Groundwater Dynamics near the Saltwater–Freshwater Interface in an Island of Seto Inland Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
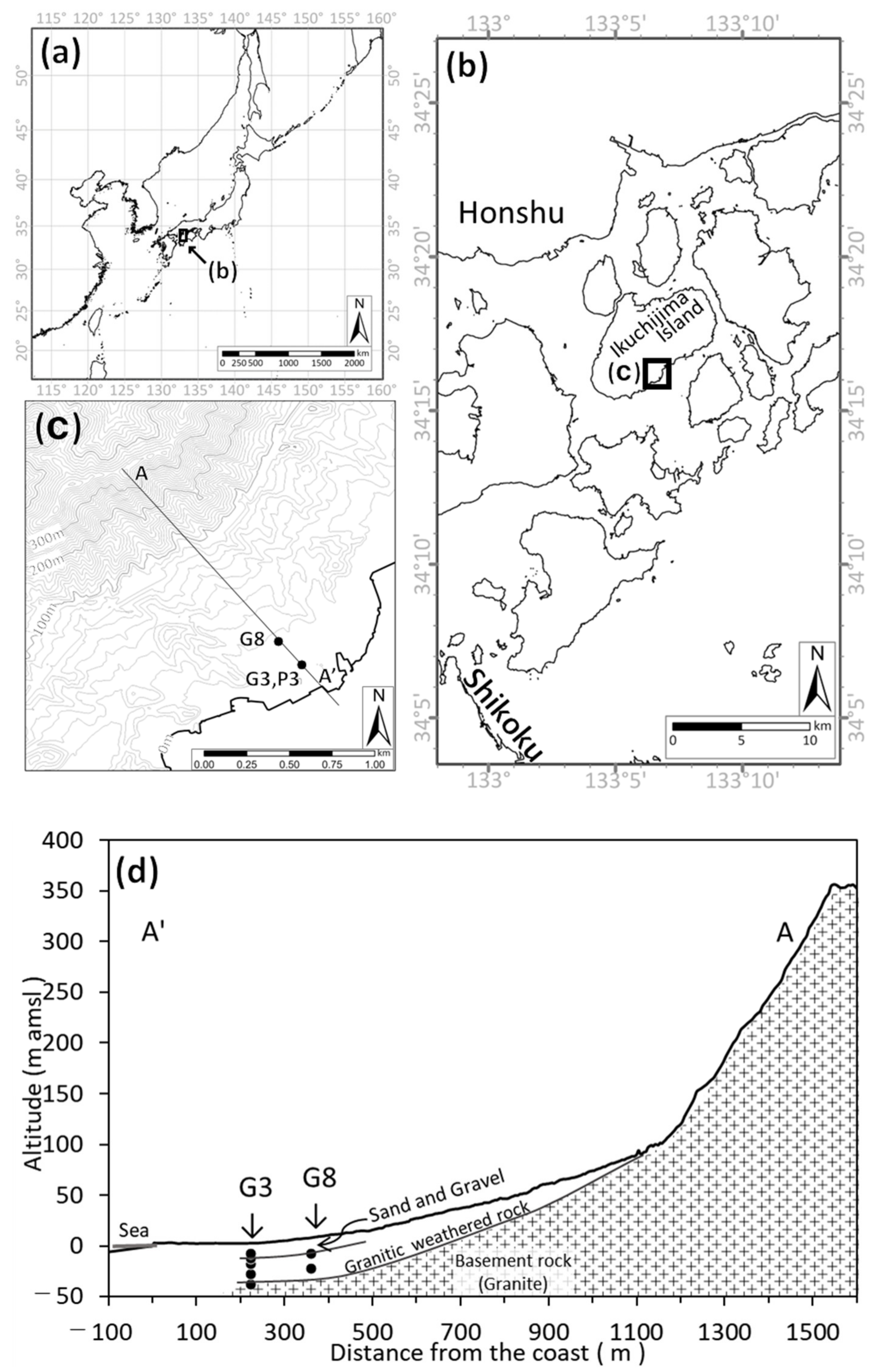
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Method
3. Results and Discussion
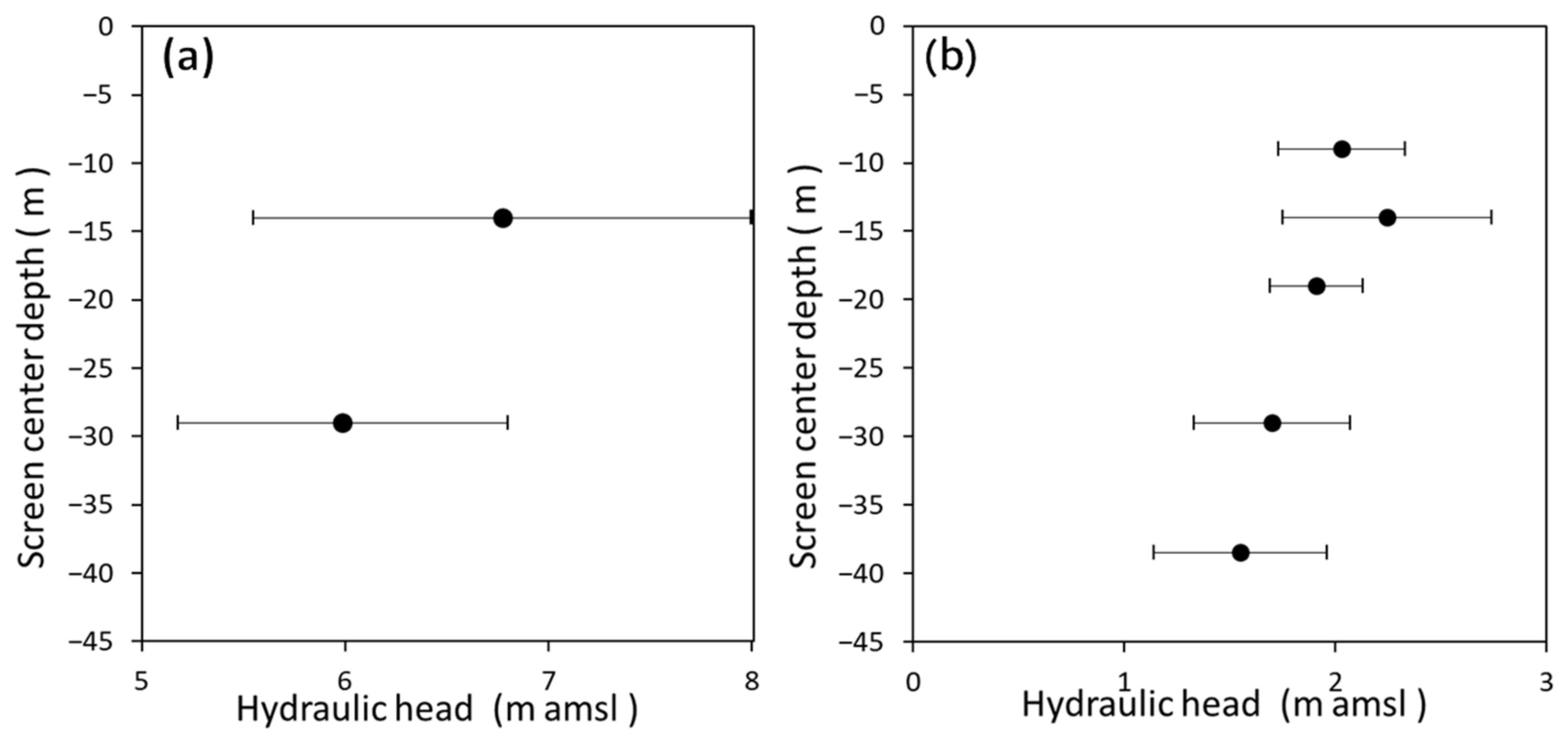
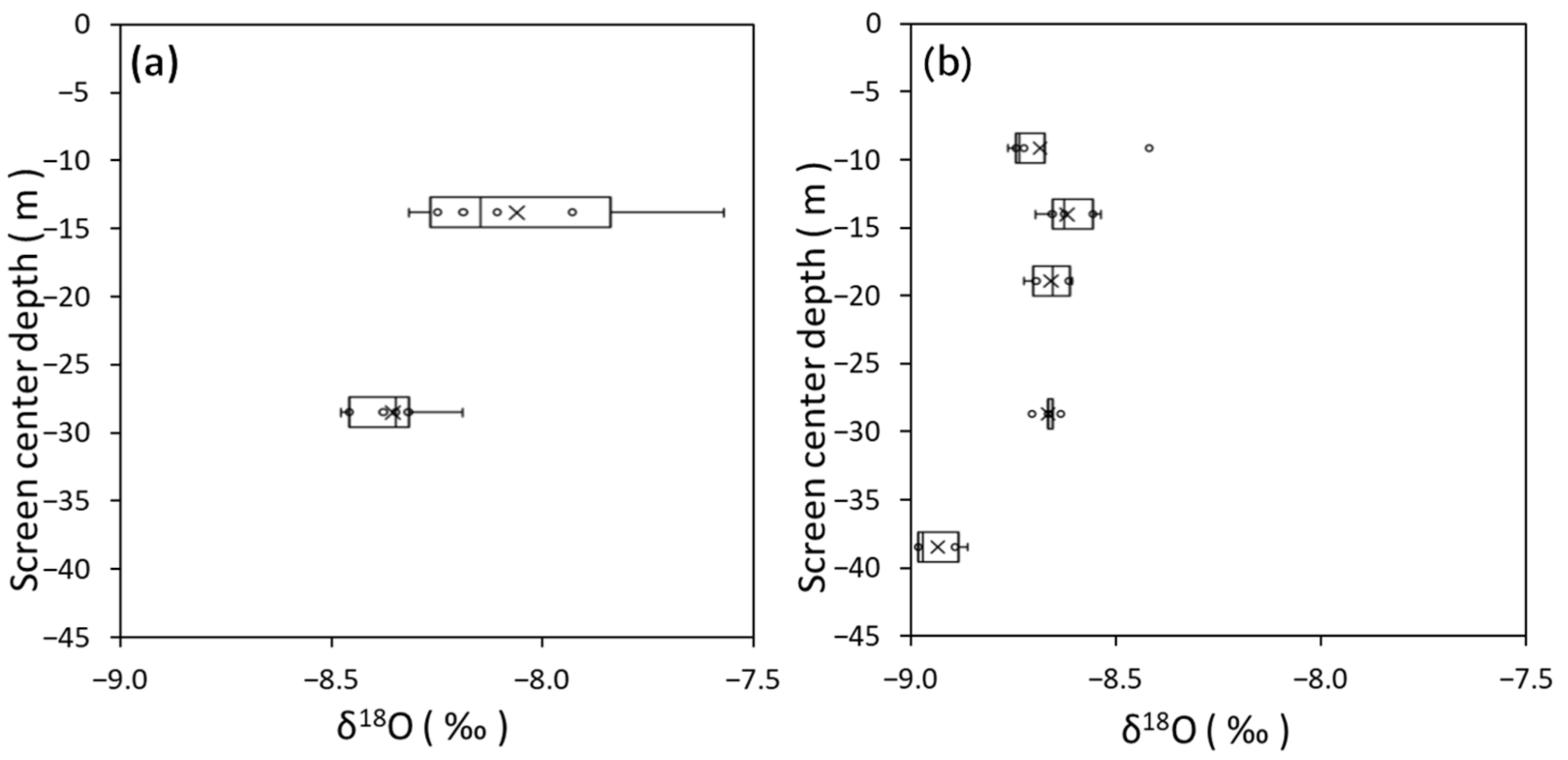
3.1. Groundwater Flow System Estimated from Hydraulic Head, δ18O, and δD
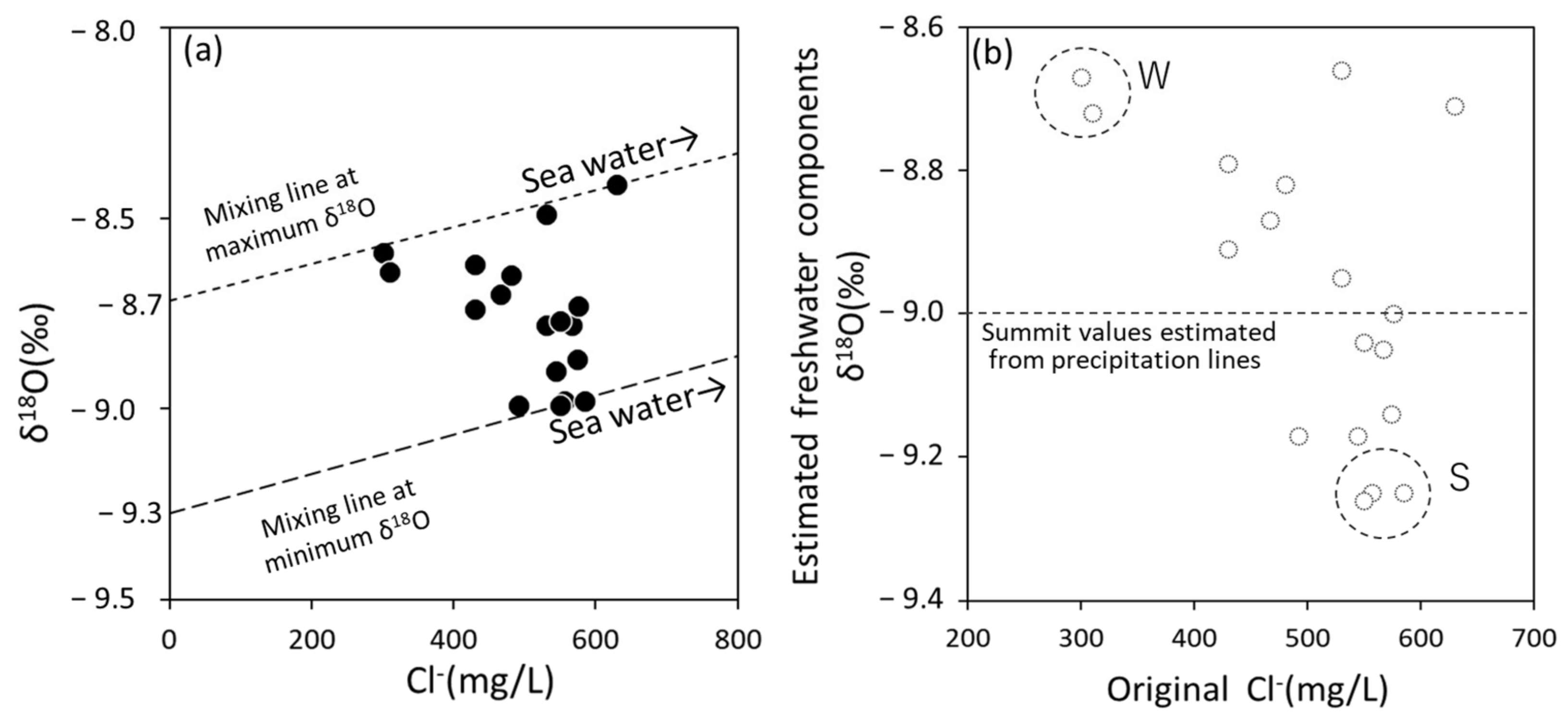
3.2. Features of Coastal Bedrock Groundwater Based on Cl− Concentration and δ18O
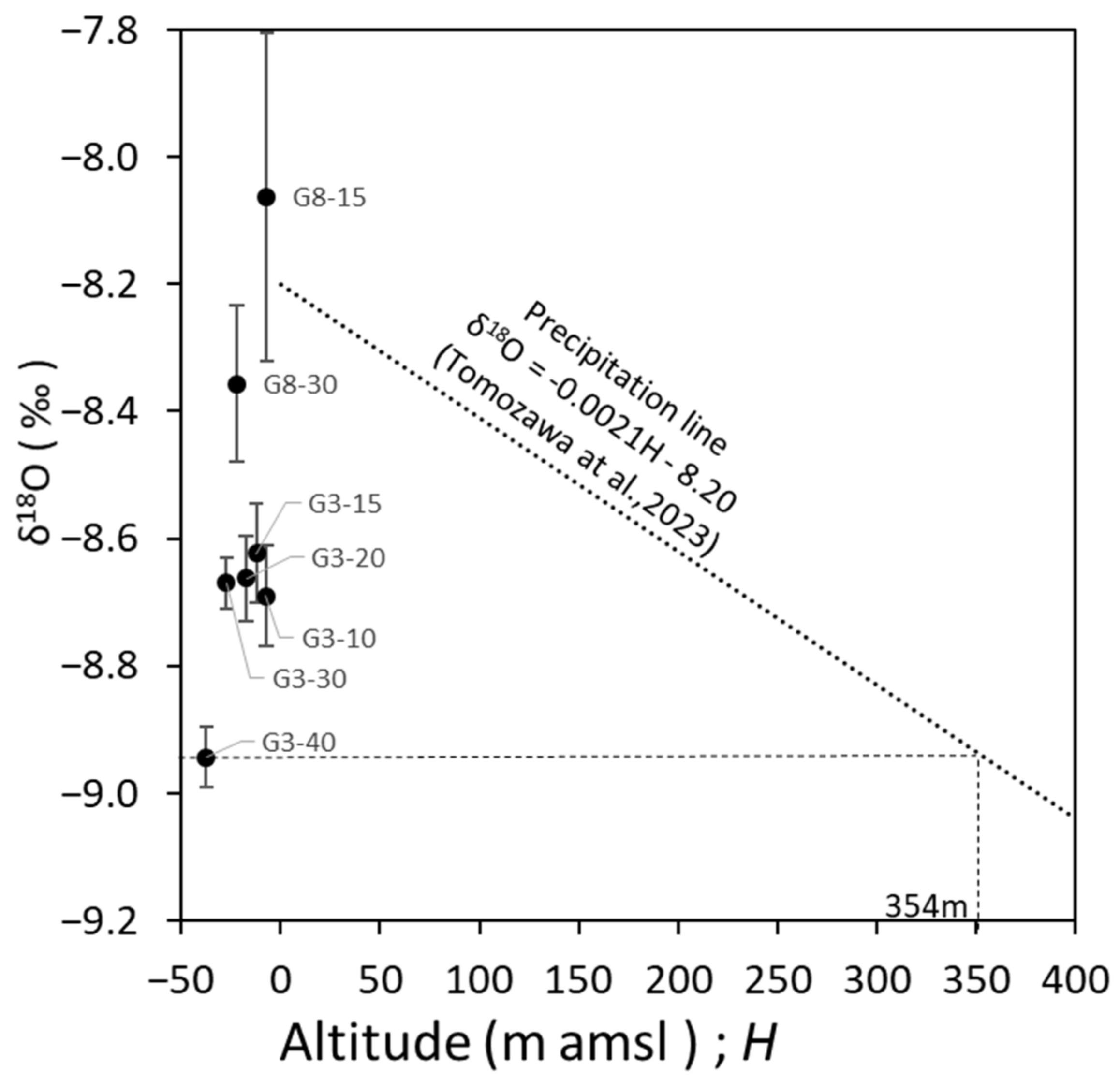
3.3. Origin Estimation of Fresh Groundwater with Low δ18O Based on the Groundwater Age Tracer
3.4. Groundwater Dynamics near the Saltwater–Freshwater Interface
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Onodera, S.; Saito, M.; Kitaoka, K. Water Environment in Seto Inland Sea Catchments: Sato Water; Kibito Publishing: Okayama, Japan, 2018; p. 266. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Holding, S.; Allen, D.M.; Foster, S.; Hsieh, A.; Larocque, I.; Klassen, J.; Van Pelt, S.C. Groundwater vulnerability on small islands. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioka, S.; Onodera, S.; Saito, M.; Rusydi, A.; Bakti, H.; Wakasa, S.A. Species and potential sources of phosphorus in groundwater in and around Mataram City, Lombok Island, Indonesia. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbi, S.; Onodera, S.; Nozaki, S.; Tomozawa, Y.; Wang, K.; Rusydi, A.F.; Saito, M. Impact of citrus agriculture on the quality of water resource in a small steep Island, Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Int. J. Geomate 2021, 20, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbi, S.; Onodera, S.; Ishida, T.; Saito, M.; Tamura, M.; Tomozawa, Y.; Nagasaka, I. Nitrate contamination in groundwater: Evaluating the effects of demographic aging and depopulation in an island with intensive citrus cultivation. Water 2022, 14, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO-IHP; UNEP. Transboundary Aquifers and Groundwater Systems of Small Island Developing States: Status and Trends; United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP): Nairobi, Kenya, 2016; p. 172. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations-Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/post2015/transformingourworld (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Ferguson, G.; Gleeson, T. Vulnerability of coastal aquifers to groundwater use and climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Shimizu, Y.; Onodera, S.; Saito, M.; Matsumori, K. Evaluation of drought impact on groundwater recharge rate using SWAT and Hydrus models on an agricultural island in western Japan. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. (PIAHS) 2015, 371, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onodera, S.; Saito, M.; Sawano, M.; Hosono, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Shimada, J.; Umezawa, Y.; Lubis, R.F.; Buapeng, S.; Delinom, R. Effects of intensive urbanization on the intrusion of shallow groundwater into deep groundwater: Examples from Bangkok and Jakarta. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3209–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onodera, S. Subsurface pollution in Asian megacities. In Groundwater and Subsurface Environments; Taniguchi, M., Ed.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2011; pp. 159–184. [Google Scholar]
- Rusydi, A.F.; Onodera, S.; Saito, M.; Hyodo, F.; Maeda, M.; Sugianti, K.; Wibawa, S. Potential Sources of Ammonium-Nitrogen in the Coastal Groundwater Determined from a Combined Analysis of Nitrogen Isotope, Biological and Geological Parameters, and Land Use. Water 2021, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusydi, A.F.; Onodera, S.; Saito, M.; Ioka, S.; Maria, R.; Ridwansyah, I.; Delinom, R. Vulnerability of groundwater to iron and manganese contamination in the coastal alluvial plain of a developing Indonesian city. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Hiyama, T. Groundwater as a Key for Adaptation to Changing Climate and Society; Speringer: Tokyo, Japan, 2014; p. 145. [Google Scholar]
- Tomozawa, Y.; Onodera, S.; Saito, M. Estimation of groundwater recharge and salinization in a coastal alluvial plain and Osaka megacity, Japan, using δ18O, δD, and Cl−. Int. J. Geomate 2019, 16, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, T.; Shimada, J.; Tsujimura, M.; Lorphensri, O.; Mikita, M.; Hagihara, A.; Onodera, S. Tracing a confined groundwater flow system under the pressure of excessive groundwater use in the lower central plain, Thailand. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 2654–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, S.; Onodera, S.; Tomozawa, Y.; Saito, M. Spatial distributions in groundwater discharge on various tidal flats in a small and steep island, western Japan. Int. J. Geomate 2021, 20, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, S.; Saito, M.; Hayashi, M.; Sawano, M. Nutrient dynamics with groundwater -seawater interactions in a beach slope of a steep island, western Japan. IAHS Publ. 2007, 312, 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, C.; Li, L.; Barry, D.A. Effect of tidal forcing on a subterranean estuary. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, P.; Robinson, C.; Li, L.; Barry, D.A.; Bakhtyar, R. Effects of wave forcing on a subterranean estuary. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W12505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Saito, M.; Onodera, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Jin, G.; Ohta, T.; Chen, J. Evaluation of the spatial distribution of submarine groundwater discharge in a small island scale using the 222 Rn tracer method and comparative modeling. Mar. Chem. 2019, 209, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Currell, M.J. Delineating multiple salinization processes in a coastal plain aquifer, northern China: Hydrochemical and isotopic evidence. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 3473–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jasechko, S. Global isotope hydrogeology—Review. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 835–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, J. Groundwater Flow System in the Bedrock Aquifer of a Mountainous Body. J. Jpn. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2001, 31, 37–47, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carol, E.; Perdomo, S.; Álvarez, M.d.P.; Tanjal, C.; Bouza, P. Hydrochemical, isotopic, and geophysical studies applied to the evaluation of groundwater salinization processes in quaternary beach ridges in a semiarid coastal area of northern Patagonia, Argentina. Water 2021, 13, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, K.; Satake, H.; Tsujimura, M. Isotopic approach to understanding the groundwater flow system within an andesitic stratovolcano in a temperate humid region: Case study of Ontake volcano, central Japan. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, J.; Inoue, D.; Satoh, S.; Takamoto, N.; Sueda, T.; Hase, Y.; Iwagami, S.; Tsujimura, M.; Ishitobi, T.; Taniguchi, M. Basin-wide groundwater flow study in a volcanic low permeability bedrock aquifer with coastal submarine groundwater discharge. IAHS Publ. 2007, 312, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kusano, Y.; Tokunaga, T.; Asai, K.; Asai, K.; Takahashi, H.A.; Morikawa, N.; Yasuhara, M. Occurrence of old groundwater in a volcanic island on a continental shelf; an example from Nakano-shima Island, Oki-Dozen, Japan. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.A. Application of multi-Isotopes and geochemical modeling for delineating recharge and salinization sources in Dahab Basin Aquifers (South Sinai, Egypt). Hydrology 2018, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Onodera, S.; Takei, T. Nitrate transport process in a small coastal alluvial fan catchment. Jpn. J. Limnol. 2005, 66, 1–10, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, M.; Onodera, S. Characteristics of seasonal NO3−-N discharge by groundwater in a coastal agricultural catchment. Jpn. J. Limnol. 2009, 70, 141–151, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerstel, E.R.T.; van Trigt, R.; Dam, N.; Reuss, J.; Meijer, H.A.J. Simultaneous determination of the 2H/1H, 17O/16O, and 18O/16O isotope abundance ratios in water by means of laser spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 5297–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamanaka, T.; Onda, Y. On Measurement Accuracy of Liquid Water Isotope Analyzer Based on Wavelength-Scanned Cavity Ring-Down Spectroscopy (WS-CRDS). Bull. Terr. Environ. Res. Cent. Univ. Tsukuba 2011, 12, 31–40. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, M. Hydrogen and oxygen isotope analyses of water samples based on the Cavity Ring-Down Spectroscopy “Water isotope analyzer”. J. Jpn. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2018, 48, 17–21. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picarro, Inc. L2130-I Analyzer Datasheet. Available online: https://www.picarro.com/support/library/documents/l2130i_analyzer_datasheet# (accessed on 26 January 2023).
- IAEA. Use of Chlorofluorocarbons in Hydrology: A Guidebook; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Asai, K.; Tsujimurai, M.; Asai, K. Excess air of groundwater in Chubu region estimated from dissolved nitrogen and argon concentrations. J. Groundw. Hydrol. 2021, 63, 267–277, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabusaki, S.; Tase, N.; Shimada, J. Vertical Profile of Stable Isotopes in Soil Water Through the Volcanic Ash Soil Layer in Japan. Bull. Geo-Environ. Sci. 2021, 13, 43–57, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tomozawa, Y.; Onodera, S.; Saito, M. Seasonal Variation of in Water Stable Isotope Ratios of Water in of Precipitation and Groundwater in a Seto Inland Sea Islands. J. Jpn. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. in press. (In Japanese with English abstract). 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kazahaya, K.; Yasuhara, M. Symposium “Springs and Groundwater in Yatsugatake Volcano”. A Hydrogen Isotopic Study of Spring Waters in Mt. Yatsugatake, Japan: Application to Groundwater Recharge and Flow Processes. J. Jpn. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 1994, 24, 107–119. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Kazahaya, K. Recharge area and flow path of groundwater: Isotope Hydrology Techniques. Chishitsu News 1997, 513, 20–25. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Badon-Ghyben, W. Nota in Verband Met de Voorgenomen Putboring Nabil Amsterdam; K. Instituut van Ingenieurs: Hague, The Netherlands.
- Herzberg, A. Die Wasserversorgung einiger Nordseebader. J. Gasbeleucht. Wasserversorg 1901, 44, 815–819. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, I.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; p. 342. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, M.; Hirakawa, T.; Matsuda, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kitaoka, K.; Kusakabe, M. The origin of thermal water from deep zones in granite rocks inferred from stable isotopic ratios of hydrogen and oxygen. J. Jpn. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2006, 36, 205–218, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, T.; Masuda, H.; Nemoto, T.; Ikawa, R.; Marui, A.; Tanimizu, M.; Ishikawa, T. Three-dimensional structure and sources of groundwater masses beneath the Osaka Plain, Southwest Japan. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 43, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Massoudieh, A.; Green, C.T.; Lee, K.K.; Kaown, D. Complexity of groundwater age mixing near a seawater intrusion zone based on multiple tracers and Bayesian inference. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Point Name | Analytical Result | Equivalent Atmospheric Concentration | Apparent Age |
|---|---|---|---|
| SF6 (f mol/kg) | SF6 (pptv) | SF6 (Year) | |
| G8-15 | 3.06 | 7.27 | 12 |
| G8-30 | 3.64 | 8.65 | 8 |
| G3-15 | 2.26 | 5.39 | 19 |
| G3-30 | 2.24 | 5.34 | 19 |
| G3-40 | 1.84 | 4.42 | 23 |
| When Cl− Concentration Is Maximum | When Cl− Concentration Is Minimum | When SF6 Is Measured | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mixing rate of G3-30 *1 | 72% | 100% | 99% |
| Mixing rate of Stagnant groudwater *2*3 | 28% | 0% | 1% |
| Estimated from SF6 | Estimated from 14C *1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Mixing rate of G3-30 | 82% | 76% *2 |
| Mixing rate of Stagnant groudwater | 18% | 24% *3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomozawa, Y.; Onodera, S.-i.; Saito, M.; Asai, K. Groundwater Dynamics near the Saltwater–Freshwater Interface in an Island of Seto Inland Sea. Water 2023, 15, 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071416
Tomozawa Y, Onodera S-i, Saito M, Asai K. Groundwater Dynamics near the Saltwater–Freshwater Interface in an Island of Seto Inland Sea. Water. 2023; 15(7):1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071416
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomozawa, Yusuke, Shin-ichi Onodera, Mitsuyo Saito, and Kazuyoshi Asai. 2023. "Groundwater Dynamics near the Saltwater–Freshwater Interface in an Island of Seto Inland Sea" Water 15, no. 7: 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071416
APA StyleTomozawa, Y., Onodera, S.-i., Saito, M., & Asai, K. (2023). Groundwater Dynamics near the Saltwater–Freshwater Interface in an Island of Seto Inland Sea. Water, 15(7), 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071416






