Abstract
Manganese is considered an emerging pollutant and it is perceived as a potential threat to human health and aquatic ecosystems. The need to determine and monitor the presence of Mn in environmental water requires increasingly precise and accurate chemical analytical techniques that provide reliable information to take timely measures in the event of potential environmental contingencies. The automation by flow analysis technique has allowed analytical procedures to isolate and preconcentrate manganese in environmental water samples. Additionally, it brings forth benefits such as greatly enhancing the sample processing capacity and a reduced time and reagent usage, leading to cost savings and minimized waste production, thereby aligning with the principles of green chemistry. In this review, a recent report of some flow analysis techniques (FIA, rFIA, SIA, MSFIA, LOV, and MPFS) is presented, highlighting the trend of automation, whose portability and miniaturization allow for complete in situ analysis. There are two remarkable analytical features from the studies evaluated here, which are sample throughput and accuracy, with a maximum processing time of 120 samples h−1 and an accuracy of 98%. The implementation of flow analysis techniques offers several advantages, such as miniaturization and portability. The discussed methodologies achieved limits of quantification as low as 0.26 µg L−1, enabling environmental monitoring that can easily detect the reference value of 0.05 mg L−1, established by the WHO and the EPA.
1. Introduction
Manganese (Mn) compounds exist naturally as solids in soil, as fine particles in water, and can also be airborne as dust particles [1,2]. Manganese is vital for the proper functioning of both humans and animals. As a trace element and an essential micronutrient, it fulfills crucial roles in numerous metabolic regulatory functions, such as the activation and operation of various cellular enzymes [3].
Manganese can exhibit 11 oxidation states, with Mn2+, Mn3+, Mn4+, Mn6+, and Mn7+ being the most common. Of these, Mn2+ and Mn3+ are the most relevant for biological systems [1,4]. While Mn is traditionally considered a trace element, it has recently been perceived as a potential emerging contaminant due to its extensive industrial applications and widespread release into the environment [5]. The release of Mn into the environment occurs at different levels mainly through industrial sources such as mining, production of alloys, agrochemicals, and others [5,6]. Mn is a main component in a wide range of products such as steel, dry-cell batteries, fireworks, fertilizers, paints, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and gasoline as an octane booster additive [3].
According to the literature, concentrations in seawater have been reported to range from 0.4 to 10 μg L−1, averaging 2 μg L−1. In contrast, in freshwater, they typically range from 1 to 200 μg L−1, with levels from <11 to >51 μg L−1 found in a river water survey in the USA [7]. Manganese is considered the 12th most abundant element in the biosphere and its concentration in Earth’s crust reaches 0.098% [8]. The presence of Mn in the oceans is due to causes such as continental shelf sediments, hydrothermal systems, desorption from atmospheric particulates, etc. High concentrations of Mn in seawater can interfere with numerous chemical processes [9]. In aquatic environments, this element exists in two main forms as follows: Mn2+ and Mn4+. The oscillation between these two forms is produced through oxidation and reduction reactions that may be biotic or abiotic [10].
The importance of monitoring this emerging pollutant derives from the need to prevent its accumulation in the environment since Mn is a potential neurotoxin and upon excessive exposure, it can cause serious health problems [5] including nervous system disruptions, kidney inflammation, male reproductive damage, infertility, and hindered fetal growth, among others [3,11].
Although Mn is abundant and broadly dispersed in nature, organisms require it only in trace amounts throughout their life cycle. The World Health Organization (WHO) has set a provisional reference value for manganese (Mn) in drinking water at 0.05 mg L−1 due to potential risks associated with Mn exposure. This guideline is provisional because, while there is some evidence of a potential hazard, the available information on health effects is limited [12]. Concentrations of this element at or below the recommended reference could alter the taste, odor, or appearance of water [13,14]. The EPA also suggests that Mn concentrations in drinking water should not surpass 0.05 mg L−1. This guideline is set with the confidence that it offers enough protection for human health [15]. Considering that Mn is a potential emerging contaminant, exhaustive monitoring of water is necessary to establish future regulations, since it is found in low concentrations in the environment (μg L−1) [5].
Trace element analysis requires a sample pretreatment, which guarantees an efficient extraction of the analyte before its detection. This allows reliable results to be achieved by reducing the presence of interferences in complex sample matrices that can decrease analytical sensitivity [16,17]. Traditionally, separation and purification processes, as well as elemental analysis, have been conducted manually, involving numerous steps and protocols. These separations typically employ a range of conventional methods such as ion exchange, liquid–liquid extraction, precipitation, and coprecipitation [18].
Of all the isolation methods to remove interferences and improve sensitivity, solid-phase extraction (SPE) has been regarded as one of the most effective and fastest methods [19,20,21]. The foundation of the SPE method is the selective distribution of analytes between the solid extraction medium and the liquid mobile phase. For Mn analysis, different species of this element can be retained through processes of ion exchange, adsorption, or chelation based on their chemical nature [20,21]. Additionally, several materials can be used as sorbents, such as chelating resins [22,23,24,25], biosorbents-based natural fibers [26], porous thermoplastic composites, modified silica, and magnetic nanoparticles [27,28,29].
In the analysis of Mn, SPE has been used in combination with numerous analytical techniques, including microwave plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (MP-AES) [26], atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) in its two variants of flame [23,24,30] and graphite furnace [25], inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) [29,31], inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) [27,28,32,33,34], and spectrophotometry-based methods [22,35]. However, the high consumption of samples and reagents and its lack of portability have led to the development of automated methodologies, which, in addition to being portable and inexpensive, are simple and highly sensitive in Mn determination in environmental water samples [18].
Furthermore, automation is one of the most attractive features of SPE. Analyte quantification follows automated SPE by integrating the detector in the flow collector or connecting the flow system to another instrument (e.g., atomic spectrometric instrumentation) [36]. In the last decade, flow analysis techniques have become prevalent for analyzing Mn in water samples. Integrating classical methods with contemporary instrumentation enables the total or partial automation of numerous conventional analytical techniques in environmental analysis. This automation results in increased simplicity and reliability, reduced analysis time, decreased sample volume and reagent consumption, and minimized sample and standards handling, thereby enhancing analyst safety. Furthermore, automation allows for sample and reagent volume regulation, improving reproducibility [18].
This review evaluates and discusses recent fully and partially automatic methodologies used for the Mn analysis in different environmental water samples, highlighting the automation trends toward methodologies involving the use of increasingly compact instrumentation, forming portable analytical monitoring systems that enable real-time analysis, and providing timely results for potential environmental contingencies. The aim of this review is to explore the positive and negative aspects of automation and highlight emerging trends influencing its development. Moreover, it seeks to illustrate the versatility of flow analysis techniques within automation, showcasing their cost-effectiveness and rapid implementation, coupled with high reproducibility. These methods are essential for optimizing processes and ensuring consistent, reliable results, solidifying their importance in the evolving landscape of automation.
A literature search was performed on 28 October 2023 in the SciFinder and Web of Science databases. The records included were peer-reviewed studies published in English between 2011 and 2023 that focused on automated methods of Mn analysis in various types of water samples. A total of 28 studies were included according to our criteria and are reviewed here.
2. Automated Analytical Techniques
The need to monitor potential emerging pollutants in natural water samples requires precise and accurate chemical analytical techniques that provide fast and reliable information to take timely measures in the event of an environmental contingency [37].
The automation through flow analysis technique is a versatile fluid handling technology that has enabled analytical procedures to isolate, preconcentrate, and quantify Mn in environmental water samples. It has facilitated the creation of reproducible methodologies with a high analysis frequency and minimal time and reagent consumption, therefore reducing costs and waste generation while contributing to green chemistry principles. With automation, analyst participation is also considerably reduced, enhancing the safe handling of reagents and samples and minimizing potential errors derived from exhaustion due to long working hours in routine analyses. In addition, advances in materials technology (e.g., 3D printing, new extraction materials, etc.) and miniaturization of detection devices (e.g., new electrode designs for voltammetry), allow portability and in situ analysis, which are essential characteristics for field practices [38].
Flow-based techniques use fluid drive modules (including peristaltic pumps, micropumps, or piston pumps), a series of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) tubing or manifolds for liquid delivery, solenoid valves, and multiposition selector valves to control liquid flow. Each component functions as an autonomous unit, offering flexibility for analytical systems implementation.
Automation can be partial or total, depending on the degree of complexity of the chemical procedure conducted, as well as the size and requirements of the detection devices used (e.g., spectrometry vs. spectrophotometry and voltammetry). In some studies, detection can be included (online), while for others, the priority is oriented to the sample pretreatment with offline determination [19,38].
Given the demands of routine environmental analysis, automatic systems tend to be developed for in situ application. Figure 1 shows a scheme in which the different automation modes for the environmental analysis of water samples are graphically detailed.
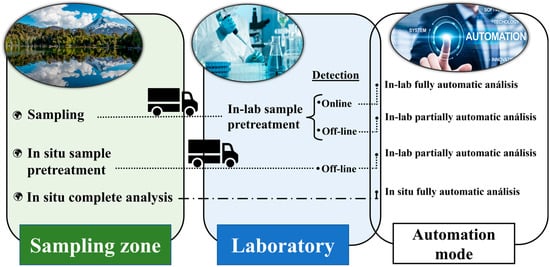
Figure 1.
Different automation modes—at the sampling site or in the laboratory.
The following review emphasizes flow techniques based on flow injection analysis (FIA), reverse flow injection analysis (rFIA), sequential injection analysis (SIA), multicommuted flow injection analysis (MCFIA), multisyringe flow injection analysis (MSFIA), lab-on-valve (LOV), and a multipumped flow system (MPFS). In addition, some studies focused on multielemental analysis have been included in this review, highlighting the analytical characteristics corresponding to Mn determination. Table 1 shows the most important characteristics and analytical parameters of the studies discussed in this work.

Table 1.
Main analytical characteristics of the methodologies discussed.
2.1. Flow Injection Analysis (FIA)
Several features render flow injection a highly appealing tool for the automation of environmental analytical methods (e.g., precise automated fluid handling, easy implementation, high injection throughput, minor cost of instrumentation, and a considerable reduction in reagents and sample volume concerning the batch analysis).
In a single-line or multiline FIA system, the solution of the sample is injected into a carrier flow solution or in a reagent flow generated by the peristaltic pump [18,38]. Figure 2 depicts an automatic FIA system for Mn determination [26]. In this scheme, a solid-phase extraction takes place on a column. Through an injection valve in the first position, the sample is passed through the column by means of a peristaltic pump, retaining the manganese. Subsequently, the injection valve in the second position allows the Mn elution for its analysis via microwave plasma atomic emission spectroscopy.
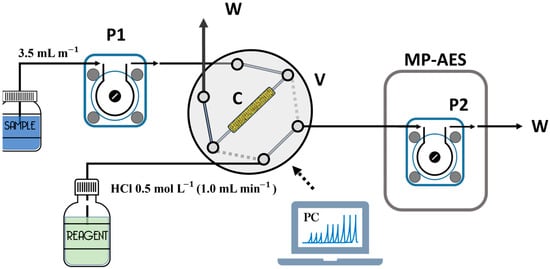
Figure 2.
Automatic system proposed by Silva et al. [26] to determine Mn in environmental water samples. C, SPE column; Mp-AES, microwave plasma atomic emission spectroscopy; P1 and P2, peristaltic pumps; V, injection valve; W, waste solution.
For the Mn environmental analysis in water samples, the use of FIA-based methodologies has allowed the development of fully automatic systems for in situ monitoring analysis. In 2017, a study by Feng et al. [24] evaluated the Mn extraction affinity of the commercial chelating resin IDA (iminodiacetate, Toyopearl AF-chelate 650 M) [49] prior to online determination with a flame atomic fluorescence spectrometer (FAFS). This work facilitated the creation of a fully automatic procedure for field detection of dissolved Mn in coastal and estuarine waters. In the proposed system, after Mn elution with 2% (v/v) HCl, the eluting solution is directly introduced into the FAFS detector with a hollow cathode lamp for detection. This method demonstrated high intraday precision with values of 1.5, 3.0, and 3.8% for Mn-enriched samples of 50, 800, and 1800.0 nmol L−1, respectively and 2.9, 4.7, and 4.8% (same standard concentrations) for interday precision. The detection limit was 0.9 nmol L−1 (n = 7, preconcentration time 120 s) with a linear range of 3–200 nmol L−1. Finally, the recovery was also considered satisfactory for samples enriched with added metals (Zn, Cu, Ni, Fe, and Al) with values between 96.8 and 99.9%. Thus, the high precision and good accuracy of the proposed system were very useful for the application to trace field analysis of dissolved Mn in estuarine and coastal waters [24].
Trends toward miniaturization and the use of flow techniques have made it possible to take full advantage of the portability advantages offered by spectrophotometry. Based on light absorption, UV–VIS is a sensitive and cost-effective method for metal determination and has been used in flow injection for Mn analysis in natural water samples [17]. In 2019, Jones et al. [45] applied a fully automated method to analyze coastal and estuarine waters. Samples were first extracted by applying ligand exchange of the dissolved complexes and chromatographic separation and concentration of Mn(III)-DFOB (desferrioxamine-B). After the separation/concentration steps, Mn(III) was quantified by UV–VIS flow injection, using a spectrophotometer with a halogen light source, and calibrated based on Tiron’s absorbance measured at 424 nm. In addition, samples from three stations were also analyzed by ICP-MS. The samples were diluted with 1% HNO3 (10-fold dilution) and exhibited flocculation of dissolved acidic polysaccharides that coeluted with Mn(III)-DFOB from the samples. Therefore, more processing steps were needed for the samples, including waiting time for floc separation, aliquot collection, and filtration. In terms of performance, there was a significant correlation between ICP-MS and FIA-S measurements (R2 = 0.89). With this new low-level DFOB extraction technique, the Mn measurements provide relevant information about the production and consumption processes of Mn(III) and help understand the environmental complexity Mn cycle [45].
In multiparameter monitoring analysis, Evans et al. [25] established an FIA method for the analysis of sea ice, using solid-phase extraction for sample preconcentration and carrying out the analysis using a GF-AAS. The NOBIAS Chelate PA-1 chelating resin (Hitachi High-Technologies Corporation) was used during the preconcentration of samples, and after this step, samples were analyzed using a GF-AAS. The analysis was performed using single-element standards for the calibration, procedural blanks with milli-Q water, and NASS-6 seawater reference material (NRCC). The recovery was acceptable with values of 100.3 ± 1.8% for spiked milli-Q samples and 87% for certified reference material (CRM). The preconcentration phase in combination with a GF-AAS allowed favorable detection limits for ambient concentration readings (LOD = 0.06 nM) and recovery above 100% [25].
The analytical advantages offered for multielemental determination with low detection and quantification limits make ICP-based methods suitable devices for environmental analysis in-laboratory. Two previous works performed fully automatic FIA ICP-OES analysis [29,31]. Cui et al. [31] used solid-phase microextraction with a synthesized alumina hollow fiber as an extraction membrane and an online coupled ICP-OES equipment to determine Mn (at 257.6 nm) along with Cu and Ni. In terms of ICP-OES analysis, the potential interferences were also examined and, under the optimal conditions, there were no significant interferences for real samples analysis. Speaking of analytical performance, the precision for Mn was 6.2% (RSD) with a detection limit (calculated as the concentration of three times the SD of the mean of 11 blank determinations) of 0.61 µg L−1 and the accuracy based on spiked water samples was between 96.7 and 100.5% [31]. A few years later, Guerrero et al. [29] established a method also using a synthesized extraction membrane based on silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles (modified with [1,5-bis(2-pyridyl)-3-sulphophenyl methylene] thiocarbonohydrazid) to determine 14 elements, including Mn, in different types of water samples. To perform this multielement analysis, they applied a novel sample introduction system coupled to ICP-OES. For Mn, they obtained a wide working line of 23–200 µg L−1, with a detection limit of 3.1 µg L−1. Moreover, the method was validated with certified reference materials from the NRCC. The reported method seemed to be fast, practical, and stable, while the precision and accuracy of the results demonstrated reliability with accuracy values of 2.11 and 2.09% at 5 and 20 mg L−1 [29].
Continuing with the ICP-based methods, Biller and Bruland [33] established a semiautomatic method using offline preconcentration with magnetic sector ICP-MS to analyze Mn and other elements in seawater samples. In this method, one of the main differences from the methods previously reported was the pretreatment of samples using UV-oxidation to destroy the strong trace elements organic ligands. The chelating resin NOBIAS-chelate PA1 was used during the preconcentration of samples, the pH was adjusted to 6.2 ± 0.3, and the trace elements were eluted with 3–4 mL of 1 N HNO3. The method was compared with references from the GEOTRACES program. From this comparison, the high accuracy of the method, particularly for Mn measurements, was highlighted with a recovery of >98% and detection limit of 0.002 nmol kg−1. Moreover, this method also showed acceptable precision with an RSD% <5 for all the elements of interest [33].
The following year, another research group developed a method as an application to the GEOTRACES program, using online extraction, flow injection, and HR-ICP-MS to determine multiple elements including Mn [34]. In this study, a fully automated system was applied called “seaFASTPico,” which is commercially available and useful for the analysis of seawater samples and other matrix–complex samples. In short, when the system is in preconcentration mode, the sample is loaded onto a chelation column, the matrix is removed while the elements of interest are chelated, and then, the chelated elements are eluted (with 1.6 M HNO3) directly into the nebulizer. The precision of this method was determined for the short term and the long term (run to run), obtaining values of 2 and 3%, respectively. The accuracy of the method was deemed acceptable for all the elements of interest, particularly for Mn, the recovery was 99 ± 5% for samples with added concentrations, and finally, the Mn measurements also demonstrated a good agreement with the GEOTRACES references for seawater samples with a detection limit of 0.002 nmol kg−1. Finally, a recent study from 2020 by Su and Lin [27] started to apply a 3D-printed column with porous monolithic packing in a flow-injection system coupled to ICP-MS. In this system, the samples were loaded to the fabricated columns, pH was adjusted to 8.0, and trace elements were eluted from the column using 0.5% (v/v) HNO3 and directed into the ICP-MS equipment. Speaking of analytical performance, the proposed method offers a wide line working range for Mn of 50–5000 ng L−1 with a detection limit of 3 ng L−1. Method reliability was determined using water reference materials (NIST, USA) and spiked samples (to a final concentration of 0.5 µg L−1). Precision (RSD%) was <3.2 and 5.6% for intraday and interday variations, respectively, while accuracy was between 95 and 106% for different types of spiked water samples [27].
Other ICP-based techniques like inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) have also been coupled to separation/preconcentration methods for the analysis of Mn. In a recent study, Manousi et al. [47] utilized a synthesized silica (sol-gel thiocyanatopropyl-functionalized) online microcolumn to determine several elements including Mn in environmental and drinking water samples. Several standard reference materials were used for quality control purposes, including CRM 1643e, IAEA-433, and SeronormTM Trace Elements Urine Level 1. Additionally, the potential interferences and the comparability with other ICP-AES-based methods were also evaluated. Trace elements with variations in emission intensity greater than ±5% were considered potential interferences; thus, several ICP-AES parameters were investigated and adjusted, with one important parameter being the nebulizer gas flow rate, which was set to 0.85 L min−1 to enhance the emission intensity of analytes. With the proposed method, a linear working range of 0.26–50 µg L−1 was possible with a detection limit for Mn of 0.08 µg L−1. The precision for Mn was 2% (RSD) and the accuracy in terms of recovery was 98%. Based on the precision results, with this proposed method, trace concentrations of manganese can be easily analyzed in environmental water samples [47].
Regarding AES, its analytical principles have been successfully applied for multielement analysis. In this sense, Zheng et al. [48], presented a fully automatic system that uses a multifunction sample injection system combined with solution cathodic glow discharge atomic emission spectrometry (SCGD-AES). This innovative equipment allowed two analytical sampling modes (continuous flow and flow injection), which were selected depending on the sample under analysis. With this system, 10 elements (Na, K, Mg, Cu, Rb, Ag, Tl, Cd, Zn, and Mn) were successfully determined. Manganese analysis was performed at a wavelength of 279.48 nm, demonstrating a high linear determination coefficient (R2) of 0.997 for continuous flow mode, with a limit of detection (LOD) of 185.19 µg L−1. Similarly, in the flow injection mode, a linear determination coefficient (R2) greater than 0.997 was achieved, with an LOD of 249.16 µg L−1.
Furthermore, the robustness of the system was demonstrated through recovery experiments, where samples fortified with different concentrations of manganese, from three different water reservoirs in China, were analyzed, achieving recoveries greater than 100% [48].
In this sense, in 2023, Silva and Pistón [26] proposed an FIA methodology with simultaneous extraction of Cu and Mn. The authors proposed the use of sisal fiber as biosorbent with an online determination with a microwave plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (MP-AES) [26]. They made a comparison, evaluating the extractions of Cu and Mn. On the one hand, they used alizarine fluorine blue (AFB) as a derivatizer of the biosorbent, and on the other hand, they only performed the analysis without derivatization.
In Figure 3, a simple diagram of this system is shown, in which a minicolumn (a glass tube of 2.2 mm internal diameter and 5 cm long) was placed in a six-port valve packed with 100 mg of sisal fiber. The proposed system was successfully applied to water samples, having Mn recoveries of 98% in spiked samples with 0.1 mg L−1, derivatizing the biosorbent with AFB.
Figure 3.
Representative scheme of the FIA automated methodology proposed by Silva and Pistón in 2023 [26].
In addition, an LOQ for manganese of 33 µg L−1 was achieved, with a precision of 3.1% (RSD, n = 6) and a capacity of 20 analyzes per hour, easily achievable without the need to renew the biosorbent, since it can be reused up to 40 times. Therefore, the present work demonstrates that the use of biosorbents can replace conventional extractants commonly used in SPE [26].
2.2. Reverse Flow Injection Analysis (rFIA)
Reverse flow injection analysis is an adaptation of the FIA technique in which a peristaltic pump propels the sample in a constant flow while a controlled volume of reagents is injected. This adaptation of FIA is not only a convenient way to minimize reagent consumption, but also an economical approach to designing a multiparameter analysis system. Both FIA and rFIA systems can be single line or multiline, depending on the number of channels of the peristaltic pump, equipped with online instrumental modules for physicochemical sample processing, according to the needs of the analyte chemical transformation. Therefore, it is highly applicable in methodologies where a colorimetric reaction can be carried out, prior to its determination by spectrophotometry, and in which the consumption of reagent solution is critical. rFIA is particularly important in water analysis due to the abundance of the sample [50]. Figure 4 describes a scheme developed from the rFIA-based systems discussed in this review, where it can easily be seen how the rFIA technique has direct application in the field, allowing in situ marine waters analysis and real-time monitoring of salinity, pH, and temperature [42].
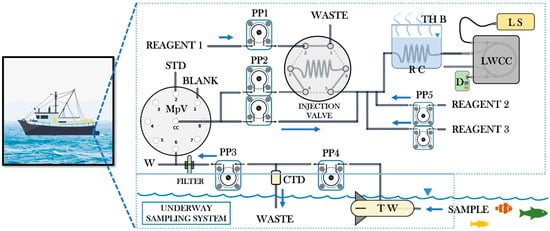
Figure 4.
Graphic scheme based on the rFIA works discussed, where it is shown that the rFIA system can form a monitoring module for on-site application. CC, central conduit; CTD, conductance-temperature-depth sensor; D, detector; LS, light source; LWCC, long-wave capillary cell; MpV, multiposition valve; PP1-PP5, peristaltic pumps; RC, reaction coil; STD, standard; TH B, thermal bath; TW, towed fish; W, waste.
Using an LWCC, the length of the optical path of light is increased for a solution product of a colorimetric reaction, since by conforming to a capillary tube, the light that shines through the liquid core is fully reflected toward the detector, so the optical signal is received with a minimum of background noise. In this way, the sensitivity and detection limits of current spectrophotometric procedures, which are essential in environmental analysis, are considerably improved [51].
A relevant application has been carried out by Feng et al. [42]. In a first work published in 2015, the constant sample flow pumping supplied by the assembly of submerged peristaltic pumps allowed the development of a method conducted on board a ship for detecting traces of dissolved Mn in estuarine and coastal waters, in which a 1 m liquid waveguide capillary cell was employed alongside spectrophotometric detection of Mn derivatization with 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol (PAN) at 574 nm. The proposed method exhibited high sensitivity with a detection limit of 3.0 nmol L−1 and a broad linear range of 10–1500 nmol L−1 for dissolved Mn in seawater. The sample throughput reached was 120 h−1 with an acceptable precision (n = 3) of 1.2% for 25 nmol L−1 and 0.8% for 500 nmol L−1. With this proposed method, a 24 h online analysis and a shipboard underway analysis of dissolved Mn are possible [42].
In 2018, the same research group built a sensitive and precise rFIA automatic system for determining nanomolar Mn concentrations in seawater. They achieved spectrophotometric detection of Mn through Mn-catalyzed oxidation of leucomalachite green with sodium periodate. Subsequently, the resulting colored complex was transported via the LWCC for detection at a wavelength of 620 nm, with background correction at 700 nm.
In this study, the method’s detection limit was 0.20 nmol L−1 (n = 8), with a quantification range of 0.5–10 nmol L−1. The relative standard deviation (RSD, n = 8) was 1.4% for seawater samples enriched with a 5 nmol L−1 Mn standard, indicating high precision. The reagent blank exhibited stability, with an RSD of 2.2% (n = 15) over 10 days. With triplicate sample runs, the sample yield was 5 h−1.
The certified seawater reference material NASS-6 was employed to assess precision, yielding good agreement. Additionally, a recovery study conducted with surface seawater samples yielded satisfactory percentages of 93% and 104% [44].
In 2017, Youngvises et al. [43] applied the rFIA technique in a fully automated system where, with a four-channel peristaltic pump, they were able to evaluate several elements at the same time, with colorimetric reagents specific for metal ions of interest (including Mn(II)). One of the main objectives of this study was to develop the IF system based on the principles of green chemistry, for which characteristics such as sample throughput and reagent efficiency were considered. Mn detection was based on a multioptical sensor with four light-emitting diodes and the wavelength for Mn(II) was 452 nm (continuous flow cells with a 10 mm optical path were used). In this work, the detection limit of the method was 16 µg L−1, with a quantification range of 0.05–3.0 mg L−1 (R2 = 0.993).
The recovery of the method based on spiked samples was 102 ± 2% and the precision was 1.9% (RSD). The sample throughput achieved was 15 samples per hour and the reagent consumption was 1.5 mg per sample. The efficiency of these parameters satisfied the objectives of the principles of green chemistry [43].
2.3. Sequential Injection Analysis (SIA)
SIA-based methodologies, unlike FIA, offer the advantage of considerably controlling and reducing the use of samples and reagent volumes. They also allow the management of several reagents to be incorporated into the same system, since its main configuration allows complex analytical objectives to be achieved.
The main components of this method are a multiple position valve (MpV) and a glass syringe that serves as a piston pump and functions as a liquid driver. Figure 5 is a clear example of an SIA system [40] in which one sample allows multiparametric analysis (manganese, iron, ammonium, and phosphate). Through sequential injections, the determinations take place with a compact colorimeter used as a detector.
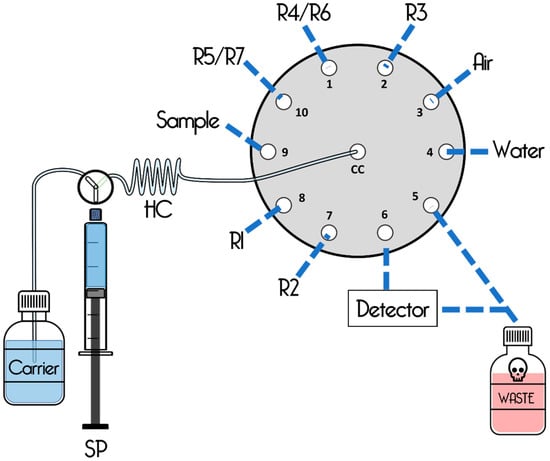
Figure 5.
Graphic scheme based on the SIA method proposed by Kaewwonglom et al., 2015 [40]. Manifold of the sequential injection colorimetric system. HC, holding coil; R1, 5% hydroxylamine; R2, 0.5% w/v 1,10-phenanthroline; R3, 0.6 mol L−1 formaldoxime; R4, 10 g L−1 ammonium molybdate; R5, 2.5% w/v ascorbic acid; R6, 0.5% w/v sodium hypochlorite; R7, 0.4 mol L−1 sodium salicylate; SP, syringe pump.
The unidirectional movement of the syringe piston is controlled by an electric motor. Therefore, precise and detailed volume manipulation can be performed at the microliter level, sequentially taking and dispensing the required volume of solutions for a given analytical run. With a three-way solenoid valve mounted on the syringe pivot, the flow of the liquid is switching in two possible ways allowing a pick up or dispense option [18].
A retention coil is installed between the pump and the central port (Cp) of the MpV to avoid cross-contamination between samples. The MpV selection ports are connected to reservoirs (reagents and sample) as well as other chemical treatment devices (thermal bath, reaction tanks, pH meter, colorimeter, etc.) or directly to a reaction coil, where the sample and the reagents react under optimal conditions, resulting in the formation of a detectable species that is monitored by the detector as illustrated in Figure 5 [52].
Unlike FIA, SIA can become a true multiparameter analysis system, because by linking the side port of one MpV with the center port of another MpV, the number of ports can be increased. This high degree of expandability is unique to SIA. Therefore, SIA is an excellent tool for developing multiparameter monitoring systems.
In addition, the use of Teflon tubing and glass syringes makes it possible to avoid the inherent disadvantages in handling peristaltic pumps, such as deterioration due to the handling of reagents (acids, bases, and solvents) and the constant calibration of these devices [18].
Like any method based on flow techniques, SIA is no exception in the development of systems that tend to miniaturization and portability when they include smaller and easy-to-transport detection devices. In this sense, electrochemistry and spectrophotometry play an important role [53,54].
The electrochemical methods have been used to determine Mn in different matrices with acceptable sensitivity (usually at the ppb level) and precision. These approaches include methods such as voltammetry (with variants like cyclic, pulse, and stripping voltammetry), amperometry, and potentiometry [55]. Particularly for automated methods, this technique has been applied with sequential injection analysis for Mn(II) levels in environmental water samples. For example, Lai et al. used differential pulse cathodic stripping voltammetry as an electrochemical detection method coupling an electrochemical flow cell and a home-made electrochemical analyzer [46].
The sequential injection methodology used in this study consisted of a syringe pump that introduces the solution and injects it into the flow cell, where the Mn is oxidized and placed on the electrode [46]. The proposed method had a high sensitivity with a detection limit (3σ/slope, n = 10) of 0.63 μg L−1, and a wide linear range for concentrations from 2.5 to 200 μg L−1 (R2 = 0.999). A solution with 50 μg L−1 Mn(II) was selected and the precision of the proposed method (%RSD, n = 21) was 5%, and after 200 tests, the analysis remained stable and then gradually decreased with more test numbers. This automated system has been validated with satisfactory recoveries (95.2–101.4%) in spiked water samples. One of the main advantages of this device is that its configuration allowed its satisfactory application in the detection of traces of Mn(II) in environmental water samples, and in the continuous monitoring in real time of the variations of Mn(II) in tap water for 14 days [46].
Kaewwonglom et al. [40] developed a system based on sequential injection and a lab-made, low-cost colorimeter based on a light-emitting diode (LED) as a light source and light dependent resistor (LDR) to analyze samples from a river (iron, manganese, phosphate, and ammonium concentrations). The quantification of Mn was based on the complexation of Mn(II) formaldoxime reagent in a basic solution (pH >10), the use of hydroxylamine to reduce Mn(IV) to Mn(II), and a LED/LDR detector to determine the colored complex using a blue LED. In terms of method performance, the precision (%RSD) for Mn was 1.3% with a dynamic range of 0.2–10 mg L−1 (R2 = 0.997) and a detection limit of 0.14 mg L−1. The sample throughput achieved was 13 samples per hour while the recovery ranged on spiked samples was 89.1–103.9% [40].
2.4. Multipumped Flow System (MPFS)
A multipumped flow system (MPFS) is a continuous flow methodology that consists of a solenoid piston pump, where a fixed amount of liquid is pushed by each stroke, and the flow rate is governed by the stroke frequency. A flexible diaphragm separates the flow channel from the working mechanism. The diaphragm retracts when the solenoid is activated, partially vacuuming the pump body.
By doing so, the liquid is forced through the intake check valve (A), and the output check valve is also closed (B). When the solenoid is deactivated, a spring forces the diaphragm downward, releasing a certain amount of liquid through check valve B while also shutting off check valve A (Figure 6B) [18].
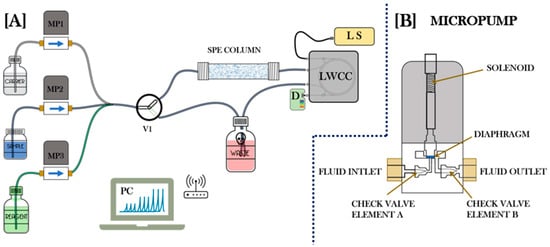
Figure 6.
(A) This scheme shows a general description of an MPFS system, where SPE is applied in the online column and the analyte determination is carried out with a spectrophotometric detector whose sensitivity is improved through an LWCC. D, detector; LWCC, liquid wave capillary cell; LS, light source; MP1-3, micropumps; V1, solenoid valve. (B) General scheme of a micropump.
Several advantages of this methodology include its easy configuration and flexibility, yet it is a highly robust and inexpensive system due to the pump arrangement that can serve as both a valve and a sample/reagent propeller. Along with these benefits, the micropump is operated individually making the consumption of reagents more efficient. However, this approach also has some limitations. The micropumps used in the MPFS are prone to particle clogging; therefore, constant calibration of distributed volume is required [18]. This methodology has been applied to determine Mn species in water samples in the past. In 2011, Silva et al. [35] designed a flow system with solenoid micropumps coupled to a spectrophotometer implemented. This MPFS was used to measure Mn in freshwater samples based on the formation of the Mn(III)/EDTA complex in a solid-phase reactor containing lead dioxide immobilized on polyester. They obtained a linear response from 25 to 1500 μg L−1 (R2 = 0.999) and an appropriate limit of detection of 6 μg L−1. Additionally, the matrix effects on Mn measurements were assessed by calculating the recovery from two spiked samples (at 50 and 100 μg L−1), achieving recoveries of 100 and 104%, respectively. Finally, they compared their methodology with Mn determinations using a graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometer (GF-AAS), obtaining a good agreement in the measurements of both analytical techniques at the 95% confidence level [35]. Figure 6A shows a general scheme where through an MPFS system, SPE is applied, and the analyte determination is carried out with a spectrophotometric detector whose sensitivity is improved through an LWCC.
2.5. Multisyringe Flow Injection Analysis (MSFIA)
MSFIA is based on an automatic burette with four syringes simultaneously working in parallel, whose pistons are connected to a single transfer rod. Moreover, the head of each syringe is configured with three-way solenoid valves to return nonrequired liquid to a reservoir, optimizing the consumption of the sample and reducing sample and reagent waste. In the latest configurations, the multisyringe’s rear panel features a power supply for the instrument, two serial ports to establish a chain of elements (with one port connected to a PC for the initial element of the chain, and the second port for connecting to the subsequent element), and four additional analog outputs. These outputs offer independently programmable voltages ranging from 2.5 to 13 V [56].
One of the main benefits of MSFIA is reducing the volume utilized. The arrangement of this technique allows to save reagents and use less sample volume because it only injects them into the system when needed. Other advantages of this technique are related to its versatility. Being a hybrid technique, it allows to gather analytical information from dynamic events occurring in flow manifolds like FIA, while also having the flexibility and robustness of SIA and the application of solenoid valves to improve efficiency like multicommuted flow injection analysis (MCFIA) [56].
Despite the numerous advantages of this technique, its main limitation lies in the movement of the four syringes during assembly. Once parameters such as dispensing volume and flow rate are set for one syringe, these values are automatically applied to the remaining syringes, based solely on the syringe size [57].
Some of the benefits of this technique include the use of less reagent volume because it allows for miniaturization and microanalysis, which translates to fewer costs, safer analyses, and less waste produced. Analytically speaking, it also offers advantages such as faster analyses, high reproducibility, and reduced potential contamination. On the other hand, some common drawbacks of this technique include poor penetration area, the absence of confluent mixing, and longer analysis time than FIA due to the wider tubes, syringe refills, and sequential injection modes required in LOV [18].
2.5.1. MSFIA-LOV
Lab-on-valve (LOV) is a methodology that has gained popularity in the last few years in flow analysis, usually referred to as the third generation. LOV is based on the incorporation of analytical units in a valve allowing for miniaturization of the analytical components and microanalysis and sub-microanalysis [58].
The integrated central port of the LOV sample processing unit is typically connected to a piston pump via a holding coil. This setup is designed to facilitate the sequential aspiration of various reagents and the sample through the unit’s peripheral ports, with the central port (Cp) managed by the MpV. In this process, precise volumes of sample and reagent are sequentially aspirated from the microfluidic device, which is positioned above a rotary selection valve. Subsequently, they are propelled by flow reversal into a stationary coil. This method demonstrates that sample handling in the sequential injection mode, utilizing forward, reversed, and halted flow, can be adapted to conduct multiple tests. These tests may include adding solutions, mixing, dilution, control, and incubation [18].
Figure 7 describes a general scheme of an MSFIA-LOV system based on Chaparro et al. (2016) [22], where Mn is extracted from the sample by SPE through a microcolumn integrated within the LOV module and its spectrophotometric detection using an LWCC. Particularly in the determination of Mn in water samples, MSFIA-LOV has been applied before although not extensively. This study explored the application of MSFIA and LOV for the analysis of Mn in sea and drinking water by online spectrophotometric detection by an LWCC. The developed MSFIA-LOV–based method relied on the catalytic effect of Mn2+ on the oxidation of Tiron by hydrogen peroxide in the presence of Pb2+ as an activator. An MSFIA-LOV-LWCC-UV–VIS system was constructed, comprising a multisyringe burette with a programmable flow rate, a selection valve module (VA 2 SW, Crison), and an autosampler (Crison) [22]. Following optimization of the method’s conditions (pH 10 with 0.019 mol L−1 2′2 bipyridyl, 0.005 mol L−1 Tiron, and 0.38 mol L−1 hydrogen peroxide), a measurement range of 0.03–35 µg L−1 for Mn determination was achieved, with a detection limit of 0.010 µg L−1. The method exhibited a repeatability of 1.4% RSD, and recoveries ranged from 92% to 103% for spiked samples of natural water [22].
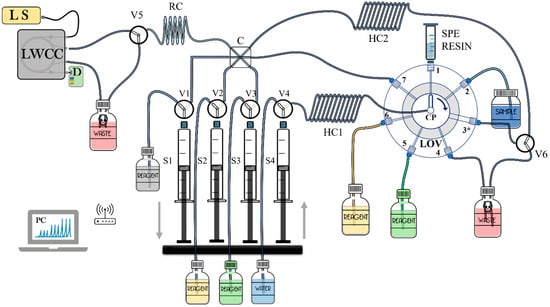
Figure 7.
Graphic scheme based on the research group of Chaparro et al. (2016) [22]. In this image, manganese is extracted from the sample using SPE through a microcolumn integrated within the LOV module and its spectrophotometric detection using an LWCC. CP, central port; D, detector; HC1-2, holding coil; LOV, lab-on-valve module; LS, light source; RC, reaction coil; V1–6, solenoid valves; S1–S4, syringes.
2.5.2. MSFIA-CHIP
Chips are defined as monolithic flow equipment that combines functions such as reaction coil, confluent mixing, temperature controlling, etc., in a small area allowing for a tiny amount of liquid to be processed. Some chips may include a sensor that is particularly useful in automating kinetic methods [18,56]. Therefore, chips allow for the introduction and mixing of solutions, analysis precision, and prevention of outer contamination. This technique is also like LOV in terms of miniaturization; thus, it also shares some of the advantages that LOV offers (i.e., reduced analysis time, analytical reliability, and minimized contamination). Some shortcomings of this technique include a limited penetration area and the potential introduction of air bubbles that can occur in this type of flow-based methodology [39].
Chips have been coupled with MSFIA to improve their performance-observing advantages in terms of a wide working range and sample throughput [59]. Particularly for the determination of Mn species in water, this technique has been applied with catalytic spectrometric methods. In 2014, Phansi et al. [39] applied this configuration for the analysis of Mn in rainwater and compared their method with a reference method based on the ICP-AES. A multisyringe piston pump module was outfitted with three 1 mL glass syringes (S1, S3, and S4) and one 5 mL glass syringe (S2). Solenoid valves (V1, V2, V3, and V4) enabled the connection of each syringe either to the chip or to the corresponding solution reservoir for refilling. The chip was built based on the work by Abouhiat et al. (2014) [59] and used three PMMA (poly methyl methacrylate) pieces of 85 × 44 × 10 mm. The multisyringe module and an autosampler were linked sequentially, utilizing an RS232C interface, to a personal computer–enabling remote control. For illumination, a DH-2000 deuterium lamp sourced from TOP Sensor Systems in Eerbeek, the Netherlands, was employed, while detection was facilitated by a USB-2000 miniature CCD spectrophotometer, manufactured by Ocean Optics Inc. based in Dunedin, FL, USA. Two methods were reported from this work as follows: an initial rate approach that consumed a greater quantity of reagents and sample volume and a fixed-time method. The fixed-time method exhibited superior reproducibility and a wider working range, leading to its selection for conducting the Mn(II) analysis within the 1–20 mg L−1 working range. The recoveries were based on Mn(II) determinations from spiked rain samples analyzed by ICP-EAS and the proposed methodology ranging from 98–103%. Moreover, this methodology was applied for the analysis of water samples with an injection throughput of 22 injections h−1. The calculated precision of this method was 0.67% (5 mg L−1, n = 15) with a limit of detection of 0.33 mg L−1, demonstrating a high sensitivity and reproducibility [39].
Additionally, Milani et al. [41] investigated the performance of chips in the determination of dissolved Mn in situ in an aquatic environment. The main part of the system was a colorimetric microfluidic chip that allowed for the injection, mixture, and measurement of the complexes resulting from reagents and samples. The device (120 × 80 × 11 mm) merged two separate manifolds, facilitating the use of two chemical procedures and allowing for simultaneous determination of two parameters. The microfluidic chip was built in 8.0 mm thick tinted PMMA. The analyzer was controlled by a custom-designed electronics package, which included three constant current sources LED drivers, eight 18-bit analog-to-digital inputs, a temperature sensor, eight spikes and hold circuits for powering the valves, a stepper motor driver for the pump, and a real-time clock. The analytical unit was controlled through a programmable autonomous state machine (ASM).
The developed methodology obtained an analysis of six samples h−1. The limit of detection for Mn was 28 nM with an estimated precision for Mn was 2.4%. This methodology was applied during a cruise to the Gotland and Landsort Deep Basins of the Baltic Sea. The Mn profile carried out in the Landsort Deep (58°35.0220′ N, 18°14.1763′ E) showed a good correspondence between the in situ analyzer and bottle measured data (73–95%), also demonstrating a low power usage, reduced reagent volume, portability, and a high tolerance to pressures (up to at least 170 bars maintaining precision and accuracy) [41]. In Figure 8, one of the described systems [39] has been selected to show, in a general way, an MSFIA-CHIP scheme and its application in determining Mn in water samples.
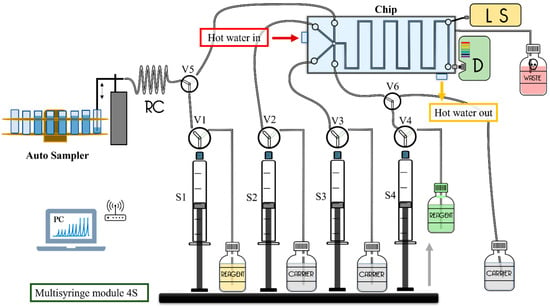
Figure 8.
Graphic scheme based on one of the MSFIA-CHIP works discussed to show, in a general way, an MSFIA-CHIP scheme and its application in the determination of manganese in water samples. CC, central conduit; D, detector; LS, light source; RC, reaction coil; S1–S4, syringes; V1–V6, solenoid valves.
3. Trends and Future Perspectives
The automation in analytical methodologies faces limitations, mainly due to the size of measurement equipment, which requires transporting samples from the site to the laboratory. However, automation enables automatic sample pretreatment, a stage involving complex steps for the analyst, thereby ensuring their safety, especially when dealing with potentially unknown contaminants. The trend toward technological advances and miniaturization could lead to fully automated analytical methodologies, allowing real-time in situ monitoring. These advantages are already being reported by the methodologies reviewed in this work.
The continuous evolution of FIA techniques offers promising prospects for future environmental analysis, especially with miniaturization and portability. When combined with spectrophotometry methods like UV–VIS, it shows potential for on-site environmental monitoring. Similarly, rFIA also demonstrates the potential for in situ analysis and real-time monitoring of water quality parameters. Moreover, the development of novel extraction methods, such as biosorbents, holds promise for enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of analysis. Further advancements in technology, including improvements in sensitivity, speed, and automation, are likely to facilitate their broader adoption for environmental monitoring.
In the same way, SIA techniques offer significant promise for continuous natural water analysis. Additionally, the portability and cost-effectiveness make it suitable for its implementation in remote areas. Continued research into SIA-based methodologies, particularly in the context of green chemistry principles, could lead to more sustainable environmental monitoring practices.
Additional development of MPFS technology could lead to enhanced capabilities and broader applications in environmental analysis. Addressing issues such as particle clogging through improved pump design or filtration systems would increase the reliability of this system for routine analysis. Also, integrating it with advanced detection techniques could expand its analytical scope and sensitivity. Future research may focus on combining an MPFS with sample preparation techniques to improve analyte preconcentration and reduce matrix interference.
Finally, it is important to mention that the integration of microfluidic chips into MSFIA systems is continually advancing, thanks to novel technology such as 3D printing and the exploration of new materials. This development expands the potential for various future applications in environmental monitoring and analytical chemistry. With further improvement, MSFIA-CHIP could enable real-time monitoring of water quality parameters in natural water bodies. The miniaturization and automation features could lead to the creation of portable analytical devices for on-site analysis in remote locations, providing rapid and accurate measurements for environmental assessment and management.
4. Conclusions
Automated flow-analysis methods have allowed the determination of Mn in water samples by coupling a wide variety of analytical detection techniques. These methods have been key in the last two decades for Mn monitoring in diverse settings, including in situ Mn determination.
The implementation of flow analysis techniques offers several advantages, highlighting the possibility of miniaturization and portability of these systems, allowing for a reduction in the volume of samples and reagents used during the analysis, the generation of waste, and the analysis time. Moreover, another important benefit linked to the reduction in sample and reagent handling is improving analysis safety and agreement with the green chemistry principles.
One of the most used automated flow systems in the determination of Mn species in water samples is based on FIA, with around half of the studies included in this review reporting having applied this technique (55%, n = 15), including partially and fully automated methods.
Two analytical features stand out from the studies evaluated here as follows: sample throughput and accuracy (% recovery). From the studies that reported sample throughput, the average processing time was around 24 samples per hour, with a maximum of 120 samples h−1 and a minimum of 5 samples h−1. In terms of accuracy, the calculated average of the recovery was around 98%, from 15 papers that reported accuracy, demonstrating the analytical reliability of automated flow-analysis methods.
It is important to emphasize that the water matrices analyzed in these studies were highly diverse, including different types of water matrices such as groundwater, seawater, natural water, and drinking water, and these methods allowed for the application of in situ studies by implementing both semiautomatic and fully automatic analysis.
Finally, this review has explored the potential of in situ Mn sensors in automation, emphasizing their suitability for field applications. These sensors offer cost-effectiveness, low energy and reagent usage, portability, robustness, high accuracy, and minimal need for direct operation, all while being selective for the target analyte. They represent an advancement of the field, impacting not only Mn analysis but also the wider adoption of automation in addressing emerging contaminants in environmental water samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.R.-M. and V.R.-S.; methodology, R.R.-M. and V.R.-S.; validation, L.O.L. and L.F.; formal analysis, R.R.-M. and V.R.-S.; investigation, R.R.-M. and V.R.-S.; resources, L.O.L. and L.F.; writing—original draft preparation, R.R.-M. and V.R.-S.; writing—review and editing, L.O.L., L.F., R.R.-M. and V.R.-S.; supervision, L.O.L. and L.F.; project administration, L.O.L. and L.F.; funding acquisition, L.O.L. and L.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support from the Centro de Investigación en Materiales Avanzados, S.C. (CIMAV) through internal project PI-2024-01 is gratefully acknowledged and we appreciate the financial support provided by CONAHCYT through project CF 2019-1727980 (Mexico), as well as the financial support from project PID2019-107604RB-I00 funded by MCIN/AEI/ 10.13039/501100011033 (Spain).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Patil, D.S.; Chavan, S.M.; Oubagaranadin, J.U.K. A review of technologies for manganese removal from wastewaters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 468–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygo-Szymanko, E.; Tobiasz, A.; Walas, S. Speciation analysis and fractionation of manganese: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, C.; Crawford, J.; McClure, P.R.; Roney, N.; Todd, G.D. Toxicological Profile for Manganese: Introduction; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. ATSDR: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 39–40. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/12399/cdc_12399_DS1.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- World Health Organization. Chapter 1: General Description. In Manganese in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/104/Rev/1; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/wash-documents/wash-chemicals/manganese-background-document.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Pinsino, A.; Matranga, V.; Roccheri, M.C. Manganese: A new emerging contaminant in the environment. In Environmental Contamination; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.P.; Reddy, P.R.; Reddy, V.K. Direct and first derivative spectrophotometric determination of manganese (II) in tap water, milk, alloy steels and plant samples. Eurasian J. Anal. Chem. India 2009, 4, 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini, R.; Placidi, D.; Cagna, G.; Fedrighi, C.; Oppini, M.; Peli, M.; Zoni, S. Manganese and Developmental Neurotoxicity. In Neurotoxicity of Metals; Advances in Neurobiology; Aschner, M., Costa, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustamov, N.; Abbasova, G. Determination of Manganese in Tap Water by a New Extraction-Photometric Method. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 5, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Neira, J.; Zhu, Q.; Aller, R.C. A new spectrophotometric method to quantify dissolved manganese in marine pore waters. Mar. Chem. 2011, 127, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürkan, R. Catalytic spectrophotometric determination of Mn (II) at trace levels using Celestine blue-KIO4-1, 10-phenantroline redox reaction. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2011, 25, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, M.; Avila, D.S.; Da Rocha JB, T.; Aschner, M. Metals, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: A focus on iron, manganese and mercury. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 575–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaria, A.B. Manganese exposure, essentiality toxicity. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 484–500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noroozifar, M.; Khorasanik-Motlagh, M.O.; Akbari, R. Speciation of manganese using a pneumatic flow injection analysis-tandem spectrometer system. Turk. J. Chem. 2007, 31, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Manganese in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; No. WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/104; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Drinking Water Health Advisory for Manganese; EPA-822-R-04-003; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ismailzadeh, A.; Masrournia, M.; Es’haghi, Z.; Bozorgmehr, M.R. An environmentally friendly sample pre-treatment method based on magnetic ionic liquids for trace determination of nitrotoluene compounds in soil and water samples by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry using response surface methodology. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 2929–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Karmakar, D.; Begum, S.N.; Ali, S.Y.; Patra, P.K. Recent trends in the analysis of trace elements in the field of environmental research: A review. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 1060866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdá, V.; Ferrer, L.; Avivar, J.; Cerda, A. Flow Analysis: A Practical Guide; Newnes: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; He, M.; Chen, B. Nanometer-sized materials for solid-phase extraction of trace elements. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2685–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk Er, E.; Dalgıç Bozyiğit, G.; Büyükpınar, Ç.; Bakırdere, S. Magnetic nanoparticles-based solid phase extraction methods for the determination of trace elements. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okenicová, L.; Žemberyová, M.; Procházková, S. Biosorbents for solid-phase extraction of toxic elements in waters. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016, 14, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, L.; Ferrer, L.; Leal, L.O.; Cerdà, V. Automatic flow analysis method to determine traces of Mn2+ in sea and drinking waters by a kinetic catalytic process using LWCC-spectrophotometric detection. Talanta 2016, 148, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yebra-Biurrun, M.C.; Carro-Mariño, N. Flow injection flame atomic absorption determination of Cu, Mn and Zn partitioning in seawater by on-line room temperature sonolysis and minicolumn chelating resin methodology. Talanta 2010, 83, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Yuan, D.; Huang, Y.; Lin, K.; Zhou, T. In-field determination of trace dissolved manganese in estuarine and coastal waters with automatic on-line preconcentration and flame atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 963, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, L.K.; Nishioka, J. Quantitative analysis of Fe, Mn and Cd from sea ice and seawater in the Chukchi Sea, Arctic Ocean. Polar Sci. 2018, 17, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Pistón, M. Evaluation of sisal fiber as biosorbent for online preconcentration and determination of Cu and Mn coupled to MP AES using the analytical greenness metric approach. Braz. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 10, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.K.; Lin, J.Y. 3D-printed column with porous monolithic packing for online solid-phase extraction of multiple trace metals in environmental water samples. Anal. Chem. 2020, 2, 9640–9648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eztrujilloi, S.; Alonsoe, V.; Silescordero, M. On-Line Solid-Phase Chelation for the Determination of Six Metals in Sea Water by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2010, 25, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, M.L.; Alonso, E.V.; Pavón, J.C.; Cordero, M.S.; De Torres, A.G. Simultaneous determination of chemical vapour generation forming elements (As, Bi, Sb, Se, Sn, Cd, Pt, Pd, Hg) and non-chemical vapour forming elements (Cu, Cr, Mn, Zn, Co) by ICP-OES. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2016, 31, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiasz, A.; Sołtys, M.; Kurys, E.; Domagała, K.; Dudek-Adamska, D.; Walas, S. Multicomutation flow system for manganese speciation by solid phase extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2017, 134, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; He, M.; Hu, B. Membrane solid phase microextraction with alumina hollow fiber on line coupled with ICP-OES for the determination of trace copper, manganese and nickel in environmental water samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 187, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, A.; Landing, W.; Bizimis, M.; Morton, P. Determination of Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in seawater using high resolution magnetic sector inductively coupled mass spectrometry (HR-ICP-MS). Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 665, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biller, D.V.; Bruland, K.W. Analysis of Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb in seawater using the Nobias-chelate PA1 resin and magnetic sector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Mar. Chem. 2012, 130, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerström, M.E.; Field, M.P.; Séguret, M.; Fischer, L.; Hann, S.; Sherrell, R.M. Automated on-line flow-injection ICP-MS determination of trace metals (Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn) in open ocean seawater: Application to the GEOTRACES program. Mar. Chem. 2013, 155, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.G.; Nóbrega, J.A.; Rocha, F.R. Exploiting Mn (III)/EDTA complex in a flow system with solenoid micro-pumps coupled to long pathlength spectrophotometry for fast manganese determination. Microchem. J. 2011, 98, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderilla, C.; Maya, F.; Leal, L.O.; Cerdà, V. Recent advances in flow-based automated solid-phase extraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, S.; Polesello, S.; Mazzoni, M.; Rusconi, M.; Petrovic, M. On-line sample extraction and purification for the LC–MS determination of emerging contaminants in environmental samples. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2015, 8, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowicz, M.; Kołacińska, K. Recent advances in flow injection analysis. Analyst 2016, 141, 2085–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phansi, P.; Henríquez, C.; Palacio, E.; Wilairat, P.; Nacapricha, D.; Cerdà, V. An automated catalytic spectrophotometric method for manganese analysis using a chip-multisyringe flow injection system (Chip-MSFIA). Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 5088–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewwonglom, N.; Jakmunee, J. Sequential injection system with multi-parameter analysis capability for water quality measurement. Talanta 2015, 144, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, A.; Statham, P.J.; Mowlem, M.C.; Connelly, D.P. Development and application of a microfluidic in-situ analyzer for dissolved Fe and Mn in natural waters. Talanta 2015, 136, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, T. Development and application of a shipboard method for spectrophotometric determination of trace dissolved manganese in estuarine and coastal waters. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 92, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngvises, N.; Suwannasaroj, K.; Jakmunee, J.; AlSuhaimi, A. Multi-reverse flow injection analysis integrated with multi-optical sensor for simultaneous determination of Mn (II), Fe (II), Cu (II) and Fe (III) in natural waters. Talanta 2017, 166, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Yuan, D.; Huang, Y.; Lin, K.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, J. A catalytic spectrophotometric method for determination of nanomolar manganese in seawater using reverse flow injection analysis and a long path length liquid waveguide capillary cell. Talanta 2018, 178, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.R.; Oldham, V.E.; Luther, G.W.; Mucci, A.; Tebo, B.M. Distribution of desferrioxamine-B-extractable soluble manganese (III) and particulate MnO2 in the St. Lawrence Estuary, Canada. Mar. Chem. 2019, 208, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Lin, F.; Qiu, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Hu, H. Development of a sequential injection analysis device and its application for the determination of Mn (II) in water. Talanta 2020, 211, 120752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousi, N.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; Zachariadis, G.A.; Anthemidis, A. Multi-element analysis based on an automated on-line microcolumn separation/preconcentration system using a novel sol-gel thiocyanatopropyl-functionalized silica sorbent prior to ICP-AES for environmental water samples. Molecules 2021, 26, 4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; He, Y.; Lai, C. Elemental Analysis of Environmental Waters by Solution Cathode Glow Discharge—Atomic Emission Spectrometry (SCGD-AES) with a Multifunctional Injection System. Anal. Lett. 2022, 55, 2273–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Islas, A.M.; Resing, J.A.; Bruland, K.W. Catalytically enhanced spectrophotometric determination of manganese in seawater by flow-injection analysis with a commercially available resin for on-line preconcentration. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2006, 4, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, F.R.; Danielson, N.D. Reverse flow-injection analysis. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 40, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páscoa, R.N.; Tóth, I.V.; Rangel, A.O. Review on recent applications of the liquid waveguide capillary cell in flow based analysis techniques to enhance the sensitivity of spectroscopic detection methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 739, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenehan, C.E.; Barnett, N.W.; Lewis, S.W. Sequential injection analysis. Analyst 2002, 127, 997–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Olmos, R.; Soto, J.C.; Zarate, N.; Araujo, A.N.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M. Sequential injection analysis using electrochemical detection: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 554, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, N.W.; Lenehan, C.E.; Lewis, S.W. Sequential injection analysis: An alternative approach to process analytical chemistry. TRAC Trends Anal. Chem. 1999, 18, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaramani, S.; Banuprakash, G.; Doreswamy, B.H. Electrochemical and Optical Methods for the Quantification of Lead and Other Heavy Metal Ions in Liquid Samples. In Heavy Metals-Their Environmental Impacts and Mitigation; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cerdà, V.; Ferrer, L.; Portugal, L.A.; de Souza, C.T.; Ferreira, S.L. Multisyringe flow injection analysis in spectroanalytical techniques—A review. TRAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró, M.; Cerdà, V.; Estela, J.M. Multisyringe flow injection analysis: Characterization and applications. TRAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avivar, J.; Ferrer, L.; Casas, M.; Cerdà, V. Lab on valve-multisyringe flow injection system (LOV-MSFIA) for fully automated uranium determination in environmental samples. Talanta 2011, 84, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhiat, F.Z.; Henríquez, C.; Palacio, E.; El Yousfi, F.; Cerdà, V. Automatic integrated system for catalytic spectrophotometric determination of vanadium in water samples. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 9142–9151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).