Release of Microplastics from Urban Wastewater Treatment Plants to Aquatic Ecosystems in Acapulco, Mexico
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. WWTP Evaluation
2.2. MP Separation
2.3. Quality Control
2.4. MP Characterization
2.5. Daily and Annual Projections of Removal Efficiencies
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MP Detection
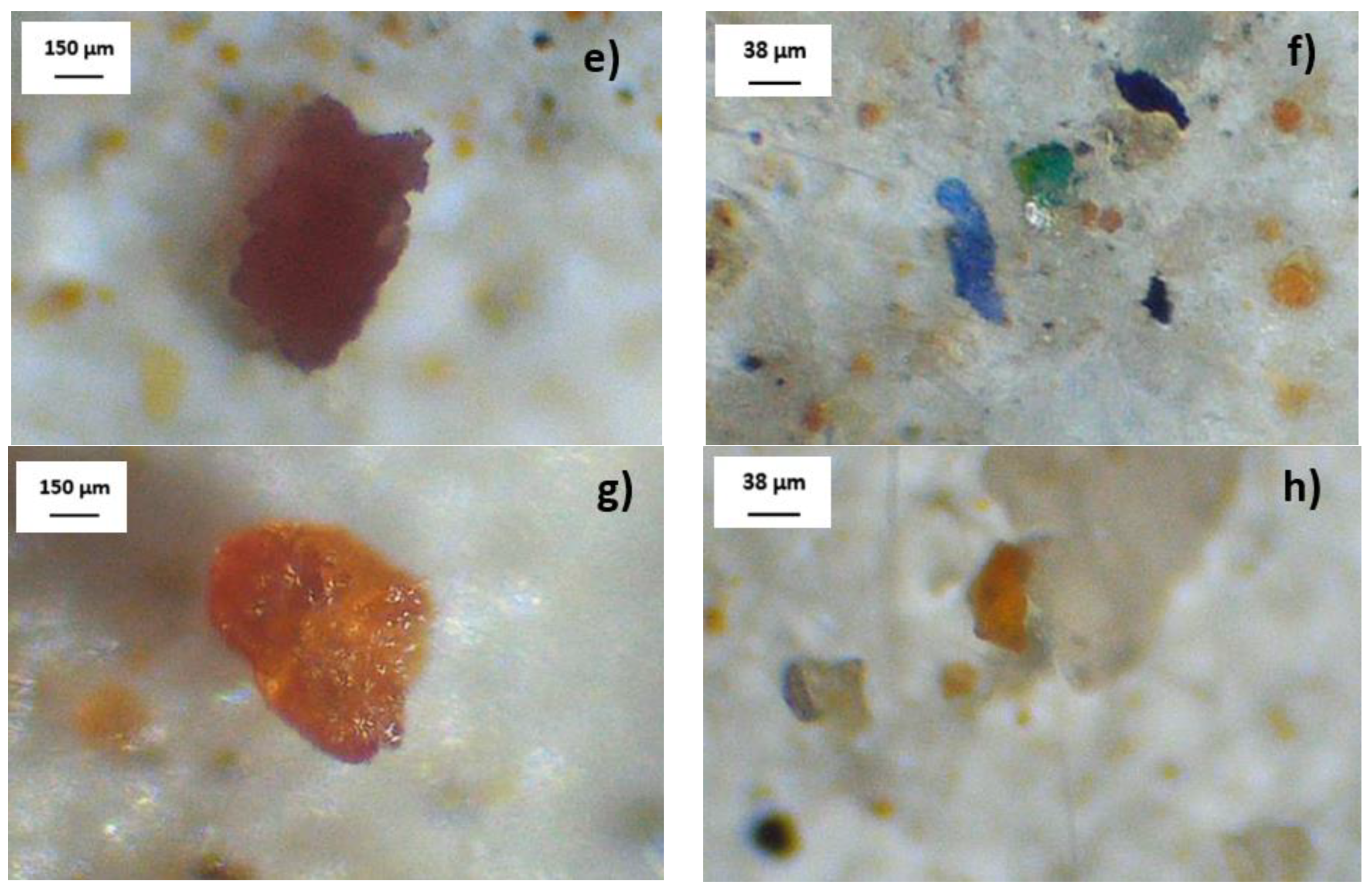
3.2. MP Physical Characterization
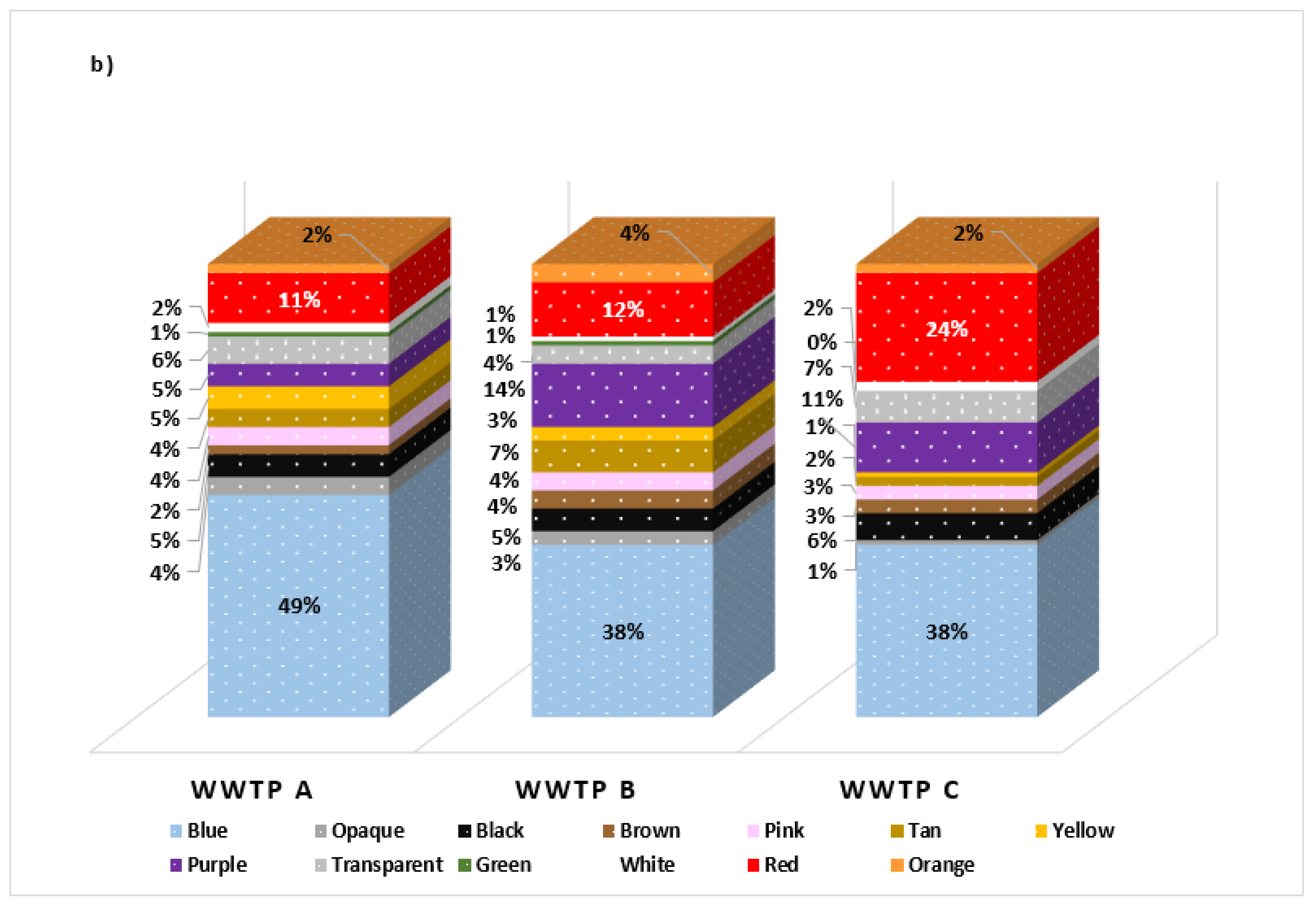
3.2.1. MP Color
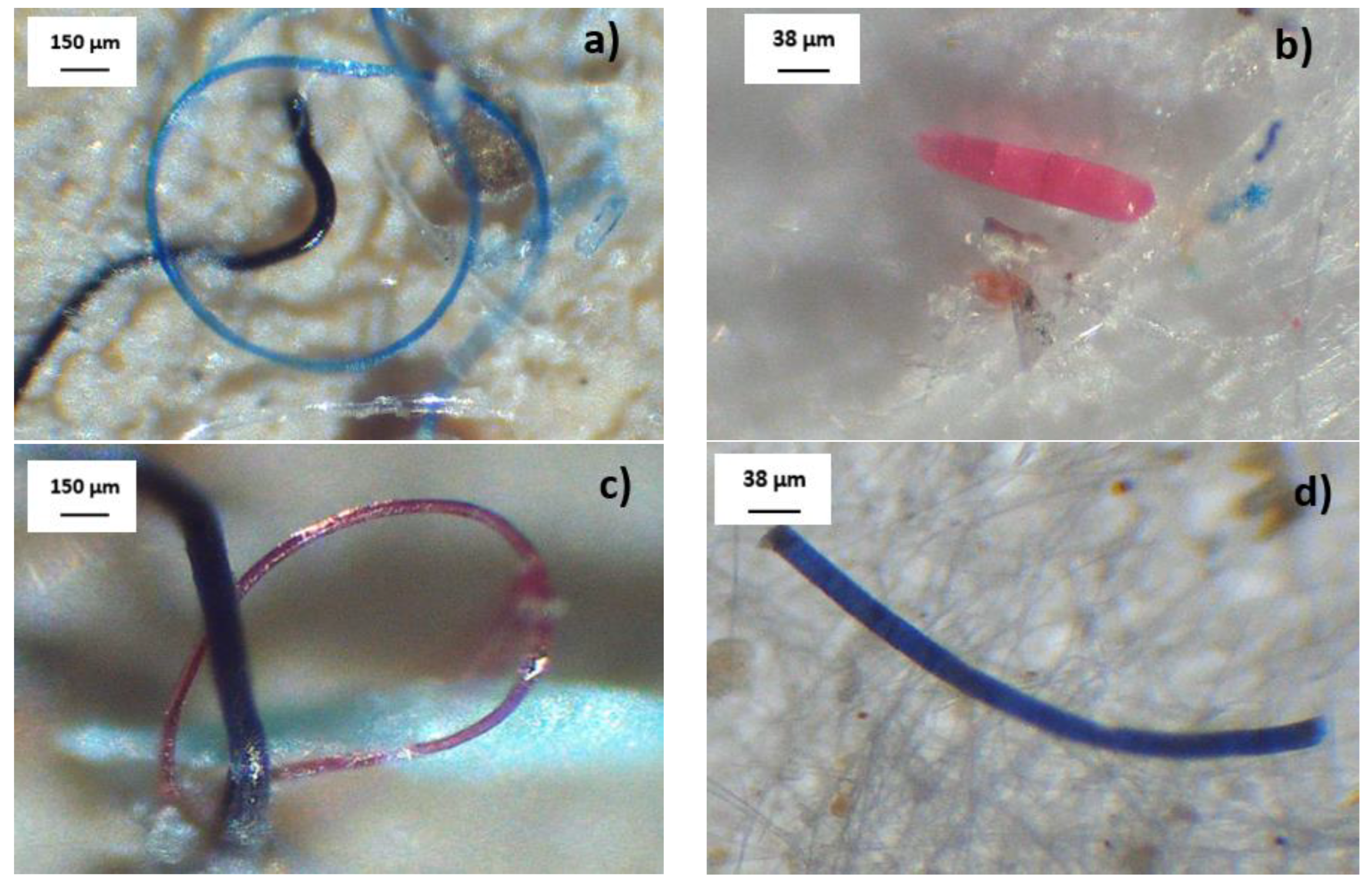
3.2.2. MP Morphology
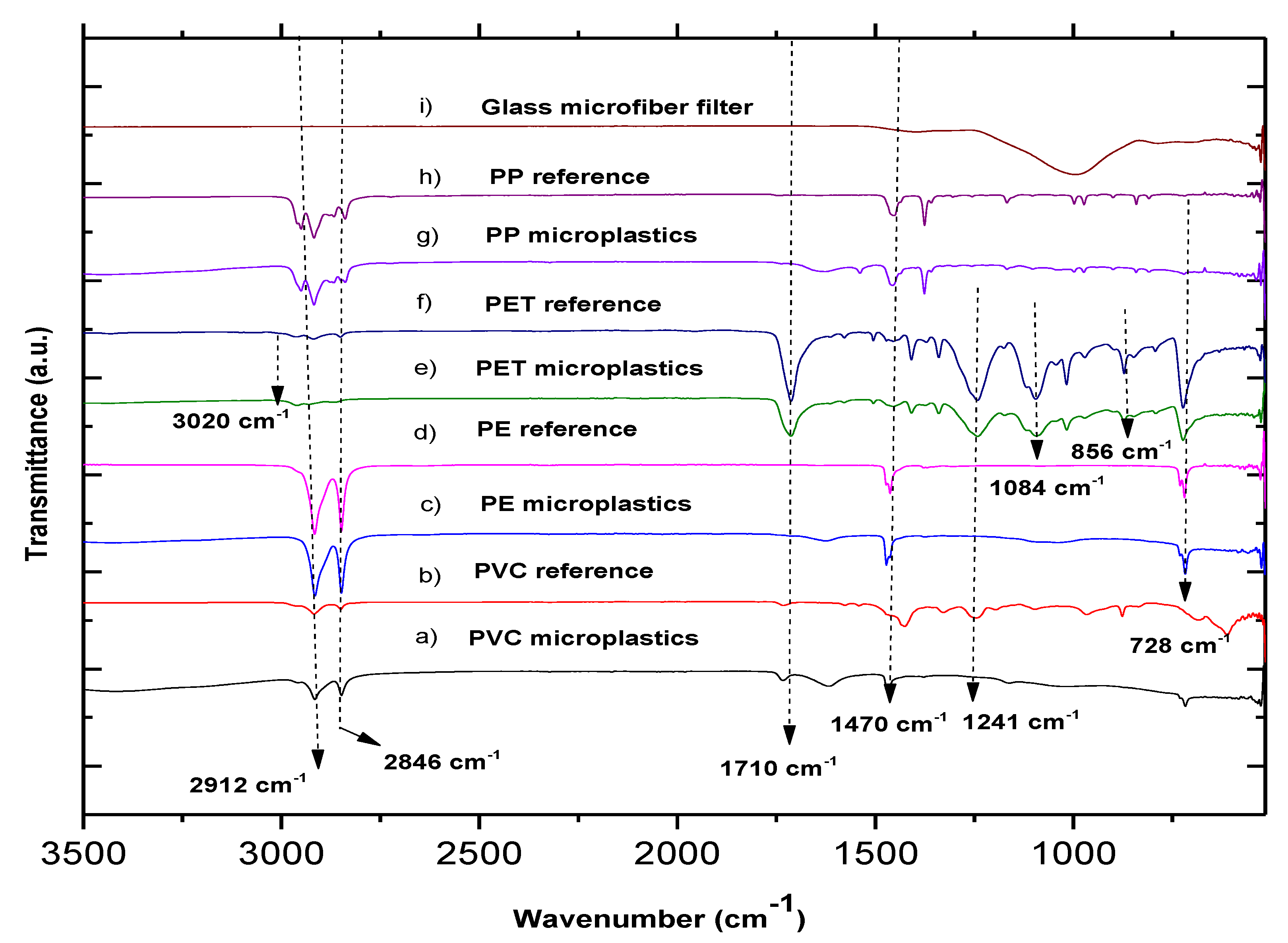
3.3. MP Characterization by FTIR
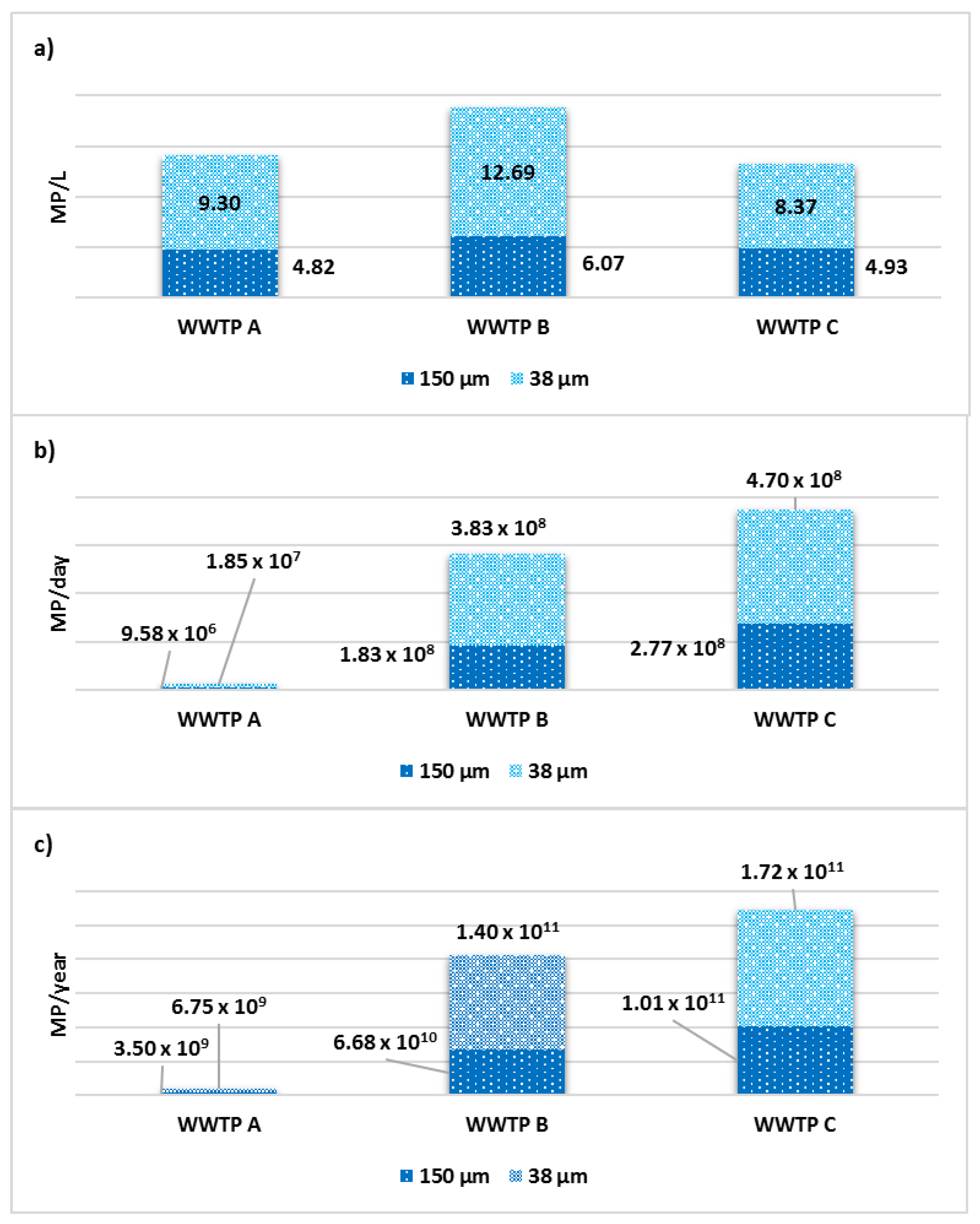
3.4. MP Concentration and Removal Efficiencies
3.5. Daily and Annual MP Emission Projections
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, L.J.J.; van Emmerik, T.; van der Ent, R.; Schmidt, C.; Lebreton, L. More than 1000 rivers account for 80% of global riverine plastic emissions into the ocean. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eaaz5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.G.L.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a consensus on the definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, K.; Rochman, C.M. Microplastics: A multidimensional contaminant requires a multidimensional framework for assessing risk. Microplastics Nanoplastics 2022, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Human Consumption of Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7068–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefato, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabl, P.; Köppel, S.; Königshofer, P.; Bucsics, T.; Trauner, M.; Reiberger, T.; Liebmann, B. Detection of various Microplastics in Human Stool. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamargo, A.; Molinero, N.; Reinosa, J.J.; Alcolea-Rodriguez, V.; Portela, R.; Bañares, M.A.; Fernández, J.F.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V. PET microplastics affect human gut microbiota communities during simulated gastrointestinal digestion, first evidence of plausible polymer biodegradation during human digestion. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çobanoğlu, H.; Belivermiş, M.; Sıkdokur, E.; Kılıç, Ö.; Çayır, A. Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of polyethylene microplastics on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhatib, D.; Oyanedel-Craver, V. A critical review of extraction and identification methods of microplátics in wastewater and drinking wáter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7037–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Park, B. Review of microplastic distribution, toxicity, análisis methods, and removal technologies. Water 2021, 13, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Dai, X.; Wang, Q.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Ni, B.J. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Detection, occurrence and removal. Water Res. 2019, 152, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, A. Depuración y Desinfección de Aguas Residuales, 5th ed.; Colegio de Ingenieros de Caminos, Canales y Puertos: Madrid, Spain, 2001; pp. 88–120. [Google Scholar]
- Calero, M.; Gody, V.; Quesada, L.; Martín-Lara, M.A. Green strategies for microplastics reduction. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 28, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvim, C.B.; Bes-Piá, M.A.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A. Separation and identification of microplastics from primary and secondary effluents and activated sludge from wastewater treatment plants. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 126293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, K.; Cui, S.; Kang, Y.; An, L.; Lei, K. Removal of microplastics in municipal sewage from China’s largest water reclamation plant. Water Res. 2019, 155, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magni, S.; Binelli, A.; Pittura, L.; Avio, C.G.; Della Torre, C.; Parenti, C.C.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. The fate of microplastics in an italian wastewater treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, F.; Ewins, C.; Carbonnier, F.; Quinn, B. Wastewater treatment works (WwTW) as a source of microplastics in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5800–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvitie, J.; Heinonen, M.; Pääkkönen, J.P.; Vahtera, E.; Mikola, A.; Setälä, O.; Vahala, R. Do wastewater treatment plants act as a potential point source of microplastics? Preliminary study in the coastal Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, Y.; Isobe, T.; Takada, H.; Kanehiro, H.; Ohtake, C.; Kaminuma, T. Plastic resin pellets as a transport medium for toxic chemicals in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, M.; Pironti, C.; Motta, O.; Miele, Y.; Proto, A.; Montano, L. Microplastics in the aquatic environment: Occurrence, persistence, análisis, and human exposure. Water 2021, 13, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOM-001-SEMARNAT-2021; Norma Oficial Mexicana—Que Establece los Límites Permisibles de Contaminantes en las Descargas de Aguas Residuales en Cuerpos Receptores Propiedad de la Nación. Comisión Nacional del Agua, Diario Oficial de la Federación: Ciudad de México, México, 2022.
- NOM-002-SEMARNAT-1996; Norma Oficial Mexicana—Que Establece los Límites Máximos Permisibles de Contaminantes en las Descargas de Aguas Residuales a los Sistemas de Alcantarillado Urbano o Municipal. Comisión Nacional del Agua, Diario Oficial de la Federación: Ciudad de México, México, 1998.
- NOM-003-SEMARNAT-1997; Norma Oficial Mexicana—Que Establece los Límites Máximos Permisibles de Contaminantes para las Aguas Residuales Tratadas que se Reúsen en Servicios al Público. Comisión Nacional del Agua, Diario Oficial de la Federación: Ciudad de México, México, 1998.
- Cámara de Diputados del H. Congreso de la Unión. Ley de Aguas Nacionales, Constitución Política Mexicana—Tiene por Objeto Regular la Explotación, Uso o Aprovechamiento de Dichas Aguas, su Distribución y Control, Así Como la Preservación de su Cantidad y Calidad para Lograr su Desarrollo Integral Sustentable; Cámara de Diputados del H. Congreso de la Unión, Diario Oficial de la Federación: Ciudad de México, México, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Masura, J.; Baker, J.; Foster, G.; Arthur, C. Laboratory Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in the Marine Environment; NOAA Marine Debris Program, 2015, Technical Memorandum NOS-OR&R-48. Available online: https://marinedebris.noaa.gov/sites/default/files/publications-files/noaa_microplastics_methods_manual.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Blair, R.M.; Waldron, S.; Gauchotte-Lindsay, C. Average daily flow of microplastics through a tertiary wastewater treatment plant over a ten-month period. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galafassi, S.; Di Cesare, A.; Di Nardo, L.; Sabatino, R.; Valsesia, A.; Fumagalli, F.S.; Corno, G.; Volta, P. Microplastic retention on small and medium municipal wastewater treatment plants and the role of the desinfection. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 10535–10546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández Fernández, J.; Cano, H.; Guerra, Y.; Puello Polo, E.; Ríos-Rojas, J.F.; Vivas-Reyes, R.; Oviedo, J. Identification and quantification of microplastics in effluents of wastewater treatment plant by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Sustainability 2022, 14, 4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Koinstinen, A.; Setälä, O. Solutions to microplastic pollution -Removal of microplastics from wastewater effluent with advanced wastewater treatment technologies. Water Res. 2017, 123, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Kim, Y. Treatment characteristics of microplastics at biological sewage treatment facilities in Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Setälä, O.; Heinonen, M.; Koistinen, A. How well is microlitter purified from wastewater?—A detailed study on the stepwise removal of microlitter in a tertiary level wastewater treatmetn plant. Water Res. 2017, 109, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamoah, B.O.; Salmi, P.; Räty, J.; Ryymin, K.; Talvitie, J.; Karjalainen, A.K.; Kukkonen, J.V.K.; Roussey, M.; Peiponen, K.E. Optical monitoring of microplastics filtrated from wastewater sludge and suspended in etanol. Polymers 2021, 13, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, L.; Mei, Q.; Dong, B.; Dai, X.; Ding, G.; Zeng, E.Y. Microplastics in sewage sludge from the wastewater plants in China. Water Res. 2018, 142, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, A.M.; O’Conell, B.; Healy, M.G.; O’Connor, I.; Officer, R.; Nash, R.; Morrison, L. Microplastics in sewage sludge: Effects of treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Int-Veen, I.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Identification of microplastics in effluents of waste water treatment plants using focal plane-based micro-Fourier transform infrared imaging. Water Res. 2017, 108, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahladakis, J.N.; Velis, C.A.; Weber, R.; Iacovidou, E.; Purnell, P. An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiras, R.; Verdejo, E.; Campoy-López, P.; Vidal-Liñán, L. Aquatic toxicity of chemically defined microplastics can be explained by functional additives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.; Filella, M. Hazardous metal additives in plastics and their environmental impacts. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NMX-E-232-CNCP-2011; Norma Oficial Mexicana—Industria del Plástico. Símbolos de Identificación de Plásticos. Dirección General de Normas, Diario Oficial de la Federación: Ciudad de México, México, 2011.
- Gies, E.A.; LeNoble, J.L.; Noël, M.; Etemadifar, A.; Bishay, F.; Hall, E.R.; Ross, P.S. Retention of microplastics in a major secondary wastewater treatment plant in Vancouver, Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.J.; Hidayaturrahman, H.; Peera, S.G.; Lee, T.G. Elimination of microplastics at different stages in wastewater treatment plants. Water 2022, 14, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Bao, T.; Hong, L.; Wu, K. Occurrence characterization and contamination risk evaluation of microplastics om Hefei’s urban wastewater treatment plant. Water 2023, 15, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayo, J.; Olmos, S.; López-Castellanos, J. Assesment of microplastics in a municipal wastewater treatment plant with tertiary treatment: Removal efficiencies and loading per day into the environment. Water 2021, 13, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, S.; Weber, F.; Kerpen, J.; Winklhofer, M.; Engelhart, M.; Barkmann, L. Elimination of microplastics by downstream sand filters in wastewater treatment. Water 2020, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Vianello, A.; Vollertsen, J. Removal of >10 µm microplastic particles from treated wastewater by a disc filter. Water 2019, 11, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syberg, K.; Nielsen, M.B.; Clausen, L.P.W.; van Calster, G.; van Wezel, A.; Rochman, C.; Koelmans, A.A.; Cronin, R.; Pahl, S.; Hansen, S.F. Regulation of plastic from a circular economy perspective. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 29, 100462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Dong, Q.; Zuo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Wu, W.M. Microplastics in a municipal wastewater treatment plant: Fate, dynamic distribution, removal efficiences, and control strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.A.; Iordachescu, L.; Tumlin, S.; Vollersten, J. A complete mass balance for plastics in a wastewater treatment plant -Macroplastics contributes more than microplastics. Water Res. 2021, 2021, 117307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Yao, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, T. A review of the removal of microplastics in global wastewater treatment plants: Characteristics and mechanims. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yuan, W.; Di, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Transfer and fate of microplastics during the conventional activated sludge process in one wastewater tratment plant of China. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lares, M.; Ncibi, M.C.; Sillanpää, M.; Sillanpää, M. Ocurrence, identification and removal of microplastic particles and fibers in conventional activated sludge process and advanced MBR technology. Water Res. 2018, 133, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Miino, M.C.; Caccamo, F.M.; Milanese, C. Microplastics in sewage sludge: A known but underrated pathway in wastewater treatment plants. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, J.K.; Park, J.H.; Zoh, K.D. Distributions of microplastics in surface wáter, fish, and sediment in the vicinity of a sewage treatment plant. Water 2020, 12, 3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.T.; Myers, E.; Schober, D.; Korzin, A.; Thege, C.; Schuhen, K. Comparision of AOP, GAC, and novel organosilane-based process for the removal of microplastics at a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Water 2023, 15, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Nord, N.B.; Bester, K.; Vollertsen, J. Microplastics removal from treated wastewater by a biofilter. Water 2020, 12, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, Z.T.; Cundy, A.B.; Croudace, I.W.; Warwick, P.E.; Celis-Hernández, O.; Stead, J.L. A rapid method for assessing the accumulation of microplastics in the sea surface microlayer (SML) of estuarine systems. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Bao, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, F.; Liu, W.; Su, H.; Zhang, R. Occurrence, bioacumulation, and risk assessment of microplastics in the aquatic environment: A review. Water 2023, 15, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, F.; Fan, C. Fate of microplastics under the influence of climate change. iScience 2023, 26, 107649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Group | Count | Sum | Average | Variance | ||
| WWPT A | 6 | 564.77 | 94.13 | 13,993.38 | ||
| WWPT B | 6 | 736.8 | 122.80 | 26,269.83 | ||
| WWPT C | 6 | 538.04 | 89.67 | 13,066.88 | ||
| ANOVA | ||||||
| Source of Variation | SS | df | MS | F | p value | F crit |
| Between Groups | 3878.58 | 2 | 1939.29 | 0.11 | 0.90 | 3.68 |
| Within Groups | 266,650.44 | 15 | 17,776.70 | |||
| Total | 270,529.01 | 17 |
| Functional Group | OH | CH2 (Stretch) | CH | C=O | CH2 (Scissor) | C-O-C | C-O | CH2 (Rock) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | 3020 | 2900 | 2800 | 1713 | 1448 | 1247 | 1084 | 728 |
| PET | PET | PET | PET | PET | PET | PET | - | |
| - | PVC | PVC | - | PVC | - | - | - | |
| - | PP | PP | - | PP | - | - | PP | |
| - | PE | - | - | PE | - | - | PE |
| WWTP A | WWTP B | WWTP C | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP (Ítems/L) 38 µm | MP (Ítems/L) 150 µm | MP (Ítems/L) 38 µm | MP (Ítems/L) 150 µm | MP (Ítems/L) 38 µm | MP (Ítems/L) 150 µm | |||||||||||||
| I | E | % r | I | E | % r | I | E | % r | I | E | % r | I | E | %r | I | E | %r | |
| June | 76.0 ± 1.62 | 1.0 ± 0.61 | 98.7 | 20.7 ± 0.48 | 1.73 ± 0.36 | 91.7 | 57.7 ± 2.25 | 0.8 ± 0.34 | 98.5 | 45.50 ± 1.64 | 1.1 ± 0.23 | 97.4 | 44.2 ± 2.92 | 0.7 ± 0.17 | 98.3 | 33.4 ± 2.53 | 0.8 ± 0.18 | 97.5 |
| July | 96.1 ± 1.26 | 2.8 ± 0.55 | 97.1 | 68.5 ± 0.93 | 2.00 ± 1.65 | 97.1 | 80.6 ± 2.67 | 2.8 ± 0.74 | 96.4 | 48.33 ± 1.91 | 1.8 ± 0.81 | 96.3 | 104 ±6.09 | 2.4 ± 0.20 | 97.7 | 39.4 ± 3.76 | 0.9 ± 0.64 | 97.5 |
| October | 174.9 ± 2.63 | 9.0 ± 0.71 | 94.8 | 66.7 ± 2.23 | 4.82 ± 0.53 | 92.8 | 159.3 ± 7.72 | 13.0 ± 1.93 | 91.8 | 103.67 ± 4.04 | 8.0 ± 0.56 | 92.3 | 150 ±8.67 | 13.5 ± 1.16 | 91.0 | 67.9 ± 4.64 | 6.2 ± 0.48 | 90.8 |
| November | 218.8 ± 3.29 | 24.3 ± 1.04 | 88.9 | 88.4 ± 0.53 | 10.73 ± 0.79 | 87.9 | 194.7 ± 13.51 | 34 ± 0.90 | 82.5 | 122.75 ± 4.76 | 13.3 ± 1.08 | 89.2 | 200 ±1.01 | 16.8 ± 0.41 | 91.6 | 88.3 ± 5.0 | 11.6 ± 0.38 | 86.8 |
| (a) | ||||||
| Influent | ||||||
| Group | Count | Sum | Average | Variance | ||
| June (dry season) | 3 | 277.58 | 92.53 | 178.11 | ||
| July (dry season) | 3 | 437.50 | 145.83 | 321.10 | ||
| October (rainy season) | 3 | 723.09 | 241.03 | 497.15 | ||
| November (rainy season) | 3 | 912.92 | 304.31 | 221.56 | ||
| ANOVA | ||||||
| Source of Variation | SS | df | MS | F | p value | F crit |
| Between Groups | 80,944.31 | 3 | 26,981.44 | 88.61 | 1.8 × 10−6 | 4.07 |
| Within Groups | 2435.85 | 8 | 304.48 | |||
| Total | 83,380.16 | 11 | ||||
| (b) | ||||||
| Effluent | ||||||
| Group | Count | Sum | Average | Variance | ||
| June (dry season) | 3 | 6.41 | 2.14 | 0.36 | ||
| July (dry season) | 3 | 12.82 | 4.27 | 0.65 | ||
| October (rainy season) | 3 | 54.67 | 18.22 | 14.60 | ||
| November (rainy season) | 3 | 110.81 | 36.94 | 91.59 | ||
| ANOVA | ||||||
| Source of Variation | SS | df | MS | F | p value | F crit |
| Between Groups | 2314.55 | 3 | 771.52 | 28.79 | 0.0001 | 4.07 |
| Within Groups | 214.37 | 8 | 26.80 | |||
| Total | 2528.93 | 11 | ||||
| Effluent | ||||||
| Group | Count | Sum | Average | Variance | ||
| WWTP A | 4 | 56.49 | 14.12 | 217.32 | ||
| WWTP B | 4 | 75.02 | 18.76 | 433.26 | ||
| WWTP C | 4 | 53.20 | 13.30 | 169.34 | ||
| ANOVA | ||||||
| Source of Variation | SS | df | MS | F | p value | F crit |
| Between Groups | 69.19 | 2 | 34.60 | 0.13 | 0.88 | 4.26 |
| Within Groups | 2459.74 | 9 | 273.30 | |||
| Total | 2528.93 | 11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-Munguía, E.J.; Rosas-Acevedo, J.L.; Ramírez-Hernández, A.; Aparicio-Saguilan, A.; Brito-Carmona, R.M.; Violante-González, J. Release of Microplastics from Urban Wastewater Treatment Plants to Aquatic Ecosystems in Acapulco, Mexico. Water 2023, 15, 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203643
Flores-Munguía EJ, Rosas-Acevedo JL, Ramírez-Hernández A, Aparicio-Saguilan A, Brito-Carmona RM, Violante-González J. Release of Microplastics from Urban Wastewater Treatment Plants to Aquatic Ecosystems in Acapulco, Mexico. Water. 2023; 15(20):3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203643
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-Munguía, Enrique J., José Luis Rosas-Acevedo, Aurelio Ramírez-Hernández, Alejandro Aparicio-Saguilan, Rosa M. Brito-Carmona, and Juan Violante-González. 2023. "Release of Microplastics from Urban Wastewater Treatment Plants to Aquatic Ecosystems in Acapulco, Mexico" Water 15, no. 20: 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203643










