Evaluation of Groundwater Quality and Contamination Using the Groundwater Pollution Index (GPI), Nitrate Pollution Index (NPI), and GIS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
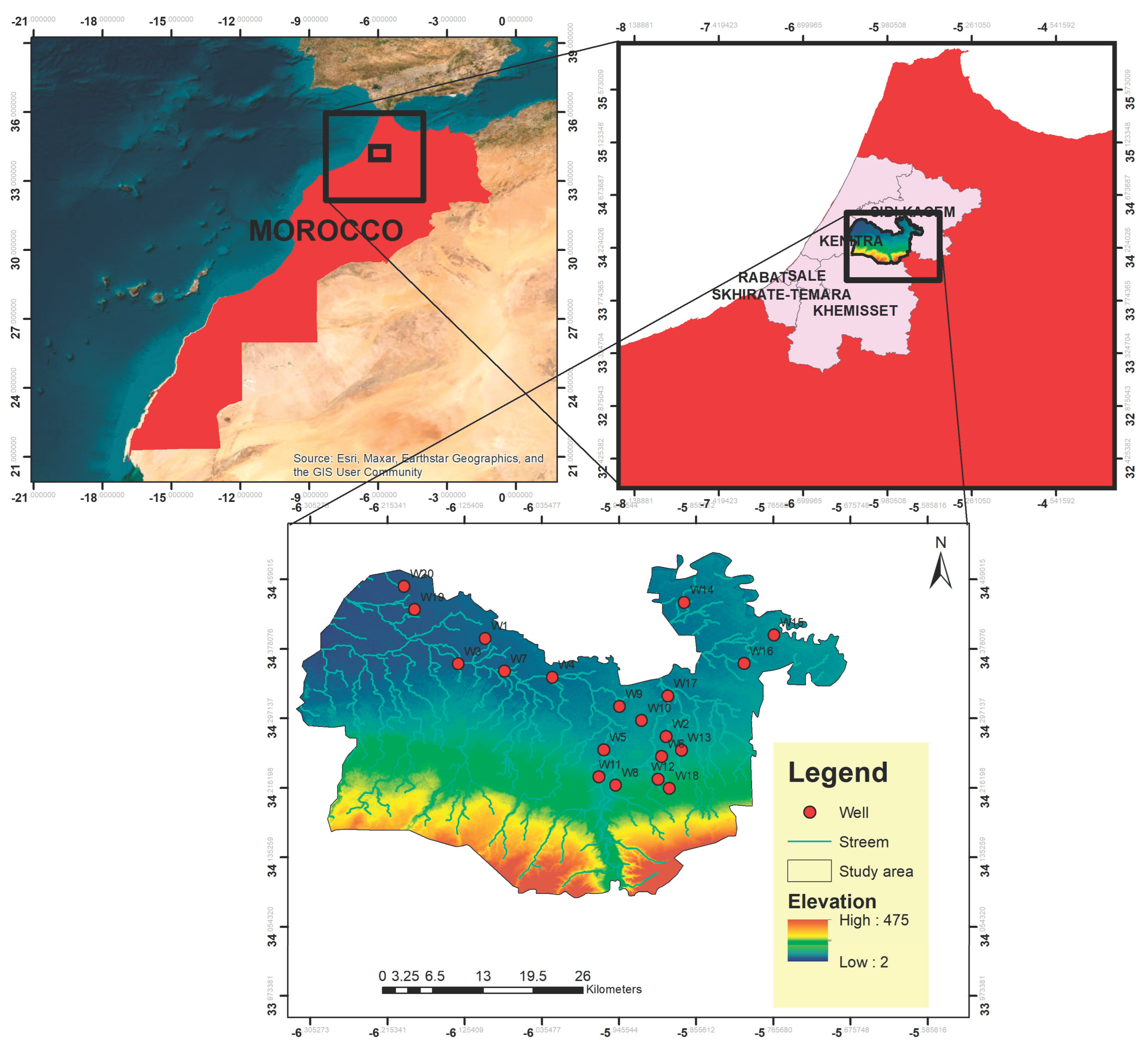
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field and Laboratory Methods
2.2.1. Pollution Index of Groundwater (PIG)
- Step 1:
- Assigning Relative Weight (RW)
- Step 2:
- Calculating Weight Parameter (WP)
- Step 3:
- Calculating of Concentration (SC)
- Step 4:
- Calculating of (PIG)
- Step 5:
- Calculating (PIG) Quality
| Parameter | RW | WP | WHO (2011) |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 4 | 0.1025641 | 7 |
| TH | 4 | 0.1025641 | 300 |
| EC | 4 | 0.1025641 | 500 |
| K+ | 1 | 0.02564103 | 12 |
| Ca2+ | 2 | 0.05128205 | 75 |
| Mg2+ | 2 | 0.05128205 | 45 |
| Na+ | 4 | 0.1025641 | 200 |
| SO42− | 5 | 0.12820513 | 250 |
| Cl− | 5 | 0.12820513 | 250 |
| NO3− | 5 | 0.12820513 | 50 |
| Sum | 29 | 1 |
2.2.2. Nitrate Pollution Index (NPI)
3. Results and Discussion
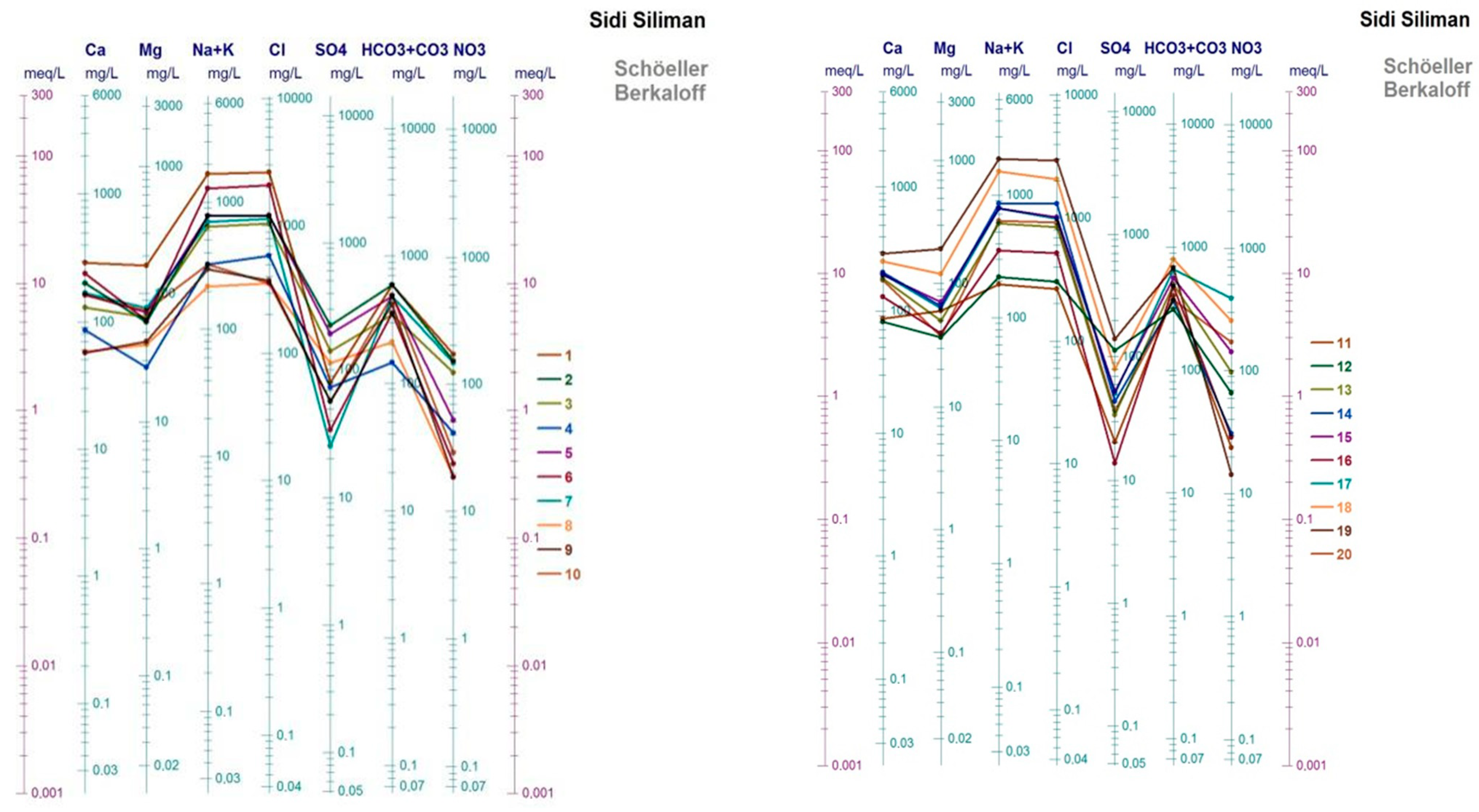
3.1. Groundwater Chemistry
3.2. Hydrochemical Facies
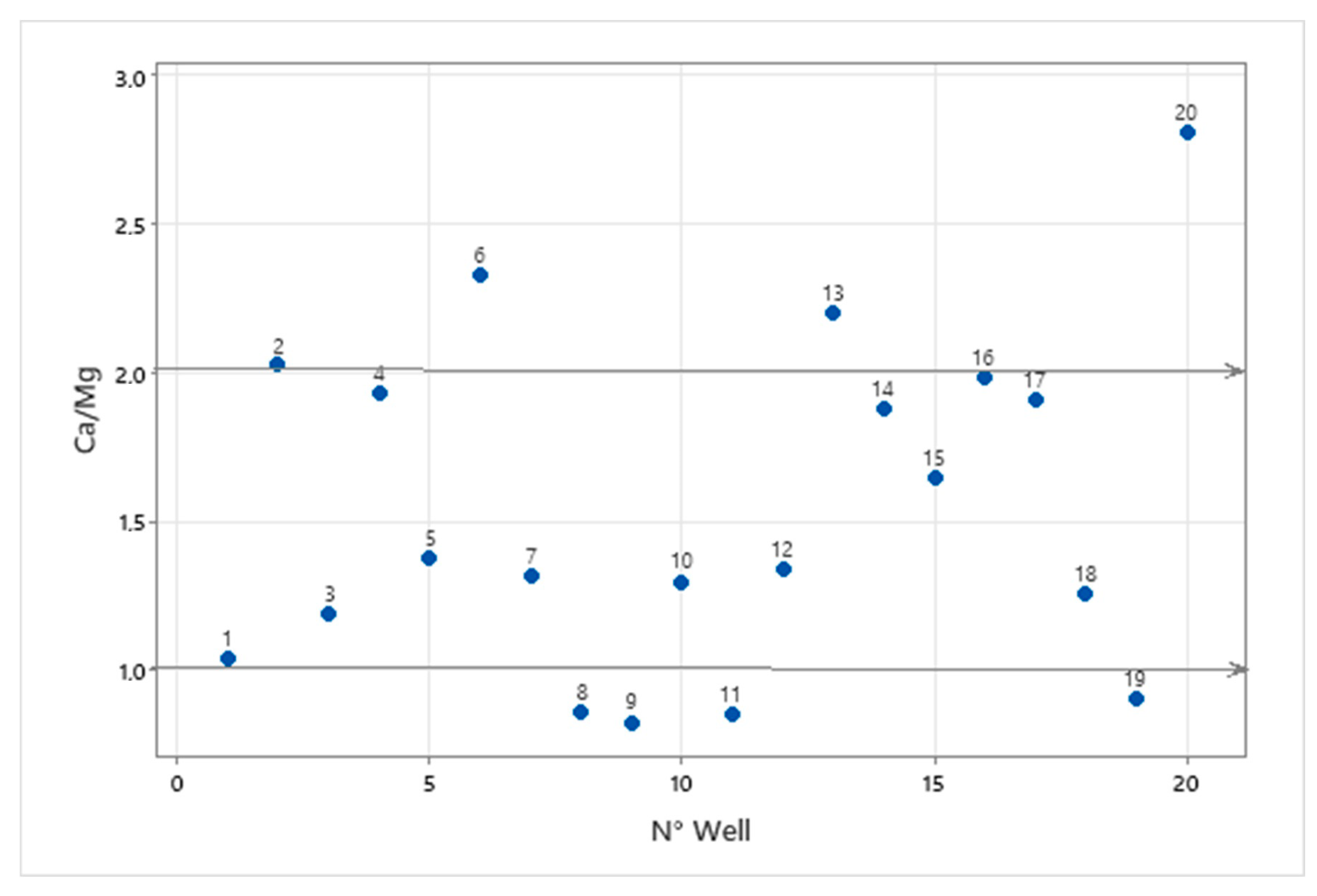
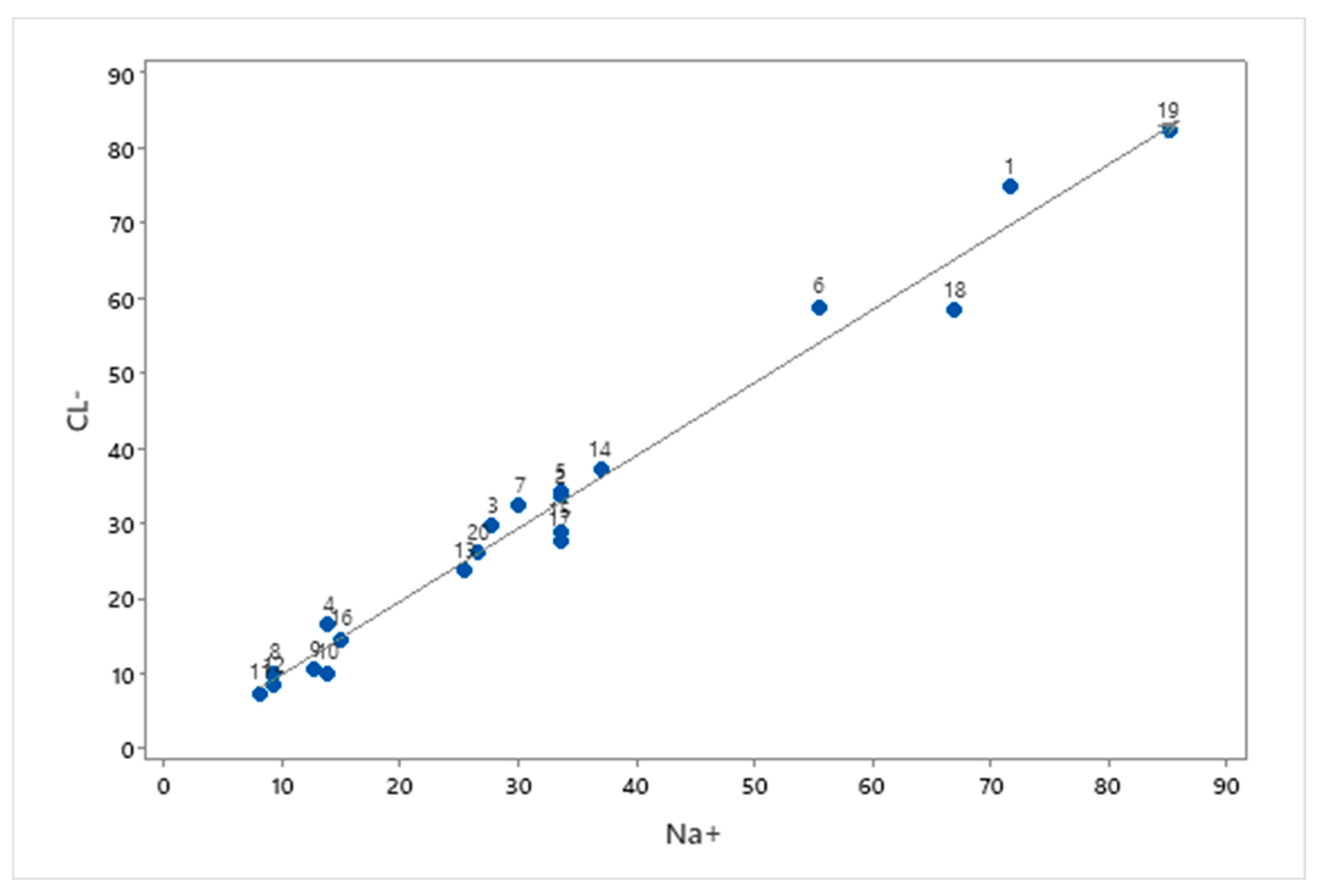
3.3. Water-Rock Interaction
3.4. Base Ion Exchange in Groundwater Chemistry
3.5. Saturation Indices of Groundwater
3.6. Groundwater Pollution Index
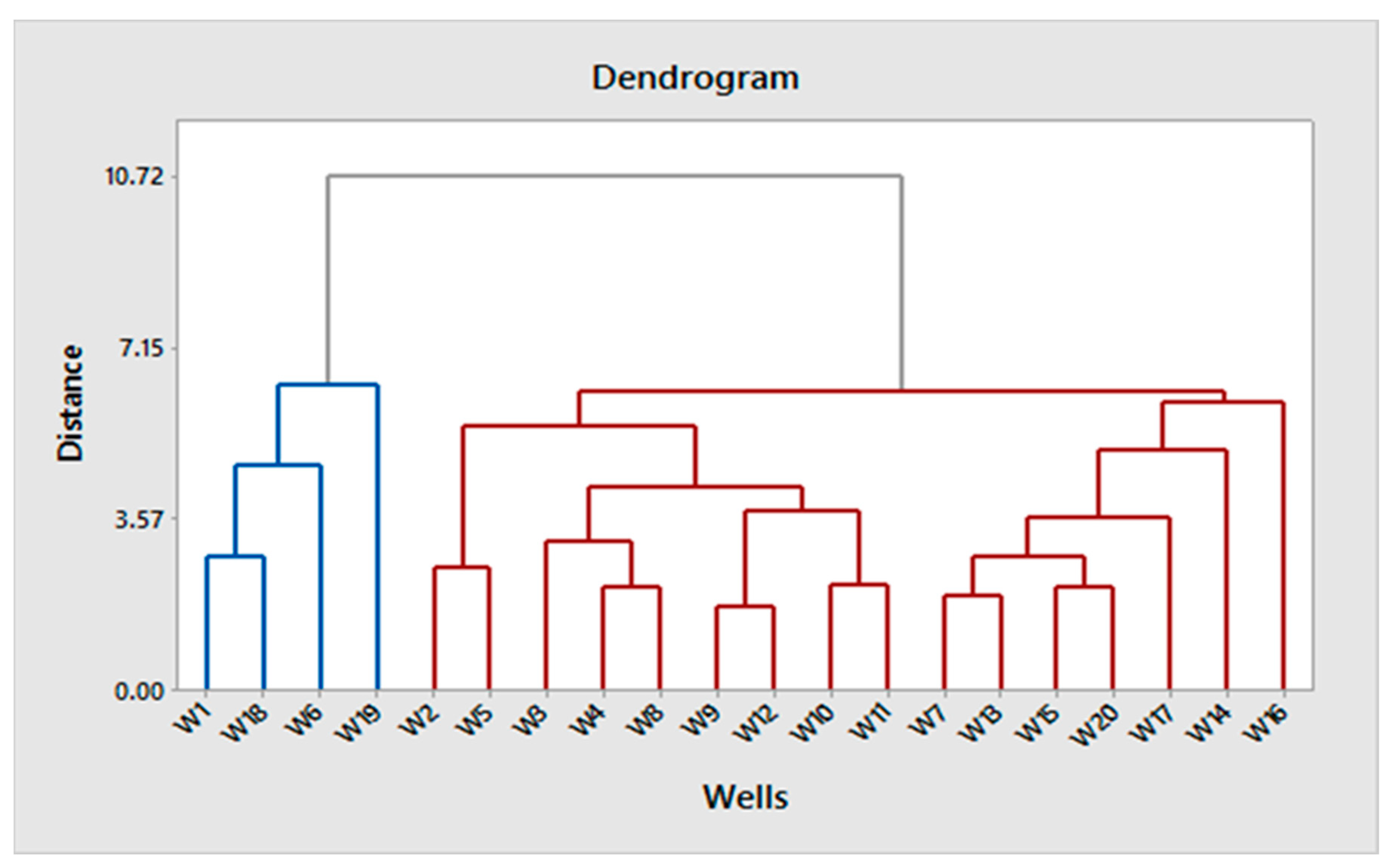
3.7. Classification Ascendant Hierarchies (CAH)
3.8. Nitrate Pollution Index (NPI)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1985; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E. Water Quality: An introduction; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, M.A.; Wani, S.A.; Singh, V.K.; Sahoo, J.; Tomar, D.; Sanswal, R. An overview of the assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation. J. Agri. Sci. Food Res. 2018, 9, 209. [Google Scholar]
- Tanvir Rahman, M.A.; Saadat, A.; Islam, M.S.; Al-Mansur, M.A.; Ahmed, S. Groundwater characterization and selection of suitable water type for irrigation in the western region of Bangladesh. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperno, D.R. The origins of plant cultivation and domestication in the New World tropics: Patterns, process, and new developments. Curr. Anthropol. 2011, 52, S453–S470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khodrani, N.; Zouahri, A.; Arfaoui, A.; Iaaich, H.; El Oumlouki, K.; Yahyaoui, A.; Fekhaoui, M. Study of physico-chemical quality of groundwater in the rural commune of SFAFAA (Sidi Slimane Gharb, Morocco). J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 2852–2860. [Google Scholar]
- Aitsi, S.; Ettaki, J.; Doumi, K.; Chabli, A.; Belghyti, D. Hydrogeochemical Study of the Hamma My Yacoube, Sidi Slimane–Morocco. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart City Applications, Safranbolu, Turkey, 27–29 October 2021; pp. 657–670. [Google Scholar]
- Darwesh, N.; Naser, R.S.; Al-Qawati, M.; Raweh, S.; El Kharrim, K.; Belghyti, D. Groundwater Quality in Sidi Slimane, Morocco. J. Health Pollut. 2020, 10, 200309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibou, J. Impacts des changements climatiques sur les ressources en eau et les zones humides du Maroc. In Proceedings of the Table Ronde Régionale en Méditerranée, Athènes, Greece, 10–11 December 2002; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Laouina, A. Conservation des eaux et des sols au Maroc: Prise en compte de la diversité géographique. Norois 2010, 214, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Mondal, P.; Ghosh, R.; Sutradhar, S. Groundwater quality assessment using multivariate statistical technique and hydro-chemical facies in Birbhum District, West Bengal, India. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, M.; Regmi, T.; Kayastha, S.P.; Bhuiyan, C. Groundwater quality and community health risk in Lalitpur Metropolitan City, Nepal–a geospatial analysis. Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2168069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseashta, A.; Maftei, C. Water Safety, Security and Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton, J. Towards a management and regulatory strategy for phosphoric acid and phosphogypsum as co-products. In Naturally Occurring Radioactive Material (NORM V); IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2008; pp. 281–295. [Google Scholar]
- Apha, A. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 21, pp. 258–259. [Google Scholar]
- Subba Rao, N. Hydrogeology: Problems with Solutions Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Geol. 2017, 49, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba Rao, N. Groundwater quality from a part of Prakasam district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba Rao, N. PIG: A numerical index for dissemination of groundwater contamination zones. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 3344–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO, G. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 216, pp. 303–304.
- Obeidat, M.M.; Awawdeh, M.; Al-Rub, F.A.; Al-Ajlouni, A. An Innovative Nitrate Pollution Index and Multivariate Statistical Investigations of Groundwater Chemical Quality of Umm Rijam Aquifer (B4), North Yarmouk River Basin, Jordan. In Water Quality Monitoring and Assessment; Vouddouris, K., Voutsa, D., Eds.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 169–188. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeller, H. Geochemistry of Groundwater. Groundwater Studies, an International Guide for Research and Practice; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1977; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, T.E.; Buswell, A.M.; Ludwig, H.F.; Langelier, W. Calcium carbonate saturation index and alkalinity interpretations [with discussion]. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1942, 34, 1667–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Liang, X.; Jin, M.; Currell, M.J.; Han, Y.; Song, X. Hydrogeochemical indicators of groundwater flow systems in the Yangwu River alluvial fan, Xinzhou Basin, Shanxi, China. Environ. Manag. 2009, 44, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, A.L.; Loucks, M.D. Solute and isotopic geochemistry and ground water flow in the central Wasatch Range, Utah. J. Hydrol. 1995, 172, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yechieli, Y.; Wood, W.W. Hydrogeologic processes in saline systems: Playas, sabkhas, and saline lakes. Earth Sci. Rev. 2002, 58, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




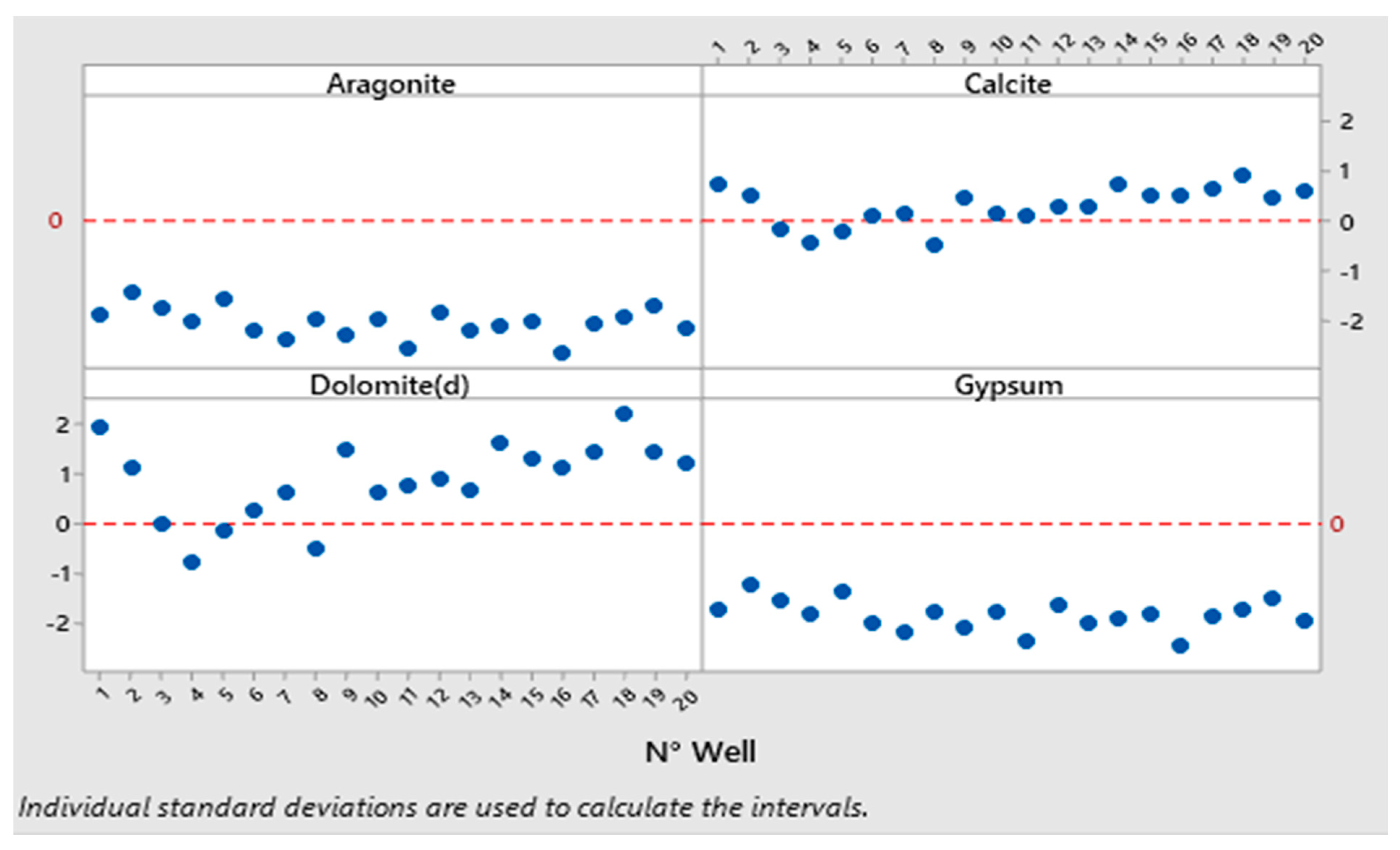

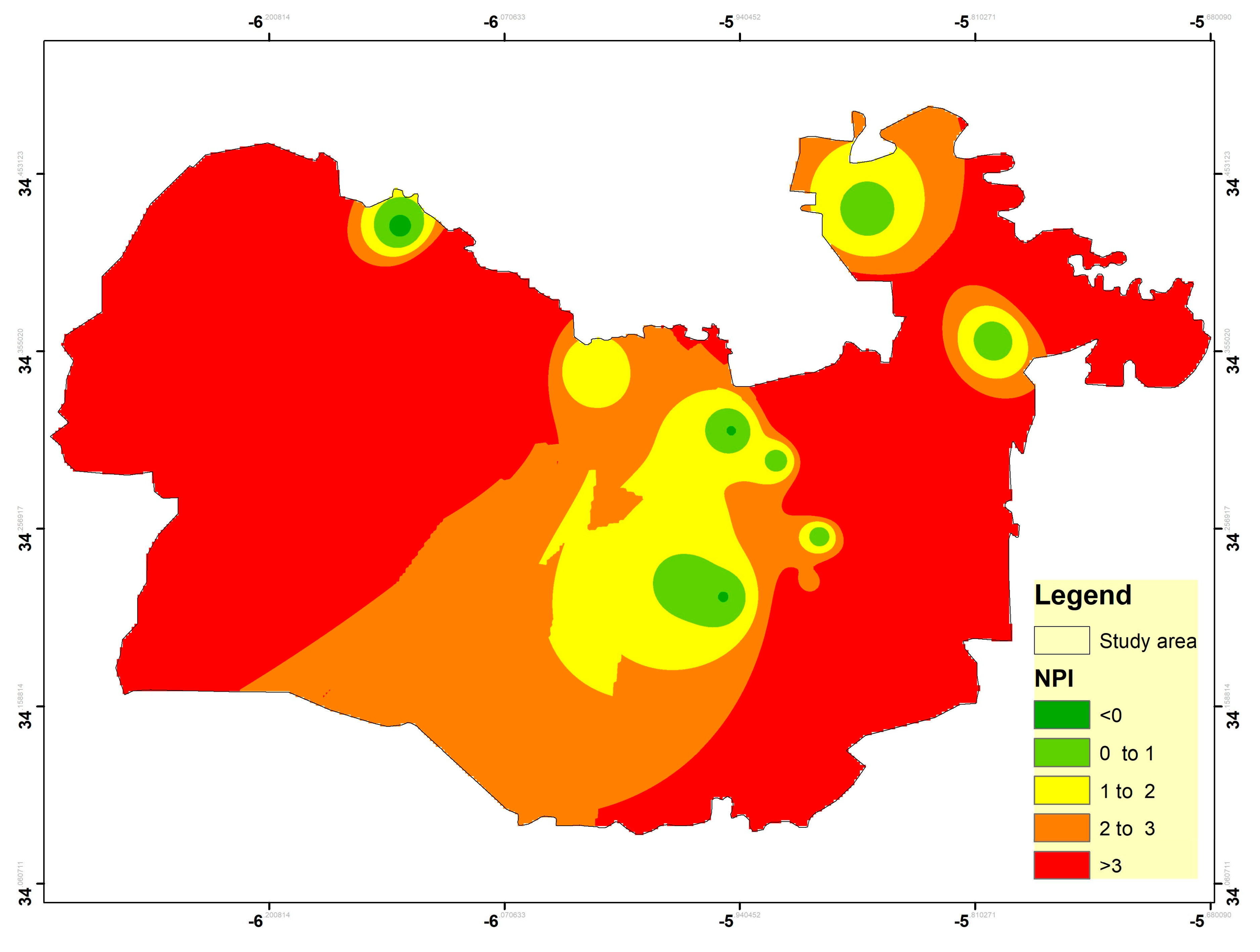
| NPI Value | NPI Interpretation |
|---|---|
| less than 0 | clean (unpolluted) |
| from 0 to 1 | low pollution |
| from 1 to 2 | moderate pollution |
| from 2 to 3 | high pollution |
| bigger than 3 | very high pollution |
| Name | Equation | Equation No. | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gibbs Ratio 1 | (6) | [21] | |
| Gibbs Ratio 2 | (7) | [21] | |
| CAI (Chloro-Alkaline Index) | (8) | [22] | |
| CAII | (9) | [22] | |
| Saturation Index (SI) | (10) | [23] |
| Variable | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | 6.74 | 7.85 | 7.3165 | 0.28 |
| EC | 1540 | 17,550 | 4915 | 3772 |
| TDS | 1001 | 11,408 | 3195 | 2452 |
| TH | 312 | 1524 | 715 | 332.7 |
| Ca2+ | 2.84 | 14.5 | 8.373 | 3.525 |
| Mg2+ | 2.22 | 16.02 | 5.927 | 3.548 |
| Na+ | 8.08 | 85.19 | 32.09 | 22.03 |
| K+ | 0.06 | 0.3 | 0.1525 | 0.0703 |
| HCO3− | 2.38 | 13.1 | 7.568 | 2.599 |
| NO3− | 0.23 | 6.24 | 1.604 | 1.557 |
| Cl− | 7.46 | 82.5 | 31.31 | 21.86 |
| SO42− | 0.29 | 4.66 | 1.647 | 1.21 |
| Pollution Category | Percentage of Wells | Number of Wells |
|---|---|---|
| Clean or Insignificant Pollution (IP) | - | - |
| Low Pollution (LP) | 20% | 4 |
| Moderate Pollution (MP) | 15% | 3 |
| High Pollution (HP) | 10% | 2 |
| Very High Pollution (VHP) | 55% | 11 |
| NPI Value | NPI Interpretation | No | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| <0 | Clean (unpolluted) | 2 | 10 |
| 0–1 | Low pollution | 3 | 15 |
| 1–2 | Moderate pollution | 5 | 25 |
| 2–3 | High pollution | 1 | 5 |
| >3 | Very significant pollution | 9 | 45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Aizari, H.S.; Aslaou, F.; Al-Aizari, A.R.; Al-Odayni, A.-B.; Al-Aizari, A.-J.M. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality and Contamination Using the Groundwater Pollution Index (GPI), Nitrate Pollution Index (NPI), and GIS. Water 2023, 15, 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203701
Al-Aizari HS, Aslaou F, Al-Aizari AR, Al-Odayni A-B, Al-Aizari A-JM. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality and Contamination Using the Groundwater Pollution Index (GPI), Nitrate Pollution Index (NPI), and GIS. Water. 2023; 15(20):3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203701
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Aizari, Hefdhallah S., Fatima Aslaou, Ali R. Al-Aizari, Abdel-Basit Al-Odayni, and Abdul-Jaleel M. Al-Aizari. 2023. "Evaluation of Groundwater Quality and Contamination Using the Groundwater Pollution Index (GPI), Nitrate Pollution Index (NPI), and GIS" Water 15, no. 20: 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203701
APA StyleAl-Aizari, H. S., Aslaou, F., Al-Aizari, A. R., Al-Odayni, A.-B., & Al-Aizari, A.-J. M. (2023). Evaluation of Groundwater Quality and Contamination Using the Groundwater Pollution Index (GPI), Nitrate Pollution Index (NPI), and GIS. Water, 15(20), 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203701








