Shear Enhanced Flotation Separation Technology in Winery Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
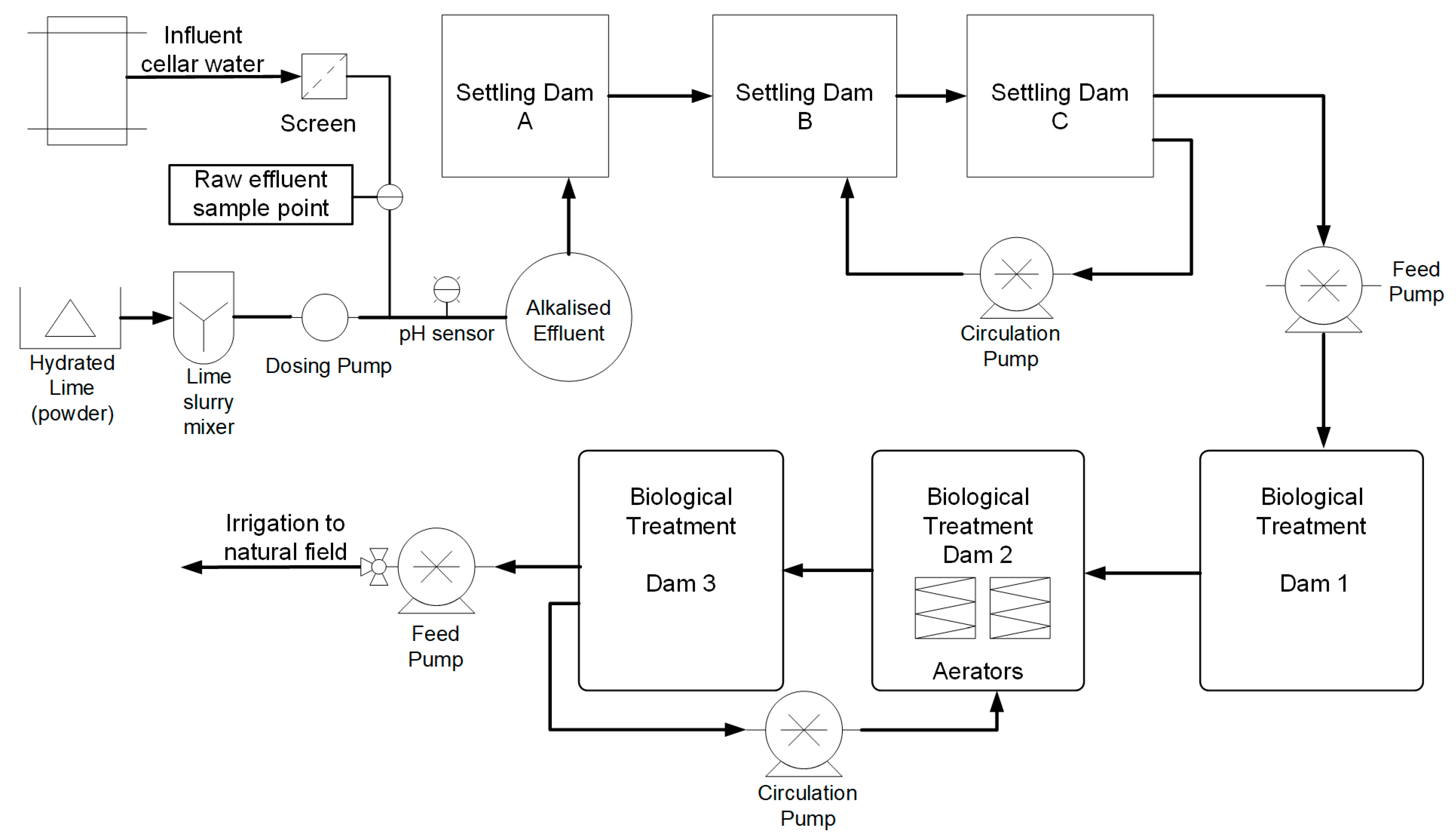
2.1. Raw Winery Effluent Collection
2.2. Alkalization Study
2.3. Coagulation and Flocculation
Coagulation and Flocculation Dosages
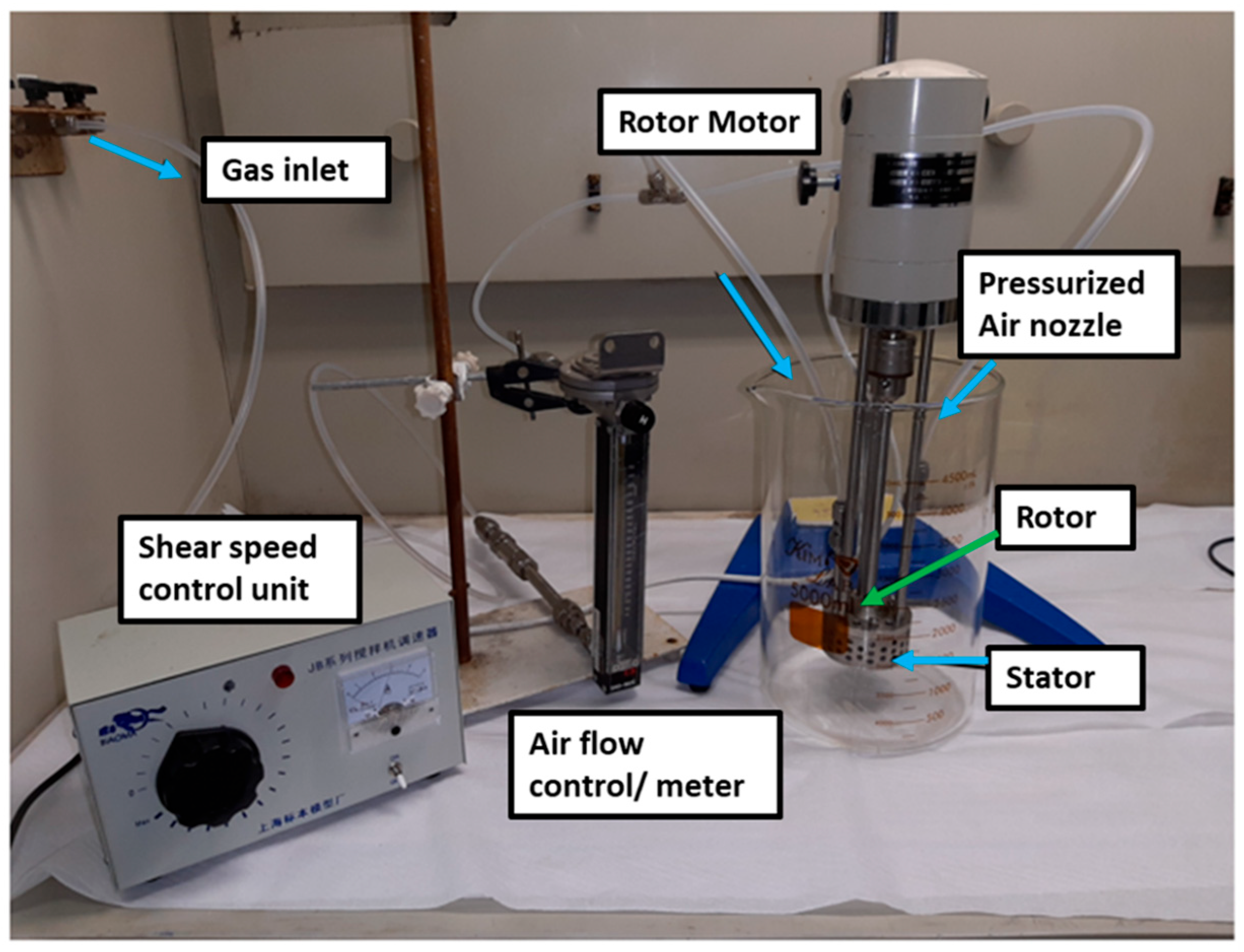
2.4. Shear Mixing
2.5. Analytical Methods
Zeta Potential
2.6. Determination of Total Suspended Solids
3. Results
3.1. Raw Winery Wastewater Composition
3.2. Alkalization
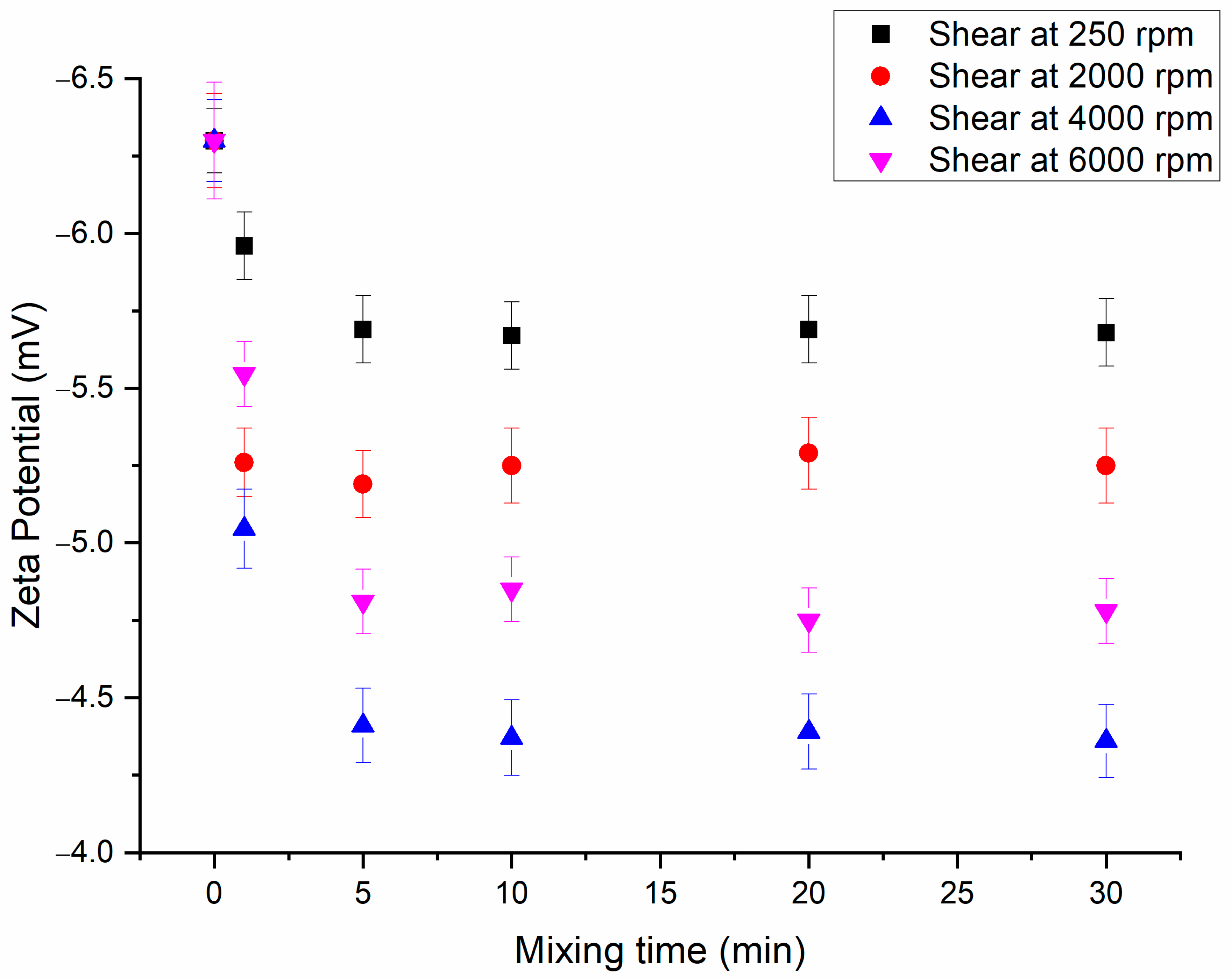
3.3. Application of Shear
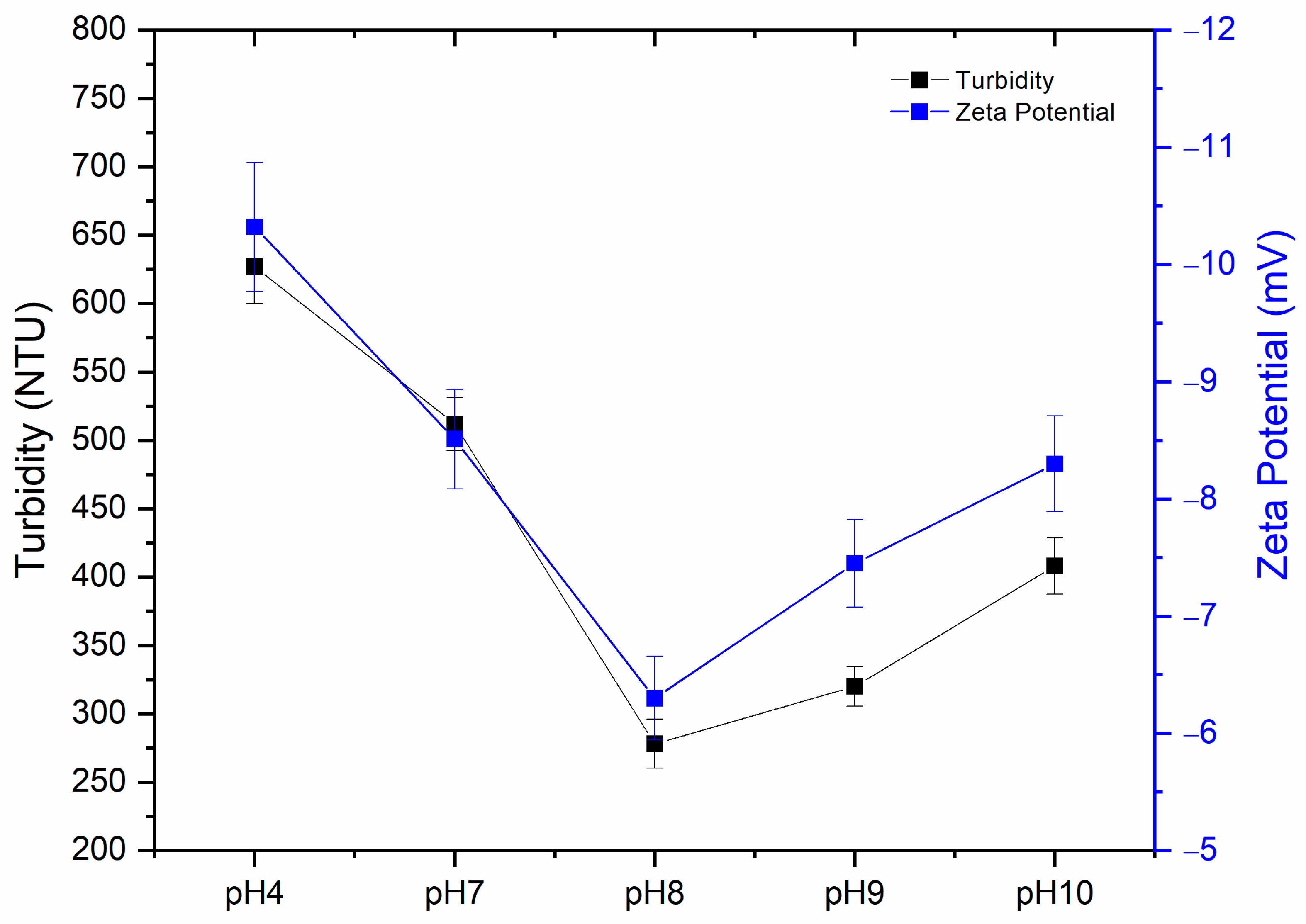
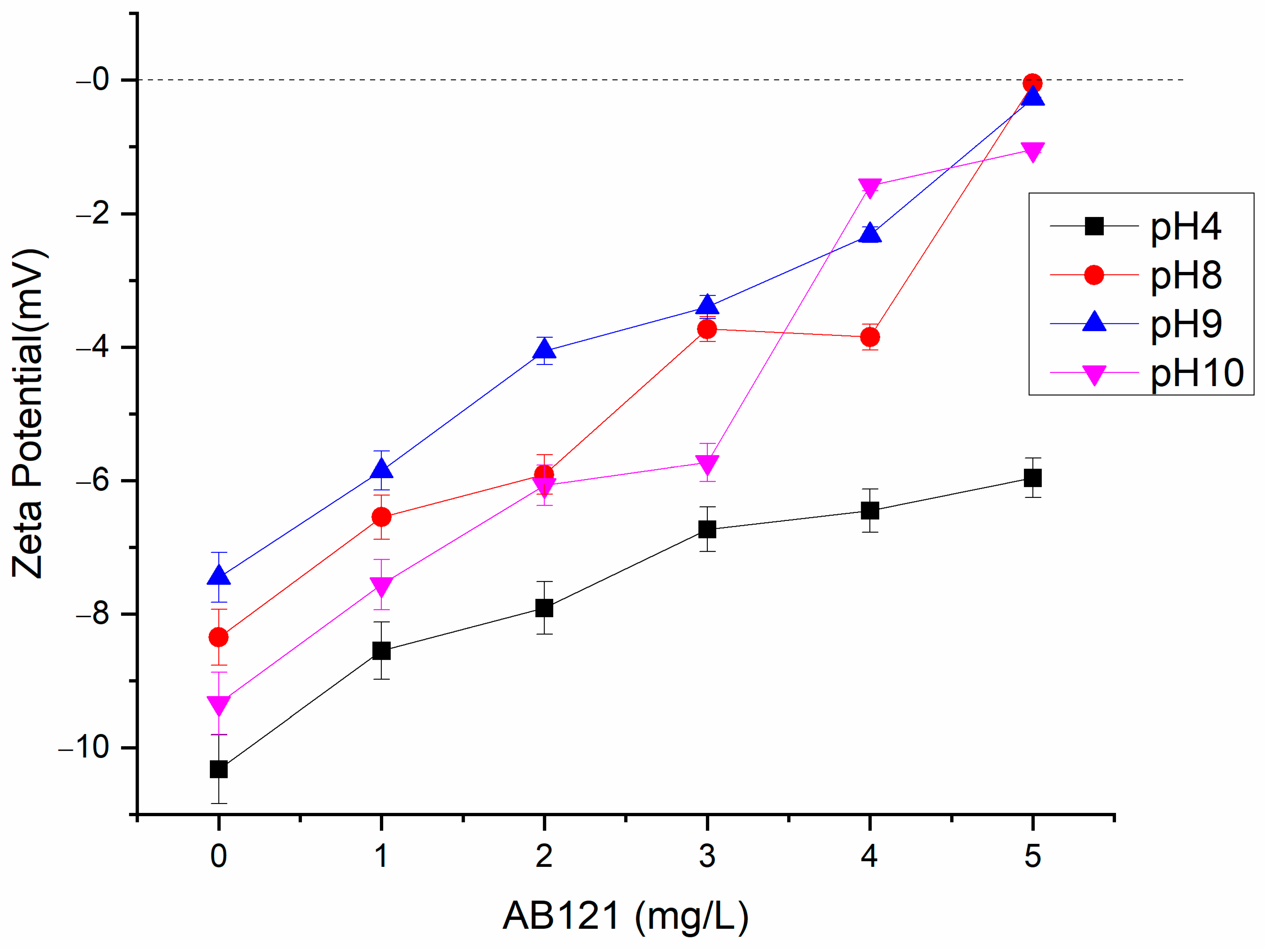
3.4. Zeta Potential Studies on Coagulation
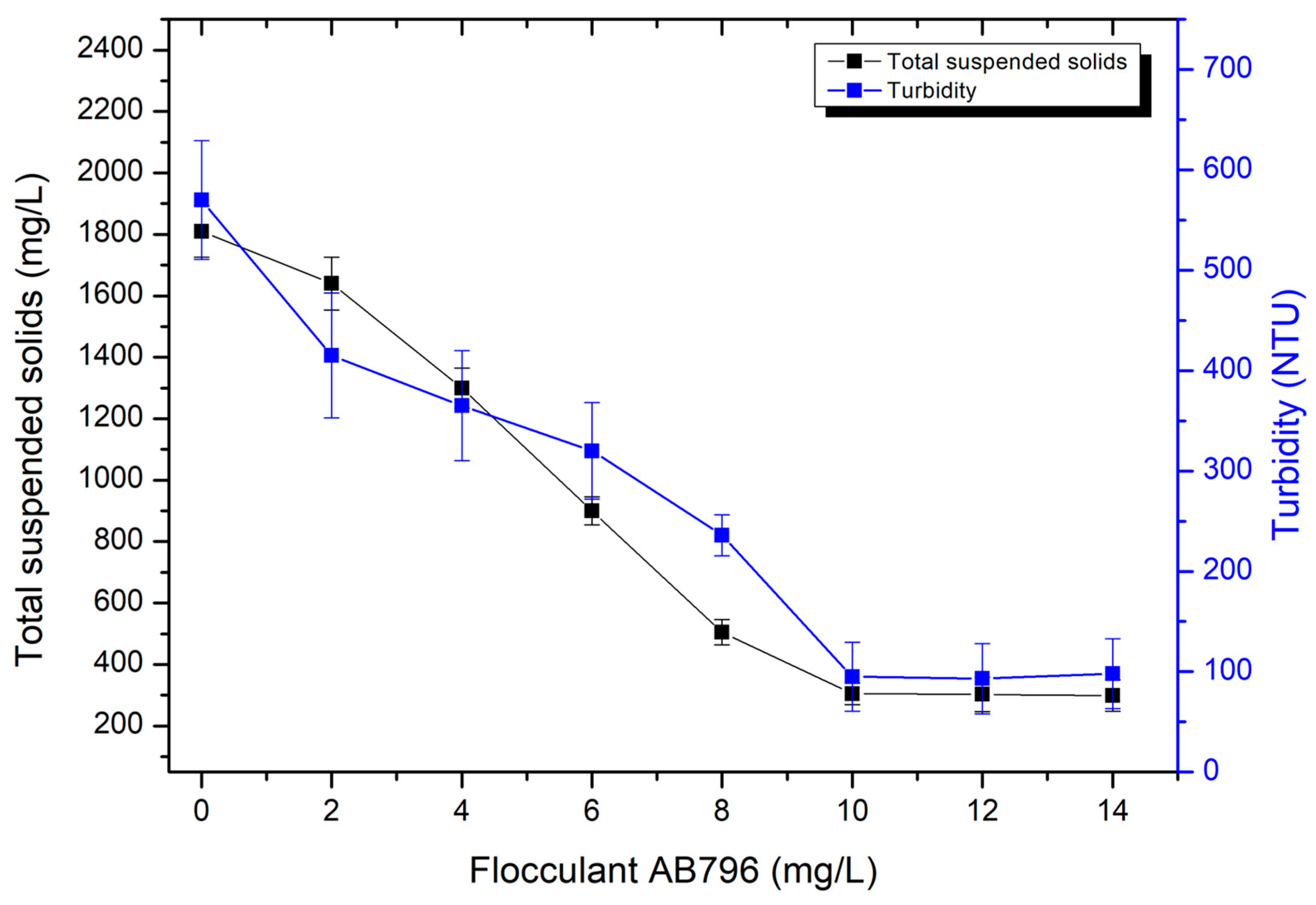
3.5. Flocculation
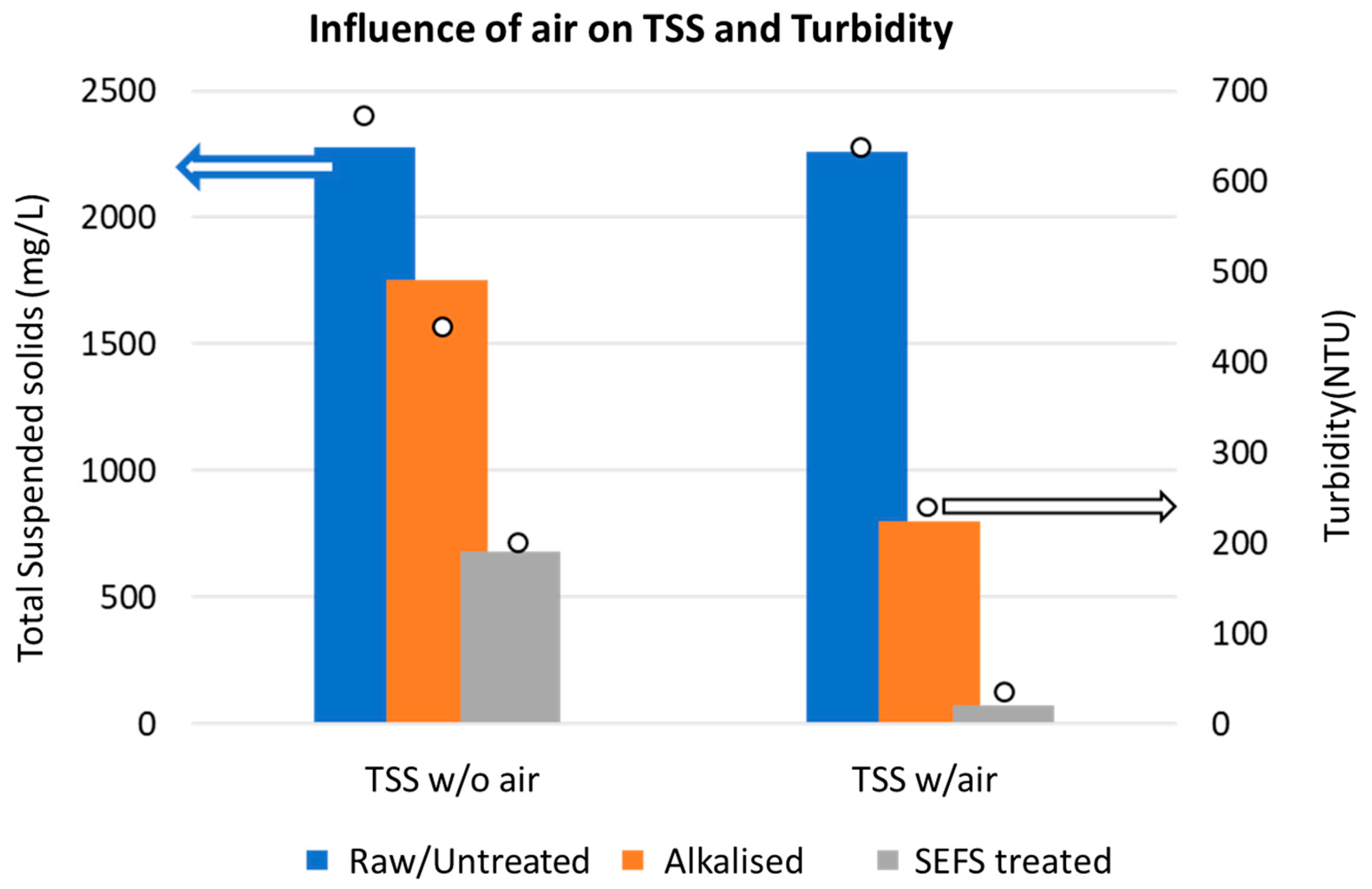
3.6. Introduction of Air
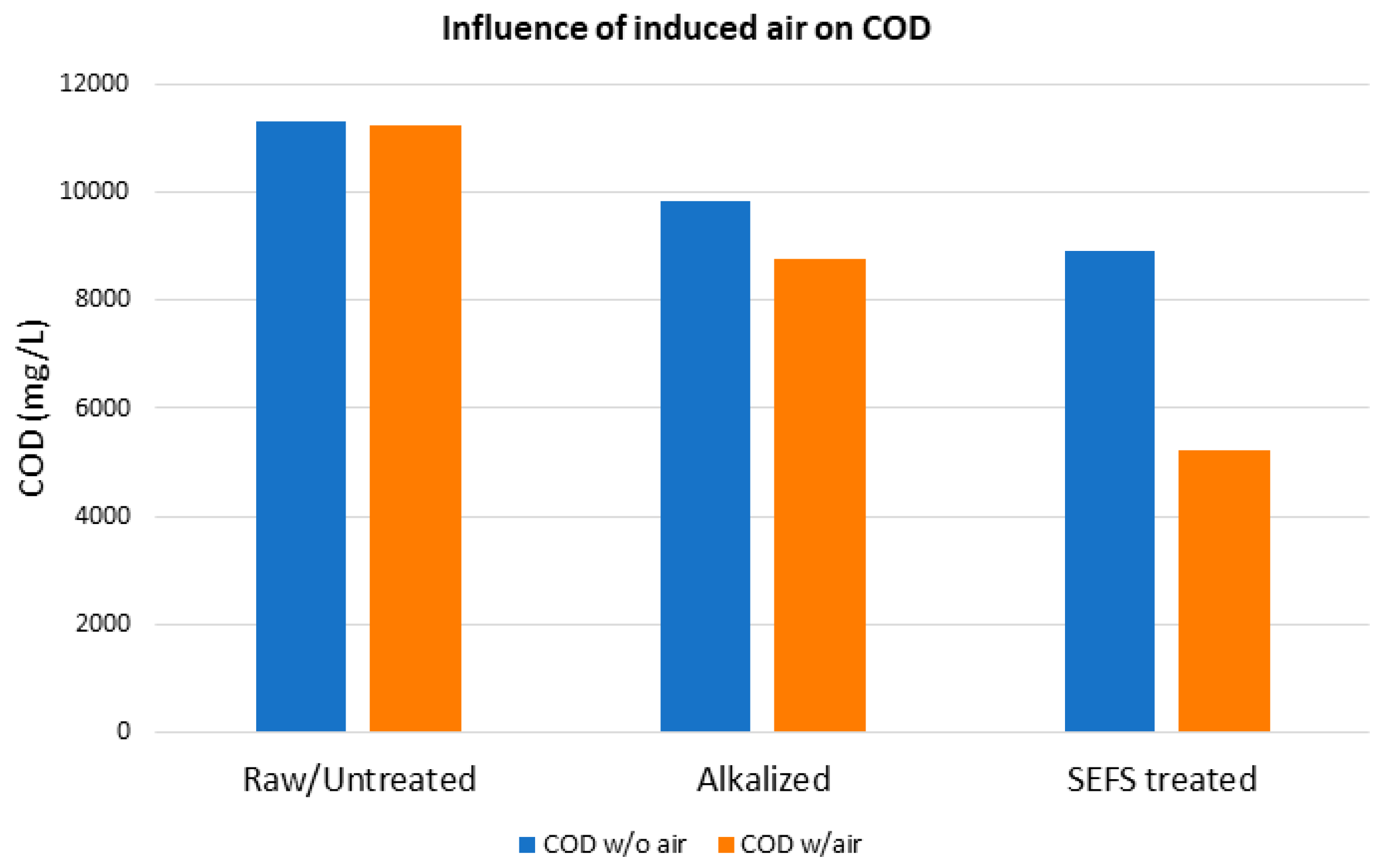
3.7. Influence of SEFS on COD
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheremisinoff, N.P. Water Sterilization Technologies. In Handbook of Water and Wastewater Treatment Technologies; Butterworth-Heinemann: Woburn, UK, 2002; pp. 446–495. ISBN 978-0-7506-7498-0. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, C.L.; Myburgh, P.A. Management of Winery Wastewater by Re-Using It for Crop Irrigation—A Review. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2018, 39, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, L.A.; Puma, G.L.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Treatment of Winery Wastewater by Physicochemical, Biological and Advanced Processes: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Schoor, L.H. Guidelines for the Management of Wastewater and Solid Waste at Existing Wineries; Winetech: Paarl, South Africa, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, J.; Baker, P.; Wills, S. Winery Wastewater Handbook: Production, Impacts and Management; Winetitles: Broadview, Australia, 2001; ISBN 1875130357. [Google Scholar]
- Smagghe, F.; Mourgues, J.; Escudier, J.L.; Conte, T.; Molinier, J.; Malmary, C. Recovery of Calcium Tartrate and Calcium Malate in Effluents from Grape Sugar Production by Electrodialysis. Bioresour. Technol. 1992, 39, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradie, A.; Sigge, G.O.; Cloete, T.E. Influence of Winemaking Practices on the Characteristics of Winery Wastewater and Water Usage of Wineries. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2014, 35, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulidzi, A.; Clarke, C.; Myburgh, P. Annual Dynamics of Winery Wastewater Volumes and Quality and the Impact of Disposal on Poorly Drained Duplex Soils. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2018, 39, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamane, X.L.; Strong, P.J.; Burgess, J.E. Treatment of Wine Distillery Wastewater: A Review with Emphasis on Anaerobic Membrane Reactors. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2007, 28, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, M.A.; Moral, R.; Paredes, C.; Pe, A.; Pe, M.D. Agrochemical Characterisation of the Solid By-Products and Residues from the Winery and Distillery Industry. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, S.; Cecconet, D.; Capodaglio, A.G. 5-Agro-Industrial Wastewater Treatment in Microbial Fuel Cells. In Integrated Microbial Fuel Cells for Wastewater Treatment; Abbassi, R., Yadav, A.K., Khan, F., Garaniya, V., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Woburn, UK, 2020; pp. 93–133. ISBN 978-0-12-817493-7. [Google Scholar]
- Braz, R.; Pirra, A.; Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Combination of Long Term Aerated Storage and Chemical Coagula-tion/Flocculation to Winery Wastewater Treatment. Desalination 2010, 263, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosse, K.P.M.; Patti, A.F.; Christen, E.W.; Cavagnaro, T.R. Review: Winery Wastewater Quality and Treatment Options in Australia. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2011, 17, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomarici, E.; Vecchio, R. Will Sustainability Shape the Future Wine Market? Wine Econ. Policy 2019, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Arienzo, M.; Quayle, W.; Christen, E.; Grocke, S.; Fattore, A.; Doan, H.; Gonzago, D.; Zandonna, R.; Bartrop, K. Developing a Systematic Approach to Winery Wastewater Management. Rep. CSL05/02. Final Report to Grape and Wine Research & Development Corporation; CSIRO Land and Water Science Report Series; CSIRO: Canberra, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, H.L.; Grismer, M.E.; Tchobanoglous, G.; Shepherd, H.L.; Grismer, M.E.; Tchobanoglous, G. Wastewater Using a Subsurface-Flow Constructed Wetland Treatment of High-Strength Winery. Water Environ. Res. 2001, 73, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalia, B.S.; Kochkodan, V.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. A Review on Membrane Fabrication: Structure, Properties and Performance Relationship. Desalination 2013, 326, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, P.K.; Barton, G.W.; Mitchell, C.A. The Future for Electrocoagulation as a Localised Water Treatment Technology. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davididou, K.; Frontistis, Z. Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Treatment of Winery Wastewater: A Review and Future Perspectives. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 2436–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donde, O.O. Wastewater Management Techniques: A Review of Advancement on the Appropriate Wastewater Treatment Principles for Sustainability. Environ. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Ladas, D.; Mavromatis, A. Wine Waste Treatment Methodology. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 1117–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlotman, D.E.; Key, D.; Bladergroen, B.J. Technological Advances in Winery Wastewater Treatment: A Comprehensive Review. South Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2022, 43, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Maldonado, E.A.; Oropeza-Guzman, M.T.; Jurado-Baizaval, J.L.; Ochoa-Terán, A. Coagulation-Flocculation Mechanisms in Wastewater Treatment Plants through Zeta Potential Measurements. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 279, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirzhner, F.; Zimmels, Y.; Shraiber, Y. Combined Treatment of Highly Contaminated Winery Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, S.; Gürbulak, E.; Eyvaz, M.; Yüksel, E. Treatment of Winery Wastewater by Electrocoagulation Process. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 5421–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzoupanos, N.D.; Zouboulis, A.I. Coagulation-Flocculation Processes in Water / Wastewater Treatment: The Application of New Generation of Chemical Reagents. In Proceedings of the 6th IASME/WSEAS International Conference on Heat Transfer, Thermal Engineering and Environment, Rhodos, Greece, 20–22 August 2008; pp. 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, L.; Lofrano, G.; Belgiorno, V. Olive Mill and Winery Wastewaters Pre-Treatment by Coagulation with Chitosan. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 2447–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemerow, N.L. Chapter 6—Removal of Colloidal Solids. In Industrial Waste Treatment; Nemerow, N.L., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Burlington, UK, 2007; pp. 79–88. ISBN 978-0-12-372493-9. [Google Scholar]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and Disadvantages of Techniques Used for Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, J.M.; Sibrell, P.L.; Ogden, S.R.; Summerfelt, S.T. Evaluation of Chemical Coagulation–Flocculation Aids for the Removal of Suspended Solids and Phosphorus from Intensive Recirculating Aquaculture Effluent Discharge. Aquac. Eng. 2003, 29, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, O.; Chaudhari, P. Review on Chemical Treatment of Industrial Waste Water. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2013, 17, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, I.; Ebrahimi, A.; Hajian, M. Comparison Study of Turbidity Removal Using Synthetized Poly-Aluminum Chloride-Sulfate and Poly-Aluminum Chloride in Aqueous Solutions. Int. J. Environ. Health Eng. 2014, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Berre, F.; Chauveteau, G.; Pefferkorn, E. Shear Induced Aggregation/Fragmentation of Hydrated Colloids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 199, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanni, M.; Baldi, G. Coagulation Efficiency of Colloidal Particles in Shear Flow. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 97, 151–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushant, A. Efficiency of Shear-Induced Agglomeration of Particulate Suspensions Subjected to Bridging Flocculation. Ph.D. Thesis, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, E. Shear, Selective and Temperature Responsive Flocculation: A Comparison of Fine Particle Flotation Techniques. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2011, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukiwe, L.N.; Alinnor, J.I. Assessment of Polyacrylamide and Aluminum Sulphate Coagulants in Turbidity Removal in Wastewater. Terr. Aquat. Environ. Toxicol. 2012, 6, 132–135. [Google Scholar]
- Teh, C.Y.; Budiman, P.M.; Pui, K.; Shak, Y.; Wu, T.Y. Recent Advancement of Coagulation − Flocculation and Its Application in Wastewater Treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4363–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, K.L.; Burritt, R.L. Critical Environmental Concerns in Wine Production: An Integrative Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 53, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q. Coagulation Behavior of Polyaluminum Chloride: Effects of PH and Coagulant Dosage. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, G. Using polyaluminium coagulants in water treatment. In Proceedings of the 64th Annual Water Industry Engineers and Operators Conference, Bendigo, Australia, 5–6 September 2001; pp. 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Hantchse, S. Why Is a Liter Not Always a Liter? Brooks Instrument, 22 April 2021.
- Mulidzi, A.R. The Effect of Winery Wastewater Irrigation on the Properties of Selected Soils from the South African Wine Region. Ph.D. Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Malvern Instruments, Ltd. Zeta Potential: An Introduction in 30 Minutes; Malvern Instruments Ltd.: Worcestershire, UK, 2011; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan, C.M.; Glasser, D.; Hildebrandt, D.; Petersen, J.; Rohwer, J. An Annual and Seasonal Characterisation of Winery Effuent in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2011, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, C.L.; Myburgh, P.A.; Lategan, E.L.; Hoffman, J.E. Seasonal Variation in Composition of Winery Wastewater in the Breede River Valley with Respect to Classical Water Quality Parameters. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2016, 37, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, F.; Rochereau, J.; Troesch, S.; Ruiz, I.; Soto, M. Wineries Wastewater Treatment by Constructed Wetlands: A Review. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 71, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Water Affairs. Revision of General Authorisations in Terms of Section 39 of the National Water Act, 1998 (Act No. 36 of 1998), No. 665. Government Gazette, 6 September 2013; No. 36820.
- Fillaudeau, L.; Bories, A.; Decloux, M. Brewing, Winemaking and Distilling: An Overview of Wastewater Treatment and Utilisation Schemes; Woodhead Publishing: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008; ISBN 9781845694678. [Google Scholar]
- Luz, S.; Rivas, J.; Afonso, A.; Carvalho, F. Immediate One-Step Lime Precipitation Process for the Valorization of Winery Wastewater to Agricultural Purposes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18382–18391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, A.G.; Charisiou, N.D.; Goula, M.A. Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide from Various Industrial Gases: A Review of The Most Promising Adsorbing Materials. Catalysts 2020, 10, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gohary, F.; Tawfik, A.; Mahmoud, U. Comparative Study between Chemical Coagulation/Precipitation (C/P) versus Coagulation/Dissolved Air Flotation (C/DAF) for Pre-Treatment of Personal Care Products (PCPs) Wastewater. Desalination 2010, 252, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awodiji, C.; Nwachukwu, A.; Onyechere, C.; Iyidiobi, R.; Nwabueze, B. The Effectiveness of Hydrated Lime as a Flocculating Agent in Water Treatment. Saudi J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2657, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Spicer, P.T.; Pratsinis, S.E. Shear-Induced Flocculation: The Evolution of Floc Structure and the Shape of the Size Distribution at Steady State. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.J.; Yiacoumi, S.; Tsouris, C. Shear-Induced Flocculation of Colloidal Particles in Stirred Tanks. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 206, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.M.; Parnichkun, M. MLP, ANFIS, and GRNN Based Real-Time Coagulant Dosage Determination and Accuracy Comparison Using Full-Scale Data of a Water Treatment Plant. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2016, 66, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Robinson, J.; Chong, M.F. A Review on Application of Flocculants in Wastewater Treatment. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2014, 92, 489–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostolska, I.; Wiśniewska, M. Application of the Zeta Potential Measurements to Explanation of Colloidal Cr2O3 Stability Mechanism in the Presence of the Ionic Polyamino Acids. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 2453–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovides, I.C.; Pantziaros, A.; Zagklis, D.; Paraskeva, C. Effect of Electrolytes/Polyelectrolytes on the Removal of Solids and Organics from Olive Mill Wastewater (OMW). J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 91, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Symeonidou, M.P.; Matis, K.A. Technologies of Winery Wastewater Treatment: A Critical Approach. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 3372–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Alias, S.; Adlan, M.N.; Faridah; Asaari, A.H.; Zahari, M.S. Colour Removal from Landfill Leachate by Coagulation and Flocculation Processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.K.W. The Strength of Aggregates Formed in Flocculation; Imperial College of Science and Technology: London, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, K.; Cen, C.; Wu, X.; Mao, R.; Zheng, Y. Role of Bulk Nanobubbles in Removing Organic Pollutants in Wastewater Treatment. AMB Express 2021, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sampling Date | pH | Turbidity | EC | Ca | TSS | TDS | COD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (25 °C) | (NTU) | (mS/m) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | |
| 23–28 March 2021 | 4.0 | 630 | 175 | 130 | 2275 | 3546 | 22,620 |
| 9–14 April 2022 | 4.5 | 570 | 230 | 222 | 1840 | 1476 | 12,400 |
| Parameter | Maximum Irrigation Volume Allowed (m3/Day) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| <50 | <500 | <2000 | |
| pH | 6–9 | 6–9 | 5.5–9.5 |
| COD (mg/L) | 5000 | 400 | 75 |
| EC (mS/m) | 200 | 200 | 70–150 |
| TSS (mg/L) | 1000 | - | <25 |
| TDS (mg/L) * | 1300 | 1300 | 488–975 |
| Sample Type | TSS (mg/L) | Turbidity (NTU) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Air | With Air | Without Air | With Air | |
| Raw/Untreated | 2275 | 2260 | 660 | 635 |
| Alkalized | 1750 | 800 | 470 | 280 |
| SEFS treated | 680 | 70 | 220 | 30 |
| % Reduction (SEFS vs. Raw) | 70 | 97 | 67 | 95 |
| Sample Type | COD (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|
| Without Air | With Air | |
| Raw/Untreated | 11,310 | 11,250 |
| Alkalized | 9820 | 8750 |
| SEFS treated | 8920 | 5220 |
| % Reduction (SEFS vs. Raw) | 21 | 54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vlotman, D.; Key, D.; Cerff, B.; Bladergroen, B.J. Shear Enhanced Flotation Separation Technology in Winery Wastewater Treatment. Water 2023, 15, 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132409
Vlotman D, Key D, Cerff B, Bladergroen BJ. Shear Enhanced Flotation Separation Technology in Winery Wastewater Treatment. Water. 2023; 15(13):2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132409
Chicago/Turabian StyleVlotman, David, David Key, Bradley Cerff, and Bernard Jan Bladergroen. 2023. "Shear Enhanced Flotation Separation Technology in Winery Wastewater Treatment" Water 15, no. 13: 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132409
APA StyleVlotman, D., Key, D., Cerff, B., & Bladergroen, B. J. (2023). Shear Enhanced Flotation Separation Technology in Winery Wastewater Treatment. Water, 15(13), 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132409







