Effects of Different Straw Mulch Rates on the Runoff and Sediment Yield of Young Citrus Orchards with Lime Soil and Red Soil under Simulated Rainfall Conditions in Southwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Soil Trough
2.2.2. Rainfall Simulator
2.2.3. Test Soil
2.2.4. Tested Citrus Tree and Straw
2.3. Simulated Rainfall Experiment
3. Results
3.1. Reduction in Runoff by Straw Mulching
3.1.1. Effects of Straw Mulching on Runoff Coefficient
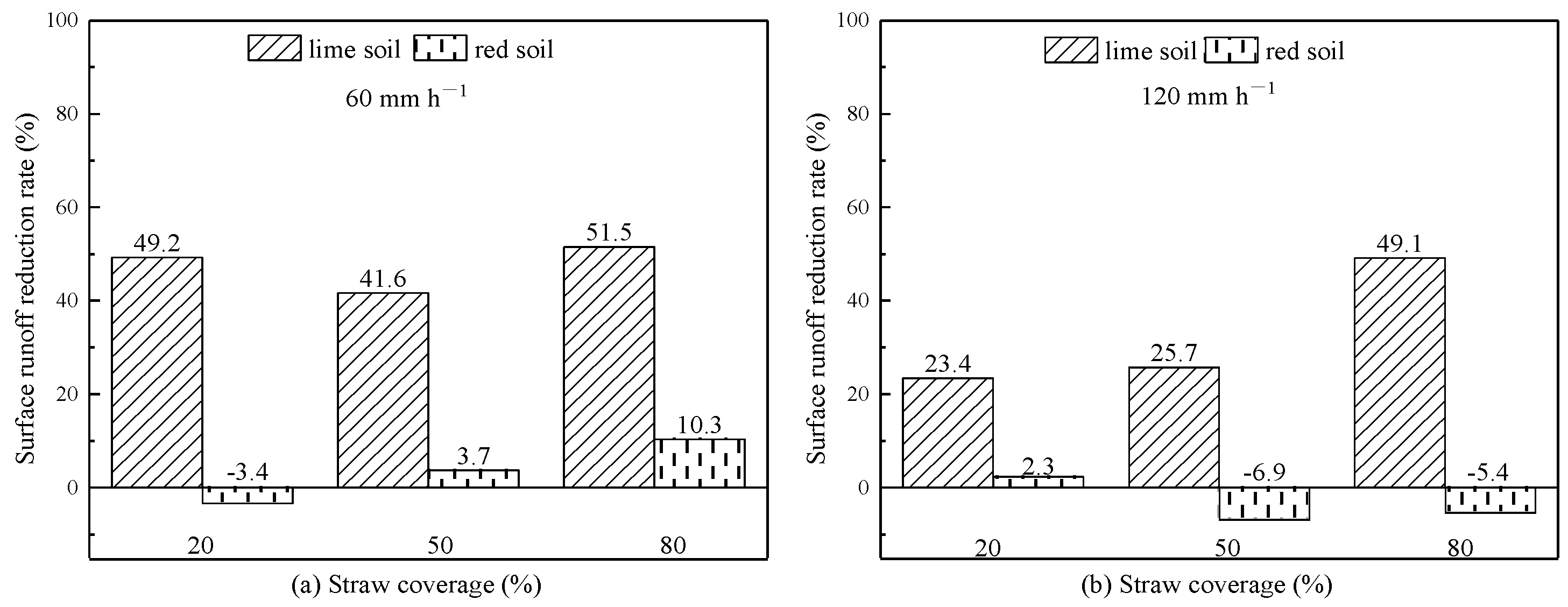
3.1.2. Impact of Straw Covering on Surface Runoff Reduction Rate
3.2. Effects of Straw Mulching on Surface Erosion Reduction
3.2.1. Impact of Straw Cover on Surface Erosion
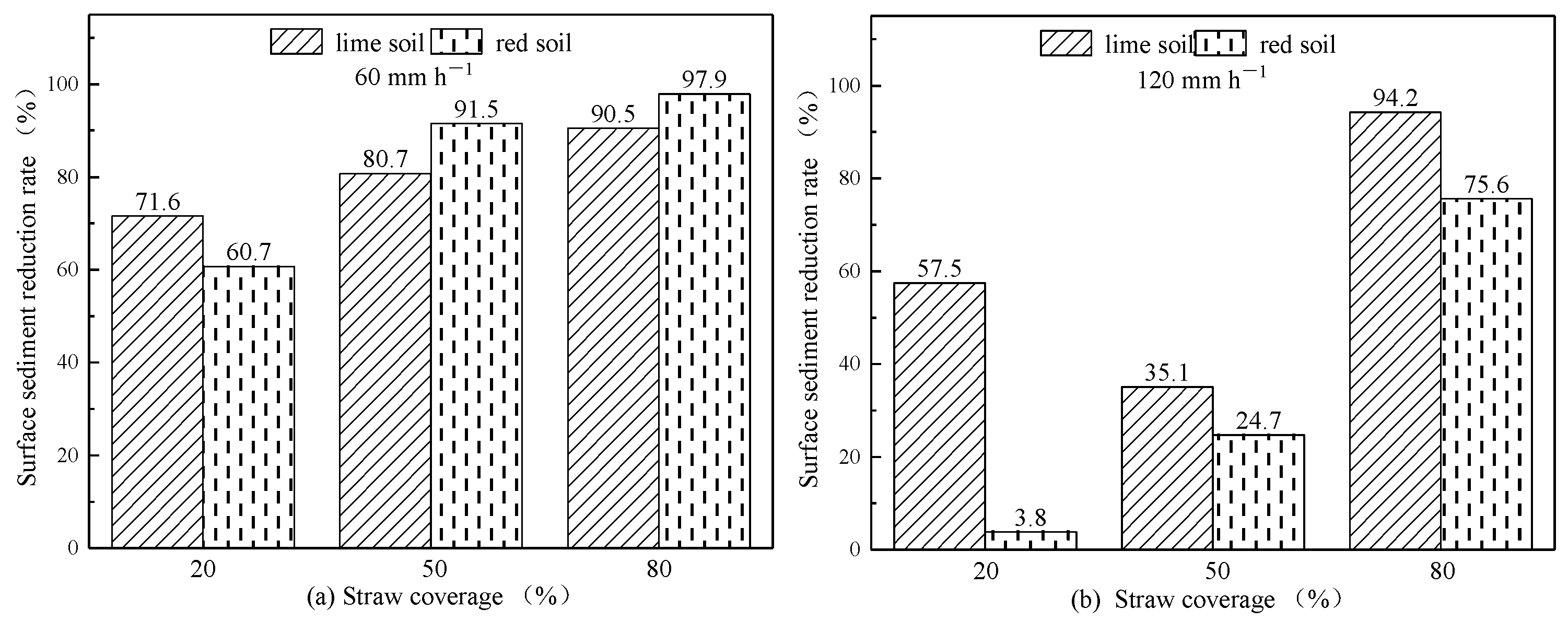
3.2.2. Impact of Straw Coverage on Surface Sediment Reduction Rate
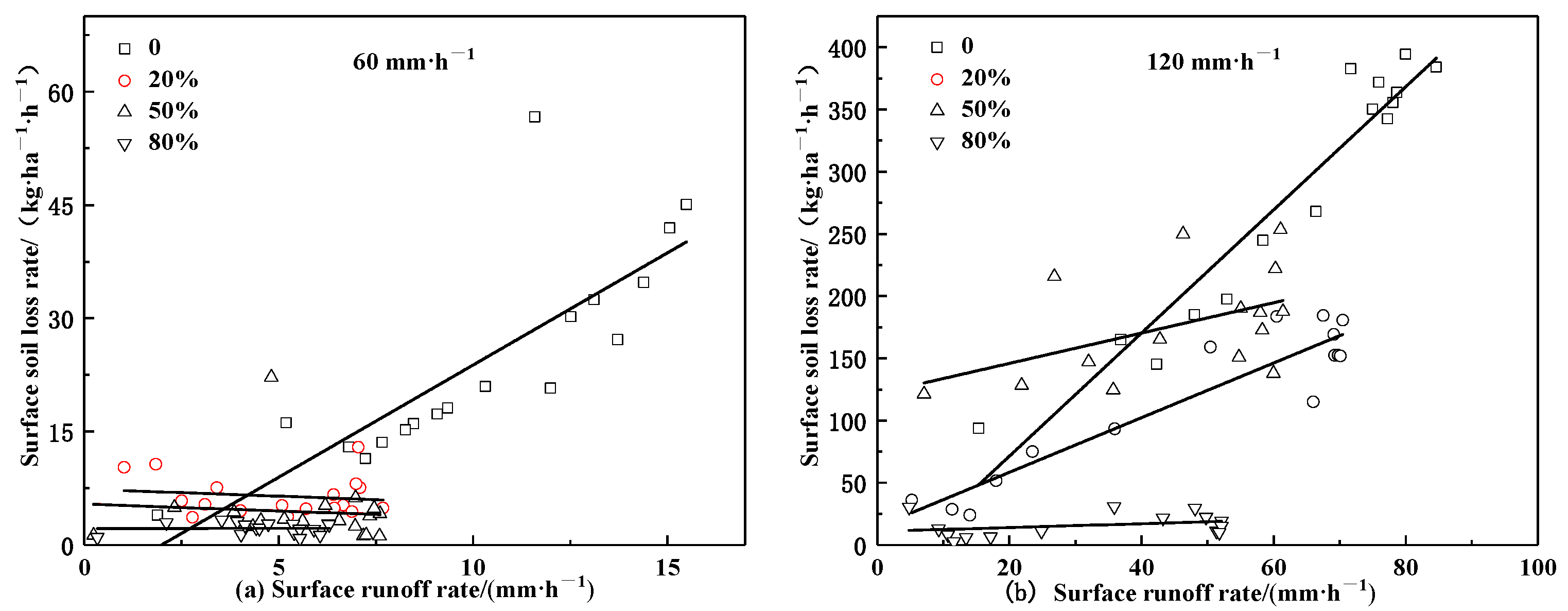
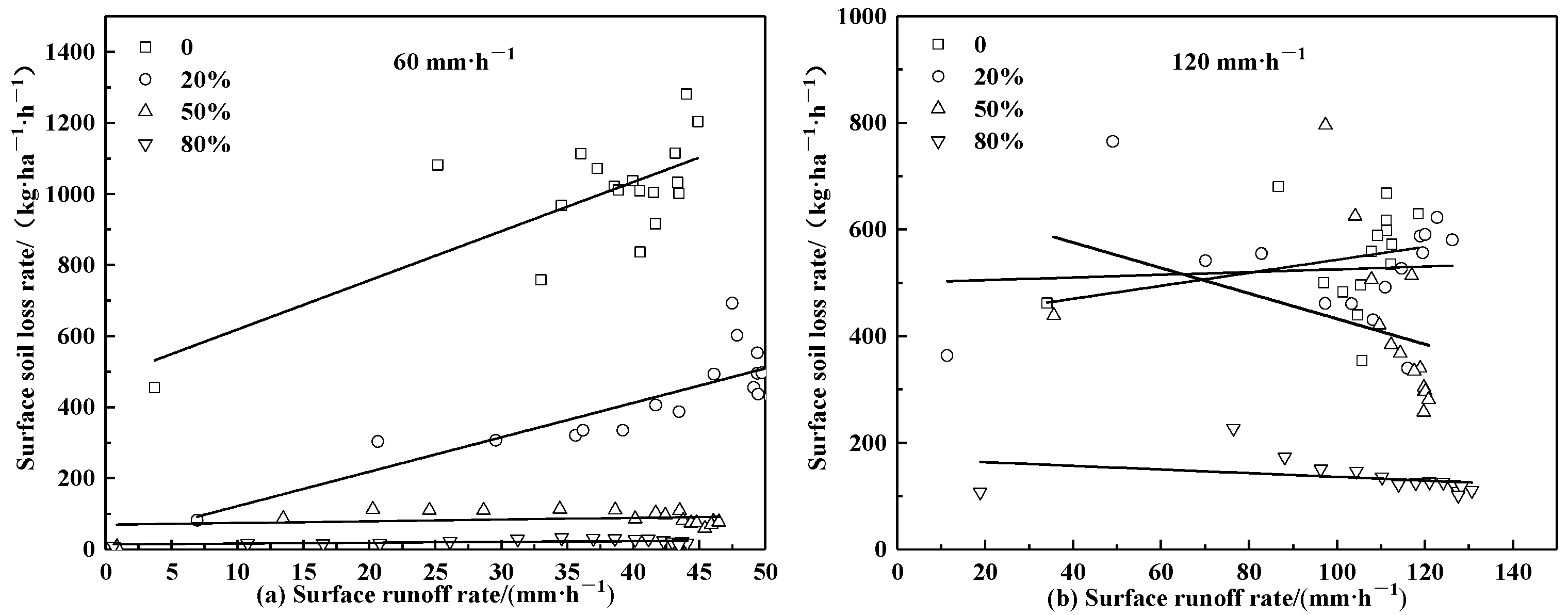
3.2.3. Effects of Straw Mulching on the Sediment Carrying Capacity of Surface Runoff
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, Z.; Lian, Y.; Qin, X. Rocky desertification in Southwest China: Impacts, causes, and restoration. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 132, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Chen, H.S.; Yue, Y.M. Experiment and demonstration on degraded mechanism and its adaptive restoration of karst ecosystems in Northwest Guangxi. Sci. Technol. 2015, 11, 179–183. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Auerswald, K.; Gu, Q.L. Reassessment of the hydrologic soil group for runoff modelling. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 212, 105034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, A.G.; Xie, S.H.; Li, Y.; Nie, X.F.; Mo, M.H. Dynamic Characteristics of Soil and Water Loss Under Long-term Experiment in Citrus Orchard on Red Soil Slope. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 32, 160–165. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cerdà, A.; Morera, A.G.; Merche, B.B. Soil and water losses from new citrus orchards growing on sloped soils in the western Mediterranean basin. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1822–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.E. Influence of Mulches on Runoff, Erosion, and Soil Moisture Depletion1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1966, 30, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasa, J.; Dostal, T.; Jachymova, B.; Bauer, M.; Devaty, J. Soil erosion as a source of sediment and phosphorus in rivers and reservoirs—Watershed analyses using WaTEM/SEDEM. Environ. Res. 2019, 171, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekalu, K.O.; Olorunfemi, I.A.; Osunbitan, J.A. Grass mulching effect on infiltration, surface runoff and soil loss of three agricultural soils in Nigeria. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaud, P.R.; Jordan, P.; Lewis, S.A.; Ashmun, L.E.; Convert, S.A.; Brown, R.E. Evaluating the effectiveness of wood shred and agricultural straw mulches as a treatment to reduce post-wildfire hillslope erosion in southern British Columbia, Canada. Geomorphology 2013, 197, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Keesstra, S.D. An economic, perception and biophysical approach to the use of oat straw as mulch in Mediterranean rainfed agriculture land. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 108, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Zhu, G.; Wei, J.; Jiang, F.; Wang, M.K.; Huang, Y. Mulching effects on erosion from steep slopes and sediment particle size distributions of gully colluvial deposits. Catena 2018, 160, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidvar, E.; Hajizadeh, Z.; Ghasemieh, H. Sediment yield, runoff and hydraulic characteristics in straw and rock fragment covers. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wei, W.; Pan, D.L. Effects of rainfall and terracing-vegetation combinations on water erosion in a loess hilly area, China. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 261, 110247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Liu, Y.F.; Jia, C.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, H.H.; Liu, B.R.; Wang, Z.J.; Zheng, J.Y.; Wu, G.L. Effects of mosaic-pattern shrub patches on runoff and sediment yield in a wind-water erosion crisscross region. Catena 2019, 174, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Unger, P.W. Soil Water Accumulation under Different Precipitation, Potential Evaporation, and Straw Mulch Conditions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes-Silva, A.A.; López-Bernal, A.; Ferreira, T.C.; Villalobos, F.J. Leaf water relations and gas exchange response to water deficit of olive (cv. Cobrançosa) in field grown conditions in Portugal. Plant Soil 2016, 402, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Orenes, F.; Guerrero, C.; Roldán, A.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Cerda, A.; Campoy, M.; Zornoza, R.; Bárcenas, G.; Caravaca, F. Soil microbial biomass and activity under different agricultural management systems in a semiarid Mediterranean agroecosystem. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 109, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Min, Z. Effects of grass vegetation coverage and position on runoff and sediment yields on the slope of Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammeraat, E.L. Scale dependent thresholds in hydrological and erosion response of a semi-arid catchment in southeast Spain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 104, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejman, J.; Iglik, I.; Paluszek, J.; Rodzik, J. Soil redistribution and crop productivity in loess areas (Lublin Upland, Poland). Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 143, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, W.; Li, P.; Shi, P.; Xu, G.; Cheng, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X. Effects of irrigation and fertilization on different potato varieties growth, yield and resources use efficiency in the Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 261, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govers, G.; Loch, R.J. Effects of initial water content and soil mechanical strength on the runoff erosion resistance of clay soils. Soil Res. 1993, 31, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadat, F.M.; Taimeh, A.Y. Effect of rainfall intensity, slope, land use and antecedent soil moisture on soil erosion in an arid environment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Yang, M. Combined influences of wheat~seedling cover and antecedent soil moisture on sheet erosion in small-flumes. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 151, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyal, S.; Pariente, S. Combined effect of rain temperature and antecedent soil moisture on runoff and erosion on Loess. Catena 2017, 158, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Mannering, J.V.; Meyer, L.D. The Effects of Various Rates of Surface Mulch on Infiltration and Erosion1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1963, 27, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHaan, R. Mulching for erosion control. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1970, 34, 928–931. [Google Scholar]
- Poulenard, J.; Podwojewski, P.; Janeau, J.L.; Collinet, J. Runoff and soil erosion under rainfall simulation of Andisols from the Ecuadorian Páramo: Effect of tillage and burning. Catena 2001, 45, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, A.H.; Woods, S.W. Effectiveness of aerial seeding and straw mulch for reducing post-wildfire erosion, north-western Montana, USA. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2008, 17, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Dami, I.; Mathers, H.M.; Dick, W.A.; Doohan, D. The Effect of Straw Mulch on Simulated Simazine Leaching and Runoff. Weed Sci. 2011, 59, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, X.; Yue, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, D. Natural regionalization for rocky desertification treatment in karst peak-cluster depression regions. Acta. Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 5490–5501. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.S.; Feng, T.; Li, C.Z.; Fu, Z.Y.; Lian, J.J.; Wang, K.L. Characteristics of Soil Erosion in the Karst Regions of Southwest China: Research Advance and Prospective. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 32, 10–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.X.; Zhou, Y.C.; Zhou, X.W.; Zhang, C.L. Differentiating Karst Soil and Soil in Karst Region——A Case Study of Houzhai River Watershed in Puding County of Guizhou Province. Soils 2020, 52, 414–420. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Eppes, M.C.; McFadden, L.D.; Matti, J.; Powell, R. Influence of soil development on the geomorphic evolution of landscapes: An example from the Transverse Ranges of California. Geology 2002, 30, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahma, A.E.; Wang, W.; Tang, Z.; Lei, T.; Warrington, D.N.; Zhao, J. Straw mulch can induce greater soil losses from loess slopes than no mulch under extreme rainfall conditions-ScienceDirect. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 232, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somchai, D.; Tawatchai, T. Soil and water conservation on steep slopes by mulching using rice straw and vetiver grass clippings. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2016, 50, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.Q. Influence of Bedrock Ups and Downs and Karst Pipeline Morphology on the Process of Soil Erosion in Karst Area. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.Y.; Chen, H.S.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Q.X.; Wang, S.; Wang, K.L. Subsurface flow in a soil-mantled subtropical dolomite karst slope: A field rainfall simulation study. Geomorphology 2015, 250, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yan, Y. Impact of near-surface hydraulic gradient on the interrill erosion process. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 71, 598–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onofiok, O.; Singer, M.J. Scanning electron microscope studies of surface crusts formed by simulated rainfall. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K. Soil hydraulic properties on the steel karst hillslopes in Northwest Guangdong, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.L.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Tu, A.G. Impacts of Soil Initial Water Content and Bulk Density on Infiltration Law of Red Soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 30, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- McDowell, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N. The effect of antecedent moisture conditions on sediment and phosphorus loss during overland flow: Mahantango Creek catchment, Pennsylvania, USA. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 3037–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ren, H.; Shi, X.; Yu, D.; Wang, H.; Sun, W.; Zhang, L. Effect of straw mulching on sediment yielding process of soil with different initial water contents. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 108–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.S.; Wei, Y.X. Soil and water conservation effects of protective tillage measures on sloping farmlang. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 7, 86–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Q.J.; Dong, W.C.; Zhao, W. Runoff and Sediment Generations and Nutrient Losses Under Different Vegetation Coverage in Loess Slope. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 26, 23–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Miyata, S.; Kosugi, K.; Gomi, T.; Mizuyama, T. Effects of forest floor coverage on overland flow and soil erosion on hillslopes in Japanese cypress plantation forests. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Soil Bulk Density/(g·cm−3) | Clay Content % (0–0.002 mm) | Silt Content % (0.002–0.02 mm) | Sand Content % (0.02–2000 mm) | Organic Matter Content/(g·kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lime soil | 1.22 | 64.29 | 24.63 | 10.71 | 12.06 |
| Red soil | 1.36 | 9.86 | 66.53 | 23.61 | 17.00 |
| Rain Intensity/(mm·h−1) | Coverage/(%) | Red Soil | Lime Soil | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Runoff | Subsurface Flow | Groundwater Flow | Surface Runoff | Subsurface Flow | Groundwater Flow | ||
| 60 | 0 | 0.62 ± 0.01 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 ab | 0.01 ± 0.001 a | 0.17 ± 0.03 a | 0.08 ± 0.02 c | 0.27 ± 0.09 b |
| 20 | 0.64 ± 0.12 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 b | 0.02 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 bc | 0.12 ± 0.03 abc | 0.28 ± 0.05 b | |
| 50 | 0.60 ± 0.06 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 ab | 0.02 ± 0.01 a | 0.09 ± 0.01 b | 0.15 ± 0.01 a | 0.29 ± 0.02 ab | |
| 80 | 0.56 ± 0.06 a | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.01 ± 0.001 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 bc | 0.10 ± 0.01 bc | 0.38 ± 0.005 a | |
| 120 | 0 | 0.43 ± 0.07 a | 0.004 ± 0.001 a | 0.01 ± 0.003 a | 0.26 ± 0.05 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 b | 0.06 ± 0.01 b |
| 20 | 0.41 ± 0.09 a | 0.02 ± 0.003 a | 0.004 ± 0.004 a | 0.19 ± 0.02 b | 0.05 ± 0.004 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 b | |
| 50 | 0.45 ± 0.07 a | 0.004 ± 0.001 a | 0.004 ± 0.002 a | 0.19 ± 0.03 bc | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.09 ± 0.01 b | |
| 80 | 0.45 ± 0.03 a | 0.004 ± 0.001 a | 0.004 ± 0.004 a | 0.13 ± 0.02 c | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.14 ± 0.02 a | |
| Rain Intensity/(mm·h−1) | Soil Type | Straw Coverage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 /(kg·ha−1) | 20% /(kg·ha−1) | 50% /(kg·ha−1) | 80% /(kg·ha−1) | ||
| 60 | Red soil | 1504.6 ± 285.3 a | 591.5 ± 79.7 b | 128.3 ± 71.4 c | 32.2 ± 17.7 c |
| Lime soil | 36.24 ± 13.27 a | 9.69 ± 2.15 b | 6.52 ± 1.27 b | 3.28 ± 0.62 b | |
| 120 | Red soil | 409.1 ± 322.8 a | 393.6 ± 528.8 a | 308.2 ± 60.5 a | 100 ± 42.7 a |
| Lime soil | 212.21 ± 54.69 a | 87.83 ± 11.75 b | 132.67 ± 22.28 b | 11.34 ± 4.88 c | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Xu, Q.; Si, Q.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Z.; Chen, H. Effects of Different Straw Mulch Rates on the Runoff and Sediment Yield of Young Citrus Orchards with Lime Soil and Red Soil under Simulated Rainfall Conditions in Southwest China. Water 2022, 14, 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071119
Gao Z, Xu Q, Si Q, Zhang S, Fu Z, Chen H. Effects of Different Straw Mulch Rates on the Runoff and Sediment Yield of Young Citrus Orchards with Lime Soil and Red Soil under Simulated Rainfall Conditions in Southwest China. Water. 2022; 14(7):1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071119
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Zechao, Qinxue Xu, Qin Si, Shuaipu Zhang, Zhiyong Fu, and Hongsong Chen. 2022. "Effects of Different Straw Mulch Rates on the Runoff and Sediment Yield of Young Citrus Orchards with Lime Soil and Red Soil under Simulated Rainfall Conditions in Southwest China" Water 14, no. 7: 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071119
APA StyleGao, Z., Xu, Q., Si, Q., Zhang, S., Fu, Z., & Chen, H. (2022). Effects of Different Straw Mulch Rates on the Runoff and Sediment Yield of Young Citrus Orchards with Lime Soil and Red Soil under Simulated Rainfall Conditions in Southwest China. Water, 14(7), 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071119






