Assessment of the Surface Water Quality of the Gomti River, India, Using Multivariate Statistical Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
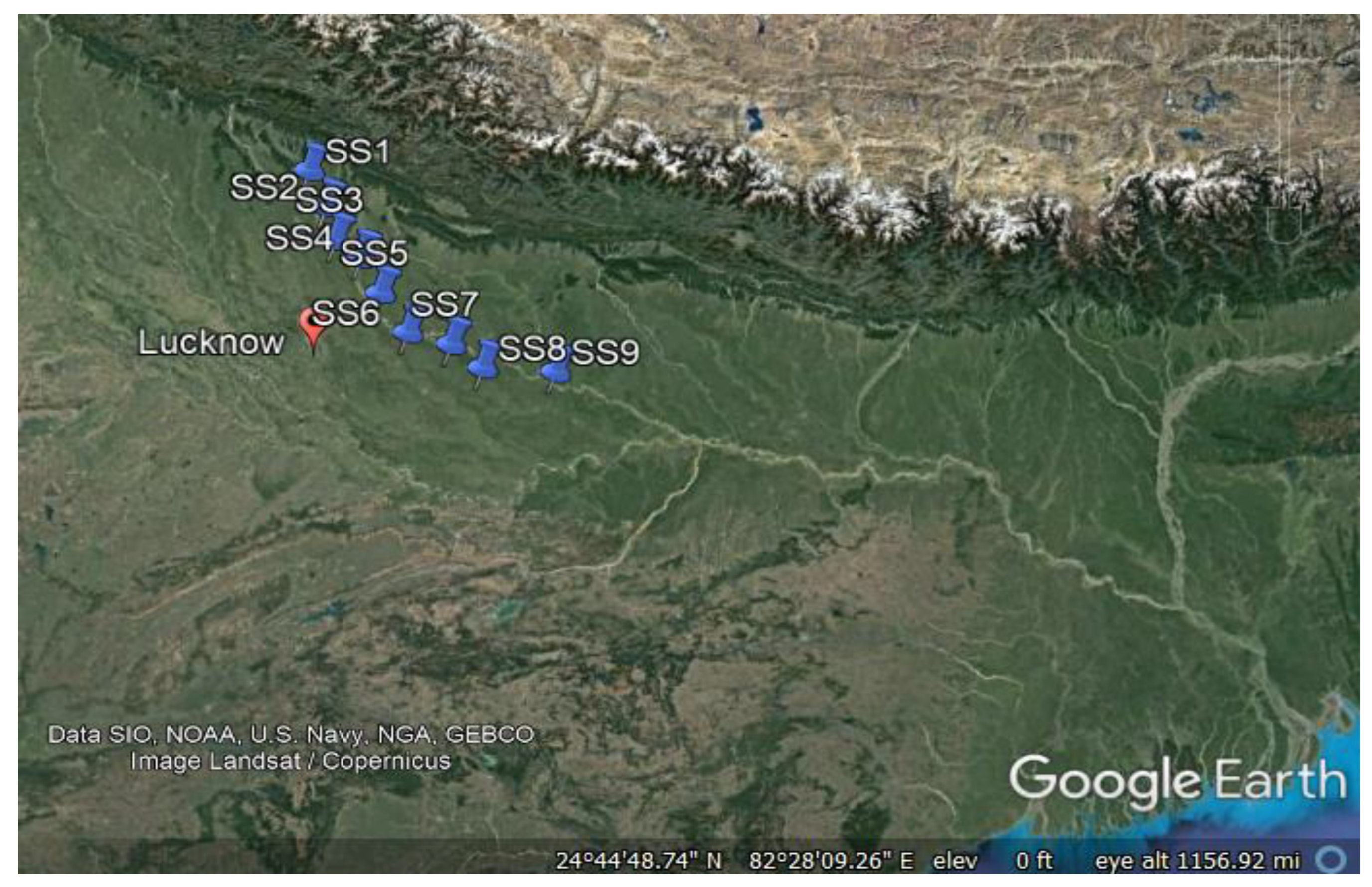
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Methodical Procedures
2.3. Data Evaluation and Multivariate Statistical Assessment
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. General Observation
3.2. Cluster Analysis
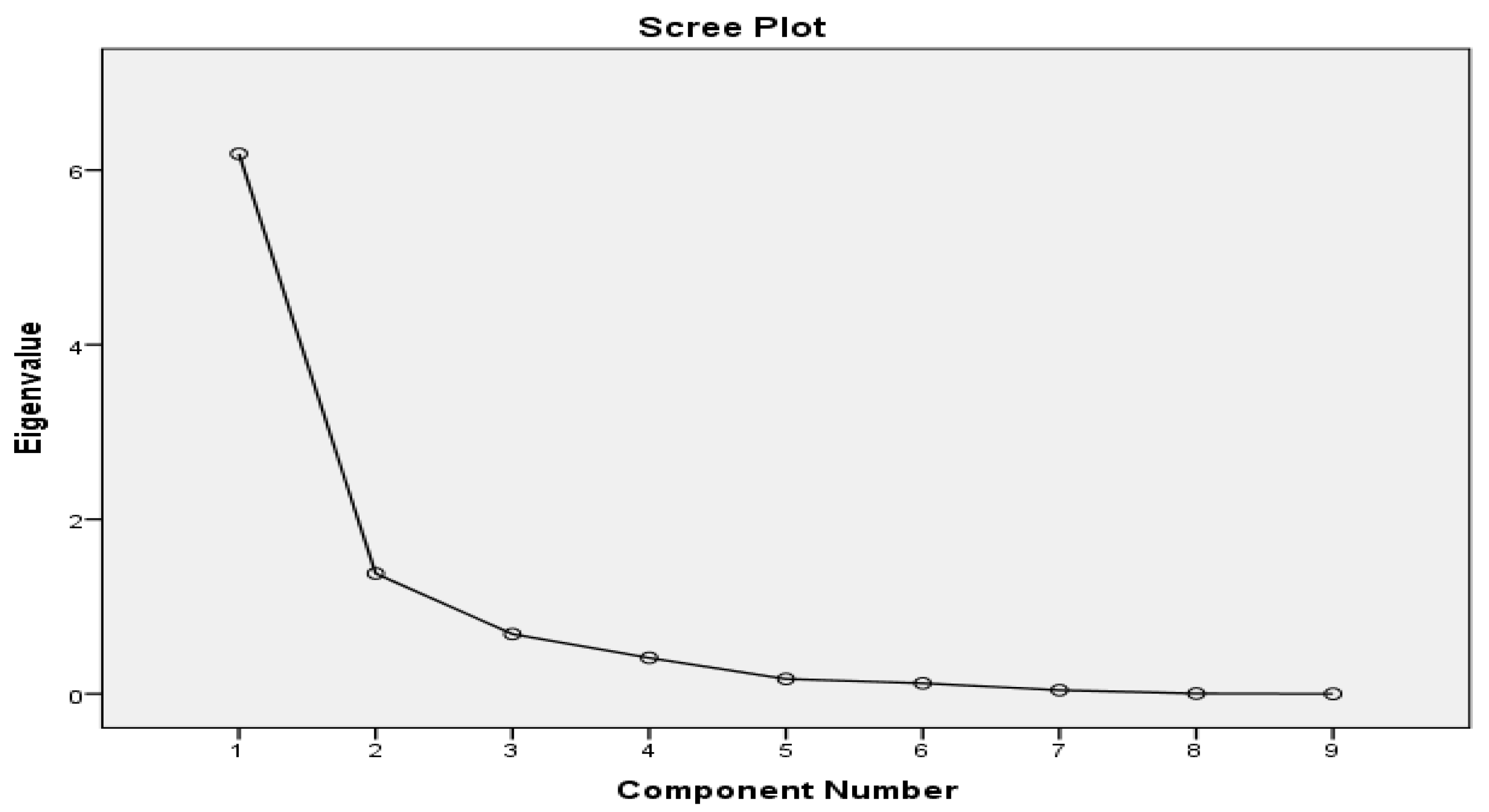
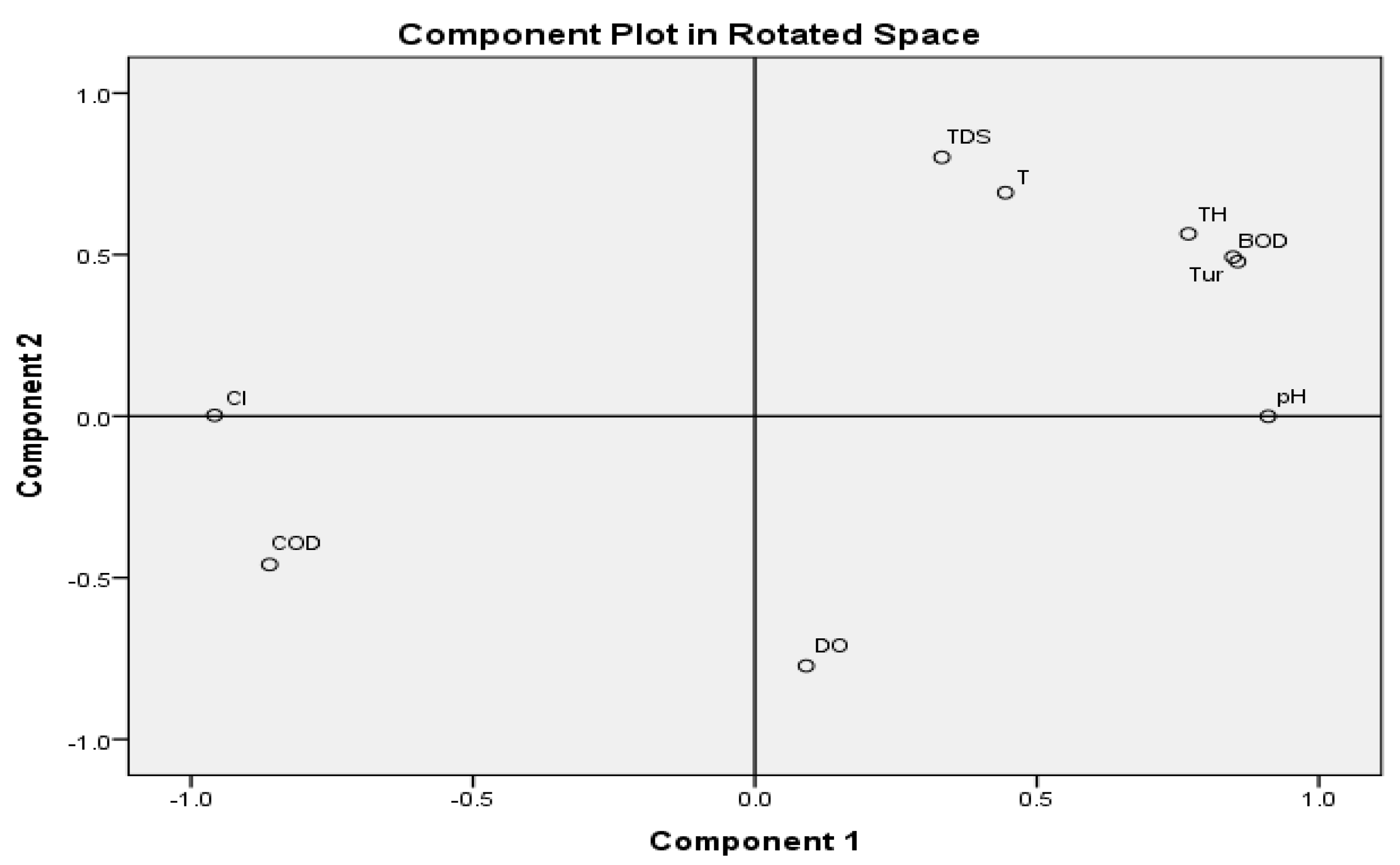
3.3. Principal Component Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, G.; Patel, N.; Jindal, T.; Srivastava, P.; Bhowmik, A. Assessment of spatial and temporal variations in water quality by the application of multivariate statistical methods in the Kali River, Uttar Pradesh, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matta, G.; Nayak, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P. Water quality assessment using NSFWQI, OIP and multivariate techniques of Ganga River system, Uttarakhand, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnorom, I.C.; Ewuzie, U.; Eze, S.O. Multivariate statistical approach and water quality assessment of natural springs and other drinking water sources in SoutheasternNigeria. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustaoğlu, F.; Tepe, Y. Water quality and sediment contamination assessment of Pazarsuyu Stream, Turkey using multivariate statistical methods and pollution indicators. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.; Reddy, A.M.; Srinivas, L.; Reddy, P.M. Assessment of Surface Water Quality in Hyderabad Lakes by Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques, Hyderabad-India. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 4, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, R.; Ahmed, Z.; Seefat, S.M.; Nahin, K.T.K. Assessment of surface water quality around a landfill using multivariate statistical method, Sylhet, Bangladesh. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; El Baghdadi, M.; Rais, J.; Aghezzaf, B.; Slassi, M. Assessment of spatial and seasonal water quality variation of Oum Er Rbia River (Morocco) using multivariate statistical techniques. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2016, 4, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Rakib, M.A.; Dampare, S.B.; Ganyaglo, S.; Suzuki, S. Surface water quality assessment in the central part of Bangladesh using multivariate analysis. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2011, 15, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, A.; Konanç, M.U. Evaluation of surface water quality and heavy metal pollution of Coruh River Basin (Turkey) by multivariate statistical methods. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouguerne, A.; Boudoukha, A.; Benkhaled, A.; Mebarkia, A.H. Assessment of surface water quality of Ain Zada dam (Algeria) using multivariate statistical techniques. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2017, 15, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyacioglu, H.; Boyacioglu, H. Surface water quality assessment by environmetric methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 131, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Mei, K.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Wang, T.; Gong, J.; Zhang, M. Impacts of land use and population density on seasonal surface water quality using a modified geographically weighted regression. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 450–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.; He, B.; Nover, D.; Yang, G.; Chen, W.; Meng, H.; Zou, S.; Liu, C. Water quality assessment and pollution source identification of the eastern poyang lake basin using multivariate statistical methods. Sustainability 2016, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Wen, J. Evaluation of physicochemical and heavy metals characteristics in surface water under anthropogenic activities using multivariate statistical methods, Garra River, Ganges Basin, India. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 26, 200280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Sabahi, M.S.; Karbassi, A.R.; Baghvand, A.; Zadeh, H.T. Multivariate statistical analysis of surface water quality based on correlations and variations in the data set. Desalination 2010, 260, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejman, A.H.; Bidhendi, G.R.N.; Karbassi, A.R.; Mehrdadi, N.; EsmaeiliBidhendi, M. Evaluation of spatial and seasonal variations in surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 6, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njuguna, S.M.; Onyango, J.A.; Githaiga, K.B.; Gituru, R.W.; Yan, X. Application of multivariate statistical analysis and water quality index in health risk assessment by domestic use of river water. Case study of Tana River in Kenya. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 133, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isiyaka, H.A.; Mustapha, A.; Juahir, H.; Phil-Eze, P. Water quality modelling using artificial neural network and multivariate statistical techniques. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 5, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Mohan, D.; Sinha, S. Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—A case study. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3980–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Sinha, S. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti river (India) using multivariate statistical techniques—A case study. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 538, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Basant, A.; Malik, A.; Jain, G. Artificial neural network modeling of the river water quality—A case study. Ecol. Modell. 2009, 220, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somvanshi, S.; Singh, K.P.; Singh, N.B.; Shukla, S.P.; Pathak, V. Integrated remote sensing and GIS approach for water quality analysis of Gomti river, Uttar Pradesh. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 3, 62–74. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Cui, B.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H. Assessment of river water quality in Pearl River Delta using multivariate statistical techniques. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 1220–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feher, I.C.; Moldovan, Z.; Oprean, I. Spatial and seasonal variation of organic pollutants in surface water using multivariate statistical techniques. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZareGarizi, A.; Sheikh, V.; Sadoddin, A. Assessment of seasonal variations of chemical characteristics in surface water using multivariate statistical methods. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 8, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Muangthong, S. Assessment of surface water quality of Songkhram River (Thailand) using environmetric techniques. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2014, 12, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonov, V.; Stratis, J.; Samara, C.; Zachariadis, G.; Voutsa, D.; Anthemidis, A.; Sofoniou, M.; Kouimtzis, T. Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4119–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Mishra, A.; Kumari, L.; Singh, R.; Pal, D.B.; Giri, D.D.; Singh, N.L.; Tiwary, D.; Mishra, P.K. Assessment of ground and surface water quality along the river Varuna, Varanasi, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penilaian, K.; Aminu, I.; Hafizan, J.; Mohd, E.T.; Mustapha, A.; Azman, A.; Isiyaka, H.A. Assessment of Surface Water Quality Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques in the Terengganu River Basin. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2015, 19, 338–348. [Google Scholar]
- Hamid, A.; Bhat, S.A.; Bhat, S.U.; Jehangir, A. Environmetric techniques in water quality assessment and monitoring: A case study. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herojeet, R.; Rishi, M.S.; Lata, R.; Dolma, K. Quality characterization and pollution source identification of surface water using multivariate statistical techniques, Nalagarh Valley, Himachal Pradesh, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2137–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ioele, G.; De Luca, M.; Grande, F.; Durante, G.; Trozzo, R.; Crupi, C.; Ragno, G. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate analysis: Case study of the crati River, Italy. Water 2020, 12, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.Y.; Lee, K.L.; Im, T.H.; Lee, I.J.; Kim, S.; Han, K.Y.; Ahn, J.M. Evaluation of water quality for the Nakdong River watershed using multivariate analysis. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2016, 5, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruddin, A.F. JurnalTeknologi Spatial and identification sources of pollution using multivariate analysis at. Spat. Charact. Identif. sources Pollut. using Multivar. Anal. Teren. River Basin Malays. 2015, 1, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- IS10500; Indian Standard Drinking Water—Specification (Second Revision). Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS): New Delhi, India, 2012.
- Khound, N.J.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Multivariate statistical evaluation of heavy metals in the surface water sources of Jia Bharali river basin, North Brahmaputra plain, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2577–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khound, N.J.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Assessment of water quality in and around Jia-Bharali river basin, North Brahmaputra Plain, India, using multivariate statistical technique. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markad, A.T.; Landge, A.T.; Nayak, B.B.; Inamdar, A.B.; Mishra, A.K. A multivariate statistical approach for the evaluation of spatial and temporal dynamics of surface water quality from the small reservoir located in the drought-prone area of South-West India: A case study of Tiru reservoir (India). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 31031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koklu, R.; Sengorur, B.; Topal, B. Water quality assessment using multivariate statistical methods-a case study: Melen river system (Turkey). Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 959–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Parihar, R.D.; Sharma, A.; Bakshi, P.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Bali, A.S.; Karaouzas, I.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; et al. Global evaluation of heavy metal content in surface water bodies: A meta-analysis using heavy metal pollution indices and multivariate statistical analyses. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumarasamy, P.; James, R.A.; Dahms, H.U.; Byeon, C.W.; Ramesh, R. Multivariate water quality assessment from the Tamiraparani river basin, Southern India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 2441–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Water quality assessment in the rivers along the water conveyance system of the Middle Route of the South to North Water Transfer Project (China) using multivariate statistical techniques and receptor modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoud, A.A. Groundwater quality assessment of the shallow aquifers west of the Nile Delta (Egypt) using multivariate statistical and geostatistical techniques. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 95, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangthong, S.; Shrestha, S. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: Case study of the Nampong River and Songkhram River, Thailand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muxika, I.; Borja, Á.; Bald, J. Using historical data, expert judgement and multivariate analysis in assessing reference conditions and benthic ecological status, according to the European Water Framework Directive. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 55, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, N.; Katyal, D.; Joshi, V. Assessment of Water Quality of Hindon River in Ghaziabad and Noida, India By Using Multivariate Statistical Methods. J. Glob. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 3, 80–90. [Google Scholar]
- Phung, D.; Huang, C.; Rutherford, S.; Dwirahmadi, F.; Chu, C.; Wang, X.; Nguyen, M.; Nguyen, N.H.; Do, C.M.; Nguyen, T.H.; et al. Temporal and spatial assessment of river surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A study in Can Tho City, a Mekong Delta area, Vietnam. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liang, X.; Xu, W.; Huang, X.; Li, X. The changes in trace metal contamination over the last decade in surface sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 439, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.W.; Lin, K.H.; Kuo, Y.M. Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 313, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, S.; Dash, M.K.; Mukherjee, C.K.; Dash, B.; Pokhrel, S. Assessment of water quality using multivariate statistical techniques in the coastal region of Visakhapatnam, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 6385–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
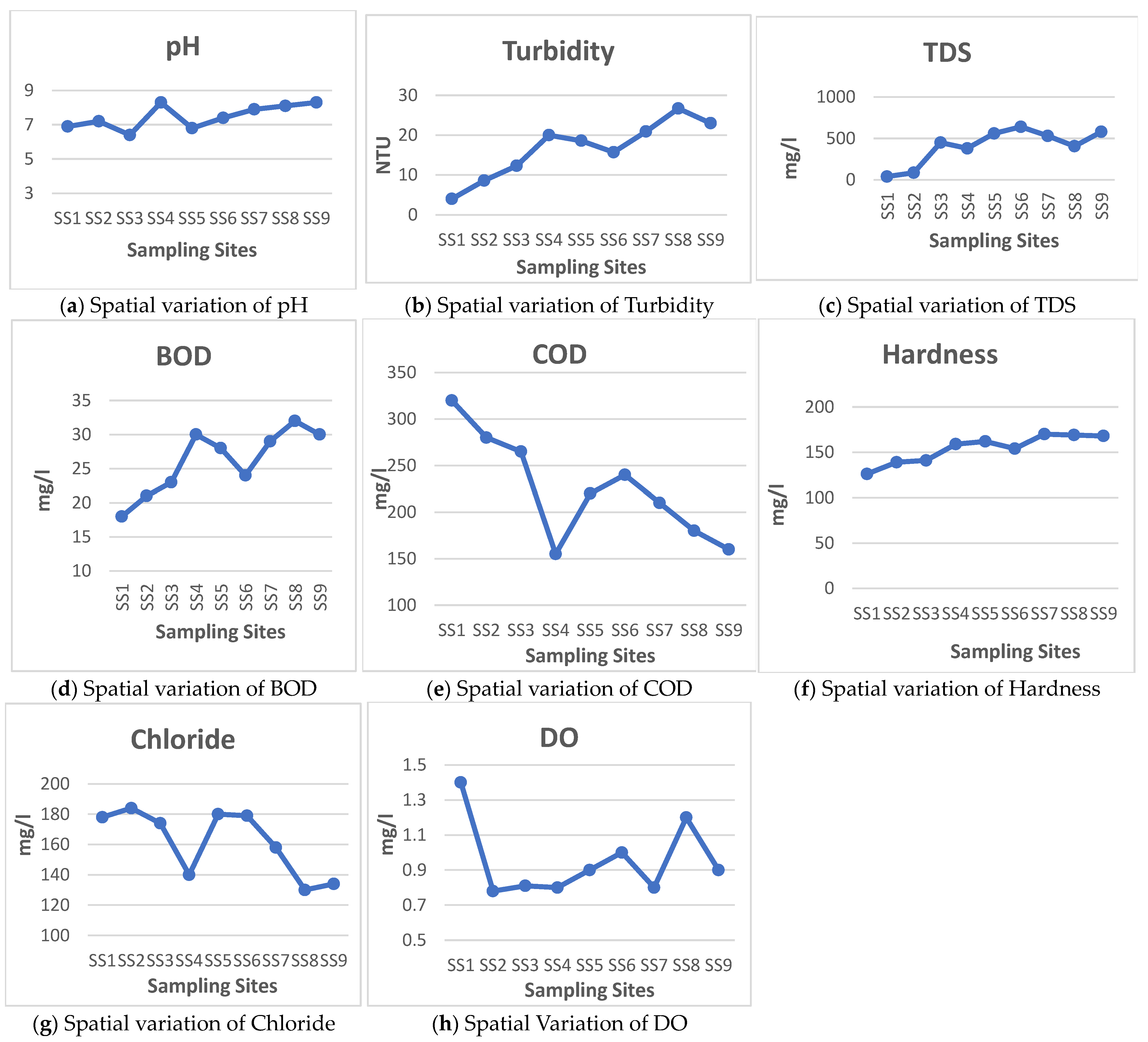

| pH | Temp. | Turbidity | TDS | BOD5 | COD | Hardness | Chloride | DO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 6.40 | 18.50 | 4.00 | 40.00 | 18.00 | 155.00 | 126.00 | 130.00 | 0.78 |
| Maximum | 8.30 | 19.80 | 26.70 | 640.00 | 32.00 | 320.00 | 170.00 | 184.00 | 1.40 |
| Mean | 7.48 | 19.32 | 16.64 | 408.00 | 26.11 | 225.56 | 154.22 | 161.89 | 0.95 |
| Stand. Error | 0.23 | 0.13 | 2.41 | 71.01 | 1.59 | 18.74 | 5.20 | 7.27 | 0.07 |
| Median | 7.40 | 19.40 | 18.60 | 450.00 | 28.00 | 220.00 | 159.00 | 174.00 | 0.90 |
| Stand. Deviation | 0.70 | 0.40 | 7.24 | 213.03 | 4.78 | 56.21 | 15.59 | 21.81 | 0.21 |
| Sample Variance | 0.49 | 0.16 | 52.38 | 45,382.00 | 22.86 | 3159.03 | 242.94 | 475.61 | 0.05 |
| Kurtosis | −1.53 | 1.02 | −0.43 | −0.20 | −1.05 | −0.86 | −0.63 | −1.74 | 1.27 |
| Skewness | −0.16 | −0.99 | −0.52 | −1.00 | −0.52 | 0.30 | −0.76 | −0.57 | 1.44 |
| pH | Temp. | Turbidity | TDS | BOD5 | COD | Hardness | Chloride | DO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||
| Temp. | 0.33 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Turbidity | 0.71 | 0.72 | 1.00 | ||||||
| TDS | 0.25 | 0.65 | 0.70 | 1.00 | |||||
| BOD5 | 0.73 | 0.70 | 0.98 | 0.64 | 1.00 | ||||
| COD | −0.81 | −0.68 | −0.92 | −0.62 | −0.95 | 1.00 | |||
| Hardness | 0.69 | 0.63 | 0.97 | 0.75 | 0.95 | −0.89 | 1.00 | ||
| Chloride | −0.85 | −0.45 | −0.79 | −0.28 | −0.81 | 0.84 | −0.68 | 1.00 | |
| DO | −0.09 | −0.35 | −0.23 | −0.37 | −0.28 | 0.35 | −0.33 | −0.03 | 1.00 |
| Characteristics | Initial | Extraction |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.00 | 0.782 |
| T | 1.00 | 0.591 |
| Tur | 1.00 | 0.956 |
| TDS | 1.00 | 0.707 |
| BOD5 | 1.00 | 0.961 |
| COD | 1.00 | 0.955 |
| TH | 1.00 | 0.921 |
| Cl | 1.00 | 0.943 |
| DO | 1.00 | 0.598 |
| Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | Total | Percentage of Variance | Cumulative Percentage | Total | Percentage of Variance | Cumulative Percentage | Total | Percentage of Variance | Cumulative Percentage |
| 1 | 5.864 | 65.161 | 65.161 | 5.864 | 65.161 | 65.161 | 5.312 | 59.022 | 59.022 |
| 2 | 1.550 | 17.225 | 82.386 | 1.550 | 17.225 | 82.386 | 2.103 | 23.363 | 82.386 |
| 3 | 0.662 | 7.359 | 89.745 | ||||||
| 4 | 0.583 | 6.481 | 96.226 | ||||||
| 5 | 0.206 | 2.293 | 98.519 | ||||||
| 6 | 0.089 | 0.985 | 99.504 | ||||||
| 7 | 0.043 | 0.482 | 99.986 | ||||||
| 8 | 0.001 | 0.014 | 100.000 | ||||||
| 9 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 100.000 | ||||||
| Component | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
| Cl | −0.952 | 0.189 |
| BOD5 | 0.930 | 0.309 |
| COD | −0.929 | −0.303 |
| Tur | 0.916 | 0.342 |
| pH | 0.881 | −0.078 |
| TH | 0.838 | 0.468 |
| Temp | 0.588 | 0.495 |
| TDS | 0.096 | 0.836 |
| DO | −0.058 | −0.771 |
| Author | Year | No. of Sampling Sites | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Singh et al. | 2005 | 08 | Agricultural soil weathering, leaching and runoff; municipal and industrial wastewater |
| Singh et al. | 2004 | 08 | Natural and anthropogenic sources of pollution |
| Singh et al. | 2009 | 08 | Wastewater drains and organic loading |
| Somvanshi et al. | 2012 | 05 | Industrial and domestic wastewater |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kushwah, V.K.; Singh, K.R.; Gupta, N.; Berwal, P.; Alfaisal, F.M.; Khan, M.A.; Alam, S.; Qamar, O. Assessment of the Surface Water Quality of the Gomti River, India, Using Multivariate Statistical Methods. Water 2023, 15, 3575. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203575
Kushwah VK, Singh KR, Gupta N, Berwal P, Alfaisal FM, Khan MA, Alam S, Qamar O. Assessment of the Surface Water Quality of the Gomti River, India, Using Multivariate Statistical Methods. Water. 2023; 15(20):3575. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203575
Chicago/Turabian StyleKushwah, Vinod Kumar, Kunwar Raghvendra Singh, Nakul Gupta, Parveen Berwal, Faisal M. Alfaisal, Mohammad Amir Khan, Shamshad Alam, and Obaid Qamar. 2023. "Assessment of the Surface Water Quality of the Gomti River, India, Using Multivariate Statistical Methods" Water 15, no. 20: 3575. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203575






