Preliminary Study on the Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Eichhornia crassipes on Co-Cultured Raphidiopsis raciborskii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material Preparation
2.1.1. E. crassipes
2.1.2. R. raciborskii
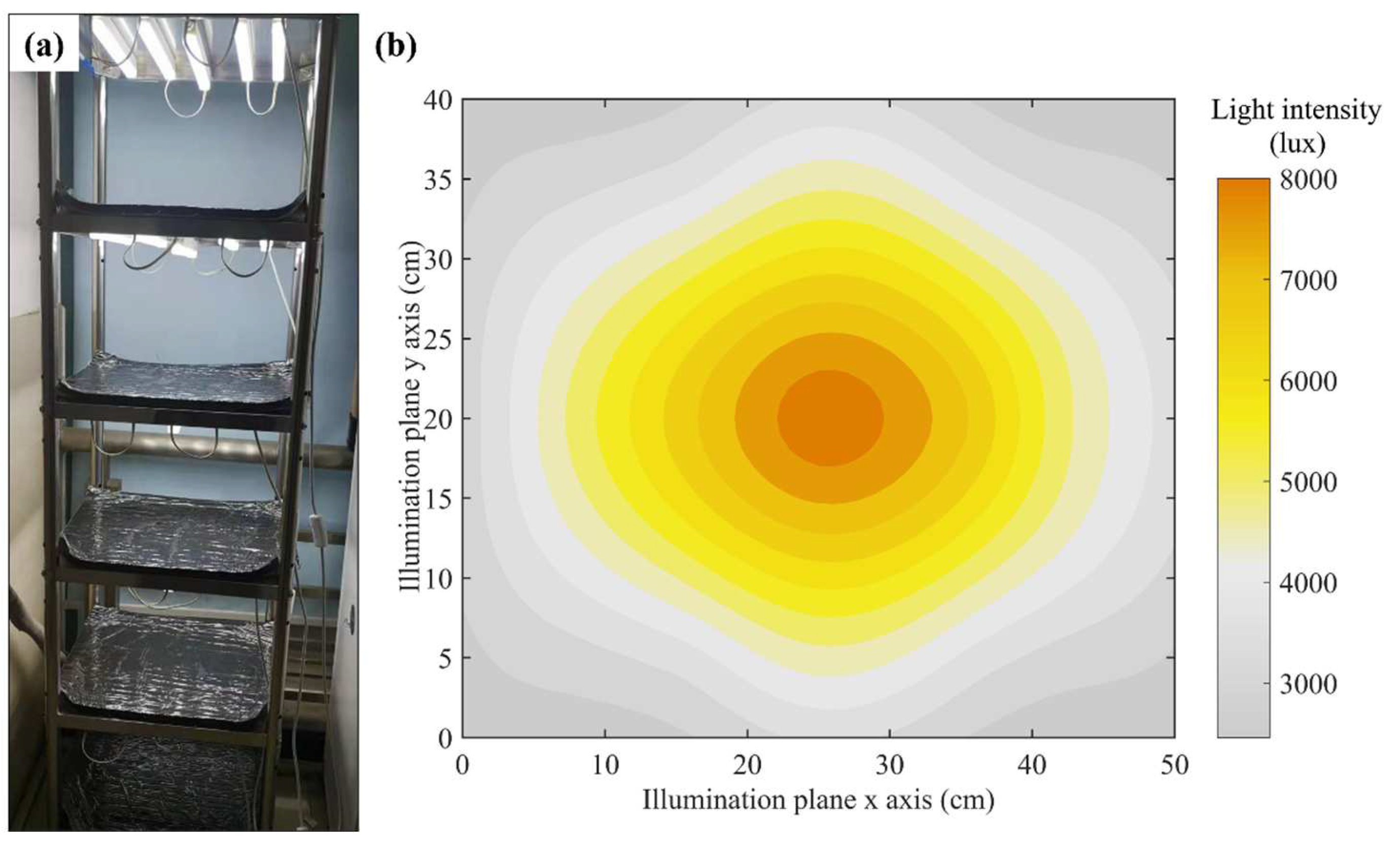
2.1.3. Self-Made Illumination Cultivation Frame
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Experiment 1: Co-Culture of E. crassipes and R. raciborskii with Different Densities
2.2.2. Experiment 2: Nutrient Enrichment Experiment
2.2.3. Experiment 3: Exposure to E. crassipes Exudates
2.3. Observations of the Growth of R. raciborskii
2.4. Measurement of Growth and Chlorophyll Fluorescence of E. crassipes
2.5. Determination of Water Quality Parameters
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Interaction between E. crassipes and R. raciborskii in Co-Culture
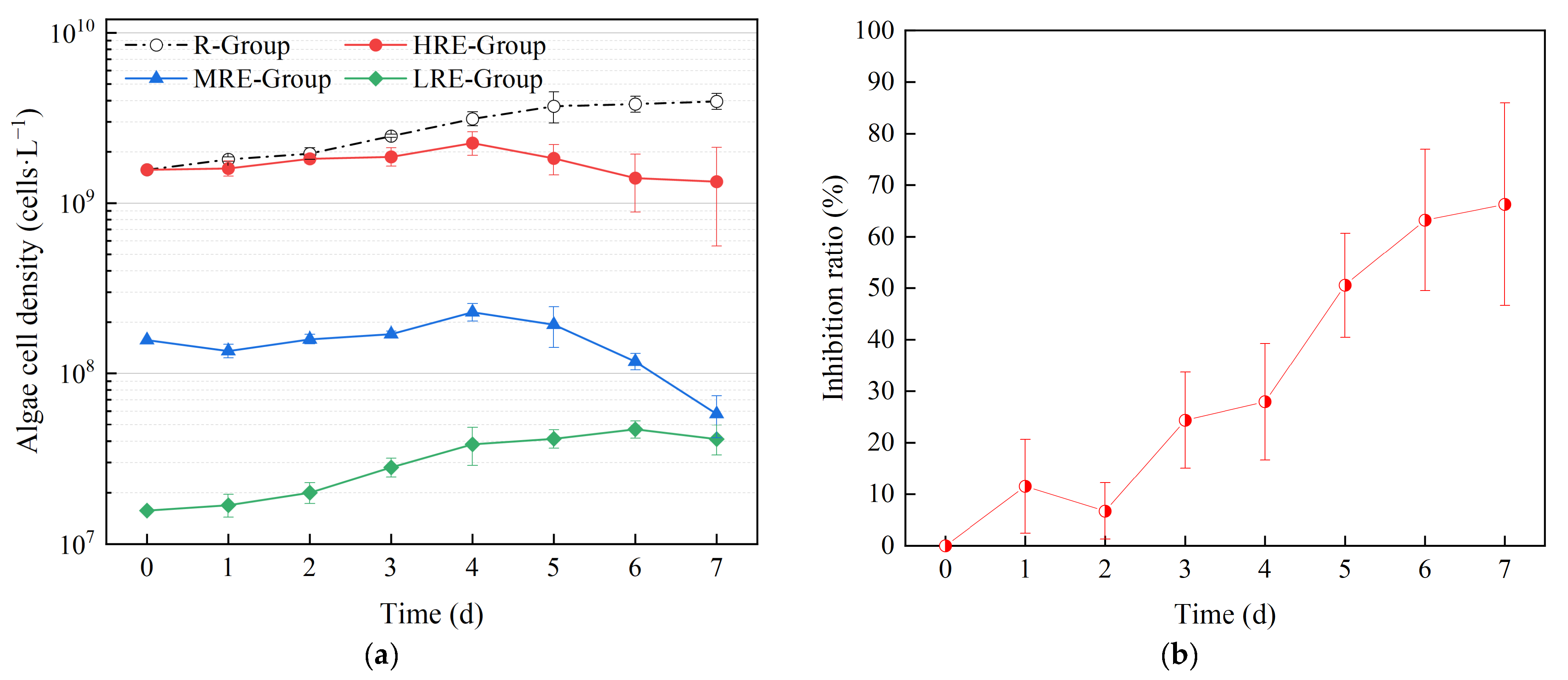
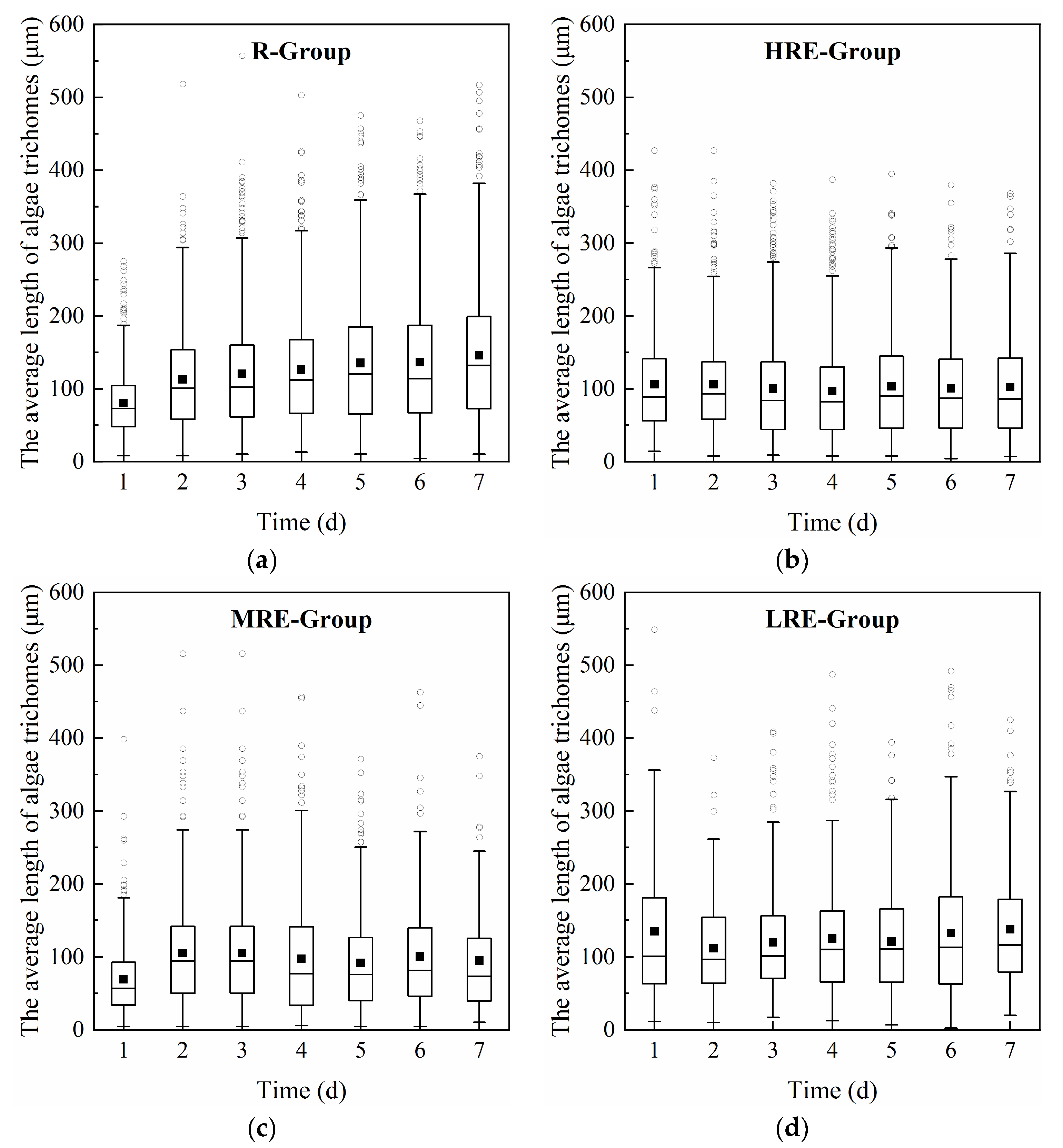
3.1.1. Effects of E. crassipes on the Growth and Trichome Size of R. raciborskii
3.1.2. Effects of R. raciborskii on the Growth and Photosynthesis of E. crassipes
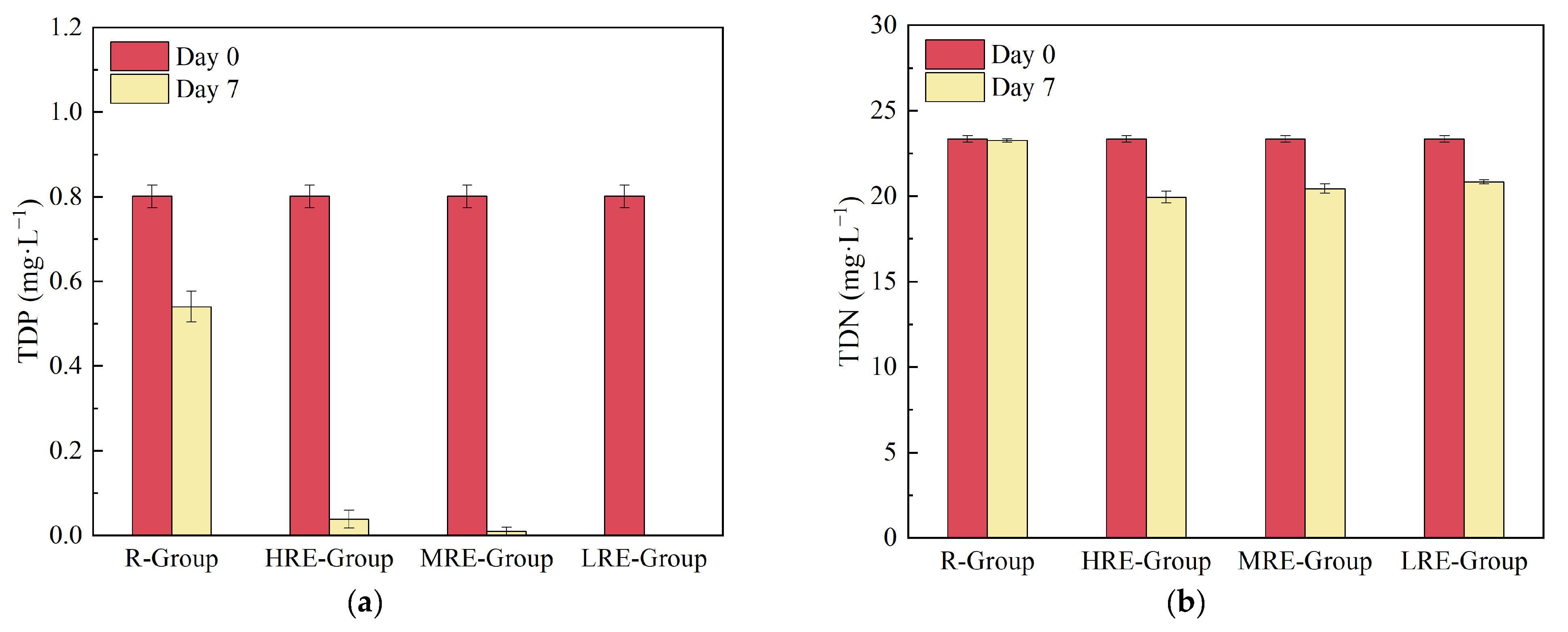
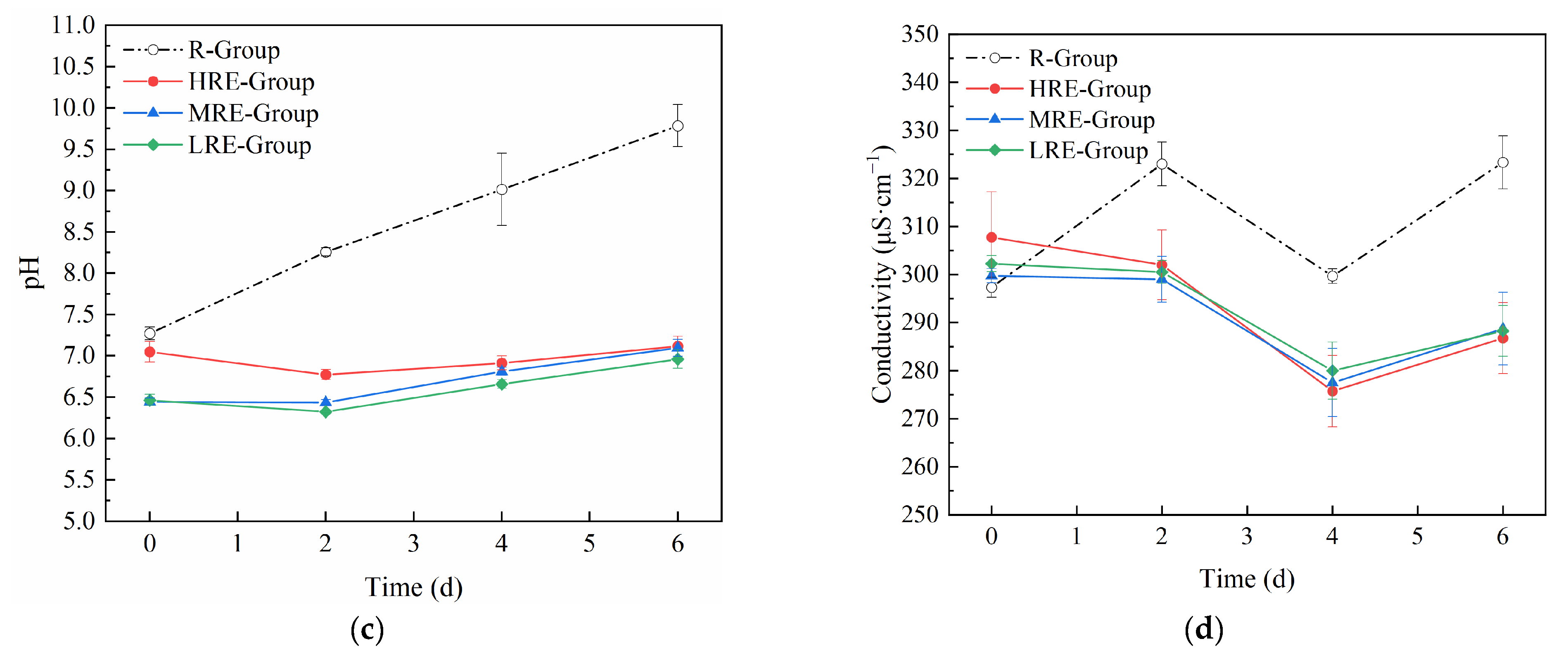
3.1.3. Changes in Nutrients and Other Water Quality Factors
3.2. Effects of Nutrients on Algae Inhibition of E. crassipes
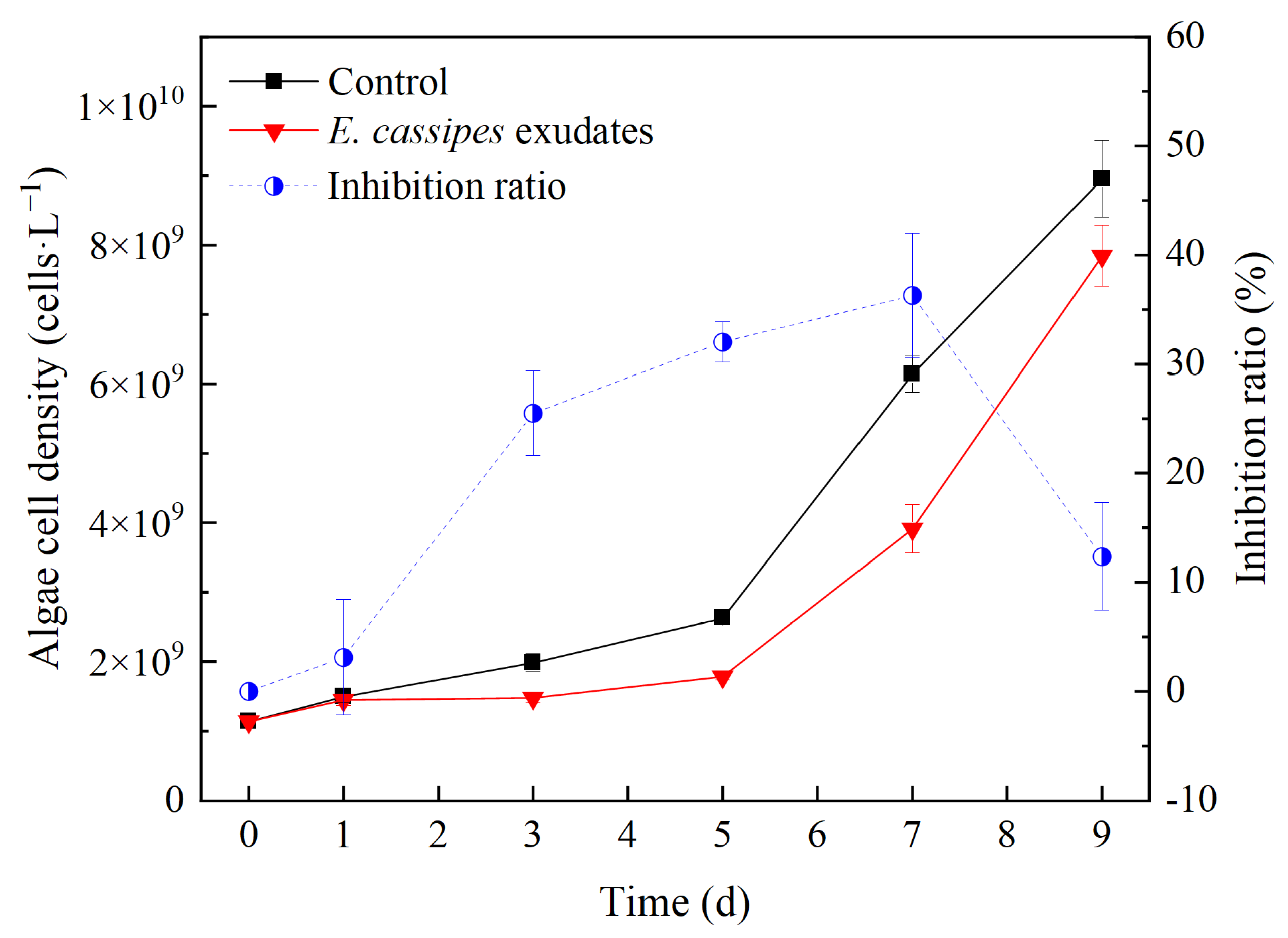
3.3. Effect of E. crassipes Exudates on the Growth of R. raciborskii
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Moal, M.; Gascuel-Odoux, C.; Ménesguen, A.; Souchon, Y.; Étrillard, C.; Levain, A.; Moatar, F.; Pannard, A.; Souchu, P.; Lefebvre, A.; et al. Eutrophication: A new wine in an old bottle? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, I.; Moore, R.E.; Runnegar, M.T.C. Cylindrospermopsin: A potent hepatotoxin from the blue-green alga Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 7941–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Pearson, L.A.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Orr, P.T.; Neilan, B.A. Increased incidence of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in temperate zones—Is climate change responsible? Water Res. 2012, 46, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidelev, S.; Koksharova, O.; Babanazarova, O.; Fastner, J.; Chernova, E.; Gusev, E. Phylogeographic, toxicological and ecological evidence for the global distribution of Raphidiopsis raciborskii and its northernmost presence in Lake Nero, Central Western Russia. Harmful Algae 2020, 98, 101889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, J.T.; Leão, P.N.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: Review of the distribution, phylogeography, and ecophysiology of a global invasive species. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Beardall, J.; Willis, A.; Orr, P.T.; Magalhaes, V.F.; Rangel, L.M.; Azevedo, S.; Neilan, B.A. Understanding the winning strategies used by the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierangelini, M.; Stojkovic, S.; Orr, P.T.; Beardall, J. Photosynthetic characteristics of two Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains differing in their toxicity. J. Phycol. 2014, 50, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recknagel, F.; Orr, P.T.; Cao, H. Inductive reasoning and forecasting of population dynamics of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in three sub-tropical reservoirs by evolutionary computation. Harmful Algae 2014, 31, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Wang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Yu, G. Occurrence of Raphidiopsis raciborskii blooms in cool waters: Synergistic effects of nitrogen availability and ecotypes with adaptation to low temperature. Env. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, S.; Aubriot, L.; Soares, M.C.S.; Gonzalez-Piana, M.; Fabre, A.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Lurling, M.; Antoniades, D.; Padisak, J.; Kruk, C. What drives the distribution of the bloom-forming cyanobacteria Planktothrix agardhii and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciechowski, J.; Fernandes, L.F.; Buck Fonseca, F.V. Morpho-physiological responses of a subtropical strain of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) to different light intensities. Acta Bot. Bras. 2016, 30, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzymski, P.; Poniedziałek, B.; Kokociński, M.; Jurczak, T.; Lipski, D.; Wiktorowicz, K. Interspecific allelopathy in cyanobacteria: Cylindrospermopsin and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii effect on the growth and metabolism of Microcystis aeruginosa. Harmful Algae 2014, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Peng, L.; Huang, X.; Han, B.P. Occurrence and dominance of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and dissolved cylindrospermopsin in urban reservoirs used for drinking water supply, South China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 3079–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Yang, Y.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, P.; Li, H.; Li, R. Interspecific competition reveals Raphidiopsis raciborskii as a more successful invader than Microcystis aeruginosa. Harmful Algae 2020, 97, 101858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, A.D.; Jones, E. Demonstration of the antagonistic action of large aquatic plants on algae and rotifers. Ecology 1949, 30, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yin, Y.; Kang, L.; Feng, L.; Liu, Y.; Du, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, L. A review: Application of allelochemicals in water ecological restoration--algal inhibition. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezbrytska, I.; Usenko, O.; Konovets, I.; Leontieva, T.; Abramiuk, I.; Goncharova, M.; Bilous, O. Potential use of aquatic vascular plants to control cyanobacterial blooms: A review. Water 2022, 14, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaeda, T.; Trung, V.K.; Manatunge, J.; Van Bon, T. Modelling macrophyte–nutrient–phytoplankton interactions in shallow eutrophic lakes and the evaluation of environmental impacts. Ecol. Eng. 2001, 16, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, P.S.; Riis, T.; Alnøe, A.B.; Peipoch, M.; Maetzke, K.; Bruus, C.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A. Macrophyte complexity controls nutrient uptake in lowland streams. Ecosystems 2015, 18, 914–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamagna, A.M.; Murphy, B.R. Ecological and socio-economic impacts of invasive water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes): A review. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Aggarwal, N.K.; Saini, A.; Yadav, A. Beyond biocontrol: Water hyacinth—Opportunities and challenges. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 9, 26–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, S.K.R.; Pandian, U.K.; Vani, C.; Bharani, R.S.A.; Kavisri, M.; Meivelu, M. Chitosan nanocomposite as an effective carrier of potential herbicidal metabolites for noteworthy phytotoxic effect against major aquatic invasive weed water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 226, 1597–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan Gonzalez, C.; Alejandra Maine, M.; Ricardo Hadad, H.; Cristina Sanchez, G.; Patricia Benavides, M.; Abel Campagnoli, M. Effects on Eichhornia crassipes under Zn stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 26957–26964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saviolo Osti, J.A.; do Carmo, C.F.; Silva Cerqueira, M.A.; Duarte Giamas, M.T.; Peixoto, A.C.; Vaz-dos-Santos, A.M.; Janson Mercante, C.T. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal from fish farming effluents using artificial floating islands colonized by Eichhornia crassipes. Aquacult. Rep. 2020, 17, 100324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabla-Hernandez, J.; Rodriguez-Espinosa, P.F.; Dellepere, A.V.; Marrugo-Negrete, J. Management proposal of a naturally occurring wetland modeled as a constructed wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 189, 106909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yan, S.; Wen, X.; Qin, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Phosphorus removal from the hyper-eutrophic Lake Caohai (China) with large-scale water hyacinth cultivation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 12975–12984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Peng, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, G.; Xue, W.; Yan, S.; et al. Effects of engineered use of water hyacinths (Eicchornia crassipes) on the zooplankton community in Lake Taihu, China. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 38, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, G.; Xiao, B.; Song, L. Reducing the phytoplankton biomass to promote the growth of submerged macrophytes by introducing artificial aquatic plants in shallow eutrophic waters. Water 2019, 11, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, D.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, S. Fenced cultivation of water hyacinth for cyanobacterial bloom control. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 17742–17752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Han, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Corresponding Responses of Microcystis aeruginosa to Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms Stress. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 4437–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanab, S.M.; Shalaby, E.A.; Lightfoot, D.A.; El-Shemy, H.A. Allelopathic effects of water hyacinth [Eichhornia crassipes]. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.H.; Zhuang, Y.Y.; Dai, S.G.; Li, T.L. Isolation and identification of extracts of Eichhornia crassipes and their allelopathic effects on algae. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 71, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Ran, X.; Bai, F.; Xu, J.; Yang, S.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z. Use of chlorophyll a fluorescence to elucidate the toxicity target of N-phenyl-2-naphthylamine on photosynthetic system of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria). Phycologia 2015, 54, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yang, S.Q.; Yang, Y.J.; Xu, J.Z.; Shi, J.Q.; Wu, Z.X. Influence of linoleic acid on growth, oxidative stress and photosynthesis of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2016, 51, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanyuan, Y.; Ziwen, Y.; Wenhao, S.; Houming, W. Isolation and identification of antialgal compounds from root system of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). Acta Phytophysiol. Sin. 1992, 18, 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.B.; Deng, P.; Wu, X.H.; Luo, S.; Gao, Y.N. Allelopathic effects of the submerged macrophyte Potamogeton malaianus on Scenedesmus obliquus. Hydrobiologia 2007, 592, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.L.; Liu, Y.G.; Zhang, P.Y.; Zeng, G.M.; Hu, X.; Li, H.Y.; Guo, Y.M.; Guo, X.R. Co-culture with Cyperus alterrnfolius induces physiological and biochemical inhibitory effects in Microcystis aeruginosa. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 56, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhou, Q.H.; Liu, B.Y.; Cheng, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wu, Z.B. Programmed cell death in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa induced by allelopathic effect of submerged macrophyte Myriophyllum spicatum in co-culture system. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2805–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.F.; Hamilton, D.P. Recent occurrence of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Waikato Lakes of New Zealand. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2003, 37, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, M.S.; Rick, J.J.; Hasenstein, K.H. Occurrence of a Cylindrospermopsis bloom in Louisiana. J. Great Lakes Res. 2010, 36, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Song, X.; Tang, X.; Zhang, S. Effects of macroalgae Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta) and Gracilaria lemaneiformis (Rhodophyta) on growth of four species of bloom-forming dinoflagellates. Aquat. Bot. 2007, 86, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varona-Cordero, F.; Gutierrez-Mendieta, F.J.; Rivera-Monroy, V.H. In situ response of phytoplankton to nutrient additions in a tropical coastal lagoon (La Mancha, Veracruz, Mexico). Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 1353–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huo, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y. Induced allelopathic effects of Thalassiosira weissflogii on colony formation in Phaeocystis globosa. Water 2021, 13, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.H.; Zou, D.H.; Hu, S.S.; Mai, G.M.; Ma, Z.L.; Li, G. Photosynthetic characteristics of three cohabitated macroalgae in the Daya Bay, and their responses to temperature rises. Plants 2021, 10, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zou, D. Interactive effects of increasing atmospheric CO2 and copper exposure on the growth and photosynthesis in the young sporophytes of Sargassum fusiforme (Phaeophyta). Chemosphere 2021, 269, 129397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Administration, S.E.P. Methods for Monitoring and Analysis of Water and Wastewater, 4th ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 246–248, 254–257. [Google Scholar]
- Shafik, H.M.; Vörös, L.; Sprőber, P.; Présing, M.; Kovács, A.W. Some special morphological features of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in batch and continuous cultures. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506–509, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F. Study on the Effect of Nitrogen Forms and Concentration on the Growth of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii; Jinan University: Guangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- de Tezanos Pinto, P.; O’Farrell, I. Regime shifts between free-floating plants and phytoplankton: A review. Hydrobiologia 2014, 740, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, Z. Effect of two macrophyte species on phytoplankton growth and water quality in a eutrophic pond. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2016, 19, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Mei, X.Y.; Gulati, R.D.; Liu, Z.W. Effects of N and P enrichment on competition between phytoplankton and benthic algae in shallow lakes: A mesocosm study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4418–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, C.A.; Moura, A.N. Effects of the manipulation of submerged macrophytes, large zooplankton, and nutrients on a cyanobacterial bloom: A mesocosm study in a tropical shallow reservoir. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L. Effects of floating-leaved macrophytes on water quality and phytoplankton: An in situ experiment in a Chinese shallow lake. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 27519–27530. [Google Scholar]
- Mulderij, G.; Van Nes, E.H.; Van Donk, E. Macrophyte–phytoplankton interactions: The relative importance of allelopathy versus other factors. Ecol. Modell. 2007, 204, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Shiah, F.-K. Factors related to the dominance of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (cyanobacteria) in a shallow pond in northern Taiwan. J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; He, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhou, Q.H.; Wu, Z.B. Comparative biotoxicity of N-Phenyl-1-naphthylamine and N-Phenyl-2-naphthylamine on cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa. Chemosphere 2017, 176, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliwinska-Wilczewska, S.; Felpeto, A.B.; Mozdzen, K.; Vasconcelos, V.; Latala, A. Physiological effects on coexisting microalgae of the allelochemicals produced by the bloom-forming cyanobacteria Synechococcus sp. and Nodularia Spumigena. Toxins 2019, 11, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.A. Macrophytes-cyanobacteria allelopathic interactions and their implications for water resources management—A review. Limnologica 2017, 63, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.C.S.; Luerling, M.; Huszar, V.L.M. Growth and temperature-related phenotypic plasticity in the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Phycol. Res. 2013, 61, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliwinska-Wilczewska, S.; Wisniewska, K.; Konarzewska, Z.; Cieszynska, A.; Barreiro Felpeto, A.; Lewandowska, A.U.; Latala, A. The current state of knowledge on taxonomy, modulating factors, ecological roles, and mode of action of phytoplankton allelochemicals. Sci Total Env. 2021, 773, 145681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, M.A.; Jankowiak, J.G.; Kramer, B.J.; Goleski, J.A.; Huang, I.S.; Zimba, P.V.; Bittencourt-Oliveira, M.d.C.; Gobler, C.J. Succession and toxicity of Microcystis and Anabaena (Dolichospermum) blooms are controlled by nutrient-dependent allelopathic interactions. Harmful Algae 2018, 74, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Śliwińska-Wilczewska, S.; Latała, A. Allelopathic activity of the bloom-forming picocyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. on the coexisting microalgae: The role of eutrophication. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2018, 103, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Guo, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Li, G. The effects of different concentrations of algal blooms on the two submerged macrophytes. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 2765–2773. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, N.; Xu, L.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, J. Allelopathic effects of harmful algal extracts and exudates on biofilms on leaves of Vallisneria natans. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Kumar, P.; Ong, B.-L. Remediation of nutrient-rich waters using the terrestrial plant, Pandanus amaryllifolius Roxb. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Y.; Pan, X.; Cui, L.; Li, W.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wei, J. Effects of plant growth form and water substrates on the decomposition of submerged litter: Evidence of constructed wetland plants in a greenhouse experiment. Water 2017, 9, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karouach, F.; Ben Bakrim, W.; Ezzariai, A.; Sobeh, M.; Kibret, M.; Yasri, A.; Hafidi, M.; Kouisni, L. A comprehensive evaluation of the existing approaches for controlling and managing the proliferation of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes): Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 9, 767871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Time | Nutrient Supplement Amount in Each Group (mg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mo-Group | mo-P-Group | co-Group | co-P-Group | co-N, K, Ca, et-Group | |
| 0 h | P: 0.36 mg, N: 8.3 mg, K: 20 mg, Ca: 15 mg, Mg: 11 mg, Fe: 1.9 mg, B: 0.75 mg, Mn: 0.77 mg, Mo: 0.23 mg, Zn: 0.075 mg, Cu: 0.031 mg, Co: 0.015 mg | ||||
| 12 h | -- | P: 0.09 | -- | P: 0.26 | N: 0.70 |
| 24 h | -- | P: 0.50 | -- | P: 0.64 | N: 4.0, K: 2.0, Ca: 1.5, Mg: 0.74, Fe: 0.19, B: 0.075, Mn: 0.077, Mo: 0.023, Zn: 0.0075, Cu: 0.0031, Co: 0.0015 |
| 48 h | -- | P: 0.31 | -- | P: 0.93 | -- |
| 72 h | -- | P: 0.19 | -- | P: 0.57 | N: 0.70, K: 2.0, Ca: 1.5, Mg: 0.74, Fe: 0.19, B: 0.075, Mn: 0.077, Mo: 0.023, Zn: 0.0075, Cu: 0.0031, Co: 0.0015 |
| Growth Indicator | Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-Group | HRE-Group | MRE-Group | LRE-Group | |
| fresh weigh increment (g) | 3.54 ± 0.74 ab | 4.36 ± 1.11 a | 3.53 ± 1.15 ab | 2.65 ± 0.31 b |
| plant height increment (cm) | 1.05 ± 0.79 a | 0.55 ± 0.06 a | 0.63 ± 0.42 a | 0.85 ± 0.50 a |
| root length increment (cm) | 0.63 ± 0.30 a | 1.00 ± 1.04 a | 0.68 ± 1.04 a | 0.85 ± 0.83 a |
| leaf number increment | 3.00 ± 1.15 a | 2.75 ± 0.96 a | 4.50 ± 2.08 a | 3.00 ± 2.00 a |
| Parameters | Time | Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-Group | HRE-Group | MRE-Group | LRE-Group | ||
| α | Day 0 | 0.192 ± 0.014 Aa | 0.212 ± 0.028 Aa | 0.191 ± 0.038 Aa | 0.212 ± 0.014 Aa |
| Day 3 | 0.235 ± 0.012 Aa | 0.231 ± 0.018 ABa | 0.232 ± 0.009 Aa | 0.224 ± 0.017 Aa | |
| Day 6 | 0.209 ± 0.014 Aa | 0.261 ± 0.020 Bb | 0.194 ± 0.026 Aa | 0.191 ± 0.017 Aa | |
| Fv/Fm | Day 0 | 0.815 ± 0.041 Xx | 0.814 ± 0.020 Xx | 0.818 ± 0.024 Xx | 0.809 ± 0.021 Xx |
| Day 3 | 0.846 ± 0.011 Xxy | 0.827 ± 0.004 Xz | 0.852 ± 0.009 XYx | 0.836 ± 0.005 Yyz | |
| Day 6 | 0.849 ± 0.011 Xx | 0.902 ± 0.024 Yy | 0.881 ± 0.038 Yxy | 0.849 ± 0.004 Yx | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, X.; Pan, W.; Hu, Y.; Zou, Y.; Huang, X. Preliminary Study on the Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Eichhornia crassipes on Co-Cultured Raphidiopsis raciborskii. Water 2023, 15, 1690. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091690
Cheng X, Pan W, Hu Y, Zou Y, Huang X. Preliminary Study on the Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Eichhornia crassipes on Co-Cultured Raphidiopsis raciborskii. Water. 2023; 15(9):1690. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091690
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Xiaowei, Weibin Pan, Yuanyuan Hu, Yulin Zou, and Xiaojia Huang. 2023. "Preliminary Study on the Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Eichhornia crassipes on Co-Cultured Raphidiopsis raciborskii" Water 15, no. 9: 1690. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091690






