Effects of Groundwater Level Control on Soil Salinity Change in Farmland around Wetlands in Arid Areas: A Case Study of the Lower Reaches of the Shiyang River Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
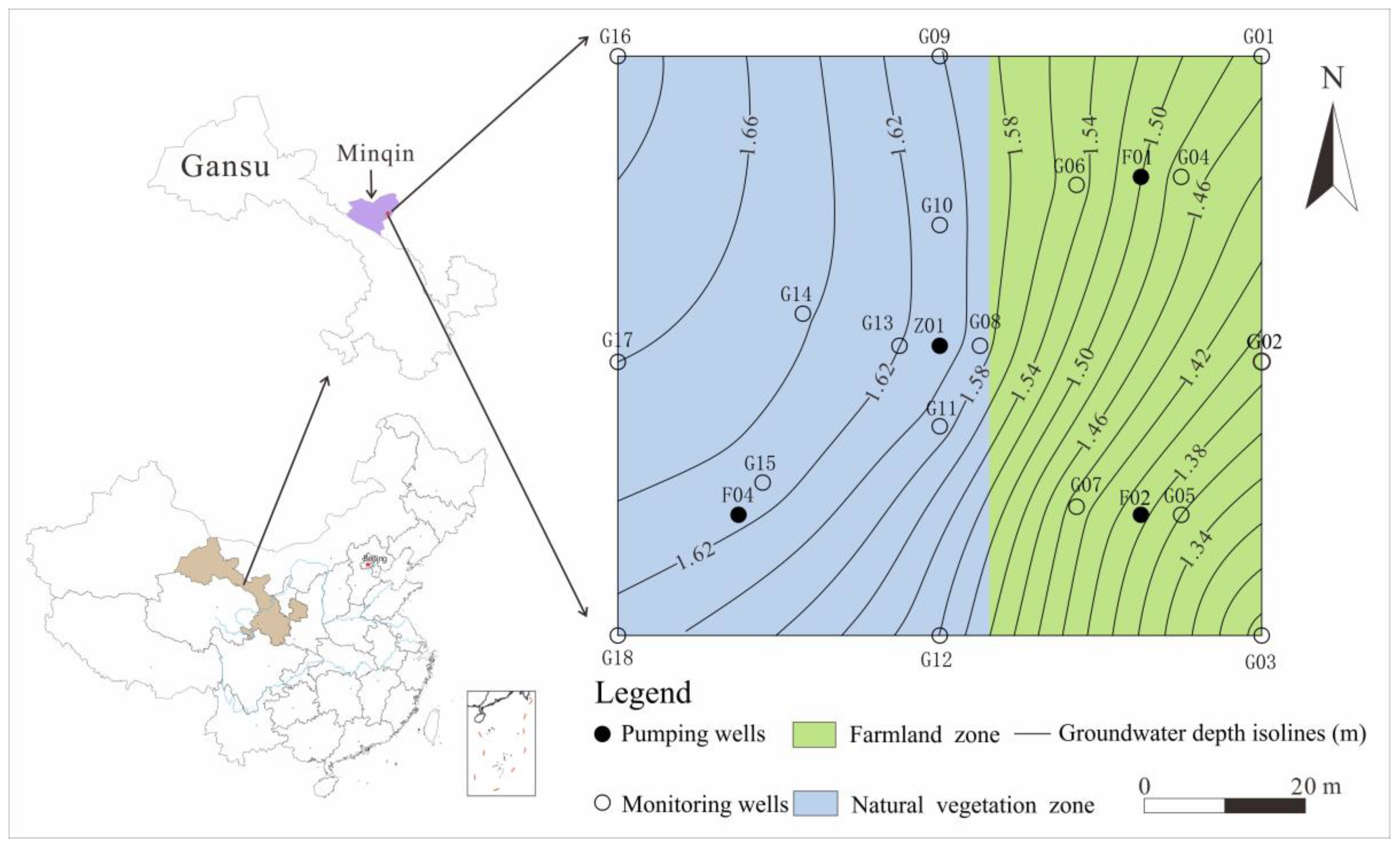
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
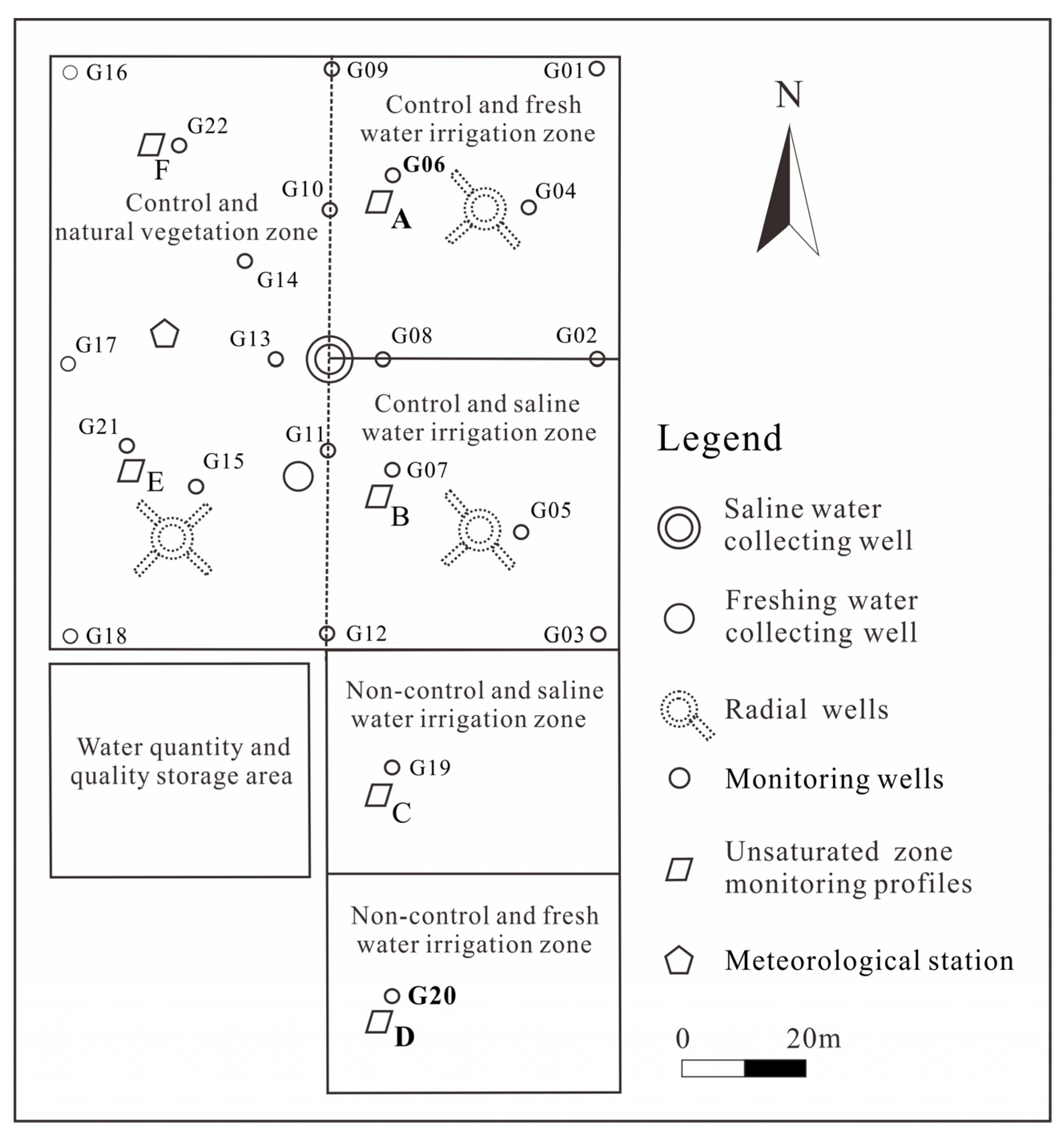
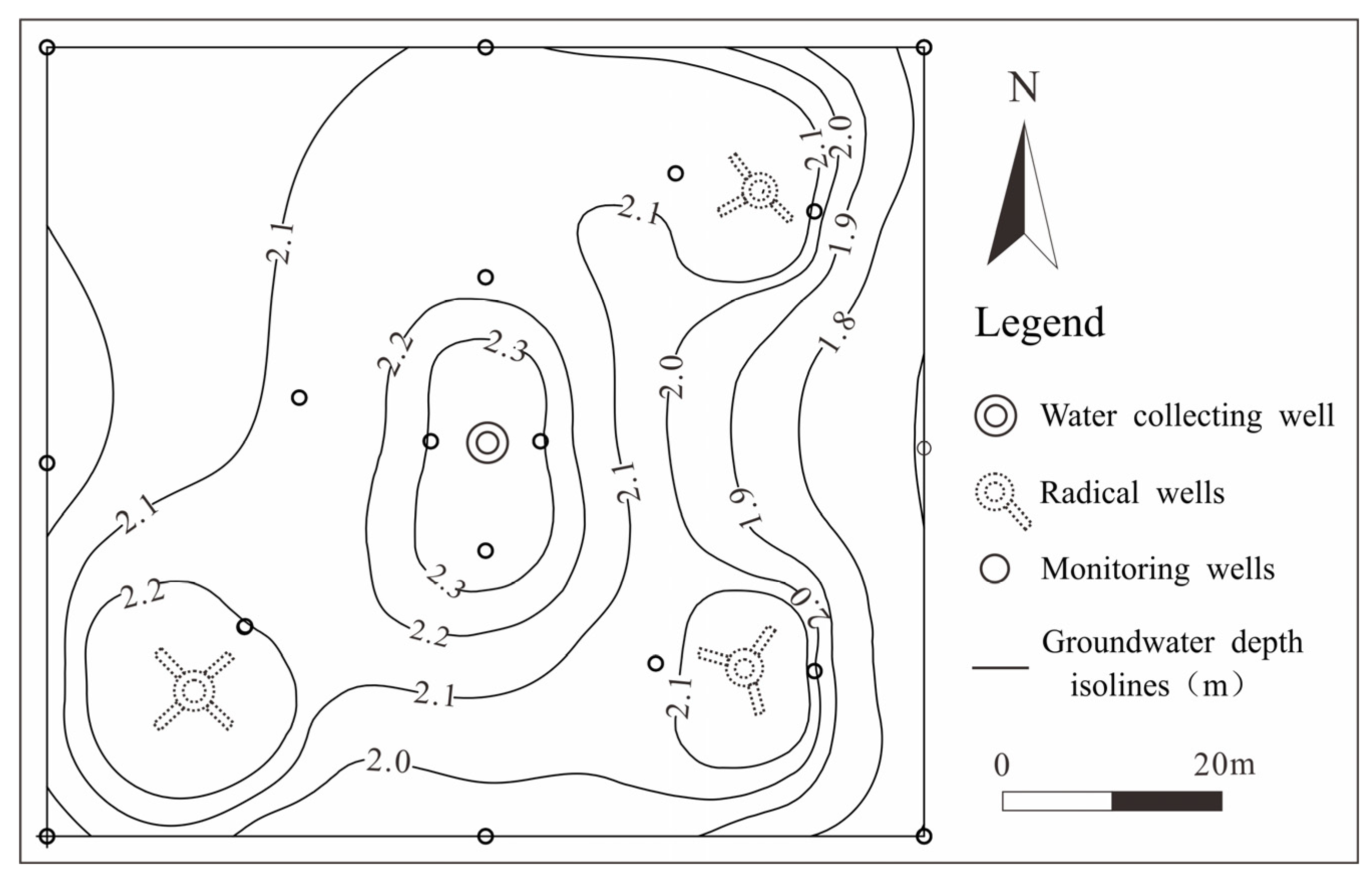
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Data Acquisition
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results
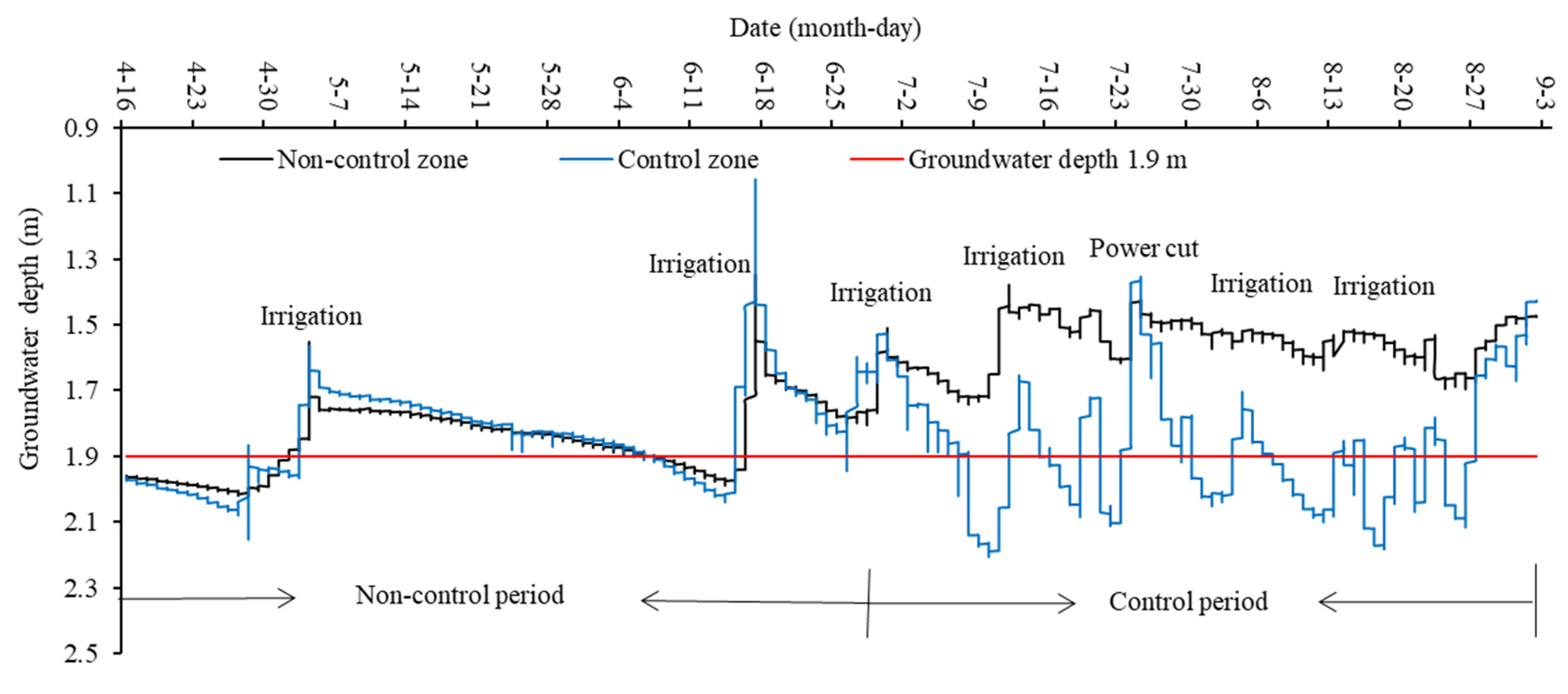
3.1. Changes in Groundwater Depth
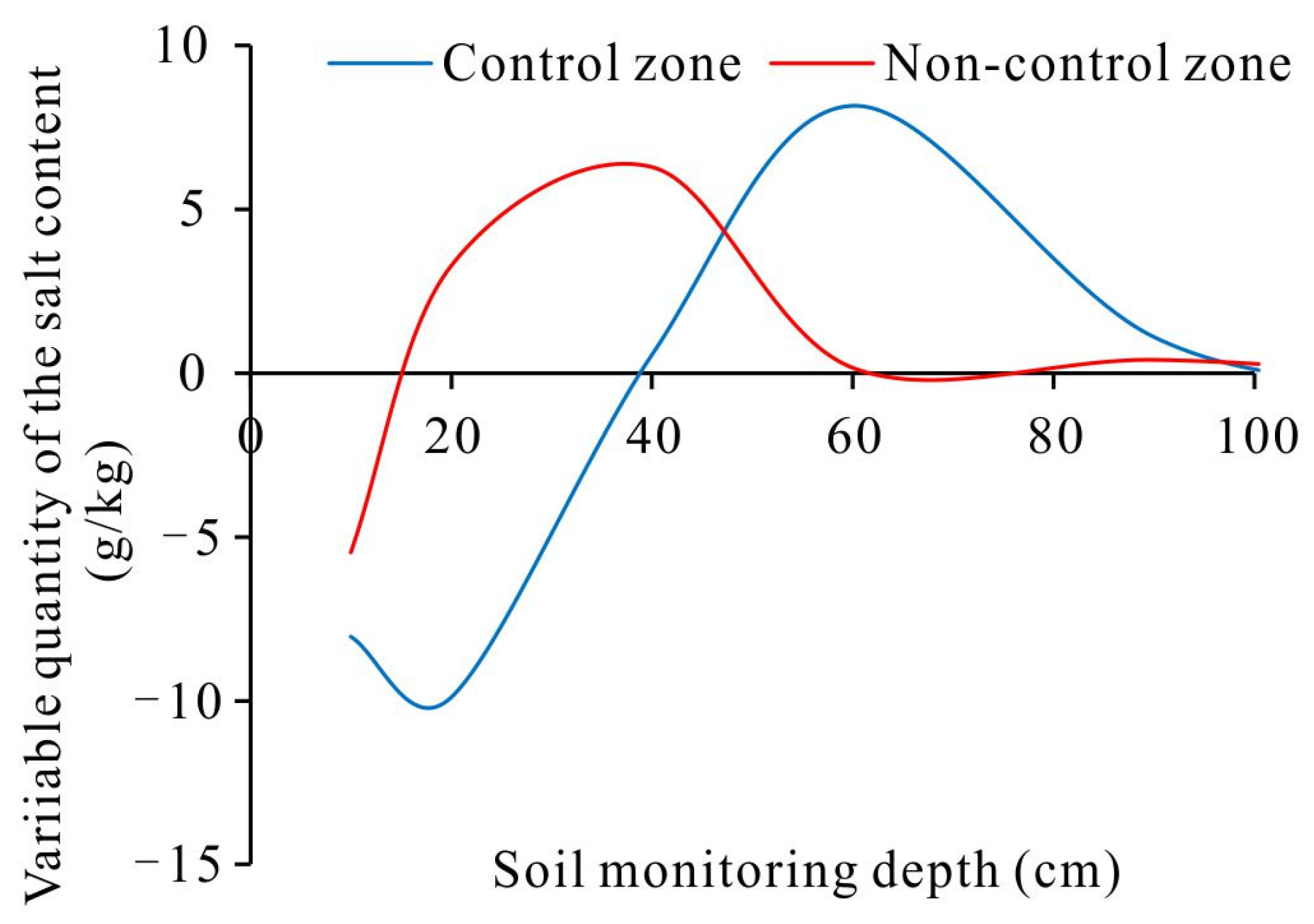
3.2. Changes in Soil Bulk Salt Content before and after the Control Period
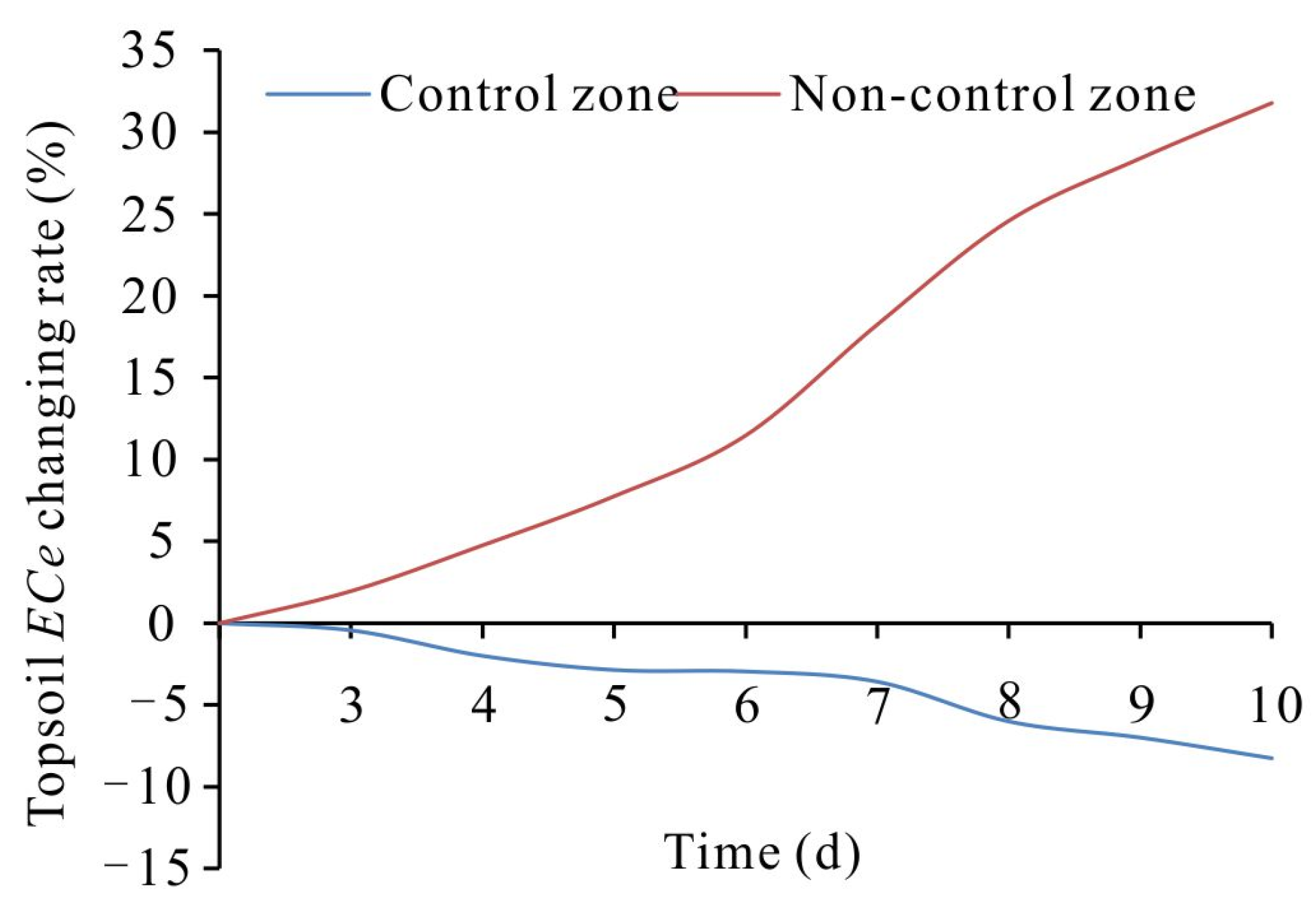
3.3. Changes in the Pore Water Electrical Conductivity of the Topsoil during the Groundwater Control Period
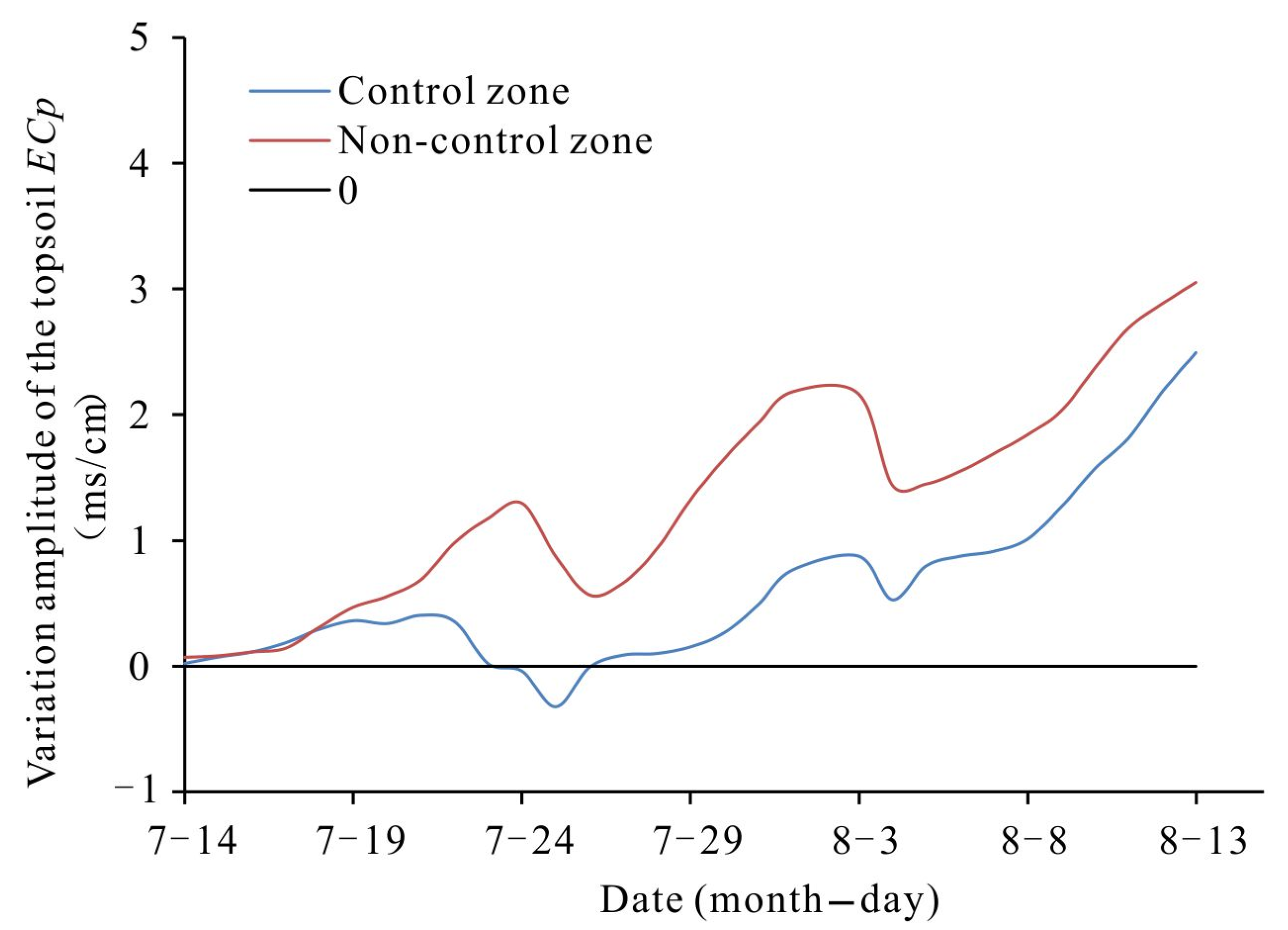
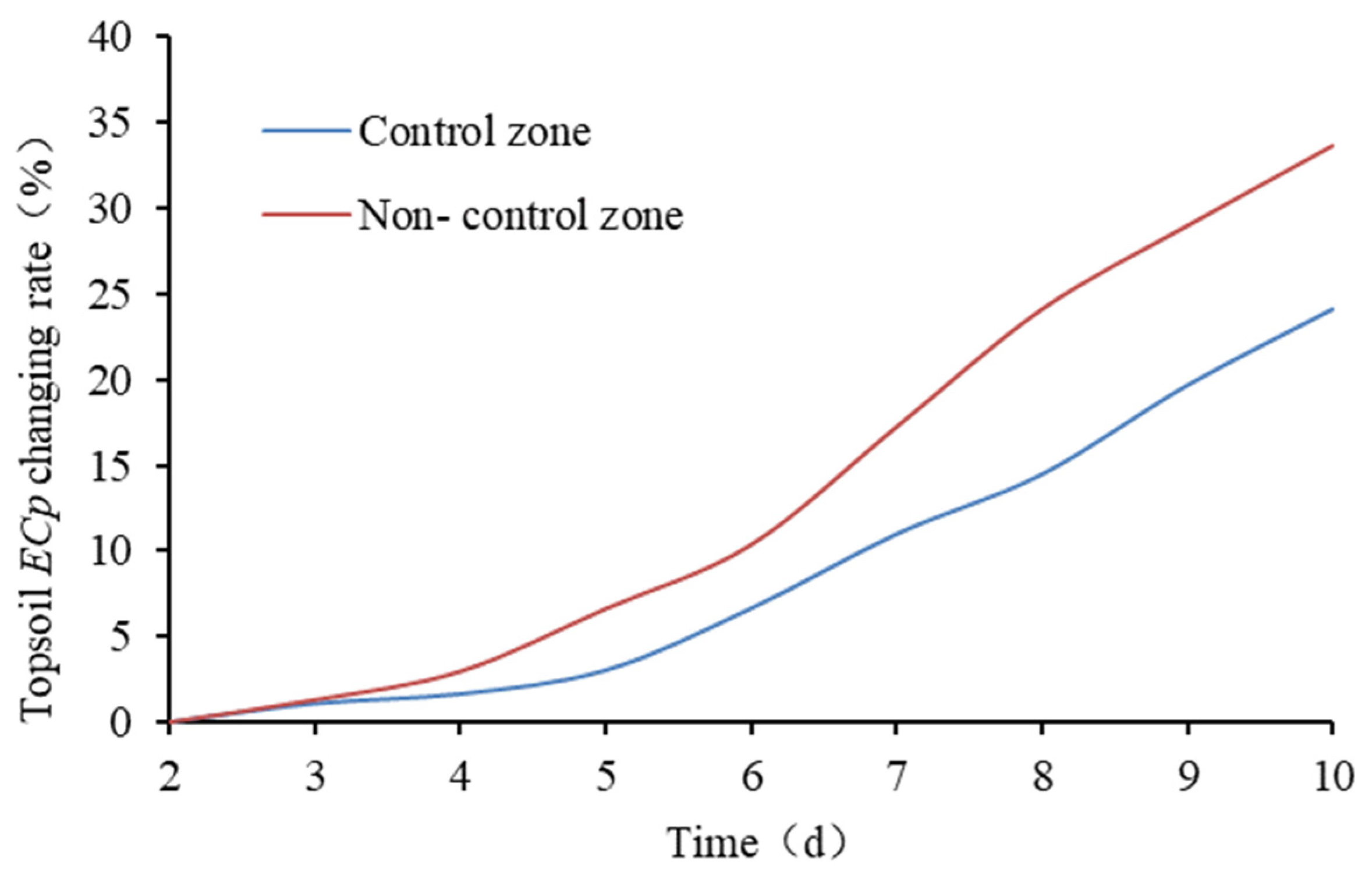
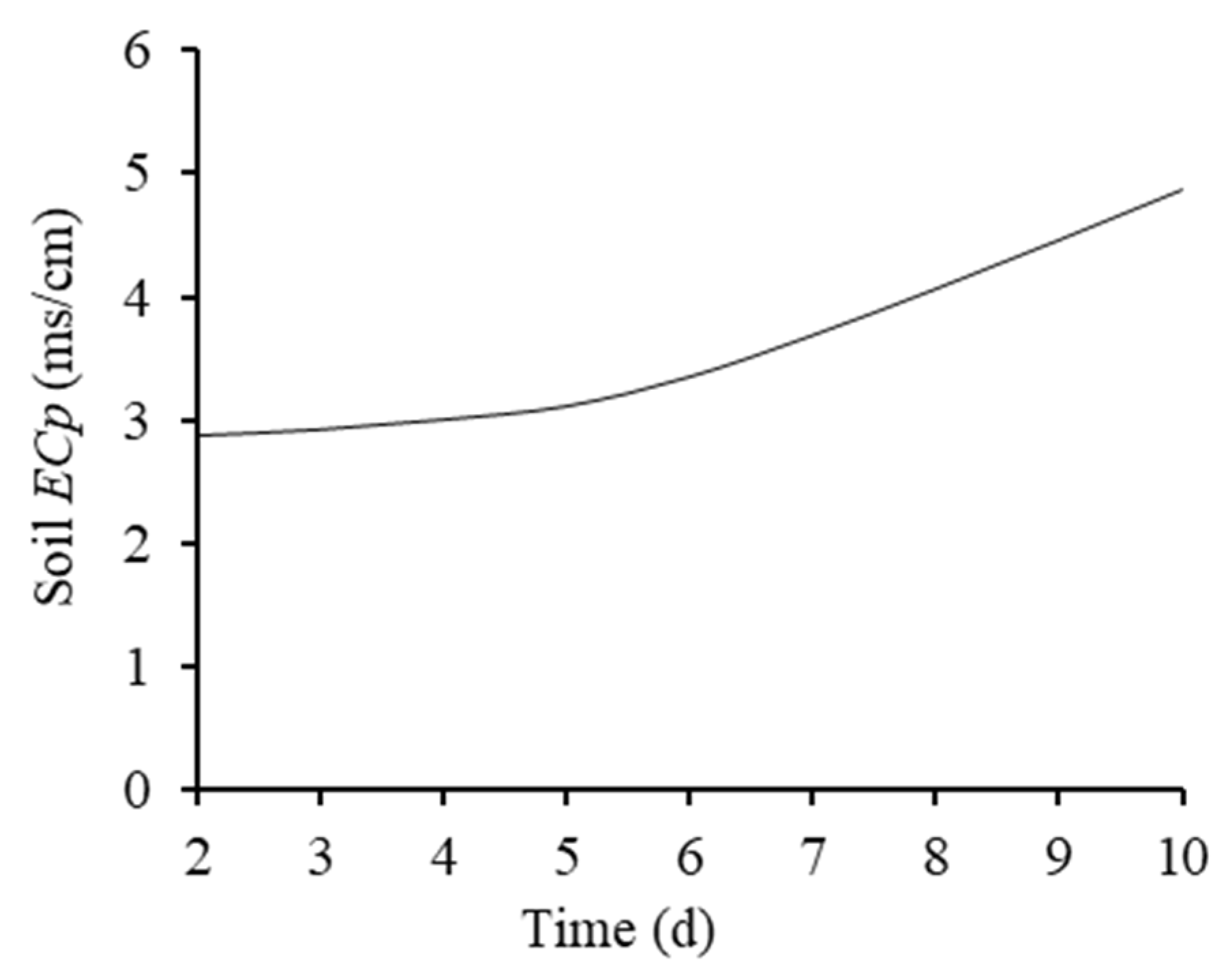
3.4. Changes in the ECp of the Topsoil in the Concentration Stage
3.4.1. Change Characteristics of the ECp of the Topsoil
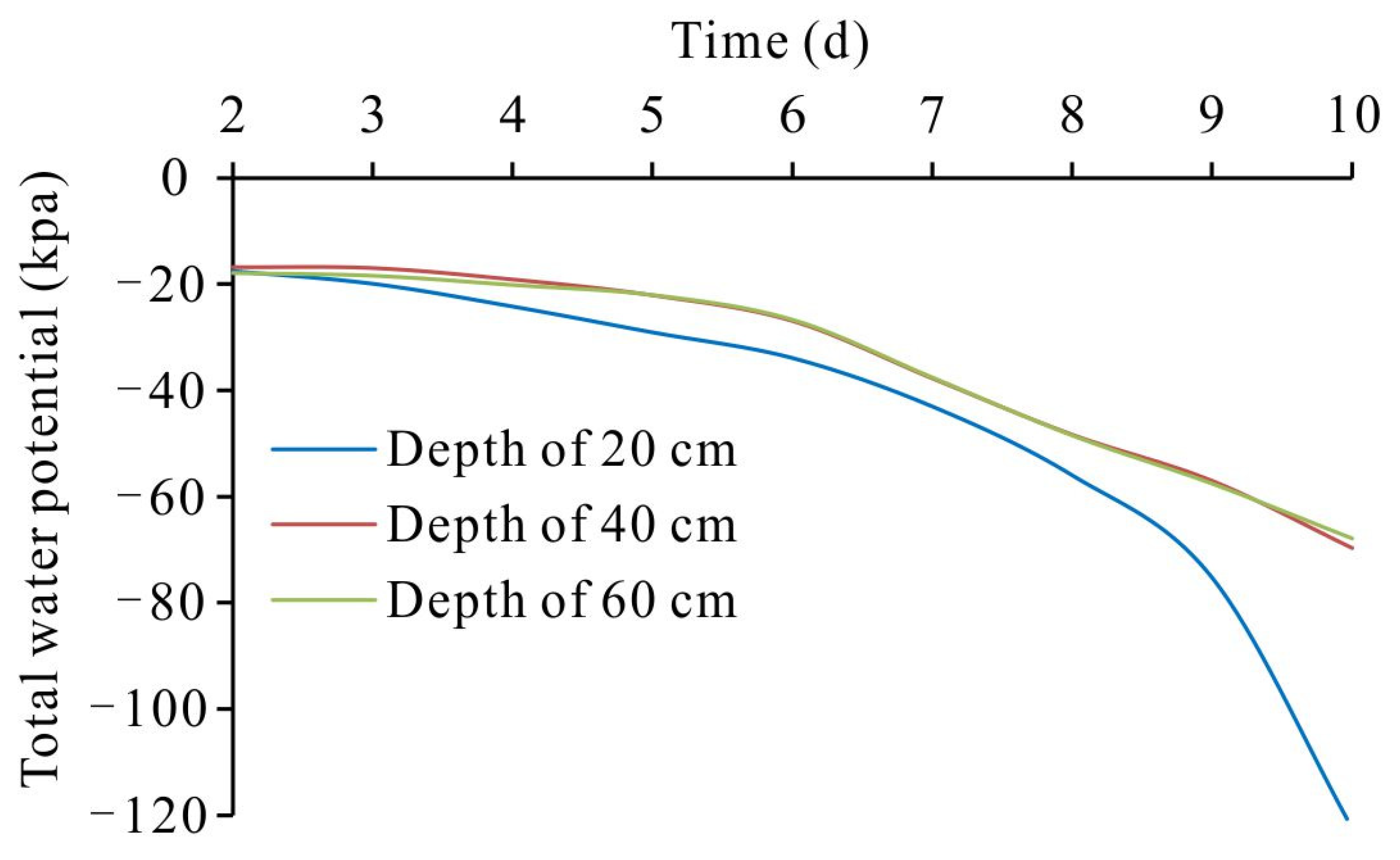
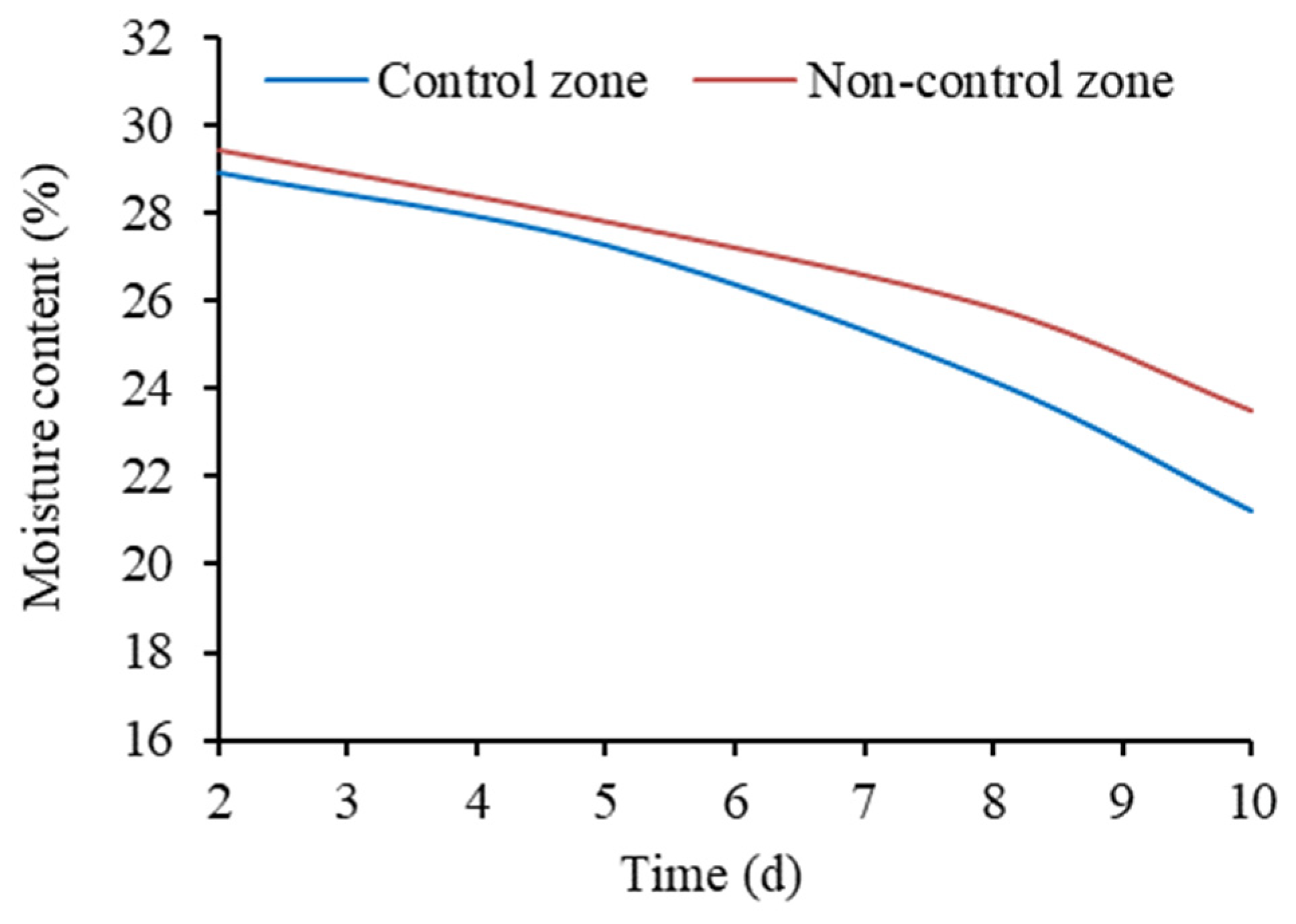
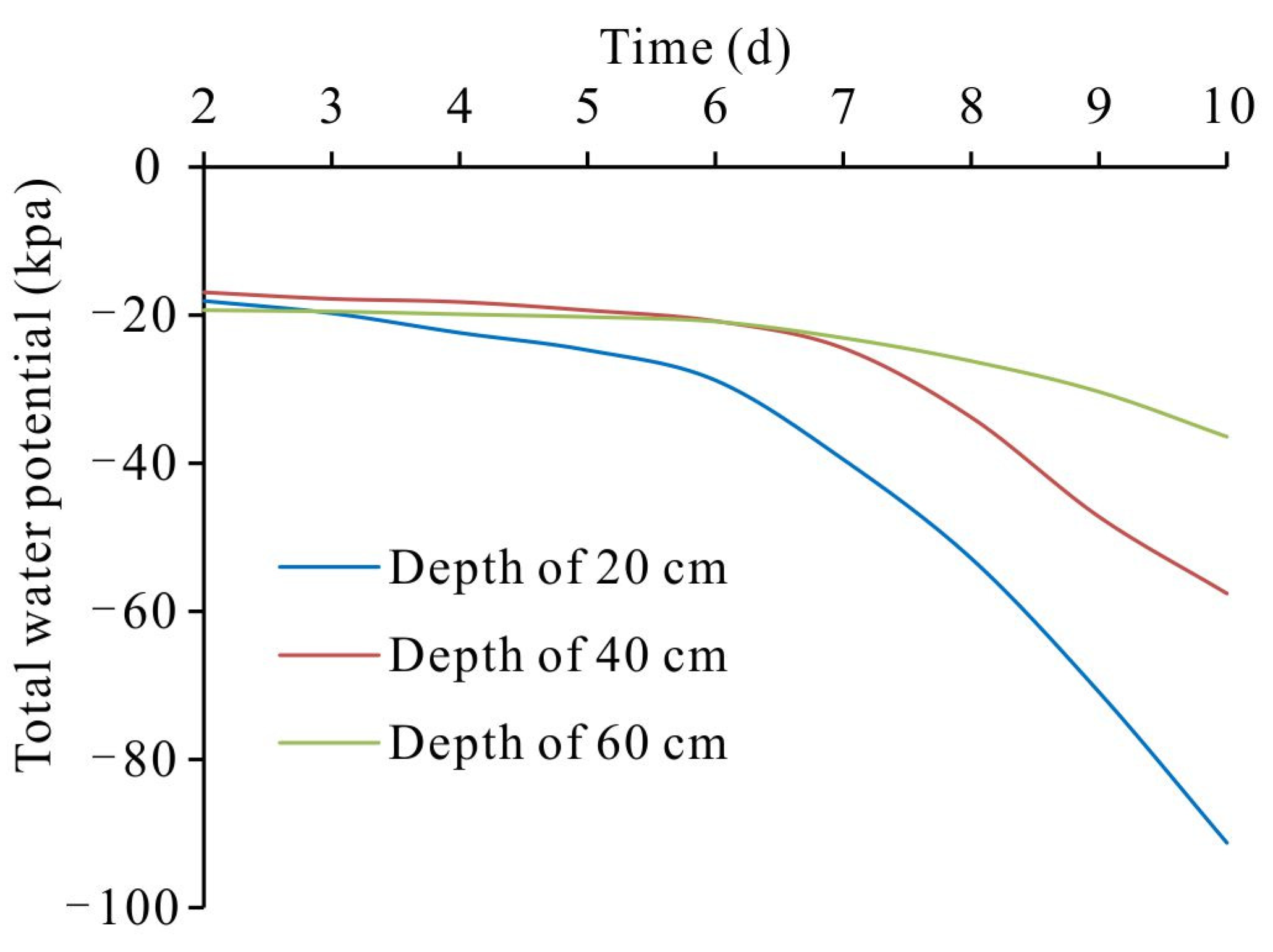
3.4.2. Analysis of Moisture and Salt Equilibrium in Topsoil Solution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Under the continuous action of groundwater control system in summer with high temperature in arid regions, the groundwater depth increases in the control zone and the depth of the salt accumulation layer moves down, creating a suitable topsoil salt environment for crop growth.
- (2)
- On an irrigation cycle scale, the groundwater control system contributes to the significant decrease in the increased amplitude of the topsoil ECp in the concentration stage of the topsoil solution, especially 3–8 days after irrigation.
- (3)
- The groundwater control system mitigates the concentration rate of the topsoil solution by increasing the groundwater depth, reducing salt transport amount from the groundwater to the topsoil and influencing the water and salt equilibrium of the topsoil solution. In the concentration stage of the soil solution, in the control zone both the moisture content and salt content of the topsoil solution are in negative equilibrium and in the non-control zone the moisture content and salt content of the topsoil solution are in negative and positive equilibrium, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Zou, J. Effects of different fallow and wetting methods on soil and vegetation properties in the middle reaches of the Heihe River: A case study of Zhangye National Wetland Park. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 3333–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yu, A.; Wang, D. Ecological risk assessment due to land use/cover changes (LUCC) in Jinghe County, Xinjiang, China from 1990 to 2014 based on landscape patterns and spatial statistics. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, M.; Bao, A.; Hu, R.; Zhao, S. Time-series analysis of Sayram Lake area changes during 1989–2014. Arid Land Geogr. 2016, 39, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Lang, X. Influence of multi-layered structure of vadose zone on ecological effect of groundwater in Arid Area: A case study of Shiyang River Basin, Northwest China. Water 2022, 14, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ge, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Feng, S. Study on relationship between soil salinization and groundwater table depth based on indicator Kriging. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Nie, Z.; Cao, L.; Wang, L.; Lu, H.; Zhu, P. Comprehensive evaluation on the ecological function of groundwater in the Shiyang River watershed. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Nie, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q. The ecological relationship of groundwater–soil–vegetation in the oasis–desert transition zone of the Shiyang River Basin. Water 2021, 13, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, S.; Zhu, J.; Liu, D.; Liao, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, Q. Influences of Phragmites australis density and groundwater level on soil water in semiarid wetland, North China: Which is more influential? Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2022, 22, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Regulations of salt and water of saline-alkali soil: A review. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2018, 26, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, H.; Gong, P.; Li, P.; Li, L.; Xu, Q.; Xue, B.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, R. Model-based optimization of design parameters of subsurface drain in cotton field under mulch drip irrigation. Water 2022, 14, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Dong, Y.; Qi, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhu, Y. Advances in ecological groundwater level threshold in Arid Oasis Regions. J. China Hydrol. 2021, 41, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ning, L.; Lu, T. Determination and the control of critical groundwater table in soil salinization area. J. Irrig. Drain. 2015, 34, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Huo, Z. Optimizing irrigation and drainage by considering agricultural hydrological process in arid farmland with shallow groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C. Simulation soil water–salt dynamics in saline wasteland of Yongji Irrigation Area in Hetao Irrigation District of China. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2020, 21, 2681–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, L.; Deng, W.; Zhai, J.; Chen, M.; Zhou, F. Groundwater regulation for coordinated mitigation of salinization and desertification in arid areas. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 271, 107758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Guo, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, G.; Fu, X.; Li, Z. Effects of irrigation amounts and groundwater regulation on soil water and salt distribution in arid region. Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Bian, J.; Zhou, Y. Estimating the spatial distribution of soil salinity with geographically weighted regression kriging and its relationship to groundwater in the western Jilin irrigation area, Northeast China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Wei, Z.; Miao, H. Quantitative Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Variations of Soil Salinization and Groundwater Depth along the Yellow River Saline–Alkali Land. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, G.; Tian, F.; Hu, H. Effect of water table depth on soil water and salt dynamics and soil salt accumulation characteristics under mulched drip irrigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Meng, Y.; Cao, N.; Li, D.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, B.; Dou, F. The effects of soil moisture and salinity as functions of groundwater depth on wheat growth and yield in coastal saline soils. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 2472–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Shi, H.; Miao, Q.; Tian, F.; Yu, D.; Zhou, L.; Liang, Z. Temporal and spatial variability analysis of soil water and salt and the influence of groundwater depth on salt in saline irrigation area. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 33, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Xiao, C.; Wang, G.; Liang, X. Study on ecological threshold of groundwater in typical salinization area of Qian’an County. Water 2021, 13, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Yan, L.; Yang, G.; Ma, J.; Deng, W. Quantifying threshold water tables for ecological restoration in Arid Northwestern China. Groundwater 2020, 58, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H. Changes in soil salinity and upland crop productivity in reclaimed land as affected by groundwater table. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2020, 53, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, S.; Luo, Y.; Tian, C.; Yin, C. Relationship between salt accumulation in topsoil of deserted land and groundwater in areas with shallow groundwater table in Kashi, Xinjiang. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2014, 51, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, H.; Hu, Z.; Wang, J. Impact of groundwater level on salt dynamics and crop growth in coastal saline soil. J. Qingdao Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2018, 35, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burian, S.J. Systems thinking for planning sustainable desert agriculture systems with saline groundwater irrigation: A review. Water 2022, 14, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.J.; Shin, M.N.; Son, J.K.; Song, J.D.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, S.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Cho, J.Y. Evaluation of soil pore-water salinity using a Decagon GS3 sensor in saline-alkali reclaimed tidal lands. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 132, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, G.; Cui, S.; Liu, S.; Nie, Z. Threshold value of ecological water table and dual control technology of the water table and its quantity in the salinized farmland around wetland in arid areas. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2022, 49, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilhorst, M.A. A Pore Water Conductivity Sensor. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1922–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, G.; Ding, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, Z. Digital mapping of soil salinization in arid area wetland based on variable optimized selection and machine learning. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ding, N.; Fu, Q.; Ding, B.; Wang, J. The measurement of electric conductivity in soil solution and analysis of its correlative factors. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2005, 17, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Jia, Z.; Luo, W. Definition, calculation and application of total water potential. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2008, 24, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, C. Evolution and prospects in modeling of water and salt transport in soils. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2016, 36, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, M.; Ling, G.; Hu, X.; Peng, X. Influence of bulk density and water content on soil electrical conductivity. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2022, 40, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Mao, X.; Shang, S. Response and contribution of shallow groundwater to soil water/salt budget and crop growth in layered soils. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 266, 107574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J. Analysis on the salt content characteristics of southern saline-alkali soil in Datong Basin and its causes. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yang, J.; Qu, Z.; Mao, W.; Wu, J. Spatiotemporal patterns and key driving factors of soil salinity in dry and wet years in an arid agricultural area with shallow groundwater table. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhang, R.; Xu, M.; Zhang, S.; Li, B. Seasonal changes and influencing factors of soil electrical conductivity in soil profile of Weibei region. J. Northwest AF Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 46, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Fu, X.; Xu, N.; Yang, X. Spatiotemporal changes and influencing factors of soil salinity in Hetao Irrigation District. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng. 2018, 36, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmamatjan, O.; Tashpolat, T.; Abdulla, A.; Deng, Y.; Mamat, S.; Zhang, F. The effects of spatial and temporal distribution of groundwater on the soil salinity in Keriya Oasis in Xinjiang. Water Sav. Irrig. 2016, 5, 23–27. Available online: https://elib.cugb.edu.cn. (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- Li, X.; Xia, J.; Zhao, X.; Yang, J. Water and salt distribution characteristics of shallow soil at different diving water levels. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 15, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Yu, H.; Jia, Y.; Xu, X.; Guo, L. Application of an in situ electrical resistivity device to monitor water and salt transport in Shandong coastal saline soil. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2015, 40, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Bian, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, P.; Meng, X. An experimental study on water infiltration capacity and water-salt dynamic transport of saline soil. Res. Explor. Lab. 2021, 40, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Depth/cm | Control Zone | Non-Control Zone | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Days after Irrigation | 10 Days after Irrigation | Variable Quantity | 2 Days after Irrigation | 10 Days after Irrigation | Variable Quantity | |
| 20 | 28.32 | 21.32 | −7.00 | 29.50 | 22.90 | −6.60 |
| 40 | 30.91 | 21.57 | −9.34 | 30.99 | 27.02 | −3.96 |
| 60 | 31.34 | 25.36 | −5.98 | 31.30 | 28.59 | −2.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Zhang, G.; Cui, S.; Nie, Z.; Cui, H.; Wang, Q. Effects of Groundwater Level Control on Soil Salinity Change in Farmland around Wetlands in Arid Areas: A Case Study of the Lower Reaches of the Shiyang River Basin, China. Water 2023, 15, 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071308
Liu P, Zhang G, Cui S, Nie Z, Cui H, Wang Q. Effects of Groundwater Level Control on Soil Salinity Change in Farmland around Wetlands in Arid Areas: A Case Study of the Lower Reaches of the Shiyang River Basin, China. Water. 2023; 15(7):1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071308
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Pengfei, Guanghui Zhang, Shangjin Cui, Zhenlong Nie, Haohao Cui, and Qian Wang. 2023. "Effects of Groundwater Level Control on Soil Salinity Change in Farmland around Wetlands in Arid Areas: A Case Study of the Lower Reaches of the Shiyang River Basin, China" Water 15, no. 7: 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071308




