Spatial Distribution and Sources of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments from Dachan Bay, Shenzhen City
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Pre-Treatment
2.3. Analytical Method
2.4. Sediment Dating
2.5. QA/QC
2.6. Statistical and Graphical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Content and Spatial Distribution of Σ15PAH in Surface Sediments of DCB
3.2. Content and Vertical Variation of Σ15PAH in Core Sediments of DCB
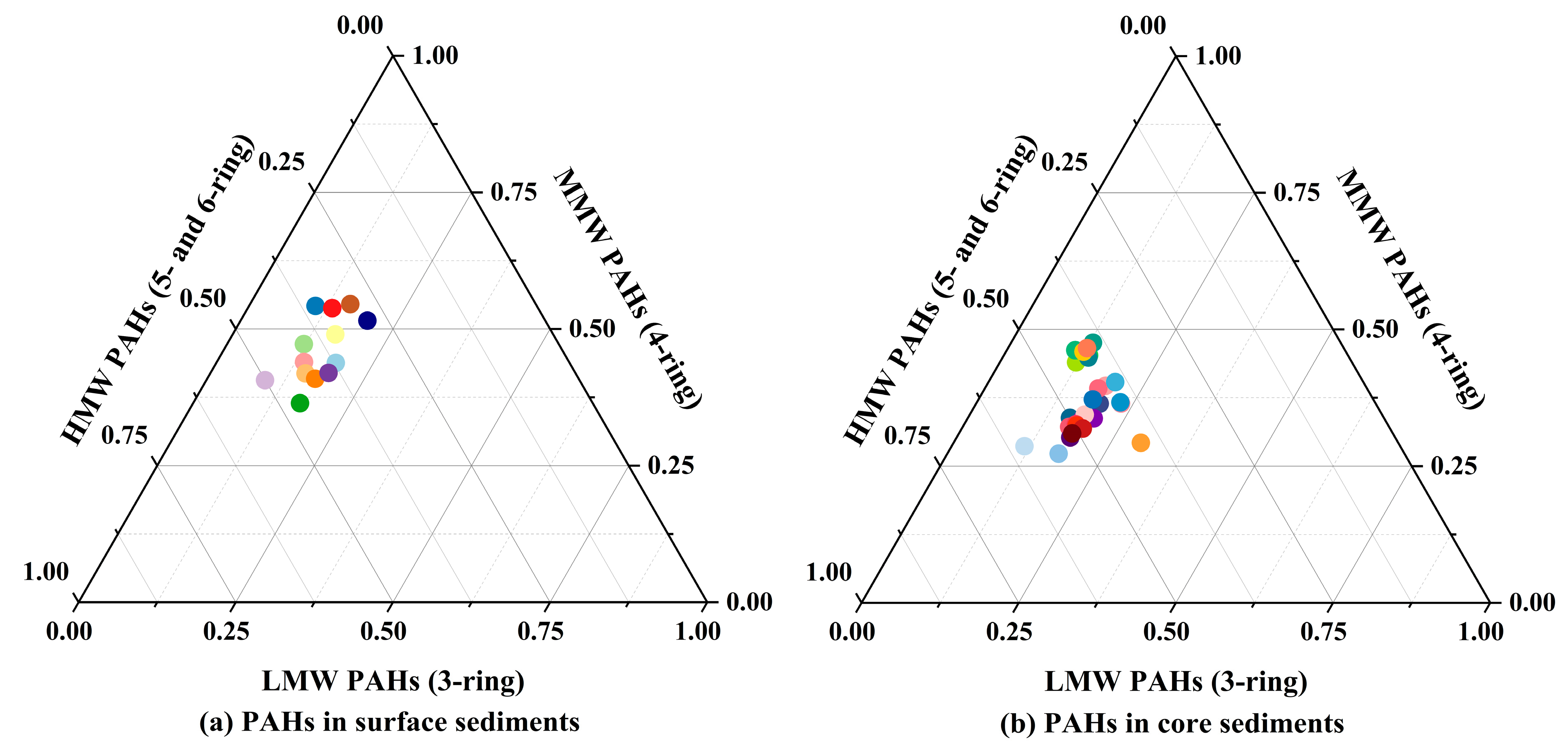
3.3. Composition Characteristics of PAHs in Sediments of DCB
3.4. Source Analysis
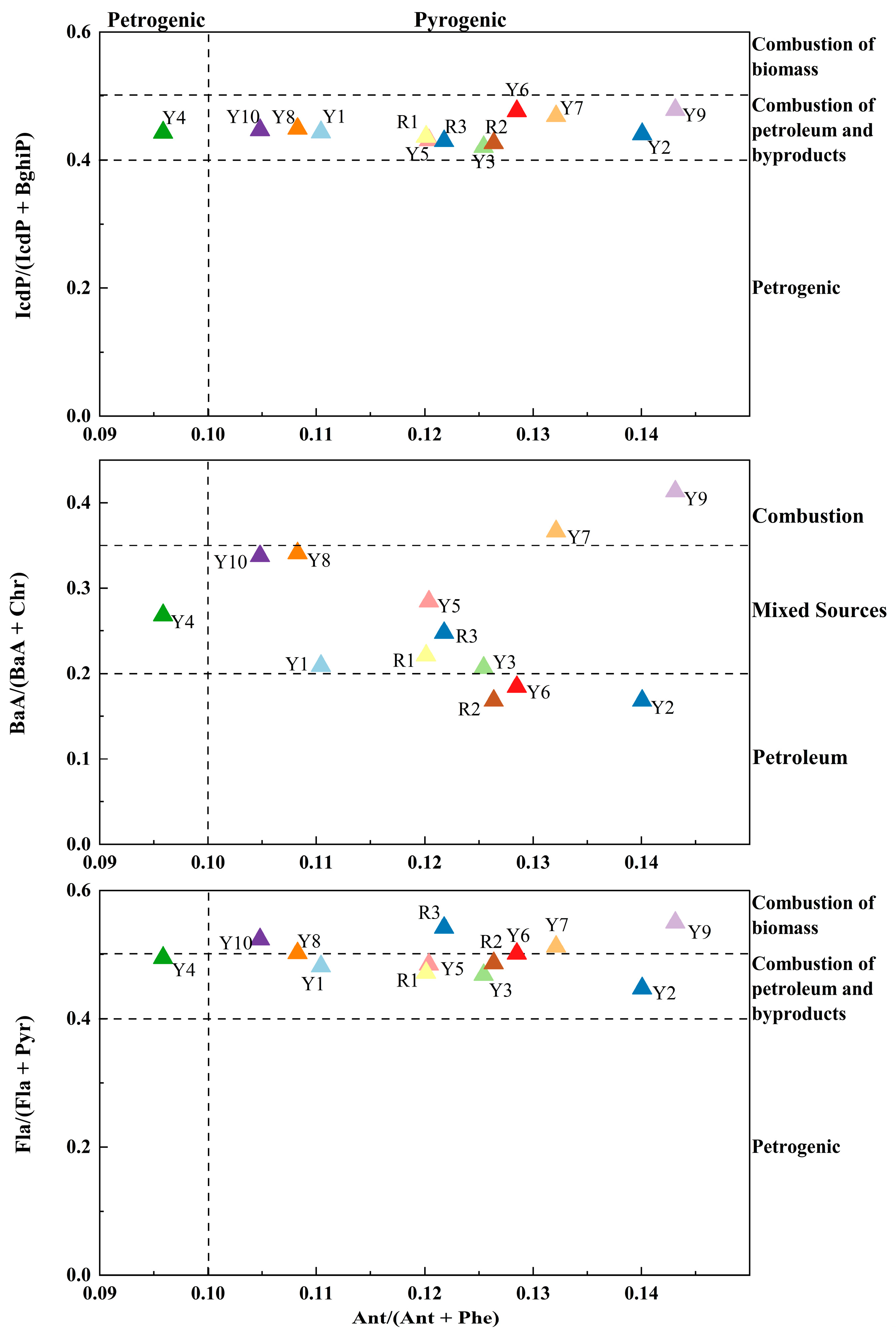
3.4.1. Sources of PAHs in Surface Sediments
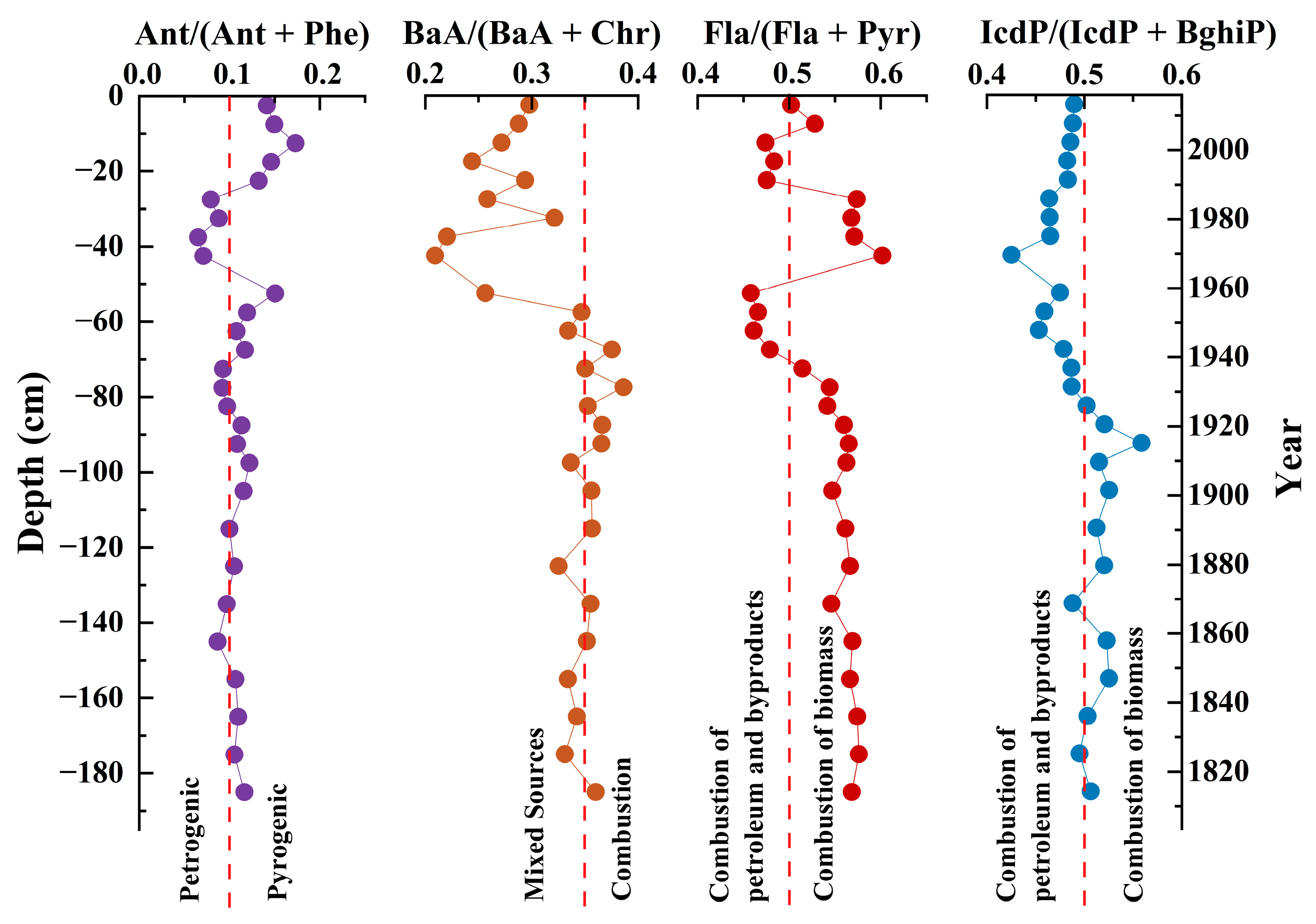
3.4.2. Sources of PAHs in Core Sediments
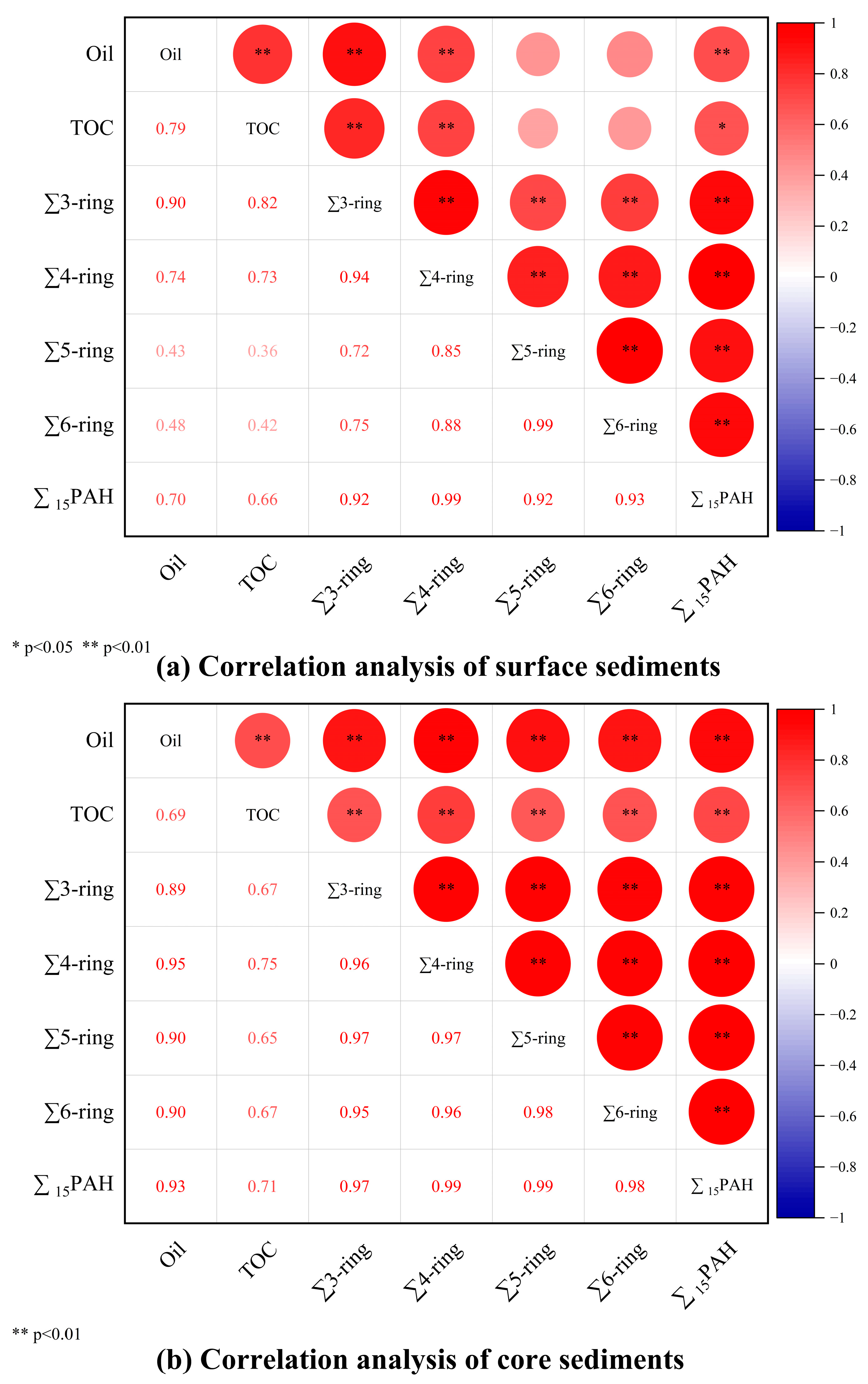
3.5. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, P.; Hayakawa, K.; Zhang, L.; Tang, N. Characteristics and influencing factors of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons emitted from open burning and stove burning of biomass: A brief review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wan, H.; Zhou, J.; Luo, D.; Huang, T.; Yang, H.; Huang, C. Sediment record of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Dianchi lake, southwest China: Influence of energy structure changes and economic development. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Wei, G.; Guan, Y.; Wong, C.; Zeng, E. Sediment records of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the continental shelf of China: Implications for evolving anthropogenic impacts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6497–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liang, J. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in green space soils in Shanghai: Source, distribution, and risk assessment. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, M.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, H. Fine particles and pyrogenic carbon fractions regulate PAH partitioning and burial in a eutrophic shallow lake. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Qin, R.; Luo, W. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Bohai Sea: A review of their distribution, sources, and risks. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2022, 18, 1705–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Gao, M.; Dong, J.; Sun, J.; Hou, G.; Liu, S.; Du, X.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y. The first high resolution PAH record of industrialization over the past 200 years in Liaodong Bay, northeastern China. Water Res. 2022, 224, 119103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Sun, X. Theory and Practice of Gulf Ecosystem: A Case Study of Jiaozhou Bay; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, H.; He, S.; Lv, S. Distributions and sources of petroleum, aliphatic hydrocarbons and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments from Bohai Bay and its adjacent river, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Qi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, X.; Liu, H.; Qu, C.; Liu, J.; Li, F. Levels, sources and potential risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in multimedia environment along the Jinjiang River mainstream to Quanzhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corminboeuf, A.; Montero-Serrano, J.-C.; St-Louis, R.; Dalpé, A.; Gélinas, Y. Pre-and post-industrial levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from the Estuary and Gulf of St. Lawrence (eastern Canada). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Liang, C.; Zhao, L. Study on Environmental Capacity and Total Pollution Control Management in Shenzhen Sea Area of the Pearl River Estuary; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Song, Z.; Sun, X.; Chen, C.; Ke, S.; Zhang, J. Heavy metals of sediment cores in Dachan Bay and their responses to human activities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, B.S.; Joshi, S.R. An evaluation of the CIC model of210Pb dating of sediments. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 1989, 14, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarzenski, P.W. 210Pb dating. In Encyclopedia of Scientific Dating Methods; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Mou, D.; Du, J.; Zhang, J. Study on comparison of excess 210Pb chronology of several models. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2008, 110, 370–374. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, G.; Yang, F.; Gao, H.; Gong, Z.; Zhu, C.; Lian, J. Vertical Distribution Characteristics of Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Sediment Core from Lake Nansihu. Environ. Sci. 2007, 28, 1590–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Li, Q.; Liu, A.; Gong, J.; Zheng, L. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) distribution in surface sediments from Yazhou Bay of Sanya, South China, and their source and risk assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 162, 111800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Chen, C.; Chen, C. Vertical profile, sources, and equivalent toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediment cores from the river mouths of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Cui, D.; Liu, A.; Li, Q.; Zheng, L.; Research, P. Distribution, sources, and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments from Daya Bay, South China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 25858–25865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J.; Cui, Z.; Su, P. Sedimentary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) along the mouth bar of the Yangtze River Estuary: Source, distribution, and potential toxicity. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 159, 111494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X. Yancheng Sources of PAHs in Sediment Distribution, the Sea and Its Response to Human Activities. Master’s Thesis, Information Engineering University, Nanjing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Lai, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yang, W.; Mai, Y.; Wang, C. Occurrence, source identification, and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of the Pearl River Delta, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 170, 112666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabouchi, I.; Khadhar, S.; Driouich Chaouachi, R.; Chekirbene, A.; Asia, L.; Doumenq, P. Study of organic pollution in superficial sediments of Meliane river catchment area: Aliphatic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniji, A.O.; Okoh, O.; Okoh, A.O. Distribution pattern and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the water and sediment of Algoa Bay, South Africa. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1303–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W. China’s Economic Growth and Environmental Quality; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, B.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gao, S.; Zeng, X.; Yu, Z. Distribution characteristics, sources and ecological risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and oxygen-containing PAHs in sediments from the Yangtze Estuary and adjacent East China Sea. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar]
- De Almeida, M.; do Nascimento, D.V.; de Oliveira Mafalda Jr, P.; Patire, V.F.; de Albergaria-Barbosa, A.C.R. Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments of a Tropical Bay influenced by anthropogenic activities (Todos os Santos Bay, BA, Brazil). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Cao, J.; Huang, S.; Zhou, P. Assessment and Implication of PAHs and Compound-Specific δ13C Compositions in a Dated Marine Sediment Core from Daya Bay, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xia, J.; Situ, J.; Tan, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Distribution and Source Identification of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon of Core Sediments from Northern South China Sea. J. Guangdong Ocean Univ. 2021, 41, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bajt, O. Sedimentary Record of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea)—Distribution, Origin and Temporal Trends. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 946618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, M.B.; Macdonald, R.W.; Vingarzan, R.; Mitchell, R.H.; Goyette, D.; Sylvestre, S. PAHs in the Fraser River basin: A critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Yang, D.; Wade, T.L.; Qian, Y. Status of persistent organic pollutants in the sediment from several estuaries in China. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 114, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hong, H.; Zhou, J.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Fate and assessment of persistent organic pollutants in water and sediment from Minjiang River Estuary, Southeast China. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui-jeung, C. East River Column; Hong Kong University Press: Hong Kong, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, D.Y. Hong Kong, China: The border as palimpsest. Made China J. 2020, 5, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S. Summary of the Preparation for Establishing the Anti-Japanese Armed Forces in Southern China in the Initial Stage of the Chinese War of Resistance against Japanese Aggression. Mil. Hist. 2016, 213, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z. Research on energy Policy of New China. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Peng, X.; Qi, S. Sedimentary record of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a sediment core from the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Hu, X.; Chen, J. Sedimentary records of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from three enclosed lakes in China: Response to energy structure and economic development. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, T.A.; Dunn, R.J. Engineering. Boating-and shipping-related environmental impacts and example management measures: A review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ytreberg, E.; Hansson, K.; Hermansson, A.L.; Parsmo, R.; Lagerström, M.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Hassellöv, I.-M. Metal and PAH loads from ships and boats, relative other sources, in the Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 182, 113904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimplis, M. Marine Pollution from Shipping Activities. In Maritime Law; Informa Law from Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 380–438. [Google Scholar]
- Putatunda, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sen, D.; Bhattacharjee, C. A review on the application of different treatment processes for emulsified oily wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 2525–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Matchinski, E.J.; Chen, B.; Ye, X.; Jing, L.; Lee, K. Marine Oil Spills—Oil Pollution, Sources and Effects. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 391–406. [Google Scholar]
- Avramidis, P.; Nikolaou, K.; Bekiari, V. Total organic carbon and total nitrogen in sediments and soils: A comparison of the wet oxidation–titration method with the combustion-infrared method. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 4, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaber, P.; Gworek, B. Surface horizons of forest soils for the diagnosis of soil environment contamination and toxicity caused by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abayi, J.; Gore, C.T.; Nagawa, C.; Bandowe, B.; Ssebugere, P. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments and fish species from the White Nile, East Africa: Bioaccumulation potential, source apportionment, ecological and health risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qu, X.; Lin, D.; Yang, K. Octanol-water partition coefficient (logKow) dependent movement and time lagging of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from emission sources to lake sediments: A case study of Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
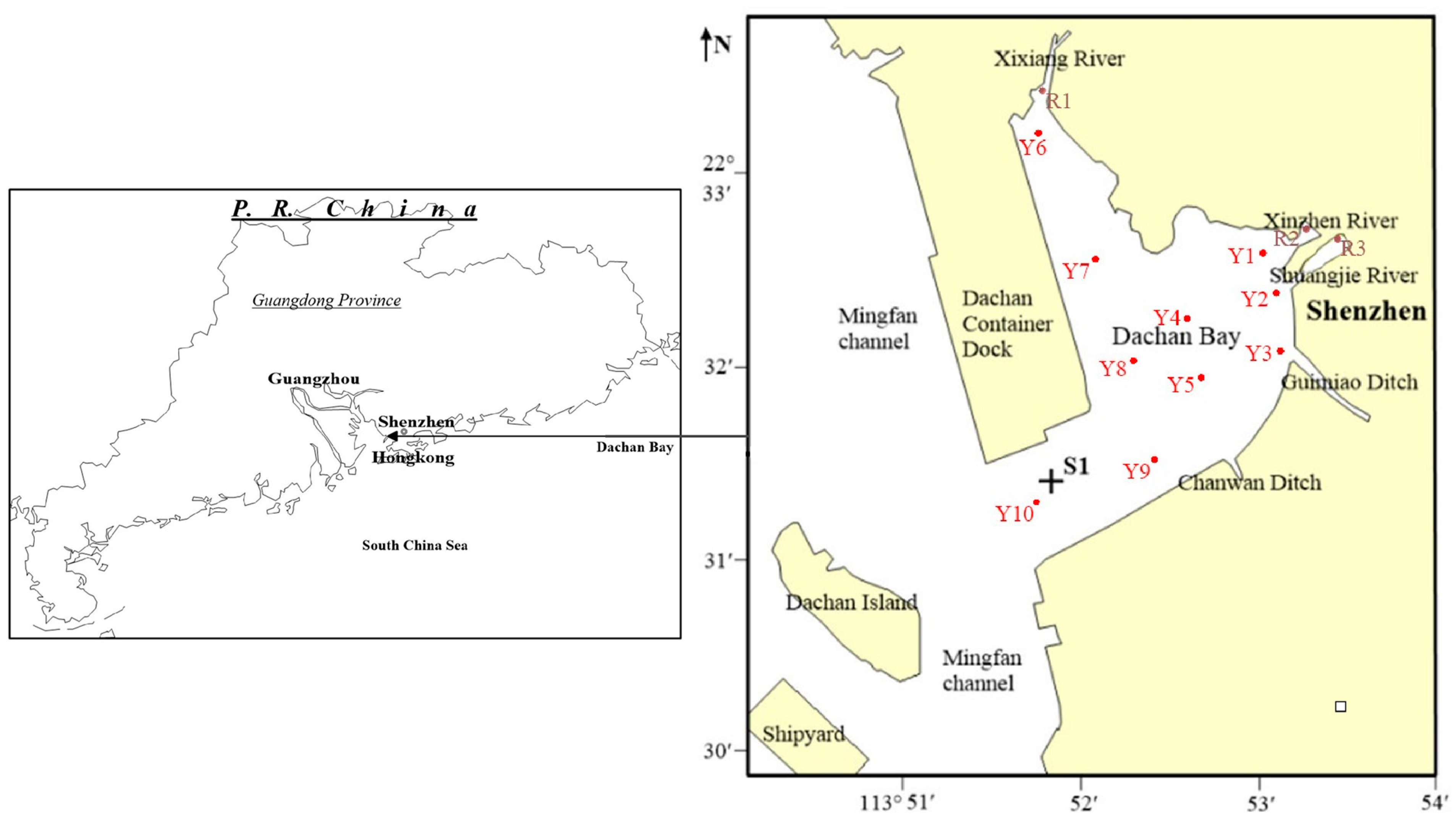
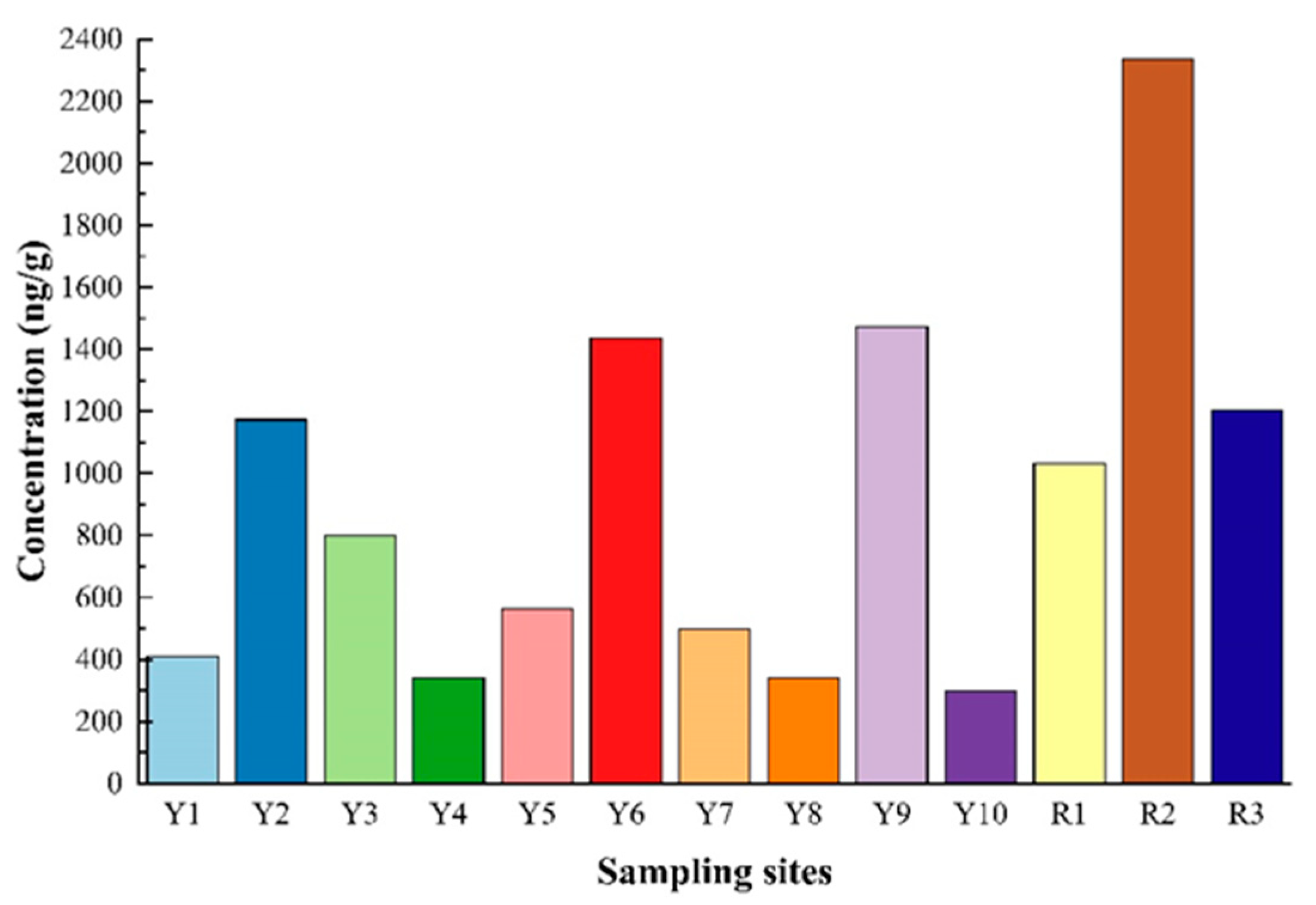

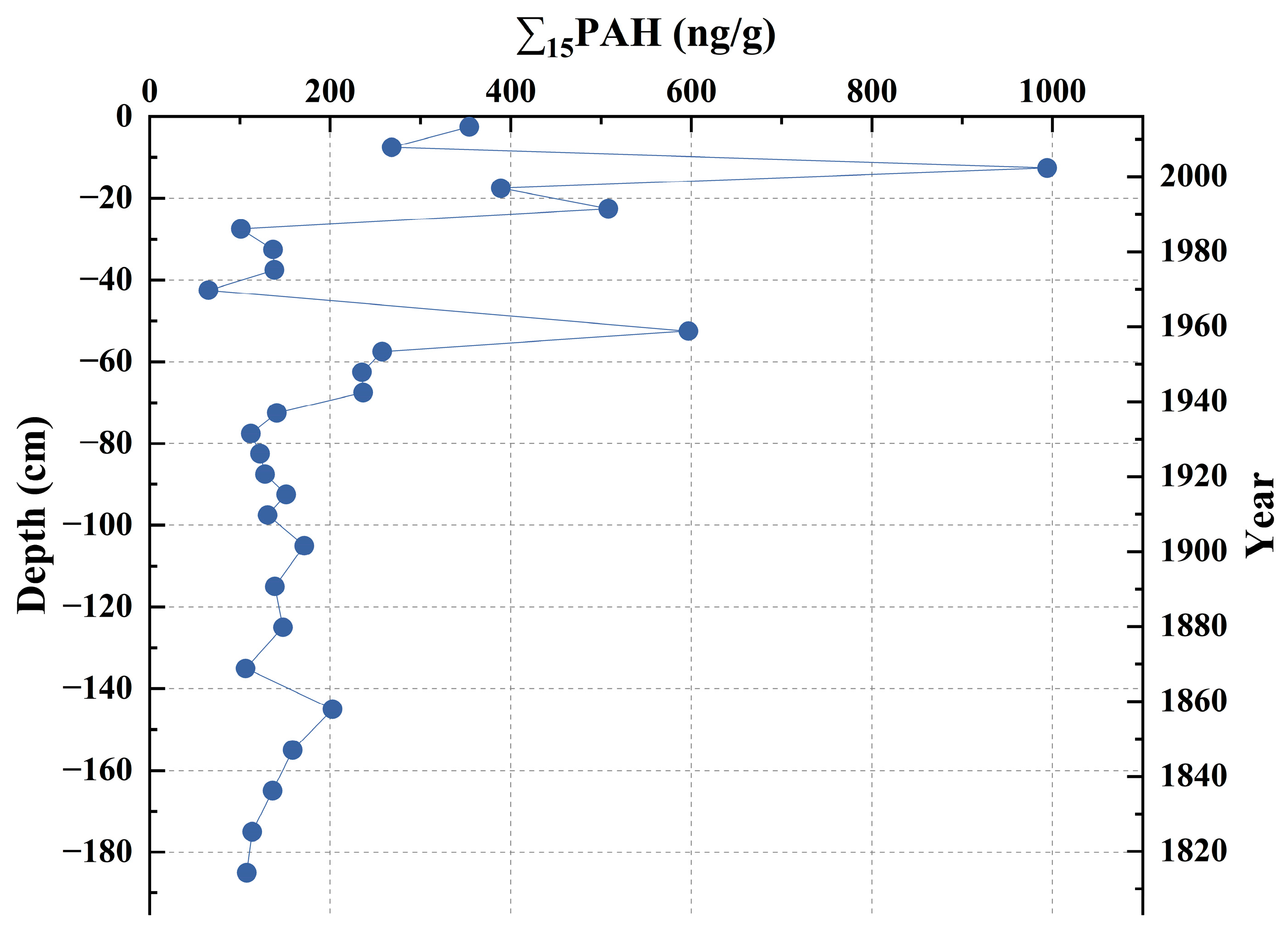
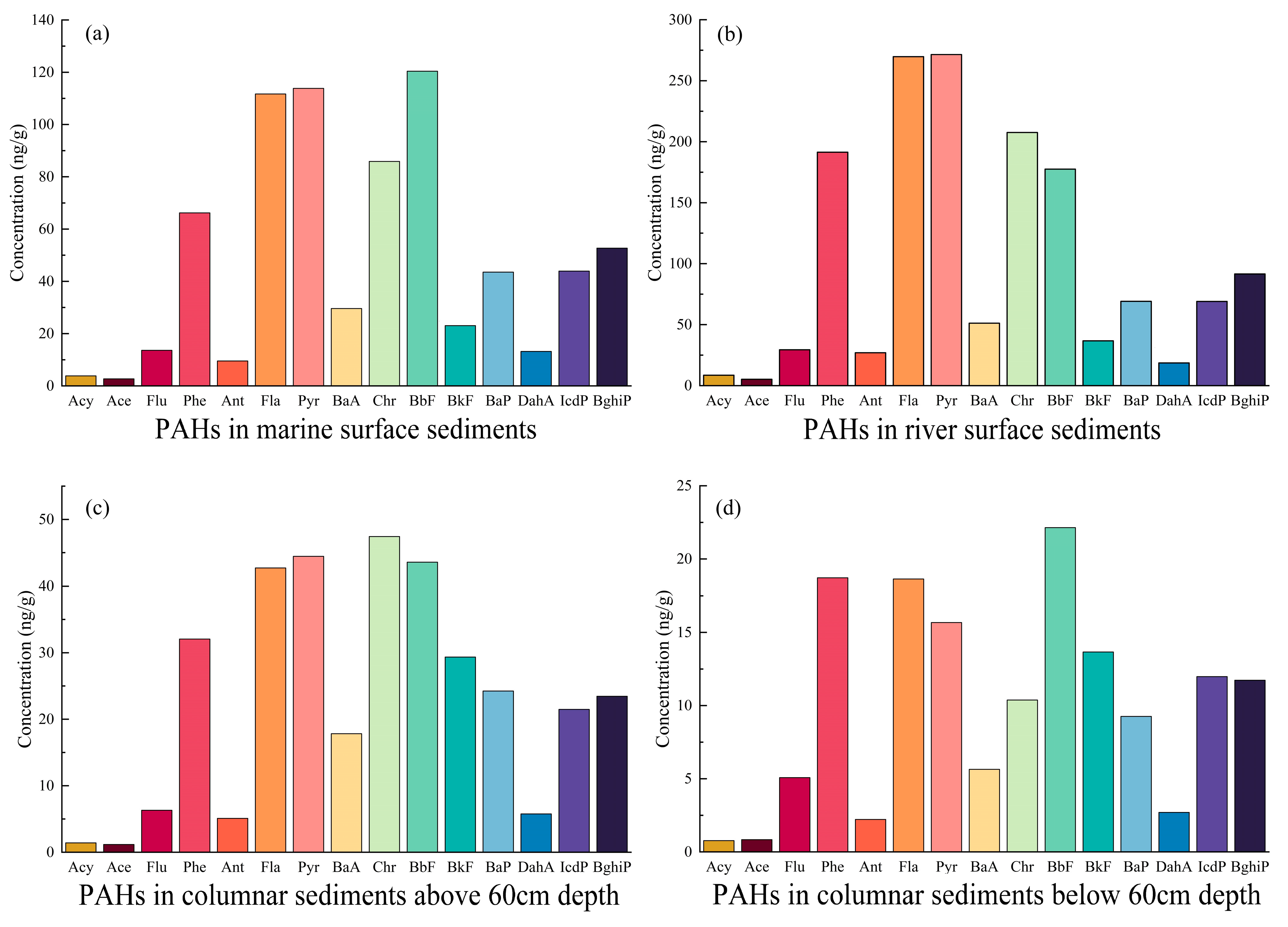
| Sampling ID | Longitude | Latitude | Sampling ID | Longitude | Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | N | E | N | ||
| Y1 | 113°52′56.64″ | 22°32′33.68″ | Y8 | 113°52′18.29″ | 22°31′58.87″ |
| Y2 | 113°53′3.62″ | 22°32′22.51″ | Y9 | 113°52′26.01″ | 22°31′30.01″ |
| Y3 | 113°53′5.11″ | 22°32′2.35″ | Y10 | 113°51′39.68″ | 22°31′14.27″ |
| Y4 | 113°52′34.96″ | 22°32′12.39″ | R1 | 113°51′45.4″ | 22°33′30.0″ |
| Y5 | 113°52′41.09″ | 22°31′49.09″ | R2 | 113°53′08.6″ | 22°32′44.8″ |
| Y6 | 113°51′43.85″ | 22°33′9.39″ | R3 | 113°53′27.0″ | 22°32′40.1″ |
| Y7 | 113°52′0.85″ | 22°32′35.22″ | S1 | 113°51′48.27″ | 22°31′22.97″ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.; Liu, B.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J. Spatial Distribution and Sources of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments from Dachan Bay, Shenzhen City. Water 2023, 15, 1848. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101848
Huang W, Liu B, Zhao H, Zhao L, Zhang J. Spatial Distribution and Sources of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments from Dachan Bay, Shenzhen City. Water. 2023; 15(10):1848. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101848
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Wenjing, Beibei Liu, Hui Zhao, Lirong Zhao, and Jibiao Zhang. 2023. "Spatial Distribution and Sources of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments from Dachan Bay, Shenzhen City" Water 15, no. 10: 1848. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101848
APA StyleHuang, W., Liu, B., Zhao, H., Zhao, L., & Zhang, J. (2023). Spatial Distribution and Sources of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments from Dachan Bay, Shenzhen City. Water, 15(10), 1848. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101848






