Agricultural Practices for Hillslope Erosion Mitigation: A Case Study in Morocco
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Study Area
2.1.1. Description of the Study Area’s Physical Environment
2.1.2. Land Uses
2.1.3. Choice of Experimental Perimeters
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Rainfall Simulation Tests
2.2.2. Soil Sampling
2.2.3. Physical Analyses of Samples
- Bulk density (Da, g/cm3):
- Total porosity (P, %) is deduced by the following formula [32]:
- Soil moisture (H, %)
- Rate of water-stable macroaggregates (MA, %)
- Detachability of soils (D, g/m2/h)
2.3. Statistical Data Processing
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Results
3.1.1. Effects of Land Uses on the Surface Conditions
3.1.2. Effects of Land Uses on Soil Physical Properties
3.1.3. Effects of Land Uses on Soils Hydrological Properties
3.1.4. Influences of Soil Parameters on Their Hydrological Properties in Larache, Taounate, and Taza Provinces of Morocco
3.2. Discussion
3.2.1. Effects of Land Uses on Surface Conditions
3.2.2. Effects of Land Uses on Soil Physical Properties
3.2.3. Effects of Land Uses on Soils Hydrological Properties
3.2.4. Influences of Soil Parameters on Hydrological Properties in Larache, Taounate, and Taza Provinces of Morocco
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; Nadal-Romero, E.; Lana-Renault, N.; Beguería, S. Erosion in Mediterranean landscapes: Changes and future challenges. Geomorphology 2013, 198, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raclot, D.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Annabi, M.; Sabir, M.; Smetanova, A. Main Issues for Preserving Mediterranean Soil Resources from Water Erosion Under Global Change. Land Degrad. Develop. 2018, 29, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Conservation des ressources naturelles en zones arides. Cah. FAO Conserv. Des. Sols. 1990, 50, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Antipolis, S. Les Menaces sur les Sols dans les Pays Méditerranéens. Etude Bibliographique; Cahiers du Plan Bleu; Plan Bleu: Marseille, France, 2003; Volume 2, p. 80. [Google Scholar]
- Chaibou, A. Etude des Impacts des Utilisations et des Autres Usages des Terrains Forestiers sur le Comportement Hydrologique et L’érosion des Sols dans la Zone D’amsitten en Vue de Son Aménagement; Mémoire de 3ème cycle; ENFI: Salé, Morocco, 2010; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Tian, F.X.; Warrington, D.N.; Zheng, S.Q.; Zhang, Q. Efficacy of grass for mitigating runoff and erosion from an artificial loessial earthen road. Trans. ASABE 2010, 53, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, C.X.; Liu, G.; Zhao, Y.G.; Shu, C.B.; Shen, E.S.; Liu, C.; Tan, Q.H.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y. The effects of typical grass cover combined with biocrusts on slope hydrology and soil erosion during rainstorms on the Loess Plateau of China: An experimental study. Hydrol. Process. 2022, 37, e14794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, M.; Tăut, I.; Rebrean, F.A.; Szilard, B.; Arion, I.D.; Dîrja, M. Determining the Anti-Erosion Efficiency of Forest Stands Installed on Degraded Land. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girona-García, A.; Vieira, D.C.; Silva, J.; Fernández, C.; Robichaud, P.R.; Keizer, J.J. Effectiveness of post-fire soil erosion mitigation treatments: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 217, 103611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhizkar, M.; Shabanpour, M.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Zema, D.A.; Li, S.; Tanaka, N.; Cerda, A. Effects of length and application rate of rice straw mulch on surface runoff and soil loss under laboratory simulated rainfall. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ali, Y. Structure et Evolution de la Terre et des Autres Planètes. Ph.D. Thesis, Univ de Montpellier II Sciences et Techniques du Languedoc, Ecole Doctorale SIBAGHE, Université Montpellier 2, Montpeiller, France, 2007; p. 178. [Google Scholar]
- Loukili, M.; Lahlou, O.; Abouyaala, M.A.; Allaoui, M.; Ozer, A.; Salmon, M. Intérêt de la carte d’aptitude des terres dans la lutte anti-érosive par la DRS fruitière, Cas de l’amandier dans le cercle d’Aknoul, Maroc, Rif oriental. Hommes Terre l’Eau 2006, 133, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Heusch, B. Erosion du Pré-rif,une étude comparative de l’érosion hydraulique dans les collines marneuses du pré-rif occidental, annales de la recherche forestière au Maroc. SRF Rabat 1970, 12, 9–176. [Google Scholar]
- Sabir, M.; Roose, E.; Merzouk, A.; Nouri, A. Techniques traditionnelles de gestion de l’eau et de lutte antiérosive dans deux terroirs du Rif occidental (Maroc). Bull. Réseau Eros. 1999, 19, 456–471. [Google Scholar]
- Nafi, M. Part de L’arboriculture Fruitière dans le Revenu des Exploitations Agricoles du Bassin Versant Moulay Bouchta; Mémoire de fin d’étude; ENFI: Salé, Morocco, 2005; p. 117. [Google Scholar]
- Petroselli, A.; Apollonio, C.; De Luca, D.L.; Salvaneschi, P.; Pecci, M.; Marras, T.; Schirone, B. Comparative Evaluation of the Rainfall Erosivity in the Rieti Province, Central Italy, Using Empirical Formulas and a Stochastic Rainfall Generator. Hydrology 2021, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todisco, F.; Vergni, L.; Ortenzi, S.; Di Matteo, L. Soil Loss Estimation Coupling a Modified USLE Model with a Runoff Correction Factor Based on Rainfall and Satellite Soil Moisture Data. Water 2022, 14, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, Y.C.; Lebar, K.; Bezak, N. A systematic review of the incorrect use of an empirical equation for the estimation of the rainfall erosivity around the globe. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2023, 238, 104339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauro, F.; Cornelini, P.; Grimaldi, S.; Petroselli, A. Field studies on the soil loss reduction effectiveness of three biodegradable geotextiles. J. Agric. Eng. 2018, 49, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollonio, C.; Petroselli, A.; Tauro, F.; Cecconi, M.; Biscarini, C.; Zarotti, C.; Grimaldi, S. Hillslope Erosion Mitigation: An Experimental Proof of a Nature-Based Solution. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doré, L.M. Effets de la Transformation des Ecosystèmes sur les Comportements Hydrodynamiques des Sols; ENFI: Salé, Morocco, 2006; p. 166. [Google Scholar]
- Al Karkouri, J.; Laouina, A.; Roose, E.; Sabir, M. Capacité d’infiltration et risques d’érosion des sols dans la vallée des Beni Boufrah-Rif central (Maroc). Eros. Mont. Semi-Arid. Méditerranéennes 2000, 20, 342–355. [Google Scholar]
- Sabir, M.; Barthès, B.; Roose, E. Recherche d’indicateurs des risques de ruissellement et d’érosion sur les principaux sols des montagnes méditerranéennes du Rif occidental (Maroc). Sci. Changements Planétaires/Sécheresse 2004, 15, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Simonneaux, V.; Cheggour, A.; Deschamps, C.; Mouillot, F.; Cerdan, O.; Le Bissonnais, Y. Land use and climate change effects on soil erosion in a semi-arid mountainous watershed (High Atlas, Morocco). J. Arid. Environ. 2015, 122, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Sun, R.; Chen, L. Effects of soil conservation techniques on water erosion control: A global analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Assaoui, N.; Bouiss, C.E.; Sadok, A. Assessment of Water Erosion by Integrating RUSLE Model, GIS and Remote Sensing–Case of Tamdrost Watershed (Morocco). Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2023, 24, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiki, A.; Faleh, A.; Navas, A.; Bouhlassa, S. Assessing soil erosion and control factors by the radiometric technique in the Boussouab catchment, Eastern Rif, Morocco. Catena 2007, 71, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, H.; Fox, H.; Harrouni, M.; Alami, A. Environmental challenges in the Rif mountains, northern Morocco. Environ. Conserv. 1998, 25, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henri, P. Etude de la conception des techniques paysannes de Gestion et Conservation de l’Eau et des Sols dans un territoire du pré-rif Marocain. In Rapport de Stage en 2ème Année à l’IUT Génie Biologique de Saint Etienne; France, 2012; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Roose, E. Méthodes de mesure des états de surface du sol, de la rugosité et des autres caractéristiques qui peuvent aider au diagnostic de terrain des risques de ruissellement et d’érosion, en particulier sur les versants cultivés des montagnes. Bull.-Réseau Eros. 1996, 16, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.J.; Black, I.A. Estimation of soil organic carbon by the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, G.R. Bulk Density. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1 Physical and Mineralogical Properties, Including Statistics of Measurement and Sampling; Black, C.A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 1965; pp. 374–390. [Google Scholar]
- Globe. Protocole de mesure d’humidité du sol par gravimétrie. 2005; 19. [Google Scholar]
- Pojasok, T.; Kay, B.D. Assessment of a combination of wet sieving and turbidimetry to characterize the structural stability of moist aggregates. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1990, 70, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roose, E.; Smolikowski, B. Comparaison de trois techniques de mesure de l’infiltration sur fortes pentes: Monocylindre et 2 simulateurs de pluies. Application à un versant de la vallée de Godim au Cap Vert. Bull. Réseau Eros. 1997, 17, 282–296. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffé, H. The Analysis of Variance; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, J.R.; Hill, H.O. A study of the shrinking and swelling properties of the rendzina soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 1944, 9, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.C. Controlled soil cracking as a possible means of moisture conservation on wheatlands of the southwestern Great Plains. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Keppel, R.V.; Hickey, J.J.; Wallace, D.E. Performance of local aquifers as influenced by stream transmission losses and riparian vegetation. Trans. ASAE 1964, 7, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Soil Taxonomy, Soil Conservation Service. Soil Survey Staff Soil Taxonomy: A basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys. In USDA Agric. Handbook No. 436; National Bureau of Soil Survey and Land Use Planning (ICAR), India Offset Press: New Delhi, India, 1978; p. 754. [Google Scholar]
- Pieri, C. Fertilité des terres de savane. In Bilan de Trente ans de Recherche et de Développement Agricole au Sud du Sahara; Ministère Français de la Coopération et du Développement: Paris, France, 1989; p. 444. [Google Scholar]
- Hien, V.; Sedogo, M.P. Étude des effets de la jachère de courte durée sur la production et l’évolution des sols dans différents systèmes de culture du Burkina Faso. In Proceedings of the La jachère en Afrique de l’Ouest. Atelier International, Montpellier, France, 2–5 December 1991; Editions ORSTOM. pp. 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Roose, E. Introduction à la Gestion Conservatoire de L’eau, de la Biomasse el de la Fertilité des Sols (GCES); Bulletin Pédologique F.A.O.: Montpellier, France, 1994; n. 70; p. 420. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, R.; Quantin, P. Observation sur l’évolution à long termede la fertilité des sols cultivés à Grimari (Rép. Centrafricaine). Série 1972, 27, 667–739. [Google Scholar]
- Valentin, C. État de dégradation de 2 terroirs Sénoufo-Nord Côte-d’Ivoire, Abidjan, Iirsda, 1989, 9p. multigr.
- Coulomb, I.; Caneill, J.; et Manichon, H. Comportement du sol au labour: Méthode d’analyse et évaluation des conséquences de l’état initial du sol sur l’état transformé par le labour Agronomie. EDP Sci. 1992, 13, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R.; Reicosky, D.C.; Hanson, J.D. Evolution of the plow over 10,000 years and the rationale for no (till farming. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 93, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traoré Kalifa, B.; Mc Carthy, G.; Gigou Jacques Doumbia Mamadou, D.; Bagayoko, A.; Yost Russell, S.; Konaré, H.; Dioni, L.; Coulibaly, H.; Sidibe, A.; Kablan Richard, A. Aménagement en courbes de niveau et conservation du carbone. In: Gestion de la biomasse, érosion et séquestration du carbone. Séquestration du carbone et érosion des sols. In Land Use, Erosion and Carbon Sequestration. 2. Soil Erosion and Carbon Sequestration; Roose, E., De Noni, G., Prat, C., Ganry, F., Bourgeon, G., Eds.; IRD, CIRAD-AMIS-AGRONOMIE: Paris, France, 2004; pp. 568–577. [Google Scholar]
- Tribak, A. Contraintes du milieu et fragilité d’un espace montagnard marocain: Les montagnes du Prérif oriental. Ann. Géographie 2002, 625, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiffin, J. La Dégradation Structurale des Couches Superficielles du Sol sous L’action des Pluies. Ph.D. Thesis, Sciences Agronomiques, INA Paris-Grignon, Paris, France, 1984; p. 423. [Google Scholar]
- Bresson, L.M.; Boiffin, J. Morphological characterization of soil crust development stages on an experimental field. Geoderma 1990, 47, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mazi, M.; El-fengour, M.; Houari, A. The influence of clearing followed by cultivation on the fertility and stability of a fersiallitic soil in the central Rif Morocco. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Stud. 2019, 2, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, G.; Boizard, H.; Roger-Estrade, J.; Boiffin, J.; Guerif, J. Field study of soil compaction due to traffic in northern France: Pore space and morphological analysis of the compacted zones. Soil Tillage Res. 1991, 51, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.A.; Anderson, W.K. Soil compaction in cropping systems-A review of the nature, causes and possible solutions. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 82, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebrugge, F.; During, R.A. Reducing tillage intensity-a review of results from a long-term study in Germany. Soil Tillage Res. 1999, 53, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, G.; Cousin, I.; Sillon, J.F.; Bruand, A.; Guerif, J. Effect of compaction on the porosity of a silty soil: Influence on unsaturated hydraulic properties. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2001, 52, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhees, W.B. The effect of soil compaction on crop yield. In Agricultural Research Service; SAES: Milan, Italy, 1986; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Reeder, R.C.; Hakansson, I. Subsoil compaction by vehicles with high axial load extent, persistence and crop response. Soil Tillage Res. 1994, 29, 277–304. [Google Scholar]
- Wahl, N.A.; Bens, O.; Buczko, U.; Hangen, E.; Huttl, R.F. Effects of conventional and conservation tillage on soil hydraulic properties of silty-loamy soil. Phys. Chem. Earth 2004, 29, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipiec, J.; Kus, J.; Slowinska-Jurkiewicz, A.; Nosalewicz, A. Soil porosity and water infiltration as influenced by tillage methods. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 89, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strudley, M.W.; Green, T.R.; Ascough, J.C. Tillage effects on soil hydraulic properties in space and time: State of the science. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 99, 4–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dounias, I. Etudes et Travaux n 19, les systèmes de culture à base de couverture végétale et semis direct en zones tropicales: Synthèse bibliographique. Cent. Natl. D’etudes Agron. Régions Chaudes 2001, 164. [Google Scholar]
- Scopel, E.; Findeling, A.; Chavez-Guerra, E.; Corbeels, M. Impact of direct sowing mulch-based cropping systems on soil carbon, soil erosion, and maize yield. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2005, 25, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesfin, S.; Oliveira Almeida, L.A.; Yazew, E.; Bresci, E.; Castelli, G. Spatial Variability of Soil Moisture in Newly Implemented Agricultural Bench Terraces in the Ethiopian Plateau. Water 2019, 11, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, R. Étude des Etats de Surface du Sol et de Leur Dynamique pour Différentes Pratiques de Travail du Sol. Mise au Point d’un Indicateur de Ruissellement. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Strasbourg, Strasbourg, France, 2009; p. 210. [Google Scholar]
- Cosandey, C.; Robinson, M. Hydrologie Continentale; Éditions Armand COLIN: Paris, France, 2000; p. 360. [Google Scholar]
- Darboux, F.; Gascuel-Odoux, C.; Davy, P. Effects of surface water storage by soil roughness on overland flow generation. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2002, 27, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaad, F.J.P.M.; Van der Zijp, M.; Van Dijk, P.M. Soil conservation and maize cropping Systems on slopping loess soils in the Netherlands. Soil Tillage Res. 1998, 46, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappus, P. Bassin expérimental dʹAlrance-étude des lois de lʹécoulement-application au calcul et à la prévision des débits. Houille Blanche 1960, 493–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MidWest Plan Service (MWPS). Conservation Tillage Systems and Management; Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering Department, Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 2000; p. 270. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahams, A.D.; Parsons, A.J.; Wainwright, J. Resistance to overland flow on semiarid grassland and shrubland hillslopes, Walnut Gulch, Southern Arizona. J. Hydrol. 1994, 156, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangen, E.; Buczko, U.; Bens, O.; Brunotte, J.; Huttl, R.F. Infiltration patterns into two soils under conventional and conservation tillage: Influence of the spatial distribution of plant roots structures and soil animal activity. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 63, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anken, T.; Weisskopf, P.; Zihlmann, U.; Forrer, H.; Jansa, J.; Perhacova, K. Long-term tillage system effects under moist cool conditions in Switzerland. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 78, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.; Taveres-Filho, J.; Tessier, D. Effect of compaction on soil physical and hydraulic properties: Experimental results and modeling. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
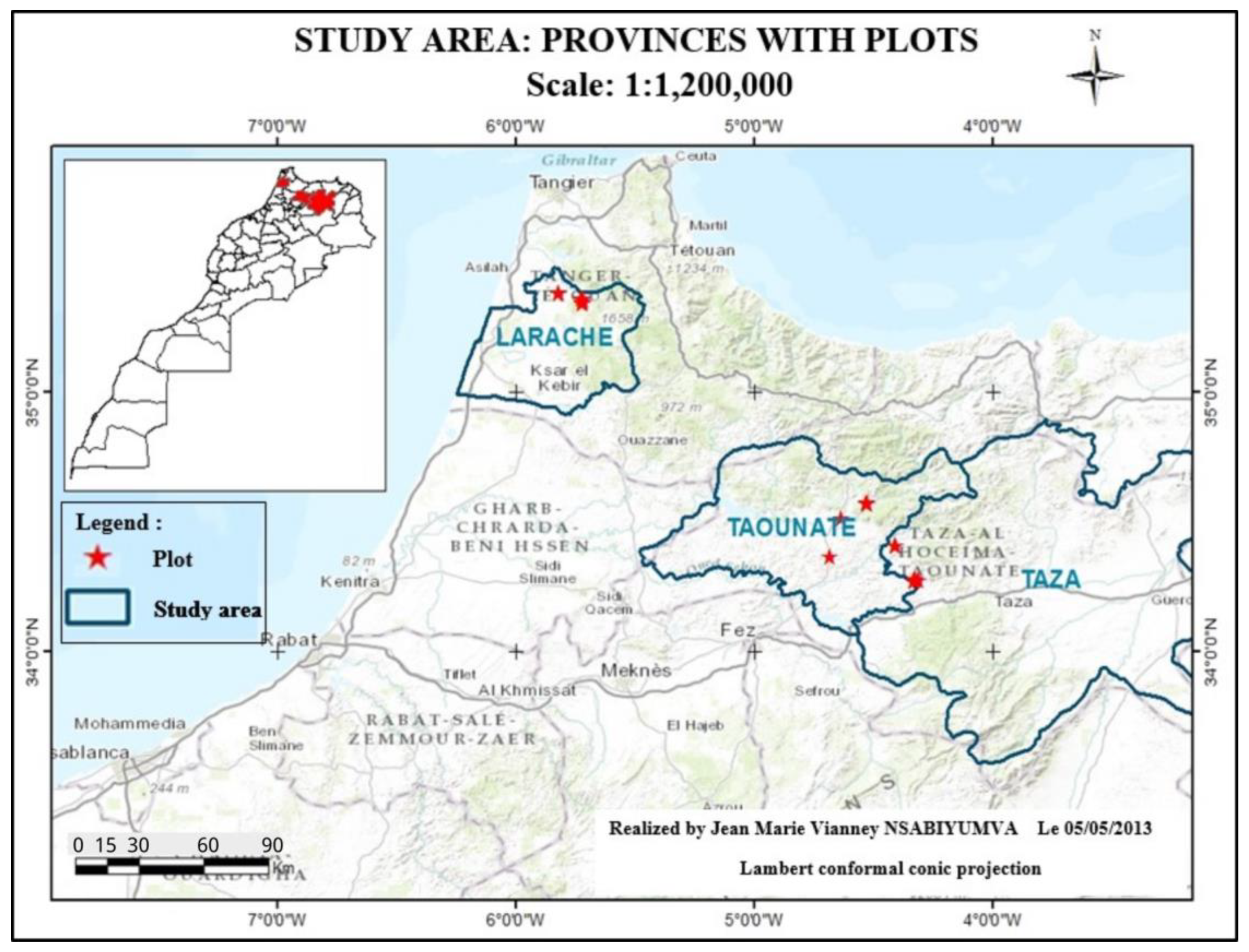


| Project Area | Zone 1 | Zone 2 | Zone 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provinces | Larache | Taounate | Taza |
| Study Perimeters | Ain Maabad Dar Lkhil | El Gara | Ahl Zaouia |
| Ain Hadid | Faytora | Lkassibat | |
| Sidi Ait Atmane | Ait Maalla |
| Sites | Geology | Soils |
|---|---|---|
| Larache | marly material of the Cretaceous; schistose scales and quartzite debris | little evolved soils of erosion; calcimagnesic soils with vertic caracter and vertic soils |
| Taounate | clayey marls | vertic soils eroded |
| Taza | Soft bedrock or hard geological bedrock and marly material | mineral soils, little evolved soils, calcimagnesic soils, isohumic soils, and soils with iron sesquioxides |
| Provinces | Larache | Taounate | Taza | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Uses | Matorral | Fallow | Plowing | Fallow | Plowing | Fallow | Plowing |
| Organic matter | |||||||
| OM (%) | 4.43 | 3.56 | 2.8 | 3.46 | 3.1 | 2.56 | 2.03 |
| Surface conditions | |||||||
| SN (%) | 1.08 a | 9.00 a | 83.69 b | 22.83 a | 75.67 b | 18.25 a | 90.83 b |
| SC (%) | 99.25 b | 91.00 b | 16.31 a | 77.17 a | 24.50 b | 81.75 b | 9.17 a |
| SO (%) | 99.90 b | 90.78 a,b | 78.67 a | 96.67 a | 90.17 b | 92.33 b | 82.50 a |
| SF (%) | 0.10 a | 9.22 a,b | 19.67 b | 3.34 a | 9.83 b | 7.58 a | 17.50 a |
| PEN (kg/cm2) | 0.71 a | 0.68 a | 0.59 a | 0.37 a | 0.25 a | 1.30 a | 1.50 a |
| SS (kg/cm2) | 2.49 b | 2.37 a,b | 1.69 a | 3.22 a | 2.06 b | 2.80 a | 2.63 a |
| Ir (%) | 3.16 a | 16.94 a,b | 22.17 b | 21.21 a | 44.33 b | 16.12 a | 31.26 a |
| Provinces | SF (%) | SG (%) | Arg (%) | LG (%) | LF (%) | Texture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Larache | 7.60 | 7.62 | 40.81 | 29.15 | 14.81 | Sandy clay |
| Taounate | 16.92 | 3.37 | 39.24 | 25.86 | 14.60 | Silty-clayey |
| Taza | 6.92 | 12.66 | 37.61 | 19.46 | 23.37 | Fine clay silt |
| Provinces | Larache | Taounate | Taza | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Uses | Matorral | VPO | Fallow | Plowing | Fallow | Plowing | Fallow | Plowing |
| Soil Physical Properties | ||||||||
| Da10 (g/cm3) | 0.79 a | 0.82 a | 0.90 a | 0.88 a | 1.01 a | 1.20 b | 0.90 a | 1.00 a |
| Da20 (g/cm3) | 0.87 a | 0.93 a | 0.99 a | 0.88 a | 1.11 a | 1.31 a | 1.00 a | 1.14 b |
| Da30 (g/cm3) | 1.09 a | 0.94 a | 1.00 a | 0.92 a | 1.31 a | 1.27 a | 1.03 a | 1.13 a |
| P10 (%) | 70.22 a | 69.14 a | 65.99 a | 66.65 a | 61.97 b | 54.64 a | 66.10 a | 62.25 a |
| P20 (%) | 67.00 a | 65.01 a | 62.70 a | 66.86 a | 58.75 a | 50.54 a | 62.26 b | 56.72 a |
| P30 (%) | 58.71 a | 64.42 a | 62.10 a | 65.19 a | 58.30 a | 52.04 a | 61.03 a | 57.18 a |
| H10 (%) | 34.59 b | 29.87 a,b | 29.79 a,b | 24.49 a | 42.10 b | 18.04 a | 19.28 a | 16.93 a |
| H20 (%) | 32.31 b | 31.70 a,b | 28.51 a | 28.23 a | 40.54 b | 17.57 a | 22.03 a | 20.02 a |
| H30 (%) | 29.04 a | 46.01 a | 25.29 a | 28.13 a | 44.67 b | 20.84 a | 22.03 a | 22.10 a |
| MA (%) | 34.02 a,b | 58.37 b | 19.82 a | 17.46 a | 54.51 b | 40.94 a | 59.00 a | 43.46 a |
| Provinces | Larache | Taounate | Taza | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Uses | Fallow | Plowing | Matorral | Fallow | Plowing | Fallow | Plowing |
| Soil Hydrological Properties | |||||||
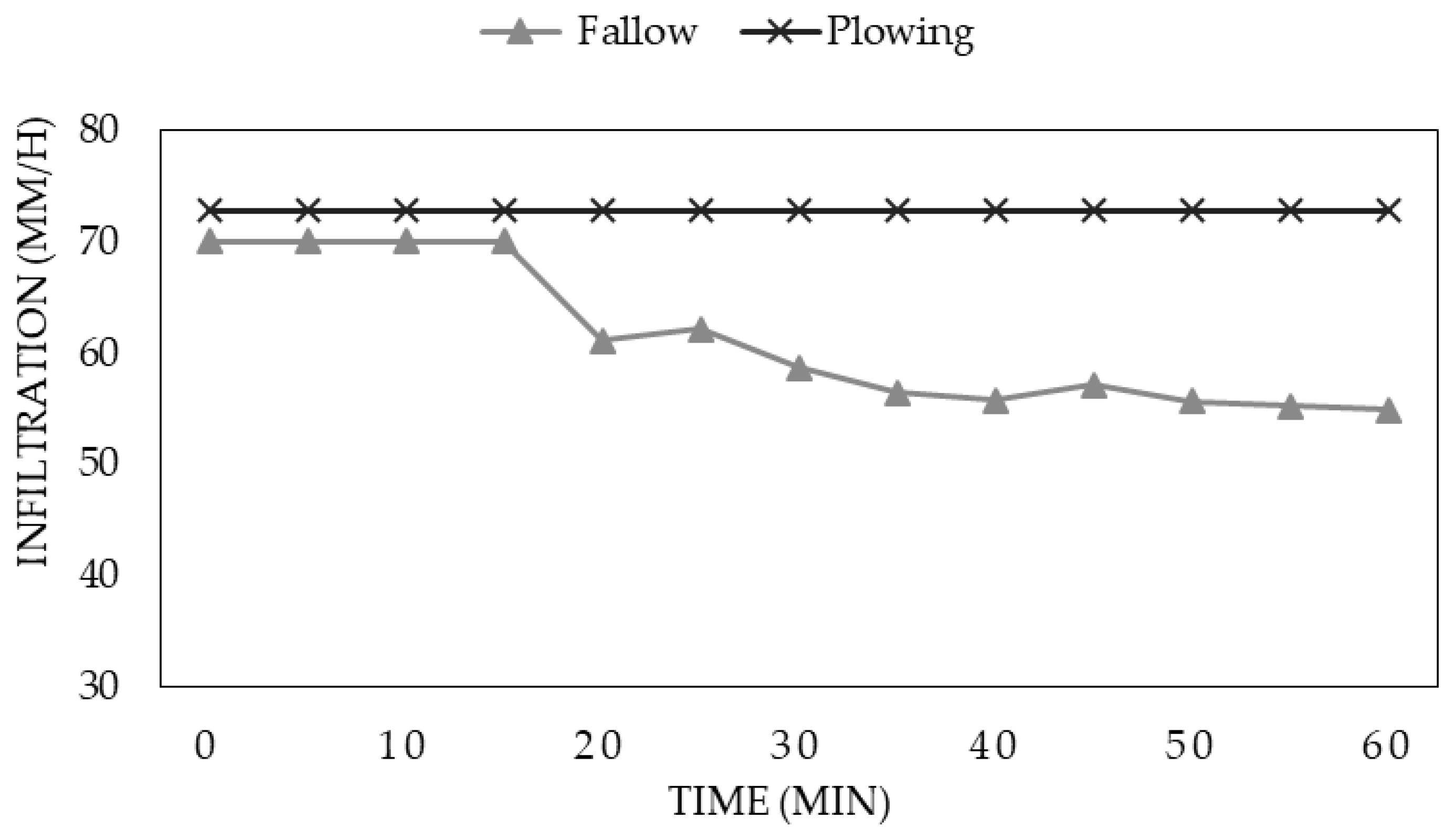
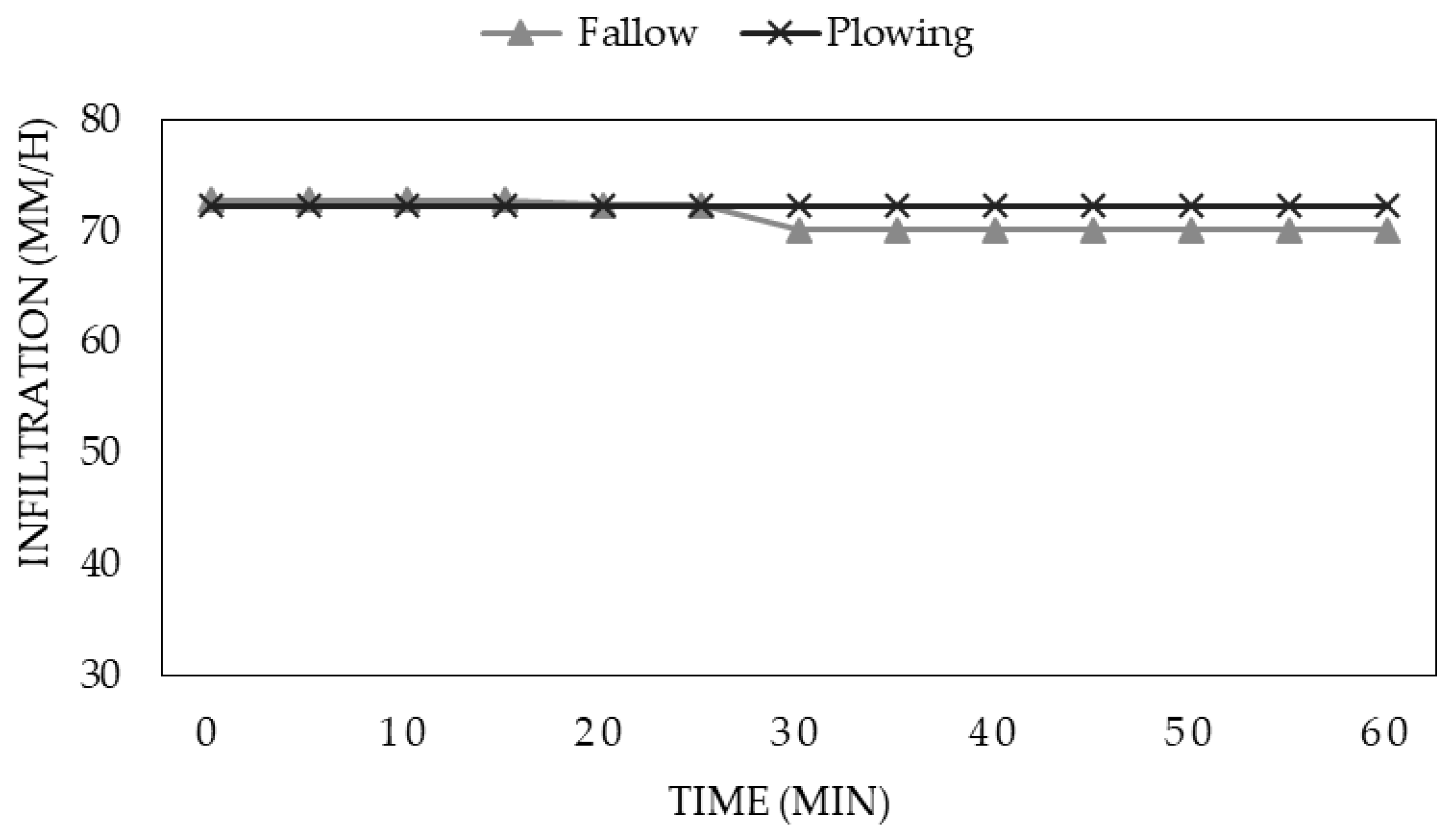
| If (mm/h) | 39.68 a | 64.70 ab | 74.4 b | 55.52 a | 73.43 a | 69.36 a | 71.53 a |
| Pi (mm/h) | 4.74 a | 24.03 a | 74.4 b | 36.57 a | 73.43 a | 46.12 a | 71.53 a |
| Kr (%) | 46.61 b | 14.63 a | 0.00 a | 13.18 a | 0.00 a | 2.23 b | 0.00 a |
| D (g/m2/h) | 2.28 a | 29.21 a | 0.00 a | 1.07 a | 0.00 a | 0.20 a | 0.00 a |
| Explanatory Variables | Regression Equations | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Final infiltration: If (mm/h) | ||
| SO | If = −50.352 + 1.289 × SO | 0.785 |
| PEN | If = 85.263 − 49.559 × PEN | 0.696 |
| SS | If = 127.589 − 33.978 × SS | 0.653 |
| P20 | If = −254.402 + 4.771 × P20 | 0.428 |
| imbibition rainwater: Pi (mm/h) | ||
| SO | Pi = −107.779 + 1.616 × SO | 0.619 |
| PEN | Pi = 62.387 − 62.319 × PEN | 0.550 |
| P10 | Pi = −499.655 + 7.865 × P10 | 0.446 |
| Runoff coefficient: Kr (%) | ||
| SO | Kr = 134.580 − 1.326 × SO | 0.696 |
| PEN | Kr = −7.292 + 55.027 × PEN | 0.564 |
| SS | Kr = − 47.579 + 34.514 × SS | 0.717 |
| Detachability: D (g/m2/h) | ||
| <60% | ||
| Explanatory Variables | Regression Equations | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Final infiltration: If (mm/h) | ||
| PEN | If = 89.09 − 80.699 × PEN | 0.464 |
| SS | If = 75.374 − 9.629 × SS | 0.858 |
| Ir | If = 0.572 + 2.729 × Ir | 0.930 |
| Imbibition rainwater: Pi (mm/h) | ||
| PEN | Pi = 112.150 − 187.376 × PEN | 0.873 |
| SS | Pi = 74.298 − 17.052 × SS | 0.938 |
| Ir | Pi = −42.142 + 4.148 × Ir | 0.749 |
| Runoff coefficient: Kr (%) | ||
| PEN | Kr = −12.165 + 61.487 × PEN | 0.400 |
| SS | Kr = −1.993 + 7.583 × SS | 0.790 |
| Ir | Kr = 56.813 − 2.145 × Ir | 0.853 |
| H10 | Kr = −8.877 + 0.402 × H10 | 0.517 |
| Detachability: D (g/m2/h) | ||
| PEN | D = −1.133 + 5.463 × PEN | 0.835 |
| SS | D = −0.056 + 0.521 × SS | 0.986 |
| Ir | D = 3.561 − 0.129 × Ir | 0.819 |
| H10 | D = −0.685 + 0.032 × H10 | 0.849 |
| Explanatory Variables | Regression Equations | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Final infiltration: If (mm/h) | ||
| SO | If = 30.777 + 0.429 × S0 | 0.603 |
| PEN | If = 77.428 − 4.427 × PEN | 0.534 |
| Ir | If = 53.539 + 0.853 × Ir | 0.824 |
| P10 | If = 40.453 + 0.451 × P10 | 0.819 |
| Imbibition rainwater: Pi (mm/h) | ||
| SO | Pi = -214.019 + 2.950 × SO | 0.874 |
| Ir | Pi = −38.642 + 4.916 × Ir | 0.839 |
| P10 | Pi = −102.471 + 2.426 × P10 | 0.726 |
| Runoff coefficient: Kr (%) | ||
| SO | Kr = 23.542 − 0.242 × SO | 0.879 |
| Ir | Kr = 8.865 − 0.391 × Ir | 0.788 |
| Detachability: D (g/m2/h) | ||
| SO | D = 2.107 − 0.022 × SO | 0.879 |
| Ir | D = 0.793 − 0.035 × Ir | 0.788 |
| P10 | D = 1.230 − 0.017 × P10 | 0.662 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vianney Nsabiyumva, J.M.; Apollonio, C.; Castelli, G.; Petroselli, A.; Sabir, M.; Preti, F. Agricultural Practices for Hillslope Erosion Mitigation: A Case Study in Morocco. Water 2023, 15, 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112120
Vianney Nsabiyumva JM, Apollonio C, Castelli G, Petroselli A, Sabir M, Preti F. Agricultural Practices for Hillslope Erosion Mitigation: A Case Study in Morocco. Water. 2023; 15(11):2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112120
Chicago/Turabian StyleVianney Nsabiyumva, Jean Marie, Ciro Apollonio, Giulio Castelli, Andrea Petroselli, Mohamed Sabir, and Federico Preti. 2023. "Agricultural Practices for Hillslope Erosion Mitigation: A Case Study in Morocco" Water 15, no. 11: 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112120
APA StyleVianney Nsabiyumva, J. M., Apollonio, C., Castelli, G., Petroselli, A., Sabir, M., & Preti, F. (2023). Agricultural Practices for Hillslope Erosion Mitigation: A Case Study in Morocco. Water, 15(11), 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112120










