Contamination Characteristics and Source Identification of Groundwater in Xishan Coal Mining Area of Taiyuan Based on Hydrochemistry and Sulfur–Oxygen Isotopes
Abstract
1. Introduction
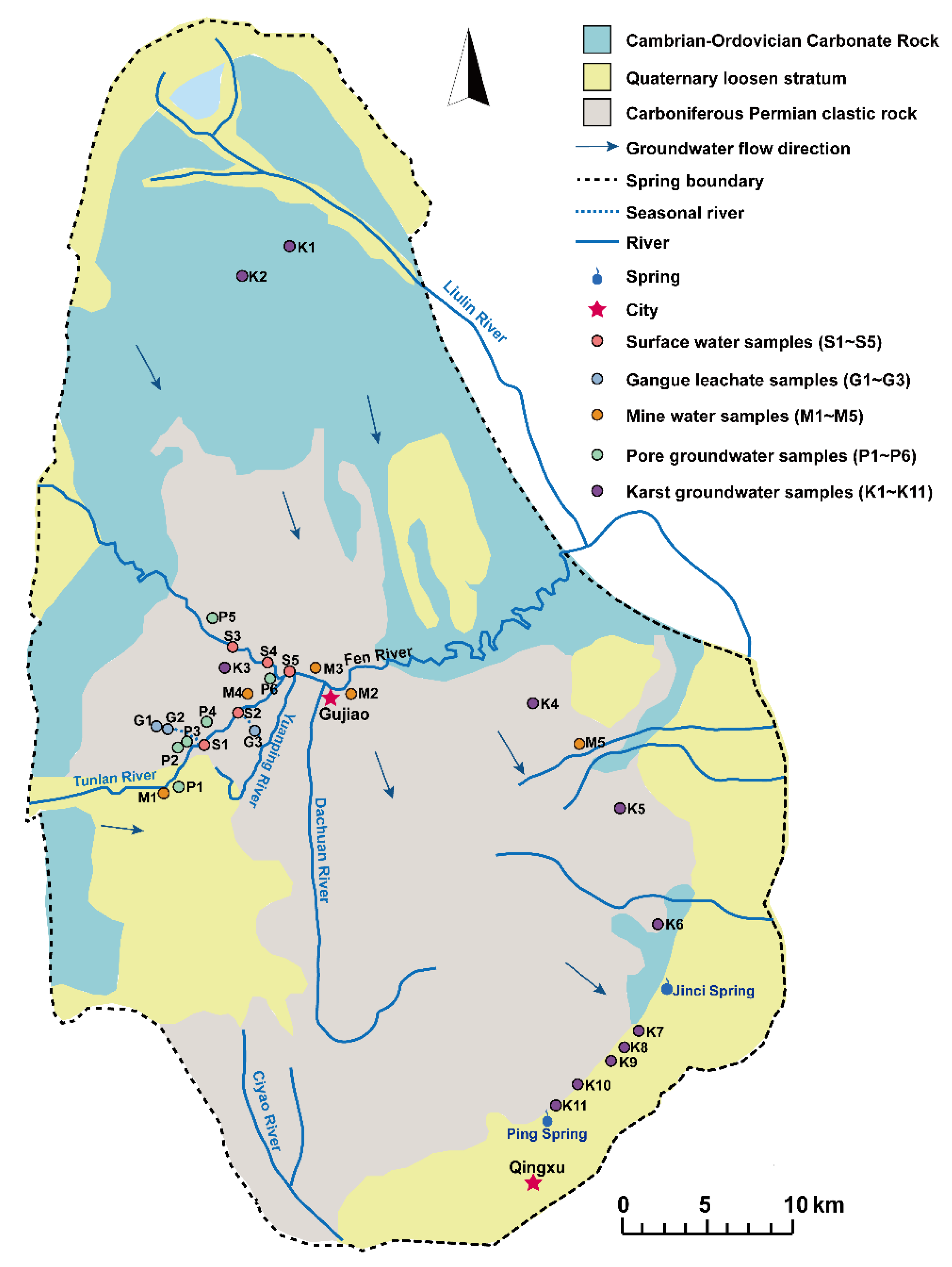
2. Hydrogeological Background of Study Area
3. Materials and Method
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. Physicochemical Indicators
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Physicochemical Parameters of Samples
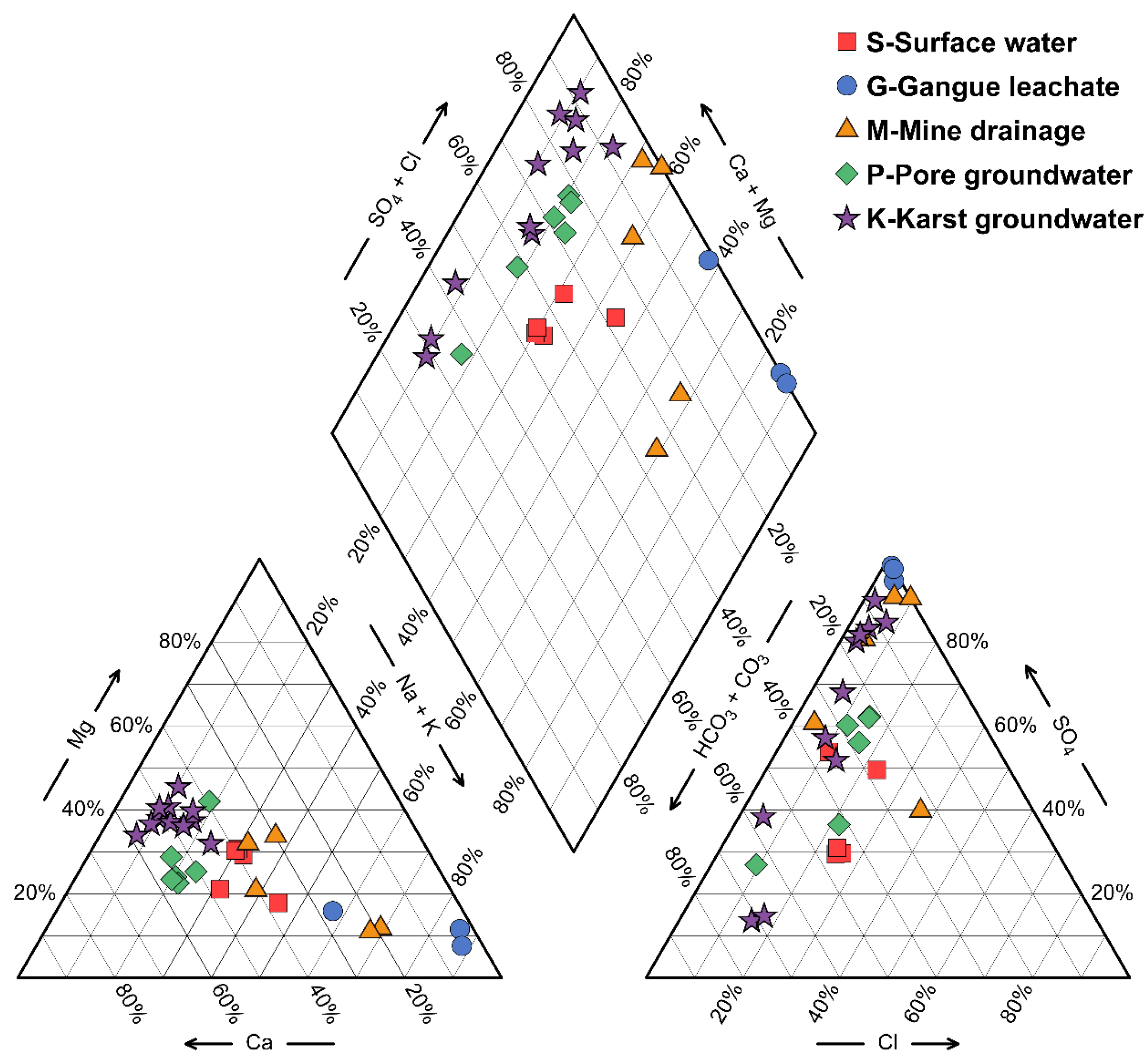
4.2. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Samples
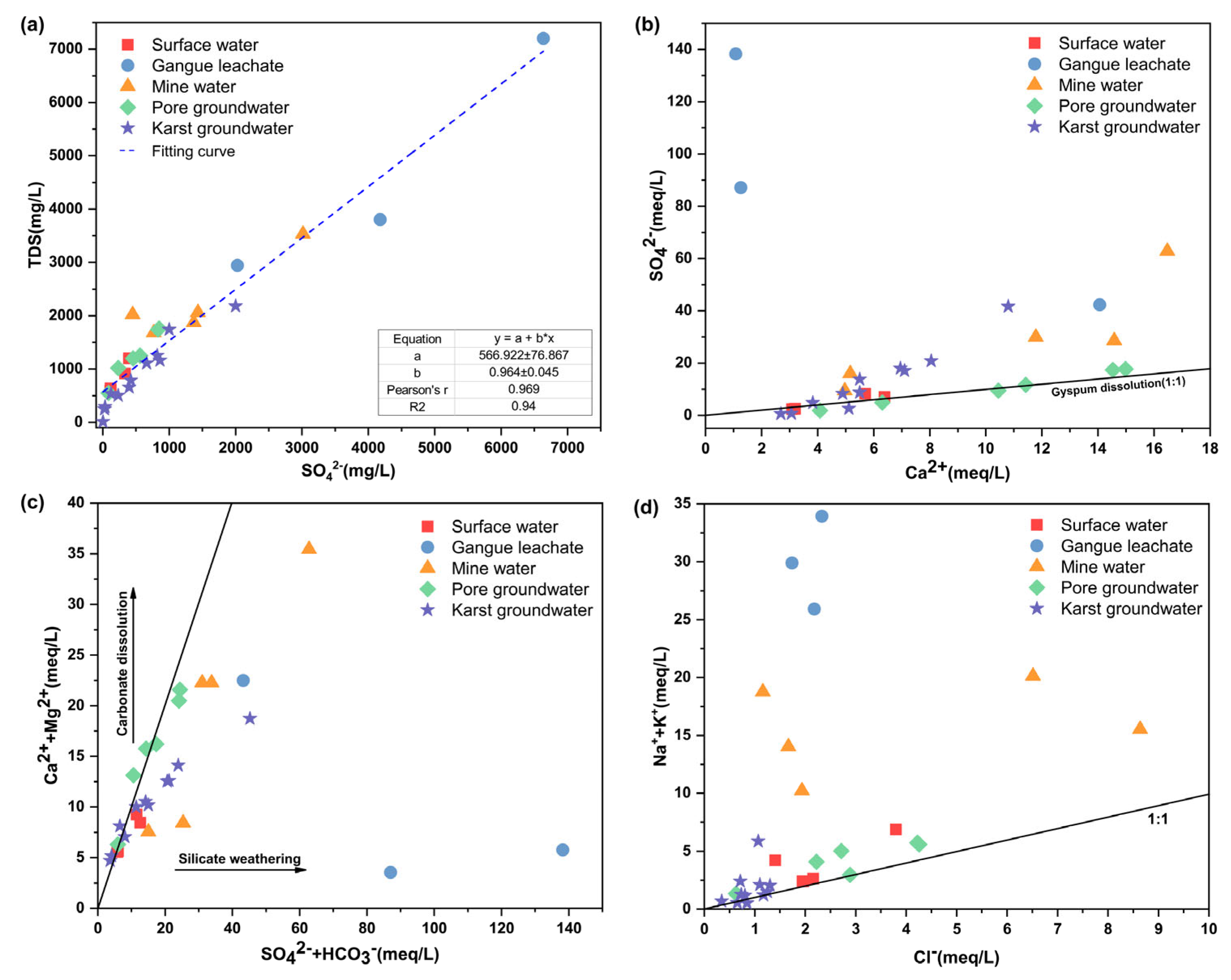
4.3. Analysis of Water–Rock Interaction of Water Samples
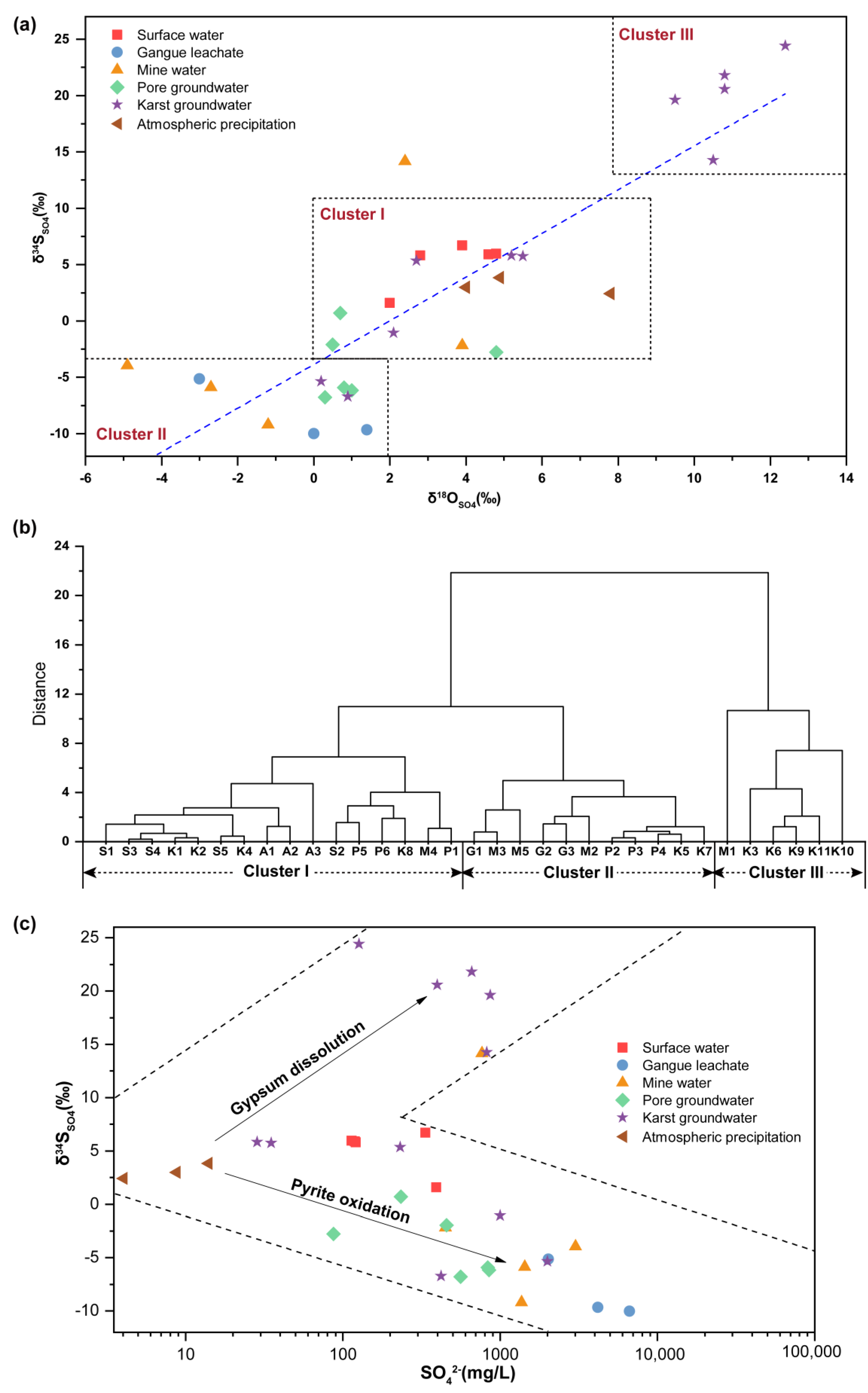
4.4. Distribution of Sulfur and Oxygen Isotopes in Water Samples
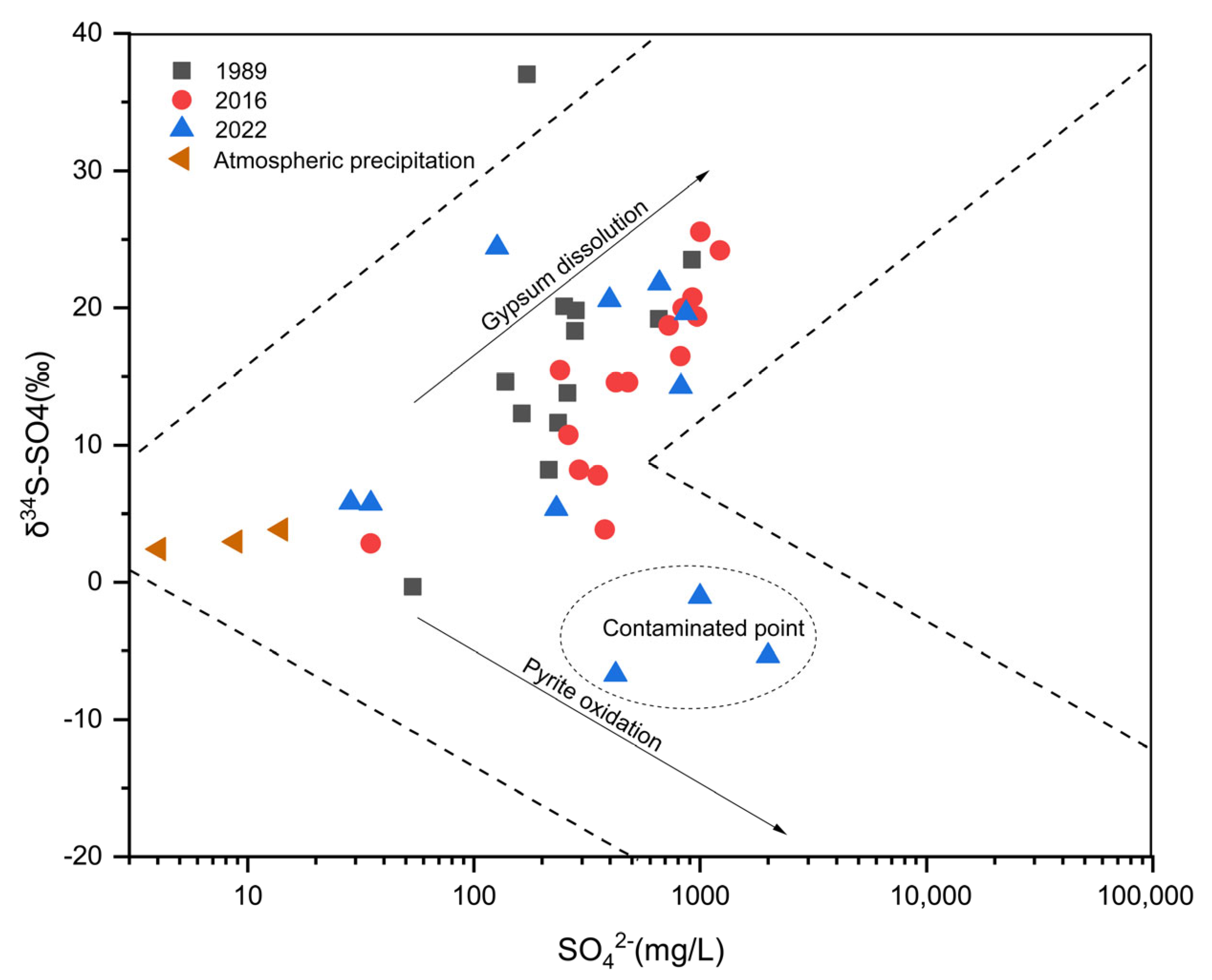
4.5. Identification of Groundwater Contamination Sources Based on Sulfur Isotopes
4.6. Temporal Variation of Sulfate Pollution in the Jinci Spring Area
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, L. Comprehensive development and utilization of abandoned mine resources, help achieve the goal of “emission peak and carbon neutralization”. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2021, 39, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Y.; Wang, J.M. Comprehensive utilization and environmental risks of coal gangue: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 117946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.Y.; Zhou, L. Risk Assessment and Control of Groundwater Pollution in Abandon Mine; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.N.I.; Ortega-Camacho, D.; Acosta-González, G.; Leal-Bautista, R.M.; Fox, W.E.; Cejudo, E. A multi-approach assessment of land use effects on groundwater quality in a karstic aquifer. Heliyon 2020, 6, e3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheibani, S.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Safaie, A.; Simmons, C.T. Influence of lakebed sediment deposit on the interaction of hypersaline lake and groundwater: A simplified case of lake Urmia, Iran. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Q.H.; Li, L. Hydrochemical characteristics and estimation of the dissolved inorganic carbon flux in the Donghe River Basin of western Hunan. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2019, 46, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.X.; Ding, Y.J.; Zeng, G.X.; Wu, J.K.; Qin, J. Major ion chemistry of surface water in the upper reach of Shule River basin and the possible controls. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 3315–3324. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zou, S.Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, R.K.; Dang, Z.W.; Pan, M.Q.; Zhu, D.N.; Zhou, C.S. Major ionic characteristics and factors of karst groundwater at Huixian karst wetland, China. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Sappa, G.; Vitale, S.; Ferranti, F. Identifying Karst Aquifer Recharge Areas using Environmental Isotopes: A Case Study in Central Italy. Geosciences 2018, 8, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannous, M.; Theilen-Willige, B.; Troeger, U.; Falk, M.; Siebert, C.; Bauer, F. Hydrochemistry and environmental isotopes of spring water and their relation to structure and lithology identified with remote sensing methods in Wadi Araba, Egypt. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 2245–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.B.; Chi, B.M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.W.; Wang, M.Y. Relationship between surface water and groundwater in the Liujiang basin-hydrochemical constrains. Adv. Earth Sci. 2017, 32, 789–799. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.H.; Jia, Y.F.; Yang, Y.; Gu, H.B.; Huan, H. Transformation relationship of different water body in Donggong River basin based on hydrochemistry. Res. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, B.C.; Putaud, J.P. Stable isotopes: Natural and anthropogenic sulphur in the environment. Atmos. Res. 1993, 29, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, M.; Breit, G.N.; Cozzarelli, I.M. Processes affecting δ34S and δ18O values of dissolved sulfate in alluvium along the Canadian River, central Oklahoma, USA. Chem. Geol. 2009, 265, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingri, J.; Torssander, P.; Andersson, P.S.; Mrth, C.M.; Kusakabe, M. Hydrogeochemistry of sulfur isotopes in the Kalix River catchment, northern Sweden. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 12, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, A.G.; Liu, Y.D. Using sulfur and oxygen isotopes of sulfate to track groundwater contamination from coal mine. Hydrogrology Eng. Geol. 2014, 41, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Stempvoort, D.; Krouse, H.R. Controls of δ18O in sulphate: Review of experimental data and application to specific environments. Environ. Geochem. Sulfide Oxid. 1994, 31, 447–479. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K. Water Chemistry and Sulfur-Oxygen Isotopes Geochemistry Characteristics of Xijiang River. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.H.; Liang, Y.P.; Lu, H.P.; Tang, C.L.; Shen, H.Y.; Wang, Z.H. Chemical characteristics and environmental significance of SO42− and sulfur isotope in the karst. Carsologica Sin. 2019, 38, 867–875. [Google Scholar]
- Akcil, A.; Koldas, S. Acid mine drainage (AMD): Causes, treatment and case studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2005, 14, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T. A Numerical Simulation on the Influence of Underground Water Flow Regime Caused by Coal Mining in Taiyuan Xishan Coal Area. Master’s Thesis, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.S. Hydrogeochemical Evolution Characteristics and Simulation of Karst Groundwater in the Jinci Spring Area. Master’s Thesis, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H. Purifying barite for oxygen isotope measurement by dissolution and reprecipitation in a chelating solution. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DZ/T 0064.49-2021; Methods for Analysis of Groundwater Quality—Part 49: Determination of Carbonated, Bicarbonate Ions, Hydroxy—Titration. Ministry of Natural Resources of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Zhang, H.L.; Wang, C.; Pang, W.; Teng, Y.; Qi, H. Using sulfur and oxygen isotope to trace the source of sulphate in Baotuquan spring area of Jinan. Geol. Surv. China 2019, 6, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 14848-2017; Standard for Groundwater Quality. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Qureshi, A.; Maurice, C.; Öhlander, B. Potential of coal mine waste rock for generating acid mine drainage. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 160, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Seyf-Laye, A.M.; Ibrahim, T.; Gbandi, D.; Chen, H. Tracking sources of groundwater nitrate contamination using nitrogen and oxygen stable isotopes at Beijing area, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 707–715. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Feng, Q.; Liang, H. Effects of long-term discharge of acid mine drainage from abandoned coal mines on soil microorganisms: Microbial community structure, interaction patterns, and metabolic functions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 53936–53952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K. Hydrogeochemical Characteristic Analysis and Hydrogeochemical Simulation of Karst Groundwater in Jinci Spring Area. Master’s Thesis, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, J.; Du, C.Y.; Qiao, X.J.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhou, P.P.; Li, G.M.; Wu, R.J.; Sun, Z.H. Hydrochemical features of Xishan karst groundwater system in Taiyuan. Carsologica Sin. 2008, 27, 353–358. [Google Scholar]
- Soulsby, C.; Chen, M.; Ferrier, R.C.; Helliwell, R.C.; Jenkins, A.; Harriman, R. Hydrogeochemistry of shallow groundwater in an upland Scottish catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 12, 1111–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Zeng, J.; Liang, J.; Yuan, D.; Pan, X. Impacts of acid mine drainage on karst aquifers: Evidence from hydrogeochemistry, stable sulfur and oxygen isotopes. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 761, 143223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ye, Y.H. Improvement and application of Schukalev groundwater hydrochemical classification method:taking groundwaters in Jinjiang city, Fujian Province as an example. Resour. Surv. Environ. 2014, 35, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.C.; Zhou, J.W.; Zhu, H.H.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Q.X.; Zhu, Y. Characteristics of sulfur isotope in water bodies near the Zhaoyuan gold mine area and its indicative function of pollution sources. Hydrogrology Eng. Geol. 2020, 47, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Okiongbo, K.S.; Akpofure, E. Identification of hydrogeochemical processes in groundwater using major ion chemistry: A case study of Yenagoa and environs, southern Nigeria. Glob. J. Geol. Sci. 2015, 12, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, S.; Anandhan, P.; Prasanna, M.V.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Vasanthavigar, M. Major ion chemistry and identification of hydrogeochemical processes controlling groundwater in and around Neyveli Lignite Mines, Tamil Nadu, South India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 3451–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Pan, X.D.; Lan, G.J.; Peng, C.; Liang, J.P.; Zeng, J. Seasonal variation and sources identification of dissolved sulfate in a typical karst subterranean stream basin using sulfur and oxygen isotope. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 4267–4274. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Lu, C. Tracing sulfate origin and transformation in an area with multiple sources of pollution in northern China by using environmental isotopes and Bayesian isotope mixing model. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Hu, Y.Y.; Ren, J.F.; Qu, K.; Yin, N.; Yu, H.J.; Ma, G.G. Sulfur and lead isotope composition and tracing for sources of ore-forming materials in Beiming river iron deposits, southern Taihang mountains. Geoscience 2011, 25, 846–852. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.L.; Zheng, X.Q.; Liang, Y.P. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation causes of ground karst water systems in the Longzici spring catchment. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 2087–2095. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.Y.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, S.L. Geochemical characteristics of sulfur and nitrogen isotopic compositions in rains of Guiyang in summer. Geochimica 2003, 32, 248–254. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, J.M.; Huang, X.Y.; Liu, S.T.; Zhang, Z.Y. Sources of dissolved heavy metals in river water of the Yiluo River basin based on sulfur isotope of sulfate. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 2549–2559. [Google Scholar]
- Petelet-Giraud, E.; Klaver, G.; Negrel, P. Natural versus anthropogenic sources in the surface- and groundwater dissolved load of the Dommel river (Meuse basin): Constraints by boron and strontium isotopes and gadolinium anomaly. J. Hydrol. 2009, 369, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.L. Application of stable isotope to the research on karst water in Taiyuan area. Carsologica Sin. 1989, 8, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.L.; Zheng, X.Q.; Liang, Y.P.; Zhang, F.W.; Jing, Z. The hydraulic connection between Jinci and Pingquan in Taiyuan Shanxi and its contribution to the reflow of Jinci spring. Geol. China 2020, 47, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar]


| Number | Surface Water | Gangue Leachate | Mine Water | Pore Groundwater | Karst Groundwater | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Average | Min | Max | Average | Min | Max | Average | Min | Max | Average | Min | Max | Average | |
| PH | 7.97 | 8.55 | - | 3.22 | 6.54 | - | 4.72 | 7.89 | - | 7.63 | 8.20 | - | 7.80 | 8.39 | - |
| TDS | 597 | 1200 | 790.80 | 2940 | 7200 | 4646.67 | 1680 | 3530 | 2232.00 | 550 | 1760 | 1253.33 | 248.00 | 2180.00 | 950.91 |
| K+ | 2.89 | 4.06 | 3.29 | 7.31 | 25.63 | 17.38 | 3.23 | 8.73 | 5.61 | 1.53 | 4.62 | 3.05 | 0.63 | 7.98 | 2.36 |
| Na+ | 53.08 | 155.76 | 83.05 | 584.75 | 765.41 | 677.77 | 229.85 | 461.01 | 358.46 | 29.40 | 128.86 | 92.79 | 11.60 | 130.00 | 38.81 |
| Ca2+ | 61.89 | 127.75 | 86.29 | 21.70 | 281.26 | 109.42 | 99.39 | 329.44 | 211.88 | 81.67 | 299.70 | 205.93 | 53.80 | 216.00 | 115.45 |
| Mg2+ | 29.32 | 34.28 | 31.11 | 27.19 | 101.12 | 61.41 | 30.87 | 227.50 | 103.05 | 26.56 | 81.74 | 63.33 | 23.90 | 95.00 | 54.75 |
| Cl− | 49.95 | 134.95 | 80.10 | 61.80 | 82.80 | 74.03 | 41.19 | 306.71 | 141.44 | 22.35 | 151.17 | 100.20 | 12.27 | 46.20 | 32.32 |
| SO42− | 114.01 | 393.90 | 216.83 | 2029.00 | 6637.00 | 4282.00 | 449.06 | 3015.38 | 1407.59 | 87.26 | 850.37 | 504.01 | 28.60 | 2000.00 | 598.94 |
| CO32− | 4.71 | 14.12 | 9.89 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 9.42 | 1.57 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| HCO3− | 208.21 | 277.61 | 236.21 | 0.00 | 59.40 | 19.80 | 0.00 | 569.59 | 261.34 | 253.68 | 409.24 | 343.02 | 78.00 | 331.00 | 204.50 |
| F− | 0.48 | 0.84 | 0.62 | 1.32 | 2.09 | 1.77 | 0.50 | 3.83 | 1.71 | 0.38 | 0.67 | 0.51 | - | - | - |
| NH4+ | 0.11 | 1.06 | 0.49 | - | - | - | 0.20 | 8.90 | 2.52 | 0.00 | 5.28 | 1.32 | - | - | - |
| NO3− | 2.69 | 19.23 | 7.11 | - | - | - | 0.00 | 1.94 | 0.84 | 18.96 | 96.15 | 42.94 | - | - | - |
| Al | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 37.60 | 23.88 | 0.02 | 75.50 | 15.16 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | - | - | - |
| Ba | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 32.50 | 45.70 | 40.77 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.20 | 0.09 | - | - | - |
| Fe | 0.06 | 0.57 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 690.00 | 279.68 | 0.12 | 34.20 | 7.28 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 2.03 | - |
| Mn | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 5.61 | 53.50 | 27.44 | 0.12 | 17.40 | 4.69 | 4.63 | 10.00 | 7.32 | 0.00 | 1.49 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, D.; Feng, Q.; Gong, M. Contamination Characteristics and Source Identification of Groundwater in Xishan Coal Mining Area of Taiyuan Based on Hydrochemistry and Sulfur–Oxygen Isotopes. Water 2023, 15, 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061169
Chen D, Feng Q, Gong M. Contamination Characteristics and Source Identification of Groundwater in Xishan Coal Mining Area of Taiyuan Based on Hydrochemistry and Sulfur–Oxygen Isotopes. Water. 2023; 15(6):1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061169
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Di, Qiyan Feng, and Min Gong. 2023. "Contamination Characteristics and Source Identification of Groundwater in Xishan Coal Mining Area of Taiyuan Based on Hydrochemistry and Sulfur–Oxygen Isotopes" Water 15, no. 6: 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061169
APA StyleChen, D., Feng, Q., & Gong, M. (2023). Contamination Characteristics and Source Identification of Groundwater in Xishan Coal Mining Area of Taiyuan Based on Hydrochemistry and Sulfur–Oxygen Isotopes. Water, 15(6), 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061169






