Control of Loose Deposits in a Simulated Drinking Water Distribution System Using Ultrafiltration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of the Tap Water
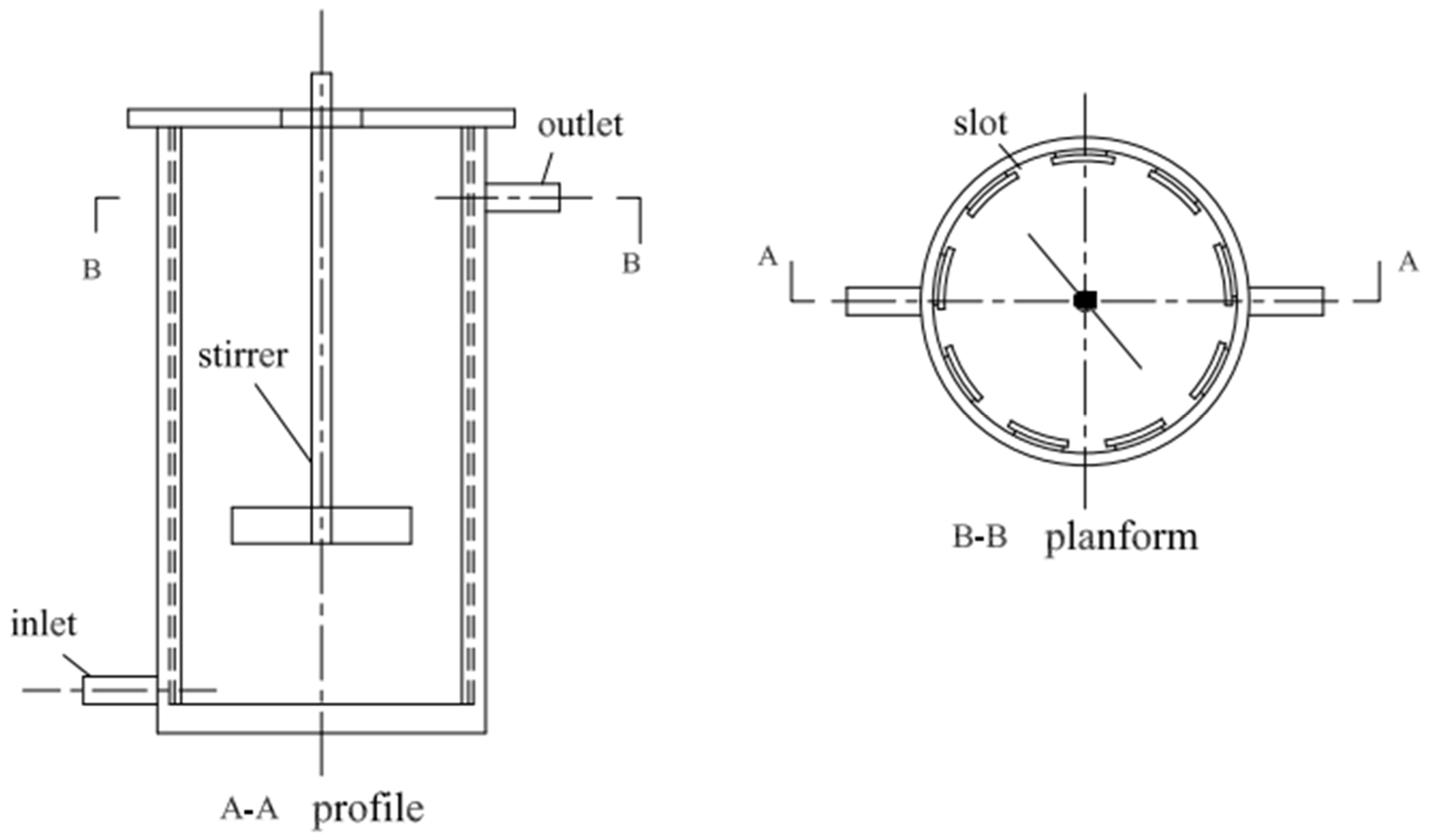
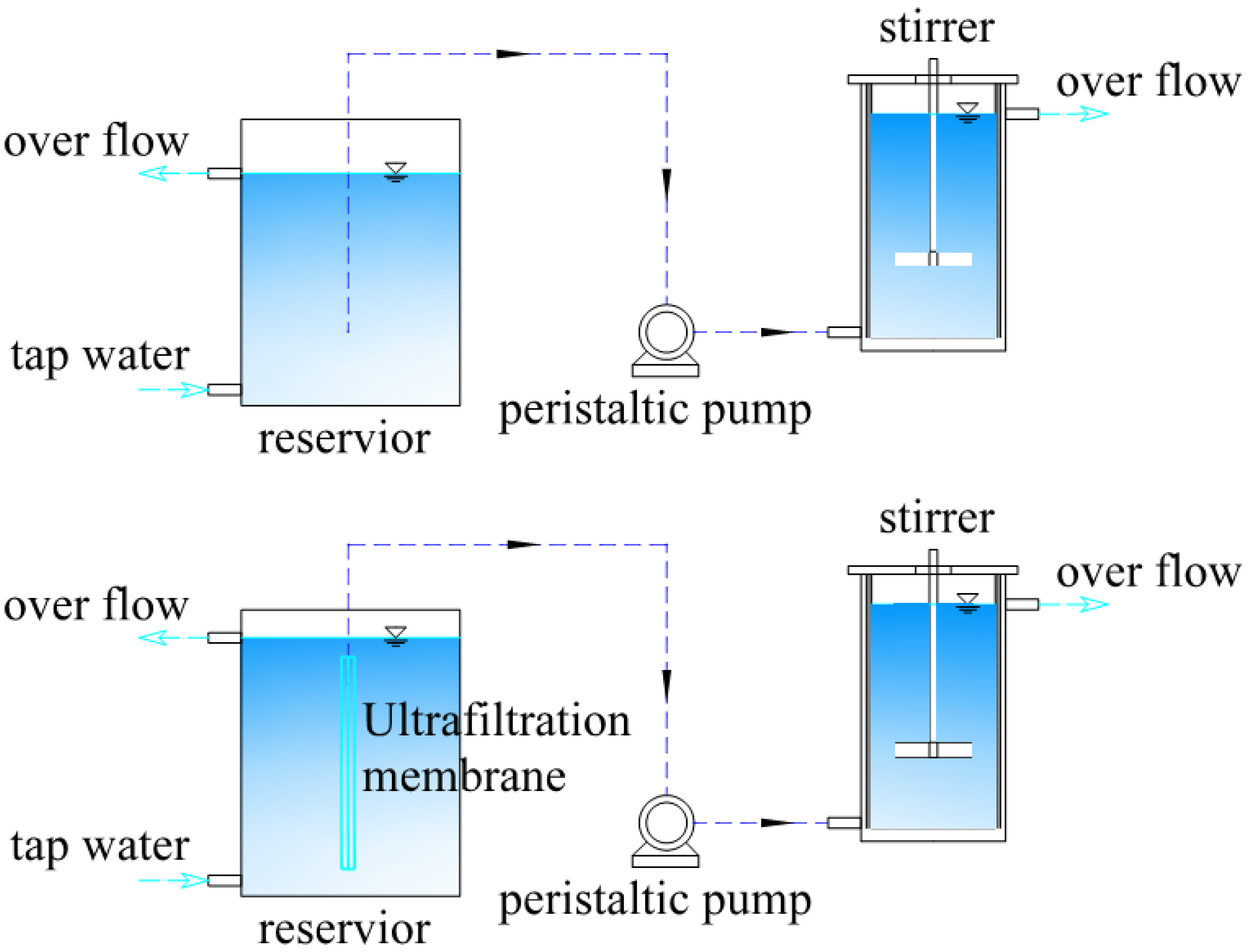
2.2. Reactor Design and Operation
2.3. Analysis Method
3. Results
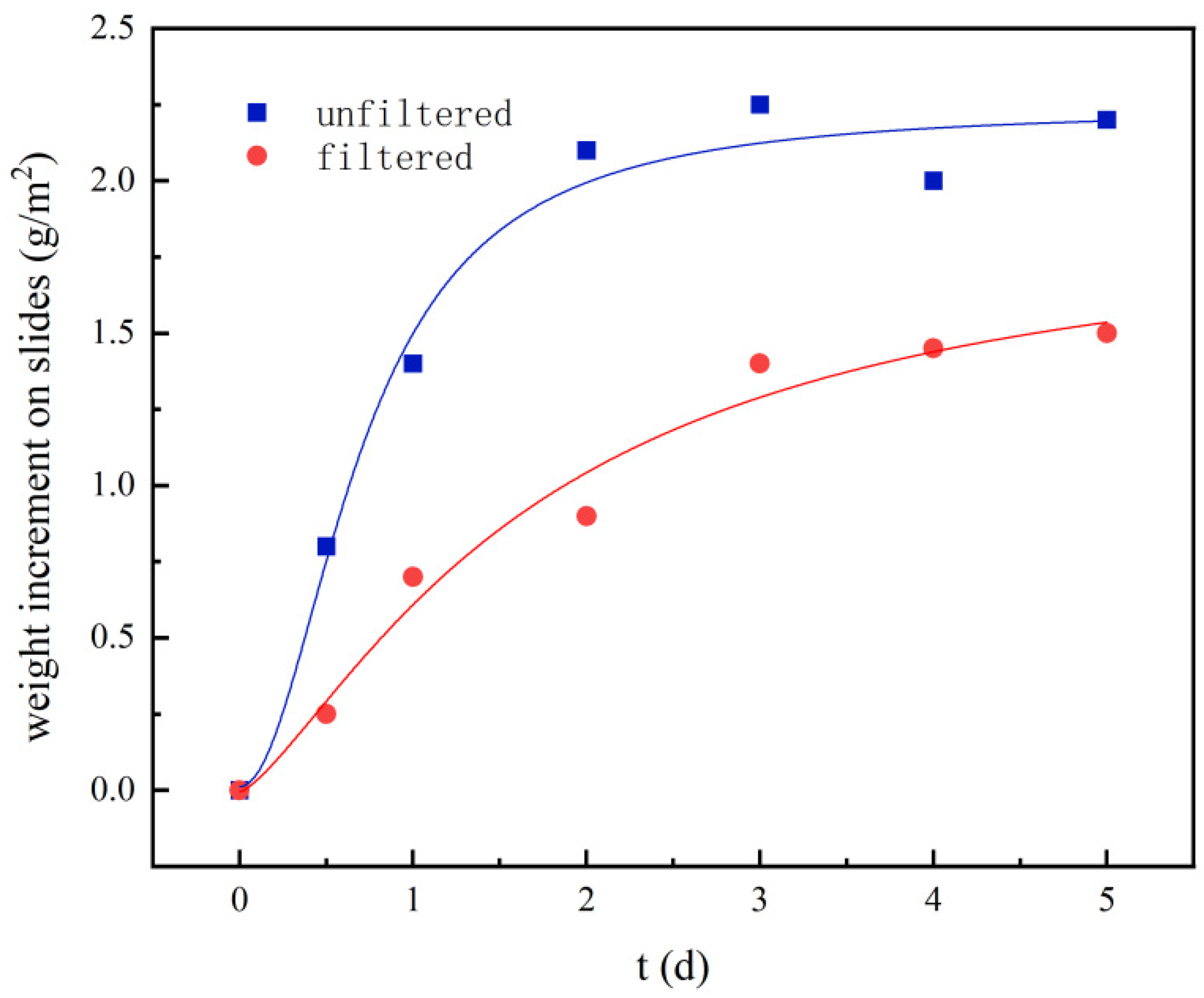
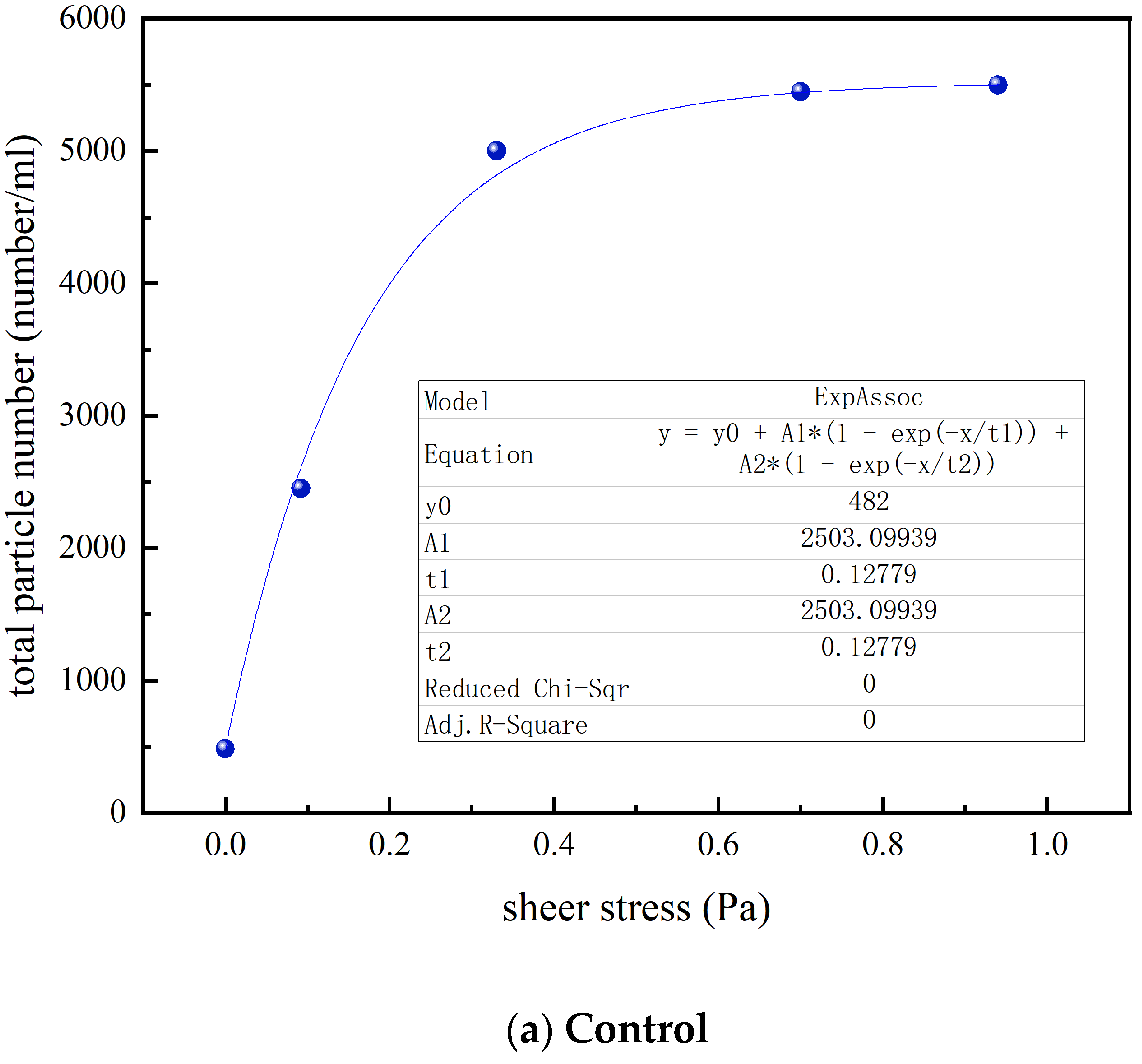
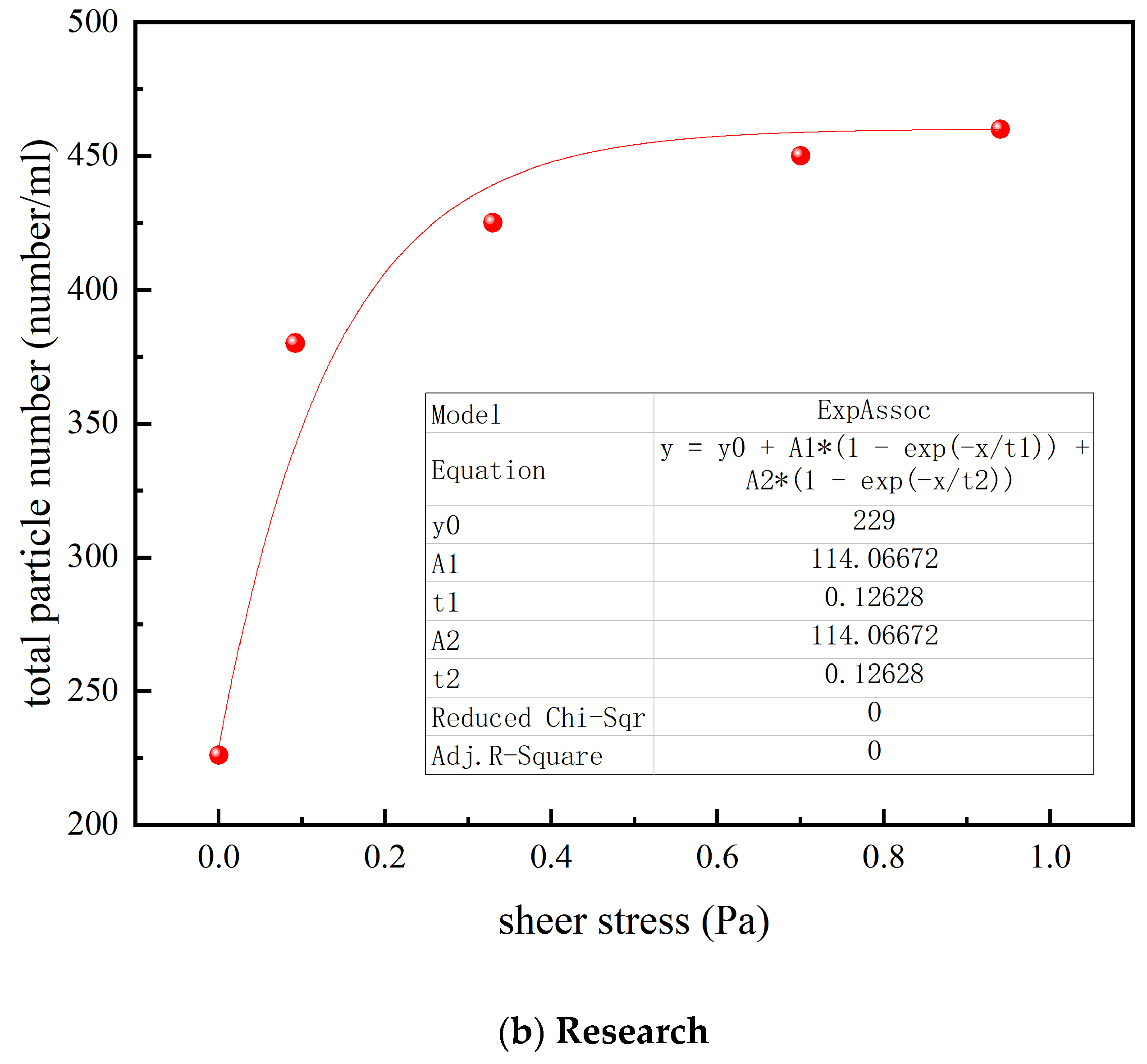
3.1. Effect of the Ultrafiltration on the Accumulation of Loose Deposits
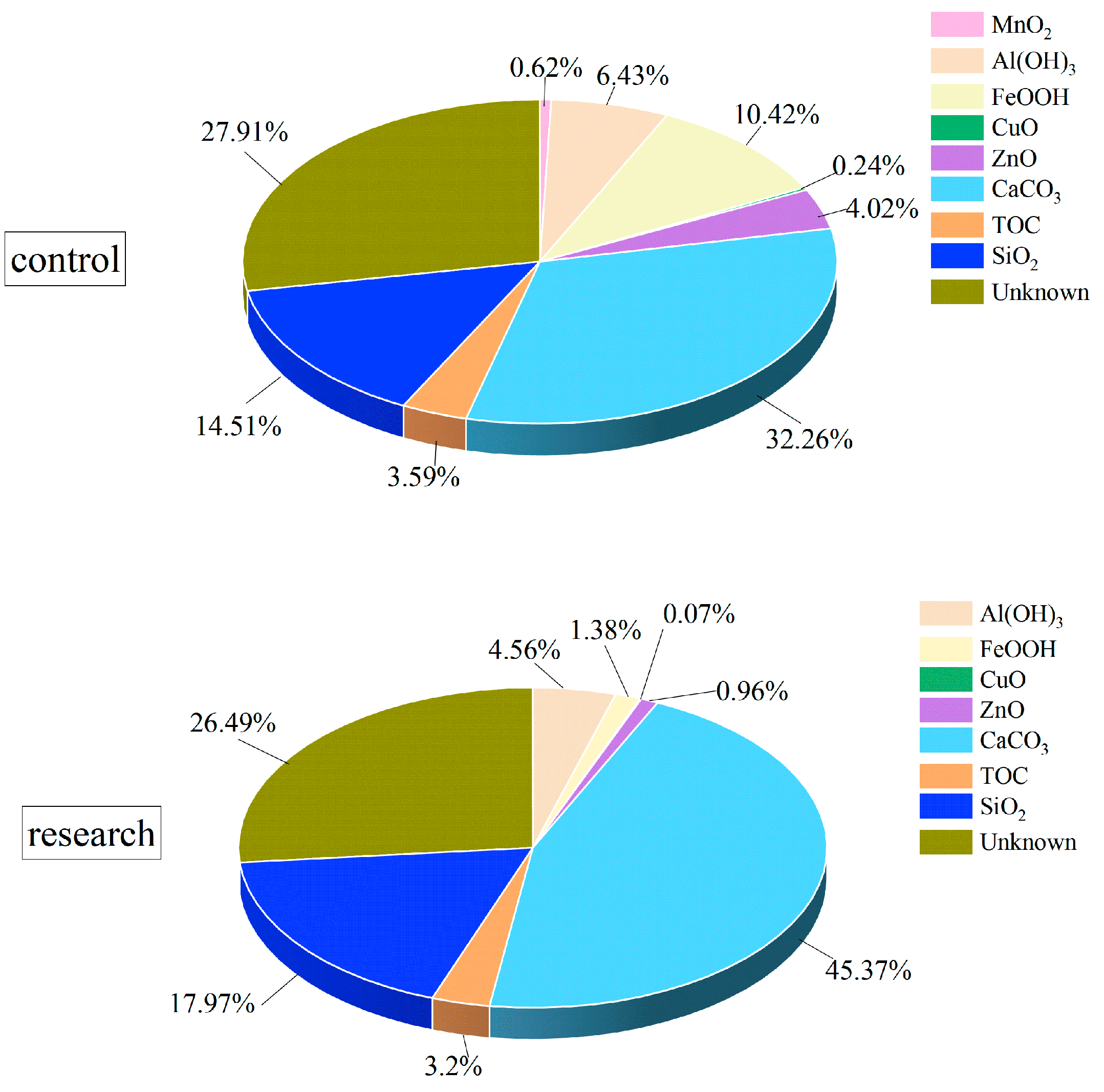
3.2. Composition of Loose Deposits for the Filtered and Unfiltered Conditions
3.3. Effect of the Loose Deposits on the Water Quality with and without Ultrafiltration
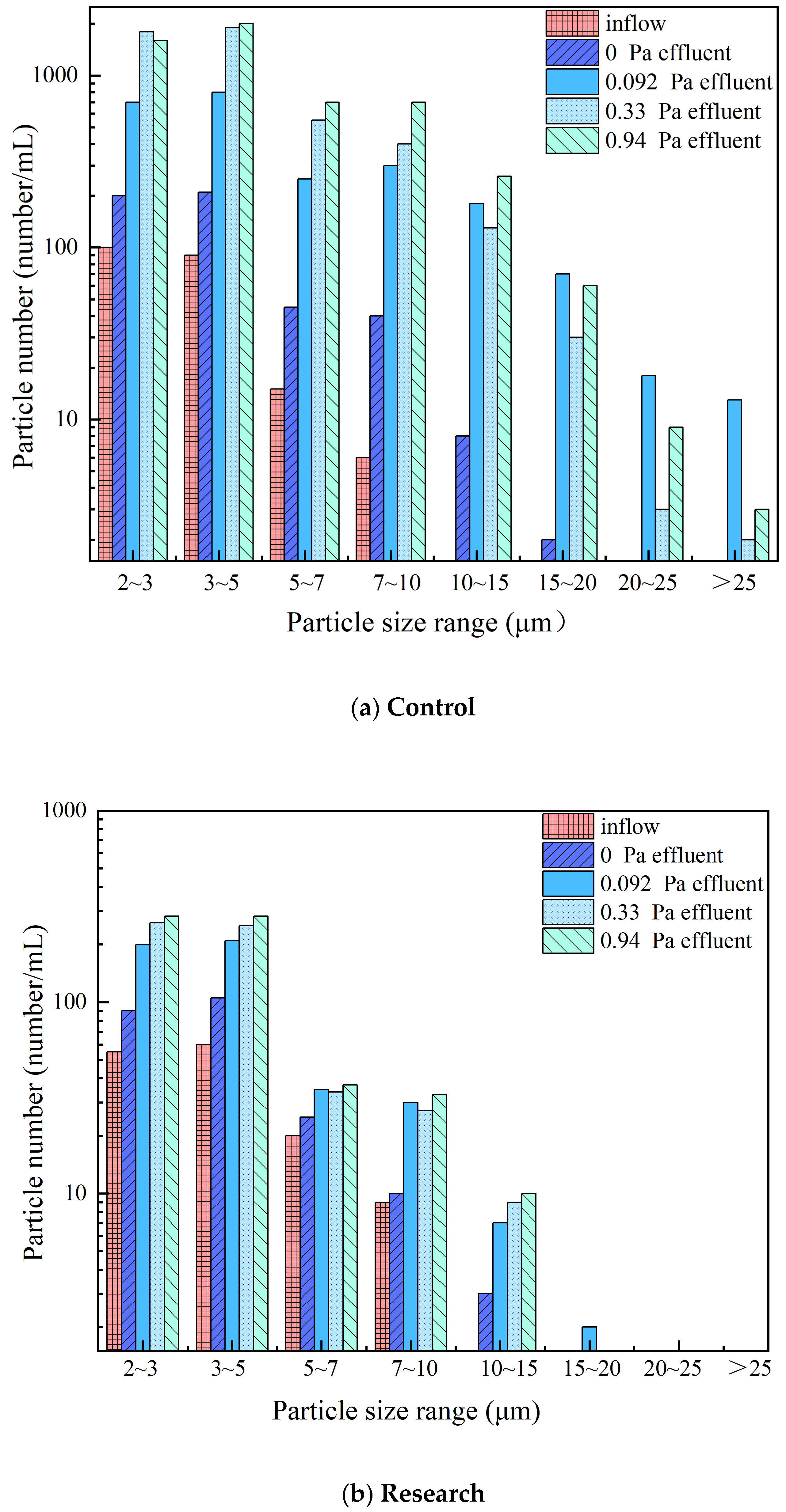
3.4. Effect of UF on the Particle Count and Size Distribution
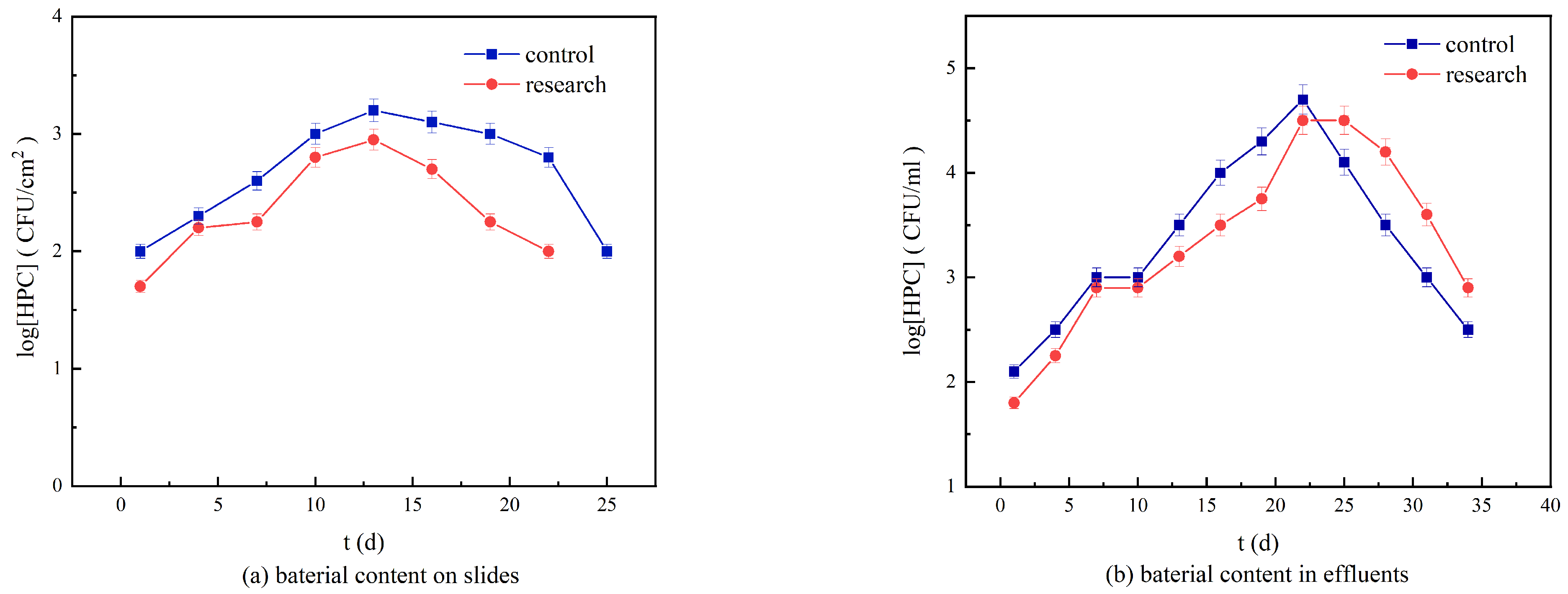
3.5. Bacterial Content in the Loose Deposits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deines, P.; Sekar, R.; Husband, P.S.; Boxall, J.B.; Osborn, A.M.; Biggs, C.A. A new coupon design for simultaneous analysis of in situ microbial biofilm formation and community structure in drinking water distribution systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.; Pai, T.; Qiu, J. The impacts of the AOC concentration on biofilm formation under higher shear force condition. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 111, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, Q.; Song, L.; Shi, B. Risk assessment of heavy metals in pipe scales and loose deposits formed in drinking water distribution systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 652, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ma, X.; Chen, R.; Yu, Y.; Tao, H.; Shi, B. Field studies of manganese deposition and release in drinking water distribution systems: Insight into deposit control. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lut, M.; Knibbe, W.-J.; van der Wielen, P.; Liu, W.; Medema, G.; van der Meer, W. Hotspots for selected metal elements and microbes accumulation and the corresponding water quality deterioration potential in an unchlorinated drinking water distribution system. Water Res. 2017, 124, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tian, Y.; Guo, H.; Liu, R.; He, N.; Li, Z.; Zhao, W. Study on the occurrence of typical heavy metals in drinking water and corrosion scales in a large community in northern China. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Han, B.; Chen, R.; Shi, B. Structural transformation and potential toxicity of iron-based deposits in drinking water distribution systems. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M.; Kirmeyer, G.J.; Antoun, E. Developing and Implementing a Distribution System Flushing Program. J. AWWA 2002, 94, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Bakker, G.L.; Li, S.; Vreeburg, J.H.G.; Verberk, J.Q.J.C.; Medema, G.J.; Liu, W.T.; Van Dijk, J.C. Pyrosequencing Reveals Bacterial Communities in Unchlorinated Drinking Water Distribution System: An Integral Study of Bulk Water, Suspended Solids, Loose Deposits, and Pipe Wall Biofilm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5467–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poças, A.; Rebola, N.; Cordeiro, B.; Rodrigues, S.; Benoliel, M.J.; Vreeburg, J.; Menaia, J. Methodology for Sampling Drinking Water Discolouration Loose Deposits at Low Velocities. Water Supply 2013, 13, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Shi, B.; Bai, Y.; Sun, H.; Lytle, D.A.; Wang, D. Effect of sulfate on the transformation of corrosion scale composition and bacterial community in cast iron water distribution pipes. Water Res. 2014, 59, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ding, Y.; Xu, H.; Jin, J.; Shi, B. Characterization and release profile of (Mn, Al)-bearing deposits in drinking water distribution systems. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrière, A.; Gauthier, V.; Desjardins, R.; Barbeau, B. Evaluation of loose deposits in distribution systems through: Unidirectional flushing. J. AWWA 2005, 97, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Summeren, J.; Blokker, M. Modeling particle transport and discoloration risk in drinking water distribution networks. Drink. Water Eng. Sci. 2017, 10, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, A.S.; Filion, Y. The interplay of suspended sediment concentration, particle size and fluid velocity on the rapid deposition of suspended iron oxide particles in PVC drinking water pipes. Water Res. X 2022, 15, 100143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, V.; Gérard, B.; Portal, J.-M.; Block, J.-C.; Gatel, D. Organic matter as loose deposits in a drinking water distribution system. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, X.; van der Meer, W.; Medema, G.; Liu, G. Capturing and tracing the spatiotemporal variations of planktonic and particle-associated bacteria in an unchlorinated drinking water distribution system. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torvinen, E.; Suomalainen, S.; Lehtola, M.J.; Miettinen, I.T.; Zacheus, O.; Paulin, L.; Katila, M.-L.; Martikainen, P.J. Mycobacteria in Water and Loose Deposits of Drinking Water Distribution Systems in Finland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacheus, O.M.; Lehtola, M.J.; Korhonen, L.K.; Martikainen, P.J. Soft deposits, the key site for microbial growth in drinking water distribution networks. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y. Research on the Formation and Shedding Rule of Loose Sediment in Water Supply Pipe Wall. China Water Wastewater 2015, 31, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtola, M.J.; Laxander, M.; Miettinen, I.T.; Hirvonen, A.; Vartiainen, T.; Martikainen, P.J. The effects of changing water flow velocity on the formation of biofilms and water quality in pilot distribution system consisting of copper or polyethylene pipes. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2151–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Hu, L.; Shi, J.; Liu, G.; Yin, Y.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, G. Dissolved metal ion removal by online hollow fiber ultrafiltration for enhanced size characterization of metal-containing nanoparticles with single-particle ICP-MS. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 126, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marais, S.; Ncube, E.; Msagati, T.; Mamba, B.; Nkambule, T.T. Comparison of natural organic matter removal by ultrafiltration, granular activated carbon filtration and full scale conventional water treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6282–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Zhou, R.; Xu, Y.; Yang, S. Biofilm Growth Characteristics in the Internal Surface of Water Supply Pipelines. Water Purif. Technol. 2010, 29, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Yu, J. Mixing Equipment; Chemical Industry Press Industrial Equipment and Information Engineering Publishing Center: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.D.; Ravindran, V.; Pirbazari, M. Modeling and process evaluation of membrane bioreactor for removing biodegradable organic matter from water. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 84, 494–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreeburg, J.; Schippers, D.; Verberk, J.; van Dijk, J. Impact of particles on sediment accumulation in a drinking water distribution system. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4233–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerke, T.L.; Little, B.J.; Maynard, J.B. Manganese deposition in drinking water distribution systems. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 541, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Water Quality Parameter | TOC/(mg·L–1) | NH4-N/(mg·L–1) | UV254 | pH | Turbidity/NTU | Chloramine/(mg·L–1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | 2.580 ± 0.30 | 0.092 ± 0.002 | 0.069 ± 0.002 | 7.10 ± 0.02 | 0.62 ± 0.12 | 0.13 ± 0.02 |
| Rotation Speed (r/min) | Shear Stress (Pa) | Corresponding Velocity in an Actual Pipeline (m/s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d = 100 mm | d = 200 mm | d = 300 mm | d = 400 mm | ||
| 100 | 0.0484 | 0.125 | 0.133 | 0.138 | 0.141 |
| 200 | 0.1256 | 0.209 | 0.222 | 0.231 | 0.237 |
| 300 | 0.2194 | 0.282 | 0.301 | 0.312 | 0.320 |
| 400 | 0.3261 | 0.350 | 0.372 | 0.386 | 0.396 |
| 500 | 0.4438 | 0.413 | 0.440 | 0.456 | 0.468 |
| 600 | 0.5714 | 0.474 | 0.504 | 0.523 | 0.536 |
| 700 | 0.7080 | 0.532 | 0.569 | 0.587 | 0.602 |
| 800 | 0.8528 | 0.588 | 0.626 | 0.649 | 0.666 |
| 900 | 1.0053 | 0.642 | 0.684 | 0.709 | 0.727 |
| Component | Al | Fe | Cu | Zn | Ca | Si | Mn | TOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| research/control | 47.5–48.2% | 8.9–9.2% | 18.8–19.0% | 16.0–18.3% | 94.2–95.6% | 83.0–85% | 0 | 59.7–60.1% |
| Sample | Element Concentration/(μg/L) | TOC/(mg/L) | Bacteria Content/(CFU/mL) | Turbidity/NTU | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Cu | Pb | Al | Fe | Zn | ||||
| Unfiltered | 1.9 | 2.5 | 1.2 | 35.8 | 23.1 | 111.2 | 1.71 | 74 | 0.62 |
| Filtered | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24.8 | 6.5 | 104.0 | 1.60 | <10 | 0.15 |
| Element | 0 Pa | 0.092 Pa | 0.33 Pa | 0.70 Pa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Research | Control | Research | Control | Research | Control | Research | Control | |
| Al | 24.8 | 35.1 | 26.1 | 46.9 | 26.3 | 53.8 | 35.1 | 55.8 |
| As | 0.42 | 0.53 | 0.46 | 0.64 | 0.48 | 0.65 | 0.50 | 0.66 |
| Ca | 9003 | 10,362 | 10,231 | 10,819 | 10,523 | 11,435 | 10,915 | 11,848 |
| Cr | 0.22 | 0.62 | 0.36 | 0.56 | 0.41 | 0.60 | 0.46 | 1.08 |
| Cu | 1.29 | 2.53 | 3.63 | 6.65 | 4.49 | 12.6 | 8.03 | 13.8 |
| Fe | 6.51 | 23.1 | 9.64 | 68.8 | 11.6 | 71.2 | 12.2 | 79.5 |
| Mn | 0.57 | 1.88 | 1.81 | 2.68 | 1.97 | 3.03 | 2.04 | 3.59 |
| Pb | 0.20 | 1.16 | 3.89 | 13.9 | 7.36 | 23.1 | 8.17 | 29.3 |
| Zn | 104 | 111 | 123 | 137 | 141 | 159 | 146 | 164 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Hou, H.; Qiu, M.; Zhou, L. Control of Loose Deposits in a Simulated Drinking Water Distribution System Using Ultrafiltration. Water 2023, 15, 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122210
Zhang Y, Hou H, Qiu M, Zhou L. Control of Loose Deposits in a Simulated Drinking Water Distribution System Using Ultrafiltration. Water. 2023; 15(12):2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122210
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yongji, Huimin Hou, Mengyu Qiu, and Lingling Zhou. 2023. "Control of Loose Deposits in a Simulated Drinking Water Distribution System Using Ultrafiltration" Water 15, no. 12: 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122210
APA StyleZhang, Y., Hou, H., Qiu, M., & Zhou, L. (2023). Control of Loose Deposits in a Simulated Drinking Water Distribution System Using Ultrafiltration. Water, 15(12), 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122210






