2003, 3, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, W.; Wilson, C. The Literature of Bibliometrics, Scientometrics, and Informetrics. Scientometrics 2001, 52, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; He, M.; Hao, F.; Liu, H.; Zhu, W. Heavy metal loss from agricultural watershed to aquatic system: A scientometrics review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Yan, E.; Cui, M.; Hua, W. Examining the usage, citation, and diffusion patterns of bibliometric mapping software: A comparative study of three tools. J. Informetr. 2018, 12, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H. A scientometrics review on nonpoint source pollution research. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.N.; Lu, X.L.; Wu, C.Y. The Knowledge Mapping of Domestic Ecological Security Research—Bibliometric Analysis Based on Citespace. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 3693–3703. [Google Scholar]
- Long, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Tu, S. Land Use Transitions: Progress, Challenges and Prospects. Land 2021, 10, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Bolan, N.S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W. Visualizing the emerging trends of biochar research and applications in 2019: A scientometric analysis and review. Biochar 2020, 2, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mmolawa, K.; Or, D. Root zone solute dynamics under drip irrigation: A review. Plant Soil 2000, 222, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R. Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, M.; Flexas, J.; Pinheiro, C. Photosynthesis Under Drought and Salt Stress: Regulation Mechanisms from Whole Plant to Cell. Ann. Bot. 2008, 103, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Vinocur, B.; Altman, A. Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: Towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 2003, 218, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-K. Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.; Harris, P.J.C. Potential biochemical indicators of salinity tolerance in plants. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stillwell, A.; Sanders, K.; Osborne, R.; Greene, D.; Pedersen, D.; Webber, M. An integrated energy, carbon, water, and economic analysis of reclaimed water use in urban settings: A case study of Austin, Texas. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2011, 1, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski Patricia, A.; Stillwell Ashlynn, S.; Wu Jy, S.; Schwarz Peter, M. Energy-Water Nexus: Potential Energy Savings and Implications for Sustainable Integrated Water Management in Urban Areas from Rainwater Harvesting and Gray-Water Reuse. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2015, 141, A4015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B. Re-thinking wastewater landscapes: Combining innovative strategies to address tomorrow’s urban wastewater treatment challenges. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2009, 60, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhara Chary, N.; Kamala, C.T.; Samuel Suman Raj, D. Assessing risk of heavy metals from consuming food grown on sewage irrigated soils and food chain transfer. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 69, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, M.; Kiran, B.; Rani, S.; Rani, A.; Kaur, B.; Mittal, N. Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables irrigated with water from different sources. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S. Heavy metal pollution in China: Origin, pattern and control. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2003, 10, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toze, S. Reuse of effluent water—Benefits and risks. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, E.; Petit, C. Towards the use of metal-organic frameworks for water reuse: A review of the recent advances in the field of organic pollutants removal and degradation and the next steps in the field. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 22484–22506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, I.; Rizzo, L.; McArdell, C.S.; Manaia, C.M.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for the release of antibiotics in the environment: A review. Water Res. 2013, 47, 957–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T.V.M. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Sajad, M.A. Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattan, R.K.; Datta, S.P.; Chhonkar, P.K.; Suribabu, K.; Singh, A.K. Long-term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and groundwater—A case study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 109, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mowelhi, N.M.; Soliman, S.; Barbary, S.; El-Shahawy, M.I. Agronomic aspects and environmental impact of reusing marginal water in irrigation: A case study from Egypt. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2006, 53, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.-J.; Liu, S.-Q.; Liu, Y.-L.; Yan, Y.-L. Health risk assessment of heavy metals for edible parts of vegetables grown in sewage-irrigated soils in suburbs of Baoding City, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 3503–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A.; Bonerz, M.; Herrmann, N.; Teiser, B.; Andersen, H.R. Irrigation of treated wastewater in Braunschweig, Germany: An option to remove pharmaceuticals and musk fragrances. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.T.; Bouwer, E.J.; Coelhan, M. Occurrence and biodegradability studies of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products in sewage effluent. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 86, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-L.; Wong, M.-H. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs): A review on environmental contamination in China. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christou, A.; Agüera, A.; Bayona, J.M.; Cytryn, E.; Fotopoulos, V.; Lambropoulou, D.; Manaia, C.M.; Michael, C.; Revitt, M.; Schröder, P.; et al. The potential implications of reclaimed wastewater reuse for irrigation on the agricultural environment: The knowns and unknowns of the fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistant bacteria and resistance genes—A review. Water Res. 2017, 123, 448–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Spongberg, A.; Witter, J.; Fang, M.; Czajkowski, K. Uptake of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products by Soybean Plants from Soils Applied with Biosolids and Irrigated with Contaminated Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6157–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macherius, A.; Eggen, T.; Lorenz, W.; Moeder, M.; Ondruschka, J.; Reemtsma, T. Metabolization of the Bacteriostatic Agent Triclosan in Edible Plants and its Consequences for Plant Uptake Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10797–10804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, B.; Scheytt, T.; Asbrand, M.; Casas, A.M. Pharmaceuticals as indictors of sewage-influenced groundwater. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Chen, H.; Jiang, L.; Inyang, M.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Cao, X.; Yang, L.; Xue, Y.; Li, H. Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole on biochar and its impact on reclaimed water irrigation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209–210, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Preciado, D.; Matamoros, V.; Savé, R.; Muñoz, P.; Biel, C.; Bayona, J.M. Uptake of microcontaminants by crops irrigated with reclaimed water and groundwater under real field greenhouse conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 3629–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Using Reclaimed Water for Agricultural and Landscape Irrigation in China: A Review. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 66, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.-R.; Cook, S.; Geballe, G.; Burch, W., Jr. Rainwater Harvesting Agriculture: An Integrated System for Water Management on Rainfed Land in China’s Semiarid Areas. AMBIO A J. Hum. Environ. 2009, 29, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazin, B.; Sterk, G.; Temesgen, M.; Abdulkedir, A.; Stroosnijder, L. Rainwater harvesting and management in rainfed agricultural systems in sub-Saharan Africa—A review. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2012, 47–48, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, H.J.; Evenari, M.; Nessler, U. Rainwater-harvesting agriculture for food production in arid zones: The challenge of the African famine. Appl. Geogr. 1986, 6, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oweis, T.; Hachum, A. Water harvesting and supplemental irrigation for improved water productivity of dry farming systems in West Asia and North Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Zhang, S.; Yue, T. Environmental and economic assessment of rainwater harvesting systems under five climatic conditions of Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, U.; Ahmad, S.R.; Abbas, S.; Javed, M.A.; Usman, M. Identification of potential sites for rainwater storage to enhance agricultural practices in kirthar mountain range. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 59, 579–588. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Sarwar, A.; Islam, F.; Majid, A.; Tariq, A.; Ali, M.; Gulzar, S.; Khan, M.I.; Sardar Ali, M.A.; Israr, M.; et al. Rainwater harvesting for agriculture development using multi-influence factor and fuzzy overlay techniques. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Tong, D.; Crosson, C.; Zhang, Y. A GIS-based approach to assessing the capacity of rainwater harvesting for addressing outdoor irrigation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 223, 104416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A.; McKinney, N.; Ries, R. An approach to quantifying rainwater harvesting potential using imagery, geographic information systems (GIS) and LiDAR data. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2018, 18, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Fu, T.G.; Gao, H.; Liu, J.T. Review on Cadmium Pollution from Sewage Irrigation in Farmland Soil. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2022, 38, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, K.; Lee, T.; Choi, B.G.; Hong, S. Rainwater Harvesting System for Contiunous Water Supply to the Regions with High Seasonal Rainfall Variations. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.R.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, F.; Ali, M.E.A. Desalination of high salinity brackish water by an NF-RO hybrid system. Desalination 2020, 491, 114445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yin, Z.; Liu, T.; Xin, Q. Modeling and analyzing supply-demand relationships of water resources in Xinjiang from a perspective of ecosystem services. J. Arid Land 2022, 14, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, M.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z. Response of Water-Salt Migration to Brackish Water Irrigation with Different Irrigation Intervals and Sequences. Water 2019, 11, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cui, B.; Hu, C.; Wu, H.; Gao, F. Effects of mixed irrigation using brackish water with different salinities and reclaimed water on a soil-crop system. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2021, 11, 632–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cui, B.; Hu, C.; Wu, H.; Gao, F. Effect of Mixed Irrigation of Brackish Water and Reclaimed Water on Soil Properties and Irrigation Effect Evaluation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y. Advances in Soil Water-Salt Transport of Drip Irrigation Under Mulch with Saline Water. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2012, 28, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.-J.; Lv, P.-P.; Wang, Y.-M.; Su, R.-D.; Kong, X.-Y. Effect of brackish water drip irrigation on the growth of zucchini in greenhouse in North China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 11042–11048. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, F.-L.; Yao, R.-J.; Yang, J.-S.; Wang, X.-P.; Cheng, Q.; Li, H.-Q. The effects of soil amendment with different materials on soil salt distribution and its ion composition under brackish-water drip irrigation. J. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 39, 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Cui, B.; Huang, P.; Hu, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Silicon Improves Soil Environment and Promotes Crop Growth under Compound Irrigation via Brackish Water and Reclaimed Water. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, S.; Liu, H.; Men, B.; Hao, Z.; Qian, P.; Yan, H.; Hao, Q.; Niu, Y.; et al. Impact of Long-Term Reclaimed Water Irrigation on the Distribution of Potentially Toxic Elements in Soil: An In-Situ Experiment Study in the North China Plain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Response of Soil and Crop to Mixed Irrigation Using Brackish and Reclaimed Water. J. ASABE 2022, 65, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cui, B.; Zeleke, K.T.; Hu, C.; Wu, H.; Cui, E.; Huang, P.; Gao, F. Risk of Secondary Soil Salinization under Mixed Irrigation Using Brackish Water and Reclaimed Water. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kang, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Effects of alternate partial root-zone irrigation on soil microorganism and maize growth. Plant Soil 2008, 302, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, M.S.; El-Abedin, T.Z.; Al-Ghobari, H.M. Rational water use by applying regulated deficit and partial root-zone drying irrigation techniques in tomato under arid conditions. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 79, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Bai, X.; Pei, L.; Pan, H. A research on application of water treatment technology for reclaimed water irrigation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 15930–15937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Hu, Y.; Guan, X.; Xu, L. Advances in research of reclaimed water irrigation in China. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljanabi, A.A.; Mays, L.W.; Fox, P. Optimization Model for Agricultural Reclaimed Water Allocation Using Mixed-Integer Nonlinear Programming. Water 2018, 10, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, P.; Ren, S.; Ma, N. The Effect of Multi-Years Reclaimed Water Irrigation on Dryland Carbon Sequestration in the North China Plain. Water 2021, 13, 3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros-Olza, M.; Blanco-Gutiérrez, I.; Esteve, P.; Gómez-Ramos, A.; Bolinches, A. Using reclaimed water to cope with water scarcity: An alternative for agricultural irrigation in Spain. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 125002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Piernas, A.B.; Plaza-Bolaños, P.; Gilabert, A.; Agüera, A. Application of a fast and sensitive method for the determination of contaminants of emerging concern in wastewater using a quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe-based extraction and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1653, 462396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Piernas, A.B.; Plaza-Bolaños, P.; Agüera, A. Assessment of the presence of transformation products of pharmaceuticals in agricultural environments irrigated with reclaimed water by wide-scope LC-QTOF-MS suspect screening. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceylan, A.; Ertem, M.; Ilcin, E.; Ozekinci, T. A special risk group for hepatitis E infection: Turkish agricultural workers who use untreated waste water for irrigation. Epidemiol. Infect. 2003, 131, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colon, B.; Toor, G. A Review of Uptake and Translocation of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products by Food Crops Irrigated with Treated Wastewater. Adv. Agron. 2016, 140, 75–100. [Google Scholar]
- Shahriar, A.; Tan, J.; Sharma, P.; Hanigan, D.; Verburg, P.; Pagilla, K.; Yang, Y. Modeling the fate and human health impacts of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in reclaimed wastewater irrigation for agriculture. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Ma, M.; Hu, Y.; Yu, W.; Liu, H.; Bao, Z. The fate and impacts of pharmaceuticals and personal care products and microbes in agricultural soils with long term irrigation with reclaimed water. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 251, 106862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomno, R.M.; Nzeve, J.K.; Mailu, S.N.; Shitanda, D.; Waswa, F. Heavy metal contamination of water, soil and vegetables in urban streams in Machakos municipality, Kenya. Sci. Afr. 2020, 9, e00539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Kurosawa, K. Contamination of the Summer and Winter Vegetables by Heavy Metals in a Multi-Industry District of Bangladesh. J. Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 2020, 65, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.P.; Zhang, W.L.; Pan, N.; Jiao, W.T. Ecological risks of reclaimed water irrigation: A review. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2012, 33, 4070–4080. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, S.; Chen, W.; Wen, X.; Chang, A.C. Integration of HYDRUS-1D and MODFLOW for evaluating the dynamics of salts and nitrogen in groundwater under long-term reclaimed water irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2019, 37, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.; Ren, S.; Yang, P.; Li, C.; Xue, Y.; Huang, L. Modeling the Risk of the Salt for Polluting Groundwater Irrigation with Recycled Water and Ground Water Using HYDRUS-1D. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liao, R.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Yin, S. Quantitative assessment of groundwater pollution risk in reclaimed water irrigation areas of northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, W.; Xu, D.; Liu, H. Variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (pah) contents in the vadose zone and groundwater under long-term irrigation using reclaimed water. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.M.; Liu, Z.P.; Xia, T.X.; Chen, M.D. Effects of seawater irrigation on soil safety and crop yield in coastal semi-arid area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 25, 2446–2449. [Google Scholar]
- El Zarroug, M.R.; Daghari, I.; Kompany, J.R.; Muanda, C.; Shanak, N. Potential of solar desalination for irrigation in Tunisia. LHB-Hydrosci. J. 2020, 6, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Bai, B.; Cai, C. Study on Effect of Seawater Irrigation to Soil Properties in Yellow River Delt. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2004, 18, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.P.; Liu, L.; Chen, M.D.; Deng, L.Q.; Zhao, G.M.; Tang, Q.Z.; Xia, T.X. Study on the irrigation systems in agriculture by seawater. J. Nat. Resour. 2003, 18, 423–429. [Google Scholar]
- Rozema, J.; Flowers, T. Ecology. Crops for a salinized world. Science 2008, 322, 1478–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, J.W.; Wan, B.J.; Dai, J.Y.; Tang, H.S.; Sun, M.F. Research progress on molecular genetics of rice salt tolerance. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2021, 22, 881–889. [Google Scholar]
- Rasel, M.; Tahjib-Ul-Arif, M.; Hossain, M.A.; Hassan, L.; Farzana, S.; Brestic, M. Screening of salt-tolerant rice landraces by seedling stage phenotyping and dissecting biochemical determinants of tolerance mechanism. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 1853–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xun, W.; Chen, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Feng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, R. Plant salt-tolerance mechanism: A review. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Qiao, Z. Analysis and discussion on seawater desalination by reverse osmosis technology. Ind. Water Treat. 2011, 31, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Zhou, T. Research on Seawater Desalination Integrated Technology. Environ. Eng. 2017, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, R.C.; Yue, K.; Wang, Y.S.; Cao, Y. Research progress and prospect of seawater desalination technology. Xiandai Huagong/Mod. Chem. Ind. 2017, 37, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, G.; Feng, H. Technical Progress in Seawater Desalination Technology at Home and Abroad. China Water Wastewater 2008, 20, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Elimelech, M.; Phillip, W.A. The Future of Seawater Desalination: Energy, Technology, and the Environment. Science 2011, 333, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkl, M.; Brunner, N.; Amerasinghe, P.; Mahesh, J.; Kumar, D.; Asolekar, S.R.; Sonkamble, S.; Ahmed, S.; Wajihuddin, M.; Pratyusha, A.; et al. Stakeholder Views, Financing and Policy Implications for Reuse of Wastewater for Irrigation: A Case from Hyderabad, India. Water 2015, 7, 300–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahri, A.; Brissaud, F. Wastewater reuse in Tunisia: Assessing a national policy. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 33, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, W. State Regulations and Guidelines for Wastewater Reuse for Irrigation in the US. Water 2021, 13, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Manaia, C.; Berendonk, T.U.; Cytryn, E.; Bayona, J.; Chefetz, B.; Slobodnik, J.; Kreuzinger, N.; Rizzo, L.; Malato, S.; et al. COST Action ES1403: New and Emerging challenges and opportunities in wastewater reuse (NEREUS). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 7183–7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirra, L.; Russo, S.; Borrello, M. Exploring Factors Shaping Farmer Behavior in Wastewater Utilization for Agricultural Practices: A Rapid Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, J.; Donzier, J.F.; Noel, C. A comparison of the water management systems in France and China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, H.; Liu, F.; Wang, F.; Gao, Q.; Hao, S.; Yan, H.; Hu, H. Policy, standard and typical case studies of water reuse in Japan. Water Wastewater Eng. 2023, 49, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chatila, J.G. Reclaimed Waste Water in Some Middle Eastern Countries: Pricing and Perspective. Can. J. Dev. Stud./Rev. Can. D’études Dév. 2004, 25, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilmany, E.A.; Newton, S.; Goeringer, P.; Rosenberg Goldstein, R.E. Reclaimed Water Use Regulations in the U.S.: Evaluating Changes and Regional Patterns in Patchwork State Policies from 2004–2023. Water 2024, 16, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazza, M. Wastewater recycling and reuse in the Near East Region: Experience and issues. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2003, 3, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoushtarian, F.; Negahban-Azar, M. Worldwide Regulations and Guidelines for Agricultural Water Reuse: A Critical Review. Water 2020, 12, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).