Dripping Rainfall Simulators for Soil Research—Design Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- general data: year of publication, author and title of the scientific paper in which the simulator was applied or described, simulator type designation,
- structural support: role, conditions in which it is placed (laboratory or field), existence of wind protection, portability, shape of elements, material of which the structural support elements are made, type of support, number of support points, height at which the water tank with drippers is placed, existence and type of water tank with drippers levelling system,
- water tank: role, shape, form, material of which it is made, position in relation to other elements of the simulator, volume,
- water moving mechanism: type,
- mechanism of water flow regulation and simulator operation: type, existence of oscillations of water tank with drippers, type of measuring equipment, position of measuring equipment,
- water tank with drippers: type, shape, material of which it is made, dimensions, modularity, type of its connection with drippers, number of drippers, distance between drippers,
- drippers: designation of the type and subtype, diameter.
3. Results and Discussion
- structural support,
- water tank,
- water moving mechanism,
- mechanism of water flow regulation and simulator operation
- water tank with drippers and
- drippers.
3.1. Structural Support

3.2. Water Tank
3.3. Water Moving Mechanism
3.4. Mechanism of Water Flow Regulation and Simulator Operation


3.5. Water Tank with Drippers


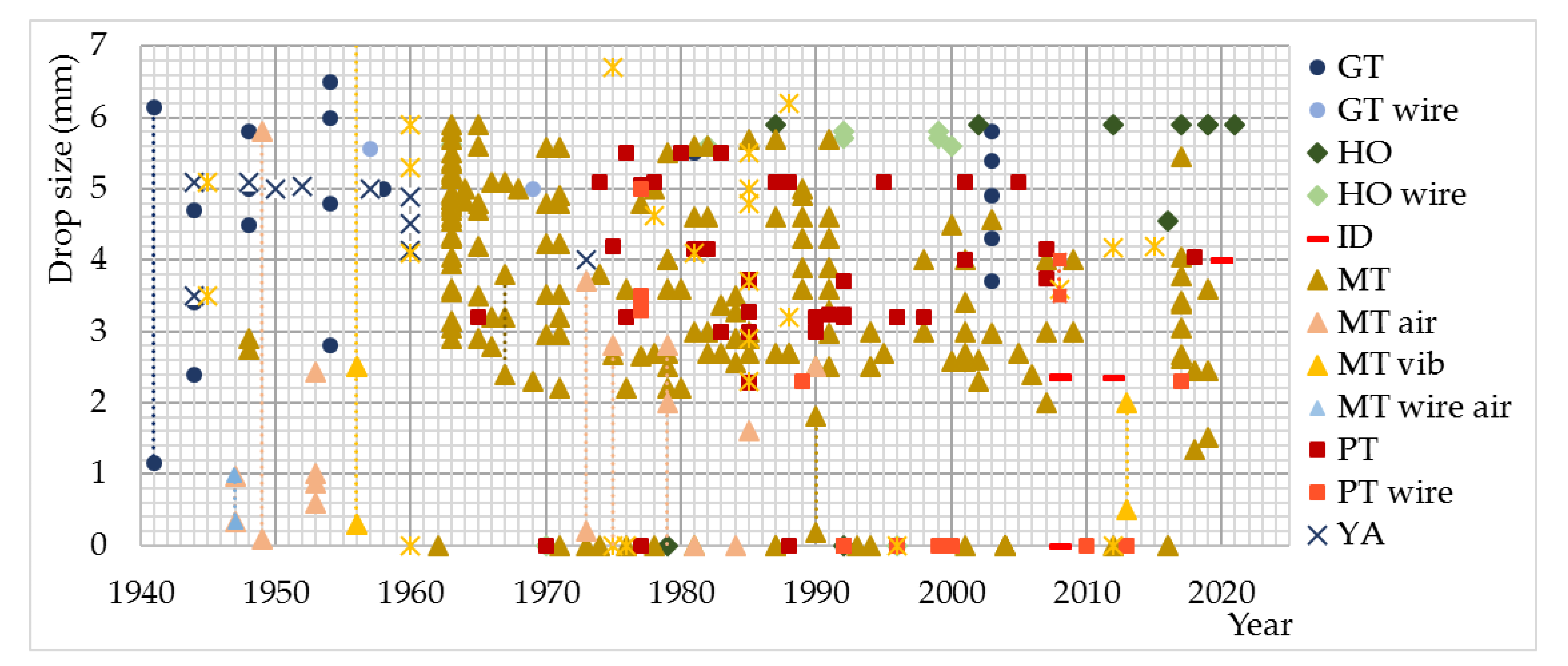
| Type or Subtype of DRS | Water Movement Mechanism | Water Tank with Drippers | WTD Box Type Shape | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-1944 a | W. pump | CCW | / | [91,103] |
| E-1944 b | W. pump | CCW | / | [104] |
| E-1944 c | W. pump | CCW | / | [105] |
| E-1944 d | W. pump | CCW | / | [92] |
| E-1944 e | W. pump | CCW | / | [93] |
| E-1944 f | W. pump | CCW | / | [106] |
| E-1948 | Gravity | Box | Complex | [107,108,109] |
| R-1953 | Air pump | Box | Cylindrical | [110] |
| A-1957 a | Gravity | Box | Cylindrical | [111,112] |
| A-1957 b | Gravity | Box | Cylindrical | [28,47] |
| A-1957 c | Gravity | Box | Cylindrical | [113] |
| A-1957 d | Gravity | Box | Cylindrical | [46] |
| R-1960 | Not Sp. | Box | Cylindrical | [79] |
| M-1963 | W. pump | Box | Cylindrical | [62,63,114,115,116,117] |
| C-1965 a | Not Sp. | Box | Rectangular | [17,118] |
| C-1965 b | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [18] |
| C-1965 c | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [49,64,119] |
| C-1965 d | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [50,120] |
| C-1965 e | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [1,121,122,123,124] |
| C-1965 f | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [51,87,125,126] |
| C-1965 g | Not Spec. | Not Spec. | Not Spec. | [127] |
| C-1965 h | Not Spec. | Not Spec. | Not Spec. | [128] |
| C-1965 i | Not Spec. | Box | Rectangular | [24,90,129] |
| S-1966 | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [24] |
| B-1971 | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [85] |
| W-1973 a | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [41,130,131,132] |
| W-1973 b | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [32,133] |
| W-1973 c | Not Spec. | Box | Rectangular | [134] |
| K-1974 | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [81,84,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147] |
| D-1975 a | Not Spec. | Not Spec. | Not Spec. | [21,148,149] |
| D-1975 b | Gravity | Dendritic | / | [22,150] |
| G-1975 | Not Spec. | Not Spec. | Not Spec. | [151] |
| R-1975 | Specific | / | / | [73] |
| H-1976 | Not Spec. | Box | Rectangular | [152,153] |
| W-1976 | Not Spec. | Not Spec. | Not Spec. | [154] |
| I-1979 | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [54] |
| T-1979 | Gravity | Box | Cylindrical | [39] |
| C-1984 | W. pump | Tubes | / | [155] |
| R-1985 a | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [40]; |
| R-1985 b | Not Spec. | Box | Rectangular | [97,156] |
| T-1985 | Not Spec. | Box | Cylindrical | [56] |
| F-1987 a | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [23] |
| F-1987 b | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [82] |
| K-1987 a | Gravity | Box | Complex | [96,100,101,157,158,159,160] |
| K-1987 b | Gravity | Box | Complex | [161] |
| C 1988 | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [57] |
| B-1989 a | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [8,43,77] |
| B-1989 b | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [89,162] |
| B-1989 c | Air pump | Box | Rectangular | [60] |
| B-1989 d | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [163,164] |
| L-1991 | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [95,165] |
| B-1992 | Gravity | Box | Cylindrical | [45,86,166] |
| A-1994 | Not Spec. | Box | Rectangular | [167] |
| H-1996 | Not Spec. | Not Spec. | Not Spec. | [168] |
| L-1998 | Not Spec. | Box | Rectangular | [66,169,170] |
| B-2000 | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [19] |
| R-2000 | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [80,98] |
| D-2001 | Not Spec. | Box | Rectangular | [171] |
| H-2001 a | Gravity | Box | Cylindrical | [69] |
| H-2001 b | W. pump | Box | Cylindrical | [88,172,173] |
| H-2001 c | W. pump | Box | Cylindrical | [67] |
| J-2001 | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [42] |
| W-2001 | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [25] |
| A-2006 | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [174] |
| C-2007 | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [99] |
| D-2008 | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [76,175] |
| F-2008 | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [61] |
| V-2008 | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [4] |
| B-2012 | Not Spec. | Box | Rectangular | [26] |
| R-2012 | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [74] |
| C-2013 | Not Spec. | Box | Rectangular | [10] |
| H-2013 | Gravity | Box | Rectangular | [59] |
| N-2016 | Not Spec. | Tubes | / | [53] |
| F-2017 | Not Spec. | Box | Cylindrical | [70] |
| M-2017 | Gravity | Box | / | [94] |
| X-2017 | Not Spec. | Box | Cylindrical | [78] |
| W-2018 | W. pump | Box | Rectangular | [58] |
| N-2020 | Not Spec. | Tubes | / | [5,176] |
| Simulator Type Mark | Research Paper Authors and Year of Publishing |
|---|---|
| L 1941 | [177] |
| M 1944 | [178] |
| L 1947 | [48] |
| G 1949 | [179] |
| M 1954 | [180] |
| M 1956 | [181] |
| P 1962 | [75] |
| M 1963 | [182] |
| P 1963 | [183,184] |
| M 1965 | [44,185,186] |
| M 1967 | [187,188] |
| B 1975 | [189] |
| R 1976 | [190] |
| A 1981 a | [191,192,193,194] |
| A 1981 b | [72,195] |
| A 1981 c | [196] |
| B 1981 | [197] |
| S 1981 | [55] |
| F 1983 a | [198] |
| F 1984 b | [83] |
| F 1984 c | [68] |
| RI 1985 | [65] |
| G 1988 | [199] |
| R 1990 | [200] |
| M 2003 | [201] |
| F 2007 | [202] |
| R 2012 | [52,203] |
| Y 2016 | [204] |
| YA 2016 | [205] |
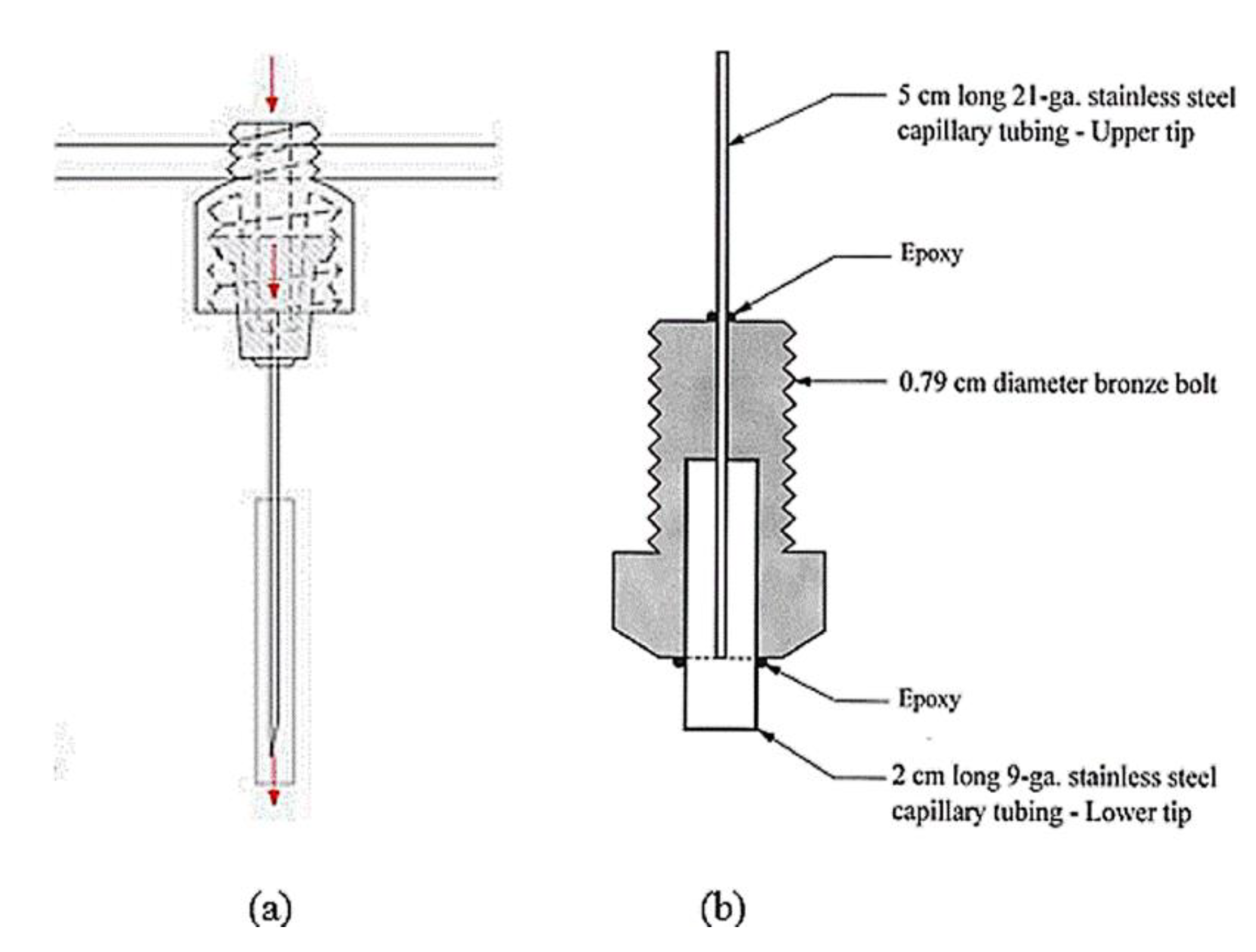
3.6. Drippers
- tubes,
- metal tubes (MT) (hypo needle tubes, hypodermic syringe needles, syringe needles, hypodermic needles with rectangular tip, protruding needles, blunted needles, hypodermic tubing, stainless steel tubing, stainless steel tubes, milled stainless steel tubing, stainless steel capillary tubes, drip needles made from hypodermic tubing, coper tubing, coper tubes, brass tubes) [62,75,135,174,194],
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riezebos, T.H.; Seyhan, E. Essential Conditions of Rainfall Simulation for Laboratory Water Erosion Experiments. Earth Surf. Process. 1977, 2, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.D.; Harmon, W.C. Susceptibility of Agricultural Soils to Interrill Erosion. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.; Kleinman, P. Effect of Rainfall Simulator and Plot Scale on Overland Flow and Phosphorus Transport. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 2172–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vahabi, J.; Nikkami, D. Assessing Dominant Factors Affecting Soil Erosion Using a Portable Rainfall Simulator. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2008, 23, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, J.; Anta, J.; Suárez, J.; Puertas, J. Development and Calibration of a New Dripper-Based Rainfall Simulator for Large-Scale Sediment Wash-off Studies. Water 2020, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bubenzer, G.D.; Meyer, L.D. Simulation of Rainfall and Soils for Laboratory Research. Trans. ASAE 1965, 8, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, I.D.; Hirschi, M.C.; Barfield, B.J. Kentucky Rainfall Simulator. Trans. ASAE 1983, 26, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowyer-Bower, T.A.S.; Burt, T.P. Rainfall Simulators for Investigating Soil Response to Rainfall. Soil Technol. 1989, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boxel, J.H. Numerical Model for the Fall Speed of Rain Drops in a Rain Fall Simulator. In Workshop on Wind and Water Erosion; University of Amsterdam: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 77–85. Available online: https://pure.uva.nl/ws/files/2778495/171269_VanBoxel_1998_GENT_ModelFallSpeedRaindrops.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- Corona, R.; Wilson, T.; D’Adderio, L.P.; Porcù, F.; Montaldo, N.; Albertson, J. On the Estimation of Surface Runoff through a New Plot Scale Rainfall Simulator in Sardinia, Italy. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 19, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, R.B. An Improved Rainfall Simulator for Use in Erosion Research. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1970, 7, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, A.; Alberto, F.; Machín, J.; Galán, A. Design and Operation of a Rainfall Simulator for Field Studies of Runoff and Soil Erosion. Soil Technol. 1990, 3, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunye, F.O.; Boussabaine, H. Development of a Rainfall Test Rig as an Aid in Soil Block Weathering Assessment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2002, 16, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrinho, A.; Gómez-Macpherson, T.; Gómez, H. A Portable Integrated Rainfall and Overland Flow Simulator. Soil Use Manag. 2008, 24, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrić, O. Eksperimentalno Istraživanje Procesa Na Slivu: Padavine, Oticaj i Erozija Tla; University of Novi Sad: Novi Sad, Serbia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Živanović, N.; Rončević, V.; Spasić, M.; Ćorluka, S.; Polovina, S. Construction and Calibration of a Portable Rainfall Simulator Designed for in Situ Researches of Soil Resistance to Erosion. Soil Water Res. 2022, 17, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, V.T.; Harbaugh, T.E. Raindrop Production for Laboratory Watershed Experimentation. J. Geophys. Res. 1965, 70, 6111–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeuwig, R.O. Infiltration and Water Repellency in Granitic Soils; Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1971; Volume 111. [Google Scholar]
- Battany, M.C.; Grismer, M.E. Development of a Portable Field Rainfall Simulator for Use in Hillside Vineyard Runoff and Erosion Studies. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grismer, M. Standards Vary in Studies Using Rainfall Simulators to Evaluate Erosion. Calif. Agric. 2012, 66, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Ploey, J.; Moeyersons, J. Runoff Creep of Coarse Debris: Experimental Data and Some Field Observations. Catena 1975, 2, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imeson, A.C. A Simple Field-Portable Rainfall Simulator for Difficult Terrain. Earth Surf. Process. 1977, 2, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farres, P.J. The Dynamics of Rainsplash Erosion and the Role of Soil Aggregate Stability. Catena 1987, 14, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; El-Swaify, S.A. Characterizing Interrill Sediment Size by Partitioning Splash and Wash Processes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Grismer, M.E. Diazinon Transport through Inter-Row Vegetative Filter Strips: Micro-Ecosystem Modeling. J. Hydrol. 2001, 247, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böker, J.; Zanzinger, H.; Bastian, M.; Németh, E.; Eppel, J. Surface Erosion Control Investigations for a Test Field on a Steep Embankment of German Autobahn A3. 2012. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Helmut-Zanzinger/publication/297730907_Surface_erosion_control_investigations_for_a_test_field_on_a_steep_embankment_of_German_Autobahn_A3/links/56e2acf908ae3328e07877e9/Surface-erosion-control-investigations-for-a-test-field-on-a-steep-embankment-of-German-Autobahn-A3.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- Meyer, L.D. Simulation of Rainfall for Soil Erosion Research. Trans. ASAE 1965, 8, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcqueen, I.S.; United States Department of the Interior, Geological Survey. In Development of a Hand Portable Rainfall-Simulator Infiltrometer; 1963; Volume 482. Available online: https://books.google.com.hk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=99l-U1NPJeQC&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&dq=28.%09Mcqueen,+I.S.%3B+United+States+Department+of+the+Interior,+Geological+Survey.+In+Development+of+a+Hand+Portable+Rainfall-Simulator+Infiltrometer%3B+1963%3B+Volume+482.&ots=ZIchDBPdn0&sig=w1F74PXipy-_crmsQjPl7fv544w&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- Steinhardt, R.; Hillel, D. A Portable Low—Intensity Rainfall simulator for Field and Laboratory Use. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1966, 30, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.J. A Critique of Methods of Simulating Rainfall. Water Resour. Res. 1970, 6, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.D.; Harmon, W.C. Multiple-Intensity Rainfall Simulator for Erosion Research on Row Sideslopes. Trans. ASAE 1979, 22, 100–0103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onstad, C.A.; Radke, J.K.; Young, R.A. Outdoor Portable Rainfall Erosion Laboratory. In Erosion and Sediment Transport Measurement: Symposium; IAHS Publication: Wallingford, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, J.F.; Bertrand, A.R. Water Infiltration into Soils. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1960; pp. 311–363. [Google Scholar]
- Mutchler, C.K.; Hermsmeier, L.F. A Review of Rainfall Simulators. Trans. ASAE 1965, 8, 67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yakubu, M.L.; Yusop, Z. Adaptability of Rainfall Simulators as a Research Tool on Urban Sealed Surfaces—A Review. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 996–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngasoh, F.G.; Mbajiorgu, C.C.; Kamai, M.B.; Okoro, G.O. A Revisit of Rainfall Simulator as a Potential Tool for Hydrological Research; Intech Open: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Amerman, C.R. Proceedings of the Rainfall Simulator Workshop: Tucson, Arizona; Western Region. 1979. Available online: https://books.google.co.kr/books?hl=en&lr=&id=-DlDble2vPsC&oi=fnd&pg=PR10&dq=37.%09Amerman,+C.R.+Proceedings+of+the+Rainfall+Simulator+Workshop:+Tucson,+Arizona%3B+Western+Region:+1979.&ots=EfI0yi30Ef&sig=FHwt-mgWeTSikAH1gbX7IHV2e9c&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- Cerdà, A. Simuladores de Lluvia y Su Aplicación a La Geomorfología: Estado de La Cuestión. Cuad. De Investig. Geográfica Geogr. Res. Lett. 1999, 25, 45–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tricker, A.S. The Design of a Portable Rainfall Simulator Infiltrometer. J. Hydrol. 1979, 41, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, C.H.; Meyer, B.; Frede, H.-G. A Portable Rainfall Simulator for Studying Factors Affecting Runoff, Infiltration and Soil Loss. Catena 1985, 12, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakensiek, D.L.; Rawls, W.J.; Hamon, W.R. Application of an Infiltrometer System for Describing Infiltration into Soils. Trans. ASAE 1979, 22, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joel, A.; Messing, I. Infiltration Rate and Hydraulic Conductivity Measured with Rainfall simulator and Disc Permeameter on Sloping Arid Land. Arid. Land Res. Manage. 2001, 15, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, M.G.; Fenton, O.; Cummins, E.; Clarke, R.; Peyton, D.; Fleming, G.; Cormican, M. Health and Water Quality Impacts Arising from Land Spreading of Biosolids. Environ. Prot. Agency Res. Rep. 2017, 200. [Google Scholar]
- Mutchler, C.K. Using the Drift of Waterdrops during Fall for Rainfall Simulator Design. J. Geophys. Res. 1965, 70, 3899–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, R. Development of a Portable Rainfall Simulator Infiltrometer for Infiltration, Runoff and Erosion Studies. Agric. Water Manag. 1992, 22, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, C.P. Rainfall Response of Degraded Soil Following Reforestation in the Copper Basin, Tennessee, USA. Environ. Manage. 2000, 26, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summer, R.M. Field and Laboratory Studies on Alpine Soil Erodibility, Southern Rocky Mountains, Colorado. Earth Surf. Process. 2007, 7, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, W.R. A Microburette for Producing Small Liquid Drops of Known Size. J. Sci. Instrum. 1947, 24, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, W.H. Simulated Rainfall Studies of Selected Plant Communities and Soils in Five Rangeland Watersheds of Nevada. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nevada, Reno, Reno, NV, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Munn, J.R.; Huntington, G.L. A Portable Rainfall Simulator for Erodibility and Infiltration Measurements on Rugged Terrain. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1976, 40, 622–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekuti, A.; Gifford, G.F.; Malekuti, A.; Gifford, G.F. Natural Vegetation as a Source of Diffuse Salt within the Colorado River Basin 1. Jawra J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1978, 14, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryżak, M.; Bieganowski, A. Using the Image Analysis Method for Describing Soil Detachment by a Single Water Drop Impact. Sensors 2012, 12, 11527–11543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nampulá, J.L.C.; Lara, C.M.G.; Medinilla, E.E.; Herrera, R.G.; Toledo, P.V.; Sánchez, R.A.V. Diseño y Calibración de Un Simulador Automático de Lluvia. Espac. I+D Innovación Más Desarro 2016, 5, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelsen, C.E.; Israelsen, E.K.; Fletcher, J.E.; Fifield, J.S.; Canfield, R.V. Erosion Control Product Testing. 1979. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/water_rep/367/ (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- Savat, J. Work Done by Splash: Laboratory Experiments. Earth Surf. Process. 1981, 6, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.L.; James, L.G. Water Droplet Impact and Its Effect on Infiltration. Trans. ASAE 1985, 28, 1506–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commandeur, P.R. Soil Erosion Studies Using Rainfall Simulation on Forest Harvested Areas in British Columbia. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Erosion, Debris Flows and Environment in Mountain Regions, Chengdu, China, 5–9 July 1992; IAHS Publication: Oxfordshire, UK, 1992; pp. 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Fang, N.F.; Yue, Z.J.; Shi, Z.H.; Hua, L. Raindrop Size and Flow Depth Control Sediment Sorting in Shallow Flows on Steep Slopes. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 9978–9995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X. Effects of Rainfall Intensity, Underlying Surface and Slope Gradient on Soil Infiltration under Simulated Rainfall Experiments. Catena 2013, 104, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.T.; Foster, I.D.L.; Pratt, C.J. The Role of Urban Surfaces (Permeable Pavements) in Regulating Drainage and Evaporation: Development of a Laboratory Simulation Experiment. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Gálvez, J.; Barahona, E.; Mingorance, M.D. Measurement of Infiltration in Small Field Plots by a Portable Rainfall Simulator: Application to Trace-Element Mobility. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2008, 191, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutchler, C.K.; Moldenhauer, W.C. Applicator for Laboratory Rainfall Simulator. Trans. ASAE 1963, 6, 220–222. [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn, W.H.; Meeuwig, R.O.; Skau, C.M. A Mobile Infiltrometer for Use on Rangeland. J. Range Manag. 1974, 27, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, E.; Grant, W.J. TB22: Design, Construction and Calibration of a Laboratory Rainfall Simulator. In Technical Bulletins of the Maine Agricultural & Forest Experiment Station. 1966. Available online: https://scholar.google.com.hk/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=64.%09Blackburn%2C+W.H.%3B+Meeuwig%2C+R.O.%3B+Skau%2C+C.M.+A+Mobile+Infiltrometer+for+Use+on+Rangeland.+J.+Range+Manag.+1974%2C+27%2C+322.+https%3A%2F%2Fdoi.org%2F10.2307%2F3896835.&btnG= (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- Riezebos, H.T.; Epema, G.F. Drop Shape and Erosivity Part II: Splash Detachment, Transport and Erosivity Indices. Earth Surf. Process. 1985, 10, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-J.; Lu, T.-F.; Hong, J.-H. Experimental Study of Extreme Shear Stress for Shallow Flow under Simulated Rainfall. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, C.; Yang, P.; Zeng, W.; Chen, W.; Xu, Y.; Xu, H.; Zha, Y.; Wu, J.; Huang, J. Impact of Raindrop Diameter and Polyacrylamide Application on Runoff, Soil and Nitrogen Loss via Raindrop Splashing. Geoderma 2019, 353, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farres, P.J.; Cousen, S.M. An Improved Method of Aggregate Stability Measurement. Earth Surf. Process. 1985, 10, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilig, A.; DeBruyn, D.; Walter, M.T.; Rose, C.W.; Parlange, J.-Y.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Sander, G.C.; Hairsine, P.B.; Hogarth, W.L.; Walker, L.P. Testing a Mechanistic Soil Erosion Model with a Simple Experiment. J. Hydrol. 2006, 317, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, G.-L.; Zheng, T.-H.; Li, B.-Q.; Zhang, T. Splash Detachment and Transport of Loess Aggregate Fragments by Raindrop Action. Catena 2017, 150, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubi, S.; Mokhtari, J.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Zeraatpisheh, M. Erodibility of Calcareous Soils as Influenced by Land Use and Intrinsic Soil Properties in a Semiarid Region of Central Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.P.; Gupta, S.C. Sand Detachment by Single Raindrops of Varying Kinetic Energy and Momentum. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1989, 53, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römkens, M.J.M.; Glenn, L.F.; Nelson, D.W.; Roth, C.B. A Laboratory Rainfall Simulator for Infiltration and Soil Detachment Studies1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1975, 39, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Su, D.; Li, P.; He, Z. Experimental Study of the Impact of Rainfall Characteristics on Runoff Generation and Soil Erosion. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424–425, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, R.S. An Apparatus for Forming Waterdrops; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1962; Volume 61. [Google Scholar]
- Dunkerley, D.L. Intra-Storm Evaporation as a Component of Canopy Interception Loss in Dryland Shrubs: Observations from Fowlers Gap, Australia. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 1985–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Naghizadeh, R. The Impact of Cultivation Practice and Wheelings on Runoff Generation and Soil Erosion on the South Downs: Some Experimental Results Using Simulated Rainfall. Soil Use Manag. 1992, 8, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Liu, G.; Abd-Elbasit, M.A.M.; Zhang, X.C.; Liu, P.L.; Zheng, F.L.; Zhang, J.Q.; Hu, F.N. Effects of Slaking and Mechanical Breakdown on Disaggregation and Splash Erosion: Effects of Splash Erosion on Aggregate Breakdown. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.W. Soil Detachment Caused by Rainfall. Soil Sci. 1960, 89, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, T.P.; Thompson, A.L. Rainfall Simulator for Laboratory Studies. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2000, 16, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hignett, C.T.; Gusli, S.; Cass, A.; Besz, W. An Automated Laboratory Rainfall Simulation System with Controlled Rainfall Intensity, Raindrop Energy and Soil Drainage. Soil Technol. 1995, 8, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, J.P.; Shakesby, R.A. Soil Hydrophobicity Effects on Rainsplash: Simulated Rainfall and Photographic Evidence. Earth Surf. Process. 1993, 18, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousen, S.M.; Farres, P.J. The Role of Moisture Content in the Stability of Soil Aggregates from a Temperate Silty Soil to Raindrop Impact. Catena 1984, 11, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.H.; Hutka, J.; Moss, A.J.; Kinnell, P.I.A. Use of a Versatile Experimental System for Soil Erosion Studies. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977, 41, 610–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubenzer, G.D.; Jones, B.A. Drop Size and Impact Velocity Effects on the Detachment of Soils Under Simulated Rainfall. Trans. ASAE 1971, 14, 625–628. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Panigrahy, N.; Philip, G. Modified Rainfall Simulator Infiltrometer for Infiltration, Runoff and Erosion Studies. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 41, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrant, D.G.; Miller, W.W.; Mahannah, C.N.; Narayanan, R. Infiltration Evaluation of Four Mechanical Rainfall Simulation Techniques in Sierra Nevada Watersheds 1. Jawra J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1990, 26, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Walter, M.T.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Parlange, J.-Y.; Nakano, K.; Rose, C.W.; Hogarth, W.L. Investigating Ponding Depth and Soil Detachability for a Mechanistic Erosion Model Using a Simple Experiment. J. Hydrol. 2003, 277, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, I.D.L.; Fullen, M.A.; Brandsma, R.T.; Chapman, A.S. Drip-Screen Rainfall Simulators for Hydro-and Pedo-Geomorphological Research: The Coventry Experience. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2000, 25, 691–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; El-Swaify, S.A.; Sutherland, R.A. Partitioning Interrill Splash and Wash Dynamics: A Novel Laboratory Approach. Soil Technol. 1996, 9, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, W.D.; Pomerene, W.H. A Rainfall Applicator. Agric. Eng. 1944, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, L.J. Erosion Control in Engineering Works. Agric. Eng. 1952, 33, 155–157. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, O.K.; Costel, G. A Mobile Infiltrometer 1. Agron. J. 1957, 49, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maore, J.M.; Mihara, M. Development of Portable Artificial Rainfall Simulator for Evaluating Sustainable Farming in Kenya. Int. J. Environ. Rural. Dev. 2017, 8, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Shainberg, I.; Mamedov, A.I.; Levy, G.J. Role of Wetting Rate and Rain Energy in Seal Formation and Erosion 1. Soil Sci. 2003, 168, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlak, M. Determination of Soil Erosion over Different L and Uses by Mini Rainfall Simulator. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2012, 10, 929–933. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, C.H.; Helming, K. Dynamics of Surface Sealing, Runoff Formation and Interrill Soil Loss as Related to Rainfall Intensity, Microrelief and Slope. Z. Für Pflanz. Und Bodenkd. 1992, 155, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.L.; Ghidey, F.; Regmi, T.P. Raindrop Energy Effects on Chemical and Sediment Transport. Trans. ASAE 2001, 44, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.A.; Walsh, R.P.D. A Portable Rainfall Simulator for Field Assessment of Splash and Slopewash in Remote Locations. Earth Surf. Process. 2007, 32, 2052–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombino, G.; Denisi, P.; Gómez, J.; Zema, D. Water Infiltration and Surface Runoff in Steep Clayey Soils of Olive Groves under Different Management Practices. Water 2019, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamphorst, A. A Small Rainfall Simulator for the Determination of Soil Erodibility. Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 1987, 35, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijkelkamp—Laboratory Equipment. Available online: https://en.eijkelkamp (accessed on 7 July 2018).
- Bisal, F. The Effect of Raindrop Size and Impact Velocity on Sand-Splash. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1960, 40, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodburn, R. The Effect of Structural Condition on Soil Detachment by Raindrop Impact. Agric. Eng. 1948, 29, 154–156. [Google Scholar]
- Osborn, B. Measuring Soil Splash and Protective Value of Cover on Range Land: Methods and Equipment Used in Range Cover Evaluations in Texas and Oklahoma; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T.; Anderson, H.W. Splash Erosion Related to Soil Erodibility Indexes and Other Forest Soil Properties in Hawaii. Water Resour. Res. 1973, 9, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekern, P.C., Jr.; Muckenhirn, R.J. Water Drop Impact as a Force in Transporting Sand. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1948, 12, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mcintyre, D.S. Permeability Measurements of Soil Crusts Formed by Raindrop Impact. Soil Sci. 1958, 85, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcintyre, D.S. Soil Splash and the Formation of Surface Crusts by Raindrop Impact. Soil Sci. 1958, 85, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasbash, D.J. The Production of Water Spray of Uniform Drop Size by a Battery of Hypodermic Needles. J. Sci. Instrum. 1953, 30, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.E.; Kirkham, D.; Nielsen, D.R. A Portable Rainfall-Simulator Infiltrometer and Physical Measurements of Soil in Place. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1957, 21, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldenhauer, W.C.; Kemper, W.D. Interdependence of Water Drop Energy and Clod Size on Infiltration and Clod Stability. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1969, 33, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, M.J. Design of a Hand-Portable Rainfall-Simulating Infiltrometer, with Trial Results from the Otutira Catchment. J. Hydrol. 1970, 117–132. [Google Scholar]
- Moldenhauer, W.C.; Long, D.C. Influence of Rainfall Energy on Soil Loss and Infiltration Rates: I. Effect over a Range of Texture. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1964, 28, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldenhauer, W.C.; Koswara, J. Effect of Initial Clod Size on Characteristics of Splash and Wash Erosion1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1968, 32, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriels, D.; Moldenhauer, W.C. Size Distribution of Eroded Material from Simulated Rainfall: Effect over a Range of Texture. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1978, 42, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, L.D. Micromorphological Study of Surface Seals Developed under Simulated Rainfall. Geoderma 1987, 40, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, P.E. Runoff from Watershed Models. Water Resour. Res. 1970, 6, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurow, T.L.; Blackburn, W.H.; Warren, S.D.; Taylor, C.A. Rainfall Interception by Midgrass, Shortgrass, and Live Oak Mottes. J. Range Manag. 1987, 40, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnais, Y.L.; Singer, M.J. ECrusting, Runoff, and Erosion Response to Soil Water Content and Successive Rainfalls. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, L.R.; Lehman, O.R.; Sharpley, A.N. Bromide and Phosphate in Runoff Water from Shaped and Cloddy Soil Surfaces. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1983, 47, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, L.R.; Lehman, O.R. The Extent and Nature of Rainfall—Soil Interaction in the Release of Soluble Chemicals to Runoff. J. Environ. Qual. 1983, 12, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, L.R. Modeling Soluble Chemical Transfer to Runoff with Rainfall Impact as a Diffusion Process. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.C.; Singer, M.J. Crust Formation Effects on Soil Erosion Processes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrant, D.G.; Miller, W.W.; Mahannah, C.N.; Narayanan, R. Site—Specific Erosivity Evaluation of a Sierra Nevada Forested Watershed Soil. J. Environ. Qual. 1991, 20, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naslas, G.D.; Miller, W.W.; Gifford, G.F.; Fernandez, G.C.J. Effects of Soil Type, Plot Condition, and Slope on Runoff and Interrill Erosion of Two Soils in the Lake Tahoe Basin 1. Jawra J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1994, 30, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, M.K.; Blackburn, W.H. Grazing Systems: Their Influence on Infiltration Rates in the Rolling Plains of Texas. J. Range Manag. 1981, 34, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.P.; Seney, J.P. Erosional Impact of Hikers, Horses, Motorcycles, and off-Road Bicycles on Mountain Trails in Montana. Mt. Res. Dev. 1994, 14, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A.; Wan, Y.; Ziegler, A.D.; Lee, C.-T.; El-Swaify, S.A. Splash and Wash Dynamics: An Experimental Investigation Using an Oxisol. Geoderma 1996, 69, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, G.L. Infiltration under a Rainfall Simulator. 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Jeppson, R.W.; Rawls, W.J.; Hamon, W.R.; Schreiber, D.L. Use of Axisymmetric Infiltration Model and Field Data to Determine Hydraulic Properties of Soils. Water Resour. Res. 1975, 11, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.A. A Method of Measuring Aggregate Stability under Waterdrop Impact. Trans. ASAE 1984, 27, 1351–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freebairn, D.M.; Gupta, S.C. Microrelief, Rainfall and Cover Effects on Infiltration. Soil Tillage Res. 1990, 16, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.P.; Jarrett, A.R.; Hoover, J.R. Detachment and Splash of a Cohesive Soil by Rainfall. Trans. ASAE 1985, 28, 1878–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Splash Erosion: Some Observations on the Splash-Cup Technique. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1974, 38, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.H.; Kinnell, P.I.A.; Green, P. Transport of a Noncohesive Sandy Mixture in Rainfall and Runoff Experiments. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1978, 42, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aston, A.R. Rainfall Interception by Eight Small Trees. J. Hydrol. 1979, 42, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.J.; Walker, P.H.; Hutka, J. Raindrop-Stimulated Transportation in Shallow Water Flows: An Experimental Study. Sediment. Geol. 1979, 22, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Laboratory Studies on the Effect of Drop Size on Splash Erosion. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1982, 27, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.J.; Green, P. Movement of Solids in Air and Water by Raindrop Impact. Effects of Drop-Size and Water-Depth Variations. Soil Res. 1983, 21, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwitz, S.R. Interception Storage Capacities of Tropical Rainforest Canopy Trees. J. Hydrol. 1985, 77, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.J.; Green, T.W. Erosive Effects of the Large Water Drops (Gravity Drops) That Fall from Plants. Soil Res. 1987, 25, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. The Influence of Flow Discharge on Sediment Concentrations in Raindrop Induced Flow Transport. Soil Res. 1988, 26, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.J. Effects of Flow Velocity Variation on Rain Driven Transportation and the Role of Rain Impact in the Movement of Solids. Soil Res. 1988, 26, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Particle Travel Distances and Bed and Sediment Compositions Associated with Rain-Impacted Flows. Earth Surf. Process. 2001, 26, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.L.; Silburn, D.M. Hydraulic Properties of Rain Impact Surface Seals on Three Clay Soils-Influence of Raindrop Impact Frequency and Rainfall Intensity during Steady State. Soil Res. 2002, 40, 1069–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Sediment Transport by Medium to Large Drops Impacting Flows at Subterminal Velocity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 902–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ploey, J.; Mücher, H.J. A Consistency Index and Rainwash Mechanisms on Belgian Loamy Soils. Earth Surf. Process. 1981, 6, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ploey, J. A Stemflow Equation for Grasses and Similar Vegetation. Catena 1982, 9, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierda, A.; Veen, A.W.L. A Rainfall Simulator Study of Infiltration into Arable Soils. Agric. Water Manag. 1992, 21, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriels, D.; De Boodt, M. Erosion Reduction Factors for Chemically Treated Soils: A Laboratory Experiment. In SSSA Special Publications; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1975; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Houk, D.; Green, T. A Note on Surface Waves Due to Rain. J. Geophys. Res. 1976, 81, 4482–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.; Houk, D.F. The Mixing of Rain with Near-Surface Water. J. Fluid Mech. 1979, 90, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, N.E.; Gifford, G.F. Rainfall Interception by Cool-Desert Shrubs. J. Range Manag. 1976, 29, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevone, B.I.; Yang, Y.S.; Winner, W.E.; Storks-Cotter, I.; Long, S.J. A Rainfall Simulator for Laboratory Use in Acidic Precipitation Studies. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1984, 34, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, C.H.; Joschko, M. A Note on the Reduction of Runoff from Crusted Soils by Earthworm Burrows and Artificial Channels. Z. Pflanzenernaehr. Bodenkd. 1991, 154, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrà, B.G.; Bombino, G.; Denisi, P.; Plaza-Àlvarez, P.A.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Zema, D.A. Water Infiltration after Prescribed Fire and Soil Mulching with Fern in Mediterranean Forests. Hydrology 2021, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlavčová, K.; Danáčová, M.; Kohnová, S.; Szolgay, J.; Valent, P.; Výleta, R. Estimating the Effectiveness of Crop Management on Reducing Flood Risk and Sediment Transport on Hilly Agricultural Land—A Myjava Case Study, Slovakia. Catena 2019, 172, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danacova, M. The Impact of Slope Gradients on the Generation of Surface Runoff in Laboratory Conditions. In Proceedings of the 17th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference SGEM2017, Water Resources, Forest, Marine and Ocean Ecosystems, Vienna, Austria, 27–29 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cerdà, A.; García-Fayos, P. The Influence of Seed Size and Shape on Their Removal by Water Erosion. Catena 2002, 48, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, T.M.; van Deurzen, F.J.M.P.; Eppink, L.A.A.J.; Ruytenberg, R.E. Comparison of Infiltration Rates Measured with an Infiltrometer, a Rainulator and a Permeameter for Erosion Research in SE Nigeria. Soil Technol. 1992, 5, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgleish, H.Y.; Foster, I.D.L. 137Cs Losses from a Loamy Surface Water Gleyed Soil (Inceptisol); a Laboratory Simulation Experiment. Catena 1996, 26, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, C.; Anton, H. Design and Application of a Drip-Type Rainfall Simulator Adapted to Steep Topography and Low Intensity-Rainfall Characteristics in the Coastal Range of Southern Chile. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 9–24 April; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, C.H.; Coppus, R.; Iroumé, A.; Huber, A.; Bronstert, A. Runoff Generation and Soil Erosion Processes after Clear Cutting: Runoff and Erosion After Clear Cutting. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2013, 118, 814–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, J.; Ben-Hur, M.; Gal, M.; Levy, G.J. Rain Energy and Soil Amendments Effects on Infiltration and Erosion of Three Different Soil Types. Soil Res. 1991, 29, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Singh, R. Determination of Soil Hydrologic Properties under Simulated Rainfall Condition. Agric. Water Manag. 1996, 29, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agassi, M.; Bloem, D.; Ben-Hur, M. Effect of Drop Energy and Soil and Water Chemistry on Infiltration and Erosion. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heathwaite, A.L.; Johnes, P.J. Contribution of Nitrogen Species and Phosphorus Fractions to Stream Water Quality in Agricultural Catchments. Hydrol. Process. 1996, 10, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-Y.; Chen, J.-Y.; Chang, F.-H.; Lu, T.-F. Characteristics of Shallow Rain-Impacted Flow over Smooth Bed. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1998, 124, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-Y.; Chen, J.-Y.; Hong, J.-H.; Lu, T.-F.; Liu, C.-S. Turbulence Intensities of Shallow Rain-Impacted Flow over Rough Bed. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2001, 127, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimoyiannis, D.G.; Valmis, S.; Vyrlas, P. A Rainfall Simulation Study of Erosion of Some Calcareous Soils. Glob. Nest 2001, 3, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Todd Walter, M.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Hogarth, W.L.; Parlange, J.-Y. Rainfall Induced Chemical Transport from Soil to Runoff: Theory and Experiments. J. Hydrol. 2004, 295, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Walter, M.T.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Parlange, J.-Y.; Richards, B.K.; Hogarth, W.L.; Rose, C.W. Investigating Raindrop Effects on Transport of Sediment and Non-Sorbed Chemicals from Soil to Surface Runoff. J. Hydrol. 2005, 308, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zreig, M. Control of Rainfall-Induced Soil Erosion with Various Types of Polyacrylamide (8 Pp). J. Soils Sediments 2006, 6, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerley, D. Effects of Rainfall Intensity Fluctuations on Infiltration and Runoff: Rainfall Simulation on Dryland Soils, Fowlers Gap, Australia: Rainfall Intensity Fluctuations in Fowlers Gap. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 2211–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, J.; Anta, J.; Suárez, J.; Puertas, J. Hydraulic, Wash-off and Sediment Transport Experiments in a Full-Scale Urban Drainage Physical Model. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laws, J.O. Measurements of the Fall-Velocity of Water-Drops and Raindrops. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1941, 22, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccalla, T.M. Water-Drop Method of Determining Stability of Soil Structure. Soil Sci. 1944, 58, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, R.; Kinzer, G.D. The Terminal Velocity of Fall for Water Droplets in Stagnant Air. J. Meteorol. 1949, 6, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magono, C. On the Shape of Water Drops Falling in Stagnant Air. J. Meteorol. 1954, 11, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magarvey, R.H.; Taylor, B.W. Apparatus for the Production of Large Water Drops. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1956, 27, 944–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruse, R.M.; Larson, W.E. Effect of Soil Shear Strength on Soil Detachment Due to Raindrop Impact1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977, 41, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, R.S. The Influence of a Thin Water Layer on Waterdrop Impact Forces. Int. Assoc. Sci. Hydrol. Publ. 1963, 65, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, R.S. Waterdrop Impact Forces. Trans. ASAE 1965, 8, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutchler, C.K.; Hansen, L.M. Splash of a Waterdrop at Terminal Velocity. Science 1970, 169, 1311–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutchler, C.K.; Larson, C.L. Splash Amounts from Waterdrop Impact on a Smooth Surface. Water Resour. Res. 1971, 7, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, P.V.; Osheroff, T. Splashing of Drops on Shallow Liquids. Science 1967, 158, 1184–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macklin, W.C.; Hobbs, P.V. Subsurface Phenomena and the Splashing of Drops on Shallow Liquids. Science 1969, 166, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce-Okine, E.; Lal, R. Soil Erodibility as Determined by Raindrop Technique. Soil Sci. 1975, 119, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.T. The Behavior of Large, Low-Surface-Tension Water Drops Falling at Terminal Velocity in Air. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1976, 15, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Durrah, M.; Bradford, J.M. New Methods of Studying Soil Detachment Due to Waterdrop Impact. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1981, 45, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Durrah, M.M.; Bradford, J.M. The Mechanism of Raindrop Splash on Soil Surfaces. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Durrah, M.M.; Bradford, J.M. Parameters for Describing Soil Detachment Due to Single Waterdrop Impact. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Bradford, J.M. Single Waterdrop Splash Detachment and Mechanical Properties of Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.P.; Gupta, S.C.; Rawls, W.J. Soil Detachment by Single Raindrops of Varying Kinetic Energy. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, P.V.; Turco, R.F.; Stott, D.E.; Bradford, J.M. Organic Polymers’ Effect on Soil Shear Strength and Detachment by Single Raindrops. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsma, E.; Valenzuela, C.R. Drop Testing Aggregate Stability of Some Soils near Merida, Spain. Earth Surf. Process. 1981, 6, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, P.B.; Cruse, R.M. Soil Water Matric Potential Effects on Aggregate Stability. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1983, 47, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadir, H.; Payne, D. The Formation and Characteristics of Splash Following Raindrop Impact on Soil. J. Soil Sci. 1988, 39, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard, D.L. A System for Producing Various Sizes, Numbers, and Frequencies of Uniform-Size Drops. Trans. ASAE 1990, 33, 1767–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzai, L.; Bouhadef, M. Water Drop Erosivity: Effects on Soil Splash. J. Hydraul. Res. 2003, 41, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furbish, D.J.; Hamner, K.K.; Schmeeckle, M.; Borosund, M.N.; Mudd, S.M. Rain Splash of Dry Sand Revealed by High-Speed Imaging and Sticky Paper Splash Targets. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryżak, M.; Bieganowski, A.; Polakowski, C. Effect of Soil Moisture Content on the Splash Phenomenon Reproducibility. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-K.; Hsieh, P.-R.; Yuter, S.E.; Cheng, L.-W.; Tsai, C.-L.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, Y. Measuring Droplet Fall Speed with a High-Speed Camera: Indoor Accuracy and Potential Outdoor Applications. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yakubu, M.L.; Yusop, Z.; Fulazzaky, M.A. The Influence of Rain Intensity on Raindrop Diameter and the Kinetics of Tropical Rainfall: Case Study of Skudai, Malaysia. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utah State University. Hydraulic Testing & Calibration. Usu.edu. Available online: https://uwrl.usu.edu/hydraulics/hydraulic-testing (accessed on 19 August 2022).







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rončević, V.; Živanović, N.; Ristić, R.; Boxel, J.H.v.; Kašanin-Grubin, M. Dripping Rainfall Simulators for Soil Research—Design Review. Water 2022, 14, 3309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203309
Rončević V, Živanović N, Ristić R, Boxel JHv, Kašanin-Grubin M. Dripping Rainfall Simulators for Soil Research—Design Review. Water. 2022; 14(20):3309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203309
Chicago/Turabian StyleRončević, Vukašin, Nikola Živanović, Ratko Ristić, John H. van Boxel, and Milica Kašanin-Grubin. 2022. "Dripping Rainfall Simulators for Soil Research—Design Review" Water 14, no. 20: 3309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203309





