Abstract
This paper analyses complex hydrological and hydrogeological properties of a deep karstic lake and its surroundings. Red Lake (Croatia) is a cryptodepression in the karst massif rich in well-developed extreme surface karst forms and underground conduit system. It is interconnected with other close water bodies and offers information on groundwater movement and characteristics. The article analyses hourly data on precipitation and water levels in Red Lake and compares them with data on discharges from near Opačac Spring for a period of five years. Data gaps in the record caused by operational interruptions of the measuring equipment were compensated by the use of neural networks. The study of the hydrodynamics of karst surroundings under recession was conducted by observing the receding water levels and corresponding lake’s volumetry. By isolating recession periods from the record of integral water volume change, some of the common techniques in recession analysis were performed aiming to acquire new knowledge on the hydrogeological regime of the karst system at the field scale. Additionally, spectral analysis was used as another tool of karst system characterisation since it enables the signal decomposition in the frequency domain and detection of dominant flow processes.
1. Introduction
The dynamics of water in karst, a specific area with the circulation of surface and groundwater and with an abundance of different landforms, is extremely complex and dependent on various mechanisms and parameters. The availability of water in karst as a heterogeneous spatial medium depends on land cover, the vegetation of the catchment area, the degree of karstification, and the development of karst processes [1], but also external factors-precipitation, alternation of dry and rainy seasons, humidity, temperature, and other climatic parameters. In addition, the karst aquifer is highly vulnerable to pollution and saltwater intrusion, resulting in groundwater quality degradation. The era of climate change, increasing temperatures, decreasing precipitation and groundwater levels, water salinization, and the simultaneous increase in water demand are putting pressure on karst groundwater resources. According to Stevanović [2], up to 9.2% of the world’s population are consumers of karst water, which further raises the issue of water availability in karst. Several authors address the current problem of water availability in karst areas. Thus, Bonacci [3] analyzed a karst feature on the island of Cres, which is affected by water reduction and salinization. Both Ožanić and Rubinić [4] researched the same karst area, emphasizing the importance of monitoring various parameters in order to gain and maintain new knowledge and protect the area. Thus, the objective of this work is to learn more about the dynamics of karst water in Red Lake and the wider area, which is not free of negative impacts on karst aquifers, and to define the prevailing hydrologic regime. Accordingly, in the future, it is possible to apply appropriate measures for the sustainability and protection of water resources in the area.
Red Lake, as one of the most impressive karst features of the Dinaric Karst, is located near the town of Imotski. Its impressiveness stems from its extreme dimensions and topography, which make it one of the deepest karst features in the world [5]. The deepest point measured is 6 m below sea level or a total depth of 528.9 m [5]. Due to the exceptional depth and location in an inaccessible area with steep slopes around the lake, access to the lake is difficult and requires the use of special equipment and higher financial resources. This proves the lack of measurement and scientific papers on Red Lake.
Most of the available literature deals with defining Red Lake and its origin. Thus, the research of Gavazzi [6] and Cvijić [7] from the beginning of the 20th century states that Red Lake and the adjacent Blue Lake were formed by the collapse of the cave ceiling [8]. Roglić [9], on the other hand, defines them as cylindrically shaped dolines in which the hydrological regimes are separated and considers Red Lake as a younger doline [10]. Based on research conducted between 1955 and 1958, Petrik [11] also defines Red Lake as a younger doline of all karst features in the area [10]. He emphasises the common origin of the waters of Red and Blue Lake. According to Petrik, the different fluctuations of the water level in lakes are related to the unequal capacity of karst conduits [12]. A different view of the origin of the lakes is held by Milanović [13] and Bahun [14]. Milanović believes that lakes were formed by chemical action on the limestone, while Bahun considers Red Lake as a deep pit and Blue Lake as a sinkhole, both formed by the collapse of existing sinkholes after the Miocene Lake dried up [10,15].
Recent research in the 21st century brings new assumptions and new insights. Thus, Bonacci and Roje-Bonacci [16] describe Red and Blue Lake as natural piezometers connected to the main karst conduit, with Red having a direct connection and Blue having an indirect connection. Since both lakes show similar behaviour, the authors assign them to the same karst aquifer. An expedition led by M. Garašić [5] determined the elevation of the lake bottom of −6 m a.s.l. and the dimensions of the lake bottom and surface. The same author claimed the possible existence of a cave channel and a groundwater stream at the bottom of the lake. Using technologies based on LIDAR and hydroacoustics, Andrić et al. [15,17,18] have determined a computer model of the geometry of Red Lake and the strength of the return echo at different elevations. Furthermore, using the lake’s geometry model, volumetry data was derived, consequently a reliable volume curve as a function of the lake’s water level.
Despite numerous geological, hydrogeological and hydrological studies, due to the extremely complex system of surface and groundwater circulation in karst, both the catchment boundaries and the directions of groundwater circulation are unknown [15,16]. To better understand the hydrological regime of Red Lake, an analysis of the quasi-recession curves and the corresponding envelope or master recession curve (MRC) was performed in this paper. It is an alternative method to well-established geophysical methods, proven as a reliable tool for characterizing the hydrogeological regime and geometry of karstic aquifers using magnetic resonance sounding (MRS) and electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) [19]. The use of recession analysis allows the determination of aquifer characteristics, storage properties and capacity, and the effects of various factors on the runoff process [20]. It also highlights the distinction of the two flow characteristics, involving base flow through the fissured matrix, and the quick flow through the conduit system [21]. In addition, spectral analysis or frequency domain analysis has been used to observe the periodicity of signals, interdependence, and time delay between signals. Spectral analysis was performed using precipitation data from the Imotski gauging station in combination with the integral water quantities of Red Lake and discharges from the Opačac Spring. The interrelation and dependence between Red Lake and Opačac Spring were determined by the spectral analysis of the integral water quantities of Red Lake and the discharges of Opačac Spring.
2. Study Area
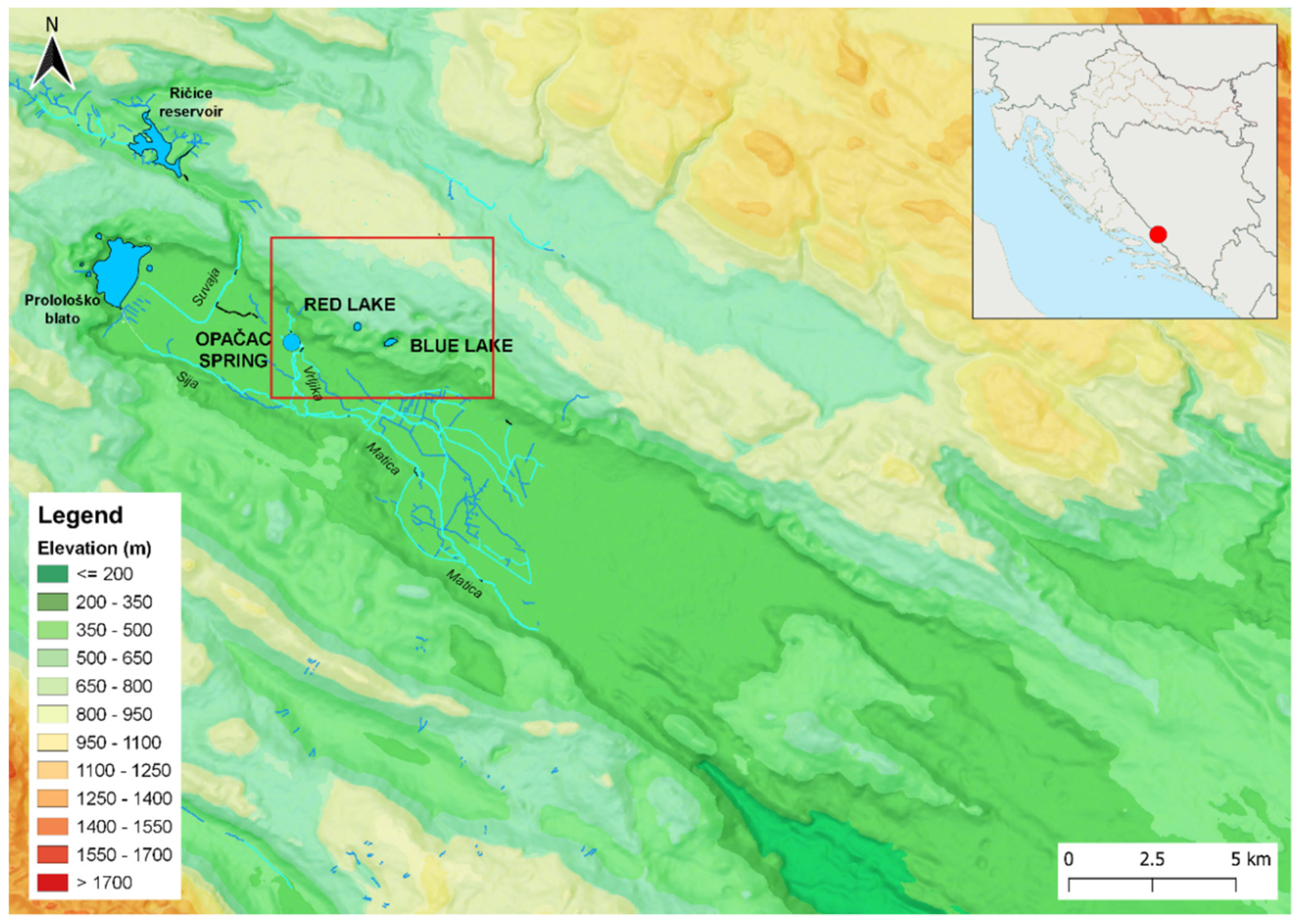
Red Lake is located near the town of Imotski (Croatia) in the central part of the Dinaric Karst, or more precisely, in the northeastern higher part of Imotsko Polje (Figure 1). Imotsko polje is an example of polje in karst, defined by Bonacci as “depressions in the limestone karst, generally elliptical with relatively gently sloping bottoms from the spring zone to the swallowhole zone” [1]. The best-known phenomena are the Blue and Red Lakes, although there are up to 18 similar karst forms in the same area, dry or permanently filled with water [5]. The most important spring is Opačac, which serves as a water supply of the Imotski region.
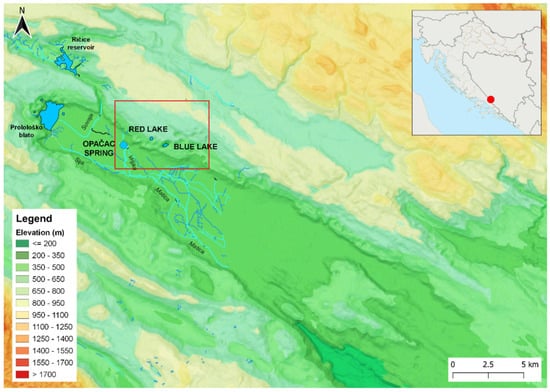
Figure 1.
Hypsometric map of the study area with its surroundings.
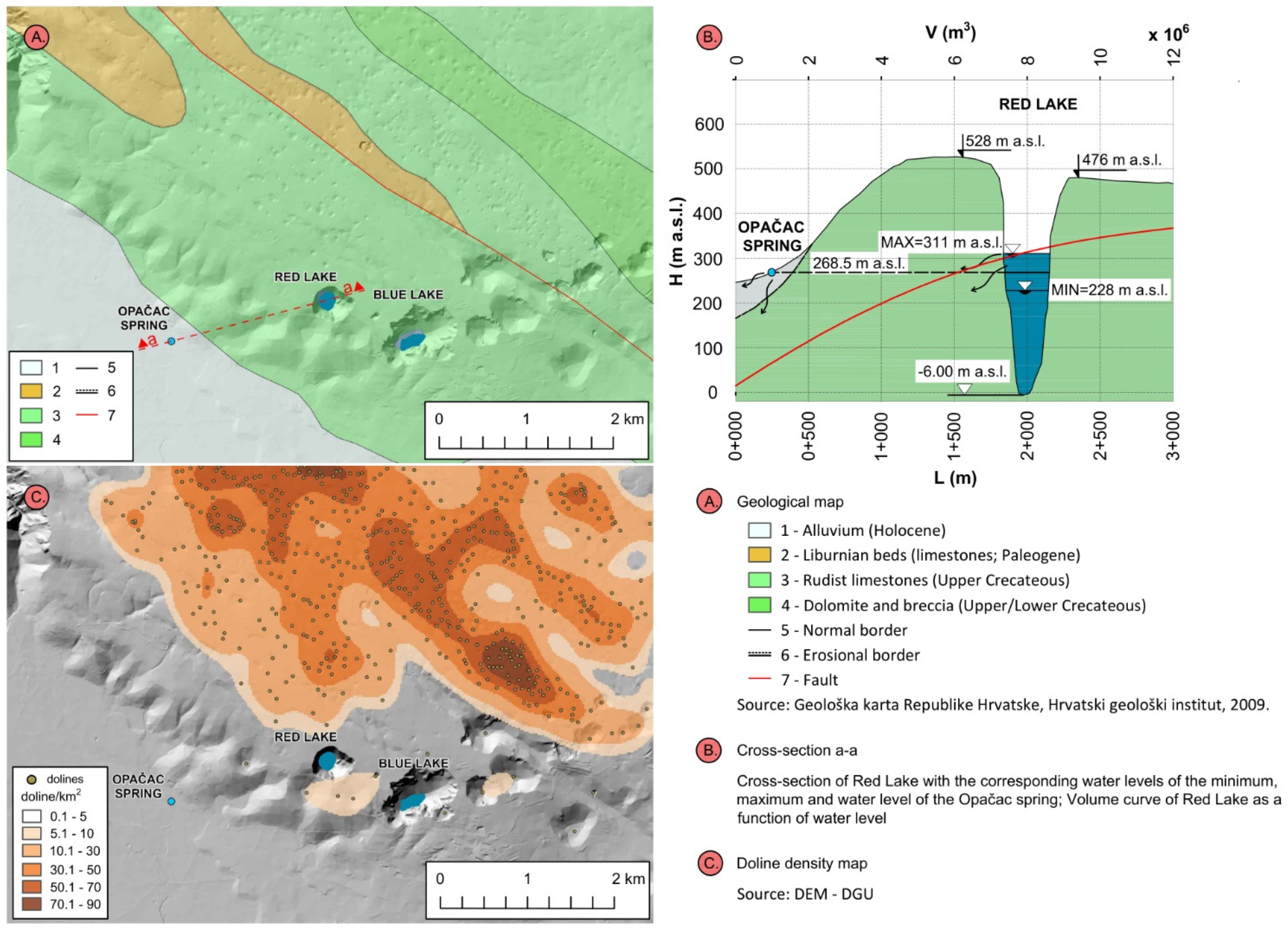
The hydrogeological characteristics of the study area are influenced by the geological composition, structures, and geomorphological development (Figure 2). The area can be divided into two main geomorphological units: (1) higher NE karst plateau in the hinterland of Red and Blue Lake and (2) negative morphostructural unit of Imotsko polje [22]. The NE karst plateau consists of carbonate rocks, mainly Upper Cretaceous limestone, partially Cretaceous dolomite, and Eocene limestone. Carbonate rocks are highly karstified and without any surface streams, clearly indicating diffuse infiltration of precipitation feeding karst aquifer. This large karst plateau has less pronounced morpholineaments of Dinaric and NE–SW direction and numerous karst phenomena. The Dinaric orientation is determined by geological structures and is clearly detectible by the spatial distribution of hypsometrical belts and morphometric indicators such as relative relief in the form of parallel belts. The linear extension and change in the width of these belts indicate a change in the stages in the relief evolution. The morpholineaments are in close relation with the high seismicity connected with the displacements of the Adriatic microplate [23]. Using 5 × 5 m DEM, at the plateau area of 27 km2, there are 601 dolines identified, with an average density of 22 dolines/km2. According to Pahernik [24], who determined doline density for Croatia, this is a low-density value. The area NE of Imotski (Rudine) is an area of high density (70–90 dolines/km2) with a high impact of precipitation infiltration and importance for karst water quality. The most spacious surface karst features are collapsed dolines with Red Lake and Blue Lake as the largest ones. According to the topo map and Croatian Cave Cadastre [25], there is known 15 caves, mostly vertical shafts (up to 100 m deep) in the vadose zone. The Polje has a flat bottom filled and flattened by younger, mostly Holocene, deposits (alluvium, marl, sand, and clay) [12,15] with prevalent fluvio-accumulational and fluvio-denudational relief forms. The Polje is important as a local base level with the occurrence of springs at the contact along the base of the karst plateau with Opačac Spring as one of the biggest springs.
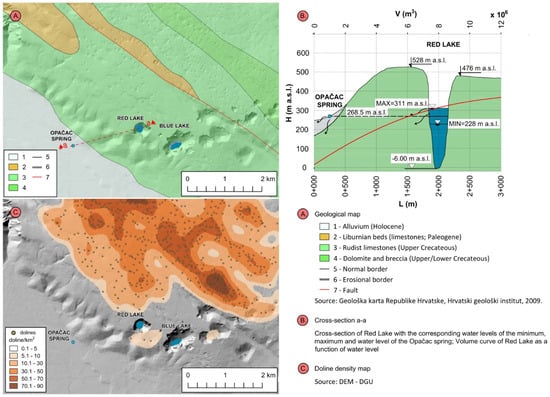
Figure 2.
Geological map of the study area (A), the cross-section a-a combined with the volume curve of Red Lake as a function of water level (B) and doline density map (C).
The study area is characterized by a Mediterranean climate with the influence of continental climate. According to the Köppen-Geiger [26] climate classification, it belongs to class Cfb, defined as a temperate humid climate with warm summer. The average annual temperature ranges between 12 °C and 14 °C, while the annual rainfall ranges between 750 and 2350 mm, with an average of about 1500 mm [15,27]. The maximum rainfall occurs in the colder season, in October and November, while minimum rainfall occurs in July and August. This phenomenon is characteristic of the maritime precipitation regime.
The natural and semi-natural landscape is prevailing within the study area, which is generally a favourable status for groundwater quality due to the predominance of autogenous karst infiltration. The area of Red and Blue Lakes is characterized by a mosaic landscape where most environmental pressure originates from the urban area of Imotski and nearby arable lands. The Imotsko polje is characterized by a cultivated landscape with a predominance of arable land, which, depending on the intensity of anthropogenic influences, can negatively affect the quality of groundwater and surface water. Increased water use for the needs of the population, growing tourism and agriculture in the light of climate change can also have a negative impact on surface and groundwater bodies.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Used
In this article, data on the daily water level of Red Lake are analysed together with data on precipitation observed at the Imotski State Hydrometeorological Institute (DHMZ) measuring station from 28 September 2013 to 20 March 2019. In order to compare the regime of hydrological functioning of the Red Lake and the Opačac system, data on discharges from the Opačac Spring are also included in the analysis.
The new variable, integral volume change (IVC), was defined as the daily volume change of the lake in order to better observe the oscillations and functioning of the lake and compare it with the discharges at Opačac. Therefore, the corresponding values of volume change for each water level were calculated using the existing morphometric model of Red Lake (Figure 1). The morphometric model defining the volume curve as a function of water level was established on extensive research by Andrić and Bonacci [15,18].
Due to technical difficulties in measurement, a complete data set is not available, so the missing data were replaced by using neural networks. Neural networks are a model of artificial intelligence based on a set of interconnected data that model the neurons in the biological brain. In this paper, a dynamic nonlinear neural network model was used because the value of the output variable at a given time depends on the input/output values in previous time periods [28]. The output values are predicted based on the connection between input and output values. The dynamic nonlinear model is defined as follows:
where f is a nonlinear function, u(t) values of input variables and y(t) values of output variables [28].
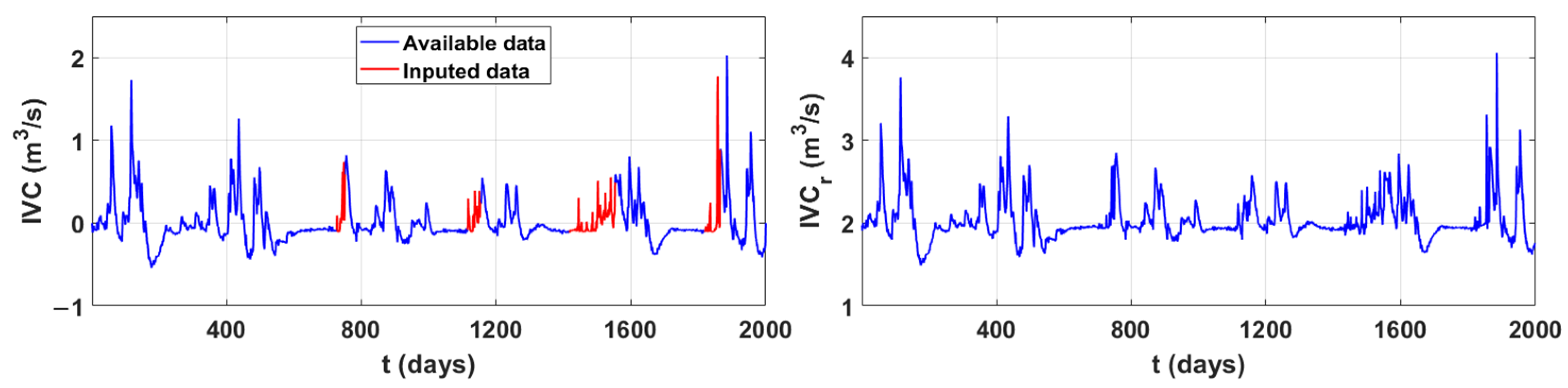
The input data for predicting the values of integral volume change are: air temperature, relative humidity and precipitation measured at the Imotski monitoring station. Since the chosen dynamic nonlinear model is a multilayer network, it contains hidden layers of neurons in addition to the layer with input and output values. The chosen number of hidden layers is 10. Since most physical and biological processes involve delays, the time delay is also included in the calculation [29]. Training of the neural network was carried out with the first 727 values, validation with the next 388 values, and testing with the next 885 values out of a total of 2000. Training of the data was carried out using Bayesian regularisation, a mathematical method for solving problems in domains where limited data is available. The method is based on Bayes’ conditional probability theorem [30]. All of these steps were performed using the MATLAB software package (version R2021a (9.10)). The results of applying the neural network to the integral volume change of the lake are shown in Figure 3.
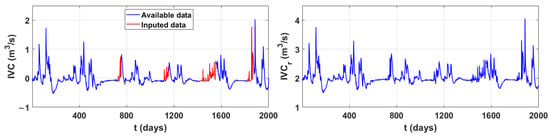
Figure 3.
Integral volume changes of Red Lake with imputed missing values obtained using neural networks. The transformed values of the integral volume changes.
To avoid negative values of the integral volume changes in recession analysis, the transformation of the obtained data was performed by adding the maximum of the calculated quantities to each of the values (IVCr). The transformed values of integral volume changes are shown in Figure 3.
3.2. Method Used
3.2.1. Recession Curve Analysis
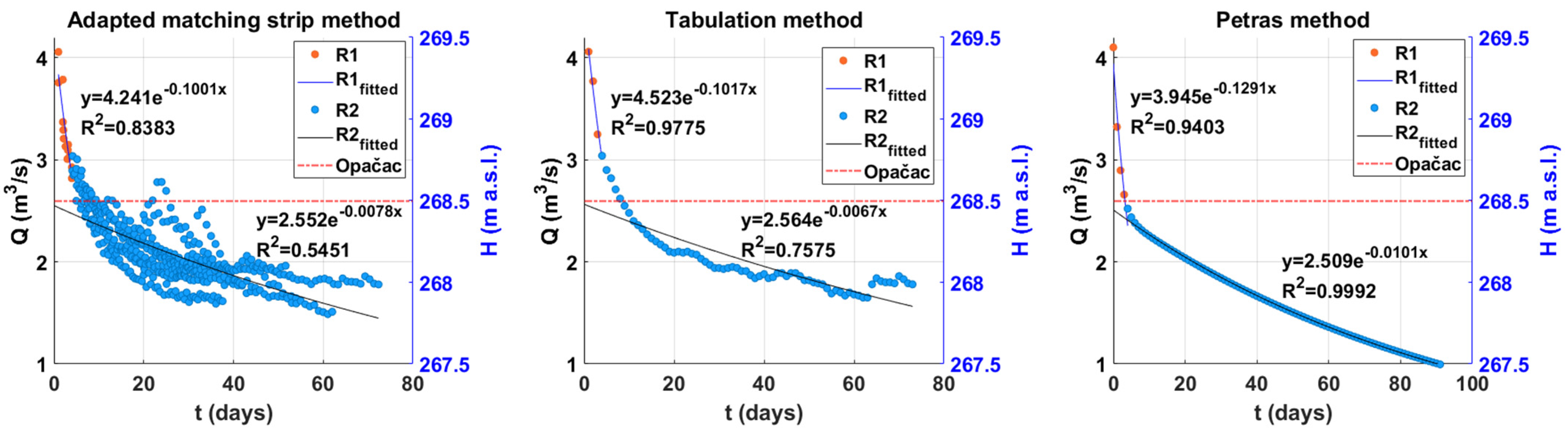
The aquifer system was identified by analysing the recession segments of the integral volume changes of Red Lake. The segment of the hydrograph showing the gradual decrease in a runoff with little or no precipitation is called the recession curve. Each recession period is a short-term event with specific characteristics that depend on the variability of water storage, the rate of depletion of underground reserves, losses, and also on aquifer characteristics [31,32]. Moreover, the variability of each recession period is also due to the different spatial distribution of precipitation and climatic conditions. In order to determine the characteristics of the recession periods, it is necessary to minimize the variability of the individual recession periods by averaging them, for the reasons stated above. The data are averaged by creating an envelope of individual recession segments, the master recession curve (MRC). The MRC provides information on the average characteristics of the runoff components, i.e., the hydrologic function of the lake and the surrounding area. The methods used in constructing the master recession curve include the adapted matching strip method, the tabulation method, and the Petras method.
The simplest method is the tabulation method. The starting value of MRC in the tabulation method is the highest starting value of all the recession segments. The other segments are sorted from higher to lower and arranged in columns until they match horizontally [33,34]. The final values of MRC are the averaged values of all recession segments.
In the matching strip method, all recession segments are plotted, superimposed, and horizontally adjusted until a composite curve is obtained—MRC [31]. When we consider a large number of recession segments, this method is impractical, so the adapted matching strip method is used [35,36]. The first step in this method is to sort the recession segments from highest to lowest. The first recession segment, the segment with the highest initial value, is tested with different regression models (linear, logarithmic, second-order polynomial, power and exponential). The model that best fits the observed recession segment is the model with the highest coefficient of determination (R2). The second recession segment, the one with the second-highest initial value, is translated to its proper position according to the corresponding time shift. The next step is to test the composite curve of the first and second recession segments with regression models. The most appropriate regression model is selected and the next recession segment is translated to the corresponding position on the previously defined curve. The procedure is repeated for all recession segments and the result is MRC.
According to Petras [37], each recession curve can be divided into segments and modelled with Maillet’s equation. In this way, each segment is defined with the initial discharge Q0 and the recession coefficient α:
The representation of Maillet’s equation on the semi-logarithmic paper is the straight line. The same equation can be expressed as follows:
The procedure consists of approximating an empirical curve by a straight line. The slope of the straight line is α1, and the intersection with the y-axis is Q01. By subtracting the remaining values of the empirical curve from the values of the straight line, the empirical values of the second segment are obtained. Then, the second segment is approximated by the straight line with slope α2 and y-axis intercept Q02. The procedure is repeated for n segments of the recession curve, which are merged into a single curve according to the principle of superposition:
Since this study involves a lake and not a stream, it is necessary to clarify some of the terms used in the recession analysis as a basis for considering periods of no precipitation. First, the representation of the movement of the integral volume changes cannot be called a hydrograph because these quantities include the input and output volumes of water to the lake. The same applies to recession curves, which in this case reflect oscillations in the movement of water volumes during the non-precipitation period and are called quasi-recession curves. Accordingly, the recession coefficients that define the nature of the depletion of water supplies are called quasi-recession coefficients. To obtain quasi-recession curves with corresponding quasi-recession coefficients, the recession periods of the hourly water volume change of the lake were isolated, normalized, and log-transformed.
3.2.2. Correlation and Spectral Analysis
Correlation quantifies the linear dependence of time series. The autocorrelation function measures the correlation of two observed series with different time lags and indicates the similarity of the observed data series with the same lagged series. Below is a brief overview of the autocorrelation function with the corresponding expressions [38,39,40].
where C (k) is the autocovariance and σ is the standard deviation.
According to Denić-Jukić et al. [38], the truncation point m represents the domain of the function or the range of the time interval in which the analysis is performed. The recommendation is that the value of the variable m does not exceed the value of n/3, because for values in the range between n/3 and n/2 the results start to change, while after n/2 they are no longer accurate [40].
The observation of how much resemblance exists between two different time series is obtained from the cross-correlation function. The cross-correlation function (CCF) between two time series is defined as follows:
where Cxy and Cyx are covariances and σx and σy are the standard deviations of the two observed series [38,39,41]. Spectral analysis, unlike correlation analysis, analyses signals in the frequency domain. Therefore, the spectral density function represents a Fourier transform of the autocorrelation function. Both functions describe a stationary stochastic process containing the same information but in a different domain. The identification of periodic phenomena, expressed in terms of the detection of different peaks, is defined by the spectral density function as follows [38,39]:
for frequencies f = l/2 m, l = 0, 1, 2, …, m.
The cross-spectral density function defines the relationship between two signals in the frequency domain, as opposed to the cross-correlation function, which defines the relationship in the time domain. The Fourier cross-spectral density function is a transformation of the cross-correlation function [41]. It is represented as a function of the quadrature spectrum ψxy (f) and the co-spectrum Λxy (f) [39,41].
The coherence function COxy and the gain function Gxy may be defined using the known values of the spectral density functions Sx and Sy, as well as the cross-spectral density function Sxy [42]:
The coherence function, COxy, expresses the linearity of the input–output relationship between signals. It ranges from 0 to 1, with 0 denoting no correlation and 1 denoting the strongest correlation between two signals at frequency f. The gain function represents the output signal’s amplification (>1) or attenuation (<1) in contrast to the input signal.
When considering the cross-spectral density function Sxy as a complex number, the amplitude αxy and phase ϕxy functions may be constructed using the complex number’s trigonometric form.
The amplitude function, according to Larocque [39], identifies the manner the system has changed the input signal. The phase function depicts the time difference between the signals that have been processed.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Lake’s Dynamics and Recession Periods
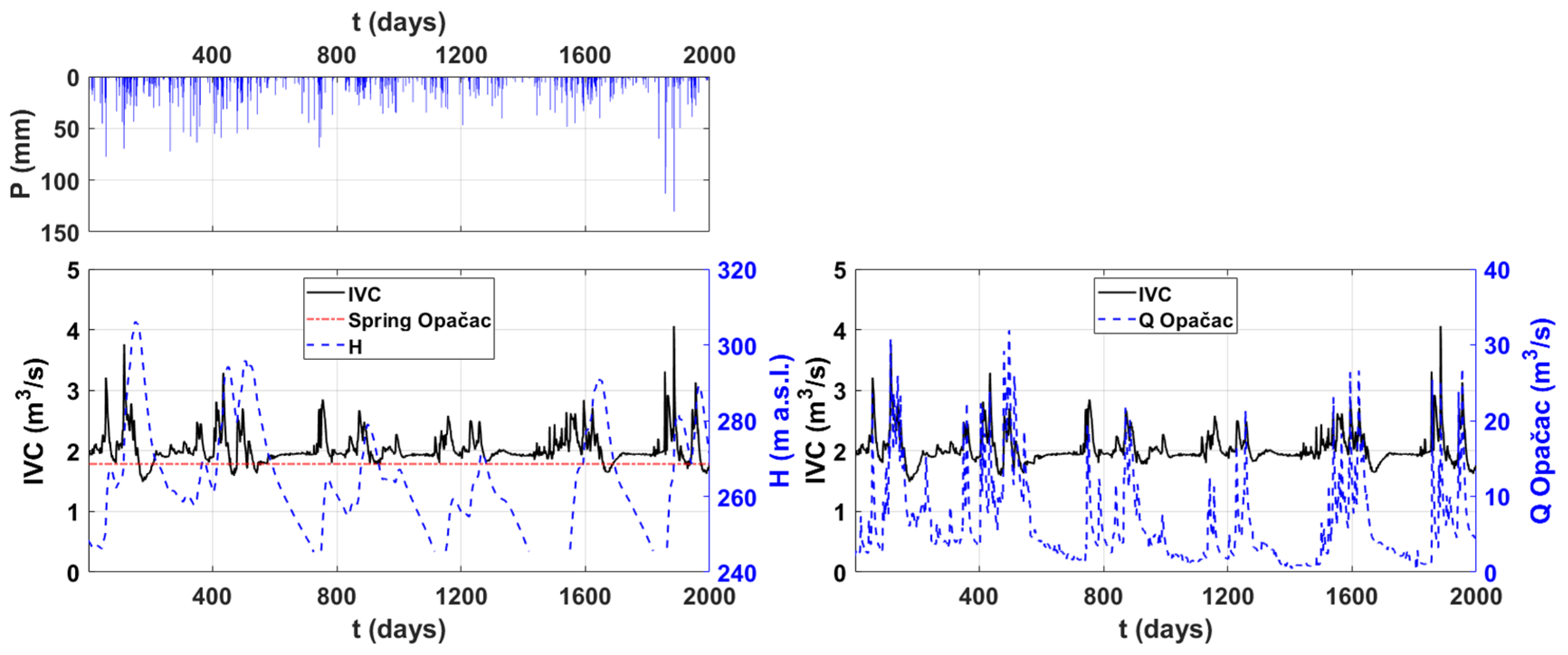
The data on the lake’s water level, as well as the amount of precipitation observed at the Imotski gauging station and the computed integral volume changes (IVC) in the lake, are shown in Figure 4. The integral volume changes in Red Lake were also compared to the discharges from Opačac Spring. The occurrence of peaks in integral volume changes was compared with the quantity of precipitation. Short-term precipitation, regardless of intensity, has been found to have no major impact on integral volume changes as compared to long-term precipitation, which accumulates more water. As an example, rainfall of 72.5 mm on the 264th day of observation did not result in a substantial change in both the integral volume change and the water level in the lake. While precipitation from the 110th to the 160th day, during which the longest period without precipitation was only four days, replenished subsurface reserves and caused the second-highest peak in integral volume changes. Underground reserves, which are dependent on the size and number of karst conduits, pores, and fractures, have a substantial impact on integral volume changes variations. When the underground reserves are replenished, the integral change in volume reaches its maximum, after which direct runoff is activated during the no precipitation period.
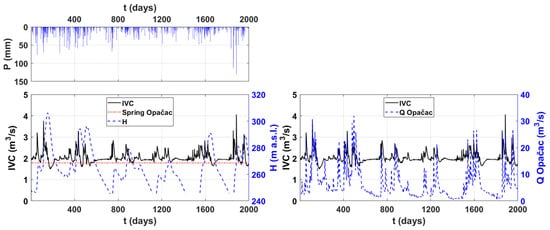
Figure 4.
Comparison of precipitation at the Imotski gauging station with Red Lake integral volume changes (IVC), related water levels (H), and Opačac Spring discharges.
The water level in the lake oscillates in response to the precipitation’s temporal distribution (Figure 4). A shift in the slope of the water level (H) is detected in Red Lake at a water level of 268.5 m above sea level, which corresponds to the height of Opačac Spring. For water levels below 268.5 m a.s.l, the discontinuity reveals a slower fall in the water level, reflecting a slower depletion of water supplies. Above 268.5 m a.s.l., there are a greater number of peaks and they are more significant. Quantities above this value cause the lake to fill more quickly, but they also cause the lake to discharge once it reaches the critical level of 268.5 m a.s.l. This phenomenon could be explained by the existence of a karst conduit connecting Red Lake and the spring of Opačac. Therefore, a comparison was made between the integral volume changes and discharges at Opačac, which is shown in Figure 4. Between those quantities can be seen the coincidence among peaks and recession periods. During recession periods, comparable values can be seen, followed by the filling of Red Lake when the discharge of the Opačac increases. To better explain the interaction between these two systems, the results of recession and spectral analysis are given below.
Analysis of the quasi-recession curves using three approaches yielded a composite curve and average values of the quasi-recession coefficients (Figure 5). The composite curve is divided into two sections: the steeper section reflects the quick runoff of water reserves, while the gentler section represents the slow baseflow. The quasi-recession coefficients differ in the same way: α1 denotes quick emptying of channels and cracks in karst and a more permeable aquifer, whereas α2 denotes slower emptying of subsurface reserves. As a result, recession coefficients are used to describe the predominant flow mechanisms in the karst aquifer. The average value of the quasi-recession coefficient α1 is 0.1103, while α2 is 0.082. A shift in the slope of the master recession curve indicates a change in the value of quasi-recession coefficients. Looking at the quasi-recession coefficients, the dominance of base flow over direct flow is undeniable. This can be explained by the dominance of the rock matrix in the karst, which causes slow drainage of water from smaller pores and cracks. It is obvious that groundwater plays an important role in the formation of integral volume changes in Red Lake, which is why the lake never dries up. As previously stated, the shift in the quasi-recession coefficient occurs around the level of Opačac Spring. To better understand the functioning of the lake, but also its connection with the spring, the signals were analysed in the time and frequency domain.
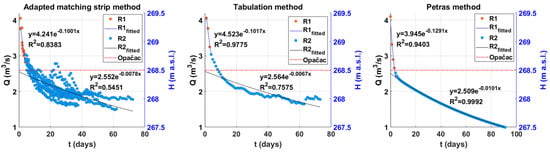
Figure 5.
Master recession curve obtained by Adapted matching strip method, Tabulation and Petras method.
4.2. Analysis in Spatial and Frequency Domain
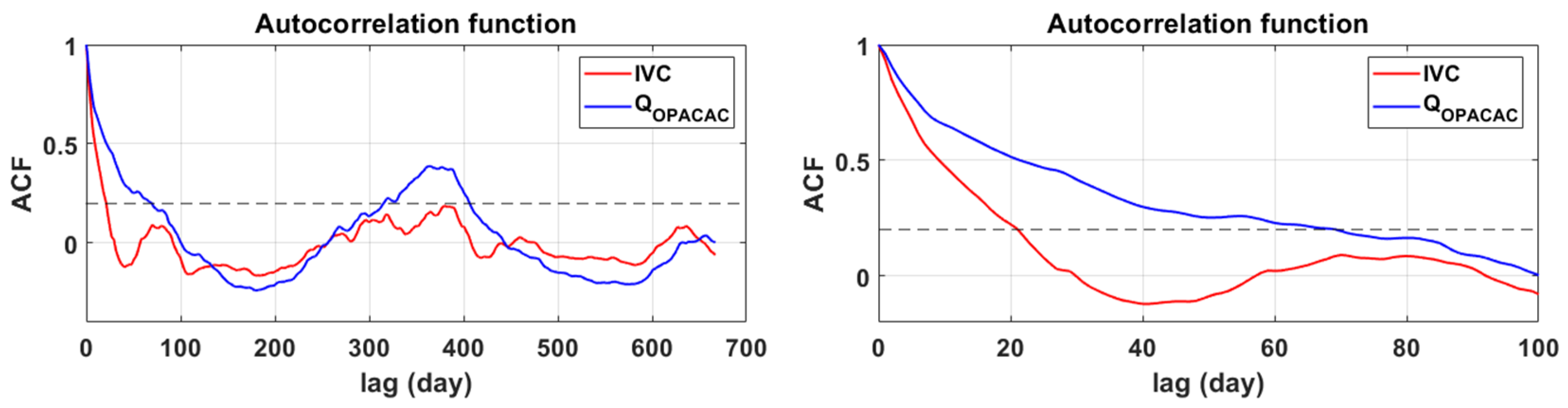
The correlation analysis was used to determine the autocorrelation function for integral volume changes in Red Lake and discharges at Opačac Spring, as well as the cross-correlation function between these two data and the cross-correlation function of precipitation with integral volumes and discharges in Opačac. The autocorrelation function can be used to quantify the memory effect of the system, which is measured by the time delay at which the autocorrelation function reaches 0.2 [40,41]. The memory effect shows how water is stored, namely by filling and emptying subsurface reserves. Figure 6 depicts the 21-day memory effect for Red Lake and the 69-day memory effect for Opačac Spring. As a result, the Opačac hydrogeological system is far more inert than the Red Lake system, where water retention in the karst network is significantly shorter than at Opačac.
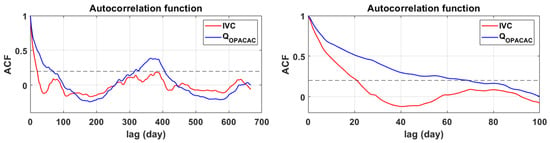
Figure 6.
Autocorrelograms of integral volume changes of Red Lake and discharges on Opačac Spring.
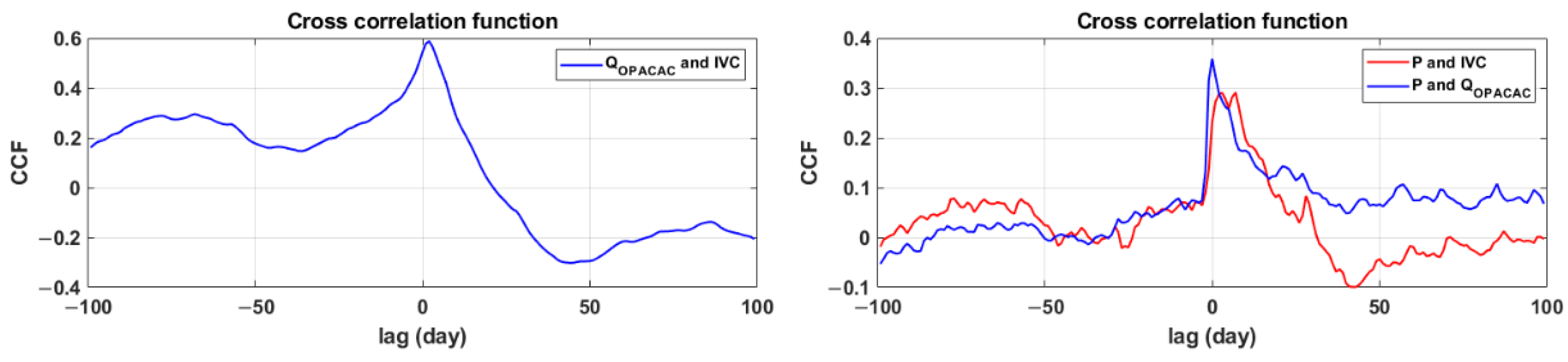
The cross-correlation function accepts values ranging from −1 to 1, with 1 denoting a high correlation between the two observed series and −1 denoting a negative or inverse correlation, which means the variables move in opposing directions. Uncorrelated series have correlation values close to zero. With a lag of 100 days, the values of the cross-correlation function of integral volume changes and discharges at Opačac reveal a moderate connection between the two systems (Figure 7). The asymmetry of the function and the statistically significant value of the cross-correlation function with a lag of 3 days suggest the system’s correlation, while the value of the cross-correlation function diminishes for a longer number of days. Cross-correlation analysis also shows the response of the Opačac and Red Lake systems to precipitation. The Opačac system reaches the highest value for lag = 0, which means that it responds to precipitation without a time lag, unlike Red Lake, which responds to precipitation after 7 days. The values of the cross-correlation function are more significant in the Opačac system than in Red Lake, indicating that Red Lake is fed by groundwater and to a lesser extent by precipitation. Both systems show a similar trend in the cross-correlation function, suggesting their correlation.
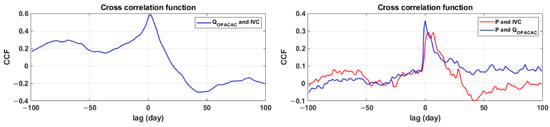
Figure 7.
Cross correlation functions of discharges at Opačac Spring with integral volume changes in Red Lake and their combination with precipitation.
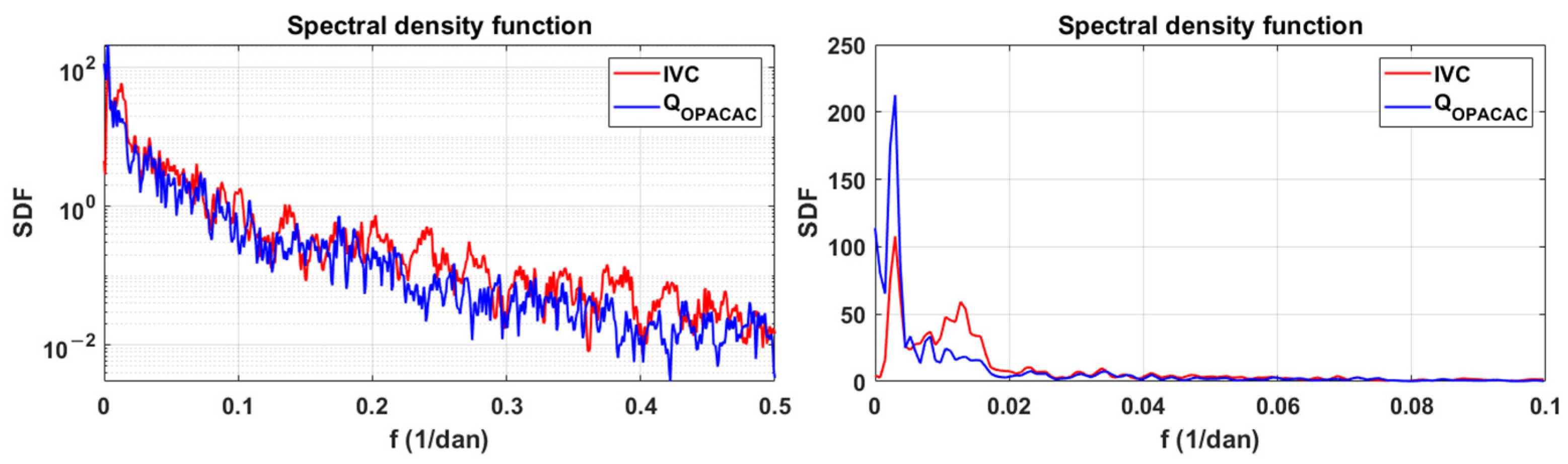
The spectral density functions for integral volume changes in Red Lake and discharges at Opačac are shown in Figure 8. The spectral density function shows the power distribution of the analysed series within the low-frequency range. At Red Lake and Opačac, the periodicity occurs with a frequency of 0.003, which corresponds to a period of 333 days. The observed periodicity corresponds to the period of one hydrological year.
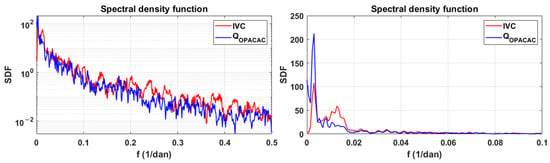
Figure 8.
Spectral density functions of integral volume changes in Red Lake and discharges at Opačac.
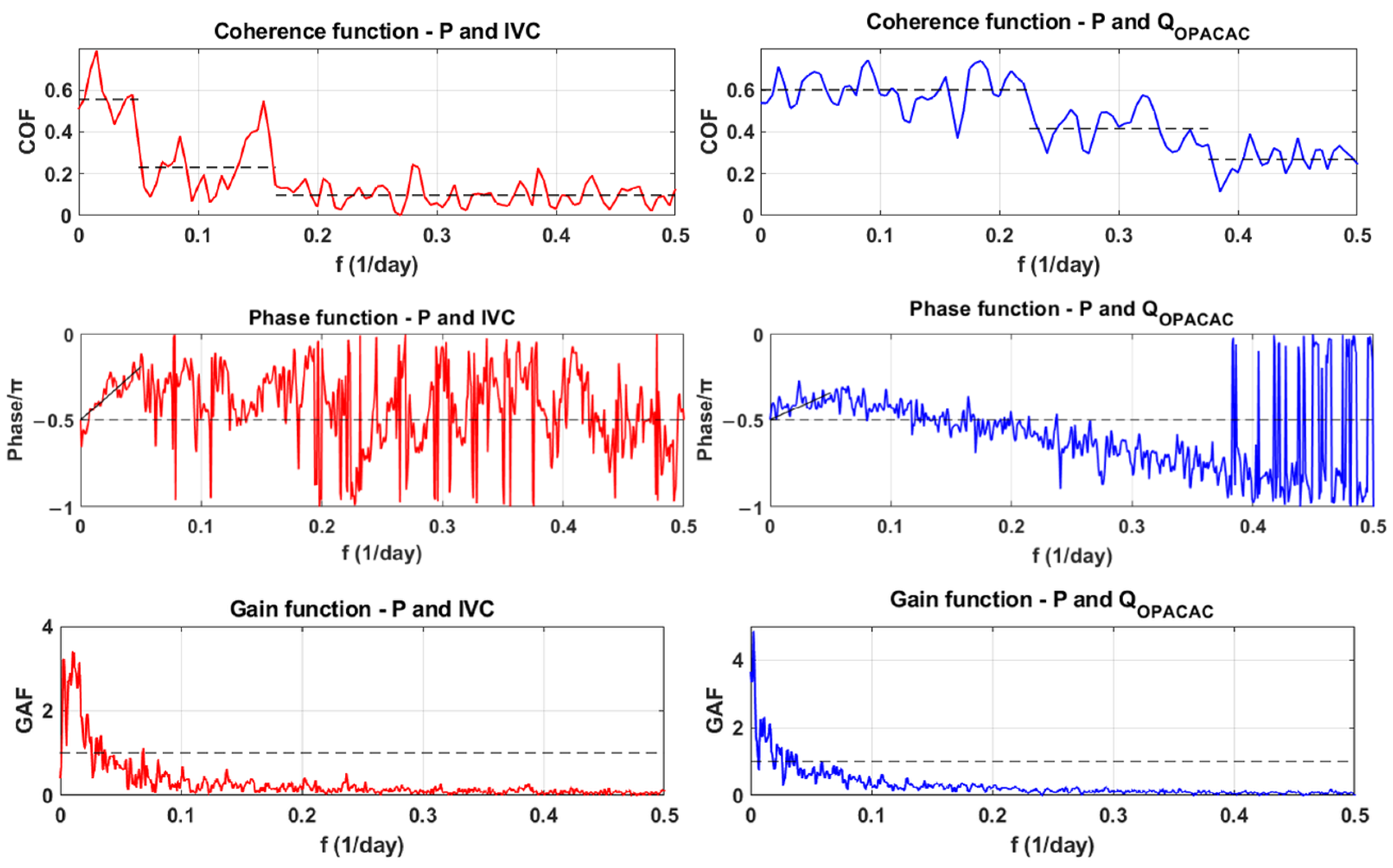
In the spectral analysis, precipitation was used as the input signal, while integral volume changes in Red Lake and discharges at Opačac were used as outputs. The results of the analysis are the coherence function, the phase function, and the gain function, which are shown in Figure 9. The coherence function determines whether changes in the output signal correspond to changes in the input signal [41]. The analysis shows that for precipitation and integral volume changes in Red Lake, coherence is lost for frequencies above 0.05 (periods shorter than 20 days), while when comparing precipitation signals with discharges at Opačac, coherence is lost for frequencies above 0.23 (periods shorter than 4 days). The trend of coherence of discharges at Opačac is significantly higher than the trend of coherence of integral volume changes in Red Lake, indicating the dominance of base flow in Red Lake compared to Opačac, where rapid runoff is more pronounced. The phase function shows the delay between the two observed signals at different frequencies. The signal behaviour is similar to that of the coherence function. The phase function for Red Lake shows good alignment up to a frequency of 0.05 and for Opačac up to a frequency of 0.23. The input signal is attenuated at higher frequencies. It is also possible to define an average lag equivalent to the slope of the trend line passing through the coordinate system’s origin using the phase function [41]. The average lag delay between integral volume changes in Red Lake is 12 days, while for Opačac it is 6 days. Based on the known values of the cross-spectrum’s amplitude and the spectral density function of the input signal, the attenuation or gain function is defined, depending on the value of Gxy. The values of Gxy > 1 indicate amplification of the input signal, while the values of Gxy < 1 indicate attenuation of the input signal. The input signal is attenuated at high frequencies and amplified at low frequencies. Analysis of integral volume changes in Red Lake showed attenuation of the input signal at frequencies above 0.036 and in Opačac discharges at frequencies above 0.0038.
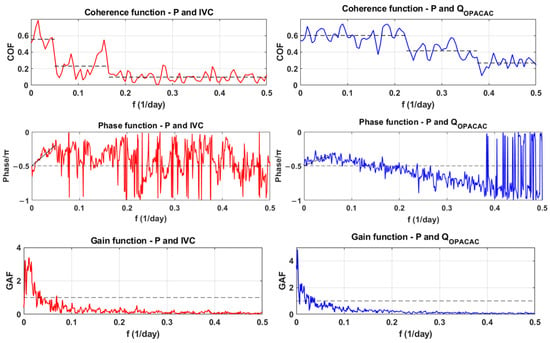
Figure 9.
Coherence, phase and gain function of integral volume changes in Red Lake and discharges at Opačac Spring.
5. Conclusions
The problems of water availability in karst and its protection are presently actualized more than ever, considering the challenges generated by the climate changes. This paper assesses different tools for characterizing the particular hydrogeological karst system by studying its hydrological dynamics. A novel approach is the recession analysis registered in the karst lake.
Analysing the nearby recorded precipitation signal that corresponds with the data record on Red Lake’s integral water volume changes shows that short-term precipitation has no substantial influence on the hydrodynamics of the lake. It suggests that predominant regional flow in the Dinaric karst is mostly responsible for the water levels in Red Lake. Fluctuations of integral volume changes are registered after intense precipitation or after the replenishment of subsurface reserves in karst conduit, pores, and fissures, whereupon a direct flow is activated. The cross-correlation analysis of the precipitation signal, water volume change in Red Lake and the discharge of Opačac Spring show that Red Lake responds to precipitation after 7 days, in contrast to Opačac, which exhibits no time lag. The regional flow system in the Dinaric Karst towards the Adriatic Sea is mainly responsible for the hydrogeological regime of the lake. It is formed on a larger recharge area and depends strongly on climate and meteorological parameters within the Dinaric belt. By isolating and decomposing quasi-recession curves, different flow regimes were detected suggesting the same conclusion on the predominant recharge mechanism of the lake. Registered larger time lag in the phase function on Red Lake data suggests the same.
Locally, on the field scale, Opačac Spring influences the hydrodynamics of Red lake. Slope discontinuity of the hydrograph representing the integral volume change in the lake and the shift in the quasi-recession coefficient can be registered at a certain altitude of 268.5 m a.s.l. which coincides with the position of Opačac Spring. It indicates the presence of a probable conduit connection between these two systems.
The dominance of base flow indicates the crucial role of groundwater in the formation of integral volume changes of Red lake. The longer memory effect of Red Lake compared to Opačac by analysing autocorrelation functions suggests the longer water storage in the subsurface. The coherence function shows that Red Lake has a far lower tendency of coherence than Opačac Spring, demonstrating once again the relevance of groundwater in the lake’s hydrogeological system and the dominance of the base flow.
The research presented in this article contributes to a better understanding of Red Lake, which is one of the most remarkable karst formations in the world. Since the surrounding karst massif is the main water source for the population of the region, the assessment of available water resources is a quintessential task for hydrologists and hydrogeologists. Some of the applied methods such as the study on karst system behaviour by observing recession in the karst lake can be used in different topographic settings, yet this particular study case shows that cryptodepressions in karst and their hydrodynamics reveal insights into fundamental hydrogeological characteristics on the field and regional scale.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation and writing of the original draft, A.V.; conceptualization, investigation, data validation, supervision and review and editing, I.A.; visualization and editing, N.B.; validation and review, O.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported through project KK.05.1.1.02.0024, “VODIME—Waters of Imotski region” a project financed by Croatian Government and the European Union through the European Structural Fund—within the call “Strengthening the applied research for climate change adaptation measures”. This research was partially supported through project KK.01.1.1.02.0027, a project co-financed by the Croatian Government and the European Union through the European Regional Development Fund—the Competitiveness and Cohesion Operational Programme.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bonacci, O. Karst Hydrology With Special Reference to the Dinaric Karst; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Stevanović, Z. Karst Waters in Potable Water Supply: A Global Scale Overview. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacci, O. Preliminary Analysis of the Decrease in Water Level of Vrana Lake on the Small Carbonate Island of Cres (Dinaric Karst, Croatia). Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2018, 466, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ožanić, N.; Rubinić, J. Hidraulic Limitation of Exploitation Vrana Lake for Water Supply (Croatia). In Proceedings of the XXIX IAHR Congress—21st Century: The New Era for Hydraulic Research and its Applications, Beijing, China, 16–21 September 2001; pp. 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Garašić, M. New Speleohydrogeological Research of Crveno Jezero (Red Lake) near Imotski in Dinaric Karst Area (Croatia, Europe)—International Speleodiving Expedition “Crveno Jezero 98”. In Proceedings of the 13th International Congress of Speleology, Brasilia, Brazil, 15–22 July 2001; pp. 457–460. [Google Scholar]
- Gavazzi, A. Die Seen Des Karstes (Karst Lakes). In Abhandlungen der K. K. Geographischen Gesellschaft; Lechner: Vienna, Austria, 1903; Volume 5, p. 136. [Google Scholar]
- Cvijić, J. Geomorfologija 2 (Geomorphology 2); Srpska Akademija Nauka i Umetnosti: Beograd, Serbia, 1926. [Google Scholar]
- Andrić, I.; Jukić, B.; Bonacci, O. Pregled Recentnih Znanstvenih Istraživanja Vezanih Za Crveno i Modro Jezero u Imotskom. In Zavičajna Baština—Problemi i Perspektive u Upravljanju Baštinom; Parlov, M., Kolovrat, I., Biočić, M., Eds.; Crkva u Svijetu: Split, Croatia, 2018; pp. 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Roglić, J. Imotsko Polje—Fizičko-Geografske Osobine. (Physical-Geographic Characteristics of Imotski Polje). Poseb. Izd. Geogr. Druš. 1938, 21, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Bonacci, O. Crveno i Modro Jezero Kod Imotskog. Hrvat. Vode 2006, 14, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Petrik, M. Hidrografska Mjerenja u Okolici Imotskog (Hydrographic Measurements near Imotski). Ljetop. JAZU 1960, 64, 266–286. [Google Scholar]
- Bojanić, L.; Ivičić, D.; Batić, V. Hidrogeologija Imotskog Polja s Osvrtom Na Značaj u Regionalnom Smislu. Geol. Vjesn. 1981, 34, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Milanović, P.T. Karst Hydrogeology; Water Resources Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 1981; p. 434. [Google Scholar]
- Bahun, S. O Postanku Crvenog i Modrog Jezera Kod Imotskog. Geol. Vjesn. 1991, 44, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Bonacci, O.; Andrić, I. Morphological Study of Red Lake in Dinaric Karst Based on Terrestrial Laser Scaning and Sonar System. Acta Carsolog. 2014, 43, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonacci, O.; Roje-Bonacci, T. Interpretation of Groundwater Level Monitoring Results in Karst Aquifers: Examples from the Dinaric Karst. Hydrol. Processes 2000, 14, 2423–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrić, I.; Bonacci, O.; Jukić, B. Rezultati Najnovijih Hidroloških i Geomorfoloških Istraživanja Crvenog Jezera Kod Imotskog. Hrvat. Vode 2013, 21, 344–348. [Google Scholar]
- Andrić, I.; Bonacci, O.; Jukić, B. Hidrološka Mjerenja Na Crvenom Jezeru u Razdoblju Od 28. Rujna 2013. Do 10. Rujna 2015. Hrvat. Vode 2017, 25, 253–258. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Bielsa, C.; Lambán, L.J.; Plata, J.L.; Rubio, F.M.; Soto, R. Characterization of a Karstic Aquifer Using Magnetic Resonance Sounding and Electrical Resistivity Tomography: A Case-Study of Estaña Lakes (Northern Spain). Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallaksen, L.M. A Review of Baseflow Recession Analysis. J. Hydrol. 1995, 165, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, H.A. Flow Recession Equations for Karst Systems. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdilar, S. Reljef Zavale Imotskog Polja i Njegovo Geoekološko Vrednovanje; Augustini: Zagreb, Croatia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dragicevic, I.; Prelogovic, E.; Vlado, K.U.K.; Buljan, R. Recent Tectonic Activity in the Imotsko Polje Area. Geol. Croat. 1999, 52, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahernik, M. Prostorna Gustoća Ponikava Na Području Republike Hrvatske. Hrvat. Geogr. Glas. 2012, 74, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katastar Speleoloških Objekata Republike Hrvatske. Available online: https://crospeleo.mingor.hr (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Šegota, T.; Filipčić, A. Köppenova Podjela Klima i Hrvatsko Nazivlje. Geoadria 2003, 8, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonacci, O.; Roje-Bonacci, T. Water Losses from the Ričice Reservoir Built in the Dinaric Karst. Eng. Geol. 2008, 99, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The MathWorks, Inc. About Identified Nonlinear Models. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/ident/ug/about-nonlinear-model-identification.html (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Ojha, A.K.; Mallick, D.; Mallick, C. Existence and Global Logarithmic Stability of Impulsive Neural Networks with Time Delay. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1002.1164. [Google Scholar]
- Burden, F.; Winkler, D. Bayesian Regularization of Neural Networks. In Artificial Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 23–42. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, R.J.; McMahon, T.A. Evaluation of Automated Techniques for Base Flow and Recession Analyses. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorotto, V.; Caroni, E. A New Approach to Master Recession Curve Analysis. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toebes, C.; Morrissey, W.B.; Shorter, R.; Hendy, M. Base-Flow-Recession Curves. Handbook of Hydrological Procedures: Procedure No 8; A.R. Shearer, Government Printer: Wellington, New Zeland, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Sujono, J.; Shikasho, S.; Hiramatsu, K. A Comparison of Techniques for Hydrograph Recession Analysis. Hydrol. Processes 2004, 18, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posavec, K.; Parlov, J.; Nakić, Z. Fully Automated Objective-Based Method for Master Recession Curve Separation. Ground Water 2010, 48, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posavec, K.; Bacani, A.; Nakic, Z. A Visual Basic Spreadsheet Macro for Recession Curve Analysis. Ground Water 2006, 44, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petras, I. An Approach to the Mathematical Expression of Recession Curves. Water SA 1986, 12, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Denić-Jukić, V.; Lozić, A.; Jukić, D. An Application of Correlation and Spectral Analysis in Hydrological Study of Neighboring Karst Springs. Water 2020, 12, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larocque, M.; Mangin, A.; Razack, M.; Banton, O. Contribution of Correlation and Spectral Analyses to the Regional Study of a Large Karst Aquifer (Charente, France). J. Hydrol. 1998, 205, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangin, A. Pour Une Meilleure Connaissance Des Systèmes Hydrologiques à Partir Des Analyses Corrélatoire et Spectrale. J. Hydrol. 1984, 67, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, A.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Study of Hydrographs of Karstic Aquifers by Means of Correlation and Cross-Spectral Analysis. J. Hydrol. 1995, 168, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatfield, C. The Analysis of Time Series: An Introduction, 6th ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).