The Study on the Genesis of Underground Brine in Laizhou Bay Based on Hydrochemical Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
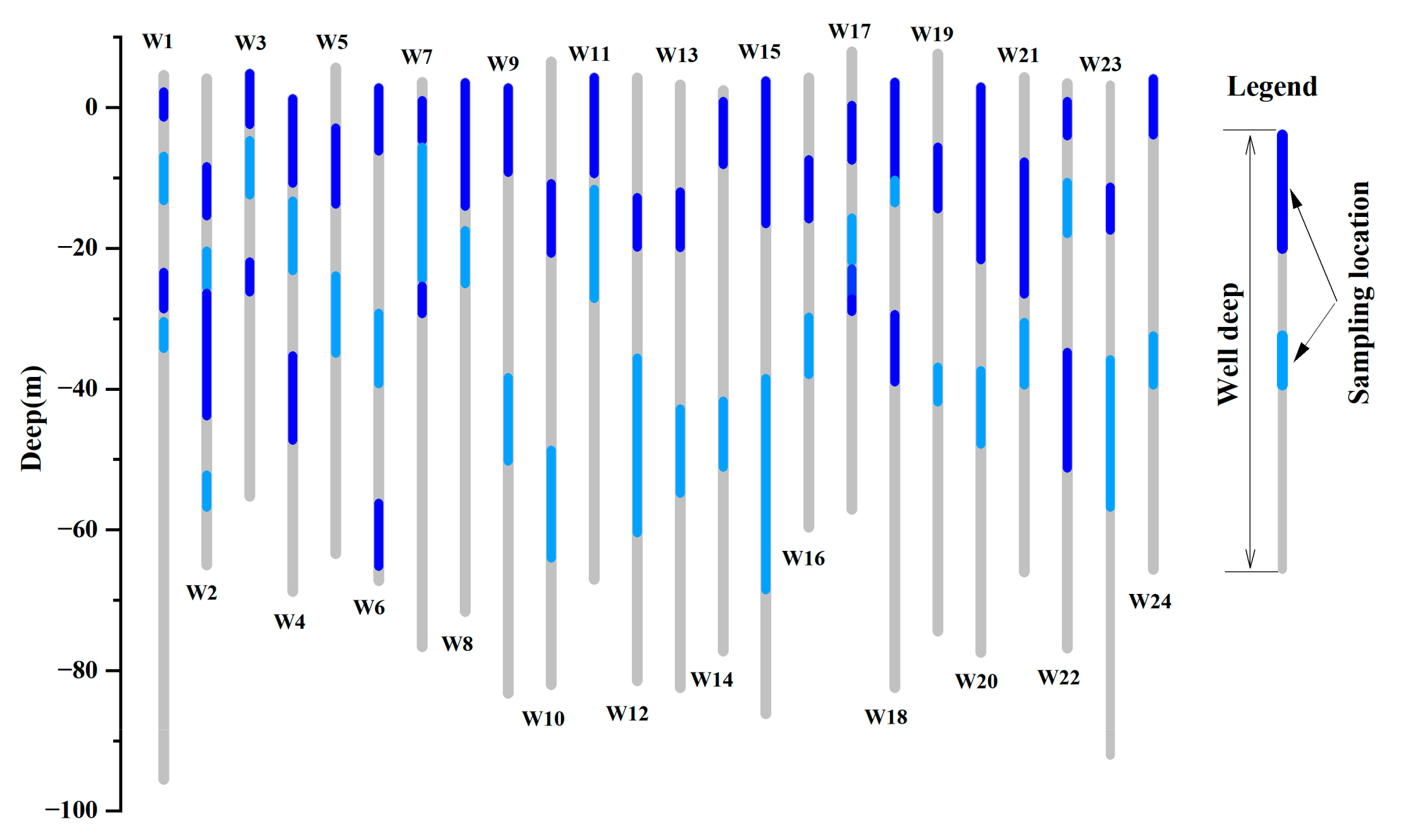
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Research Methods
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Analysis
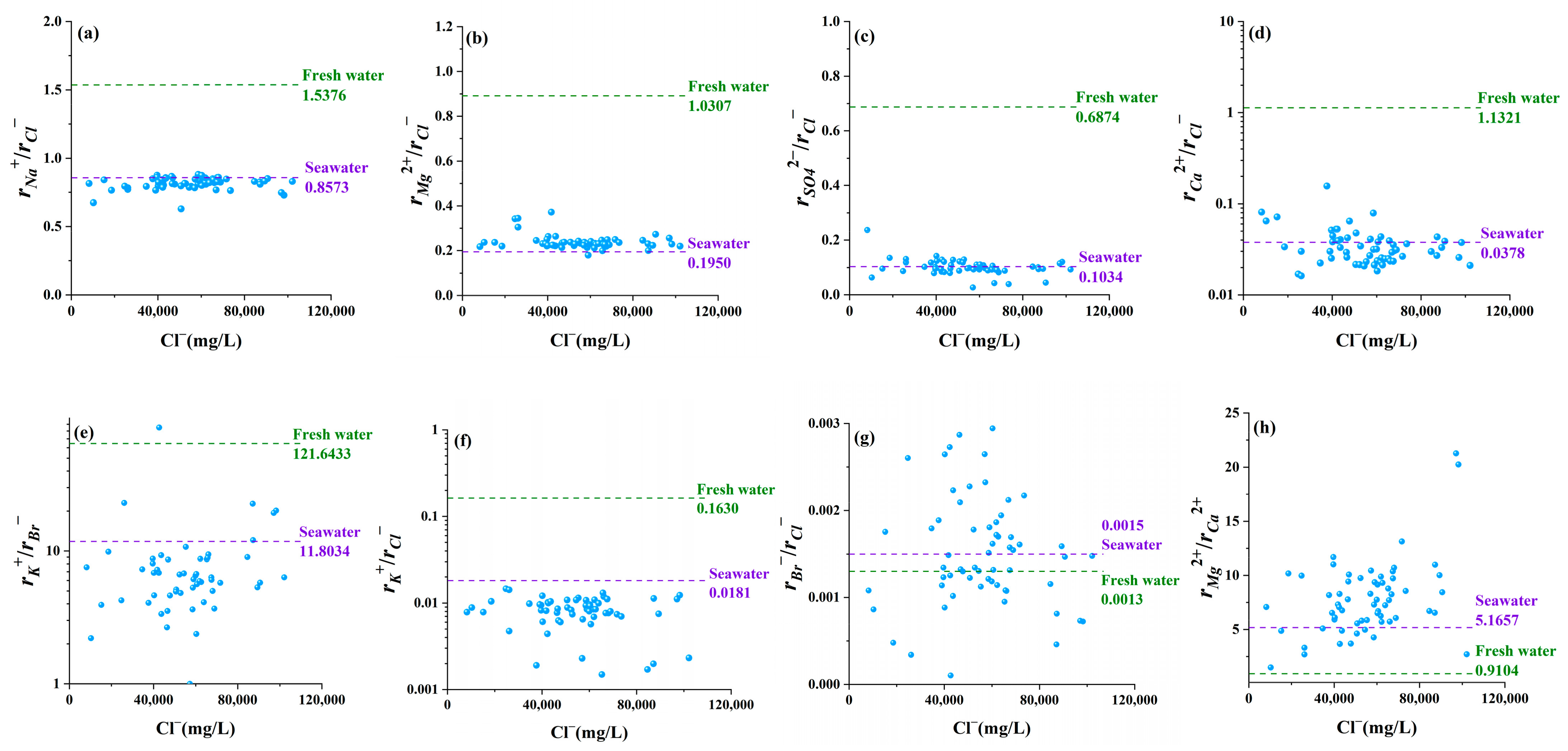
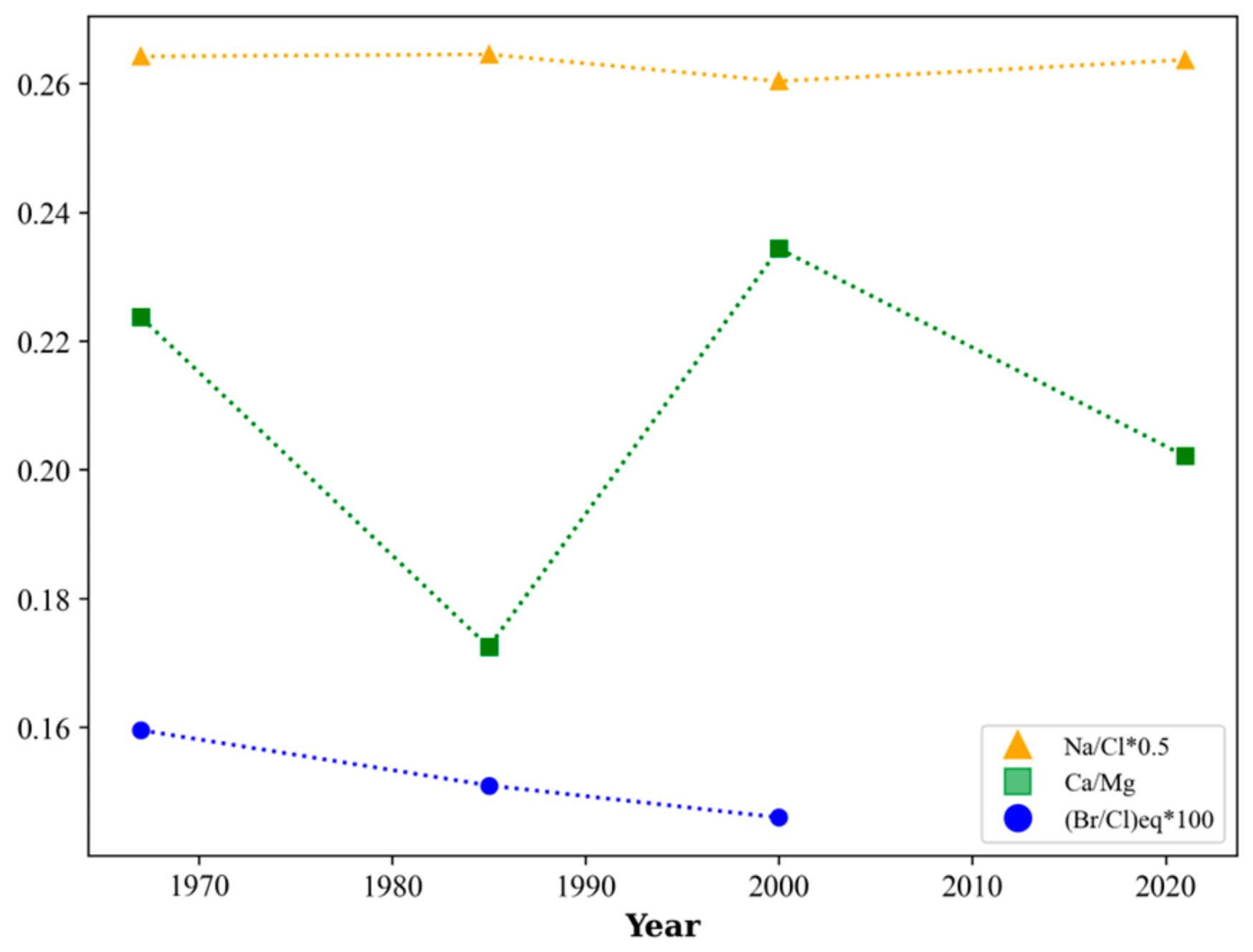
3.2. Relationship between Major Ionic Ratios and Cl
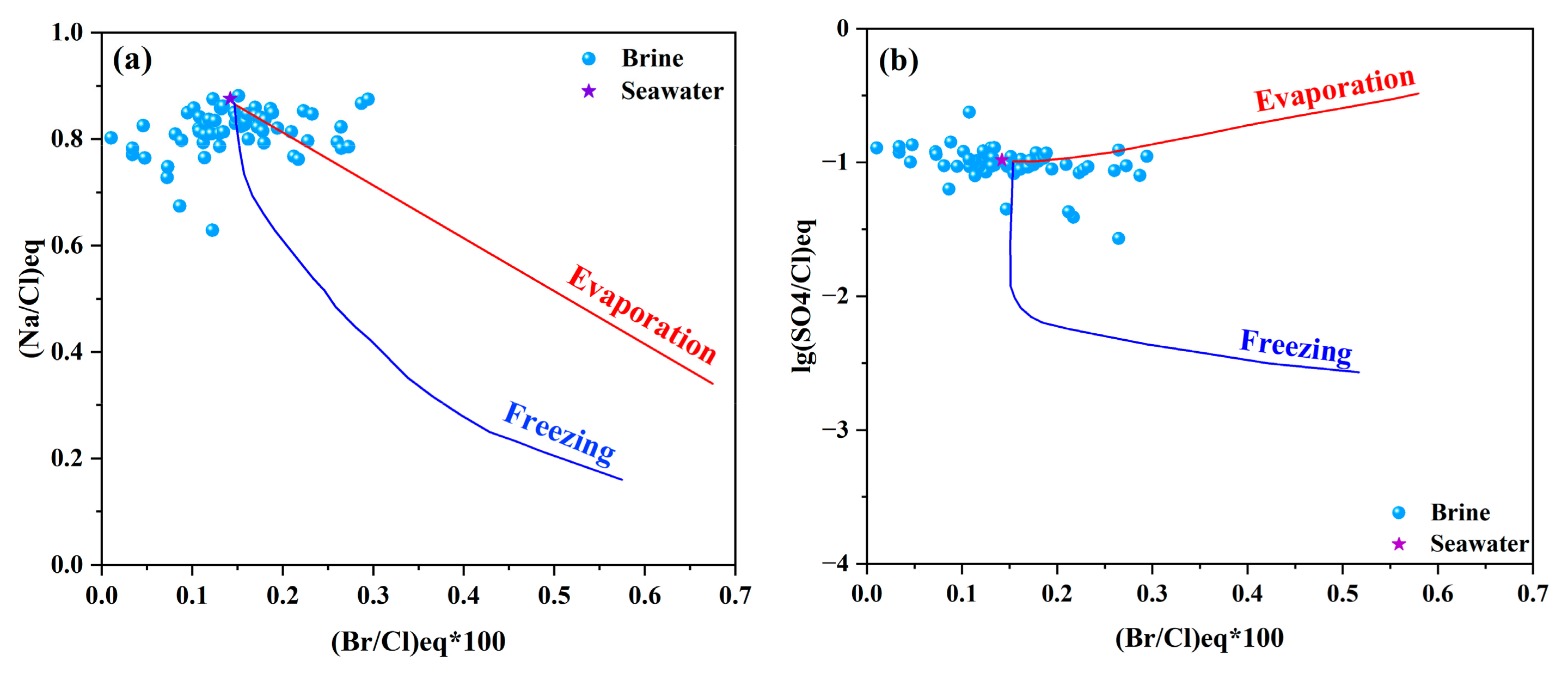
3.3. Na/Cl-Br/Cl and SO4/Cl-Br/Cl
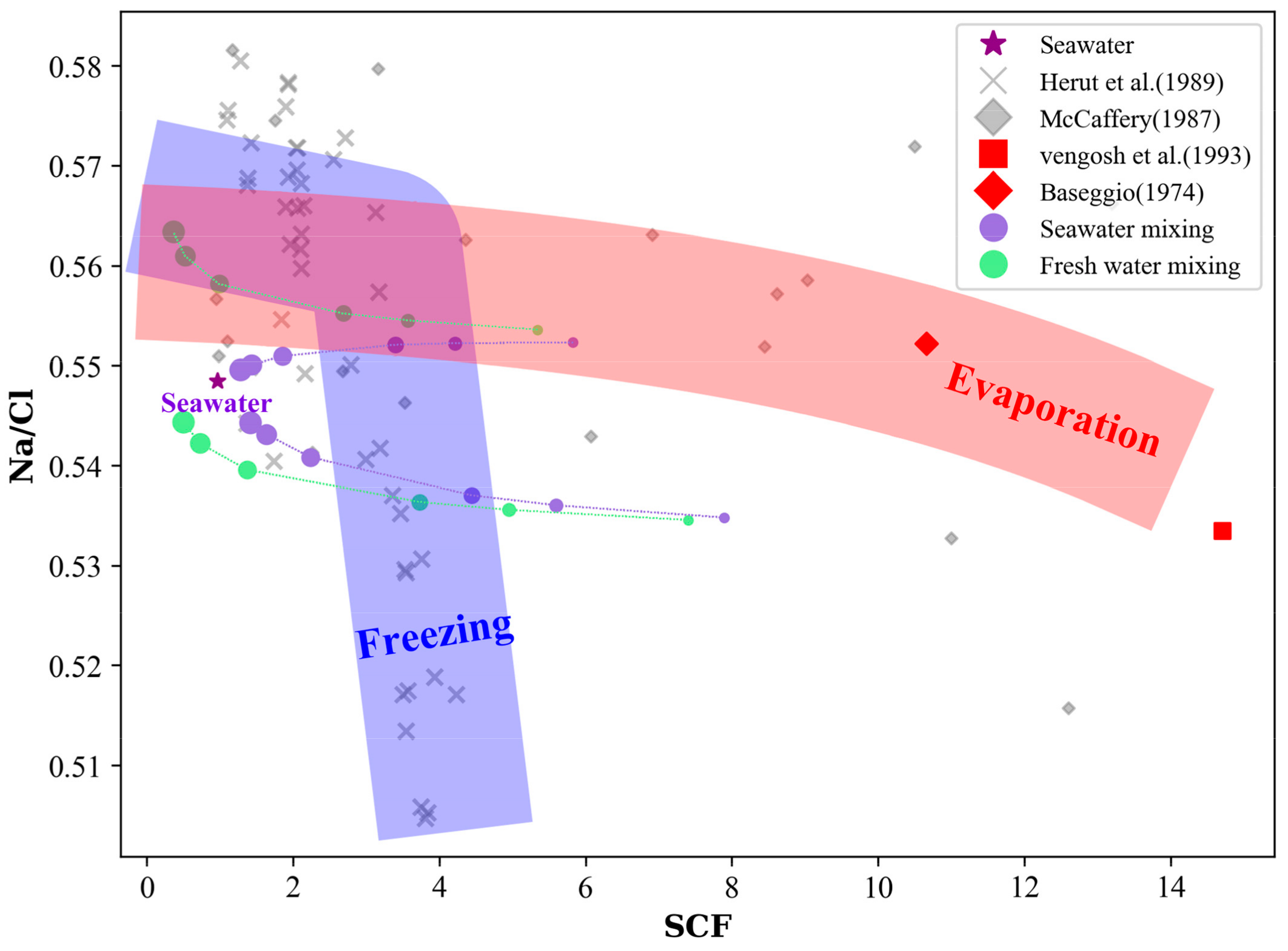
3.4. Na/Cl-SCF and Ca/Mg-SCF
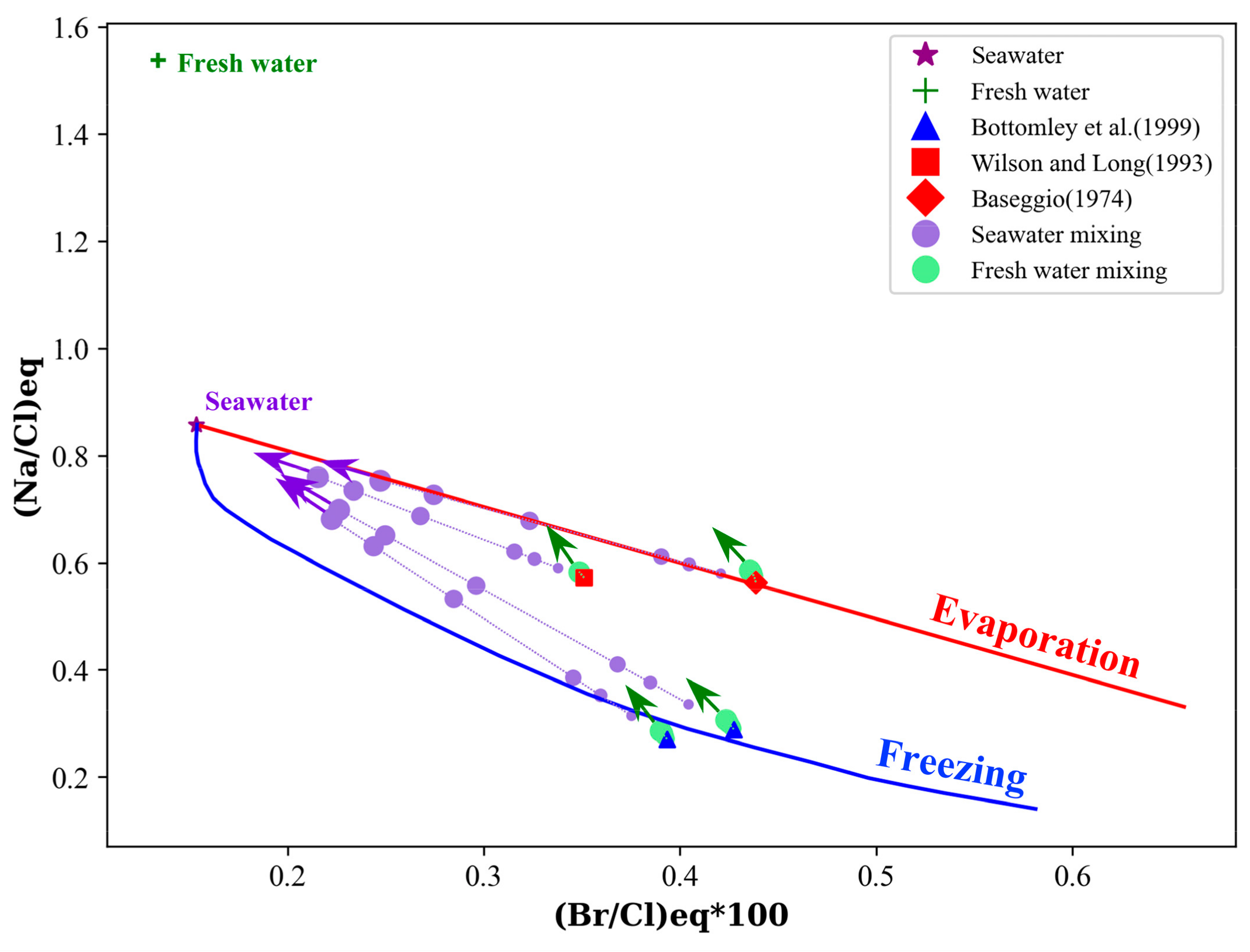
3.5. Mixing Simulation
4. Discussion
4.1. Sources of Brine Chemical Components
4.2. Seawater Concentration Pathways
4.3. Effects of Mixing
4.4. Impact of Other Factors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Starinsky, A.; Katz, A. The formation of natural cryogenic brines. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Y.; Frank, T.D.; Fielding, C.R. Cryogenic brine and its impact on diagenesis of glaciomarine deposits, mcmurdo sound, antarctica. J. Sediment. Res. 2018, 88, 898–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahana, G.; Cooper, Z.S.; Carpenter, S.D.; Deming, J.W.; Eicken, H. Intra-ice and intra-sediment cryopeg brine occurrence in permafrost near Utqia vik (Barrow). Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2021, 32, 427–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, T.D.; Haacker, E.M.K.; Fielding, C.R.; Yang, M.Y. Origin, distribution, and significance of brine in the subsurface of Antarctica. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 234, 104204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaffrey, M.A.; Lazar, B.; Holland, H.D. The evaporation path of sea water and the coprecipitation of Br− and K+ with halite. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1987, 57, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herut, B.; Starinsky, A.; Katz, A.; Bein, A. The roll of seawater freezing in the formation of subsurface brines. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Xu, X.; Liang, J.; Yang, C.; Huang, M.; Su, Q. Machine learning-based seawater concentration pathway prediction. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 94, 107336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, A.B. Origin and chemical evolution of brines in sedimentary basins. Okla. Geol. 1978, 79, 60–77. [Google Scholar]
- Hanor, J.S.; McIntosh, J.C. Diverse origins and timing of formation of basinal brines in the Gulf of Mexico sedimentary basin. Geofluids 2007, 7, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Z. Reearch progress of quaternary underground brine along coastal areas of the Bohai Sea in Shandong province. Shandong Land Resour. 2014, 30, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Wu, H. The origin of undground brines in the coastal plain of Laizhou Bay. Geol. Rev. 1982, 28, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Cheng, Z. Composition research for underground brine along ShanDong coastal flatlands on Bohai Sea. Mar. Sci. Bull. 1990, 9, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, L.; Liu, X. The geochemical anomaly and its causes in the concentrated underground seawater of Laizhou Bay. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1990, 21, 585–588. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, H. Characteristics of sedimentary seawater in post-Pleistocene strata on the south coast of Laizhou Bay and its formation environment. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1996, 18, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Meng, G.; Wang, S. Geochemistry modeling of quaternary subsurface brines in sourh coast of the Laizhou Bay, the Bohai Sea-taking brines from core-aoli501 in Changyi area as an example. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2003, 23, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M.; Song, X.F.; Currell, M.J.; Yang, J.L.; Xiao, G.Q. Chemical and isotopic constraints on evolution of groundwater salinization in the coastal plain aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Ma, T.; Chen, L.; Shan, H.; Xiao, C.; Lu, Y.; Liu, C.; Cai, H. Genesis of salinized groundwater in Quaternary aquifer system of coastal plain, Laizhou Bay, China: Geochemical evidences, especially from bromine stable isotope. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 59, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Ma, C.; Zhou, A.; Qi, H.; Liu, C.; Cai, H.; Zhu, H. Using hydrochemical and stable isotopic (delta H-2, delta O-18, delta B-11, and delta Cl-37) data to understand groundwater evolution in an unconsolidated aquifer system in the southern coastal area of Laizhou Bay, China. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 90, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Chen, X.; Guan, Q.; Tian, C.; Liu, D.; Xu, D. Study on the Sources of Salinity of Groundwater in Holocene and Late Pleistocene Sediments Based on Hydrochemical and Isotopic Methods in Southern Laizhou Bay. Water 2022, 14, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Meng, G.; Wang, S. Quaternary Underground Brine in the Coastal Areas of the Northern China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Kohfahl, C.; Song, X.; Xiao, G.; Yang, J. Geochemical and isotopic evidence for palaeo-seawater intrusion into the south coast aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 863–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.Q.; Wu, J.C.; Ye, S.J.; Zhang, Y.X. Hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical studies for salt water intrusion on the south coast of Laizhou Bay, China. Ground Water 2000, 38, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Liu, S.; Jia, C.; Gao, M.S.; Chang, W.B.; Wang, Y.J. Hydrochemical characteristics and functions of groundwater in southern Laizhou Bay based on the multivariate statistical analysis approach. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 250, 107153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landmeyer, J.E.; Belval, D.L. Water-Chemistry and Chloride Fluctuations in the Upper Floridan Aquifer in the Port Royal Sound Area, South Carolina, 1917–93; Water-Resources Investigations Report 96-4102; U.S. Geological Survey: Columbia, SC, USA, 1996.
- Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Su, Q.; Tong, H.; Xu, X.; Gao, Z.; Liu, W. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Irrigation Suitability Evaluation of Groundwater with Different Degrees of Seawater Intrusion. Water 2020, 12, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karro, E.; Marandi, A.; Vaikmae, R. The origin of increased salinity in the Cambrian-Vendian aquifer system on the Kopli Peninsula, northern Estonia. Hydrogeol. J. 2004, 12, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, C. Progress on Hydrogeochemical Method Applied in Groundwater Stud. Yellow River 2019, 41, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.-Y.; Peng, T.-R.; Liou, T.-S. Identification of the origin of salinization in groundwater using multivariate statistical analysis and geochemical modeling: A case study of Kaohsiung, Southwest Taiwan. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, L.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Bertrand, G.; Kloppmann, W.; Aquilina, L.; Martins, V.; Hirata, R.; Montenegro, S.; Pauwels, H.; Chatton, E.; et al. Origins and processes of groundwater salinization in the urban coastal aquifers of Recife (Pernambuco, Brazil): A multi-isotope approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 530, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bein, A.; Arad, A. Formation of saline groundwaters in the baltic region through freezing of seawater during glacial periods. J. Hydrol. 1992, 140, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottomley, D.J.; Katz, A.; Chan, L.H.; Starinsky, A.; Douglas, M.; Clark, I.D.; Raven, K.G. The origin and evolution of Canadian Shield brines: Evaporation or freezing of seawater? New lithium isotope and geochemical evidence from the Slave craton. Chem. Geol. 1999, 155, 295–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yu, Z.; Ning, J.; Chen, H.; Mi, T. Genesis of underground brine along south coast of Laizhou Bay: Hydrochemical characteristics. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2006, 24, 435–442. [Google Scholar]
- Baseggio, G. The Composition of Sea Water and Its Concentration. Fourth Symp. Salt North. Ohio Geol. Soc. 1974, 2, 351–358. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, T.P.; Long, D.T. Geochemistry and isotope chemistry of michigan basin brines—Devonian formations. Appl. Geochem. 1993, 8, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A.; De Lange, G.J.; Starinsky, A. Boron isotope and geochemical evidence for the origin of Urania and Bannock brines at the eastern Mediterranean: Effect of water-rock interactions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 3221–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Yu, H.; Peng, C.; Xu, X. The Hydrochemical Characteristics of Underground Brine along the South of Laizhou Bay. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1010–1012, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhu, W.; Zhong, Z. Basic Course for Hydrographic Geochemistry; Geology Press: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, J.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, X. Chemical composition of underground brine in shore along Laizhou Bay. Mar. Sci. 2005, 29, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.; Hou, G. Evolutionary process of saline-water intrusion in Holocene and Late Pleistocene groundwater in southern Laizhou Bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C. Origin and evolution of underground brine in coastal plain of laizhoui bay. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 1993, 9, 78–96. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, A.B.; Trout, M.L.; Pickett, E.E. Preliminary report on the origin and chemical evolution of lead and zinc rich oil field brines in central Mississippi. Econ. Geol. 1974, 69, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Zhang, D.; Tan, Z. Ground brine resource and its exploitation in shandong province. Geol. Surv. Res. 2008, 31, 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Q.; Hang, H.; Guan, C. Utilization of underground brine resources and phase diagram analysis in Laizhou Bay. J. Salt Sci. Chem. Ind. 2023, 4, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Yuan, C. Evaluation of underground brine resources along the northern coast of Laizhou Bay. Sea-Lake Salt Ind. Chem. Eng. 2000, 29, 38–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]



| Parameters | Average Value (mg/L) | Percentage of Meq (Brine) | Brine/ Seawater | Brine/ Freshwater | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brine | Seawater | Freshwater | ||||
| Na+ | 29,275 | 10,760 | 104.80 | 37.26% | 2.72 | 279.34 |
| K+ | 513 | 387 | 18.90 | 0.38% | 1.33 | 27.16 |
| Mg2+ | 4475 | 1294 | 37.14 | 10.77% | 3.46 | 120.48 |
| Ca2+ | 1044 | 413 | 67.26 | 1.52% | 2.53 | 15.52 |
| Cl− | 55,214 | 19,353 | 105.10 | 45.57% | 2.85 | 525.37 |
| SO42− | 7255 | 2712 | 97.89 | 4.42% | 2.68 | 74.11 |
| Br− | 185 | 67 | 0.32 | 0.07% | 2.76 | 581.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Yu, Y.; Su, Q.; Yang, L.; Fu, T.; Liu, W.; Chen, G.; Lyu, W. The Study on the Genesis of Underground Brine in Laizhou Bay Based on Hydrochemical Data. Water 2023, 15, 3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213788
Chen B, Yu Y, Su Q, Yang L, Fu T, Liu W, Chen G, Lyu W. The Study on the Genesis of Underground Brine in Laizhou Bay Based on Hydrochemical Data. Water. 2023; 15(21):3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213788
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Bo, Ying Yu, Qiao Su, Lin Yang, Tengfei Fu, Wenquan Liu, Guangquan Chen, and Wenzhe Lyu. 2023. "The Study on the Genesis of Underground Brine in Laizhou Bay Based on Hydrochemical Data" Water 15, no. 21: 3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213788
APA StyleChen, B., Yu, Y., Su, Q., Yang, L., Fu, T., Liu, W., Chen, G., & Lyu, W. (2023). The Study on the Genesis of Underground Brine in Laizhou Bay Based on Hydrochemical Data. Water, 15(21), 3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213788






