Emerging Contaminants Decontamination of WWTP Effluents by BDD Anodic Oxidation: A Way towards Its Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Operating Variables on the Electrochemical Oxidation of Neonicotinoid Pesticides in a WWTP Effluent
3.1.1. Neonicotinoids Removal as the Target Variable
3.1.2. Kinetics as the Target Variable
3.1.3. TOC Removal as the Target Variable
3.1.4. Energy Efficiency as the Target Variable
3.2. Influence of Supporting Electrolyte Type on WWTPe Treatment
3.3. Influence of the Real Aqueous Matrix
3.4. Electrochemical Oxidation of a Broad Group of Emerging Pollutants in a WWTP Effluent
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Residuos de Plaguicidas en los Alimentos; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Linhart, C.; Panzacchi, S.; Belpoggi, F.; Clausing, P.; Zaller, J.G.; Hertoge, K. Year-round pesticide contamination of public sites near intensively managed agricultural areas in South Tyrol. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R.; Schindler, M.; Elbert, A. Overview of the status and global strategy for neonicotinoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, V. Neonicotinoid poisoning and management. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 23, S260–S262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmatin, J.M.; Giorio, C.; Girolami, V.; Goulson, D.; Kreutzweiser, D.P.; Krupke, C.; Liess, M.; Long, E.; Marzaro, M.; Mitchell, E.A.; et al. Environmental fate and exposure; neonicotinoids and fipronil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 35–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Main, A.R.; Michel, N.L.; Headley, J.V.; Peru, K.M.; Morrissey, C.A. Ecological and Landscape Drivers of Neonicotinoid Insecticide Detections and Concentrations in Canada’s Prairie Wetlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8367–8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaafsma, A.; Limay-Rios, V.; Xue, Y.; Smith, J.; Baute, T. Field-scale examination of neonicotinoid insecticide persistence in soil as a result of seed treatment use in commercial maize (corn) fields in southwestern Ontario. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Ge, Y.; Zuo, P.; Shi, D.; Jia, S. Degradation of Thiamethoxam in aqueous solution by ozonation: Influencing factors, intermediates, degradation mechanism and toxicity assessment. Chemosphere 2016, 146, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cai, T.; Cheng, C.; Xiong, Z.; Ding, D. Degradation of acetamiprid in UV/H2O2 and UV/persulfate systems: A comparative study. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acero, J.L.; Real, F.J.; Javier Benitez, F.; Matamoros, E. Degradation of neonicotinoids by UV irradiation: Kinetics and effect of real water constituents. Separ. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.N.; Bote, S.D.; Gogate, P.R. Degradation of imidacloprid using combined advanced oxidation processes based on hydrodynamic cavitation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1770–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebik-Elhadi, H.; Frontistis, Z.; Ait-Amar, H.; Amrani, S.; Mantzavinos, D. Electrochemical oxidation of pesticide thiamethoxam on boron doped diamond anode: Role of operating parameters and matrix effect. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2018, 116, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, J.R.; González, T.; Correia, S. BDD electrochemical oxidation of neonicotinoid pesticides in natural surface waters. Operational, kinetic and energetic aspects. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 298, 113538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Sirés, I.; Scialdone, O. A critical review on latest innovations and future challenges of electrochemical technology for the abatement of organics in water. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 328, 122430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Ganiyu, S.O.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Mousset, E.; Olvera-Vargas, H.; Trellu, C.; Zhou, M.; Mehmet, A.O. Recent advances in electro-Fenton process and its emerging applications. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 53, 887–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Oturan, M.A. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: Advances in formation and detection of reactive species and mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 27, 100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palo, P.; Dominguez, J.R.; Sánchez-Martín, J.; González, T. Electrochemical degradation of carbamazepine in aqueous solutions-optimization of kinetic aspects by design of experiments. Clean-Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaaoui, N.; Saad, M.E.K.; Moussaoui, Y.; Allagui, M.S.; Bedoui, A.; Elaloui, E. Anodic oxidation of o-nitrophenol on BDD electrode: Variable effects and mechanisms of degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Rong, F.; Fu, D. Electrochemical degradation of ethidium bromide using boron-doped diamond electrode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 107, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzadilla, W.; Espinoza, L.C.; Diaz-Cruz, M.S.; Peña-Farfal, C.; Salazar, R. Simultaneous degradation of 30 pharmaceuticals by anodic oxidation: Main intermediaries and by-products. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Han, Q.; Li, C.; Jin, X.; Dai, Z. Influencing factors of venlafaxine degradation at boron-doped diamond anode. Arabian J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, J.R.; González, T.; Correia, S.; Domínguez, E.M. Sonochemical degradation of neonicotinoid pesticides in natural surface waters. Influence of operational and environmental conditions. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 5th ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Meijide, J.; Gómez, J.; Pazos, M.; Sanromán, M.A. Degradation of thiamethoxam by the synergetic effect between anodic oxidation and Fenton reactions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 319, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahim, M.B.; Ammar, H.B.; Abdelhédi, R. Electrochemical removal of the insecticide imidacloprid from water on a boron-doped diamond and Ta/PbO2 anodes using anodic oxidation process. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 2602–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wei, F.; Zhang, L.; Yao, Y. Electrochemical oxidation of the pesticide nitenpyram using a Gd-PbO2 anode: Operation parameter optimization and degradation mechanism. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 2120–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E.; Boye, B.; Sirés, I.; Garrido, J.A.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Arias, C.; Cabot, P.L.; Comninellis, C. Electrochemical destruction of chlorophenoxy herbicides by anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton using a boron-doped diamond electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 4487–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selcuk, H.; Sene, J.J.; Anderson, M.A. Photoelectrocatalytic humic acid degradation kinetics and effect of pH, applied potential and inorganic ions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2003, 78, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, K.; dos Santos, E.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A. Fundamentals and advances on the mechanisms of electrochemical generation of persulfate and sulfate radicals in aqueous medium. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2022, 38, 100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, N.T.; Nguyen, X.C.; Le, P.C.; Juzsakova, T.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D. Electrochemical degradation of pesticide Padan 95SP by boron-doped diamond electrodes: The role of operating parameters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velappan, K.; Sachio, Y.; Mallaiya, K.; Muthu, M. Anodic oxidation of isothiazolin-3-ones in aqueous medium by using boron-doped diamond electrode. Diam. Relat. Mat. 2016, 69, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comninellis, C.; Nerini, A. Anodic oxidation of phenol in the presence of NaCl for wastewater treatment. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1995, 25, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontistis, Z.; Antonopoulou, M.; Yazirdagi, M.; Kilinc, Z.; Konstantinou, I.; Katsaounis, A.; Mantzavinos, D. Boron-doped diamond electro-oxidation of ethyl paraben: The effect of electrolyte on by-products distribution and mechanisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 195, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streat, M.; Sweetland, L.A.; Horner, D.J. Removal of pesticides from water using hypercrosslinked polymer phases: Part 3-Mini-column studies and the effect of fulvic and humic substances. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 1998, 76, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Decisión de Ejecución (UE). 2020/1161 de la Comisión, de 4 de agosto de 2020, por la que se establece una lista de observación de sustancias a efectos de seguimiento a nivel de la Unión en el ámbito de la política de aguas, de conformidad con la Directiva. In Diario Oficial de La Unión Europea; Serie L, 257, 6 de agosto; European Commission Decisión de Ejecución (UE): Maastricht, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Murillo-Sierra, J.C.; Sirés, I.; Brillas, E. Advanced oxidation of real sulfamethoxazole + trimethoprim formulations using different anodes and electrolytes. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, L.B.; Garcia, L.F.; Caetano, M.P. Electrochemical remediation of amoxicillin: Detoxification and reduction of antimicrobial activity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 291, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

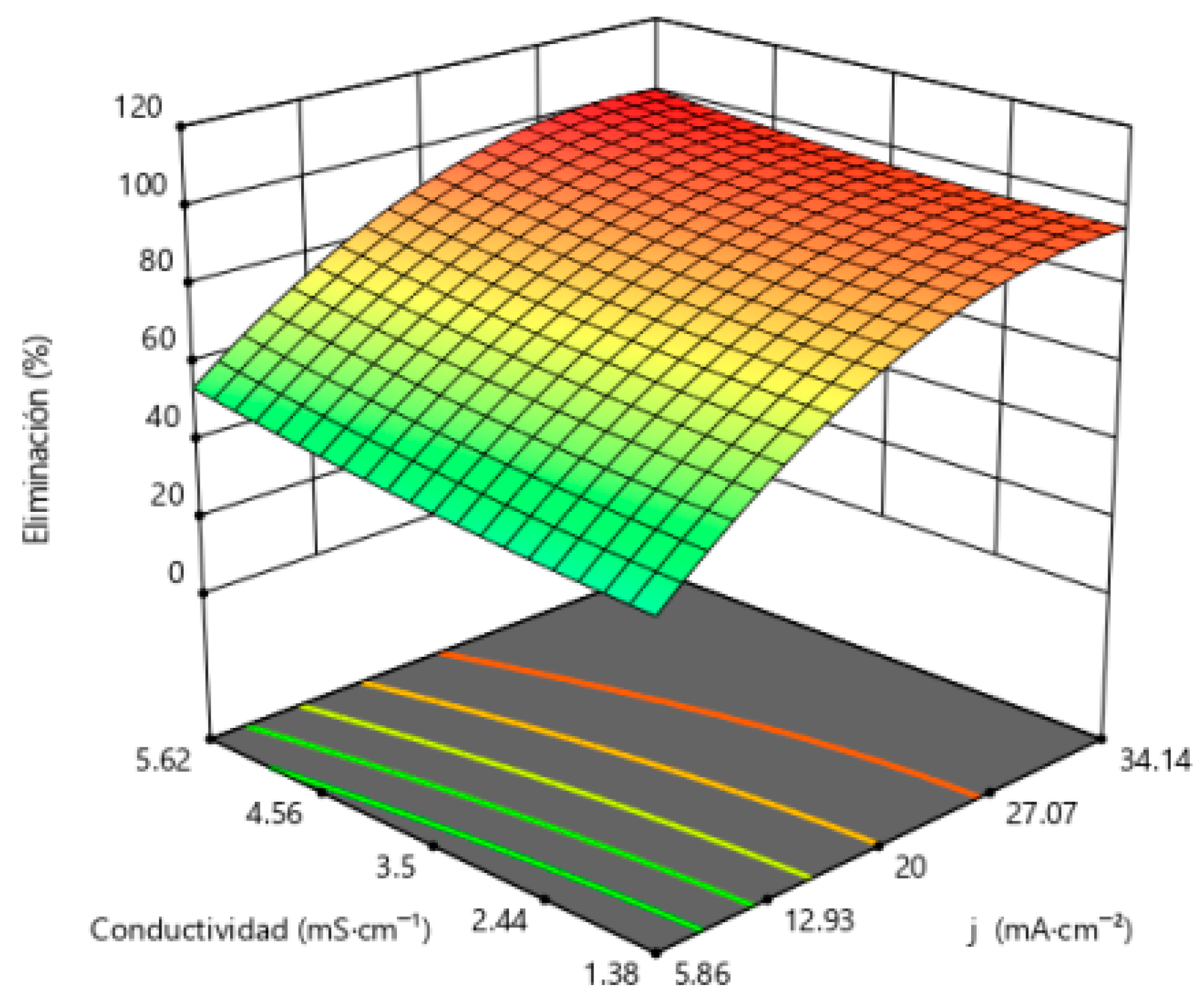
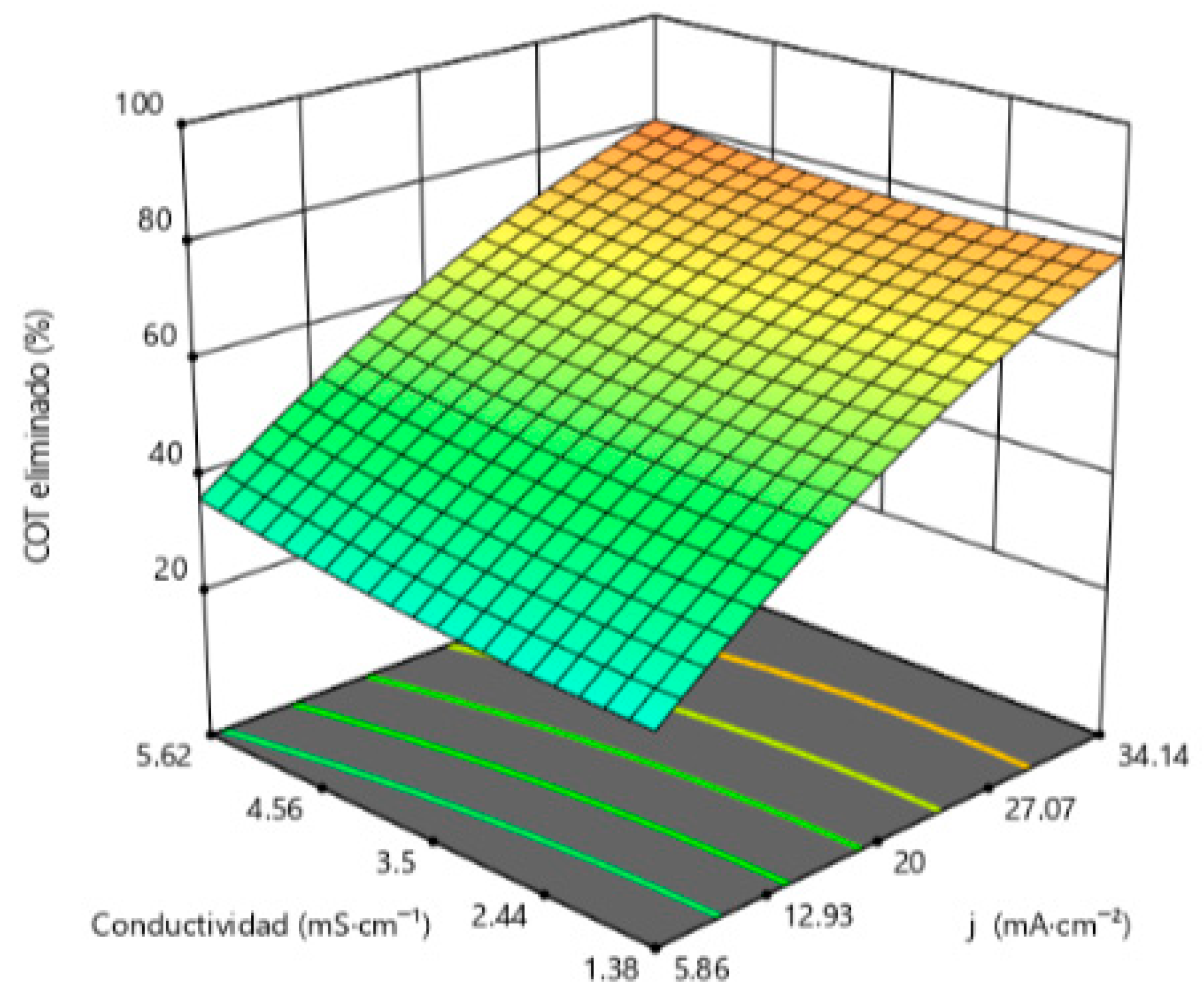
| Experiment | Coded Variables | Real Variables | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| j (mA·cm−2) | C (mS·cm−1) | |||
| EO-1 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 3.5 |
| EO-2 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 3.5 |
| EO-3 | 1.41 | 0 | 34.14 | 3.5 |
| EO-4 | 1 | −1 | 30 | 2.0 |
| EO-5 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 3.5 |
| EO-6 | 1 | 1 | 30 | 5.0 |
| EO-7 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 3.5 |
| EO-8 | −1.41 | 0 | 5.6 | 3.5 |
| EO-9 | −1 | 1 | 10 | 5.0 |
| EO-10 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 3.5 |
| EO-11 | 0 | −1.4142 | 20 | 1.4 |
| EO-12 | −1 | −1 | 10 | 2.0 |
| EO-13 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 3.5 |
| EO-14 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 3.5 |
| EO-15 | 0 | 1.4142 | 20 | 5.6 |
| EO-16 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 3.5 |
| Exp. | ETMX,60 (%) | EICP,60 (%) | EACP,60 (%) | ETCP,60 (%) | ETMX,120 (%) | EICP,120 (%) | EACP,120 (%) | ETCP,120 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EO-1 | 96.0 | 97.3 | 85.1 | 99.0 | 100 | 100 | 97.5 | 100 |
| EO-2 | 96.9 | 97.6 | 85.8 | 99.1 | 100 | 100 | 98.2 | 100 |
| EO-3 | 100 | 100 | 97.8 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| EO-4 | 98.6 | 98.6 | 93.5 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| EO-5 | 97.1 | 98.2 | 88.1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.4 | 100 |
| EO-6 | 100 | 99.6 | 96.7 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| EO-7 | 95.9 | 97.5 | 84.1 | 99.0 | 100 | 100 | 97.3 | 100 |
| EO-8 | 73.7 | 75.9 | 45.0 | 75.0 | 92.6 | 94.1 | 72.0 | 94.4 |
| EO-9 | 86.9 | 89.6 | 65.4 | 94.2 | 98.0 | 98.7 | 87.9 | 100 |
| EO-10 | 95.5 | 96.8 | 82.2 | 98.6 | 100 | 100 | 96.5 | 100 |
| EO-11 | 95.6 | 96.3 | 82.1 | 98.5 | 100 | 100 | 96.1 | 100 |
| EO-12 | 83.4 | 85.0 | 58.6 | 91.0 | 96.4 | 98.5 | 81.4 | 97.8 |
| EO-13 | 95.7 | 97.1 | 85.3 | 99.1 | 100 | 99.6 | 97.7 | 100 |
| EO-14 | 97.1 | 97.5 | 85.7 | 99.0 | 100 | 100 | 98.4 | 100 |
| EO-15 | 98.8 | 98.9 | 93.2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| EO-16 | 96.7 | 97.7 | 86.8 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 97.7 | 100 |
| Experiment | kTMX (min−1) | kICP (min−1) | kACP (min−1) | kTCP (min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EO-1 | 0.0536 | 0.0593 | 0.0310 | 0.0800 |
| EO-2 | 0.0560 | 0.0609 | 0.0330 | 0.0803 |
| EO-3 | 0.0920 | 0.1062 | 0.0625 | 0.1438 |
| EO-4 | 0.0731 | 0.0840 | 0.0457 | 0.1153 |
| EO-5 | 0.0564 | 0.0638 | 0.0345 | 0.0911 |
| EO-6 | 0.0894 | 0.0981 | 0.0523 | 0.1389 |
| EO-7 | 0.0534 | 0.0592 | 0.0308 | 0.0804 |
| EO-8 | 0.0220 | 0.0237 | 0.0104 | 0.0265 |
| EO-9 | 0.0332 | 0.0368 | 0.0176 | 0.0451 |
| EO-10 | 0.0542 | 0.0566 | 0.0285 | 0.0730 |
| EO-11 | 0.0491 | 0.0531 | 0.0277 | 0.0750 |
| EO-12 | 0.0287 | 0.0351 | 0.0143 | 0.0352 |
| EO-13 | 0.0536 | 0.0611 | 0.0314 | 0.0819 |
| EO-14 | 0.0574 | 0.0604 | 0.0336 | 0.0786 |
| EO-15 | 0.0696 | 0.0755 | 0.0433 | 0.0885 |
| EO-16 | 0.0544 | 0.0626 | 0.0325 | 0.0846 |
| Experiment | ETOC (%) | Experiment | ETOC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EO-1 | 58.37 | EO-09 | 45.39 |
| EO-2 | 59.11 | EO-10 | 58.00 |
| EO-3 | 77.09 | EO-11 | 54.85 |
| EO-4 | 74.91 | EO-12 | 42.67 |
| EO-5 | 60.00 | EO-13 | 60.80 |
| EO-6 | 75.47 | EO-14 | 58.12 |
| EO-7 | 60.26 | EO-15 | 62.55 |
| EO-8 | 27.33 | EO-16 | 58.33 |
| Experiment | SEC (kW·h·g−1) | Experiment | SEC (kW·h·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EO-1 | 0.0107 | EO-9 | 0.0052 |
| EO-2 | 0.0107 | EO-10 | 0.0108 |
| EO-3 | 0.0172 | EO-11 | 0.0144 |
| EO-4 | 0.0163 | EO-12 | 0.0064 |
| EO-5 | 0.0105 | EO-13 | 0.0103 |
| EO-6 | 0.0131 | EO-14 | 0.0107 |
| EO-7 | 0.0102 | EO-15 | 0.0090 |
| EO-8 | 0.0046 | EO-16 | 0.0107 |
| Electrolyte | ETMX,60 (%) | EICP,60 (%) | EACP,60 (%) | ETCP,60 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EO-NaCl | 83.1 | 91.1 | 64.8 | 100 |
| EO-NaNO3 | 92.0 | 91.4 | 79.7 | 90,6 |
| EO-Na2SO4 | 98.6 | 99.3 | 93.5 | 100 |
| Experiment | kTMX (min−1) | R2 | kICP (min−1) | R2 | kACP (min−1) | R2 | kTCP (min−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EO-NaCl | 0.0312 | 0.99 | 0.0395 | 1.00 | 0.0216 | 0.976 | 0.0334 | 0.99 |
| EO-NaNO3 | 0.0410 | 1.00 | 0.0402 | 1.00 | 0.0259 | 0.999 | 0.0387 | 1.00 |
| EO-Na2SO4 | 0.0731 | 1.00 | 0.0840 | 1.00 | 0.0457 | 0.999 | 0.1153 | 1.00 |
| Parameter | RW-1 (Guadiana River) | RW-2 (Reservoir Villar del Rey) | RW-3 (Almendalejo WWTP) | RW-4 (Badajoz WWTP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.95 | 8.11 | 8.72 | 7.57 |
| Conductivity (μS·cm−1) | 641 | 151 | 2332 | 538 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 0.58 | 0.44 | 0.98 | 0.61 |
| TOC (mg·L−1) | 7.04 | 8.69 | 20.04 | 9.66 |
| COD (mg O2·L−1) | 22.4 | 26.8 | 60.7 | 29.7 |
| Total phosphorus (mg P·L−1) | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.99 | 1.27 |
| Total nitrogen (mg N·L−1) | 2.3 | 1.6 | 11.6 | 12.1 |
| Nitrate (mg NO3−·L−1) | 8.5 | 1.3 | 30.5 | 23.7 |
| Nitrite (μg NO2−·L−1) | 51 | 634 | 57 | 621 |
| Ammonium (mg NH4+·L−1) | 0.23 | 0.78 | 1.17 | 3.87 |
| A254nm (cm−1) | 0.135 | 0.140 | 0.559 | 0.183 |
| Total solids (mg·L−1) | 360 | 250 | 1690 | 410 |
| Fixed solids (mg·L−1) | 285 | 175 | 1390 | 325 |
| Volatile solids (mg·L−1) | 75 | 75 | 300 | 85 |
| Exp. | ETMX,60 (%) | EICP,60 (%) | EACP,60 (%) | ETCP,60 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RW-1 | 100 | 100 | 97.4 | 100 |
| RW-2 | 97.1 | 97.6 | 88.7 | 99 |
| RW-3 | 74.9 | 86,0 | 55.4 | 100 |
| RW-4 | 98.6 | 98.6 | 93.5 | 100 |
| Experiment | kTMX (min−1) | R2 | kICP (min−1) | R2 | kACP (min−1) | R2 | kTCP (min−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RW-1 | 0.0908 | 1.00 | 0.1005 | 1.00 | 0.0600 | 1.00 | 0.1745 | 1.00 |
| RW-2 | 0.0567 | 1.00 | 0.0577 | 1.00 | 0.0353 | 1.00 | 0.0765 | 1.00 |
| RW-3 | 0.0202 | 1.00 | 0.0376 | 0.99 | 0.0126 | 0.99 | 0.3643 | 0.96 |
| RW-4 | 0.0731 | 1.00 | 0.084 | 1.00 | 0.0457 | 1.00 | 0.1153 | 1.00 |
| Experiment | EFLZ,10 (%) | EIMZ,10 (%) | ETBZ,10 (%) | EPNZ,10 (%) | EFLZ,60 (%) | EIMZ,60 (%) | ETBZ,60 (%) | EPNZ,60 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Azole pesticides | 23.9 | 96.3 | 73.8 | 77.5 | 80.6 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Experiment | EAMX5 (%) | ETMP5 (%) | EDVF5 (%) | ESMX5 (%) | EAMX10 (%) | ETMP10 (%) | EDVF10 (%) | ESMX10 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics/ Antidepressants | 98.2 | 57.8 | 100 | 98.2 | 100 | 88.8 | 100 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dominguez, J.R.; González, T.; Correia, S.E.; Núñez, M.M. Emerging Contaminants Decontamination of WWTP Effluents by BDD Anodic Oxidation: A Way towards Its Regeneration. Water 2023, 15, 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091668
Dominguez JR, González T, Correia SE, Núñez MM. Emerging Contaminants Decontamination of WWTP Effluents by BDD Anodic Oxidation: A Way towards Its Regeneration. Water. 2023; 15(9):1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091668
Chicago/Turabian StyleDominguez, Joaquin R., Teresa González, Sergio E. Correia, and Maria M. Núñez. 2023. "Emerging Contaminants Decontamination of WWTP Effluents by BDD Anodic Oxidation: A Way towards Its Regeneration" Water 15, no. 9: 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091668
APA StyleDominguez, J. R., González, T., Correia, S. E., & Núñez, M. M. (2023). Emerging Contaminants Decontamination of WWTP Effluents by BDD Anodic Oxidation: A Way towards Its Regeneration. Water, 15(9), 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091668








