A Novel Approach of Monitoring Ulva pertusa Green Tide on the Basis of UAV and Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
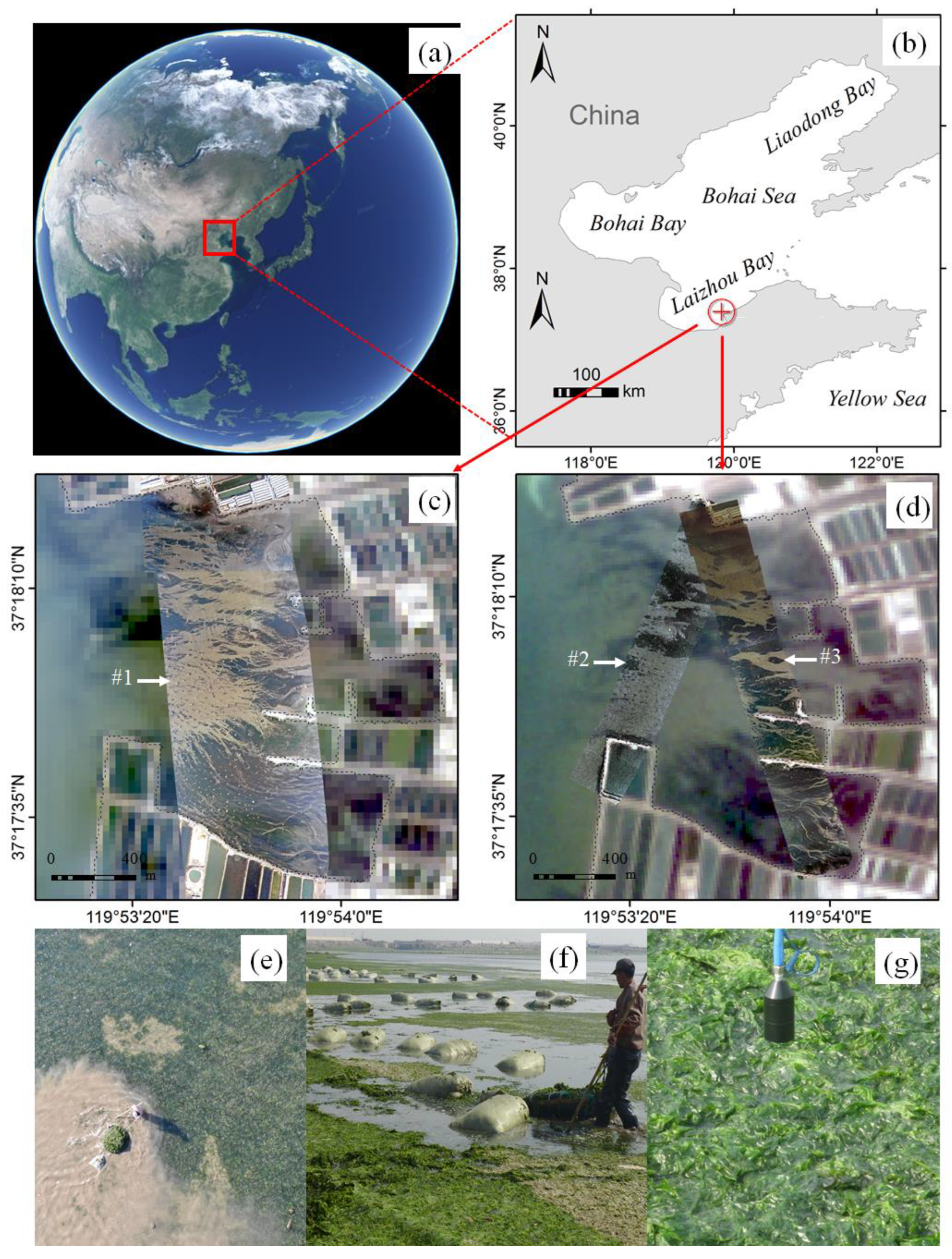
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
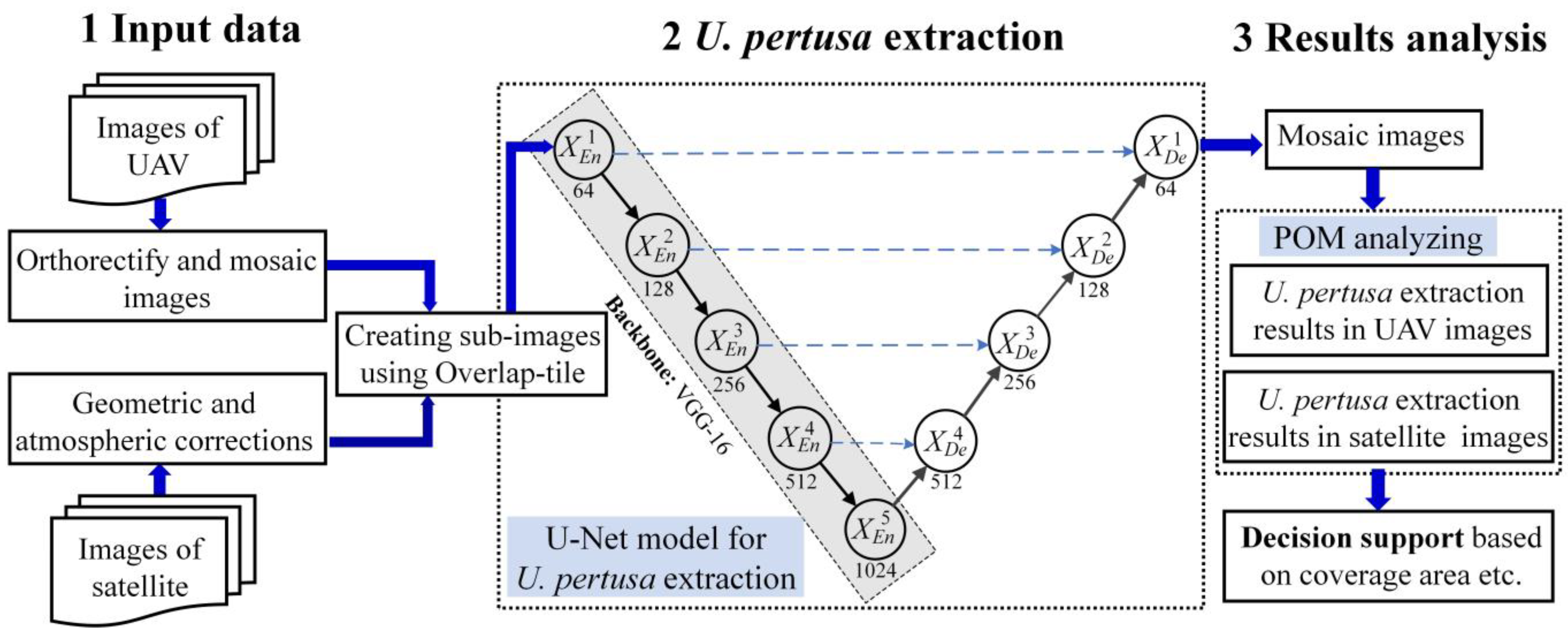
3. U. pertusa Extraction and Quantification Workflow
3.1. Data Preprocessing
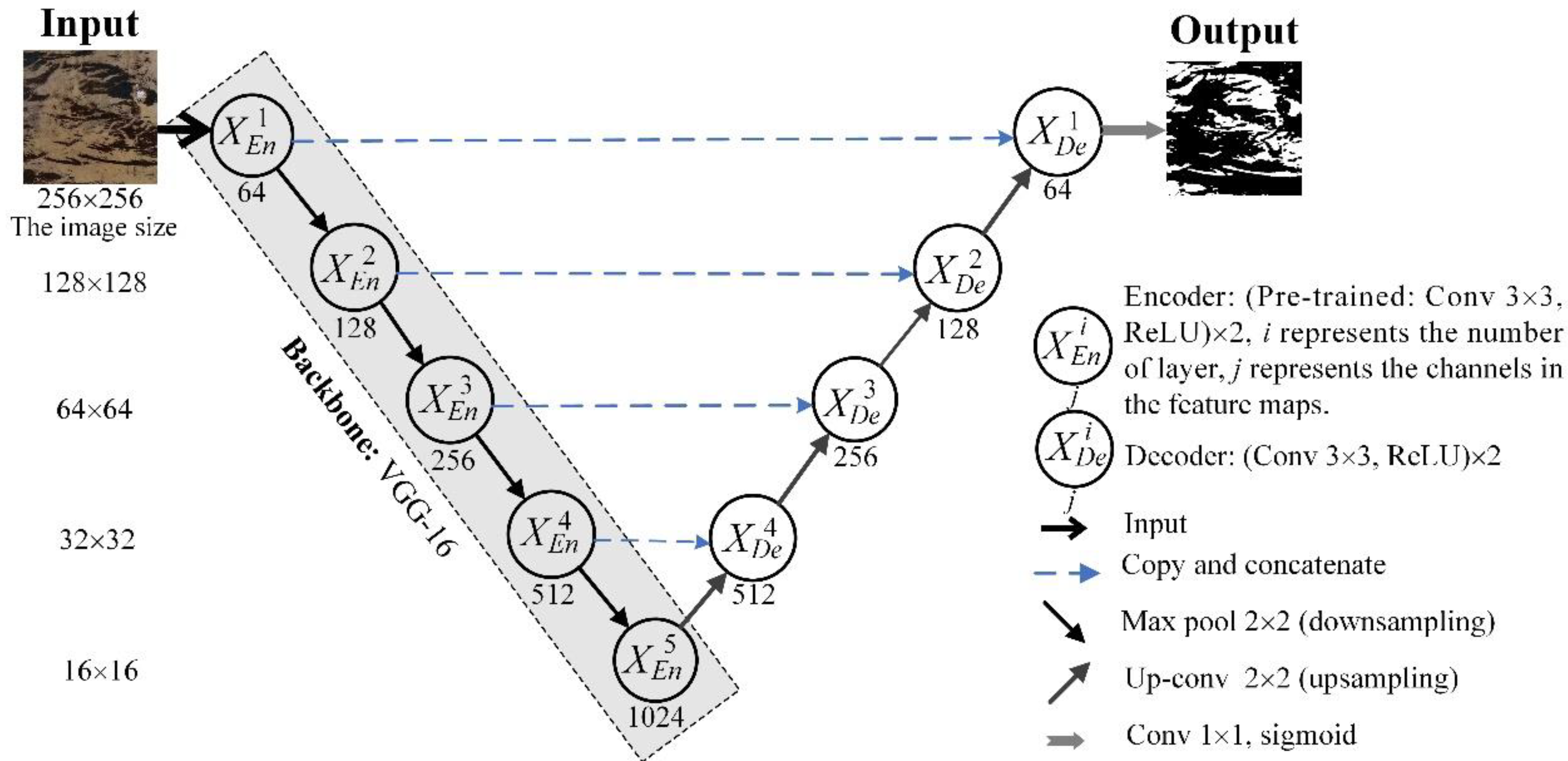
3.2. Model Structure
3.3. Model Training and Accuracy Evaluation
4. Results and Discussion
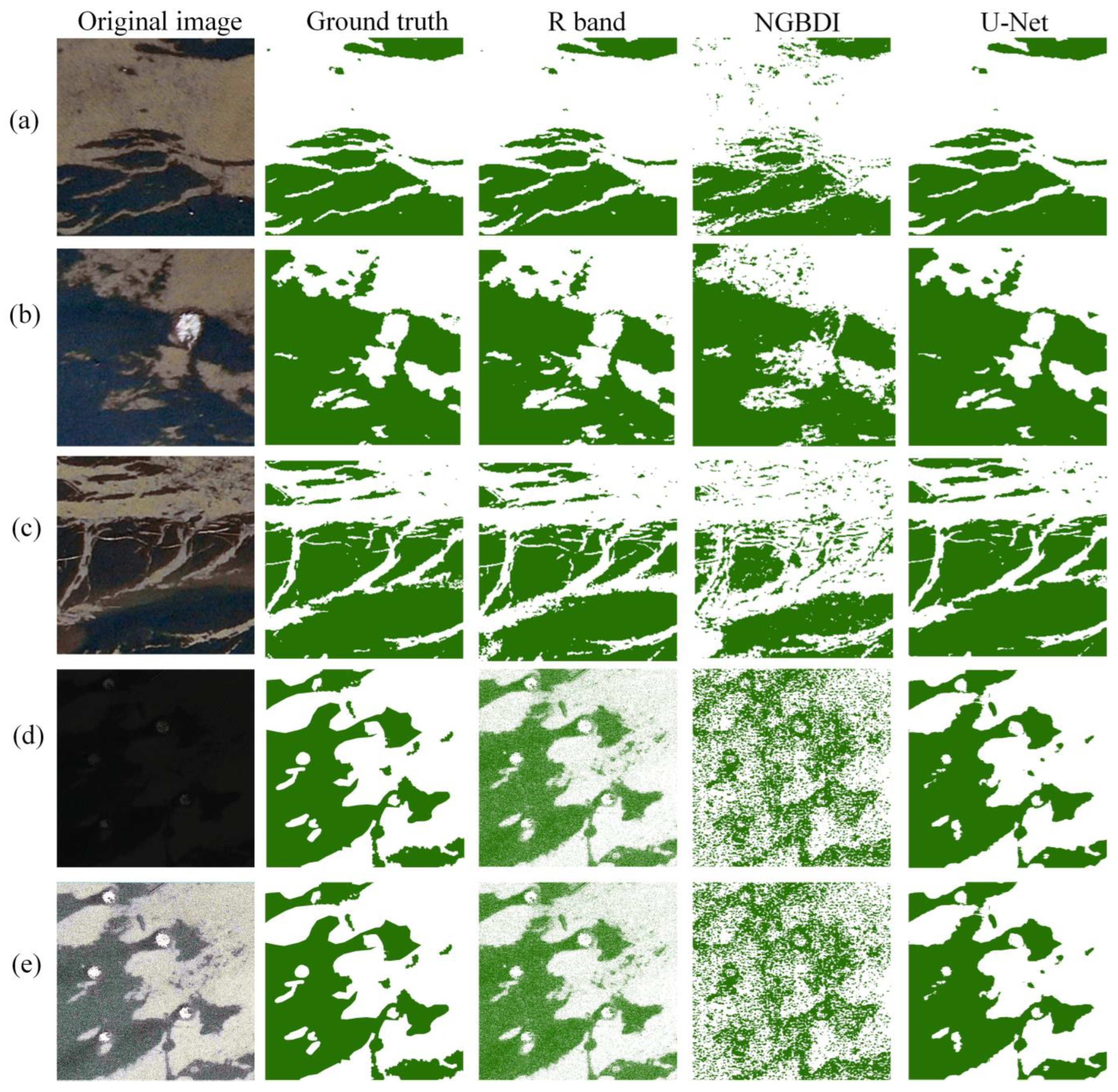
4.1. Ulva pertusa Extraction Performance from the UAV Images
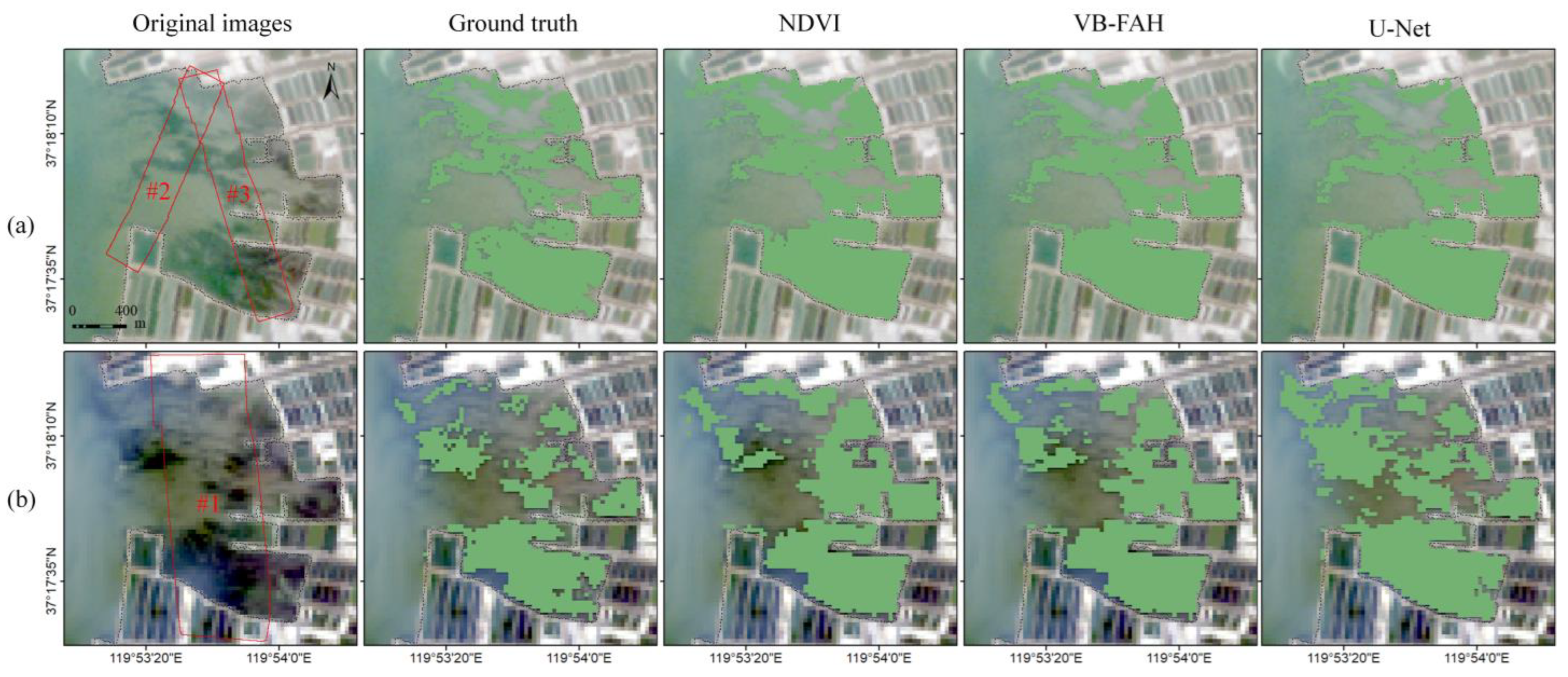
4.2. Ulva pertusa Extraction Performance from the Satellite Images
- (1)
- The lower-resolution satellite images contain mixed pixels that overestimate the U. pertusa areas in the regions corresponding to UAV images #1 and #3.
- (2)
- U. pertusa, as a benthic macroalgae, is sensitive to water depth. In the region corresponding to UAV image #2, the deeper water hinders the detection of U. pertusa with satellite remote sensing, resulting in a smaller area.
- (3)
- Furthermore, both index-based and U-Net model extractions only provide binary information on the presence or absence of U. pertusa (0 for non-Ulva pertusa pixels and 1 for U. pertusa pixels), without quantifying the U. pertusa content within each pixel.
4.3. Discussion
4.3.1. Strengths and Weaknesses for U. pertusa Extraction Based on UAVs and the U-Net Model
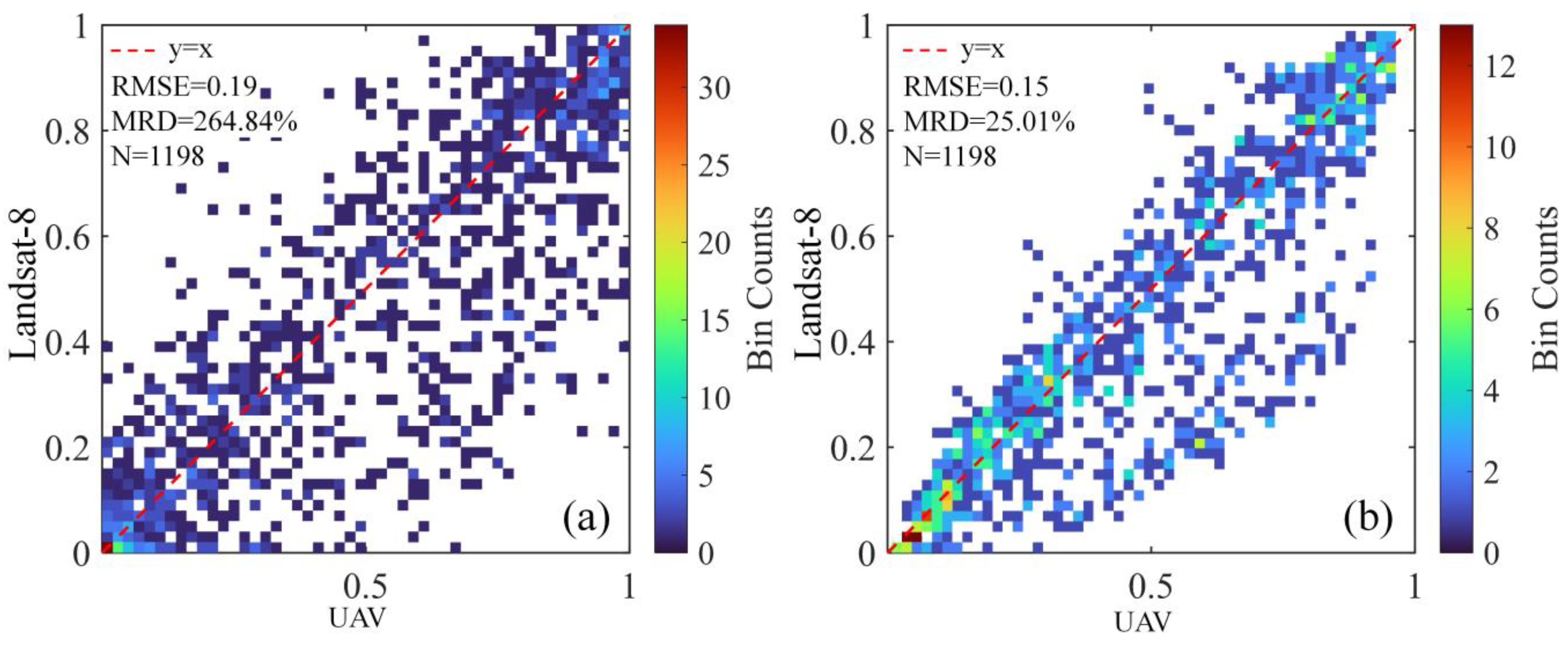
4.3.2. Improving the Accuracy of Monitoring U. pertusa in Satellite Remote Sensing Based on POM Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smetacek, V.; Zingone, A. Green and golden seaweed tides on the rise. Nature 2013, 504, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gower, J.; King, S. Seaweed, seaweed everywhere. Science 2019, 365, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, C.M.; Bruhn, A.; Krause-Jensen, D. A seaweed aquaculture imperative to meet global sustainability targets. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.G.; An, D.Y.; Zheng, X.Y.; Wei, Z.N.; Wang, X.H.; Li, L.; Tian, L.Q.; Chen, J. Monitoring seaweed aquaculture in the Yellow Sea with multiple sensors for managing the disaster of macroalgal blooms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.M.; Qi, L.; Hu, L.B.; Cui, T.W.; Xing, Q.G.; He, M.X.; Wang, N.; Xiao, Y.F.; Sun, D.Y.; Lu, Y.C.; et al. Mapping Ulva prolifera green tides from space: A revisit on algorithm design and data products. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 116, 103173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.G.; Hu, C.M. Mapping macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea using HJ-1 and Landsat data: Application of a virtual baseline reflectance height technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.; Hu, C.M.; Borstad, G.; King, S. Ocean color satellites show extensive lines of floating sargassum in the Gulf of Mexico. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3619–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.; Young, E.; King, S. Satellite images suggest a new Sargassum source region in 2011. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Q.; Hu, C.M.; Barnes, B.B.; Mitchum, G.; Lapointe, B.; Montoya, J.P. The great Atlantic Sargassum belt. Science 2019, 365, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.M. A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.B.; Choi, B.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, Y.G. Tracing floating green algae blooms in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea using GOCI satellite data and Lagrangian transport simulations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, X.L.; Liu, Y.J.; Fu, M.; Xiao, J. Interannual variations of Sargassum blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea during 2017–2021. Harmful Algae 2023, 126, 102451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.M.; Wang, M.Q.; Shang, S.L.; Wilson, C. Floating algae blooms in the East China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 11501–11509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, B.E.; Barile, P.J.; Matzie, W.R. Anthropogenic nutrient enrichment of seagrass and coral reef communities in the Lower Florida Keys: Discrimination of local versus regional nitrogen sources. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 308, 23–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohorquez, J.; Papaspyrou, S.; Yufera, M.; van Bergeijk, S.A.; Garcia-Robledo, E.; Jimenez-Arias, J.L.; Bright, M.; Corzo, A. Effects of green macroalgal blooms on the meiofauna community structure in the Bay of Cadiz. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 70, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.B.; Song, W.; Wang, Z.L.; Ding, D.W.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, X.L.; Lie, Y. Distribution of green algae micro-propagules and their function in the formation of the green tides in the coast of Qinhuangdao, the Bohai Sea, China. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 38, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreyers, L.; van Emmerik, T.; Biermann, L.; Le Lay, Y.F. Spotting green tides over brittany from space: Three decades of monitoring with Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraiola, K.M.S.; Miura, T.; Martinez, J.; Lopes, K.H.; Amidon, F.; Torres-Pérez, J.; Spalding, H.L.; Williams, T.; So, K.; Sachs, E.; et al. Using commercial high-resolution satellite imagery to monitor a nuisance macroalga in the largest marine protected area in the USA. Coral Reefs 2023, 42, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.W.; Liu, J.Q.; Zou, B.; Wang, Q.M.; Zeng, T.; Guo, M.H.; Zhu, H.T.; Zou, Y.R.; Tang, J.W. The satellite remote sensing system used in emergency response monitoring for Entermorpha prolifera disaster and its application. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 31, 52–64. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Perrie, W.; Liu, Q.R.; He, Y.J. Detection of macroalgae blooms by complex SAR imagery. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.J.; Ma, C.F.; Liu, J.Q.; Wei, H.Y. Quantifying ocean surface green tides using high-spatial resolution thermal im-ages. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 36592–36602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, T.W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.E.; Jia, Y.J.; Zhao, W.J.; Wang, Z.L.; Meng, J.M. Satellite monitoring of massive green macroal-gae bloom (GMB): Imaging ability comparison of multi-source data and drifting velocity estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5513–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zheng, X.Y.; Wei, Z.N.; Zou, J.Q.; Xing, Q.G. A spectral-mixing model for estimating sub-pixel coverage of sea-surface floating macroalgae. Atmos.-Ocean 2018, 56, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Q.; Hu, C.M. Mapping and quantifying Sargassum distribution and coverage in the Central West Atlantic using MODIS observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 183, 350–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo-Masat, O.M.; Raffo, M.P.; Rodríguez-Pérez, D.; Arijón, M.; Sánchez-Carnero, N. How far can we classify macroalgae remotely? An example using a new spectral library of species from the south west atlantic (argentine patagonia). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Hedley, J.; Giardino, C.; Roelfsema, C.; Brando, V.E. Remote sensing of shallow waters–A 50 year retrospective and future directions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahtmäe, E.; Kotta, J.; Lõugas, L.; Kutser, T. Mapping spatial distribution, percent cover and biomass of benthic vegetation in optically complex coastal waters using hyperspectral CASI and multispectral Sentinel-2 sensors. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Q.; Hu, C.M. Satellite remote sensing of pelagic Sargassum macroalgae: The power of high resolution and deep learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Yu, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.M.; Gong, Q.L. Biological characteristics and molecular systematics studies on common green algae of Ulvaceae. Period. Ocean. Univ. China 2010, 40, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, M.M.; Zheng, X.Y.; Xing, Q.G.; Liu, H.L. Remote sensing estimation of green macroalgae Ulva pertusa based on unmanned aerial vehicle and satellite image. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2022, 41, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Sung, S. Evaluating spatial resolution for quality assurance of UAV images. Spat. Inf. Res. 2016, 24, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Iglovikov, V.; Mushinskiy, S.; Osin, V. Satellite imagery feature detection using deep convolutional neural network: A kaggle competition. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.06169. [Google Scholar]
- Iglovikov, V.; Shvets, A. TernausNet: U-Net with VGG11 encoder pre-trained on imagenet for image segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.05746. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J.L. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, F.; Qi, Y.X.; Deng, L.F.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, S.T. New research methods for vegetation information extraction based on visible light remote sensing images from an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 78, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J. A survey on object detection in optical remote sensing images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 117, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.W.; Liang, X.J.; Gong, J.L.; Tong, C.; Xiao, Y.F.; Liu, R.J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Assessing and refining the satellite-derived massive green macro-algal coverage in the Yellow Sea with high resolution images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Lu, Y.; Hu, L.B.; Jiao, J.N.; Zhang, M.W.; Liu, Y.X. Uncertainty in the optical remote estimation of the biomass of Ulva prolifera macroalgae using MODIS imagery in the Yellow Sea. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 18620–18627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.Q.; Tian, J.Y.; Wang, J.R.; Wang, X.; Li, W. A novel remote sensing index for brine shrimp (Artemia) slick detection in salt lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 286, 113428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sensor/Source | Data Level | No. | Capture Date | Time/UTC+8 | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat-8 OLI GF-1 WFV | L2 | - | 24 October 2020 | 10:49 | 30 m |
| L1A | - | 11 November 2020 | 11:08 | 16 m | |
| DJI Mavic2 FC2220 | - | #1 | 24 October 2020 | 11:08 | 0.17 m |
| - | #2 | 11 November 2020 | 10:52 | 0.10 m | |
| - | #3 | 11 November 2020 | 11:23 | 0.12 m |
| Method | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 87.38 | 79.76 | 93.27 | 0.83 |
| NGBDI | 57.97 | 64.11 | 55.55 | 0.54 |
| U-Net | 96.46 | 94.84 | 92.42 | 0.92 |
| Method | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | 82.54 | 71.42 | 90.80 | 0.80 |
| VB-FAH | 85.05 | 74.59 | 92.96 | 0.83 |
| U-Net | 85.11 | 74.05 | 96.44 | 0.83 |
| Method | Region#1 of Landsat-8 | Region#2 of GF-1 | Region#3 ofGF-1 |
| NDVI | 0.62 km2 | 0.16 km2 | 0.40 km2 |
| VB-FAH | 0.59 km2 | 0.14 km2 | 0.37 km2 |
| U-Net | 0.70 km2 | 0.12 km2 | 0.33 km2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, Q.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Hou, Y.; Meng, M.; Liu, C. A Novel Approach of Monitoring Ulva pertusa Green Tide on the Basis of UAV and Deep Learning. Water 2023, 15, 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173080
Xing Q, Liu H, Li J, Hou Y, Meng M, Liu C. A Novel Approach of Monitoring Ulva pertusa Green Tide on the Basis of UAV and Deep Learning. Water. 2023; 15(17):3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173080
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Qianguo, Hailong Liu, Jinghu Li, Yingzhuo Hou, Miaomiao Meng, and Chunli Liu. 2023. "A Novel Approach of Monitoring Ulva pertusa Green Tide on the Basis of UAV and Deep Learning" Water 15, no. 17: 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173080
APA StyleXing, Q., Liu, H., Li, J., Hou, Y., Meng, M., & Liu, C. (2023). A Novel Approach of Monitoring Ulva pertusa Green Tide on the Basis of UAV and Deep Learning. Water, 15(17), 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173080






