Heavy Metal Content in Fish of the Barguzin River (Eastern Cisbaikalia) and Assessment of Potential Risks to Human Health
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water and Sediments Sampling
2.3. Fish Sampling
2.4. Laboratory Analyses
2.5. Calculation of Accumulation Levels
2.5.1. Contamination Factor for HMs in the Sediments
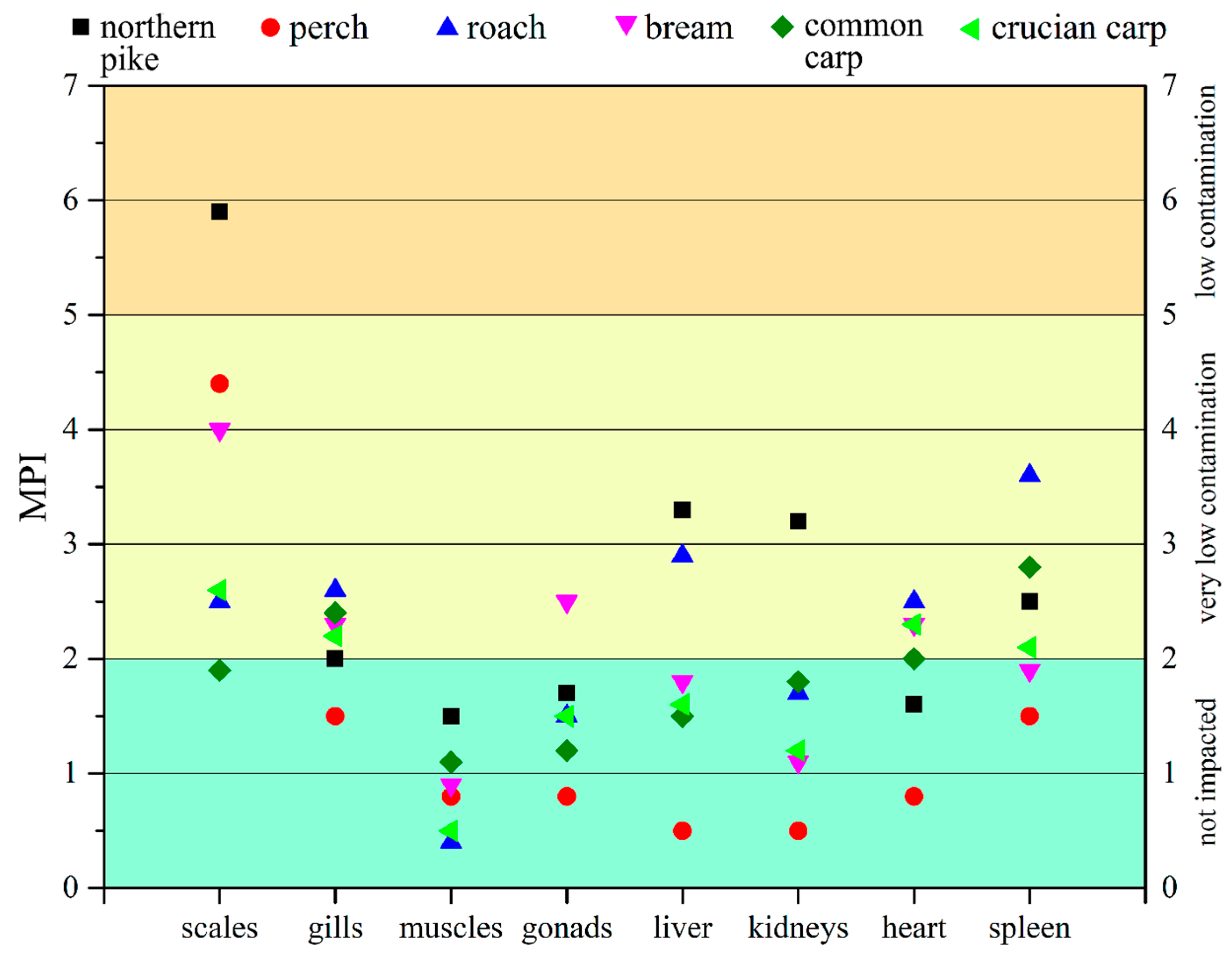
2.5.2. Metal Pollution Index (MPI) of Fish Organs and Tissues
2.6. Human Health Risk Assessment
2.6.1. Fish Condition Factor
2.6.2. Target Hazard Quotient
2.6.3. The Hazard Index
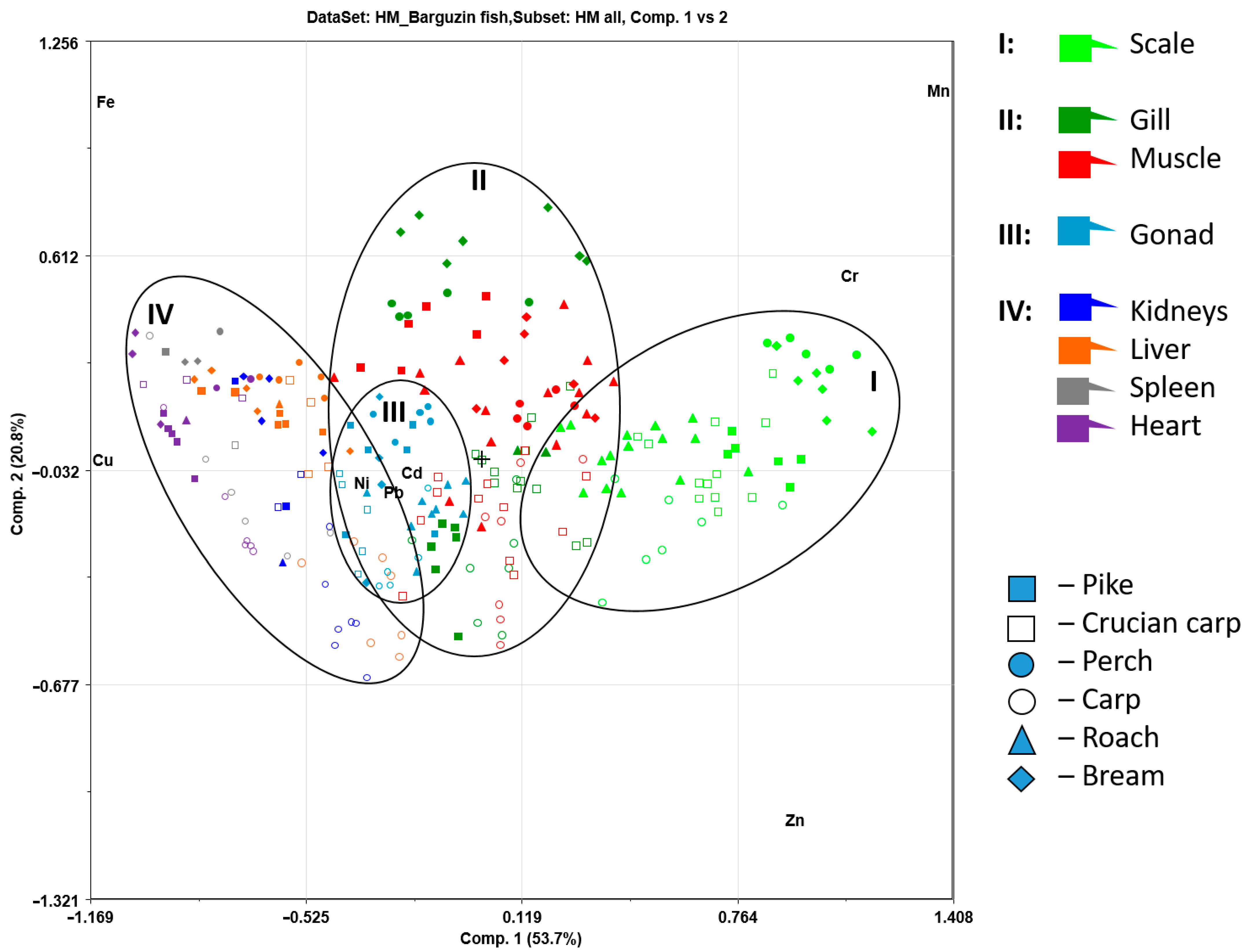
2.7. Principal Component Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
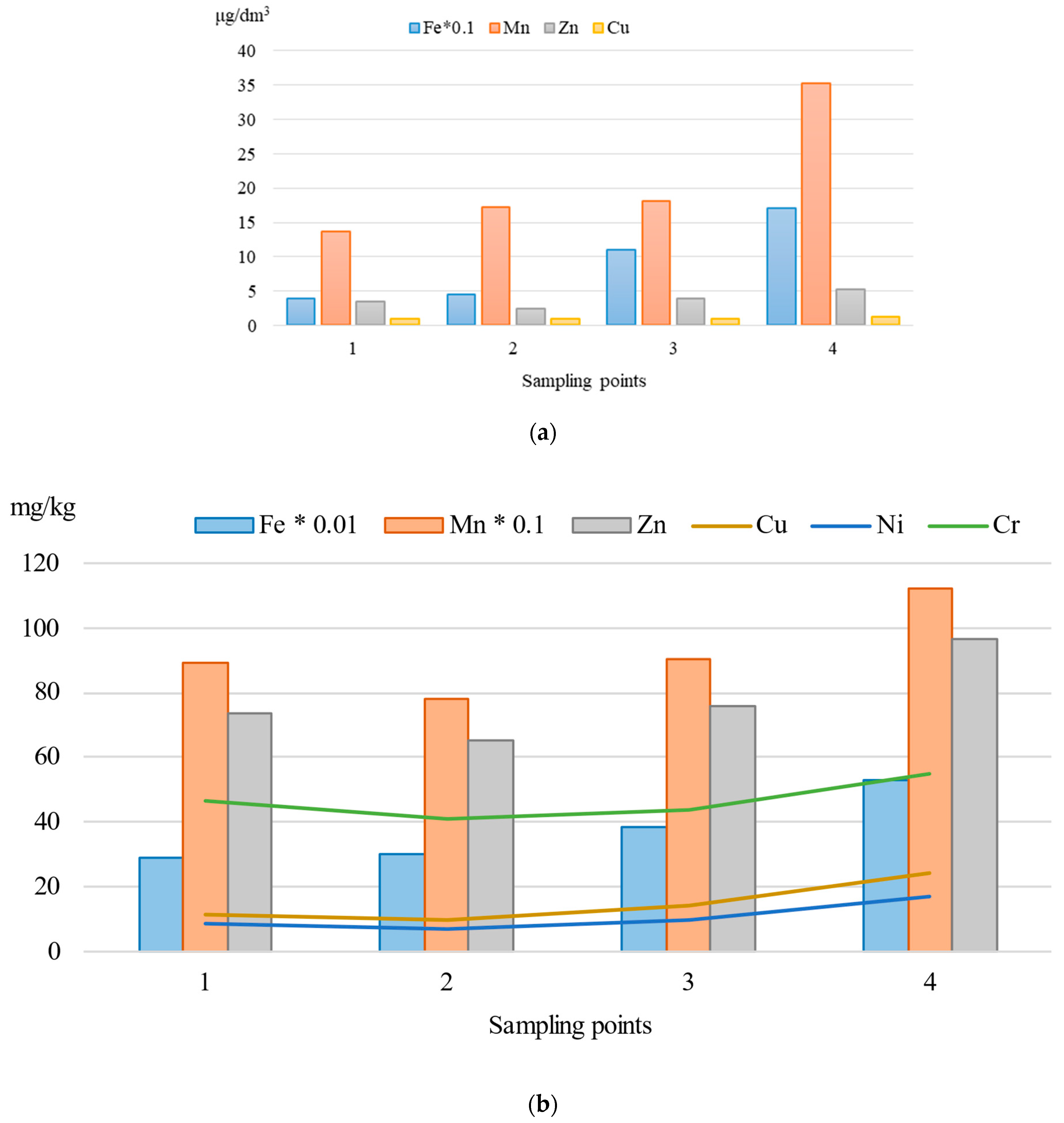
3.1. Heavy Metal Content in Water and Sediments of the Barguzin River
3.2. Fish Biometrics
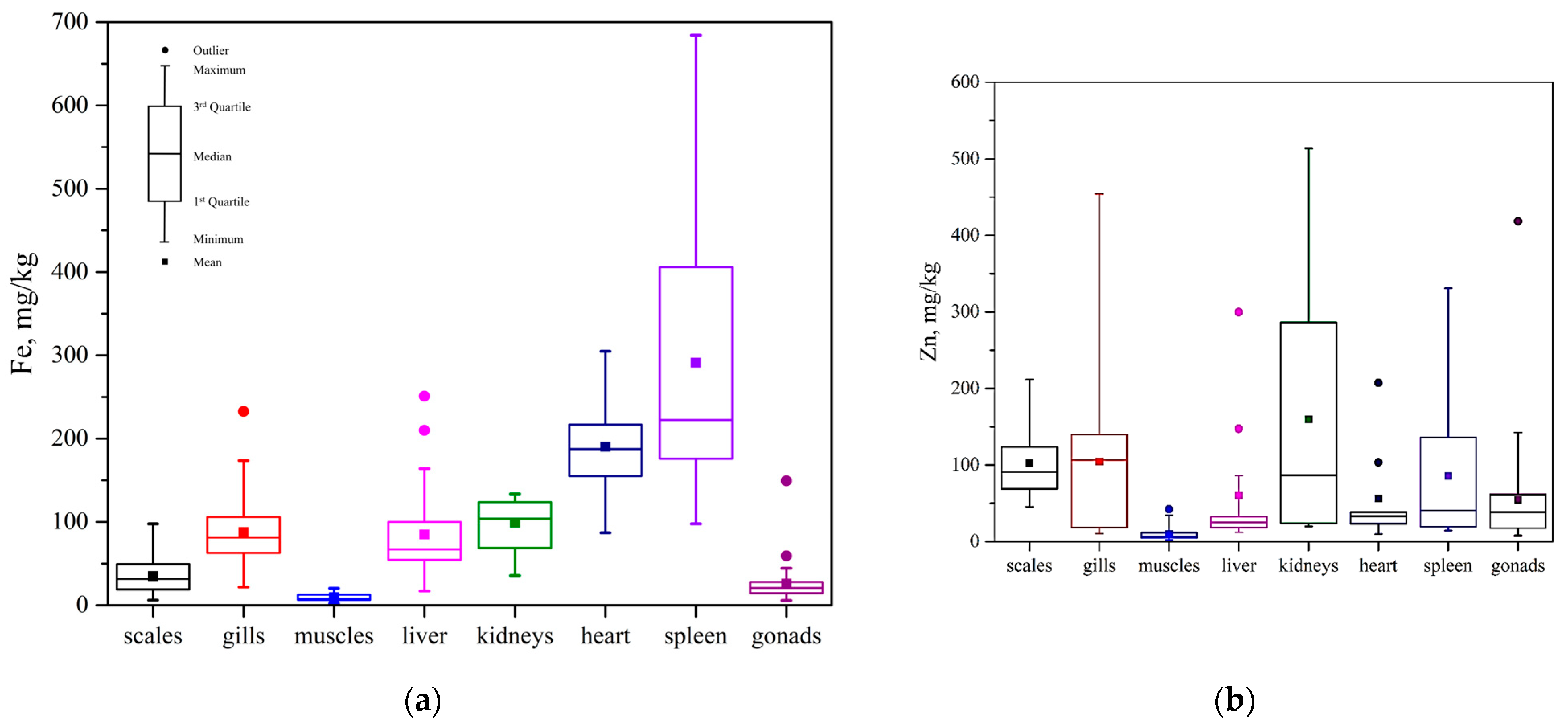
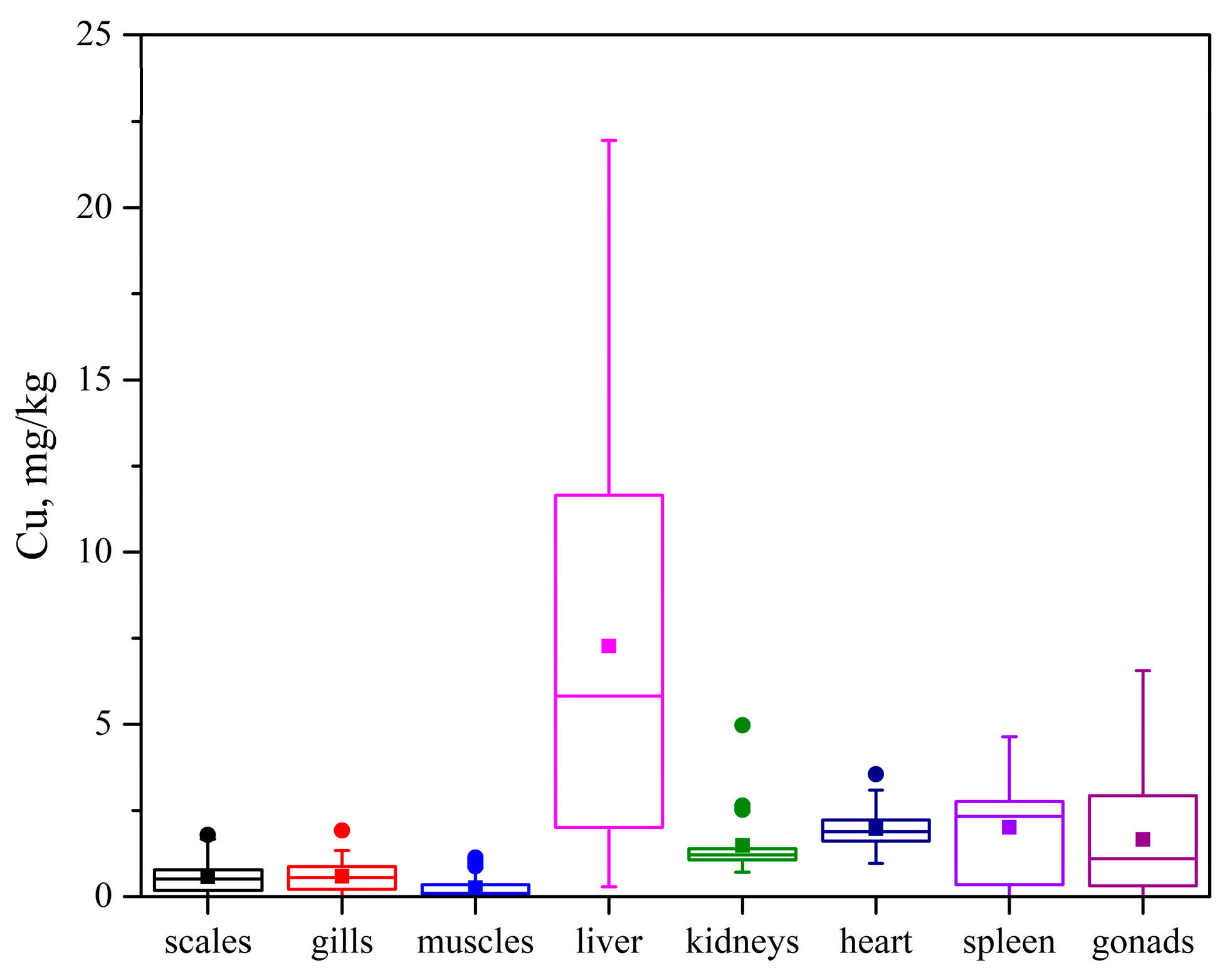
3.3. Heavy Metal Content in Fish Tissues
| Fish Species | Fe | Mn | Zn | Cu | Pb | Cd | Ni | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern pike | 12.69 − 15.72 14.31 ± 1.19 | 0.61 − 2.68 1.22 ± 0.75 | 2.62 − 5.43 3.95 ± 1.06 | n.d. − 1.07 0.37 ± 0.13 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Perch | 5.83 − 8.44 6.67 ± 1.07 | 0.56 − 0.87 0.75 ± 0.12 | 4.52 − 5.81 5.23 ± 0.54 | n.d. − 0.07 0.03 ± 0.00 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.08 − 0.14 0.10 ± 0.04 |
| Roach | 6.0 − 18.19 10.75 ± 4.05 | 0.33 − 4.34 1.36 ± 1.23 | 4.05 − 16.44 7.87 ± 3.09 | n.d. − 0.62 0.46 ± 0.41 | n.d. − 0.29 0.09 ± 0.06 | n.d. − 0.20 0.06 ± 0.02 | n.d. − 0.27 0.09 ± 0.04 | n.d. − 0.14 0.09 ± 0.02 |
| Bream | 2.20 − 8.77 6.44 ± 2.21 | 0.18 − 1.45 0.91 ± 0.45 | 2.15 − 5.13 3.74 ± 1.08 | n.d. − 0.32 0.16 ± 0.05 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. − 0.15 0.08 ± 0.07 |
| Common carp | 3.77 − 9.76 6.51 ± 2.36 | 0.21 − 1.20 0.68 ± 0.33 | 6.26 − 42.21 18.86 ± 15.62 | n.d. − 0.76 0.27 ± 0.19 | n.d. | n.d. − 0.03 0.01 ± 0.00 | n.d. | n.d. − 0.14 0.13 ± 0.03 |
| Crucian carp | 5.25 − 20.37 9.64 ± 4.53 | 0.06 − 1.24 0.60 ± 0.31 | 9.57 − 17.11 12.98 ± 2.55 | n.d. − 0.35 0.12 ± 0.11 | n.d. | n.d. − 0.16 0.05 ± 0.02 | n.d. − 0.30 0.16 ± 0.08 | n.d. − 0.15 0.12 ± 0.03 |
| Tolerable and permissible levels of HMs in the fish muscles, mg/kg w.w. | ||||||||
| Russian Regulations [21] | – | – | – | – | 1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | – |
| USEPA, 1983 [68] | – | – | 480 | 120 | 4 | – | – | 8 |
| MAFF, 2000 [69] | – | – | 50 | 20 | 2 | 0.2 | – | – |
| WHO, 2000 [70] | 109 | 1 | – | 30 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 30 | 0.15 |
| FAO, 2000 [29] | 180 | 0.5 | 30 | 30 | 2 | 0.5 | 55 | – |
| EC Regulation, 2006 [71] | – | – | – | – | 0.3 | 0.1 | – | – |
3.4. Human Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, X. Effects of Water Pollution on Human Health and Disease Heterogeneity: A Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, e880246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhzadeh, H.; Hamidian, A.H. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish species of Iran: A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 3749–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, I.; Lone, F.A.; Bhat, R.A.; Mir, S.A.; Dar, Z.A.; Dar, S.A. Concerns and Threats of Contamination on Aquatic Ecosystems. In Bioremediation and Biotechnology: Sustainable Approaches to Pollution Degradation; Hakeem, K.R., Bhat, R.A., Qadri, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama Aziz, K.H.; Mustafa, F.S.; Omer, K.M.; Hama, S.; Hamarawf, R.F.; Rahman, K.O. Heavy metal pollution in the aquatic environment: Efficient and low-cost removal approaches to eliminate their toxicity: A review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 17595–17610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Ren, B. Trends and Sources of Heavy Metal Pollution in Global River and Lake Sediments from 1970 to 2018. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; de Voogt, P., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Singh, N.; Rai, S.N.; Kumar, A.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, M.P.; Sahoo, A.; Shekhar, S.; Vamanu, E.; Mishra, V. Heavy Metal Contamination in the Aquatic Ecosystem: Toxicity and Its Remediation Using Eco-Friendly Approaches. Toxics 2023, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujari, M.; Kapoor, D. Heavy metals in the ecosystem: Sources and their effects. In Heavy Metals in the Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib Jawad, S.; Shihab, A.F.; Al-Taher, Q.M. Heavy metal concentrations in water, sediments, Cladophora and two fish species from Al-Masab Alamm River, Al-Nassiriya, Iraq. Casp. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 20, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczyńska, J.; Pietrzak-Fiećko, R.; Purkiewicz, A.; Łuczyński, M.J. Assessment of Fish Quality Based on the Content of Heavy Metals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Authman, M.M.N.; Zaki, M.S.; Khallaf, E.A.; Abbas, H.H. Use of Fish asBio-indicator of the Effects of Heavy Metals Pollution. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2015, 6, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, J.C.; Woodford, D.J.; Snow, G.C. Evaluating the effectiveness of freshwater fishes as bio-indicators for urban impacts in the Crocodile (West) catchment, South Africa. Water SA 2019, 45, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komov, V.T.; Stepanova, I.K.; Gremyachikh, V.A. Mercury content in muscles of fish from water bodies of northwest Russia: Causes of intensive accumulation and assessment of negative effect on human health status. Curr. Probl. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 99–123. [Google Scholar]
- Golovanova, I.L. Effects of heavy metals on physiological and biochemical status of fishes and aquatic invertebrates. Inland Water Biol. 2008, 1, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjahan, M.; Taslima, K.; Shadiqur, R.M.; Al-Emran, M.; Alam, S.I.; Faggio, C. Effects of heavy metals on fish physiology—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, P.A.; Androsova, N.V. Indication of the ecological state of Siberian water bodies by the content of heavy metals in fish. Geogr. Nat. Resour. 2008, 3, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Moiseenko, T.I. Water Ecotoxicology. Theoretical and Applied Aspects; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 2009; p. 400. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.N.; Shtanko, T.I. Mercury content in fish products (Literature review). Hyg. Sanit. 2009, 1, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Rudneva, N.A. Heavy Metals and Trace Elements in Hydrobionts of the Baikal Region; Buryat Scientific Center Press: Ulan-Ude, Russia, 2001; p. 134. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshalizadeh, S.; Liyafoyi, A.R.; Fazio, F.; Mora-Medina, R.; Ayala-Soldado, N. Health risk assessment of heavy metal concentration in muscle of Chelon auratus and Chelon saliens from the southern Caspian Sea. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 3377–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pishchevaya Promyshlennost. Sanitary Rules and Norms SanPiN 2.3.2.560-96 “Hygienic Requirements for the Quality and Safety of Food Raw Materials and Food Products”, Adopted 24 Oct 1996; Pishchevaya Promyshlennost: Moscow, Russia, 1996; p. 202. [Google Scholar]
- Kawser Ahmed, M.; Baki, M.A.; Kundu, G.K.; Saiful Islam, M.; Monirul Islam, M.; Muzammel Hossain, M. Human health risks from heavy metals in fish of Buriganga river, Bangladesh. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.M.; Ali, M.L.; Bhuyan, M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.Z.; Alam, M.W.; Das, M.; Mustary, S.; Islam, M.N. Spatiotemporal variation and toxicity of trace metals in commercially important fish of the tidal Pasur River in Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 40131–40145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shan, Q.; Liang, X.; Guan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, H.; Fang, H. Levels and human health risk assessments of heavy metals in fish tissue obtained from the agricultural heritage rice-fish-farming system in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Iqbal, J.; Shi, Z.; Garrett, S.H.; Shah, M.H. Distribution and Bioaccumulation of Essential and Toxic Metals in Tissues of Thaila (Catla catla) from a Natural Lake, Pakistan and Its Possible Health Impact on Consumers. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayode, J.B. Risk Assessment of Trace Metal Intake through Consumption of Four Fish Species from Upper Region of Barrier Lagoon Coast Waters, Southwest, Nigeria. J. Environ. Pollut. Hum. Health 2021, 9, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Xi, S. The effects of heavy metals on human metabolism. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2020, 30, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyarko, E.; Boateng, C.M.; Asamoah, O.; Edusei, M.O.; Mahu, E. Potential human health risks associated with ingestion of heavy metals through fish consumption in the Gulf of Guinea. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 10, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Compilation of Legal Limits for Hazardous Substances in Fish and Fishery Products. Fisheries Circular. No. 764. Available online: https://www.fao.org/inland-fisheries/topics/detail/en/c/1150083/ (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- Drukker, V.V.; Sorokovikova, L.M.; Sinyukovich, V.N.; Potemkina, T.G.; Nikulina, I.G.; Molozhavaya, O.A.; Korovyakova, I.V. Water quality of the Barguzin River in modern conditions. Geogr. Nat. Resour. 1997, 4, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Dzyuba, A.A.; Tulokhonov, A.K.; Abidueva, T.I.; Kulagina, N.V.; Chernykh, L.A. Paleogeographic aspects of the formation of saline lakes in the Barguzin depression. Geogr. Nat. Resour. 1999, 2, 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chernousenkov, G.I.; Pankova, E.I.; Kalinina, N.V.; Ubugunova, V.I.; Rukhovich, D.I.; Ubugunov, V.L.; Tsyrempilov, E.G. Saline soils of the Barguzin depression. Soil Sci. 2017, 6, 652–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinyukovich, V.N.; Shiretorova, V.G.; Tomberg, I.V.; Sorokovikova, L.M.; Radnaeva, L.D.; Tulokhonov, A.K. Formation of the Ion Composition of the Barguzin River Waters (Lake Baikal Basin) under the Conditions of Saline Landscapes. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2020, 495, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tselyuk, D.I.; Tselyuk, I.N. Technogenic environmental heritage gold mining industry of Eastern Siberia. Explor. Prot. Subsoil 2019, 12, 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Laperdina, T.G. Estimation of mercury and other heavy metal contamination in traditional gold-mining areas of Transbaikalia. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2002, 2, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Siliceous and Organically Based Matrices. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-12/documents/3052.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2023).
- Bazarzhapov, T.Z.; Shiretorova, V.G.; Radnaeva, L.D.; Nikitina, E.P.; Bazarsadueva, S.V.; Shirapova, G.S.; Dong, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, P. Distribution of Heavy Metals in Water and Bottom Sediments in the Basin of Lake Gusinoe (Russia): Ecological Risk Assessment. Water 2023, 15, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyutyunnik, O.A.; Getsina, M.L.; Toropchenova, E.S.; Kubrakova, I.V. Microwave preparation of natural samples to the determination of mercury and other toxic elements by atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 68, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybem, B. Field sampling and preparation subsamples of aquatic organism for analysis metals and organochlorides. FAO Fisher. Tech. 1983, 212, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Förstner, U. Metal concentrations in freshwater sediments—Natural background and cultural effects. In Interactions between Sediments and Fresh Water, Proceedings of the International Symposium, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 6–10 September 1976; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1977; pp. 94–103. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usero, J.; González-Regalado, E.; Gracia, I. Trace metals in the bivalve molluscs Ruditapes decussatus and Ruditapes philippinarum from the atlantic coast of Southern Spain. Environ. Int. 1997, 23, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Khalek, A.A.; Elhaddad, E.; Mamdouh, S.; Marie, M.A.S. Assessment of metal pollution around sabal drainage in River Nile and its impacts on bioaccumulation level, metals correlation and human risk hazard using Oreochromis niloticus as a bioindicator. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 16, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczyńska, J.; Paszczyk, B.; Łuczyński, M.J. Fish as a bioindicator of heavy metals pollution in aquatic ecosystem of Pluszne Lake, Poland, and risk assessment for consumer’s health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 153, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.N.; Kaur, V.I.; Dhawan, A.; Jassal, G. Estimation of length-weight relationship and condition factor of spotted snakehead Channa punctata (Bloch) under different feeding regimes. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.O.; Ali, M.E.; Aziz, A.A.; Rafi, E.M.K. Length-weight relationships and condition factors of five freshwater fish species in Roseires reservoir, Sudan. Eur. J. Phys. Agric. Sci. 2017, 5, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gyimah, E.; Akoto, O.; Mensah, J.K.; Bortey-Sam, N. Bioaccumulation factors and multivariate analysis of heavy metals of three edible fish species from the Barekese reservoir in Kumasi, Ghana. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Regional Screening Level (RSL) Summary Table. 2017. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-screening-levels-rsls-generic-tables (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- MR 2.3.1.2432-08; Norms of Physiological Needs for Energy and Nutrients for Various Groups of the Population of the Russian Federation (Approved by the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Well-Being on July 22, 2021). Chief State Sanitary Physician of the Russian Federation: Moscow, Russia, 2021.
- Kowalski, B.R.; Bender, C.F. Pattern recognition. Powerful approach to interpreting chemical data. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 5632–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinoviev, A.Y. Visualization of Multidimensional Data; KSTU Press: Krasnoyarsk, Russia, 2000; p. 180. [Google Scholar]
- Esbensen, K. Multivariate Data Analysis; Rodionova, O.E., Ed.; IPSP RAS Press: Chernogolovka, Russia, 2005; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Urbazaeva, S.D.; Pavlov, I.A.; Bazarsadueva, S.V.; Shiretorova, V.G.; Radnaeva, L.D. Content of heavy metals in water and bottom sediments of the Barguzin river in modern conditions. Nauchnoe Obozr. 2016, 5, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Bazarzhapov, T.Z.; Shiretorova, V.G.; Radnaeva, L.D.; Suocheng, D.; Tulokhonov, A.K. Chemical composition of surface water in the main tributaries of Lake Baikal—The Selenga and the Barguzin Rivers. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 320, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagarinova, O.V.; Belozertseva, I.A.; Vorobyeva, I.B.; Vlasova, N.V.; Emelyanova, N.V.; Sorokovoi, A.A. Anthropogenic Transformations in the Mouth Area of Tributaries as Factors of Negative Impact on Lake Baikal. Water 2021, 13, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Natural Resources and Ecology of the Russian Federation. State and Protection of the Environment of the Russian Federation in 2021. Report. 2022. Available online: https://www.mnr.gov.ru/docs/gosudarstvennyy_doklad_o_sostoyanii_i_ob_okhrane_okruzhayushchey_sredy_rossiyskoy_federatsii_v_2021_/ (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- MAC. GOST 17.1.2.04-77 Nature Protection. Hydrosphere. Indices of State and Requlation for Valuation Survey of Tisnery Waters. Available online: https://gost.ruscable.ru/Index/33/33538.htm (accessed on 6 September 2023).
- Shiretorova, V.G.; Zhigzhitzhapova, S.V.; Dylenova, E.P.; Radnaeva, L.D. Accumulation of heavy metals in aquatic vegetation of the Barguzin River. In Proceedings of the Actual Problems of Ecology and Environmental Management: Cooperation for Sustainable Development and Environmental Safety (APEEM 2020), Moscow, Russia, 23–25 April 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, J.; Shah, M.H. Study of seasonal variations and health risk assessment of heavy metals in Cyprinus carpio from Rawal Lake, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2025–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolić, D.; Skorić, S.; Janković, S.; Hegediš, A.; Djikanović, V. Age-specific accumulation of toxic metal(loid)s in northern pike (Esox lucius) juveniles. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, M.L.; Santiago, S.; Nunes, M.L. Assessment of the essential element and heavy metal content of edible fish muscle. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, A.B.; Sangün, M.K.; Yağlıoğlu, D.; Turan, C. Metals (major, essential to non-essential) composition of the different tissues of three demersal fish species from İskenderun Bay, Turkey. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdoğrul, Ö.; Erbilir, F. Heavy Metal and Trace Elements in Various Fish Samples from Sır Dam Lake, Kahramanmaraş, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 130, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelstein, S.; Sharlin, J. Life Cycle Nutrition: An Evidence-Based Approach; Jones and Bartlett Publishers: Sudbury, MA, USA, 2009; p. 517. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, C.K.; Al-Mutairi, K.A. Copper and Zinc Levels in Commercial Marine Fish from Setiu, East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Toxics 2022, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulkumar, A.; Paramasivam, S.; Rajaram, R. Toxic heavy metals in commercially important food fishes collected from Palk Bay, Southeastern India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, S.; Vinagre, C.; Caçador, I.; Cabral, H.N. Heavy metal concentrations in sediment, benthic invertebrates and fish in three salt marsh areas subjected to different pollution loads in the Tagus Estuary (Portugal). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. 600/4-79-020 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes. Available online: https://www.wbdg.org/ffc/epa/criteria/epa-600-4-79-020 (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- CEFAS (MAFF). Aquatic Environment Monitoring Report No. 51 “Monitoring and Surveillance of Non-Radioactive Contaminants in the Aquatic Environment and Activities Regulating the Disposal of Wastes at Sea, 1995 and 1996”. Available online: https://www.cefas.co.uk/publications/aquatic/aemr51.pdf (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Vol. 2, Health Criteria and Other Supporting Information, 2nd ed. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/38551 (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- European Commission. Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Anandkumar, A.; Nagarajan, R.; Prabakaran, K.; Rajaram, R. Trace metal dynamics and risk assessment in the commercially important marine shrimp species collected from the Miri coast, Sarawak, East Malaysia. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2017, 16, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazunova, I.A. Content and peculiarities of heavy metals distribution in organs and tissues of fish of the Upper Ob. Izv. Altai State Univ. 2007, 3, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Vaganov, A.S. Comparative characterization of heavy metal content in commercial fish species of the Kuibyshev reservoir. Izv. Altai State Univ. 2011, 13, 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Zubkova, V.M.; Rozumnaya, L.A.; Bolotov, V.P. Heavy metal content in tissues and organs of different fish species of the Volgograd reservoir. Bull. Astrakhan State Tech. Univ. Ser. Fish. 2016, 4, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaperumal, P.; Sankar, T.V.; Viswanathan Nair, P.G. Heavy metal concentrations in fish, shellfish and fish products from internal markets of India vis-a-vis international standards. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengil, I.A.; Ozacar, M.; Türkmenler, H. Kinetic and isotherm studies of Cu(II) biosorption onto valonia tannin resin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisler, R. Nickel Hazards to Fish, Wildlife, and Invertebrates: A Synoptic Review; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey, Patuxent Wildlife Research Center: Prince George’s County, MD, USA, 1998; p. 86.
- García-Lestón, J.; Méndez, J.; Pásaro, E.; Laffon, B. Genotoxic effects of lead: An updated review. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizullah, A.; Khattak, M.N.; Richter, P.; Häder, D.P. Water pollution in Pakistan and its impact on public health—A review. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Molla, A.H.; Saha, N.; Rahman, A. Study on heavy metals levels and its risk assessment in some edible fishes from Bangshi River, Savar, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, A.; Satheesh Kumar, P.; Ram, A.; Chinnadurai, S. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in commercially important marine fishes from Mumbai Harbor, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, T.C.; Rodrigues, A.P.d.C.; Amaral, P.M.G.; de Oliveira, D.F.C.; Gonçalves, R.A.; Rodrigues e Silva, C.; Vasques, R.O.; Malm, O.; Silva-Filho, E.V.; Godoy, J.M.d.O.; et al. Evaluation of the bioaccumulation kinetics of toxic metals in fish (A. brasiliensis) and its application on monitoring of coastal ecosystems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumpu, M.B.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M.; Rayappan, J.B.B. A review on detection of heavy metal ions in water—An electrochemical approach. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 213, 515–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julia, L.B.; Zoltan, S.; Pamela, A.R. Occurrence and Mobility of Mercury in Groundwater, Ch. 5. In Current Perspectives in Contaminant Hydrology and Water Resources Sustainability; Paul, M.B., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 117–149. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, A.; Maksud, M.A.; Khan, S.R.; Lutfa, L.N.; Quraishi, S.B. Dietary intake of heavy metals from eight highly consumed species of cultured fish and possible human health risk implications in Bangladesh. Toxicol. Rep. 2017, 4, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghirad, M.; Amini Ranjbar, G.; Jooshideh, H.; Arshad, U. Heavy metal concentrations in the selected tissues of the Persian sturgeon, Acipencer persicus, from the southern coast of the Caspian Sea. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2009, 8, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamat, N.; Khalifi, K.; Movahedinia, A. Health Concerns Related to Consumption of Fish from Anzali Wetland. Clean Soil Air Water 2016, 44, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuksezgin, F.; Gonul, L.T.; Tasel, D. Total and inorganic arsenic levels in some marine organisms from Izmir Bay (Eastern Aegean Sea): A risk assessment. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Moselhy, K.M.; Othman, A.I.; Abd El-Azem, H.; El-Metwally, M.E.A. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in some tissues of fish in the Red Sea, Egypt. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2014, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, T.; Lias, K.; Norsila, D.; Syafinaz, N.S. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Squid (Loligo spp.) Tissues of Kedah-Perlis Waters, Malaysia. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2014, 18, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, F.; Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Xiao, M. Heavy metals and metalloid distribution in different organs and health risk assessment for edible tissues of fish captured from Honghu Lake. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 101672–101685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintaeva, E.T.; Bazarsadueva, S.V.; Radnaeva, L.D.; Petrov, E.A.; Smirnova, O.G. Content and character of metal accumulation in fish of the Kichera River (a tributary of Lake Baikal). Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2011, 4, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveeva, A.Y.; Kutlin, N.G.; Kardapoltseva, D.G.; Mullagalieva, A.T. Influence of anthropogenic load on accumulation of heavy metals in organs and tissues of commercial fishes. Environ. Manag. 2018, 2, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Farkas, A.; Salánki, J.; Specziár, A. Relation Between Growth and the Heavy Metal Concentration in Organs of Bream Abramis brama L. Populating Lake Balaton. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 43, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janicki, B.; Stanek, M. Distribution of heavy metals in the meat, gills and liver of common bream (Abramis brama L.) caught from Żnińskie Duże Lake (in Poland). J. Elem. 2015, 21, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanek, M.; Dąbrowski, J.; Janicki, B.; Roślewska, A.; Strzelecka, A. Impact of fish species on levels of lead accumulation in the meat of common bream (Abramis brama L.), white bream (Blicca bjoerkna L.) and common bleak (Alburnus alburnus L.) from the Vistula River (Poland). J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2015, 16, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spodniewska, A.; Barski, D. Concentration of some metals in the muscles of fish from selected lakes of Warmia and Mazury region (Poland). Acta Vet. Brno 2013, 82, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brázová, T.; Torres, J.; Eira, C.; Hanzelová, V.; Miklisová, D.; Šalamún, P. Perch and Its Parasites as Heavy Metal Biomonitors in a Freshwater Environment: The Case Study of the Ružín Water Reservoir, Slovakia. Sensors 2012, 12, 3068–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, P.A.; Androsova, N.V. Heavy metal content in muscle tissue of fish from the water bodies of the Ob river basin. Bull. Tomsk. State Univ. Ser. Biol. 2014, 4, 108–122. [Google Scholar]
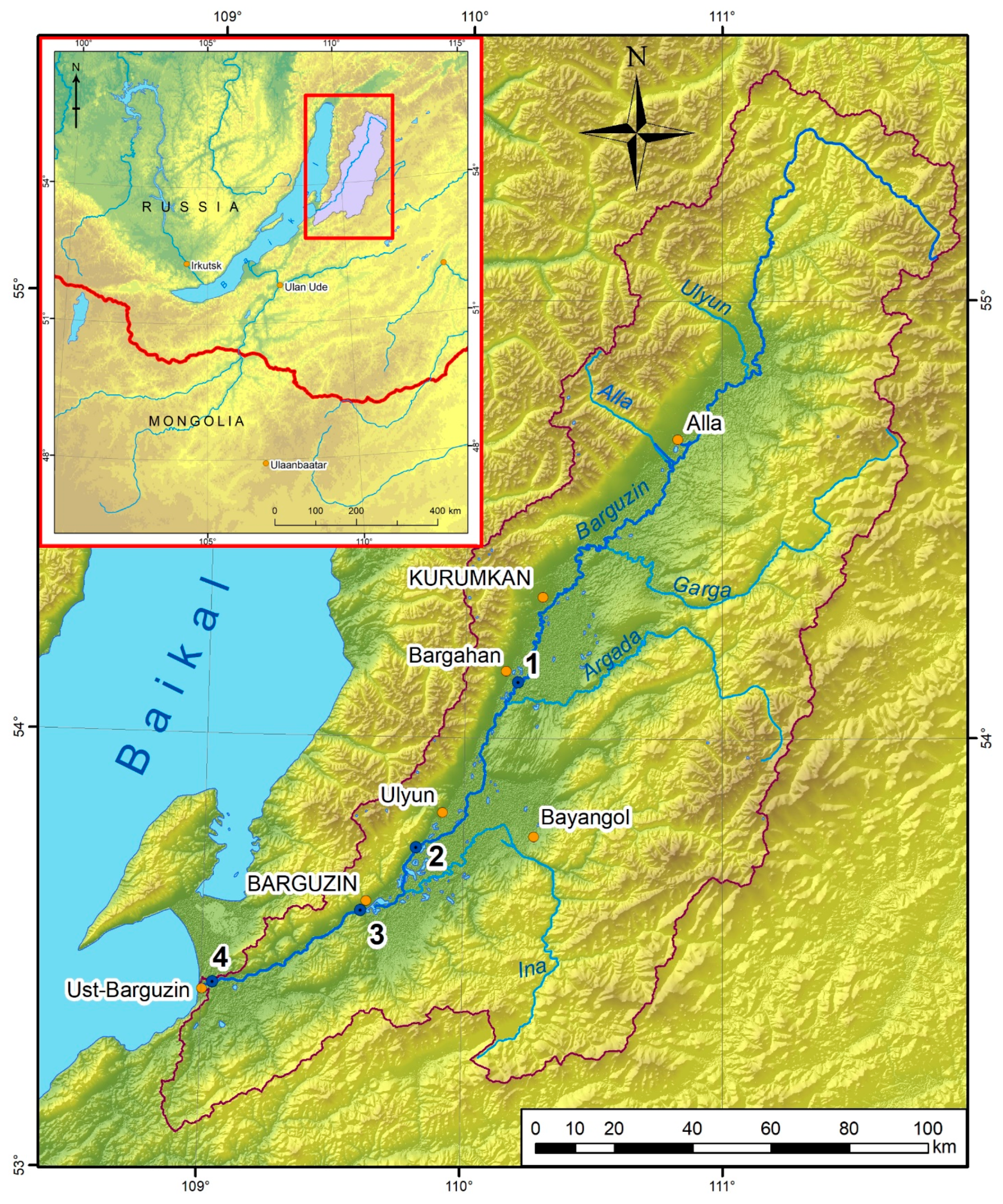


| Station Number | Location |
|---|---|
| 1 | 54°07′37.3″ N 110°12′21.0″ E |
| 2 | 53°44′43.8″ N 109°48′53.0″ E |
| 3 | 53°36′7.4″ N 109°36′20.0″ E |
| 4 | 53°25′20.6″ N 109°1′14.8″ E |
| Element | Determining Threshold * | Certified BIL-2 | Measured BIL-2 | Recovery % | Certified ERM®-BB422 | Measured ERM®-BB422 | Recovery % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 0.4 | 37,700 | 34,100 | 92 | 9.4 | 9.3 | 98.6 |
| Mn | 0.1 | 929 | 885 | 96 | 0.368 | 0.359 | 97.5 |
| Zn | 0.1 | 64 | 65 | 102 | 16.0 | 16.2 | 101.3 |
| Cu | 0.005 | 18 | 17 | 94 | 1.67 | 1.61 | 96.4 |
| Ni | 0.009 | 31 | 26 | 97 | – | – | – |
| Cr | 0.002 | 158 | 160 | 101 | – | – | – |
| Pb | 0.004 | 14 | 13 | 93 | – | – | – |
| Hg | 0.015 | – | – | – | 0.601 | 0.563 | 93.6 |
| Metal | Surface Water, µg/dm3 | Sediments, mg/kg d.w. | CF | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | MACfr | Min | Max | Mean | Clark | ||
| Fe | 17 | 202 | 74 | 100 | 29,657 | 58,277 | 39,928 | 43,500 | 0.92 |
| Mn | 2.1 | 45 | 18 | 10 | 732 | 1179 | 931 | 750 | 1.24 |
| Zn | 1.0 | 8.2 | 4.1 | 10 | 56.4 | 101 | 79.8 | 110 | 0.73 |
| Cu | 0.9 | 2.1 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 7.8 | 27.8 | 16.3 | 43 | 0.38 |
| Cr | 1.1 | 3.0 | 2.1 | 20 | 38.5 | 61.2 | 47.6 | 96 | 0.50 |
| Ni | n.d. * | 1.2 | 1.0 | 10 | 4.6 | 19.4 | 11.7 | 55 | 0.21 |
| Hg | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.01 | 0.039 | 0.091 | 0.072 | 0.30 | 0.24 |
| Fish Species | Weight (g) (W) | Total Length (cm) (L) | Fish Condition Factor (g/cm3) (K) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | |
| Roach | 26 | 97 | 59 | 12.0 | 19.5 | 16.1 | 1.18 | 1.60 | 1.38 |
| Bream | 312 | 674.5 | 550 | 30.5 | 39.0 | 36.4 | 1.05 | 1.23 | 1.12 |
| Crucian carp | 220 | 565.5 | 337 | 22.0 | 29.0 | 24.5 | 2.07 | 2.41 | 2.22 |
| Common carp | 548 | 2224 | 1309 | 31.0 | 56.0 | 43.0 | 1.22 | 1.84 | 1.51 |
| Perch | 267 | 636 | 372 | 26.5 | 34.0 | 29.3 | 1.30 | 1.62 | 1.42 |
| Northern pike | 344 | 687 | 548 | 40.0 | 50.5 | 46.1 | 0.48 | 0.62 | 0.55 |
| Metal | RfD * | THQ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern Pike | Perch | Roach | Bream | Common Carp | Crucian Carp | ||
| Fe | 7 × 10−1 | 0.020 | 0.009 | 0.015 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.013 |
| Mn | 1.4 × 10−1 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.004 |
| Zn | 3 × 10−1 | 0.013 | 0.017 | 0.025 | 0.012 | 0.061 | 0.042 |
| Cu | 4 × 10−2 | 0.009 | 0.001 | 0.011 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.003 |
| Pb | 2 × 10−3 | – ** | – | 0.029 | – | – | – |
| Cd | 1 × 10−3 | – | – | 0.019 | 0.004 | – | 0.019 |
| Ni | 2 × 10−2 | – | – | 0.002 | – | – | 0.004 |
| Cr | 3 × 10−3 | – | 0.045 | 0.113 | 0.058 | 0.042 | 0.084 |
| HI | 0.050 | 0.077 | 0.223 | 0.093 | 0.122 | 0.169 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bazarsadueva, S.V.; Shiretorova, V.G.; Nikitina, E.P.; Zhigzhitzhapova, S.V.; Taraskin, V.V.; Bazarzhapov, T.Z.; Dong, S.; Radnaeva, L.D. Heavy Metal Content in Fish of the Barguzin River (Eastern Cisbaikalia) and Assessment of Potential Risks to Human Health. Water 2023, 15, 3710. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213710
Bazarsadueva SV, Shiretorova VG, Nikitina EP, Zhigzhitzhapova SV, Taraskin VV, Bazarzhapov TZ, Dong S, Radnaeva LD. Heavy Metal Content in Fish of the Barguzin River (Eastern Cisbaikalia) and Assessment of Potential Risks to Human Health. Water. 2023; 15(21):3710. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213710
Chicago/Turabian StyleBazarsadueva, Selmeg V., Valentina G. Shiretorova, Elena P. Nikitina, Svetlana V. Zhigzhitzhapova, Vasilii V. Taraskin, Tcogto Zh. Bazarzhapov, Suocheng Dong, and Larisa D. Radnaeva. 2023. "Heavy Metal Content in Fish of the Barguzin River (Eastern Cisbaikalia) and Assessment of Potential Risks to Human Health" Water 15, no. 21: 3710. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213710





