Abstract
Investigating systematic meteorological–agricultural–hydrological drought propagation within an integrated watershed framework is crucial yet challenging for advancing robust early warning systems and targeted resilience strategies. To address this gap, this study employs the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI), standardized soil moisture index (SSMI), and nonlinear joint hydrological drought index (NJHDI) to characterize meteorological, agricultural, and hydrological drought, respectively. Utilizing the strongest correlation method, variations in the propagation time along moisture movement pathways within the system are quantified using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) model. The Yellow River basin (YRB) is selected as the case study area. Key results reveal distinct seasonal patterns in meteorological–agricultural propagation across the basin, with escalated spring and summer timescales. However, weaker correlations and limited seasonality emerge for agricultural–hydrological linkages due to sustaining baseflow buffers. Specifically, the arid and semiarid region exhibited shorter propagation time with 1–5 months, while the semiarid and semihumid region displayed longer timescales with 7–12 months. These findings provide valuable scientific references for enhancing real-time early warning systems tailored to coupled watershed systems. The integrated methodology underscores the importance of unraveling fine-scale spatiotemporal propagation variability for localized drought resilience.
1. Introduction
China is situated in eastern Asia, on the west Pacific coast, within a climate-fragile zone featuring complex geography. It lies at the intersection of two major global disaster regions—the Northern Hemisphere mid-latitude zone and Pacific Rim—resulting in frequent natural hazards [1]. Among these, drought exerts the most extensive societal impact and gravest economic losses in China [2]. However, basic research on drought in China is still relatively underdeveloped, resulting in limited defense capabilities against drought. Currently, the focus is primarily on “single passive drought resistance” rather than achieving “comprehensive active drought prevention” [3].
It is widely accepted that meteorological drought serves as the origin of other drought types, and the process by which meteorological drought triggers agricultural drought or hydrological drought is referred to as drought propagation [4,5,6]. Figure 1 de-picts the intricate interplay between meteorological drought, agricultural drought, and hydrological drought, where these phenomena both hinder and facilitate each other. Meteorological drought exacerbates the evaporation of water from the earth’s surface and shallow groundwater, leading to increased depletion of surface water and groundwater and directly initiating hydrological drought (referred to as propagation route I in Figure 1) [7]. Additionally, meteorological drought can directly induce a reduction in soil water content. Insufficient replenishment of soil water disrupts the crop water budget, resulting in decreased grain yield and subsequent agricultural drought (referred to as propagation route II in Figure 1) [8]. Prolonged agricultural drought leads to the desiccation and compaction of the aeration zone [9]. Consequently, even with the same level of precipitation, the replenishment of surface water and groundwater is diminished, thereby triggering hydrological drought (also referred to as propagation route III in Figure 1).
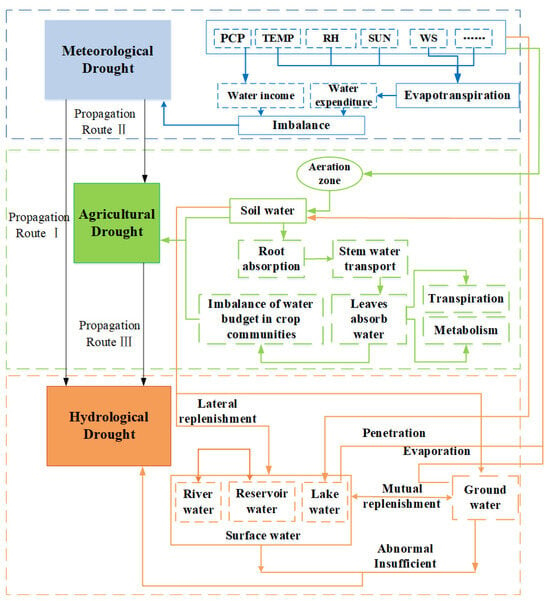
Figure 1.
Propagation process and correlation relationship within the meteorological, agricultural, and hydrological drought system based on the watershed water cycle process.
In recent years, extensive research has examined specific pathways in drought propagation including meteorological–hydrological [10,11,12,13] and meteorological–agricultural [14,15,16] linkages. For example, Ma et al. [17] conducted a comprehensive study on the relationship between meteorological drought and hydrological drought in the Huaihe River. Their investigation involved correlation analysis and the cross-transform wavelet method. In a similar vein, Li et al. [18] proposed a quantitative approach to investigate drought propagation in the Yangtze River based on multiple drought indices, cross-wavelet analysis, and spatial self-correlation method. Liu et al. [19] analyzed and studied the time it takes for meteorological drought to propagate to hydrological drought, as well as its seasonal variation characteristics, using the standardized precipitation index (SPI) and standardized runoff index (SRI) in the Wuding River basin, Kuye River basin, and Qinhe River basin. Furthermore, Bai et al. [20] contributed to the understanding of the propagation dynamics from meteorological drought to agricultural drought in the Heihe River Basin. Their study quantified the propagation time and probability during the period of 1981–2020. Additionally, they explored the sensitivities of these dynamics to different seasons and levels of drought. Marco et al. [21] investigated the mechanisms underlying the transition from meteorological to agricultural drought and its features across the Iberian Peninsula.
However, investigations into the systematic meteorological–agricultural–hydrological drought propagation sequence within an integrated watershed framework remain limited, a critical research gap. As shown in Figure 1, drought propagation, as a phenomenon in the hydrological cycle, signifies an abnormal deficit of water resulting from an imbalance in the water cycle budget [22,23,24], It is intricately connected to the hydrological cycle of a basin, where the long-term depletion of hydrological cycle elements during a drought event can trigger another type of drought through the water circulation pathway of the basin. Implementing proactive measures before the manifestation of secondary droughts within an interconnected watershed water cycle can effectively mitigate cascading socioeconomic impacts.
This study uniquely addresses this key gap by investigating the comprehensive propagation sequence of meteorological–agricultural–hydrological droughts within an integrated watershed water cycle framework. By utilizing specialized drought indices and conducting rigorous spatiotemporal correlation analysis, the study quantifies variations in the duration of propagation along the moisture movement pathways within the system, using a distributed hydrological model. Notably, distinct seasonal patterns emerge within the meteorological–agricultural–hydrological timescales, which are closely linked to water fluxes within the watershed’s hydrologic cycle.
Through the elucidation of fine-scale variability across the entire drought propagation pathway, this integrated modeling approach significantly advances our understanding of holistic early warning capabilities and provides insights for targeted adaptation strategies tailored to the watershed system. Unraveling the integrated propagation of meteorological–agricultural–hydrological droughts is crucial for the development of comprehensive early warning systems.
Therefore, this study focuses specifically on propagation routes II and III as depicted in Figure 1, examining the temporal propagation among meteorological, agricultural, and hydrological droughts within the interconnected watershed water cycle. Quantitative analysis of the time taken for propagation from meteorological to agricultural drought, as well as from agricultural to hydrological drought, is conducted. Furthermore, the study analyzes the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of propagation time across meteorological, agricultural, and hydrological droughts. These findings can serve as valuable scientific references for enhancing real-time early warning systems based on meteorological indicators, with the aim of mitigating cascading impacts of agricultural and hydrological droughts within coupled watershed systems.
2. Research Methods
Detailed methodologies are provided in this section, which mainly include the SWAT hydrological model and drought index calculation, the strongest Pearson correlation coefficient method. The flow chart of research methodology is shown in Figure 2.
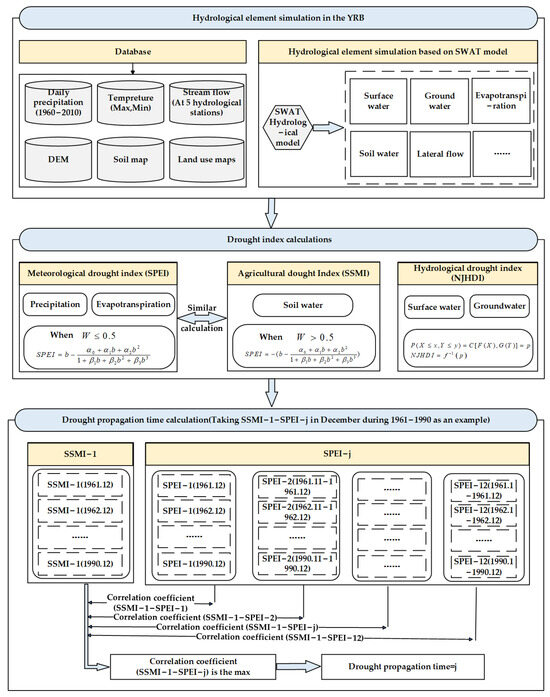
Figure 2.
The flow chart of research methodology.
2.1. SWAT Hydrological Model
The distributed hydrological model, the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT), developed by USDA-ARS, simulates hydrological processes by incorporating various basin characteristics [25,26]. It has been widely used in watershed studies and has demonstrated good simulation performance [27,28,29,30]. In this study, the SWAT model is chosen to simulate water cycle processes in the basin.
Evapotranspiration is calculated using the Penman–Monteith method, which considers various climatic and surface characteristics. Surface runoff is estimated using the Soil Conservation Service curve method, which takes into account land use and soil types. Soil water dynamics are simulated using a dynamic storage model that considers factors such as slope, hydraulic conductivity, and temporal and spatial variations in soil water content. Groundwater simulation includes shallow groundwater, which contributes to river runoff as base flow; and deep groundwater in the deep pressure saturation zone. The calculation details of shallow groundwater, deep groundwater, and water yield in the hydrological response unit are available in Josip and Lidija [31].
To evaluate the performance of the SWAT model in simulating monthly runoff, three statistical metrics were utilized: the Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient (NSE) [32], the relative error (Re), and the coefficient of determination (R2) [33]. The simulated and observed runoff time series were judged to have an acceptable fit if the following thresholds were met concurrently on a monthly scale: NSE > 0.5, |Re| < 25%, and R2 > 0.6 [34].
2.2. Drought Indexes
2.2.1. Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index
Meteorological drought occurs due to imbalances in the water cycle, resulting from anomalies in precipitation and evapotranspiration over different time scales, such as annual, seasonal, or monthly timescales [35]. To characterize meteorological drought, the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI), proposed by Vicente-Serrano et al. [36], was utilized in this study. The SPEI modifies the standardized precipitation index (SPI) by incorporating potential evapotranspiration. By capturing the deficit in atmospheric water vapor caused by discrepancies between precipitation and evapotranspiration, the SPEI effectively monitors and assesses meteorological drought. Therefore, it is well suited for monitoring and assessing meteorological drought, even under nonstationary climate warming trends, across river basins. The detailed calculation steps of SPEI can be found in Vicente-Serrano [36], with classification shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Classification standard of drought grades.
2.2.2. Standardized Soil Moisture Index
The standardized soil moisture index (SSMI) serves as a reliable indicator for evaluating soil water conditions across different time scales and exhibits a strong correlation with both meteorological and hydrological drought [37]. Therefore, this study employs the SSMI to characterize agricultural drought. The calculation approach for the SSMI parallels that of the SPEI, wherein the distribution function is employed to model the soil water series data and subsequently normalize the fitted values. The detailed calculation steps of SSMI are available in Carrão et al. [38], also with classification shown in Table 1.
2.2.3. Nonlinear Joint Hydrological Drought Index
Hydrological drought occurs when runoff and water levels in rivers and lakes are abnormally low due to imbalanced surface water and groundwater budgets within a watershed [39]. In this study, the nonlinear joint hydrological drought index (NJHDI), proposed in our previous study by Li et al. [40], was employed to characterize hydrological drought. The NJHDI comprehensively considers surface water, groundwater, and their nonlinear interconnections. Detailed procedures for the NJHDI can be found in Li et al. [40]. The classification of the NJHDI is shown in Table 1.
2.3. Drought Propagation Time
Drought propagation time refers to the lag between meteorological and agricultural drought, or between agricultural and hydrological drought. The Pearson correlation coefficient method is commonly used to measure the correlation between two variables, with values ranging from −1 to 1. The larger the value, the higher the correlation between the two variables [41]. The strongest Pearson correlation coefficient method has been widely used in recent studies to quantify propagation time [42,43,44,45]. For example, in the case of meteorological to agricultural drought, the approach is illustrated in Figure 3. The cumulative drought scale is defined from 1 to 12 months, and the correlation between meteorological and agricultural drought is maximized to determine the propagation time. Similarly, the lag between agricultural and hydrological drought is determined using the same method. Seasonal mean propagation times are calculated by averaging the monthly values. Overall, this correlation-based approach provides quantitative insights into the cascading effects of drought across meteorological, agricultural, and hydrological systems.
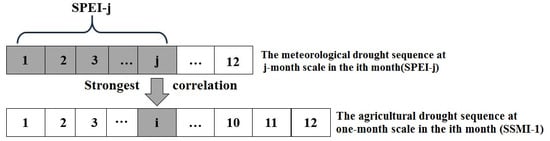
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of drought propagation time based on strongest correlation coefficient method.
3. Case Study and Data Sources
3.1. The Yellow River Basin
The Yellow River is the second largest river in China, with a drainage basin of 795,000 km2 and a main stem length of 5464 km. The climate exhibits significant variations due to the influences of atmospheric and monsoonal circulations. Precipitation exhibits substantial spatial heterogeneity, uneven seasonal distribution, and high interannual variability. The multiyear average annual precipitation is approximately 476 mm, gradually decreasing from southeast to northwest. Most areas experience high potential evapotranspiration, ranging from 800 to 1800 mm annually. Mean annual temperatures vary from −4 °C to 14 °C, increasing from northwest to southeast [46,47]. To comprehensively analyze the spatial propagation characteristics among meteorological, agricultural, and hydrological droughts, the YRB was delineated into six zones based on climatic regions, as shown in Figure 4. Detailed information regarding the climatic characteristics of each zone can be found in our previous research [40].
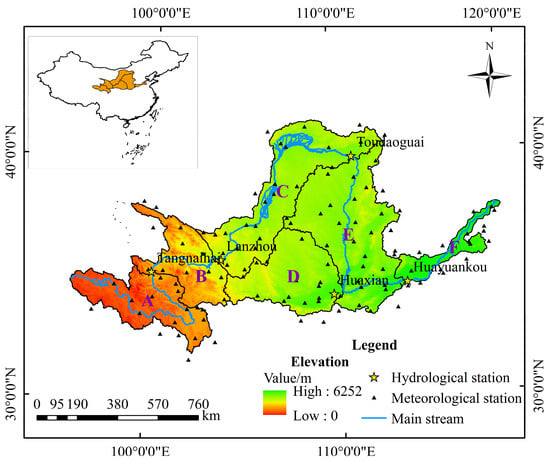
Figure 4.
Map depicting the location and topography of the YRB and its six delineated zones. Zone A encompasses a semiarid-to-semihumid region with plateau climatic characteristics. Zone B represents a transitional zone between plateau and mid-temperate climates. Zone C comprises an arid-to-semiarid region with mid-temperature climatic features. Zone D constitutes a semiarid region with warm temperature climate traits. Zone E encompasses a semiarid-to-semihumid zone with temperate continental climate. Zone F constitutes a humid region with temperate monsoonal climate characteristics.
Known as the “Mother River” of China, the YRB supplies water to major agricultural areas and over 50 large, medium, and small cities, playing a crucial role in national socioeconomic development [48,49]. However, the basin’s unique geography and climate make it susceptible to frequent drought occurrences, hence its ancient epithet of “nine droughts in ten years.” Drought poses a significant threat to ecological environments and economic-social stability in the region [50,51].
3.2. Data Sources
The data used in this study were collected from various reliable sources. Daily records of precipitation and minimum and maximum temperature (1960–2010) from 121 meteorological stations (Figure 4) were acquired from the China Meteorological Administration. Monthly naturalized streamflow data the same time period at five hydrological stations (Figure 4) were obtained from the Yellow River Conservancy Commission. Additionally, digital elevation model (DEM) with a resolution of 90 m was downloaded for the YRB from geospatial cloud databases. Furthermore, soil map with a scale of 1:1 million, classified into 10 types based on the FAO98 system, was downloaded from the Nanjing Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The soil types include calcareous cinnamon, black earth, and brown soil. Four 1:100,000 scale land use maps (1980, 1990, 2000, 2010) were acquired from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and reclassified into six types per the National Standard (GB/T21010-2007) [52], including cultivated land, grassland, forest, water bodies, barren land, and built-up areas. These long-term, high-resolution spatiotemporal datasets allowed for a robust characterization and analysis of the propagation of meteorological, agricultural, and hydrological drought propagation across the YRB.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Simulation Results of SWAT Model
Before calibrating the SWAT model, the Mann–Kendall nonparametric test [53] was utilized to identify abrupt changes in the yearly naturalized runoff records from 1961–2010 at the five hydrological stations. The results indicated breakpoints around 1985–1990 across all gauges (Figure 5). Subsequently, the study period was divided into two segments—1961–1990 and 1991–2010—for further analysis based on this finding. As the accuracy of SWAT simulation directly affects drought propagation time calculations, model parameters were calibrated and validated for both segments to ensure a robust representation of the YRB hydrologic cycle. Initially, a 1–2 year warm-up period was specified in the SWAT simulations to eliminate the default zero parameter values. The model warm-up, calibration, and validation periods are summarized in Table 2. This meticulous calibration procedure facilitated the reliable quantification of meteorological, agricultural, and hydrological drought propagation under contrasting climatic conditions before and after 1990.
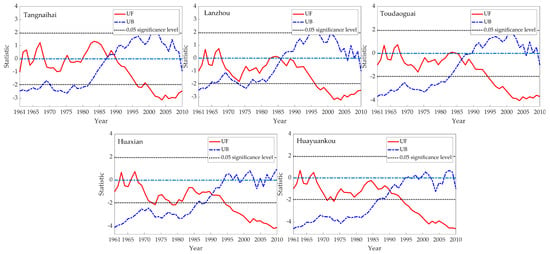
Figure 5.
Detection of abrupt points of yearly naturalized runoff from 1961−2010 at the five hydrological stations in the YRB.

Table 2.
The warm-up, calibration, and validation periods in the SWAT model.
Figure 6 presents the monthly simulated and observed runoff time series from 1961–1990 and 1991–2010 across five hydrological stations (Tangnaihai, Lanzhou, Toudaoguan, Huaxian, and Huayuankou) in the YRB. Visual inspection shows close agreement between the modeled and measured monthly runoff dynamics for both periods at all stations, indicating that SWAT accurately captured the observed runoff patterns.
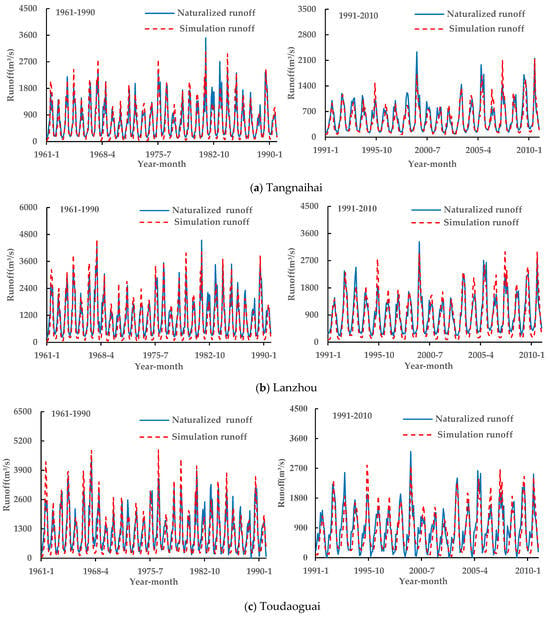
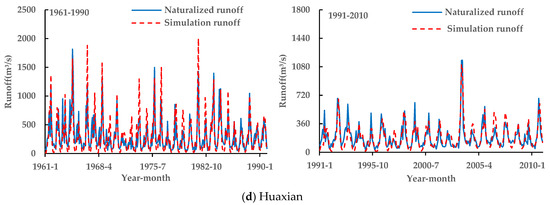
Figure 6.
Comparison of naturalized runoff and simulated runoff at five hydrological stations during two periods in the YRB.
Quantitative performance metrics in Table 3 further validate the model. NSE ranges from 0.64 to 0.83, R2 varies between 0.70 and 0.90, and Re spans 2.61 to 17.10, satisfying the thresholds of NSE > 0.5, R2 > 0.6, and Re < 25%. Therefore, the SWAT model demonstrated strong capability in simulating the observed monthly runoff dynamics across multiple stations and time periods in the YRB, as evidenced by graphical measures and statistical metrics. This provides confidence in the model’s representation of basin hydrological processes.

Table 3.
Valuation metrics results of monthly runoff simulation by SWAT model in different time periods in the YRB.
To further demonstrate the reliability of the simulated hydrological processes in this study, the modeled groundwater was evaluated against observed data. Specifically, the average annual groundwater resources from 1980–2000 were compiled for eight sub-basins demarcated per the secondary boundary delineation (Figure 7a). These observed values were compared to the simulated groundwater outputs for the corresponding sub-basins, as shown in Figure 7b. The results indicate that the SWAT model groundwater estimates were slightly higher than the observations from the Comprehensive Planning of Water Resources (CPWR), with relative errors under 10% across the sub-basins. These small overestimations can be attributed to inevitable inaccuracies in model structure and input data. Overall, the reasonable match between simulated and observed groundwater provides confidence in the credibility of the modeled hydrological processes for this study.
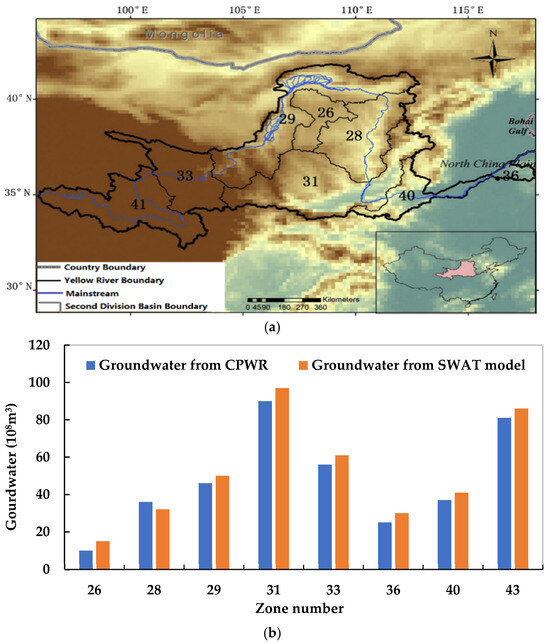
Figure 7.
(a) Zone numbers of second division sub-basin, and (b) comparison of groundwater from CPWR and SWAT model.
These results validate that with proper calibration, the SWAT model competently simulated key basin-wide hydrological processes, including infiltration, soil moisture, groundwater, overland and channel flows, across the diverse climatic regions within the YRB. The calibrated SWAT model provides a robust framework for characterizing the spatiotemporal patterns of meteorological, agricultural, and hydrological drought propagation mechanisms through the interconnected hydrometeorological system of this complex watershed.
4.2. Propagation Time of Meteorological Drought to Agricultural Drought
Figure 8 illustrates the correlation coefficients between meteorological droughts aggregated over 1–12 months and agricultural droughts over 1 month across the YRB. Warmer colors indicate higher correlation, while cooler colors denote lower correlation. The small black points indicate the maximum correlation between agricultural and meteorological drought for each given cumulative monthly meteorological drought scale. In other words, these points represent the propagation time in months from meteorological to agricultural drought during each month, corresponding to the horizontal axis cumulative monthly timescale. This correlation matrix provides insight into the spatiotemporal evolution of drought propagation from the meteorological to agricultural droughts over the YRB.
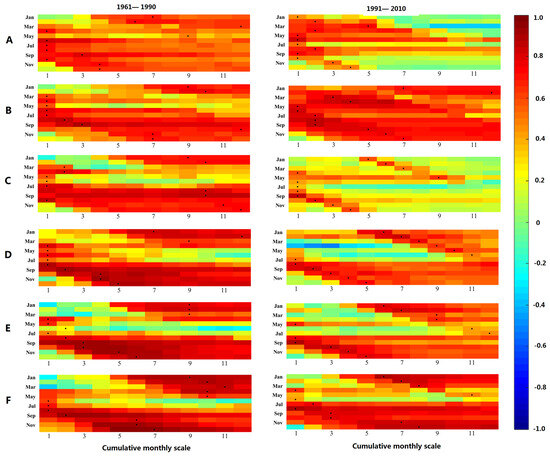
Figure 8.
The correlation coefficient between meteorological drought at 1–12 month cumulative scale and agricultural drought at 1-month scale in the YRB (note: A is the semiarid-to-semihumid region. B is the transitional zone between plateau and mid-temperate climates. C is the arid-to-semiarid region. D is the semiarid region. E is the semiarid-to-semihumid zone. F is the humid region).
Figure 8 shows a strong correlation between meteorological and agricultural drought across the YRB during 1961–1990. The relationship was slightly weaker in the upper reaches (zones A–C) compared to the middle-lower reaches (zones D–E). This suggests that soil moisture in the YRB, particularly in downstream regions, was highly sensitive to precipitation and temperature changes before 1990. This sensitivity can be attributed to the flat terrain in middle-lower areas, which enhances precipitation infiltration and soil moisture recharge. In contrast, the correlation weakened during the period from 1991 to 2010, especially in the arid–semiarid mid-latitude zone C. The sensitivity of soil moisture to climate drivers significantly declined in this zone, likely due to its location in the rain-scarce Ningmeng reach where rainless days and frequent meteorological droughts increased after 1990 [54]. Although monthly lags showed variability, distinct seasonal patterns emerged. Therefore, the mean propagation times for spring, summer, autumn, and winter in each zone were calculated during 1961–1990 and 1991–2010, and the results are summarized in Table 4.

Table 4.
Propagation time from meteorological drought to agricultural drought at seasonal scale in the YRB (unit, month).
Table 4 reveals seasonal variations in drought propagation time across the YRB. Spring saw 5–6 months, summer 2–3 months, autumn 3–5 months, and winter the longest at 6–8 months. This is similar to the results obtained by Zhang et al. [55], but the above research only explores the seasonality of drought propagation and does not systematically analyze the dynamic changes of drought propagation in different seasons from the perspective of watershed water cycle. The advantage of this article is that it not only quantifies the propagation time in different seasons, but also systematically analyzes the potential reasons for the dynamic changes of propagation time in different seasons from the perspective of watershed water cycle. The shorter summer propagation time is attributable to abundant precipitation supplying soil water, enabling quick responsiveness to meteorological deficits. High temperatures also accelerate summer evaporation. Thus, meteorological droughts can rapidly propagate into agricultural droughts. The protracted winter propagation relates to northern basin snowpack, which sustains until spring melting.
Comparing 1961–1990 and 1991–2010, propagation time extended in spring and summer but decreased in autumn and winter for most zones in the YRB. Spatially, spring propagation exhibited significant variation from 1–10 months prior to 1990, with zones B and C the shortest (1–2 months) and zone F the longest (10 months). After 1990, differences reduced to 3–9 months, with zones A and B the shortest (3 months) and zone D the longest (9 months). Pre-1990, summer propagation concentrated in zone C shifted to zone E post-1990, indicating downstream movement of long-term summer drought. Autumn propagation spanned 3–7 months before 1990, declining to 2–4 months after 1990. Pre-1990, winter propagation ranged 6–10 months, reducing by 2–9 months post-1990, especially in upper zones where increased winter temperature (Figure 9) and accelerated snowmelt shortened winter propagation from 10 to 5 months.
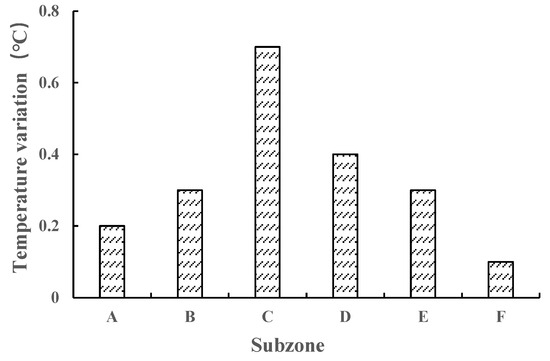
Figure 9.
Compared with the period of 1961–1990, the variation of winter temperature in six zones of the YRB during the period of 1991–2010.
Distinct seasonal and spatial patterns emerge in drought propagation time over the YRB, with clear pre- versus post-1990 shifts. These insights elucidate spatiotemporal drought evolution mechanisms in this complex basin.
4.3. Propagation Time of Agricultural Drought to Hydrological Drought
Figure 10 exhibits the correlation coefficient between agricultural drought at cumulative scales of 1 to 12 months and hydrological drought at a 1-month scale in the YRB. The color scheme represents the strength of the correlation coefficient, with redder shades indicating higher coefficients and bluer shades representing lower coefficients. The small black points indicate the most robust correlation coefficient between hydrological drought and agricultural drought at the corresponding cumulative scale of the month. These points essentially indicate the propagation time from agricultural drought to hydrological drought within the month, corresponding to the cumulative monthly scale shown on the horizontal axis.
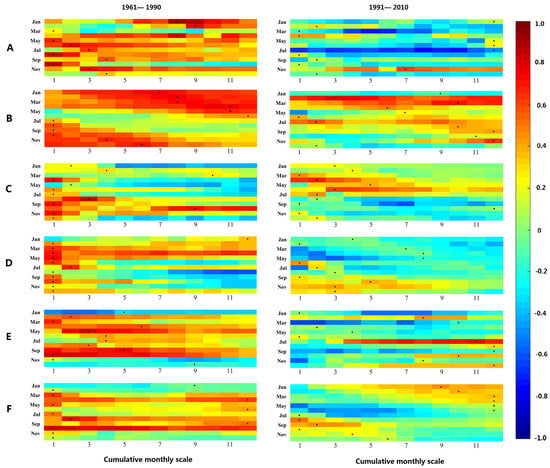
Figure 10.
The correlation coefficient between agricultural drought at 1–12 month cumulative scale and hydrological drought at 1-month scale in the YRB. (note: A is the semiarid-to-semihumid region. B is the transitional zone between plateau and mid-temperate climates. C is the arid-to-semiarid region. D is the semiarid region. E is the semiarid-to-semihumid zone. F is the humid region).
Figure 10 demonstrates that in comparison to the period of 1961–1990, the correlation between agricultural drought and hydrological drought in the YRB experienced a noticeable decline during the period of 1991–2010. This decline can be primarily attributed to the substantial migration of rural populations to economically developed urban areas after 1990, leading to a rapid expansion of urban construction land. Table 5 presents comprehensive data on the areas and proportions of change in urban construction land in the YRB from 1980 to 2010. The table reveals an upward trend in the area of urban construction land within the basin, particularly from 2000 to 2010, during which the proportion of urban construction land increased by nearly 20%. The extensive urbanization process involves the conversion of pervious surfaces into impervious ones, such as the replacement of loose pavements with cement pavements. This alteration reduces the infiltration of surface water, disrupts the natural connection between soil water and surface water, and consequently weakens the correlation between agricultural drought and hydrological drought.

Table 5.
Change area and proportion of urban construction land in the YRB from 1980 to 2010.
The propagation time from agricultural drought to hydrological drought in the six zones of the YRB exhibited a dispersed pattern, with no significant seasonal variations. However, compared to the period of 1961–1990, the propagation time from agricultural drought to hydrological drought during 1991–2010 displayed an increasing trend. This can be primarily attributed to the establishment of water and soil conservation measures in the YRB since the 1990s. The implementation of ecological and engineering measures has gradually restored vegetation and grassland areas in the basin. Particularly after 2000, these conservation efforts have yielded remarkable achievements [56]. As a result, the water holding capacity of the soil in the YRB has significantly improved, leading to increased recharge of soil water to groundwater. Consequently, the propagation time from agricultural drought to hydrological drought has been prolonged.
Spatially, zone B and zone E exhibited relatively longer propagation time of 7 to 12 months from agricultural drought to hydrological drought. This can be attributed to the presence of four large reservoirs (Longyangxia and Liujiaxia, Sanmenxia and Xiaolangdi) located in these zones [57]. The perennial water storage in these reservoirs maintains relatively high groundwater levels, allowing groundwater to supplement base flow and alleviate hydrological drought for a certain duration when agricultural drought occurs. This is consistent with the research results obtained by Omar et al. [58], which also indicated that reservoirs can help cope with drought, especially in semiarid regions. On the other hand, zone C displayed relatively shorter propagation times ranging from 1 to 5 months from agricultural drought to hydrological drought. This is because zone C is situated in the Ningmeng reach, characterized by lower rainfall and higher evaporation rates. The thicker vadose zone in the soil impedes the formation of surface runoff and underground runoff. Consequently, when the soil experiences water scarcity, it is more prone to groundwater depletion, resulting in hydrological drought. Therefore, the propagation time from agricultural drought to hydrological drought in zone C is relatively short.
In comparison to meteorological drought and agricultural drought, the correlation between agricultural drought and hydrological drought is weaker, but the propagation time is longer. This is in line with the findings of Han et al. [59]. However, the study did not conduct a quantitative or qualitative analysis of the underlying reasons behind this phenomenon. This can be primarily attributed to the sensitivity of soil water to changes in precipitation and temperature. When meteorological drought occurs, it directly leads to a decrease in soil water content, subsequently inducing agricultural drought. However, when agricultural drought occurs, the base flow can typically be replenished by the relatively stable groundwater, mitigating the drying up of rivers. Consequently, agricultural drought generally persists for a certain duration, ultimately inducing hydrological drought.
4.4. Uncertainty Analysis
Watershed hydrological models, such as the SWAT model, aim to simplify complex land surface processes occurring on the land surface by utilizing mathematical equations and parameters to simulate various components of the hydrologic cycle, including evapotranspiration, infiltration, soil moisture flow, and groundwater recharge. However, it is important to acknowledge that inherent uncertainties remain in all models’ representations of real-world watershed hydrology [12]. Although the SWAT model demonstrated satisfactory performance across different periods and regions of the YRB, uncertainties still exist in simulated water cycle variables like soil moisture, surface water, and groundwater. Three primary sources contribute to these uncertainties: (1) errors in input data such as DEM resolution, land use classification, and precipitation accuracy; (2) uncertainty in calibrated model parameters; and (3) structural deficiencies resulting from incomplete understanding of the underlying processes and conceptualization of the model. To reduce these uncertainties in future research, the implementation of the SWAT model can be improved through fusion of multisource inputs, dynamic parameter estimation techniques, and integration with complementary models to better constrain the complex hydrological cycle of the YRB. Advancing hydrological modeling frameworks play a crucial role in mitigating in coupled drought analysis.
Fundamentally, drought arises from imbalances in various components of the hydrological cycle at the basin scale. Any anomalies in hydrometeorological conditions can trigger drought onset and propagation along interconnected pathways. For example, meteorological drought deficits, which directly reduce soil moisture, may lead to agricultural drought in a linear manner. However, agricultural systems can exhibit resilience to meteorological drought if irrigation or other human interventions recharge soil water. In such cases, the meteorological–agricultural drought correlation weakens and propagation time increases. Even prolonged meteorological drought does not necessarily result in agricultural drought. Therefore, the propagation of drought involves complex nonlinear dynamics, which introduce uncertainties in quantifying the lag times associated with drought events.
In this study, the calibration of the hydrological model with naturalized streamflow removed human influences like irrigation, highlighting linear climate-driven propagation. Moving forward, the identification of nonlinear drought pathways could be achieved by employing copula models or directional information indices to capture agricultural-hydrological linkages mediated by human activities like reservoir operations across the complex watershed system. The incorporation of this nonlinearity is crucial for the development of integrated drought monitoring and early warning frameworks.
5. Conclusions
Key findings on spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of the meteorological-agricultural–hydrological drought system within the framework of the watershed water cycle in the YRB are summarized as follows:
- (1)
- Strong correlation existed between meteorological and agricultural drought, with distinct seasonal propagation time of 5–6 months in spring, 2–3 months in summer, 3–5 months in autumn, and 6–8 months in winter. Compared to 1961–1990, the propagation time increased in spring and summer but decreased in autumn and winter across most regions during 1991–2010. Notably, the propagation of winter drought in the upper basin decreased from 10 to 5 months, which can be attributed to accelerated snowmelt caused by significant warming after 1990.
- (2)
- The correlation between agricultural and hydrological drought weakened over time. The propagation time did not show seasonal differences but increased overall, potentially due to improved soil water retention from revegetation and conservation efforts since the 1990s. This enhanced soil recharges to groundwater, prolonging the lag between agricultural and hydrological droughts. Spatially, zones B and E exhibited longer propagation times of 7–12 months due to reservoir regulation that maintained high groundwater levels to sustain baseflow during agricultural droughts. In contrast, zone C had a shorter propagation time of 1–5 months due to the presence of thick vadose zones that inhibit surface and subsurface runoff generation. Overall, the propagation dynamics of meteorological–agricultural–hydrological droughts are complex and vary across the heterogeneous climate and landscape of the YRB.
- (3)
- Compared to the meteorological–agricultural coupling, the agricultural–hydrological drought correlation was weaker despite the longer propagation time. This is because soil moisture is highly sensitive to fluctuations in precipitation and temperature, leading to rapid reduction in soil water and the onset of agricultural drought. On the other hand, stable groundwater recharge sustains river baseflow during agricultural drought, delaying the emergence of hydrological deficits. Therefore, prolonged agricultural drought is typically required to propagate into hydrological systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology and writing—review and editing, Y.L. (Yunyun Li); methodology and writing—original draft, Y.H.; software, Y.L. (Yanchun Li); data curation, H.Z., formal analysis, J.F.; investigation, Q.D. and X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 52009053), Natural Science Foundation of Mianyang Normal University (Grant number QD2020A06), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 52209008, 52209013, 32101363).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request *due to privacy*.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yi, L.; Cheng, Y.Z.; Rui, L.; Min, S. An NGO disaster relief network for small and medium-scale natural hazards in China. Nat. Hazards 2022, 106, 2689. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.B.; Huang, J.J.; Yuan, Y.B.; Liu, Y.W. Climatological spatial scales of meteorological droughts in China and associated climate variability. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 129056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.X.; Li, M.; Weng, B.S.; Yan, D.H.; Dong, Z.Y.; Feng, J.M.; Wang, H. Drought-flood abrupt alteration events over China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Ma, F.; Li, H.; Chen, S.S. A review on multi-scale drought processes and prediction under global change. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 43, 225–237, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.H.; Jiang, S.H.; Ren, L.L.; Xu, C.Y.; Menzel, L.; Yuan, F.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.L. Separating the effects of climate change and human activities on drought propagation via a natural and human-impacted catchment comparison method. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Huang, S.Z.; Wang, H.Y.; Zheng, X.D.; Huang, Q.; Deng, M.J. High-resolution propagation time from meteorological to agricultural drought at multiple levels and spatiotemporal scales. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 262, 107428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.X.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Peng, T.; Chang, W.J.; Guo, J.L. Propagation from meteorological to hydrological drought and its application to drought prediction in the Xijiang River basin, South China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Huang, S.Z.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, X.D.; Su, X.L.; Leng, G.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Guo, Y.; Fang, W.; Liu, Y.J. Propagation characteristics and mechanism from meteorological to agricultural drought in various seasons. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127897. [Google Scholar]
- Giulia, B.; Francesco, A.; Simone, G.; Luca, F.; Edoardo, C.; Marta, G.; Christian, M. Disentangling the role of subsurface storage in the propagation of drought through the hydrological cycle. Adv. Water Resour. 2022, 169, 104305. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.Z.; Li, P.; Huang, Q.; Leng, G.Y.; Hou, B.B.; Ma, L. The propagation from meteorological to hydrological drought and its potential influence factors. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.F.; Chen, X.H.; Yao, H.X.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, D.J. Hydrological Drought Instantaneous Propagation Speed Based on the Variable Motion Relationship of Speed-Time Process. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 9549–9565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.K.; Ma, M.M.; Zhang, X.J.; Leng, G.Y.; Su, Z.C.; Lv, J.; Yu, Z.B.; Yi, P. Altered drought propagation under the influence of reservoir regulation. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhao, W.W. Anthropogenic drought in the Yellow River basin: Multifaceted and weakening connections between meteorological and hydrological droughts. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.G.; Wu, Z.Y.; Shao, Q.S.; He, H.; Guo, X. From meteorological to agricultural drought: Propagation time and probabilistic linkages. J. Hydrol. 2023, 46, 101329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Singh, V.P.; Ren, L.L. A global perspective on the probability of propagation of drought: From meteorological to soil moisture. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.W.; Zhang, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, R.G. Influence of irrigation and groundwater on the propagation of meteorological drought to agricultural drought. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 277, 108099. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.; Luo, L.F.; Ye, A.Z.; Duan, Q.Y. Drought Characteristics and Propagation in the Semiarid Heihe River Basin in Northwestern China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.H.; Chen, N.C.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, L.L.; Wang, X.P.; Tang, S.J.; Li, D.R.; Niyogi, D. Quantitative analysis of agricultural drought propagation process in the Yangtze River Basin by using cross wavelet analysis and spatial autocorrelation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 280, 107809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Huang, S.Z.; Fang, W.; Ma, L.; Zhang, X.D.; Huang, Q. Propagation and dynamic change of meteorological drought to hydrological drought in different seasons. Shuili Xuebao 2021, 52, 93–102, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bai, M.; Li, Z.L.; Huo, P.Y.; Wang, J.W.; Li, Z.J. Propagation characteristics from meteorological drought to agricultural drought over the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. J. Arid Land 2023, 151, 523–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, P.; Matilde, G.O.; Sonia, R.G. Multi-Scale Analysis of Agricultural Drought Propagation on the Iberian Peninsula Using Non-Parametric Indices. Water 2023, 15, 2032. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, R.B.; Jacobsen, A.L.; Ramirez, A.R.; Helms, A.M.; Traugh, C.A.; Tobin, M.F.; Heffner, M.S.; Davis, S.D. Mortality of resprouting chaparral shrubs after a fire and during a record drought: Physiological mechanisms and demographic consequences. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 20, 893–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Zhong, R.D.; Lai, C.G.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Lian, Y.Q.; Bai, X.Y. Climate change enhances the severity and variability of drought in the Pearl River Basin in South China in the 21st century. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 249, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, R.L.; Yao, R.; Shen, H.; Bian, Y.J. Responses of agricultural drought to meteorological drought under different climatic zones and vegetation types. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, B.; Shrestha, S.; Shrestha, P.K.; Talchabhadel, R. Evaluation and application of a SWAT model to assess the climate change impact on the hydrology of the Himalayan River Basin. Catena 2019, 181, 104082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederiksen, R.R.; Molina-Navarro, E. The importance of subsurface drainage on model performance and water balance in an agricultural catchment using SWAT and SWAT-MODFLOW. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 107058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Chang, J.X.; Wang, Y.M.; Jin, W.T.; Guo, A.J. Spatiotemporal Impacts of Climate, Land Cover Change and Direct Human Activities on Runoff Variations in the Wei River Basin, China. Water 2016, 8, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Q.; Fei, X.; Cong, M.; Guo, L. Impacts of manure application on swat model outputs in the xiangxi river watershed. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femeena, P.V.; Chaubey, I.; Aubeneau, A.; McMillan, S.K.; Wagner, P.D.; Fohrer, N. An improved process-based representation of stream solute transport in the soil and water assessment tools. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 2599–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathian, F.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Mansouri, B.; Vaheddoost, B. Assessment of water demand reliability using SWAT and RIBASIM models with respect to climate change and operational water projects. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 261, 107377. [Google Scholar]
- Josip, J.; Lidija, T. Fields of Application of SWAT Hydrological Model—A Review. Earth 2023, 4, 331–344. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models, part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Yapo, P. Status of automatic calibration for hydrologic models: Comparison with multilevel expert calibration. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1999, 4, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, K.M.; Vijay, P.S. A review of drought concepts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 202–216. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, S.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, S.H.; Kim, T. Analysis of drought intensity and trends using the modified SPEI in south Korea from 1981 to 2010. Water 2018, 10, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-moreno, J.I. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, K.M.; Zhu, X.Y.; Muhammad, A. Assessment of spatiotemporal characteristics of agro-meteorological drought events based on comparing Standardized Soil Moisture Index, Standardized Precipitation Index and Multivariate Standardized Drought Index. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Carrão, H.; Russo, S.; Sepulcre-Canto, G. An empirical standardized soil moisture index for agricultural drought assessment from remotely sensed data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 48, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.Q.; Jiang, G.Q.; Pei, Y.S.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.H. Hydrological drought assessment in the river basin based on Standard Water Resources Index (SWRI): A case study on the Northern Haihe River. Shuili Xuebao 2015, 46, 687–698, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Y.; Luo, L.F.; Chang, J.X.; Wang, Y.M.; Guo, A.J.; Fan, J.J.; Liu, Q. Hydrological drought evolution with a nonlinear joint index in regions with significant changes in underlying surface. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.W.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Yao, G.; Zhang, Y.K. Faulty Feeder Detection Method Based on VMD–FFT and Pearson Correlation Coefficient of Non-Power Frequency Component in Resonant Grounded Systems. Energies 2020, 13, 4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Gallardo, M.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Hannaford, J.; Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; Svoboda, M.; Dominguez-Castro, F.; Maneta, M.; Tomas-Burguera, M.; El Kenawy, A. Complex influences of meteorological drought time-scales on hydrological droughts in natural basins of the contiguous Unites States. J. Hydrol. 2018, 568, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.C.; Li, R.H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.P.; Zeng, L.L.; Tang, S.J.; Wang, W.; Li, D.R.; Niyogi, D. Drought propagation in Northern China Plain: A comparative analysis of GLDAS and MERRA-2 datasets. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hao, Z.C.; Feng, S.F.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Hao, F.H. Agricultural drought prediction in China based on drought propagation and large-scale drivers. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 107028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.T.; Liang, L.Q.; Jun, H.; Yan, D.H.; Wang, X.; Li, C.H.; Sun, T. Thresholds for triggering the propagation of meteorological drought to hydrological drought in water-limited regions of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.T.; Huang, Y.F.; Zhou, S.; Wang, K.Y.; Wang, G.Q. Effect partition of climate and catchment changes on runoff variation at the headwater region of the Yellow River based on the Budyko complementary relationship. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1166–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.X.; Wang, L.C.; Lin, A.W.; Liu, Z.J.; Li, Q.J.; Qu, S. Vegetation green up under the influence of daily minimum temperature and urbanization in the Yellow River Basin. China Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.X.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Yuan, M. Copula-based drought risk assessment combined with an integrated index in the Wei River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Z.M.; Yang, H.B.; Di, D.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Q.H.; Hussain, Z. Comprehensive evaluation of hydrological drought and its relationships with meteorological drought in the Yellow River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.H.; Ran, G.; Li, G.; Yu, Y.; Jian, S. The effects of rainfall characteristics and land use and cover change on runoff in the yellow river basin, China. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2021, 69, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X. Water and sediment yield response to extreme rainfall events in a complex large river basin: A case study of the yellow river basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 21010-2007; General Administration of Quality Supervision and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, National Standardization Administration, Classification of Land Use Status. S. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. China Standards Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Tao, G.; Si, Y.; Wei, Y.; Lian, G.; Xiao, S. Typical synoptic types of spring effective precipitation in inner Mongolia, China. Meteorol. Appl. 2014, 21, 330–339. [Google Scholar]
- Omer, A.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Saleem, F. Natural and anthropogenic influences on the recent droughts in Yellow River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ding, J.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhou, D.Y.; Zhu, Q. Investigation about the correlation and propagation among meteorological, agricultural and groundwater droughts over humid and arid/semi-arid basins in China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Bai, D.; Wang, F.; Fu, B.; Yan, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Long, D.; Feng, M. Quantifying the impacts of climate change and ecological restoration on streamflow changes based on a Budyko hydrological model in China’s loess plateau. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 6500–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.X.; Li, Y.Y.; Yuan, M.; Wang, Y.M. Efficiency evaluation of hydropower station operation: A case study of longyangxia station in the yellow river, China. Energy 2017, 135, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, C.C.; Pee, Q.S.; Luis, G. Drought Propagation under Combined Influences of Reservoir Regulation and Irrigation over a Mediterranean Catchment. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.M.; Huang, S.Z.; Zhao, J.; Leng, G.Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, H.B.; Li, Z. Long-chain propagation pathways from meteorological to hydrological, agricultural and groundwater drought and their dynamics in China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).