A Review of Research Methods and Evolution Mechanisms of Landslide-Induced Tsunamis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Landslide Surge Cases
2.1. Classification of Landslide Surges
2.2. Study on the Mechanism of Landslide Surge
3. Landslide Surge Research Methods
3.1. Theoretical Analysis of Landslide Surge
3.1.1. Surge Generation Stage
3.1.2. Propagation Stage
3.2. Physical Model Test Method
3.2.1. Physical Model
3.2.2. Surge Generation Stage
3.2.3. Propagation Process Stage
3.2.4. Surge Climbing Stage
3.3. Numerical Method
3.3.1. Surge Generation Stage
3.3.2. Propagation Process Stage
4. Study on Influence Factors and Mechanism of Landslide Surge
4.1. Sliding Body Factor
4.2. Water Body Factor
5. Difficulties and Problems of Landslide Surge Research
5.1. Theoretical Analysis Method
5.2. Physical Model Test Method
5.3. Numerical Method
6. Conclusions
6.1. Theoretical Analysis Method
6.2. Physical Model Test Method
6.3. Numerical Method
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, S. Theory and Technology of Landslide Risk Assessment; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 8–75. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Tan, Y.; Li, E. Research on quantitative of landslide assessment disaster risk in reservoir area of Kala hydropower station. Chin. J. Undergr. Space Eng. 2013, 9 (Suppl. S2), 2040–2046. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, P.Y.; Wang, P.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.L. Experimental study on the nonlinear behavior of a sailing container ship under landslide induced surges. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 9081586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Han, L.; Yu, T.; Meng, C. Effects of landslide generated impulse waves on ship impact force for pile wharf. J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 2016, 37, 878–884. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z. Physical model experiments of landslide-induced surge in Three Gorge Reservoir. Earth Sci. (J. China Univ. Geosci.) 2012, 37, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Wang, P. Prediction of the maximum near-field wave amplitude of impulse waves generated by three dimensional landslides based on momentum balance. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2018, 37, 2584–2592. [Google Scholar]
- Viroulet, S.; Sauret, A.; Kimmoun, O. Tsunami generated by a granular collapse down a rough inclined plane. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 2014, 105, 34004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, Z. Prototype physical similarity experimental study on surgegenerated by instability of cataclastic rock mass. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2013, 32, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Zweifel, A.; Hager, W.H.; Minor, H.E. Plane impulse waves in reservoirs. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2006, 132, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Diao, M.; Wang, L. Research on initial formation and attenuation of landslide-generated waves. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 47, 816–825. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Zu, F.; Wang, P.; Han, L. Head Wave Energy Analysis of Landslide Surge in Mountainous Channel Reservoir. Waterw. Eng. 2020, 143, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, X. Calculation of lenggu hydroelectric station landslide surge height based on pan jiazheng calculation method of speed and surge. Water Resour. Power 2010, 9, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, K.; Huo, Z. Review of wave amplitude prediction generatedbylandslide based on physical experiments. Geol. Miner. Resour. South China 2018, 34, 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, K.; Du, J.; Wang, Y. Analysis of surge triggered by Dayantang landslide in Shuibuya reservoir of Qingjiang river. Rock Soil Mech. 2008, 29, 3266–3270. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Yin, K.; Wang, Y. Discussion on method of landslide velocity calculation and surge prediction. Rock Soil Mech. 2008, 29, 407–411. [Google Scholar]
- Du, B. Tangyanguang landslide of tuoxi reservior-first large landslide induced by reservoir storage in China. In Proceedings of the Symposium of the Second Conference of Chinese Geotechnical and Engineering, Wuhan, China, 28–31 October 2006; China Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 918–922. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, L. Enlightenment from vajont landslide in Italy. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 1993, 5, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Hermann, M.F. Initial Phase of Landslide Generated Impulse Waves; VAW Publikationen: Zurich, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L. Destroying tsunamis generated by landslides in history. Yangtze River 1984, 2, 88. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R. Typical Catastrophic Landslide in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Yin, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Huo, Z. Analysis of waves generated by Gongjiafang landslide in Wu Gorge, three Gorges reservoir, on 23 November 2008. Landslides 2012, 9, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Dong, Y. Occurrence, geology and geomorphology of Qianjiangping landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area Study on characteristics, cause and landslide criterion. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2005, 17, 3146–3153. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Yin, Y.; Du, C. Risk management study on impulse waves generated by Hongyanzi landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir of China on 24 June 2015. Landslides 2016, 13, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, F. Preliminary study on the characteristics and formation mechanism of small dam landslide in Fuquan, Guizhou. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2015, 15, 1617–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Peng, G.; Yin, K. Surge prediction of dashiban landslide in three gorges reservoir. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2007, 14, 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, D.; Wang, G. Tangyanguang landslide in Tuoxi Reservoir. In Typtical Landslides in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1986. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen, R.M. Basic Wave Mechanics: For Coastal and Ocean Engineers; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L. Fluid Mechanics; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Fluid Mechanics; China Electric Power Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, K. Perturbation method of superposing initial surge height of landslide along reservoir shoreline. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2004, 23, 717–720. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, V. Landslide Generated Impulse Waves: Prediction of Near Field Characteristics. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, V.; Hager, H.W.; Minor, H.-E. Landslide Generated Impulse Waves in Reservoirs: Basics and Computation; VAW Publikationen: Zürich, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, V.; Hager, W.H. Impulse Product Parameter in Landslide Generated Impulse Waves. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean. Eng. 2010, 136, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizzo, A.; De Girolamo, P.; Petaccia, A. Forecasting impulse waves generated by subaerial landslides. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2005, 110, C12025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, E. Water waves generated by landslides. J. Waterw. Harb. Coast. Eng. 1970, 96, 835–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, P.; Wang, P.; Han, L.; Meng, C. China’s safety production science and technology, review of physical model test research on landslide and surge disaster. J. Saf. Sci. Technol. 2020, 16, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W. Research on factors affecting landslide surge. J. Eng. Geol. 2012, 20, 491–507. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, P.; Grilli, S.T.; Kirby, J.T.; Fryer, G.J.; Tappin, D. Landslide tsunami case studies using a Boussinesq model and a fully nonlinear tsunami generation model. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 3, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Risio, M.; Sammarco, P. Analytical modeling of landslide generated waves. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2008, 134, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.L.-F.; Lynett, P.; Synolakis, C.E. Analytical solutions for forced long waves on a sloping beach. J. Fluid Mech. 2003, 478, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Guo, H. Discussion on two methods for predicting velocity of landslides. Rock Soil Mech. 2008, 29 (Suppl. S1), 373–378. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Wang, D.; Hu, B. Analysis on reservoir landslides and its surge. J. East China Jiaotong Univ. 2003, 20, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Haugen, K.B.; Løvholt, F.; Harbitz, C.B. Fundamental mechanisms for tsunami generation by submarine mass flows in idealized geometries. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2005, 22, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursell, F.; Dean, R.G.; Yu, Y.S. Forced small-amplitude water waves: A comparison of theory and experiment. J. Fluid Mech. 1960, 7, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennard, E.H. Generation of surface waves by a moving partition. Q. Appl. Math. 1949, 7, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.M.; Wiegel, R.L. Waves generated by horizontal motion of a wall. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1972, 98, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J. Stability against Sliding of Buildings and Analysis of Landslide; China Water Power Press: Beijing, China, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wang, R.; Liu, X. On landslide surge and waveform spreading. J. Zhejiang Water Conserv. Hydropower Coll. 2003, 15, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, Q.; Hu, W. The calculation of landslide surge in reservoir. Yellow River 1980, 2, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Law, L.; Brebner, A. On Water Waves Generated by Landslides. In Proceedings of the 3rd Australasian Conference on Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics, Sydney, Australia, 25–29 November 1968; The Institution of Engineers: Sydney, Australia, 1968; pp. 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, H. Water waves generated by distant landslides. J. Hydraul. Res. 1988, 26, 307–322. [Google Scholar]
- Wiegel, R.L. Laboratory studies of gravity waves generated by the movement of a submerged body. Trans. Am. Geo Phys. Union 1955, 36, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Nik-Khah, A. Impulsive waves caused by sub-aerial landslides. J. Environ. Fluid Mech 2008, 8, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.; Wang, Y.; Huo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Study on the prediction model of initial surge amplitude of high and steep reservoir bank landslide. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2021, 28, 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Kamphuis, J.W.; Bowering, R.J. Impulse waves generated by landslides. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Washington, DC, USA, 13–18 September 1970; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, J. Comparative analysis of empirical estimation methods for landslide surge on reservoir bank. Geotech. Mech. 2014, 35, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Deng, H.; Wu, J.; Yong, M. Physical model test of landslide surge in a reservoir area of Lancang River. J. Yangtze River Acad. Sci. 2017, 34, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Jiang, C.; Deng, B.; Liu, Y. Surge height and propagation law of landslide in narrow channel near dam reservoir area. Traffic Sci. Eng. 2016, 32, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Yin, K.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Reservoir bank landslide impact surge based on physical simulation test. J. Cent. South Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2014, 45, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar]
- McFall, B.C.; Fritz, H.M. Physical modelling of tsunamis generated by three-dimensional deformable granular landslides on planar and conical island slopes. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. 2016, 472, 20160052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, F. Physical Modeling of Tsunamis Generated by Three-Dimensional Deformable Granular Landslides; Georgia Institute of Technology: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Research on Landslide-Induced Surge in Three Gorges Reservoir Area; China University of Geosciences: Wuhan, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.; Ma, Q.; Diao, M.; Jiang, L. Propagation characteristics of sub aerial landslide-generated impulse waves. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2018, 19, 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Hu, X. Calculation and research of landslide surge in mountain river-type reservoirs. J. Chongqing Jiaotong Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 30, 295–299. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, P.; Yu, T.; Chen, L. Analysis of surge climbing test of steep rock landslide in the Three Gorges reservoir area. China J. Geol. Hazards Prev. 2014, 25, 43–48+55. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.V.; Watts, G.M. Laboratory Investigation of the Vertical Rise of Solitary Wave on Impermeable Slopes; U. S. Army Corps of Engineers Beach Erosion Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Synolakis, C.E. The Runup of Solitary Waves. J. Fluid Mech. 1987, 185, 523–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.R. Auflaufen Undüberschwappen von Impulswellen an Talsperren (Run-Up and Run-Over of Impulse Waves at Dams); VAW-Mitteilung 137; ETH Zurich: Zurich, Switzerland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Biscarini, C. Computational fluid dynamics modelling of landslide generated water waves. Landslides 2010, 7, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Pacheco, A.; Murillo, J.; García-Navarro, P. A finite volume method for the simulation of the waves generated by landslides. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W. CEL algorithm study of reservoir surge Induced by landslide. J. Eng. Geol. 2012, 20, 350–354. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Yue, G.; Wang, H. Dynamic mechanism of high speed landslide surge. J. Nat. Disasters 2013, 22, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Xing, A.; Chen, L. Numerical simulation of two-dimensional water waves due to landslide based on FLUENT. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2009, 36, 90–94. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuk, D.; Yim, S.C.; Liu, P.F. Numerical modeling of submarine mass-movement generated waves using RANS model. Comput. Geosci. 2006, 32, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadie, S.; Morichon, D.; Grilli, S.; Glockner, S. Numerical simulation of waves generated by landslides using a multiple-fluid Navier-Stokes model. Coast. Eng. 2010, 57, 779–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.F.; Wu, T.R.; Raichlen, F.; Synolakis, C.E.; Borrero, J.C. Run-up and rundown generated by three-dimensional sliding masses. J. Fluid Mech. 2005, 536, 107–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, M. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics—A Meshfree Particle Method; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2003; pp. 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, K.; Han, J. Experimental research on primary wave height generated by loose earth landslide. Yangtze River 2011, 42, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Jiang, C.; Deng, B. Three dimensional numerical simulations of water waves generated by landslides and its propagation process. J. Transp. Sci. Eng. 2011, 27, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bosa, S.; Petti, M. A numerical model of the wave that overtopped the Vajont Dam in 1963. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 1763–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Yavari-Ramshe, S. Numerical simulation of wave generated by landslide incidents in dam reservoirs. Landslides 2011, 8, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, B.; Liu, G.; Chen, X. Numerical simulation of tsunami due to slope failure at Gongjiafang on Three Gorges Reservoir. Rock Soil Mech. 2015, 36, 212–218. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Heidarzadeh, M.; Pirooz, M.D.; Zaker, N.H.; Yalciner, A.C.; Mokhtari, M.; Esmaeily, A. Historical tsunami in the Makran Subduction Zone off the southern coasts of Iran and Pakistan and results of numerical modeling. Ocean Eng. 2008, 35, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.B.; Jin, F.; Sheng, J. Numerical simulations of water waves due to landslide. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2005, 22, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.M.; Ng, C.O.; Zheng, Y.H. Simulation of wave propagation over a submerged bar using the VOF method with a two-equation k-εturbulence modeling. Ocean Eng. 2004, 31, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Comparison of the Application of the Empirical Estimation Method for Reservoir Bank Landslide Surge. Henan Sci. Technol. 2021, 40, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.; Dang, F.; Chen, X. Study on the surge wave propagation in the reservoir area and its interaction mechanism with the dam. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2019, 50, 815–823. [Google Scholar]
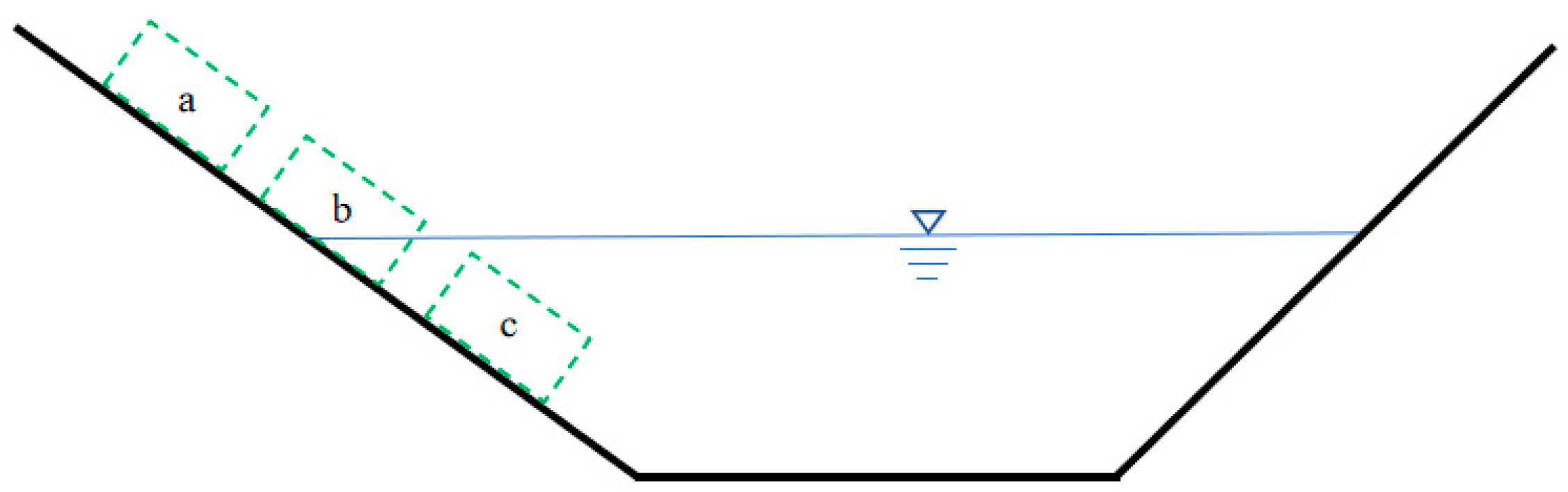
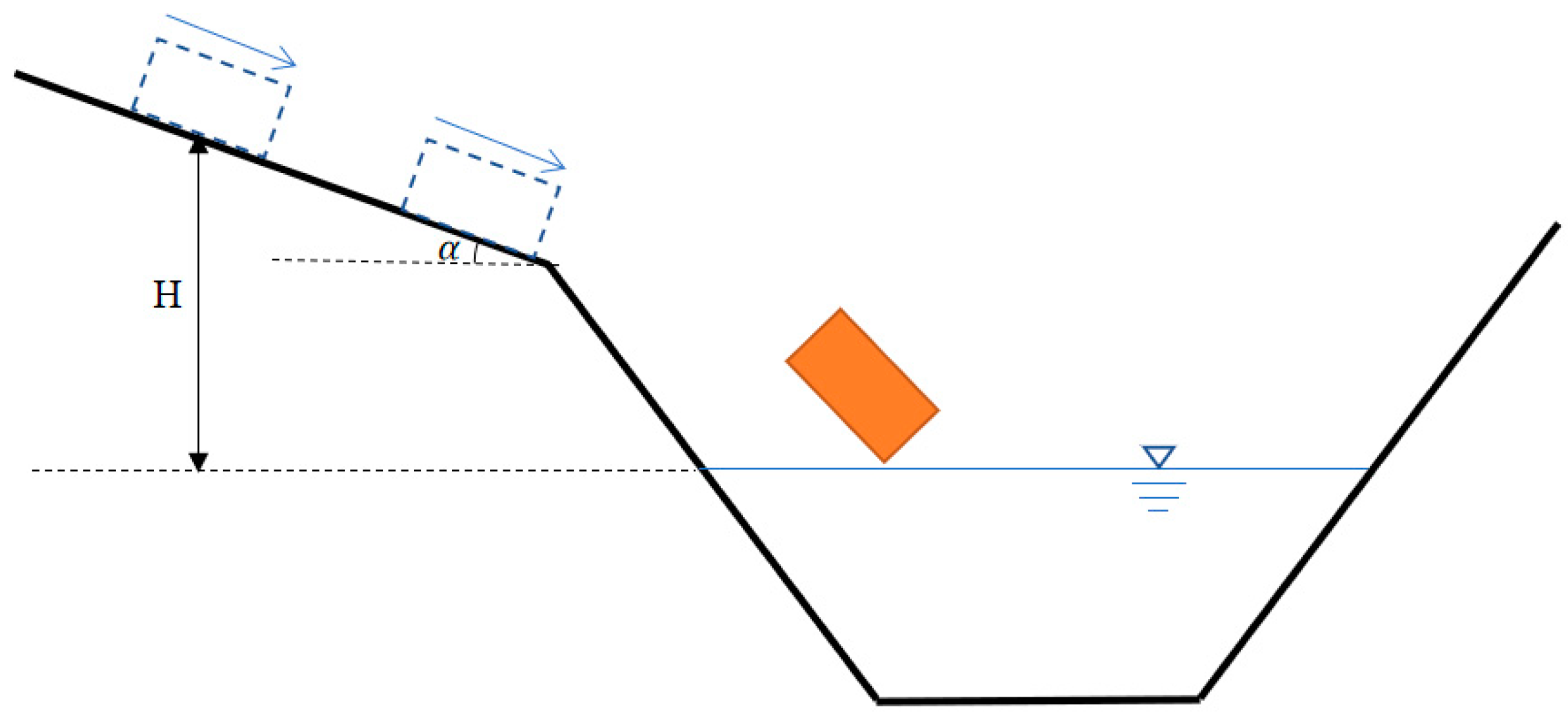
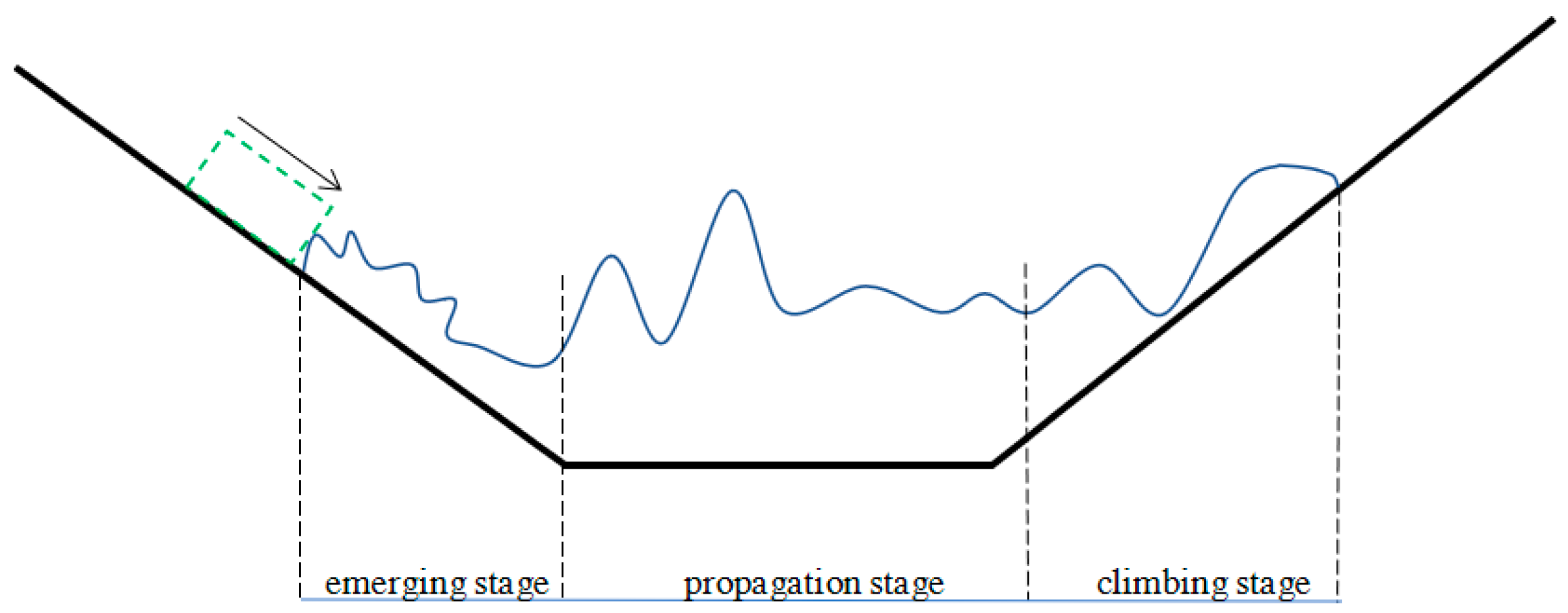
| Number | Time | Location | Landslide Volume (104 m3) | Failure Mode | Number of Deaths |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1792 | Senyun, Japan [12] | 535 | The formation of 10 m high surge. | 15,000 |
| 2 | 1933 | Diexi, Minjiang River, China [13] | - | - | 8800 |
| 3 | 1956 | Lanfjord, Norway [14] | 12 | The formation of 140 m high surge. | 32 |
| 4 | 1958 | Lituya landslide in Alaska, USA [15] | 30 | The formation of 30 m high surge. | 2 |
| 5 | 1958 | Italy Pontesei arch dam reservoir area [15] | - | A 20 m high surge over the dam. | 1 |
| 6 | 1961 | Zishui Zhexi Reservoir, Hunan Province, China [16] | 1.65 | Damage caused by 21 m high surge over dam. | 40 |
| 7 | 1963 | Italy vajont reservoir [17] | 240 | A 175 m surge overtop | 3000 |
| 8 | 1971 | Peru chungar lake shore [15] | 0.1 | The formation of 30 m high surge. | 300–500 |
| 9 | 1980 | Mount St. Helens Spirit Lake [18] | 2500 | The landslide whipped up a more than 200 m high surge | - |
| 10 | 1982 | Jibazi landslide in Yunyang County, Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China [19] | - | The river shoreline advanced inward more than 50 m, the riverbed silt height of 30 m. | - |
| 11 | 1985 | Xintan Landslide, Zigui County, Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China [20,21] | 30 | Initial waves of up to 49 m destroyed nearby ships. | 10 |
| 12 | 2002 | Stromboli, Italy [15] | - | The formation of 10.9 m high surge. | 2 |
| 13 | 2003 | Qianjiangping Village in Three Gorges Reservoir Area of China [20] | 24 | Up to 30 m surges destroyed 120 acres of farmland nearby. | 14 |
| 14 | 2007 | Shuibuya Dam, China [22] | 3 | The formation of 50 m high surge. | 1 |
| 15 | 2008 | GongJiaFang, Wushan, Chongqing, China [23] | 0.38 | Waves about 15 m high formed on the opposite bank. | - |
| 16 | 2009 | The landslide in Xiaowan | 1 | The landslide whipped up a 30 m high surge | 24 |
| 17 | 2014 | Xiaoba landslide in Guizhou province [24] | 0.33 | The landslide whipped up a 20 m high surge | 12 |
| 18 | 2015 | Chongqing Wushan Daning River Jiangdong Temple North Shore [25,26] | - | A 6 m high surge toppled nearby boats. | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xin, C.; He, Z.; Feng, W. A Review of Research Methods and Evolution Mechanisms of Landslide-Induced Tsunamis. Water 2023, 15, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101879
Xin C, He Z, Feng W. A Review of Research Methods and Evolution Mechanisms of Landslide-Induced Tsunamis. Water. 2023; 15(10):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101879
Chicago/Turabian StyleXin, Chunlei, Zhiqian He, and Wenkai Feng. 2023. "A Review of Research Methods and Evolution Mechanisms of Landslide-Induced Tsunamis" Water 15, no. 10: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101879
APA StyleXin, C., He, Z., & Feng, W. (2023). A Review of Research Methods and Evolution Mechanisms of Landslide-Induced Tsunamis. Water, 15(10), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101879






