Degradation of 2-Chlorophenol in Aqueous Solutions Using Persulfate Activated by Biochar Supported Sulfide-Modified Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Performance and Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of BC@S-nZVI
2.3. Experimental Process
2.4. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
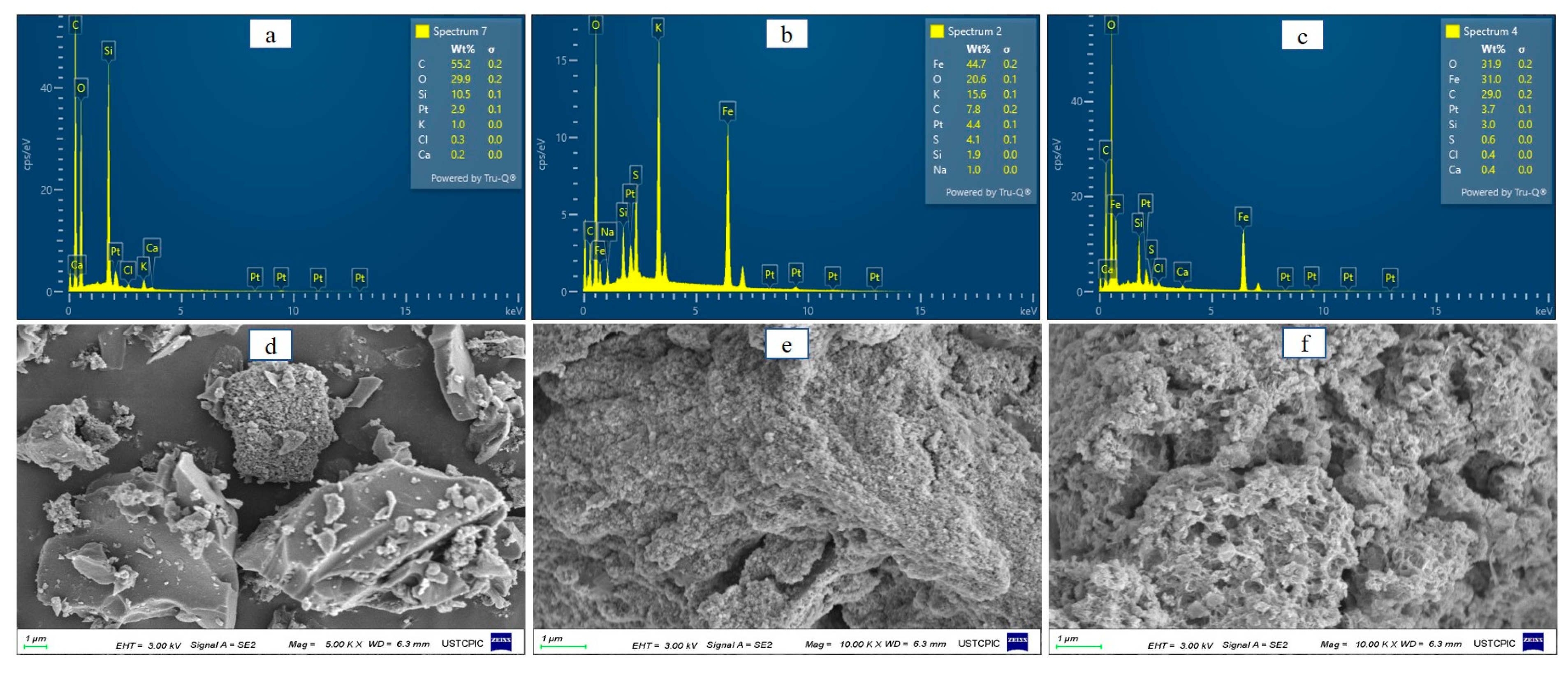
3.1. Characteristic of BC@S-nZVI Composite
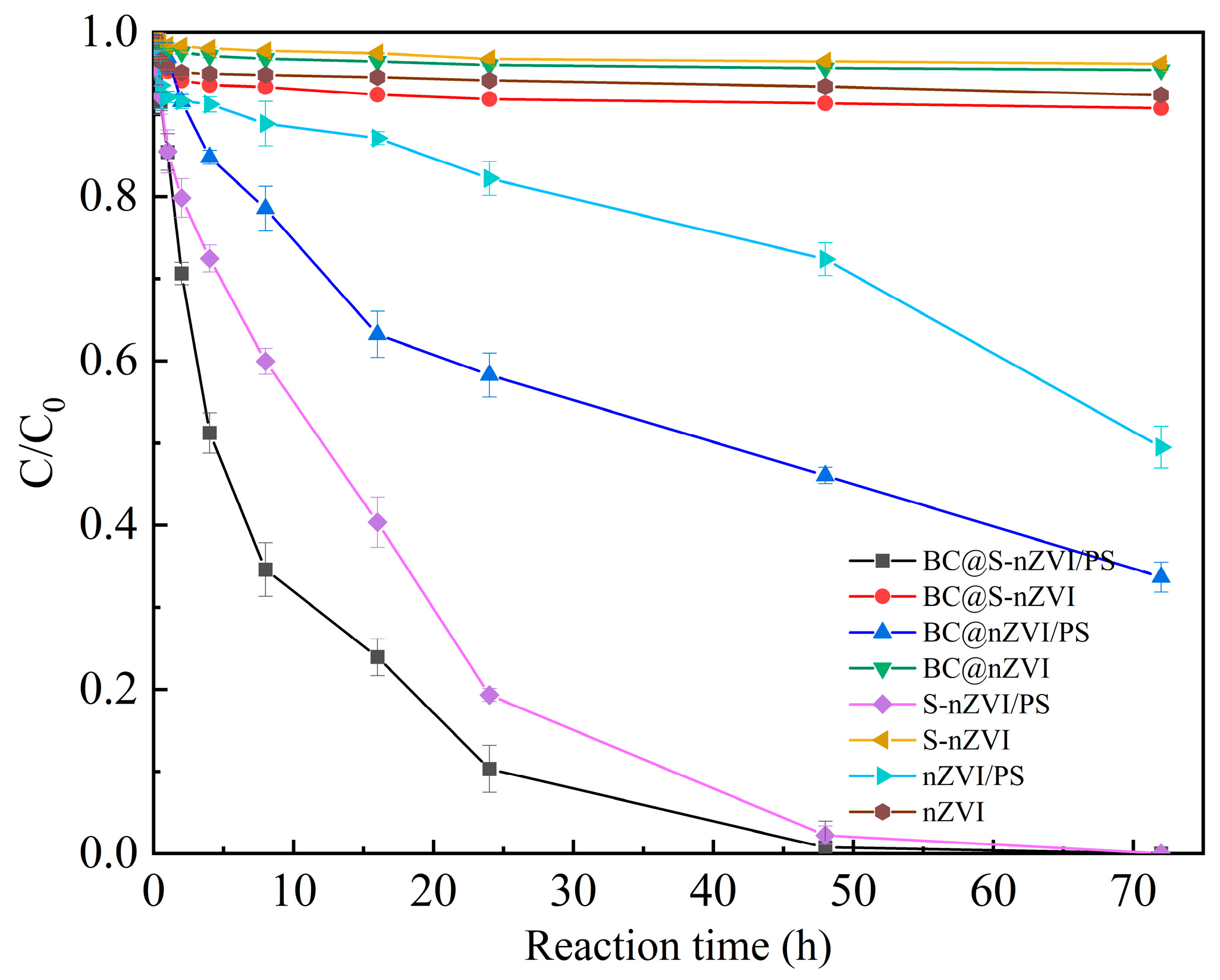
3.2. Degradation Analyses of 2-CP in Different Conditions and Systems
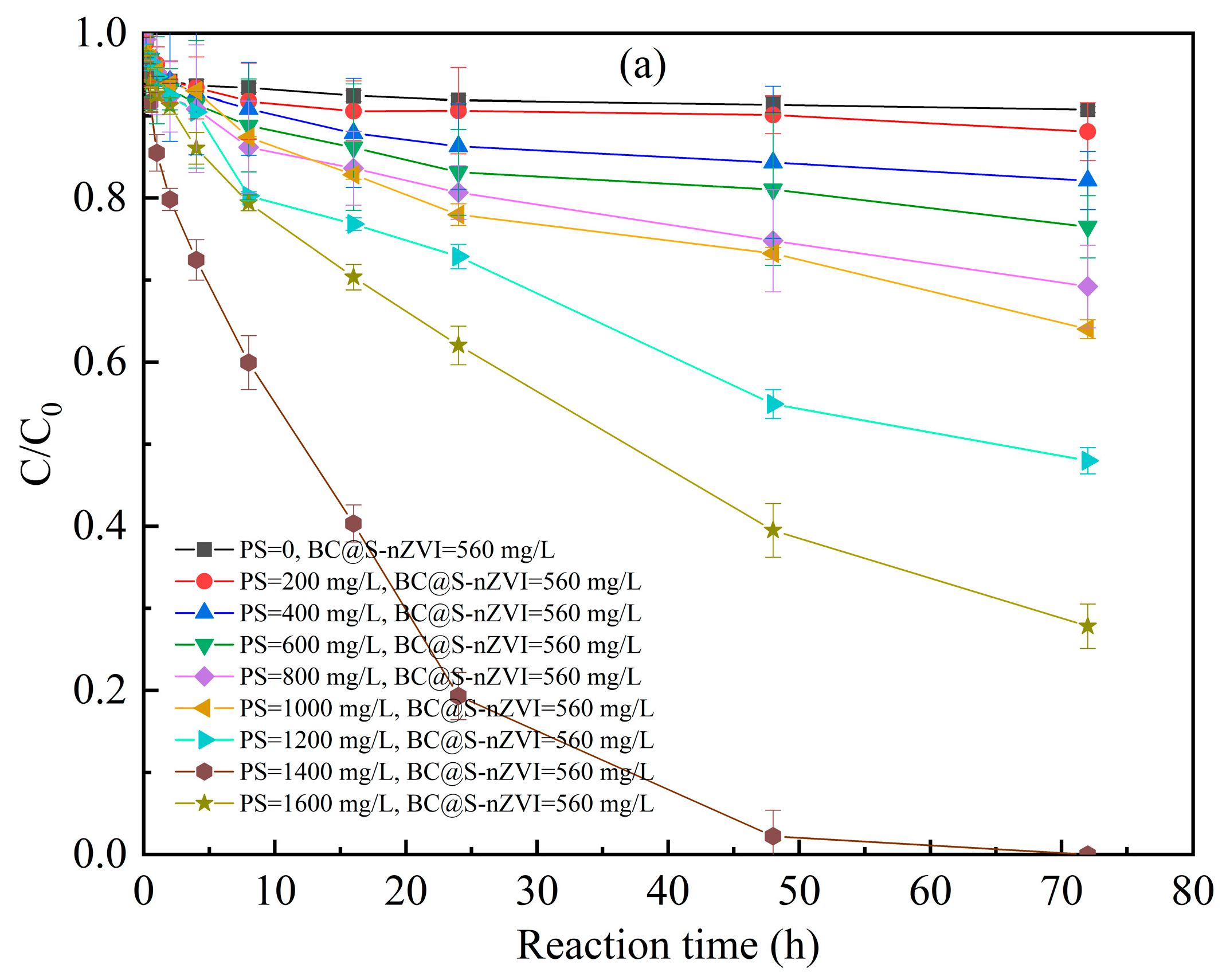
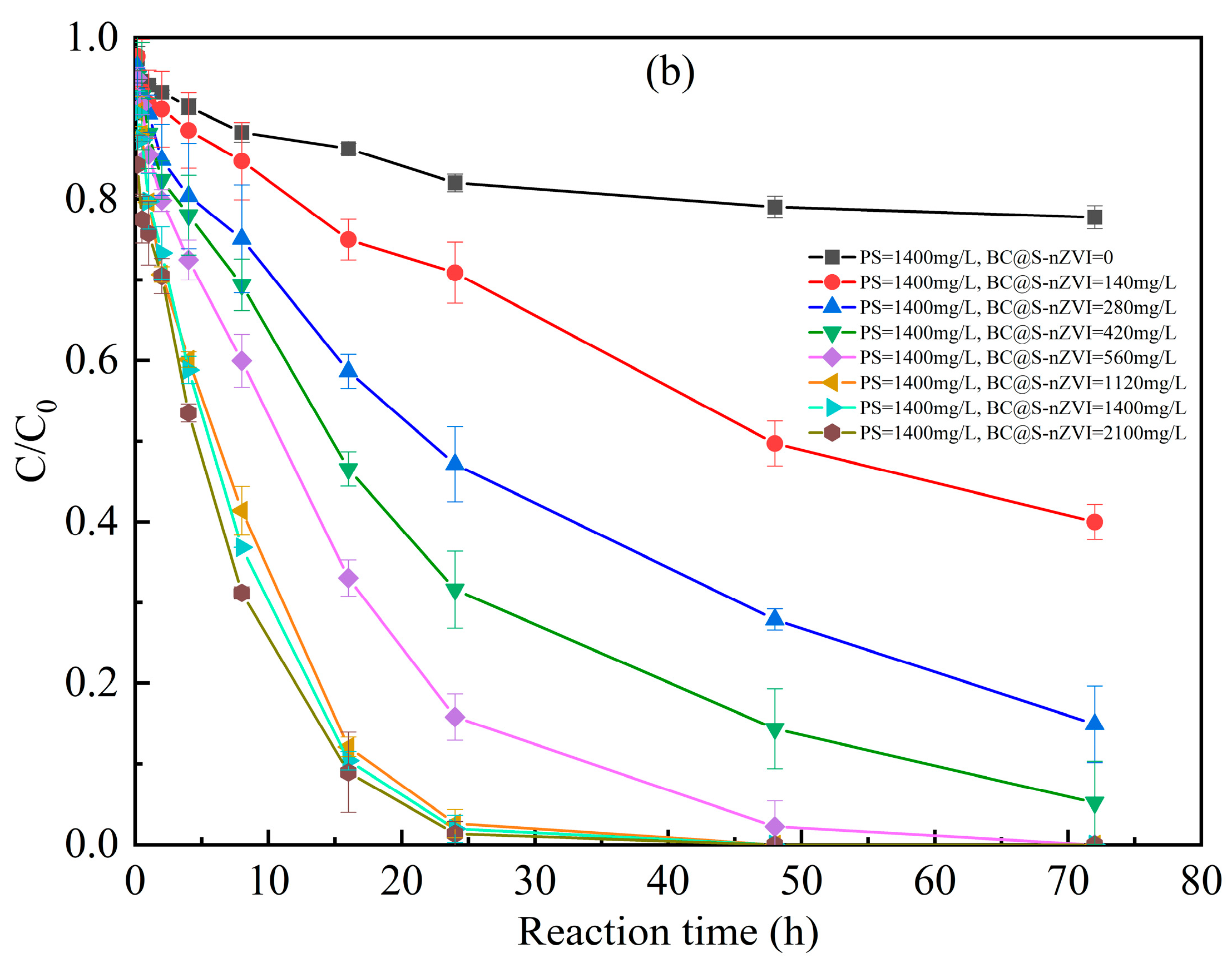
3.3. Factors Affecting the 2-CP Degradation in the BC@S-nZVI-Activated PS System
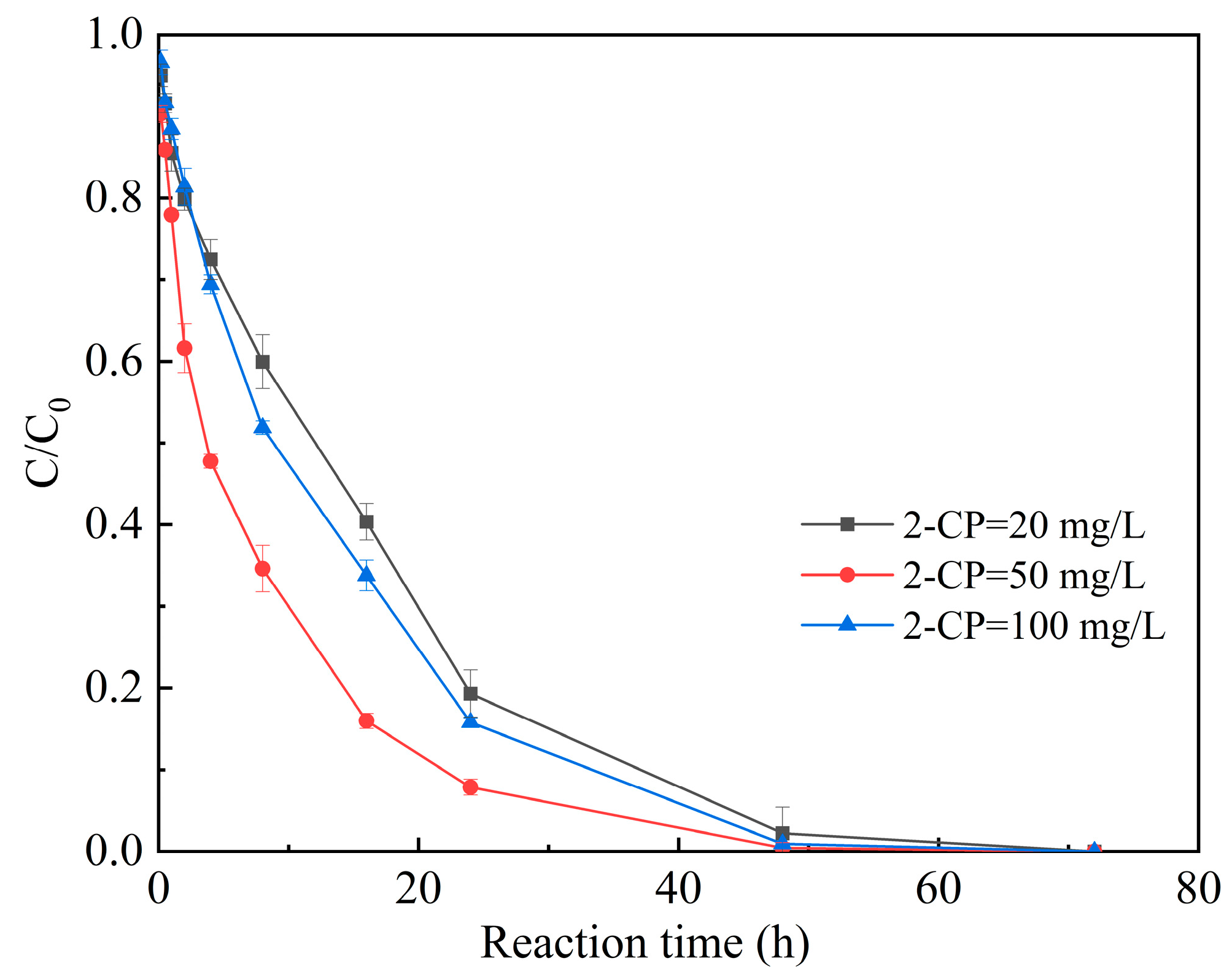
3.3.1. Initial Concentration
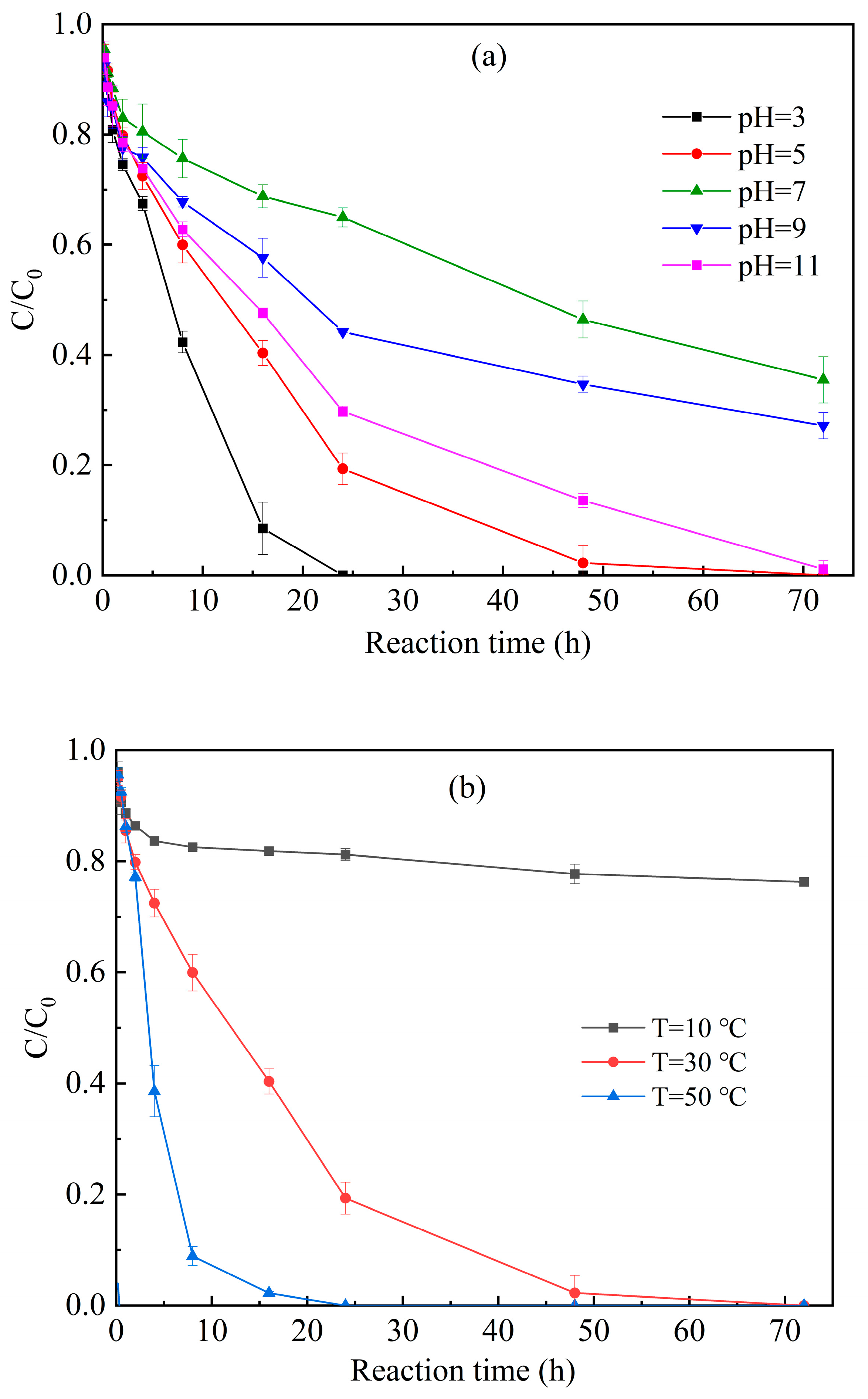
3.3.2. pH and Temperature
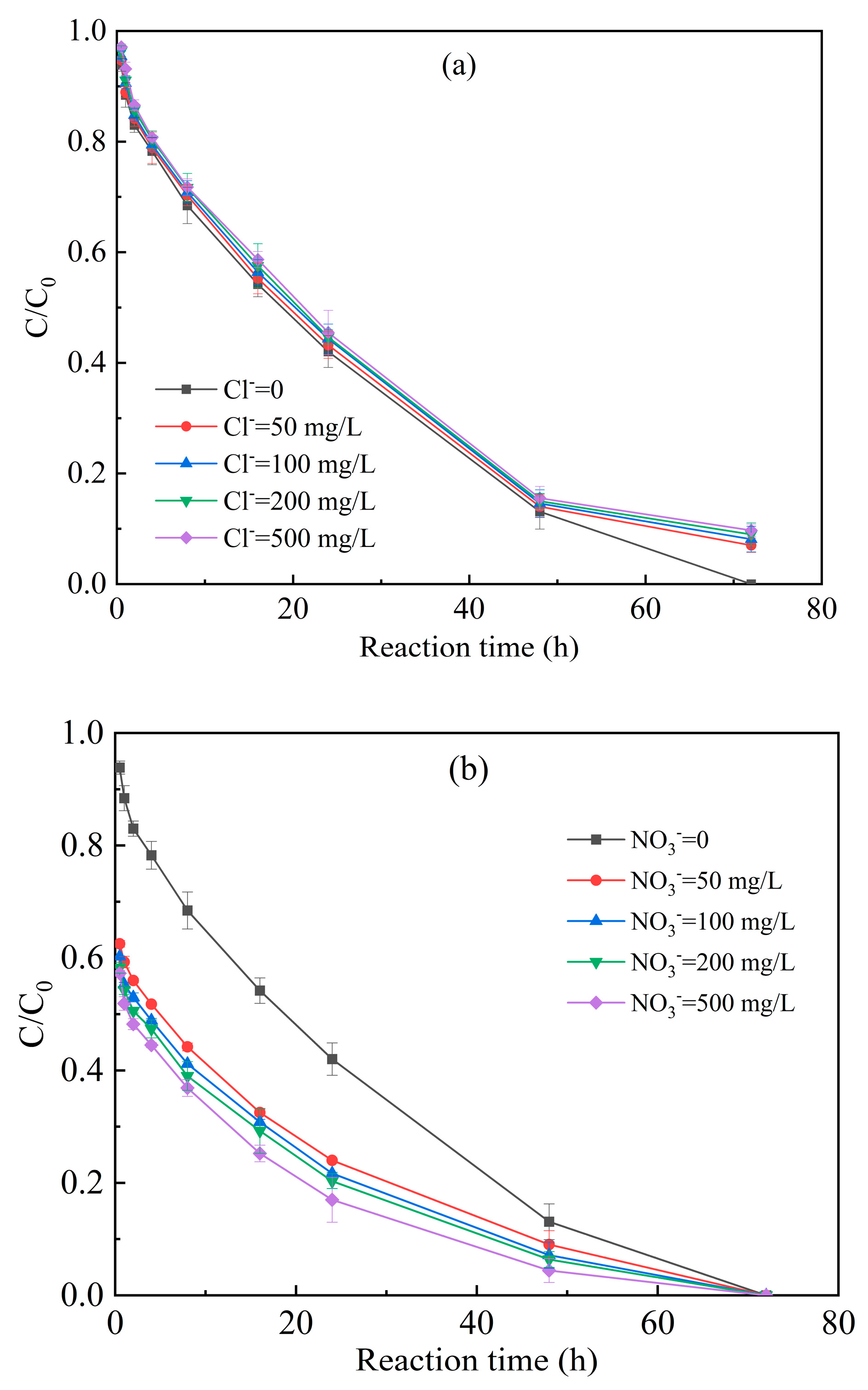
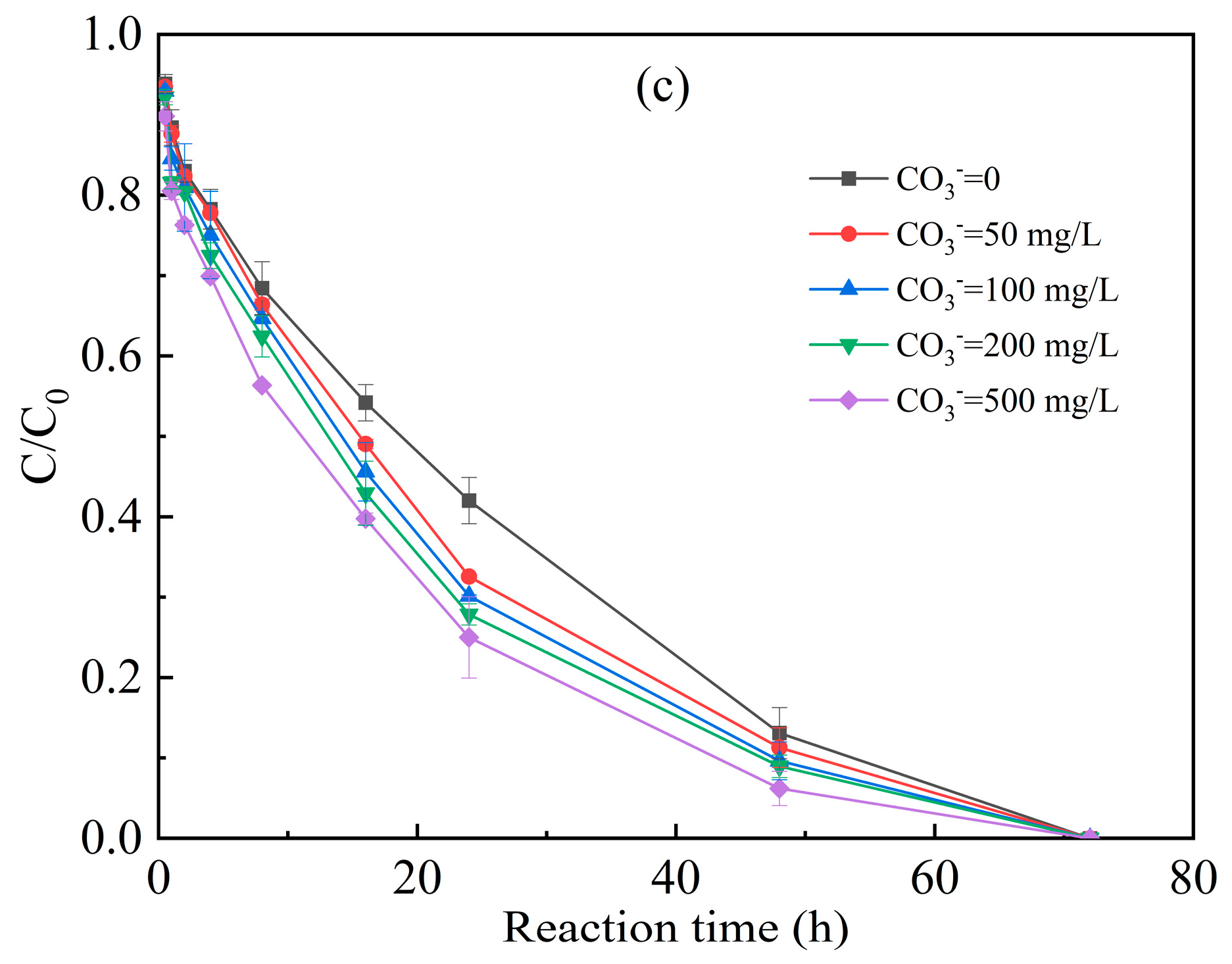
3.3.3. Inorganic Anions of Chloride, Nitrate and Carbonate
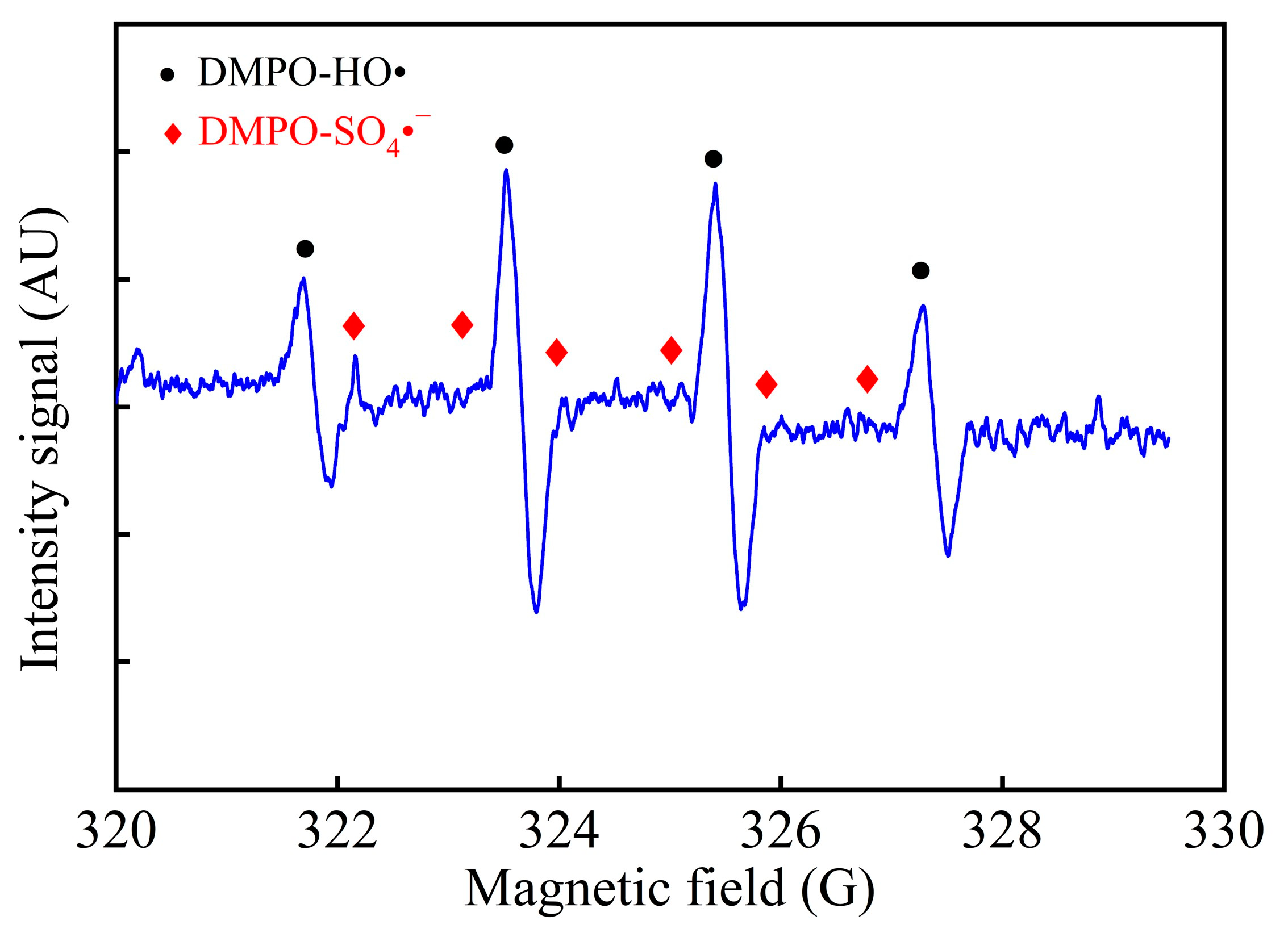
3.4. The Degradation Mechanism of 2-CP in the BC@S-nZVI/PS System
3.5. Stability of BC@S-nZVI
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Decker, S. Ullmann’s encyclopedia of industrial chemistry. Mater. Manuf. Process. 1999, 14, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, L.H.; Telliard, W.A. Priority pollutants: I-a perspective view. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1979, 13, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Fu, H.; Tang, S.Y.; Xu, K.K.; Song, X.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.M. Current situation analysis and prospect of organic contaminated sites in China. Soil 2021, 53, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.Y.; Yi, S.P.; Zheng, C.M.; Lo, I.M.C. Persulfate activation by natural zeolite supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for trichloroethylene degradation in groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Liang, H.L. Degradation mechanism of Norfloxacin in Water using Persulfate Activated by BC@nZVI/Ni. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Guo, Z.P.; Wang, Y.D.; Zhang, L.; Xue, G. Enhanced decolorization of methyl orange in aqueous solution using iron-carbon micro-electrolysis activation of sodium persulfate. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gao, M.X.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhang, R.Q.; Yang, X.; Tang, C.F.; Hu, X.J. A novel preparation of S-nZVI and its high efficient removal of Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X. Enhanced activation of peroxymonosulfate using oxygen vacancy-enriched FeCo2O4x spinel for 2,4-dichlorophenol removal: Singlet oxygen-dominated nonradical process. Colloids Surf. A 2020, 597, 124568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.Y.; Fang, L.; Liao, P.B.; Chen, H.S. Ultrasound-activated peracetic acid to degrade tetracycline hydrochloride: Efficiency and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.C.; Couttenye, R.A.; Hoag, G.E. Kinetics of heat-assisted persulfate oxidation of methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE). J. Soil Contam. 2002, 11, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Cho, Y.C.; Lin, Y.P. Activation of peroxydisulfate by carbon nanotube for the degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol: Contributions of surface-bound radicals and direct electron transfer. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J. Activation of peroxydisulfate by a novel Cu0-Cu2O@CNTs composite for 2, 4-dichlorophenol degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 754, 141883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzek, L.W.; Carter, K.E. Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: A review. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, A.; Klu, P.K.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Luo, R.; Zhang, M.; Qi, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Metal-organic framework-derived Hollow Co3O4/Carbon as Efficient Catalyst for Peroxymonosulfate Activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 363, 234–246. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Deng, D.; Guan, M.; Fang, X.; Zhu, Q. Remediation HCHs POPs-contaminated soil by activated persulfate technologies: Feasibility, impact of activation methods and mechanistic implications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 150, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Das, U.; Dalai, A.K. In-situ chemical oxidation: Principle and applications of peroxide and persulfate treatments in wastewater systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Q.; Gao, N.Y.; Deng, Y.; Yang, Y.Q.; Ma, Y. Ultraviolet (UV) light-activated persulfate oxidation of sulfamethazine in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 195, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, X.; Xi, B. Perdisulfate-Assisted Advanced Oxidation of 2,4-Dichlorophenol by Bio-inspired Iron Encapsulated Biochar Catalyst. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2021, 592, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.L.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Shin, W.S.; Hwang, I. Activation of Persulfate by Nanosized Zero-Valent Iron (NZVI): Mechanisms and Transformation Products of NZVI. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3625–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Q.; Gao, N.Y.; Wei, W.; Kang, S.F.; Xu, J.H.; Xiang, H.M.; Yin, D.Q. Ultrasound-assisted heterogeneous activation of persulfate by nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) for the propranolol degradation in water. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 49, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xing, J.; Pu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Wei, B.; Ai, Y.; Xiang, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, X. Preparation of nano-Fe0 modified coal fly-ash composite and its application for U(VI) sequestration. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 266, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xi, B.; Mao, X.; Gong, B.; Li, R.; Peng, X.; Liu, H. Removal of nitrobenzene by immobilized nanoscale zero-valent iron: Effect of clay support and efficiency optimization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 370, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirsaheb, M.; Moradi, S.; Shahlaei, M.; Wang, X.; Farhadian, N. A new composite of nano zero-valent iron encapsulated in carbon dots for oxidative removal of bio-refractory antibiotics from water. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 209, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.S.; Shaikh, H.M.; Asif, M.; Al-Ghurabi, E.H. Engineered biochar from wood apple shell waste for high-efficient removal of toxic phenolic compounds in wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.R.; Zhang, C.; Deng, J.M.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L.H.; Cheng, Y.J.; Hou, K.J.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G.M. Factors influencing degradation of trichloroethylene by sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous solution. Water Res. 2018, 135, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, M.; Georgi, A.; Kopinke, F.D.; Mackenzie, K. Sulfidation of ZVI/AC composite leads to highly corrosion-resistant nanoremediation particles with extended life-time. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Gao, X.Y.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.L.; Lowry, G.V. Distributing sulfidized nanoscale zerovalent iron onto phosphorus-functionalized biochar for enhanced removal of antibiotic florfenicol. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced degradation of bisphenol S by persulfate activated with sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 8281–8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.C.; Kong, W.J.; Gao, Y.; Kong, Y.; Dai, Z.G.; Dan, H.B.; Shang, Y.N.; Wang, S.Q.; Yin, F.J.; Yue, Q.Y.; et al. Removal of chloramphenicol by sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron activated persulfate: Performance, salt resistance, and reaction mechanisms. Chemosphere 2021, 286, 131876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Song, D.; Xu, X.J.; Hao, Y.; Sun, H. Sulfidated zero valent iron as a persulfate activator for oxidizing organophosphorus pesticides (OPPs) in aqueous solution and aged contaminated soil columns. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Dong, H.R.; Tian, R.; Li, R.; Xie, Q.Q. Remediation of Trichloroethylene-Contaminated Groundwater by Sulfide-Modified Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Supported on Biochar: Investigation of Critical Factors. Water Air Soil Poll. 2020, 231, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.C.; Jin, X.Y.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R.; Chen, Z.L. Heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of 2,4-dichlorophenol using iron-based nanoparticles and persulfate system. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.C.; Wang, J.; Gao, B.; Sato, S.; Feng, K.; Yin, W.; Igalavithana, A.D. Biochar-supported nZVI (nZVI/BC) for contaminant removal from soil and water: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 820–834. [Google Scholar]
- China Rural Statistical Yearbook; N. B. S. China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Li, H. Low fat and high fiber soybean food. Farm Prod. Process. 2011, 8, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi, N.; Pourfadakari, S.; Esmaeili, S.; Babaei, A.A. Mineralization of high saline petrochemical wastewater using Sonoelectro-activated persulfate: Degradation mechanisms and reaction kinetics. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, K.E.; Carter, K.E. Investigating the effects of heat activated persulfate on the degradation of furfural, a component of hydraulic fracturing fluid chemical additives. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, B.T.; Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Yang, Z. Oxidative degradation of chloroxylenol in aqueous solution by thermally activated persulfate: Kinetics, mechanisms and toxicities. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 368, 553–563. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.R.; Tian, D.F.; Chu, W.; Li, M.R.; Lu, X.W. Nanoscaled magnetic CuFe2O4 as an activator of peroxymonosulfate for the degradation of antibiotics norfloxacin. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Lin, Y.C. Phototransformation of Cephalosporin Antibiotics in an Aqueous Environment Results in Higher Toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12417–12426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.W.; Shen, M.X.; Liu, J.H.; Ma, Y.J.; Gong, B.N.; Liu, H.Q.; Huang, Z.J. Resource utilization of piggery sludge to prepare recyclable magnetic biochar for highly efficient degradation of tetracycline through peroxymonosulfate activation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, R.; Wang, M.; Li, W.; Song, J. Degradation of 2-Chlorophenol in Aqueous Solutions Using Persulfate Activated by Biochar Supported Sulfide-Modified Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Performance and Mechanisms. Water 2023, 15, 2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152805
Xie R, Wang M, Li W, Song J. Degradation of 2-Chlorophenol in Aqueous Solutions Using Persulfate Activated by Biochar Supported Sulfide-Modified Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Performance and Mechanisms. Water. 2023; 15(15):2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152805
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Ronghuan, Mu Wang, Weiping Li, and Junjie Song. 2023. "Degradation of 2-Chlorophenol in Aqueous Solutions Using Persulfate Activated by Biochar Supported Sulfide-Modified Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Performance and Mechanisms" Water 15, no. 15: 2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152805
APA StyleXie, R., Wang, M., Li, W., & Song, J. (2023). Degradation of 2-Chlorophenol in Aqueous Solutions Using Persulfate Activated by Biochar Supported Sulfide-Modified Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Performance and Mechanisms. Water, 15(15), 2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152805





