Significant Dynamic Disturbance of Water Environment Quality in Urban Rivers Flowing through Industrial Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
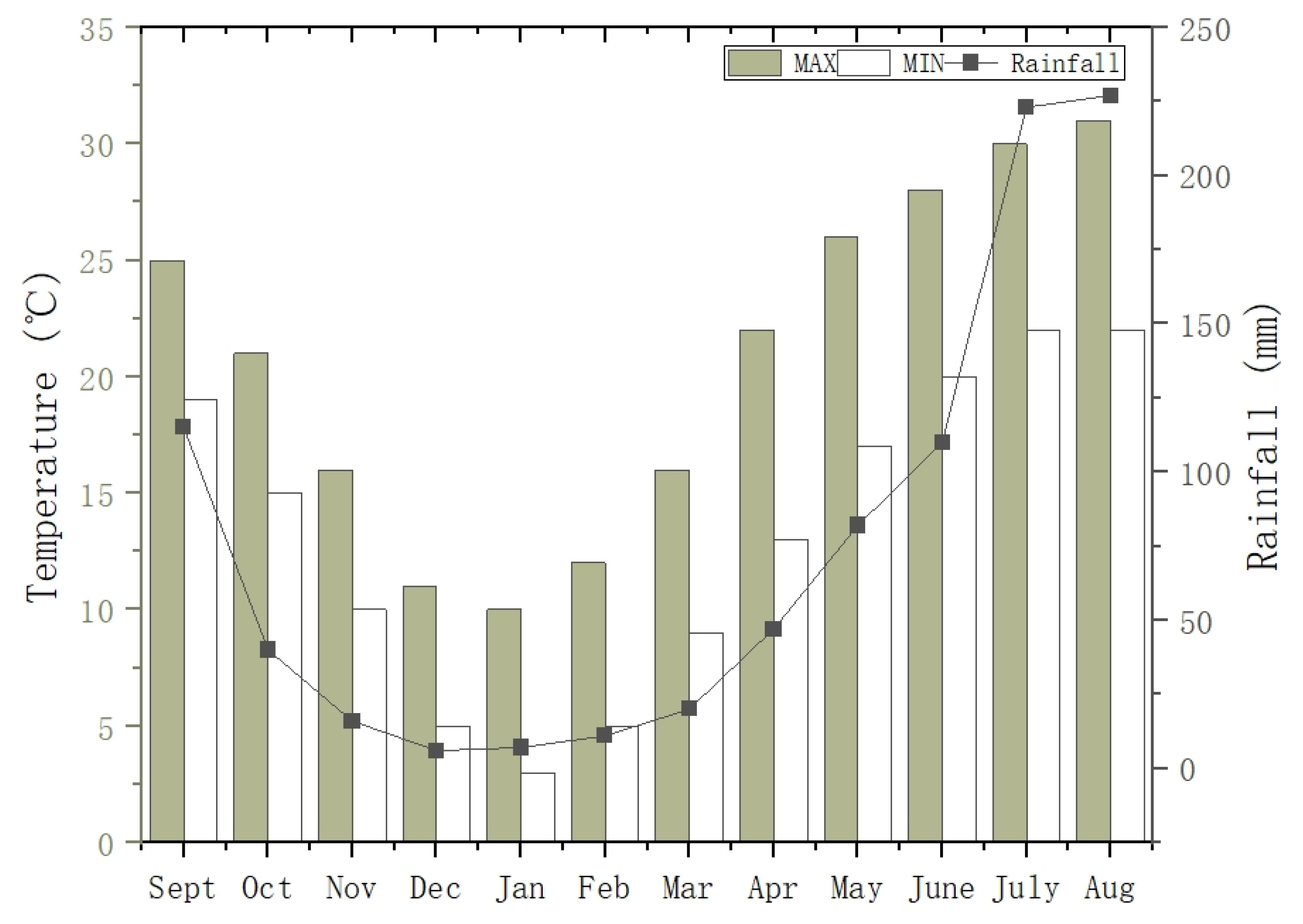
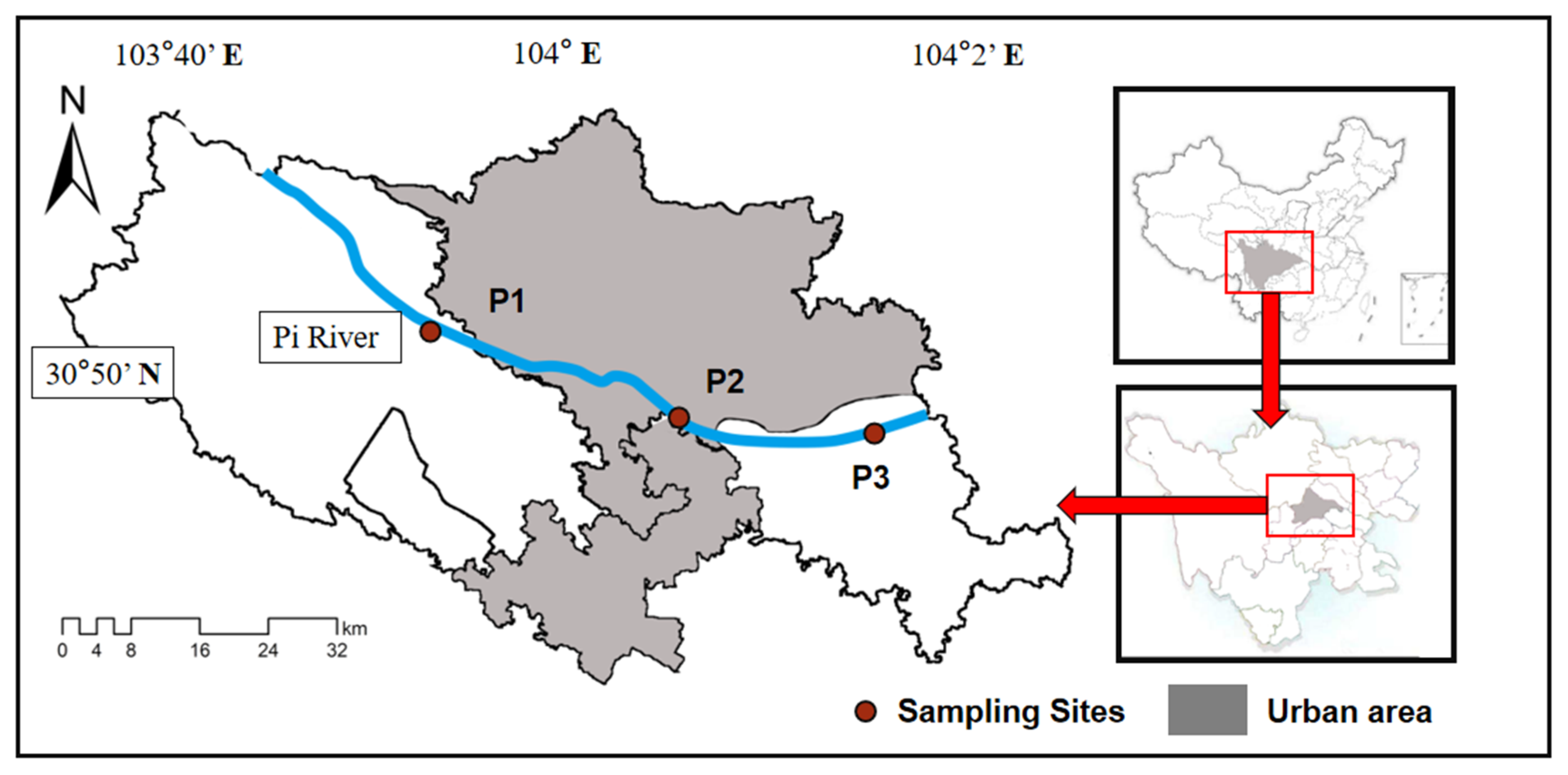
2.1. Study Area Description and Sampling Sites
2.2. Water Sampling
2.3. Measurement of Water Quality Parameters
2.4. Environmental Quality Assessment Method of Surface Water
2.4.1. Water Pollution Index
2.4.2. Trophic Level Index
2.4.3. Measurement of the Diversity and Richness of Benthic Macrobenthos
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
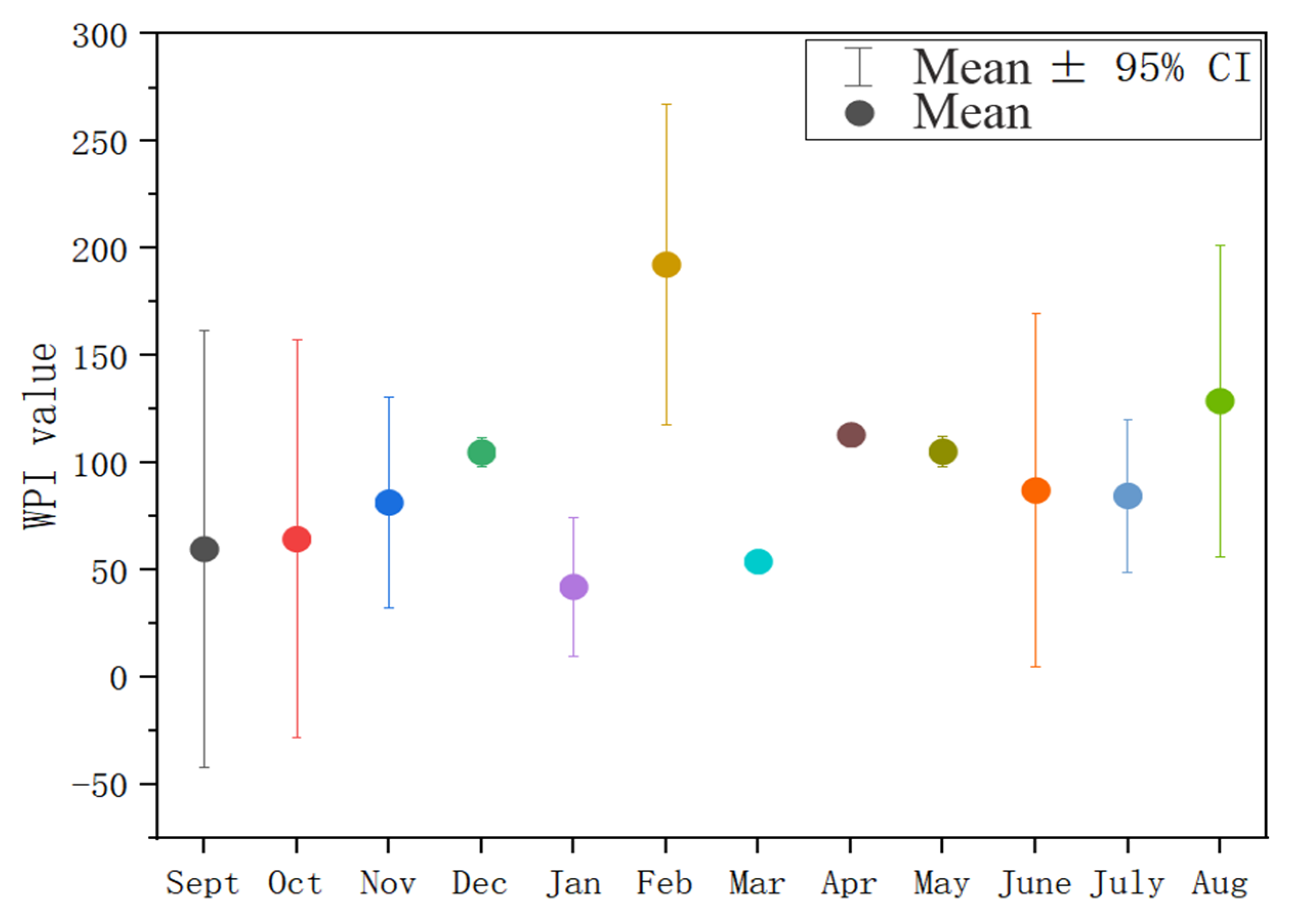
3.1. Temporal–Spatial Variation in the Water Quality Index
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variations in the TLI (∑)
3.3. Aquatic Organism Community Structures
3.3.1. Macrobenthic Community Structure
3.3.2. Algal Community Structure
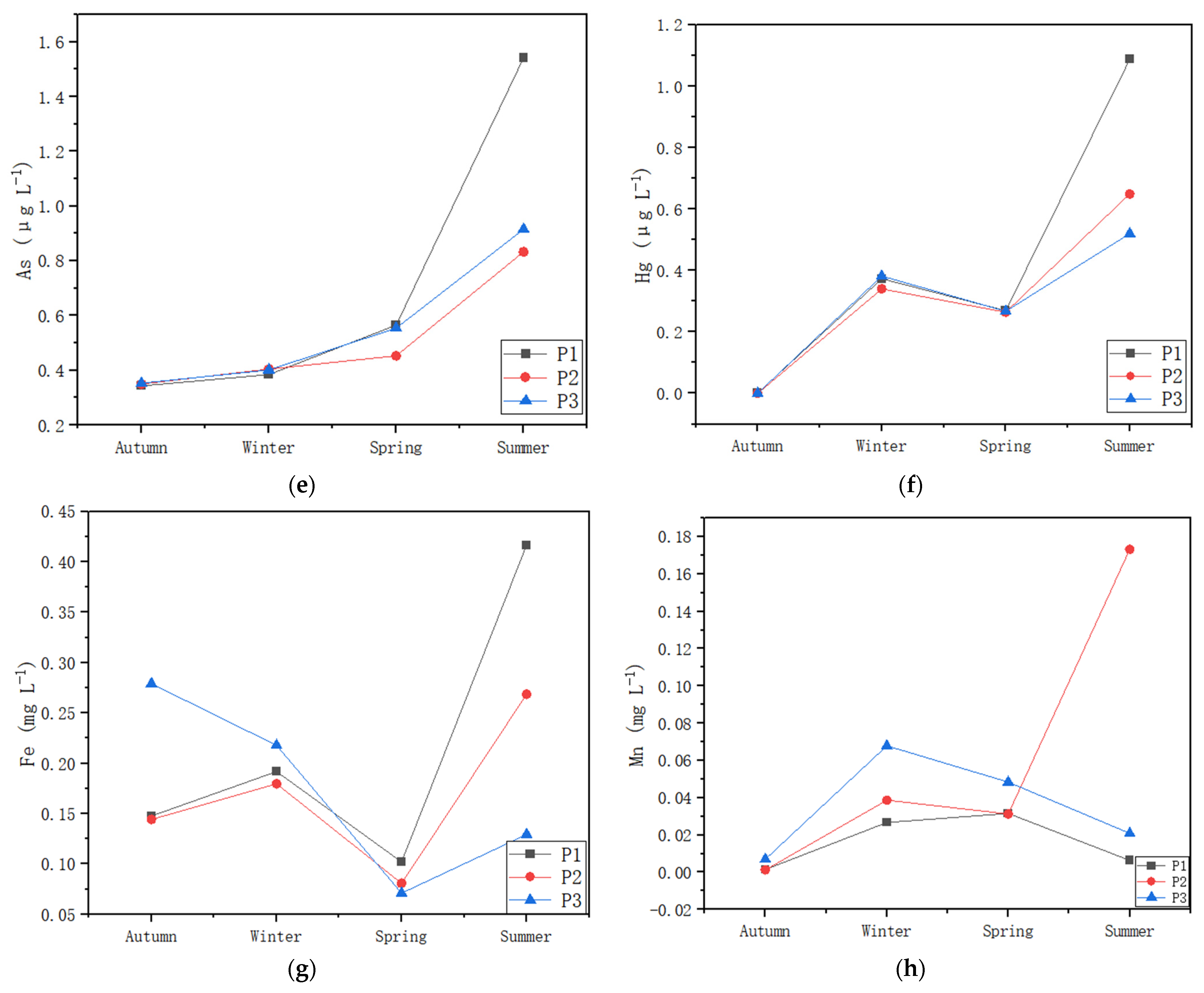
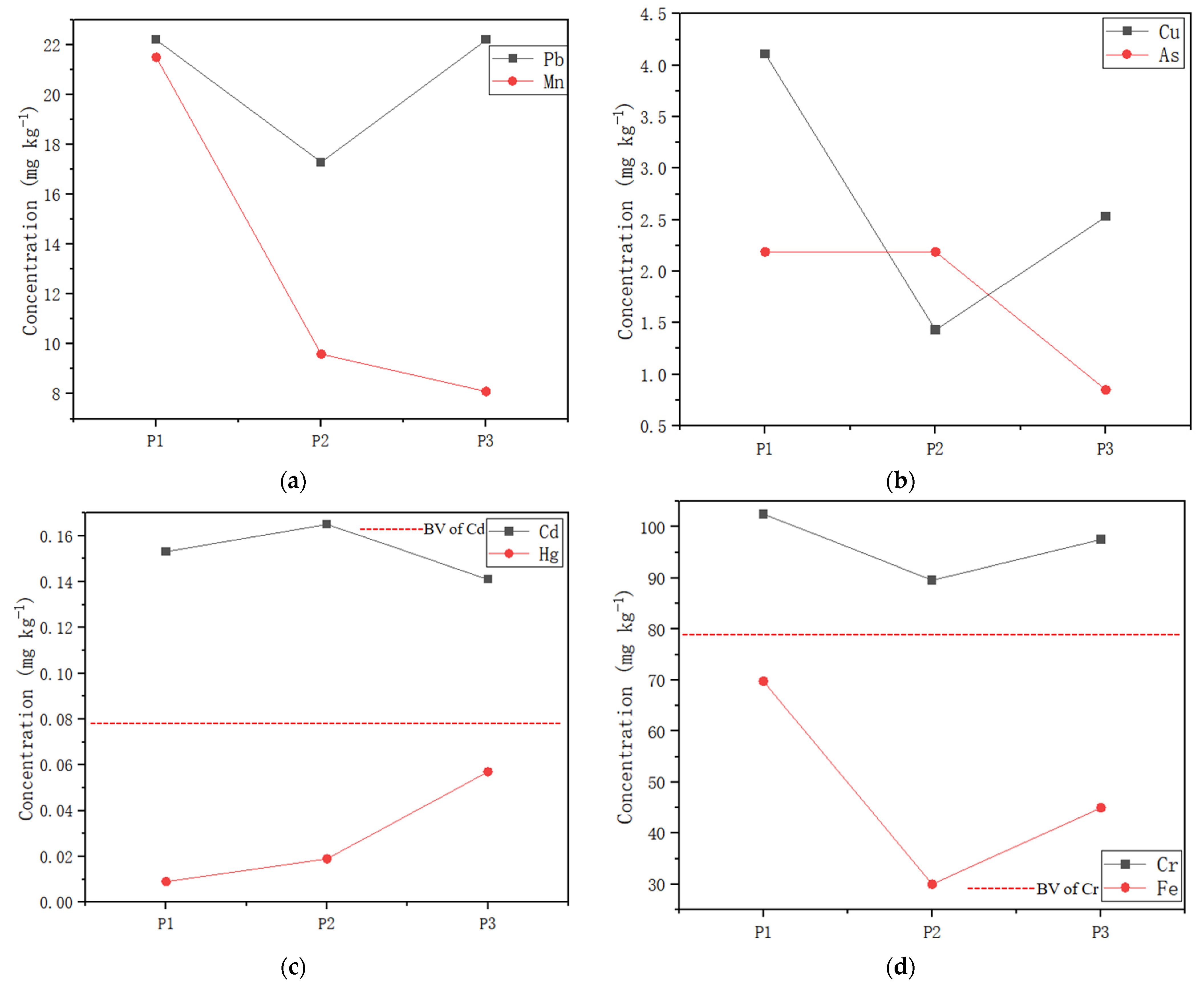
3.4. Metals in Water and Sediment
4. Discussion
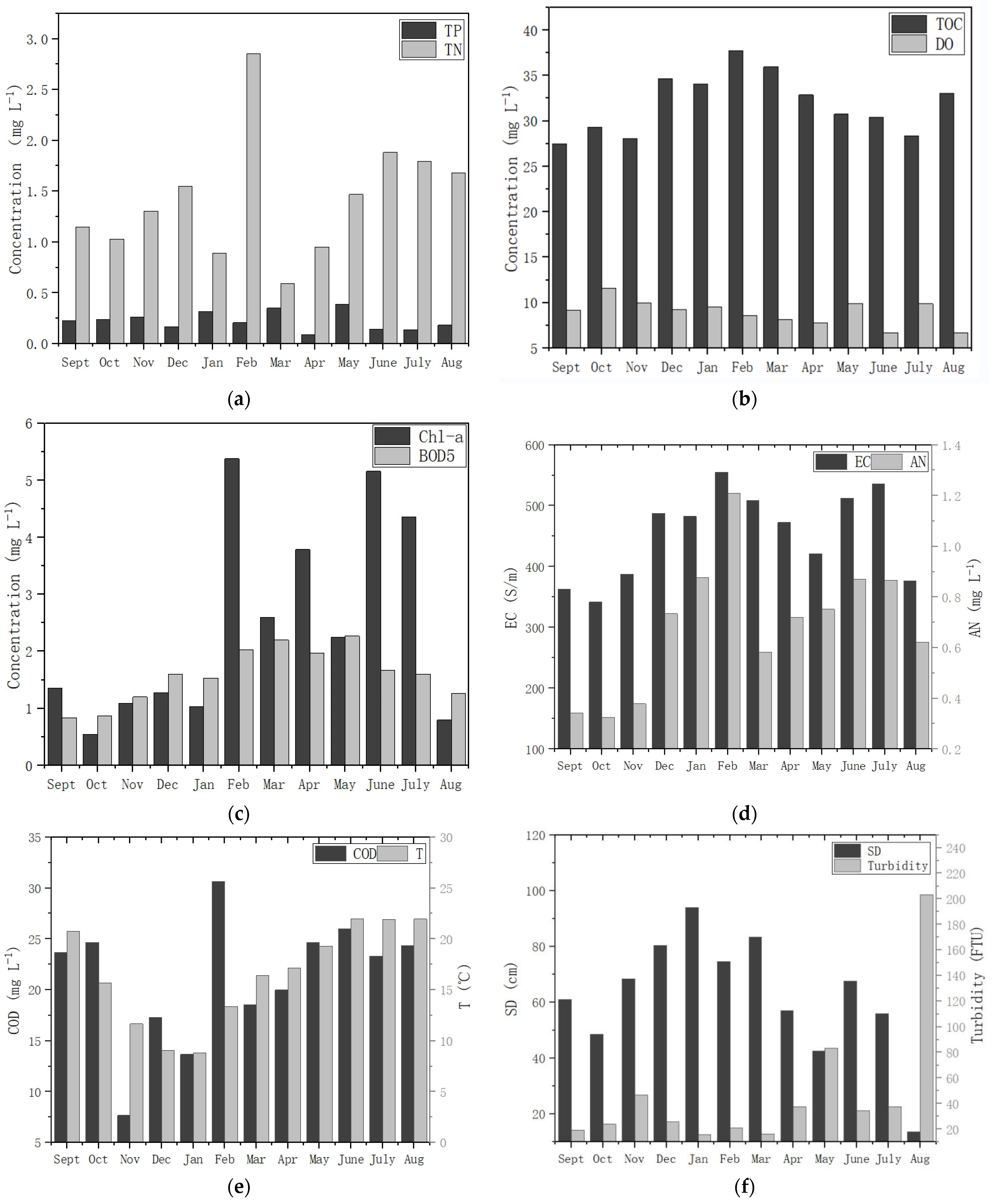
4.1. Water Environment Polluted by Nutrients
4.2. Aquatic Communities Affected by Heavy Metals in Water/Sediment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carpenter, S.R.; Christensen, D.L.; Cole, J.J.; Cottingham, K.L.; He, X.; Hodgson, J.R.; Kitchell, J.F.; Knight, S.E.; Pace, M.L. Biological control of eutrophication in lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 784–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Joye, S.B.; Howarth, R.W. Eutrophication of Freshwater and Marine Ecosystems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteagudo, L.; Moreno, J.L.; Picazo, F. River eutrophication: Irrigated vs non-irrigated agriculture through different spatial scales. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2759–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, O.E.; Chapin, F.S.; Armesto, J.J.; Berlow, E.; Bloomfield, J.; Dirzo, R.; Huber-Sanwald, E.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jackson, R.B.; Kinzig, A.; et al. Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science 2000, 287, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.W.; Kwon, H.B.; Jeon, H.P.; Koopman, B. A new recycling material for removing phosphorus from water. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.A.; Alonso, A. Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: A global assessment. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynam, C.P.; Cusack, C.; Stokes, D. A methodology for community-level hypothesis testing applied to detect trends in phytoplankton and fish communities in Irish waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 87, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Michael, I.; Fatta Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tylmann, W. Lithological and geochemical record of anthropogenic changes in recent sediments of a small and shallow lake (Lake Pusty Staw, northern Poland). J. Paleolimnol. 2005, 33, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, Z.; Hajira, T.; Othman, A.; Habeebullah, T.M.; Sayqal, A.; Assaggaf, H.M.; Ahmed, O.B.; Sultan, M.; Mohiuddin, S.; Masood, S.S.; et al. Geo-environmental approach to assess heavy metals around auto-body refinishing shops using bio-monitors. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08809. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, J.F.; Yin, H.B.; Cai, Y.J. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and risk assessment of Chaohu Lake District and main access rivers. J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 502–512. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Ao, D.; Ji, J.; Wang, X.C.; Li, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.; Xue, T.; Guo, H.; Wang, N.; Zhang, L. Insight into the risk of replenishing urban landscape ponds with reclaimed wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anon. Impacts of land use and water quality on macroinvertebrate communities in the Pearl River drainage basin, China. Hydrobiologia 2010, 652, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, B.L.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Kong, D.; Zuo, Y. Space distribution of heavy metals and its relationship with macrozoobenthos in the Heihe River, northwest China. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar]
- Costas, N.; Pardo, I.; Méndez-Fernández, L.; Martínez-Madrid, M.; Rodríguez, P. Sensitivity of macroinvertebrate indicator taxa to metal gradients in mining areas in Northern Spain. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bere, T.; Dalu, T.; Mwedzi, T. Detecting the impact of heavy metal contaminated sediment on benthic macroinvertebrate communities in tropical streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paithankar, J.G.; Saini, S.; Dwivedi, S.; Sharma, A.; Chowdhuri, D.K. Heavy metal associated health hazards: An interplay of oxidative stress and signal transduction. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudou, F.G.; Ossana, N.A.; Castañé, P.M.; Mastrángelo, M.M.; Ferrari, L. Cadmium effects on some energy metabolism variables in Cnesterodon decemmaculatus adults. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.L. Aquatic Environmental Diagnosis and Water Quality Target Management Suggestion for the Tuojiang Basin (Chengdu Section). Ecol. Environ. Monit. Three Gorges 2022, 7, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- The Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (MEEC). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 4th ed.; Chinese Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Jahan, Z.; Mohammad, W.; Shah, S.A.; Khanam, S.; Tahir, H.; Qadri, M. Characterization of sand samples from Karachi beaches using gamma Spectrometry and xrd. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2020, 189, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/TC147/SC2–PHYSICAL; Chemical and Biochemical Methods. CP 401-1214. Vernier: Geneva, Switzerland, 1971.
- Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water, National Standard of the People’s Republic of China; Ministry of Ecology and Environment, People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Brankov, J.; Milijašević, D.; Milanović, A. The Assessment of the Surface Water Quality Using the Water Pollution Index: A Case Study of the Timok River (The Danube River Basin), Serbia. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2012, 38, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Jun, H. An introduction of endocrine disrupters (EDCs). Safety Environ. Eng. 2004, 11, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Aizaki, M.; Otsuki, A.; Fukushima, T.; Kawai, T.; Hosomi, M.; Muraoka, K. Application of modified Carlson’s trophic state index to Japanese lakes and its relationships to other parameters related to trophic state. Res. Rep. Natl. Inst. Environ. Stud. 1981, 23, 13–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Z.; Tang, Y.L.; Lu, J.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Y.Q.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.E. Sources and spatial distribution of typical heavy metal pollutants in soils in Xihu scenic area. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 1516–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Neal, C.; Hilton, J.; Wade, A.J.; Neal, M.; Wickham, H. Chlorophyll-a in the rivers of eastern England. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 365, 84–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilham, S.S.; Kilham, P. The importance of resource supply rates in determining phytoplankton community structure. Am. Assoc. Adv. Sci. Symp. 1984, 85, 7–27. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, T.A.; Chau, K.W.; Duan, H.F. Machine learning based marine water quality prediction for coastal hydro-environment management. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 284, 112051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Schmalz, B.; Fohrer, N. Distribution of phytoplankton in a German lowland river in relation to environmental factors. J. Plankton Res. 2011, 33, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.Q.; Xie, P.; Li, S.X.; Tang, H.; Liu, H. The low TN: TP ratio, a cause or a result of Microcystis blooms? Water Res. 2003, 37, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, J.; Bahnwart, M.; Ockenfeld, K. Growth and Loss Processes of Riverine Phytoplankton in Relation to Water Depth. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2002, 87, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogmann, D.W.; Butalla, R.; Sprinkle, J. Blooms of Cyanobacteria on the Potomac River. Plant Physiol. 1986, 80, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhard, E.G. The plankton ecology of the upper Mississippi, Minneapolis to Winona. Ecol. Monogr. 1931, 1, 396–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.; Admiraal, W.; Bijkerk, R.; Ietswaart, T.; Prins, H. Monitoring of algae in Dutch rivers: Does it meet its goals? J. Appl. Phycol. 1998, 10, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormans, M.; Maier, H.; Burch, M.; Baker, P. Temperature stratification in the lower River Murray, Australia: Implication for cyanobacterial bloom development. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1997, 48, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cózar, A.; Echevarría, F. Size structure of the planktonic community in microcosms with different levels of turbulence. Sci. Mar. 2005, 69, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Lu, S.Y.; Li, G.D. Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment around Taihu Lake. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2010, 16, 577–580. [Google Scholar]
- Weigelhofer, G. The potential of agricultural headwater streams to retain soluble reactive phosphorus. Hydrobiologia 2017, 793, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, P.; Moss, D.; Wright, J.; Furse, M. The performance of a new biological quality score system based on macroinvertebrate over a wide range of unpolluted running waters. Water Res. 1983, 17, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.J.; McKnight, U.S.; Loinaz, M.C.; Thomsen, N.I.; Olsson, M.E.; Bjerg, P.L.; Binning, P.J.; Kronvang, B. A catchment scale evaluation of multiple stressor effects in headwater streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.X.; Su, P.; Lin, Q.D.; Song, J.X.; Sun, H.T.; Cheng, D.D.; Wang, S.Q.; Peng, J.L.; Fu, J.X. Distribution, assessment and coupling relationship of heavy metals and macroinvertebrates in sediments of the Weihe River Basin. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Q.; Zhang, S.Y.; Dai, T.F.; Gao, X.S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.Q.; Yuan, D.G.; Li, K.R. Contents and Sources of Cadmium in Farmland Soils of Chengdu Plain, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2014, 33, 898–906. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.H.; Zhou, Y.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Ma, Y.G.; Dai, Y.J. Effects of LA-GLy-VB6 on plants under PB-Cd combined stress. Urban Environ. Urban Ecol. 2001, 14, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Beutel, M.W.; Leonard, T.M.; Dent, S.R.; Moore, B.C. Effects of aerobic and anaerobic conditions on P, N, Fe, Mn and Hg accumulation in waters overlaying profundal sediments of anoligo-mesotrophic lake. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnankutty, N.; Idris, M.; Hamzah, F.M.; Manan, Y. The chemical form and spatial variation of metals from sediment of Jemberau mining region of Tasik Chini, Malaysia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 25046–25056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Z.; Liu, Q.Q.; Wang, W.J.; Sheng, Y.Q. Effects of hydraulic perturbation on rerelease of heavy metals from estuarine sediments. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2020, 36, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Devoy, J.; Géhin, A.; Müller, S.; Melczer, M.; Remy, A.; Antoine, G.; Sponne, I. Evaluation of chromium in red blood cells as an indicator of exposure to hexavalent chromium: An in vitro study. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 255, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Li, L.P.; Huang, G.L. Growth-inhibitory and metal-binding proteins in Chlorella vulgaris exposed to cadmium or zinc. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 91, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.X.; Zhang, B.Y.; Wu, S.C.; Feng, J.; Wang, G. Effects of Heavy Metal Cadmium on photosynthesis of Heterophyllum heterophyllum. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2015, 46, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Piovar, J.; Stavrou, E.; Kaduková, J.; Kimáková, T.; Bačkor, M. Influence of long-term exposure to copper on the lichen hotobiont Trebouxia erici and the free-living algae Scenedesmus quadricauda. Plant Growth Regul. 2011, 63, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
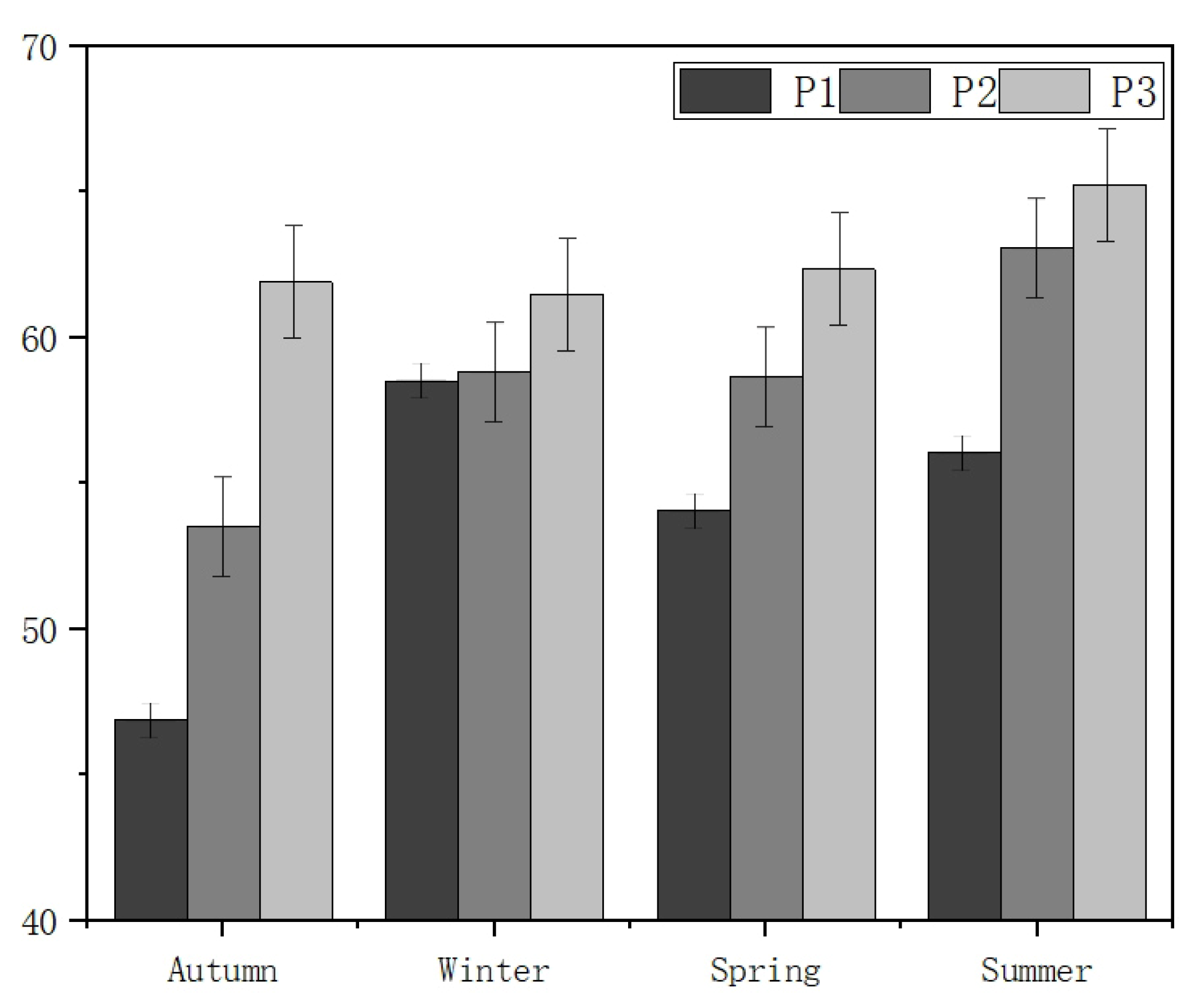
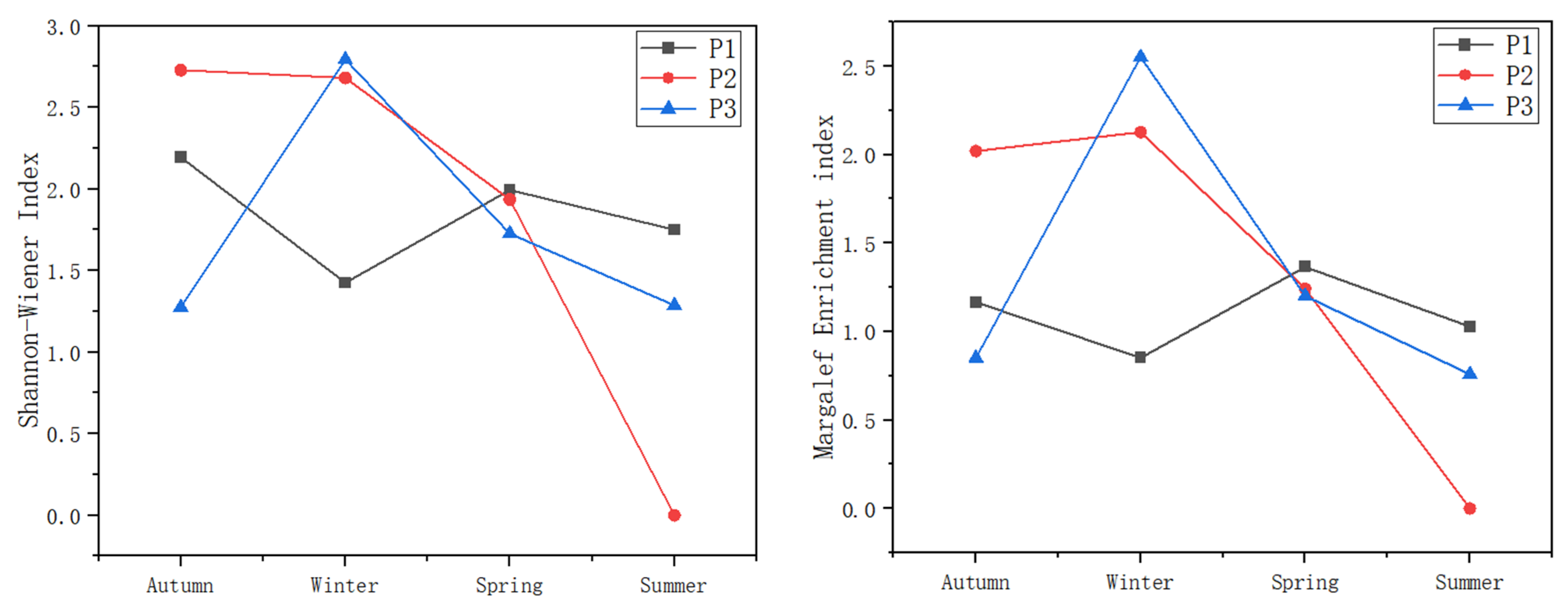
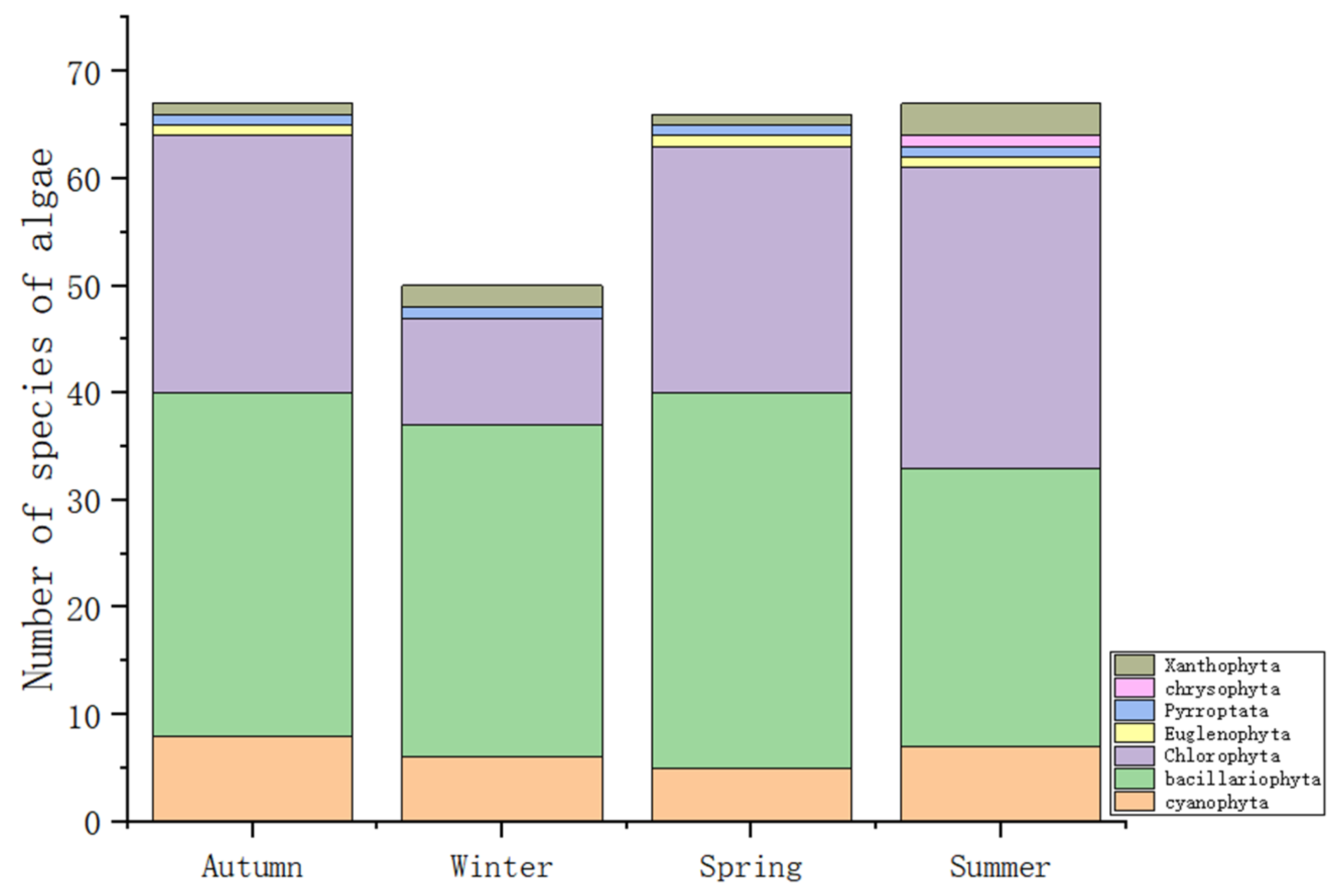
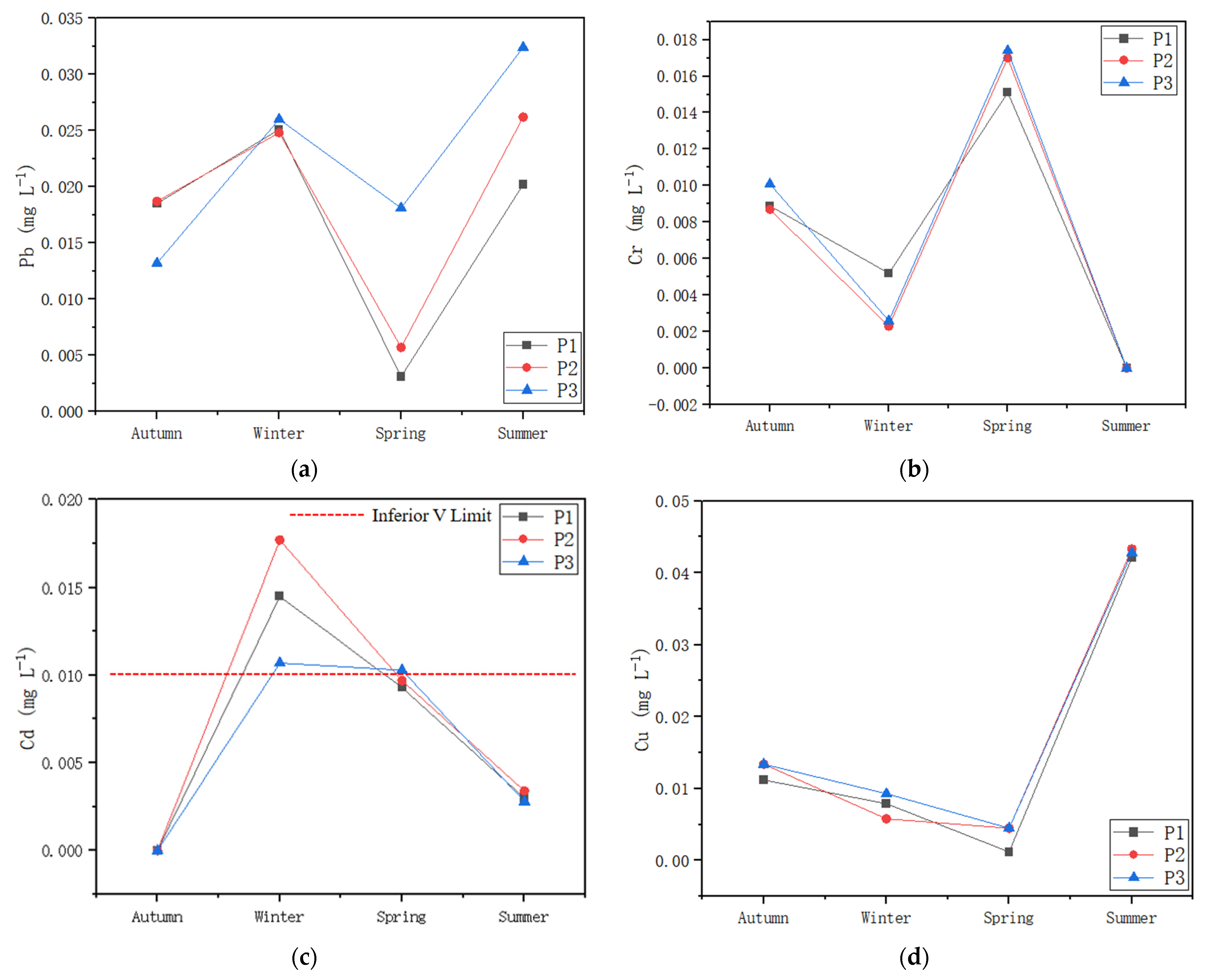
| Water Quality Categories | I | II | III | IV | V | Worse than V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPI value | ≤20 | 20 < WPI ≤ 40 | 40 < WPI ≤ 60 | 60 < WPI ≤ 80 | 80 < WPI ≤ 100 | >100 |
| Evaluation Level | Qualitative Evaluation | |
|---|---|---|
| TLI (∑) < 30 | Oligotrophic | Very clean |
| 30 ≤ TLI (∑) < 50 | Mesotrophic | Clean |
| 50 < TLI (∑) | Eutrophic | Typical |
| 50 < TLI (∑) ≤ 60 | Lightly eutrophic | Lightly polluted |
| 60 < TLI (∑) ≤ 70 | Moderately eutrophic | Moderately polluted |
| TLI (∑) > 70 | Severely eutrophic | Severely polluted |
| H’ | H’ = 0 | H’ = 0–1 | H’ = 1–2 | H’ = 2–3 | H’ > 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pollution level | No benthic communities were found; severe contamination | Heavy pollution | Moderately polluted | Mild pollution | No pollution |
| dM | dM < 1 | dM = 1–2 | dM = 2–3 | dM > 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pollution level | Heavy pollution | Moderately polluted | Mild pollution | No pollution |
| Parameters | Range | Mean ± Std |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.24–8.25 | 7.78 ± 0.22 |
| T (°C) | 6.30–26.10 | 16.50 ± 5.21 |
| SD (cm) | 4.00–122.00 | 62.29 ± 26.78 |
| Turbidity (FTU) | 6.20–205.00 | 42.97 ± 46.70 |
| EC (S m−1) | 289.00–691.00 | 453.97 ± 107.74 |
| DO (mg L−1) | 2.13–12.96 | 8.65 ± 2.55 |
| TN (mg L−1) | 0.28–3.06 | 1.43 ± 0.80 |
| TP (mg L−1) | 0.07–0.47 | 0.23 ± 0.12 |
| AN (mg L−1) | 0.15–1.35 | 0.69 ± 0.30 |
| COD (mg L−1) | 6.00–34.00 | 21.22 ± 7.76 |
| BOD5 (mg L−1) | 0.60–2.80 | 1.59 ± 0.56 |
| Chl-a (mg L−1) | 0.041–11.57 | 2.47 ± 2.30 |
| TOC (mg L−1) | 23.62–44.25 | 32.21 ± 5.41 |
| Phyla | Benthonic Invertebrates |
|---|---|
| Molluska | Cipangopaludina chinensis, Lymnaeidae, Viviparidae, Kimnoperna lacustris, Radix auricularia, R. suinhoi, Corbicula fluminea, |
| Arthropoda | Gammarus sp., Ecdyrus sp., Philopotamidae, and Cleantis sp. Macrobranchium nipponense, Caridina denticulata, Rhyacophilidae, Tendipus sp., Baetis sp., Caenis sp., and Aeshnidae |
| Annelida | Hiurdo sp., Limnodrilus sp., Hemiclepsis sp., and Glossiphonia sp. |
| Platyhelminthes | Planaria sp. |
| Period | P1 | P2 | P3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autumn | Philopotamidae, Gammarus sp. | Caridina denticulata, Philopotamidae, Gammarus sp., | Macrobranchium nipponense |
| Winter | Gammarus sp. | Philopotamidae, Gammarus sp., Rhyacophilidae, | Macrobranchium nipponense, Tendipus sp. |
| Spring | Gammarus sp. | Gammarus sp. | Tendipus sp. |
| Summer | Gammarus sp. | - | Macrobranchium nipponense |
| Parameters | Range | Std ± Mean |
|---|---|---|
| Pb (mg L−1) | 0–0.056 | 0.019 ± 0.021 |
| Cr (mg L−1) | 0–0.046 | 0.007 ± 0.014 |
| Cd (mg L−1) | 0–0.042 | 0.007 ± 0.010 |
| Hg (μg L−1) | 0–2.553 | 0.346 ± 0.499 |
| As (μg L−1) | 0–3.729 | 0.591 ± 0.760 |
| Fe (mg L−1) | 0.009–1.023 | 0.186 ± 0.195 |
| Mn (mg L−1) | 0–0.488 | 0.038 ± 0.082 |
| Cu (mg L−1) | 0–0.087 | 0.017 ± 0.026 |
| Parameters | Range | Std ± Mean |
|---|---|---|
| Pb (mg L−1) | 17.00–22.20 | 20.57 ± 2.83 |
| Cr (mg L−1) | 89.60–102.50 | 89.60 ± 102.50 |
| Cd (mg L−1) | 0.14 –0.17 | 0.15 ± 0.01 |
| Hg (μg L−1) | 0.01–0.05 | 0.03 ± 0.03 |
| As (μg L−1) | 0.85–2.19 | 1.74 ± 0.77 |
| Fe (mg L−1) | 30.00–69.80 | 48.27 ± 20.10 |
| Mn (mg L−1) | 8.10–21.50 | 13.07 ± 7.34 |
| Cu (mg L−1) | 1.43–4.11 | 2.69 ± 1.35 |
| Component 1 | Component 2 | Component 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 0.635 | 0.461 | −0.524 |
| Cr | −0.854 | −0.252 | 0.320 |
| Cd | −0.250 | 0.792 | 0.449 |
| Hg | 0.850 | 0.095 | 0.498 |
| As | 0.825 | −0.290 | 0.422 |
| Fe | 0.765 | −0.228 | 0.073 |
| Mn | 0.356 | 0.567 | 0.055 |
| Cu | 0.920 | −0.193 | −0.140 |
| Pb | Cr | Cd | Hg | As | Fe | Mn | Cu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H’ | −0.667 | −0.086 | −0.271 | 0.348 | −0.029 | −0.657 | −0.029 | −0.714 |
| dM | −0.691 | −0.058 | −0.812 * | 0.441 | −0.265 | −0.667 | −0.029 | −0.638 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Liang, L.; Dong, Q.; Wang, R.; Xu, T.; Qu, L.; Wu, Z.; Lyu, B.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q. Significant Dynamic Disturbance of Water Environment Quality in Urban Rivers Flowing through Industrial Areas. Water 2023, 15, 3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203640
Li D, Liang L, Dong Q, Wang R, Xu T, Qu L, Wu Z, Lyu B, Liu S, Chen Q. Significant Dynamic Disturbance of Water Environment Quality in Urban Rivers Flowing through Industrial Areas. Water. 2023; 15(20):3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203640
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Di, Longfei Liang, Qidi Dong, Ruijue Wang, Tao Xu, Ling Qu, Zhiwei Wu, Bingyang Lyu, Shiliang Liu, and Qibing Chen. 2023. "Significant Dynamic Disturbance of Water Environment Quality in Urban Rivers Flowing through Industrial Areas" Water 15, no. 20: 3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203640
APA StyleLi, D., Liang, L., Dong, Q., Wang, R., Xu, T., Qu, L., Wu, Z., Lyu, B., Liu, S., & Chen, Q. (2023). Significant Dynamic Disturbance of Water Environment Quality in Urban Rivers Flowing through Industrial Areas. Water, 15(20), 3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203640







