Raw Rice Husk Biochar as a Potential Valuable Industrial Byproduct for the Removal of Rhodamine B from Water
Abstract
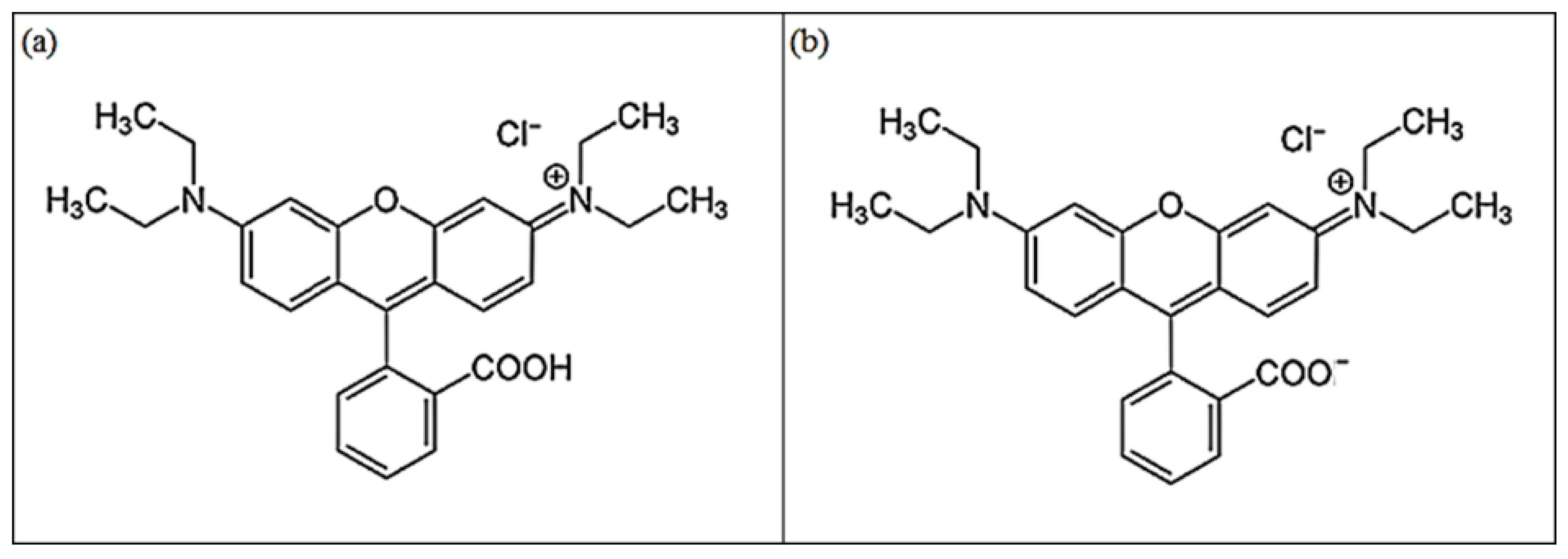
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Characterization of RRHB
2.3. RB Sorption Tests
2.4. RB Desorption Tests
3. Results and Discussion
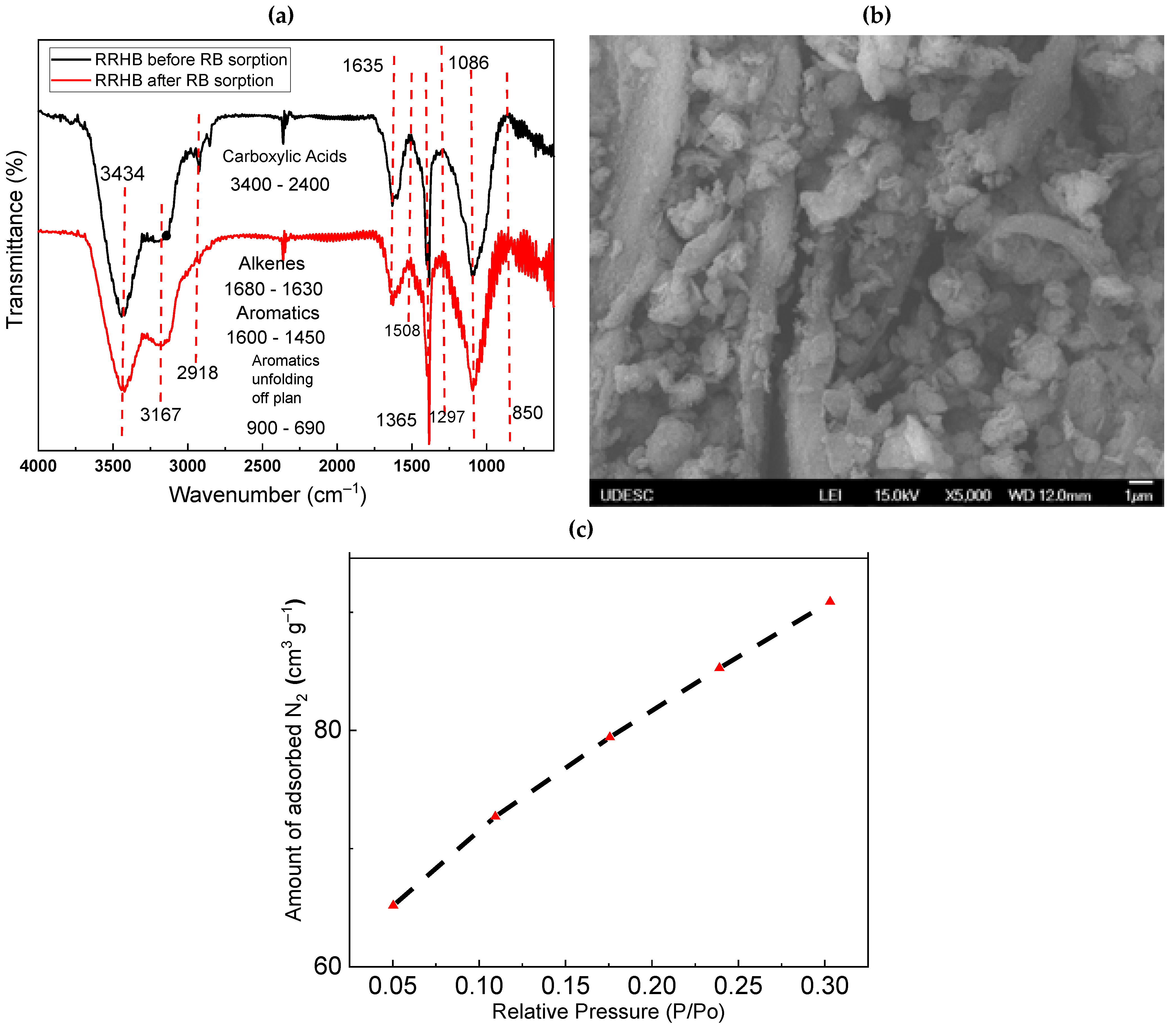
3.1. Characterization of RRHB
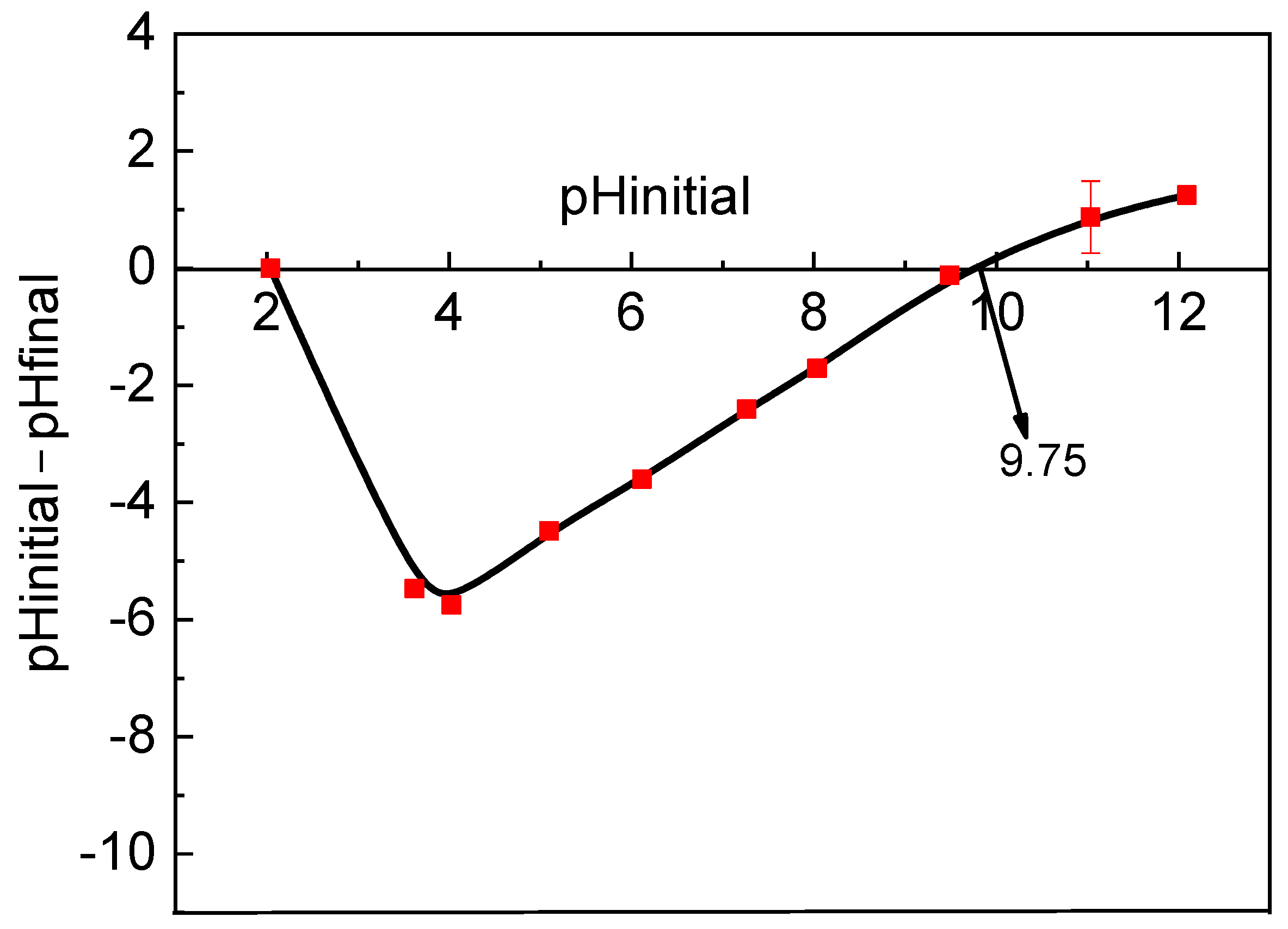
3.2. RB Sorption Variables
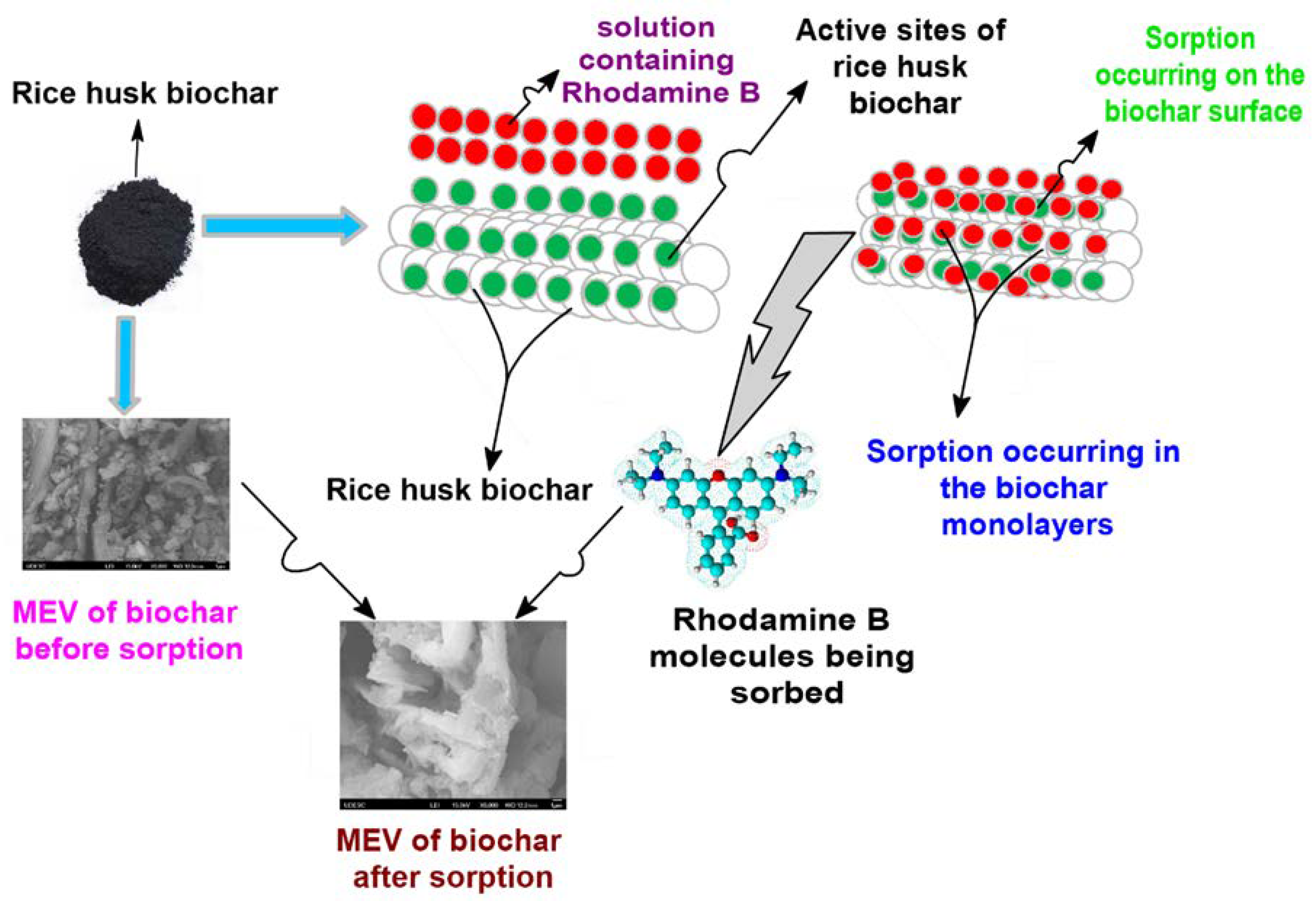
3.3. RB Sorption Kinetics on/in Biochar
3.4. Sorption Isotherm of RB on/in Biochar
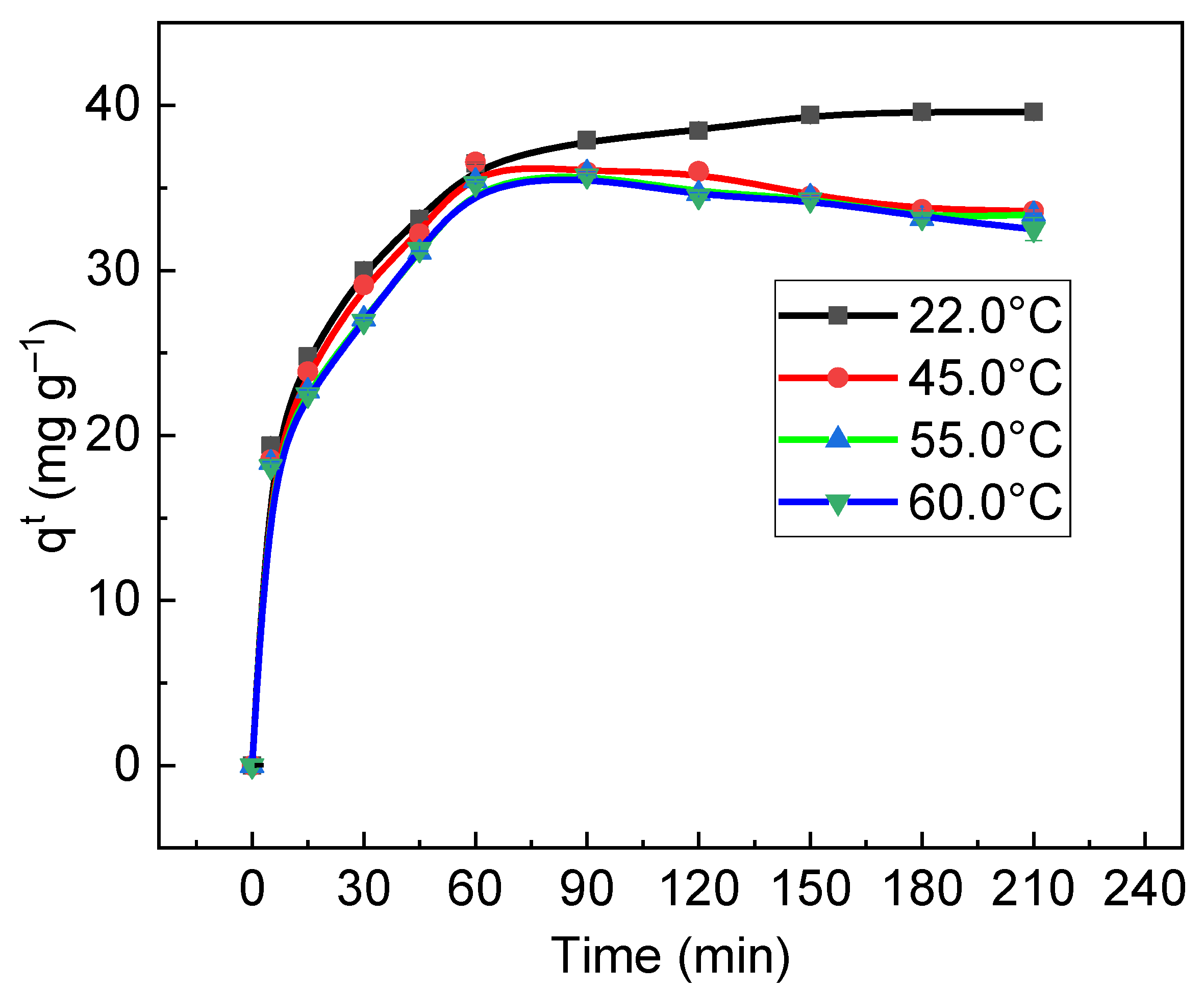
3.5. Thermodynamics of Sorption of RB on/in Biochar
3.6. Recovery of RB and Biochar
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Webb, J.; Hansen, W.; Desmond, A.; Fitzhugh, O. Water and Climate Change; Unesco: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, J.B.P.; Nogueira, P.F.; Becegato, V.A.; Becegato, V.R.; Paulino, A.T. Environmental Assessment and Toxic Metal-Contamination Level in Surface Sediment of a Water Reservoir in the Brazilian Cerrado. Water 2021, 13, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosini, D.N.; Becegato, V.A.; Dalalibera, A.; Vilela, P.B.; Xavier, J.d.A.; Duminelli, E.C. Avaliação Da Qualidade Dos Sedimentos Em Áreas Agrícolas Do Município de Bom Retiro/SC. Rev. Ibero-Am. Ciências Ambient. 2020, 11, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Available online: https://www.fao.org/home/en/ (accessed on 17 September 2023).
- Melchiors, M.S.; Piovesan, M.; Becegato, V.R.; Becegato, V.A.; Tambourgi, E.B.; Paulino, A.T. Treatment of Wastewater from the Dairy Industry Using Electroflocculation and Solid Whey Recovery. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.G.B.; Rodrigues, F.H.A.; Paulino, A.T.; Martins, A.F.; Fajardo, A.R. Recent Advances on Composite Hydrogels Designed for the Remediation of Dye-Contaminated Water and Wastewater: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, H.İ. A Versatile Hydrogel Including Bentonite and Gallocyanine for Trace Rhodamine B Analysis. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 513, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhi, T.; Prasad, A.L.; Manonmani, S. A Comparative Study of Microwave and Chemically Treated Acacia Nilotica Leaf as an Eco Friendly Adsorbent for the Removal of Rhodamine B Dye from Aqueous Solution. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mchedlov-Petrosyan, N.O.; Kholin, Y.V. Aggregation of Rhodamine B in Water. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2004, 77, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, C.A.; Guisolphi Gomes De Oliveira, L.J.; Geremias, R.; Stolberg, J. Biosorption of Rhodamine b from Aqueous Solution Using Araucaria Angustifolia Sterile Bracts. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2020, 36, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzen, M.; Sarı, A.; Saleh, T.A. Response Surface Optimization, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies for Effective Removal of Rhodamine B by Magnetic AC/CeO2 Nanocomposite. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Lacerda, V.; López-Sotelo, J.B.; Correa-Guimarães, A.; Hernández-Navarro, S.; Sánchez-Báscones, M.; Navas-Gracia, L.M.; Martín-Ramos, P.; Martín-Gil, J. Rhodamine B Removal with Activated Carbons Obtained from Lignocellulosic Waste. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 155, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, L.Y.; Mubarak, N.M.; Yee, M.J.; Yon, L.S.; Bing, C.H.; Khalid, M.; Abdullah, E.C. An Overview of Functionalised Carbon Nanomaterial for Organic Pollutant Removal. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 67, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, W.; Lin, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y. A Green Technology for the Preparation of High Capacitance Rice Husk-Based Activated Carbon. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramette, R.W.; Sandell, E.B. Rhodamine B Equilibria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1956, 78, 4872–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, T.L.; Orimolade, B.O.; Masekela, D.; Mamba, B.; Mabuba, N. The Application of Photoelectrocatalysis in the Degradation of Rhodamine B in Aqueous Solutions: A Review. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 26176–26191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulistina, D.R.; Martini, S. The Effect of Rhodamine B on the Cerebellum and Brainstem Tissue of Rattus Norvegicus. J. Public Health Res. 2020, 9, jphr.2020.1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.; Sharma, S.; Bhatt, U.; Soni, V. Toxic Effects of Rhodamine B on Antioxidant System and Photosynthesis of Hydrilla Verticillata. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2022, 3, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wu, N.; Du, J.; Zhou, L.; Lian, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, D. Occurrence of Rhodamine B Contamination in Capsicum Caused by Agricultural Materials during the Vegetation Process. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalina, F.; Abd Razak, A.S.; Krishnan, S.; Zularisam, A.W.; Nasrullah, M. A Review of Eco-Sustainable Techniques for the Removal of Rhodamine B Dye Utilizing Biomass Residue Adsorbents. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2022, 128, 103267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, P.; Xu, Y.; Song, C.; Yin, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wen, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Li, C.; et al. A Novel Strategy for the Removal of Rhodamine B (RhB) Dye from Wastewater by Coal-Based Carbon Membranes Coupled with the Electric Field. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 179, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gheethi, A.A.; Azhar, Q.M.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Yusuf, A.A.; Al-Buriahi, A.K.; Radin Mohamed, R.M.S.; Al-shaibani, M.M. Sustainable Approaches for Removing Rhodamine B Dye Using Agricultural Waste Adsorbents: A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, M.J.; Vieira, T.; Enzweiler, H.; Paulino, A.T. Chitosan/Wood Sawdust/Magnetite Composite Membranes for the Photodegradation of Agrochemicals in Water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolrahimi, N.; Tadjarodi, A. Adsorption of Rhodamine-B from Aqueous Solution by Activated Carbon from Almond Shell. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry, Online, 15 November–15 December 2019; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, T.; Artifon, S.E.S.; Cesco, C.T.; Vilela, P.B.; Becegato, V.A.; Paulino, A.T. Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for the Sorption of Metals and Dyes in Water: Isothermal, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Evaluations. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2021, 299, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhogbi, B.G.; Altayeb, S.; Bahaidarah, E.A.; Zawrah, M.F. Removal of Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Wastewater Using Activated Carbon from Palm Tree Fiber Waste. Processes 2021, 9, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, M.A.; Al-Qodah, Z.; Ngah, C.W.Z. Agricultural Bio-Waste Materials as Potential Sustainable Precursors Used for Activated Carbon Production: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 46, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonyadi, Z.; Kumar, P.S.; Foroutan, R.; Kafaei, R.; Arfaeinia, H.; Farjadfard, S.; Ramavandi, B. Ultrasonic-Assisted Synthesis of Populus Alba Activated Carbon for Water Defluorination: Application for Real Wastewater. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angin, D. Utilization of Activated Carbon Produced from Fruit Juice Industry Solid Waste for the Adsorption of Yellow 18 from Aqueous Solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 168, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Mohammadi, R.; Ramavandi, B. Elimination Performance of Methylene Blue, Methyl Violet, and Nile Blue from Aqueous Media Using AC/CoFe2O4 as a Recyclable Magnetic Composite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19523–19539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About the Theory of So-Lagergren, S. About the Theory of so-Called Adsorption of Solid Substance. Handlinger 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Ng, J.C.Y.; McKay, G. Kinetics of Pollutant Sorption by Biosorbents: Review. Sep. Purif. Methods 2000, 29, 189–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L.; Juang, R.-S. Characteristics of Elovich Equation Used for the Analysis of Adsorption Kinetics in Dye-Chitosan Systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Rossano, C.; Salucci, E.; Tesser, R.; Salmi, T.; Di Serio, M. Intraparticle Diffusion Model to Determine the Intrinsic Kinetics of Ethyl Levulinate Synthesis Promoted by Amberlyst-15. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 228, 115974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption Isotherm Models: Classification, Physical Meaning, Application and Solving Method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the Use and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherm Models: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, T.; Becegato, V.A.; Paulino, A.T. Equilibrium Isotherms, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics of the Adsorption of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid to Chitosan-Based Hydrogels. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, W.B.F.; Agassin, S.T.R.; Naidek, K.P.; Paulino, A.T. Pectin Hydrogels Modified with Montmorillonite: Case Studies for the Removal of Dyes and Herbicides from Water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.G.B.; Martins, A.F.; Paulino, A.T.; Fajardo, A.R.; Guilherme, M.R.; Faria, M.G.I.; Linde, G.A.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Recent Advances in Designing Hydrogels from Chitin and Chitin-Derivatives and Their Impact on Environment and Agriculture: A Review. Rev. Virtual Quim. 2017, 9, 370–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanauer, D.C.; de Souza, A.G.; Cargnin, M.A.; Gasparin, B.C.; Rosa, D.d.S.; Paulino, A.T. Pectin-Based Biohydrogels Reinforced with Eucalyptus Sawdust: Synthesis, Characterization, β-D-Galactosidase Immobilization and Activity. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 97, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadullah, M.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Kabir, M.S.; Mostofa, M.G.; Miyazawa, T. Chemical and Structural Evaluation of Activated Carbon Prepared from Jute Sticks for Brilliant Green Dye Removal from Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, P.; Martinez-Sanz, M.; Bonilla, M.R.; Wang, D.; Gilbert, E.P.; Stokes, J.R.; Gidley, M.J. Cellulose-Pectin Composite Hydrogels: Intermolecular Interactions and Material Properties Depend on Order of Assembly. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 162, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolls, J. Sorption of Veterinary Pharmaceuticals in Soils: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3397–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Site, A. Factors Affecting Sorption of Organic Compounds in Natural Sorbent/Water Systems and Sorption Coefficients for Selected Pollutants. A Review. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2001, 30, 187–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakatula, E.N.; Richard, D.; Neculita, C.M.; Zagury, G.J. Determination of Point of Zero Charge of Natural Organic Materials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7823–7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, C.A.; Vilela, P.B.; Becegato, V.A.; Paulino, A.T. Adsorption and Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution Using Sterile Bract of Araucaria Angustifolia as Novel Natural Adsorbent. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2019, 13, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparecida Matias, C.; Vilela, P.B.; Becegato, V.A.; Paulino, A.T. Adsorption Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid Herbicide in Novel Alternative Natural Adsorbents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, Y.; Nema, Y.; Matsuoka, K. Removal of Zwitterionic Rhodamine B Using Foam Separation. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez-Delgado, A.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, E.; Fernández-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Fernández-Calviño, D.; Conde-Cid, M.; Arias-Estévez, M. Introduction. In Sorbents Materials for Controlling Environmental Pollution; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, J.d.P.; Souza, J.A.d.; Cavalheiro, É.T.G. Characterization of Commercial Samples of Vermicompost from Bovine Manure and Evaluation of the Influence of PH and Time on Co(II), Zn(II) and Cu(II) Adsorption. Quim. Nova 2004, 27, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Kumar, R. Adsorption Studies of Hazardous Malachite Green onto Treated Ginger Waste. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, A.A.; Da Rosa, A.L.D.; Carissimi, E. Adsorption of Rhodamine B onto Commercial Activated Coal. Rev. CIATEC-UPF 2019, 11, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, W.; Smith, J.; Harriott, P. Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering, 7th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Giles, C.H.; MacEwan, T.H.; Nakhwa, S.N.; Smith, D. Studies in Adsorption. Part XI. A System of Classification of Solution Adsorption Isotherms, and Its Use in Diagnosis of Adsorption Mechanisms and in Measurement of Specific Surface Areas of Solids. J. Chem. Soc. 1960, 111, 3973–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.C.; Goyal, M. Activated Carbon Adsorption; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 9781420028812. [Google Scholar]
- Cooney, D.O. Adsorption Design for Wastewater Treatment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Do Nascimento, R.F.; de Lima, A.C.A.; Vidal, C.B.; Melo, D.d.Q.; Raulino, G.S.C. Adsorção: Aspectos Teóricos e Aplicações Ambientais, 1st ed.; UFC, Editora: Fortaleza, Bazil, 2014; ISBN 9788574851860. [Google Scholar]
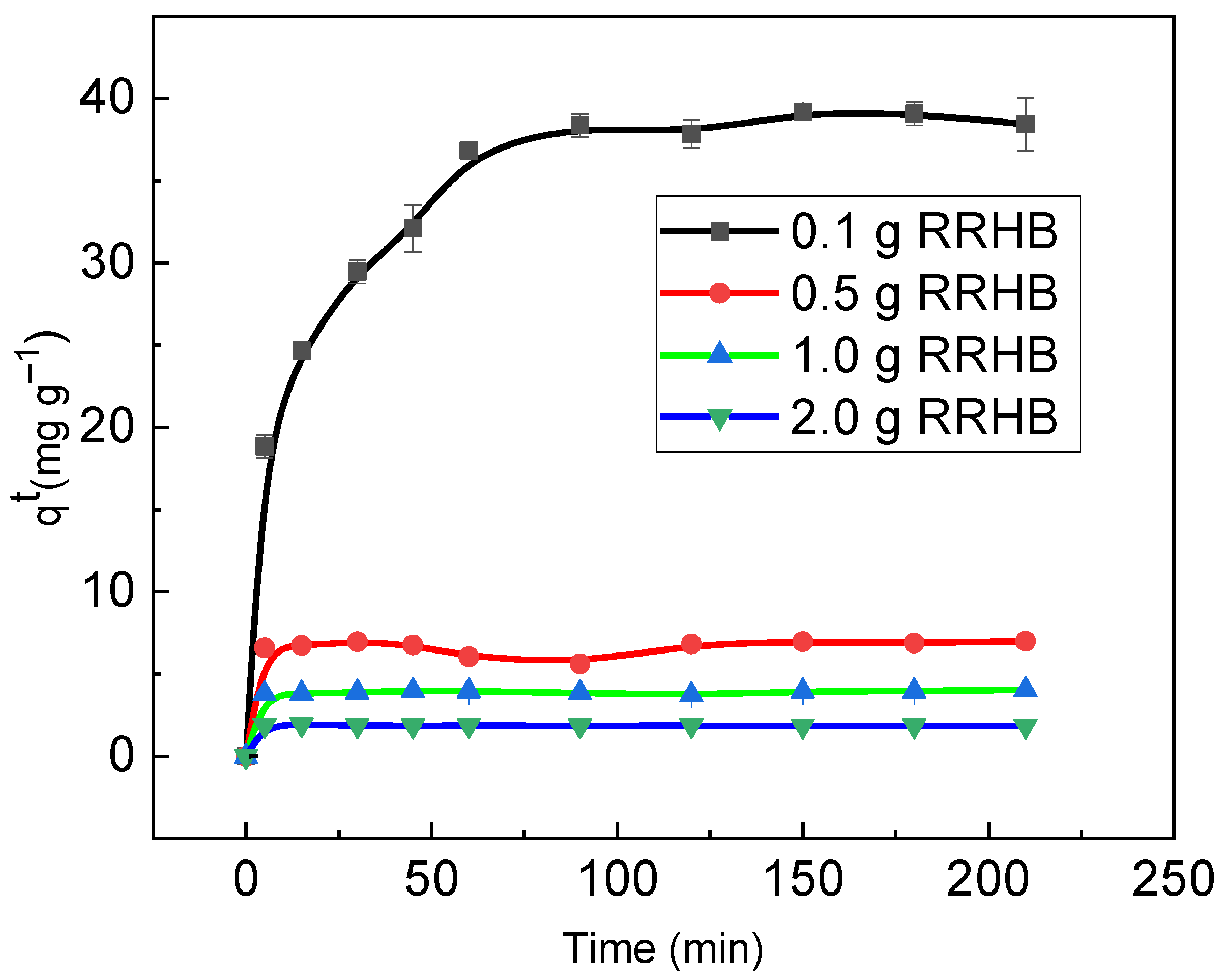

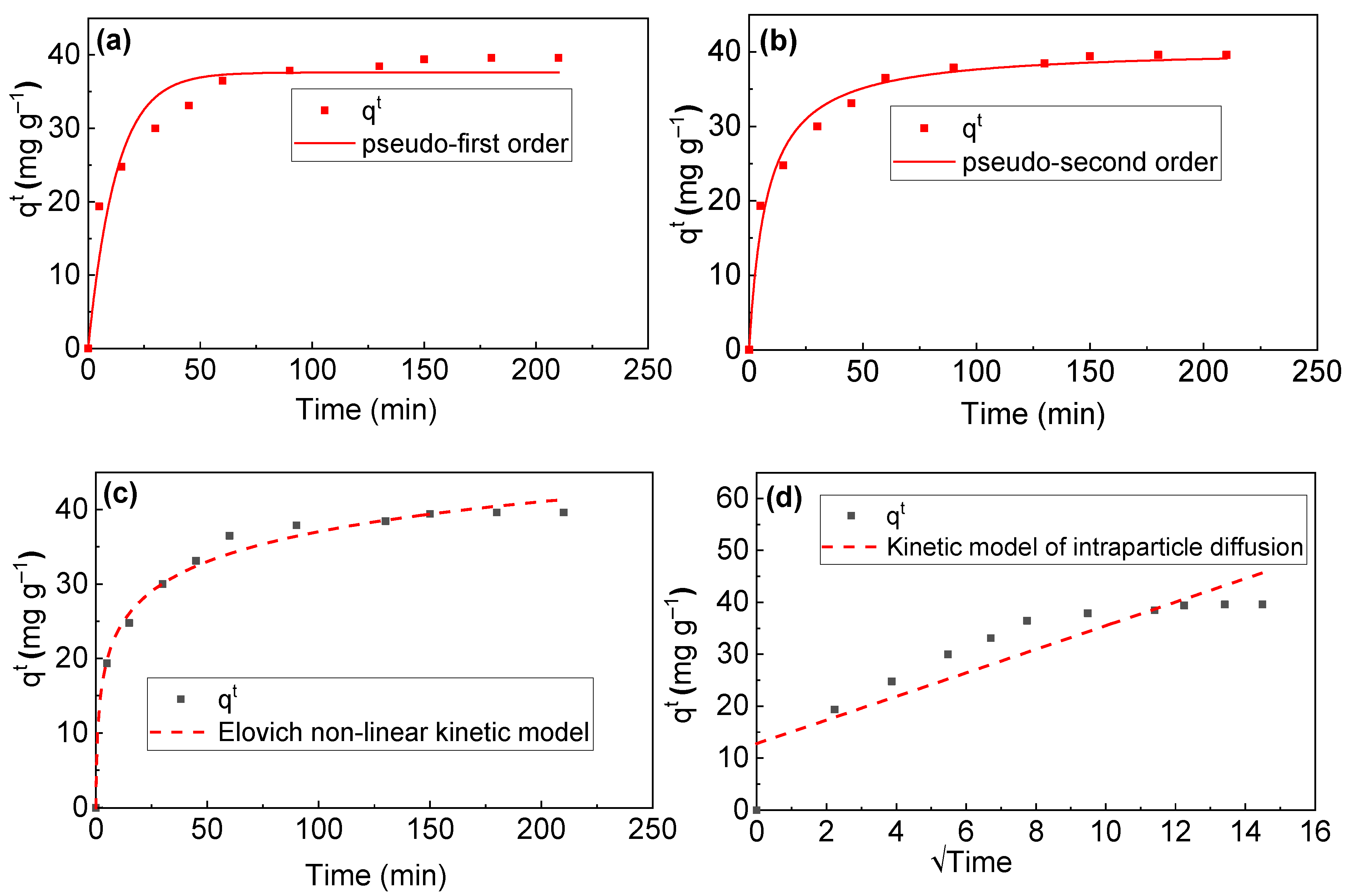
| Kinetic Model | Qmaxcalc (mg g−1) | Qmax ex (mg g−1) | χ2 | k (min−1) | α | β | R2 | Adj.R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFO | 37.60 | 39.40 | 10.3 | 0.08 | 0.9303 | 0.9340 | ||
| PSO | 40.60 | 39.40 | 2.79 | 0.03 | 0.9810 | 0.9805 | ||
| E | 1.56 | 33.90 | 0.17 | 0.9902 | 0.9801 | |||
| ID | 2.28 | 0.78 | 0.7572 |
| Model | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Langmuir | KL = 3.67 × 10−4 L mg−1 |
| RL = 0.063 | |
| R2 = 0.7709 χ2 = 117.2 | |
| Freundlich | KF = 1363.9 mg g−1 L mg−1 |
| nF = 3.34 | |
| R2 = 0.9501 χ2 = 21.0 | |
| Sips | Ks = 110.68 L mg−1 |
| ns = 1.0 × 10−10 | |
| R2 = 0.77 χ2 = 146.47 | |
| Redlich–Peterson | KRP = 110.68 L mg−1 |
| nRP = 122.09 | |
| R2 = 0.77 χ2 = 146.47 |
| Temperature (K) | Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔG°s (J mol−1) | ΔH°s (J mol−1) | ΔS°s (J mol−1) | R2 | |
| 295.15 | −6069.38 | −6019.03 | 0.17 | 0.9802 |
| 318.15 | −6073.31 | |||
| 328.15 | −6075.01 | |||
| 333.15 | −6075.87 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agassin, S.T.R.; Dognini, J.; Paulino, A.T. Raw Rice Husk Biochar as a Potential Valuable Industrial Byproduct for the Removal of Rhodamine B from Water. Water 2023, 15, 3849. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213849
Agassin STR, Dognini J, Paulino AT. Raw Rice Husk Biochar as a Potential Valuable Industrial Byproduct for the Removal of Rhodamine B from Water. Water. 2023; 15(21):3849. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213849
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgassin, Sedami Tozoun Romain, Jocinei Dognini, and Alexandre Tadeu Paulino. 2023. "Raw Rice Husk Biochar as a Potential Valuable Industrial Byproduct for the Removal of Rhodamine B from Water" Water 15, no. 21: 3849. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213849
APA StyleAgassin, S. T. R., Dognini, J., & Paulino, A. T. (2023). Raw Rice Husk Biochar as a Potential Valuable Industrial Byproduct for the Removal of Rhodamine B from Water. Water, 15(21), 3849. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213849







