Effect of Biochar on Soil-Water Characteristics of Soils: A Pore-Scale Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measurements
2.2. Materials
2.3. Methods
2.4. Preparation and Procedures
3. Results and Discussions
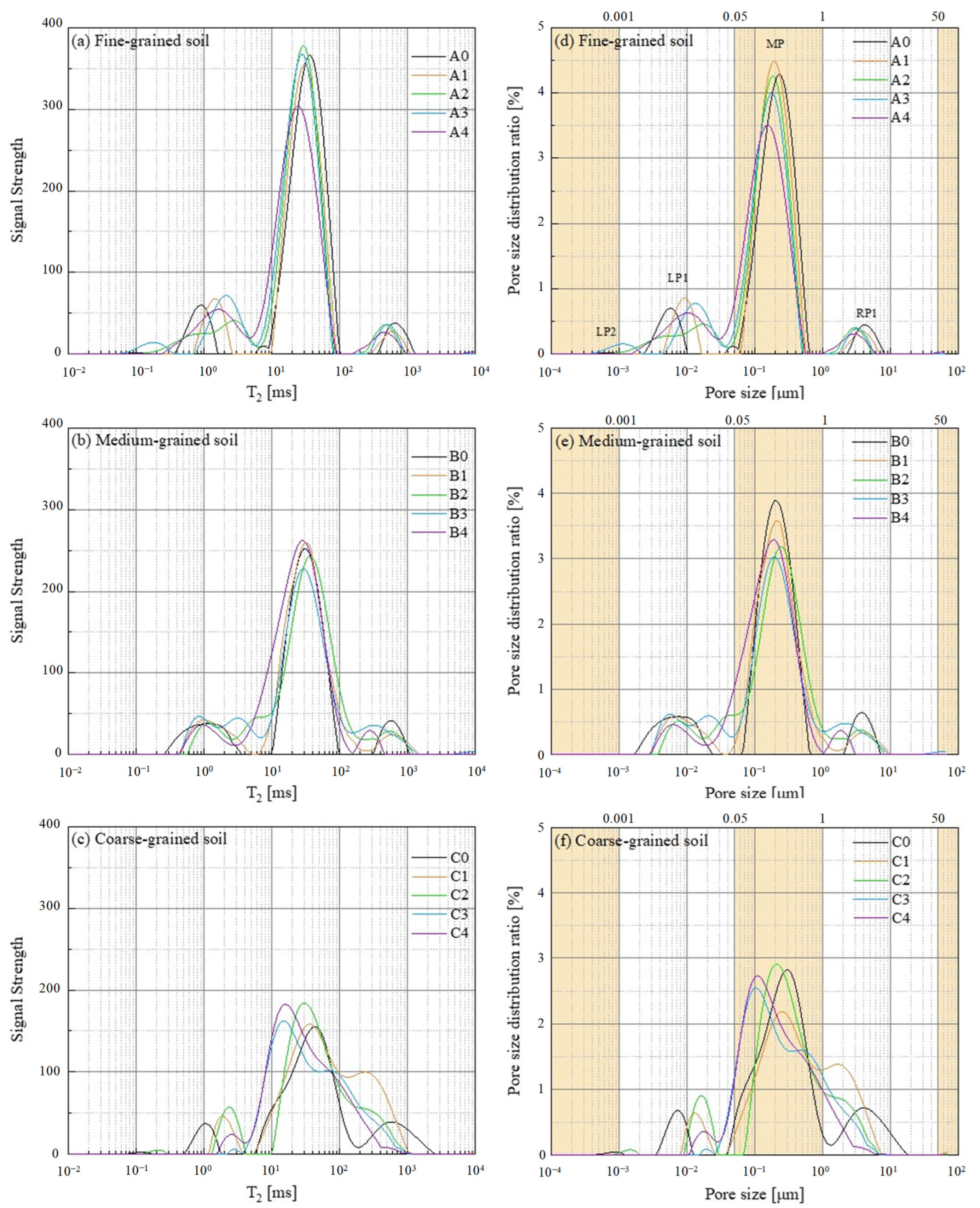
3.1. NMR Results and Analysis
3.1.1. Test Results of NMR
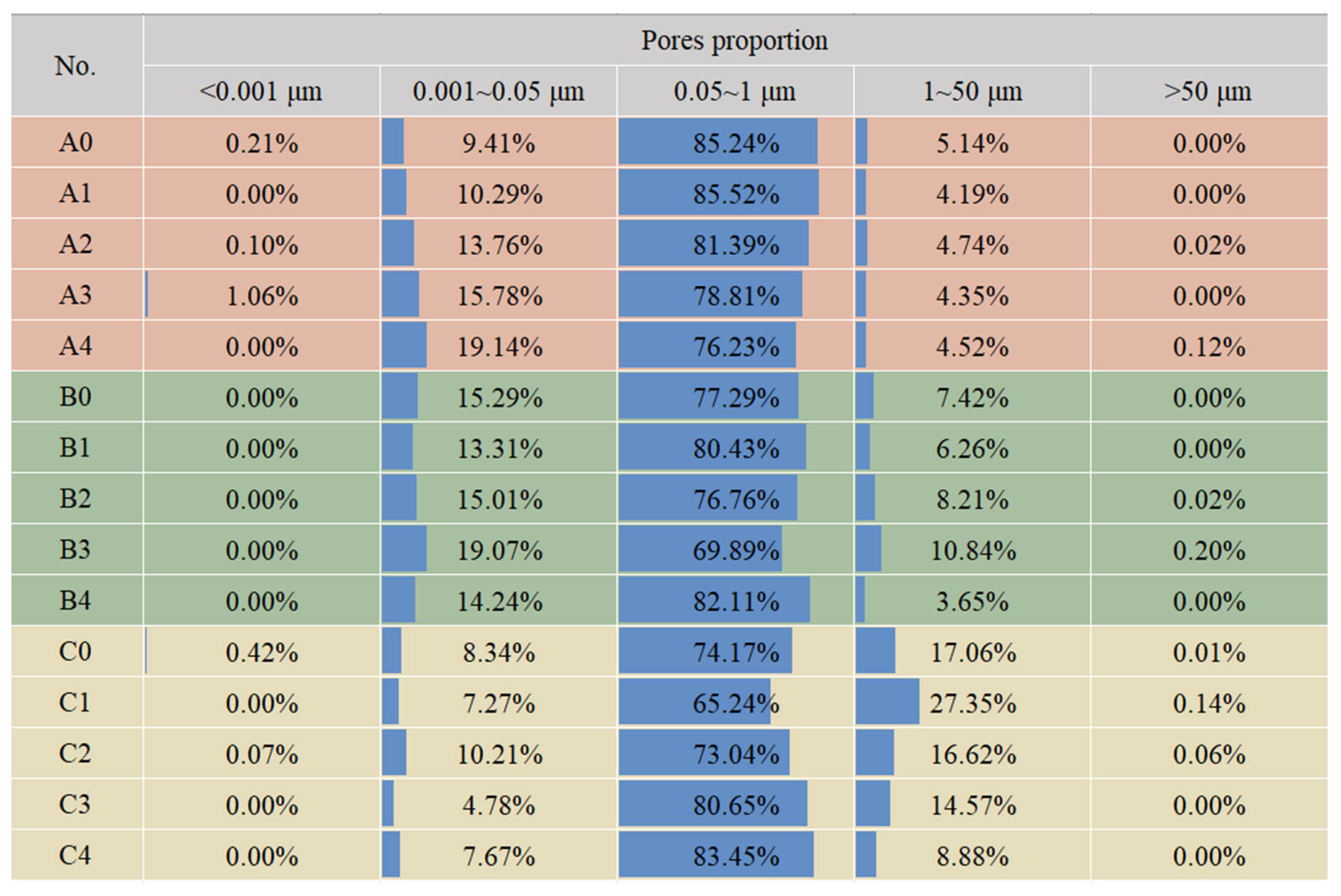
3.1.2. Pore Size Distribution
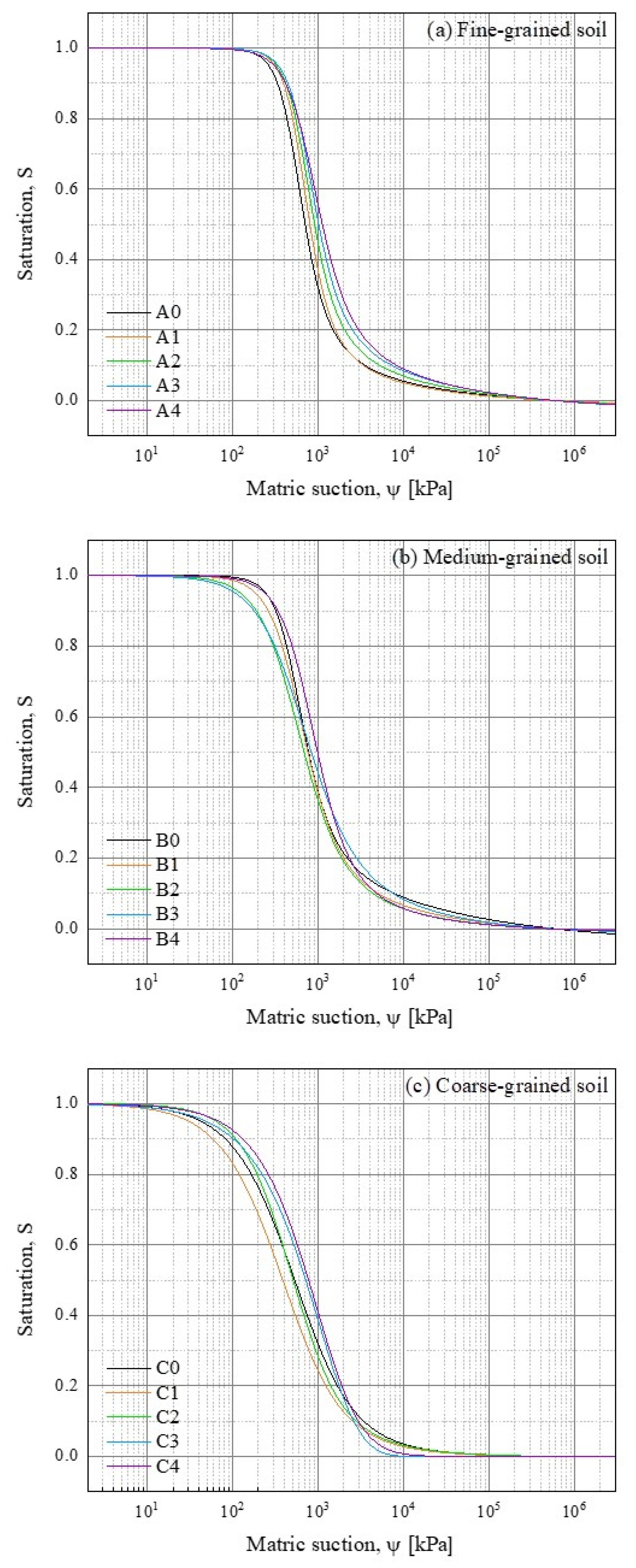
3.2. Soil Water Retention Curve
3.2.1. SWRC from PSD
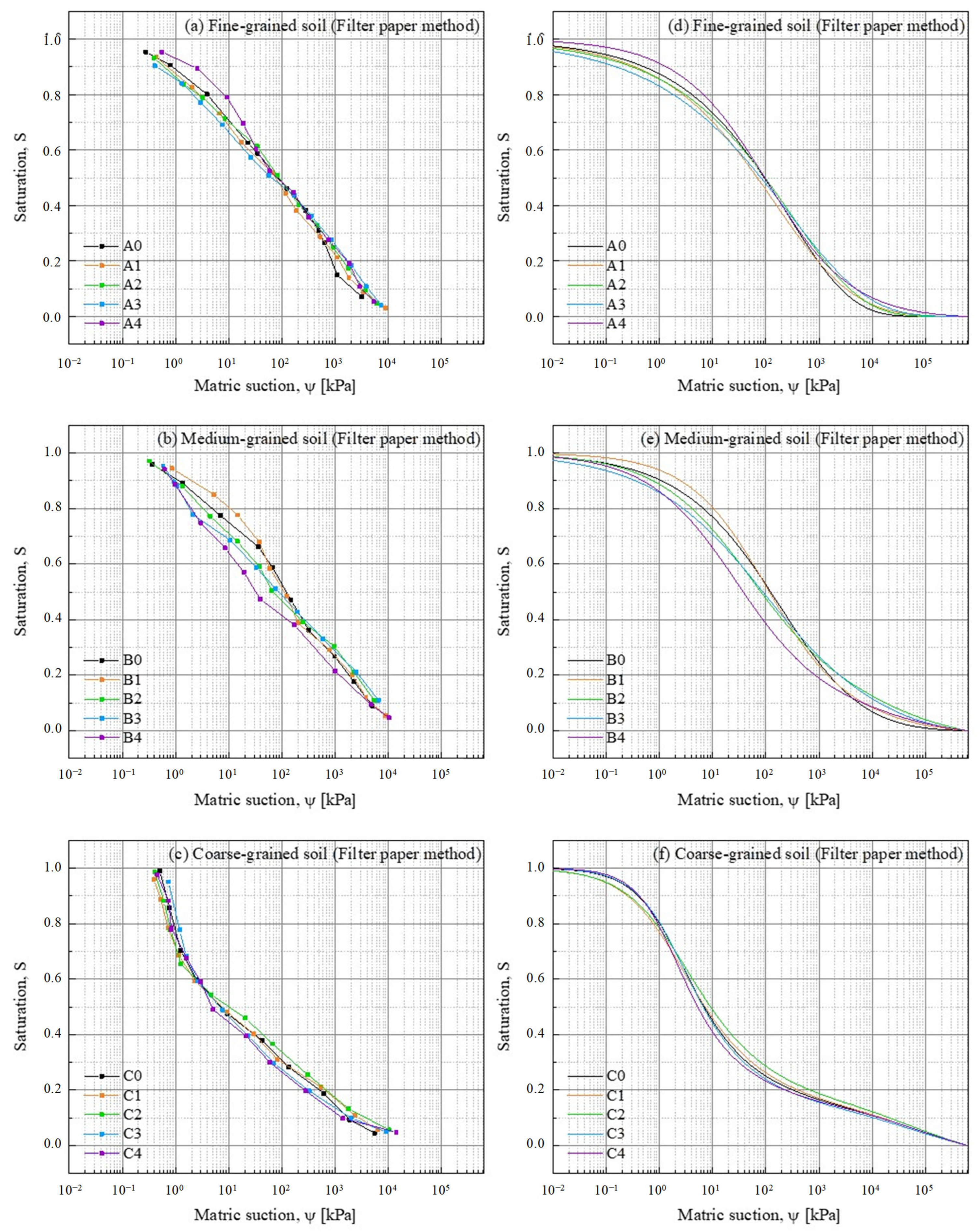
3.2.2. SWRC from Filter Paper Method
3.3. Analysis of Possible Errors in the Test
3.4. Biochar Size, Soil Particle Size, and Soil Texture Classification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for Environmental Management: Science and Technology; Earthscan: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Busscher, W.J.; Novak, J.M.; Evans, D.E.; Watts, D.W.; Niandou, M.A.S.; Ahmedna, M. Influence of pecan biochar on physical properties of a norfolk loamy sand. Soil Sci. 2010, 175, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, A.E.; Holthusen, D.; Horn, R. Changes in microstructural behaviour and hydraulic functions of biochar amended soils. Soil Till. Res. 2016, 155, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellini, M.; Giglio, L.; Niedda, M.; Palumbo, A.D.; Ventrella, D. Impact of biochar addition on the physical and hydraulic properties of a clay soil. Soil Till. Res. 2015, 154, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohi, S.; Lopez-Capel, E.; Krull, E.; Bol, R. Biochar, Climate Change and Soil: A Review to Guide Future Research; CSIRO Land and Water Science Report 05/09; CSIRO: Marsfield, Australia, 2009; 64p. [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen, F.; Jeffery, S.; Bastos, A.C.; Van Der Velde, M.; Diafas, I. Biochar Application to Soils—A Critical Scientific Review of Effects on Soil Properties, Processes and Functions; European Commission: Luxembourg, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Assadi-Langroudi, A.; O’Kelly, B.C.; Barreto, D.; Cotecchia, F.; Dicks, H.; Ekinci, A.; Garcia, E.F.; Harbottle, M.; Tagarelli, V.; Jeferson, I.; et al. Recent Advances in Nature-Inspired Solutions for Ground Engineering (NiSE). Int. J. Geosynth. Groun. 2022, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.; Dejong, J.; Akin, I.; Aleali, A.; Arson, C.; Atkinson, J.; Bandini, P.; Baser, T.; Borela, R.; Boulanger, R.; et al. Bio-inspired geotechnical engineering: Principles, current work, opportunities and challenges. Géotechnique 2022, 72, 687–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronti, S.; Alberti, G.; Delle Vedove, G.; Di Gennaro, F.; Fellet, G.; Genesio, L.; Miglietta, F.; Peressotti, A.; Vaccari, F.P. The Biochar option to improve plant yields: First results from some field and pot experiments in Italy. Ital. J. Agron. 2010, 5, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondon, M.A.; Lehmann, J.; Ramírez, J.; Hurtado, M. Biological nitrogen fixation by common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) increases with bio-char additions. Biol. Fert. Soils. 2007, 43, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzoma, K.C.; Inoue, M.; Andry, H.; Fujimaki, H.; Zahoor, A.; Nishihara, E. Effect of cow manure biochar on maize productivity under sandy soil condition. Soil Use Manag. 2011, 27, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.K.; Strezov, V.; Chan, K.Y.; Nelson, P.F. Agronomic properties of wastewater sludge biochar and bioavailability of metals in production of cherry tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhu, K.; Mattila, T.; Bergstrm, I.; Regina, K. Biochar Addition to Agricultural Soil Increased CH4 Uptake and Water Holding Capacity—Results from a Short-Term Pilot Field Study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaiman, Z.M.; Murphy, D.V.; Abbott, L.K. Biochars influence seed germination and early growth of seedlings. Plant Soil 2012, 353, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.H.; Xu, R.K. The amelioration effects of low temperature biochar generated from nine crop residues on an acidic Ultisol. Soil Use Manag. 2011, 27, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.H.; Xu, R.K.; Wang, N.; Li, J.Y. Amendment of Acid Soils with Crop Residues and Biochars. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Ye, L.L.; Wang, C.H.; Zhou, H.; Sun, B. Temperature- and duration-dependent rice straw-derived biochar: Characteristics and its effects on soil properties of an Ultisol in southern China. Soil Till. Res. 2011, 112, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, E.R.; Tsechansky, L.; Lew, B.; Cohen, E. Reducing capacity of water extracts of biochars and their solubilization of soil Mn and Fe. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.B.; Deng, C.J.; Chen, J.L.; Zhang, Q.S. The remediation effect of cotton stalk carbon on cadmium polluted soil. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 17, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar]
- Chui, L.Q. Experimental Study on Inhibition of Cd/Pb Uptake by Biochar in Contaminated Soils by Rice and Wheat. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China.
- Yu, X.Y.; Ying, G.G.; Kookana, R.S. Reduced plant uptake of pesticides with biochar additions to soil. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głąb, T.; Palmowska, J.; Zaleski, T.; Gondek, K. Effect of biochar application on soil hydrological properties and physical quality of sandy soil. Geoderma 2016, 281, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.; Ravi, K.; Garg, A. Influence of biochar on the soil water retention characteristics (SWRC): Potential application in geotechnical engineering structures. Soil Till. Res. 2020, 204, 104713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, N.; Hajabbasi, M.A.; Shirani, H.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Owens, G. Influence of corn residue biochar on water retention and penetration resistance in a calcareous sandy loam soil. Geoderma 2021, 383, 114734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głąb, T.; Żabiński, A.; Sadowska, U.; Gondek, K.; Kopeć, M.; Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Tabor, S.; Stanek-Tarkowska, J. Fertilization effects of compost produced from maize, sewage sludge and biochar on soil water retention and chemical properties. Soil Till. Res. 2020, 197, 104493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, M.; Deng, Z. A mathematically continuous model for describing the hydraulic properties of unsaturated porous media over the entire range of matric suctions. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 6860–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.; Ghosh, K.K.; Ravi, K. Influence of biochar particle size on the hydraulic conductivity of two different compacted engineered soils. Biomass Convers. Bior. 2021, 13, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.T.F.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Ng, C.W.W.; Wong, M.H. Soil-water retention behavior of compacted biochar-amended clay: A novel landfill final cover material. J. Soil Sediment. 2017, 17, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Dugan, B.; Masiello, C.A.; Gonnermann, H.M. Biochar particle size, shape, and porosity act together to influence soil water properties. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.L.; de Moraes, M.T.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Cherubin, M.R. Biochar amendment enhances water retention in a tropical sandy soil. Agriculture 2020, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagra-Mendoza, K.; Horn, R. Effect of biochar addition on hydraulic functions of two textural soils. Geoderma 2018, 326, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obour, P.B.; Danso, E.O.; Pouladi, N.; Abenney-Mickson, S.; Sabi, E.B.; Monnie, F.; Arthur, E. Soil structure characteristics, functional properties and consistency limits response to corn cob biochar particle size and application rates in a 36-month pot experiment. Soil Res. 2020, 58, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, S.; Meinders, M.B.J.; Stoof, C.R.; Bezemer, T.M.; van de Voorde, T.F.J.; Mommer, L.; van Groenigen, J.W. Biochar application does not improve the soil hydrological function of a sandy soil. Geoderma 2015, 251–252, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, W.; Harsh, J.B.; Abu-Lail, N.I.; Fortuna, A.M.; Dallmeyer, I.; Garcia-Pérez, M. The role of biochar porosity and surface functionality in augmenting hydrologic properties of a sandy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, M.; Clothier, B.; Bound, S.; Oliver, G.; Close, D. Does biochar influence soil physical properties and soil water availability? Plant Soil 2014, 376, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, H.-P.; Brümmer, G.W.; Fleige, H.; Horn, R.; Kandeler, E.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Kretzschmar, R.; Stahr, K.; Wilke, B.-M. Scheffer/Schachtschabel Soil Science; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaumann, G.E.; Bertmer, M. Soil-water interactions. In NMR Spectroscopy: A Versatile Tool for Environmental Research; Simpson, M.J., Simpson, A.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2014; pp. 291–303. [Google Scholar]
- Sleutel, S.; Cnudde, V.; Masschaele, B.; Vlassenbroek, J.; Dierick, M.; Van Hoorebeke, L.; Jacobs, P.; De Neve, S. Comparison of different nano- and micro-focus X-ray computed tomography set-ups for the visualization of the soil microstructure and soil organic matter. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Wei, C.; Wei, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, P. An NMR-Based Analysis of Soil-Water Characteristics. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2014, 45, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, N.R.A.; Preston, A.R.; Randall, E.W.; Whalley, W.R.; Whitmore, A.P. Measurement of the size distribution of water-filled pores at different matric potentials by stray field nuclear magnetic resonance. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2005, 56, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, F.; Bowe, S.; Van As, H.; Schaumann, G.E. Evaluation of 1H NMR relaxometry for the assessment of pore-size distribution in soil samples. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 60, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Buchmann, C.; Schaumann, G.E. Determination of quantitative pore-size distribution of soils with 1 H NMR relaxometry. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrie, P.J. Characterization of porous media using NMR methods. Annu. Rep. NMR Spectrosc. 2000, 41, 265–316. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, K.-J.; Bergman, D.J.; Latorraca, G.A. Handbook of Geographical Exploration-Seismic Exploration: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-Petrophysical and Logging Applications; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, F.; Rudolph, N.; Lang, F.; Schaumann, G.E. Effects of soil solution’s constituents on proton NMR relaxometry of soil samples. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 72, 1694–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, K.; Knight, R. A laboratory study to determine the effect of iron oxides on proton NMR measurements. Geophysics 2007, 72, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, G.; Xiao, L.; Prammer, M. NMR Logging: Principles and Applications; Haliburton Energy Services 1999; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2011; p. 234. [Google Scholar]
- Saidian, M.; Prasad, M. Effect of mineralogy on nuclear magnetic resonance surface relativity: A case study of middle Bakken and Three Forks formations. Fuel 2015, 161, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godefroy, S.; Korb, J.P.; Fleury, M.; Bryant, R.G. Surface nuclear magnetic relaxation and dynamics of water and oil in macroporous media. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 2001, 64, 021605/01–021605/13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteson, A.; Tomanic, J.P.; Herron, M.M.; Allen, D.F.; Kenyon, W.E. NMR relaxation of clay/brine mixtures. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2000, 3, 602–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Xing, A.; Fredlund, M.D.; Barbour, S.L. The relationship of the unsaturated soil shear to the soil-water characteristic curve. Can. Geotech. J. 1996, 33, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A Closed-form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Xing, A. Equations for the soil-water characteristic curve. Can. Geotech. J. 1994, 31, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Hong, N.; Li, L.; Kang, J.; Li, J. Effect of infiltration rate changes in urban soils on stormwater runoff process. Geoderma 2020, 363, 114158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Parikh, S.J.; Scow, K.M. Impact of biochar on water retention of two agricultural soils—A multi-scale analysis. Geoderma 2019, 340, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50123-2019; Standard for Geotechnical Testing Method. Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 9–10.
- Lal, R.; Shukla, M.K. Principles of Soil Physics; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Greenland, D.J. Soil management and soil degradation. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1981, 32, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Kang, J.; Ren, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M. A method for estimating soil water characteristic curve with limited experimental data. Geoderma 2020, 360, 114013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Yu, H.J.; Gao, X.R.; An, T.L.; Wang, Y.B.; Sun, M. Attribution analysis and Countermeasures of urban waterlogging in China. J. North China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 40, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Sun, W. Water-holding characteristics of clay mixed with biochar and mechanism of its influence. Rock Soil Mech. 2019, 40, 4722–4730. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.W.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, Q.L.; Kang, J.Y.; Li, D.X.; Wang, D.B. A relation of hydraulic conductivity—Void ratio for soils based on Kozeny-Carman equation. Eng. Geol. 2016, 213, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.W.; Santamarina, J.C. The hydraulic conductivity of sediments: A pore size perspective. Eng. Geol. 2018, 233, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.B.; Fang, H.L. Soil infiltration of green space and its importance to urban ecological security. Chin. J. Ecol. 2015, 034, 894–900. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.U.; Jiang, F.; Guo, Z.; Peng, X. Does biochar application improve soil aggregation? A meta-analysis. Soil Till. Res. 2021, 209, 104926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pituello, C.; Dal Ferro, N.; Francioso, O.; Simonetti, G.; Berti, A.; Piccoli, I.; Pisi, A.; Morari, F. Effects of biochar on the dynamics of aggregate stability in clay and sandy loam soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 827–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.M.; Li, X. Microporosity Structure of Coarse Granular Soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2010, 136, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spokas, K.A.; Novak, J.M.; Masiello, C.A.; Johnson, M.G.; Colosky, E.C.; Ippolito, J.A.; Trigo, C. Physical disintegration of biochar: An overlooked process. Environ. Sci. Tech. Lett. 2014, 1, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.Z.; Hu, N.; Li, X.; Ge, X.Y. Research on urban green space system planning response under the background of sponge city construction. Urban Dev. Stud. 2016, 7, 39–45. [Google Scholar]

| Agrotype | Ingredient | No. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcined Kaolin | Standard Sand | Biochar | ||
| Fine-grained remolded soil | 60% | 40% | 0% | A0 |
| 2% | A1 | |||
| 4% | A2 | |||
| 6% | A3 | |||
| 8% | A4 | |||
| Medium-grained remolded soil | 40% | 60% | 0% | B0 |
| 2% | B1 | |||
| 4% | B2 | |||
| 6% | B3 | |||
| 8% | B4 | |||
| Coarse-grained remolded soil | 20% | 80% | 0% | C0 |
| 2% | C1 | |||
| 4% | C2 | |||
| 6% | C3 | |||
| 8% | C4 | |||
| No. | NMR | Filter Paper Method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α (1/cm) | m | n | α (1/cm) | m | n | RMSE | |
| A0 | 0.0020 | 1.1777 | 3.4409 | 2.9 × 10−7 | 86.7163 | 0.3634 | 0.0242 |
| A1 | 0.0017 | 1.2240 | 3.5792 | 0.0005 | 7.2429 | 0.3720 | 0.0189 |
| A2 | 0.0016 | 1.1269 | 3.3615 | 1.8 × 10−7 | 69.1308 | 0.3281 | 0.0162 |
| A3 | 0.0015 | 1.0796 | 3.1761 | 6.5 × 10−6 | 19.3970 | 0.3045 | 0.0241 |
| A4 | 0.0014 | 1.1796 | 2.5773 | 0.0073 | 2.9026 | 0.4937 | 0.0274 |
| B0 | 0.0021 | 1.0195 | 3.0437 | 0.0019 | 4.1706 | 0.4299 | 0.0159 |
| B1 | 0.0020 | 1.3243 | 2.3058 | 0.0120 | 2.1993 | 0.5695 | 0.0222 |
| B2 | 0.0021 | 1.5868 | 1.8142 | 0.0373 | 1.7347 | 0.4893 | 0.0252 |
| B3 | 0.0019 | 1.5481 | 1.5213 | 0.0104 | 2.6010 | 0.3867 | 0.0310 |
| B4 | 0.0014 | 1.5256 | 2.2244 | 0.0590 | 1.8891 | 0.5154 | 0.0321 |
| C0 | 0.0018 | 2.6085 | 1.1413 | 0.7915 | 0.9594 | 0.9559 | 0.0627 |
| C1 | 0.0025 | 2.6031 | 1.1365 | 0.8710 | 1.0438 | 0.7856 | 0.0526 |
| C2 | 0.0022 | 2.2283 | 1.4129 | 0.7886 | 1.0209 | 0.7547 | 0.0632 |
| C3 | 0.0001 | 25.2130 | 0.9797 | 0.7486 | 0.9886 | 0.9726 | 0.0520 |
| C4 | 0.0005 | 6.0681 | 1.1931 | 0.9563 | 0.8931 | 1.1157 | 0.0454 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Kang, J.; Xiang, X.; Shi, H.; Ren, X. Effect of Biochar on Soil-Water Characteristics of Soils: A Pore-Scale Study. Water 2023, 15, 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101909
Chen X, Li L, Li X, Kang J, Xiang X, Shi H, Ren X. Effect of Biochar on Soil-Water Characteristics of Soils: A Pore-Scale Study. Water. 2023; 15(10):1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101909
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xin, Linfei Li, Xiaofeng Li, Jianyu Kang, Xiang Xiang, Honglian Shi, and Xingwei Ren. 2023. "Effect of Biochar on Soil-Water Characteristics of Soils: A Pore-Scale Study" Water 15, no. 10: 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101909





