Estimation of Evapotranspiration and Soil Water Content at a Regional Scale Using Remote Sensing Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
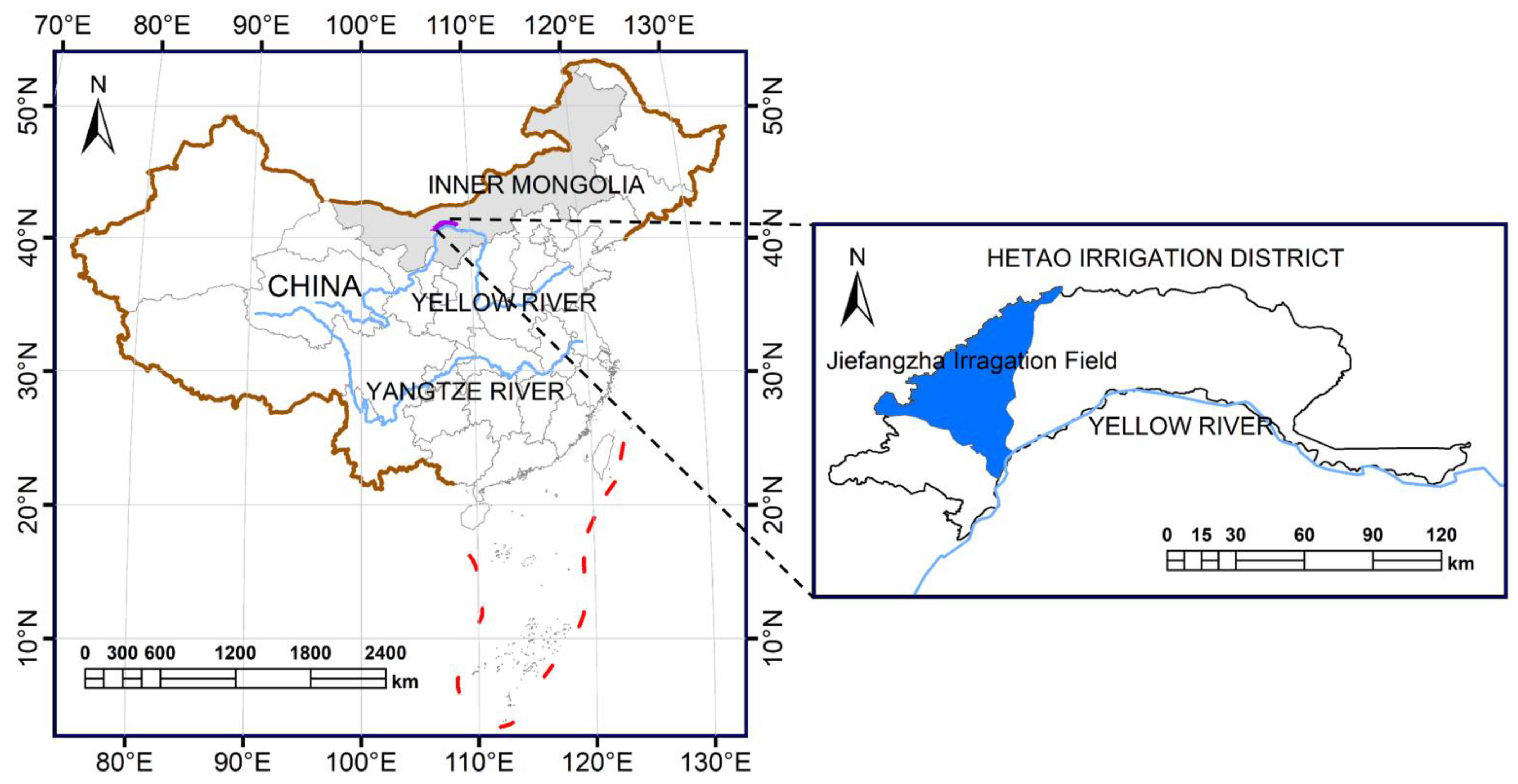
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
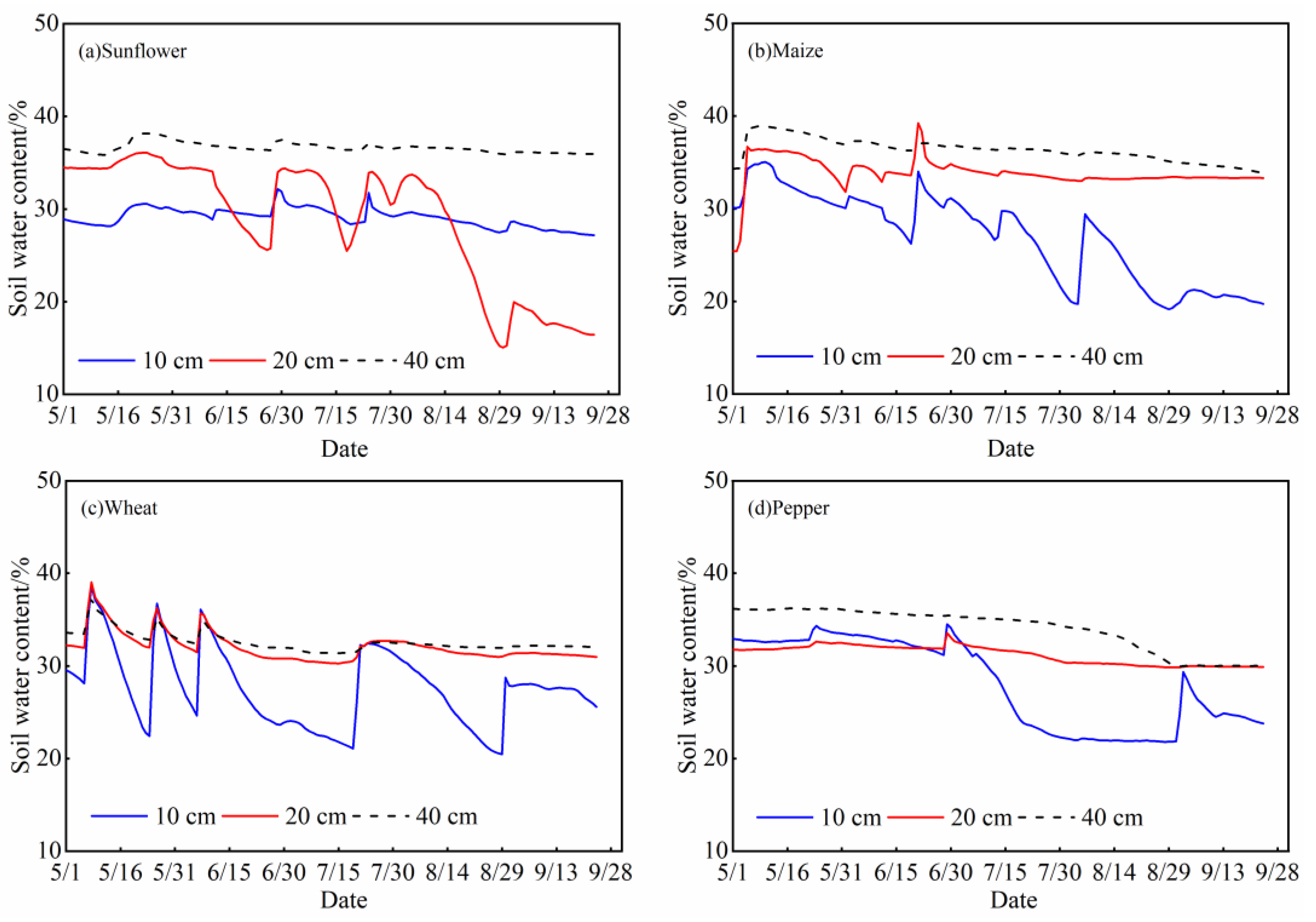
2.2.1. In-Situ Measurement
2.2.2. Remote Sensing Data
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Data Fusion Method
2.3.2. ISODATA Cluster Algorithm and Spectral Matching
2.3.3. SEBS Model
2.3.4. CWSI Method
2.3.5. Statistical Metrics
3. Results
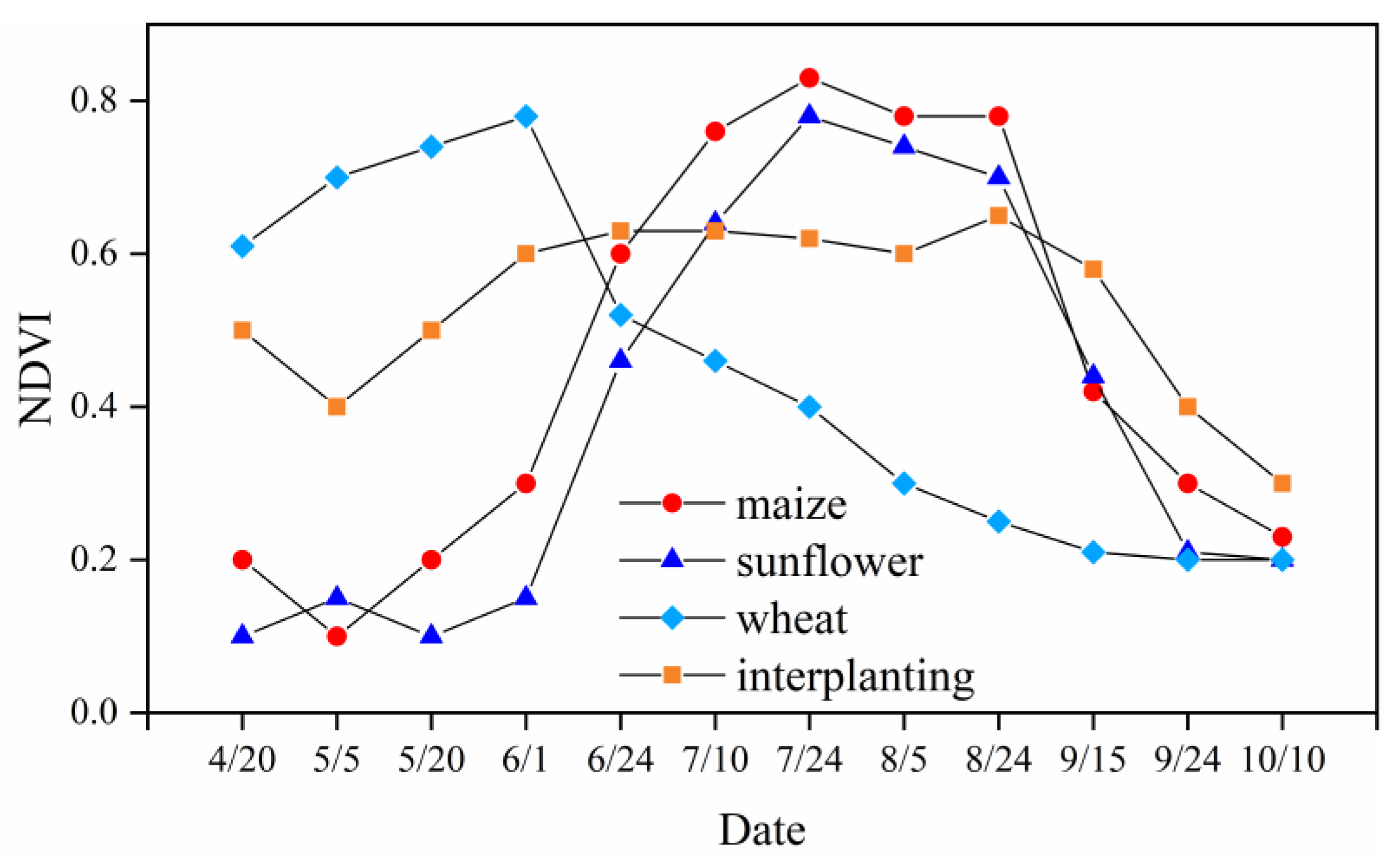
3.1. Planting Structure
3.2. Spatial Distribution of the ET
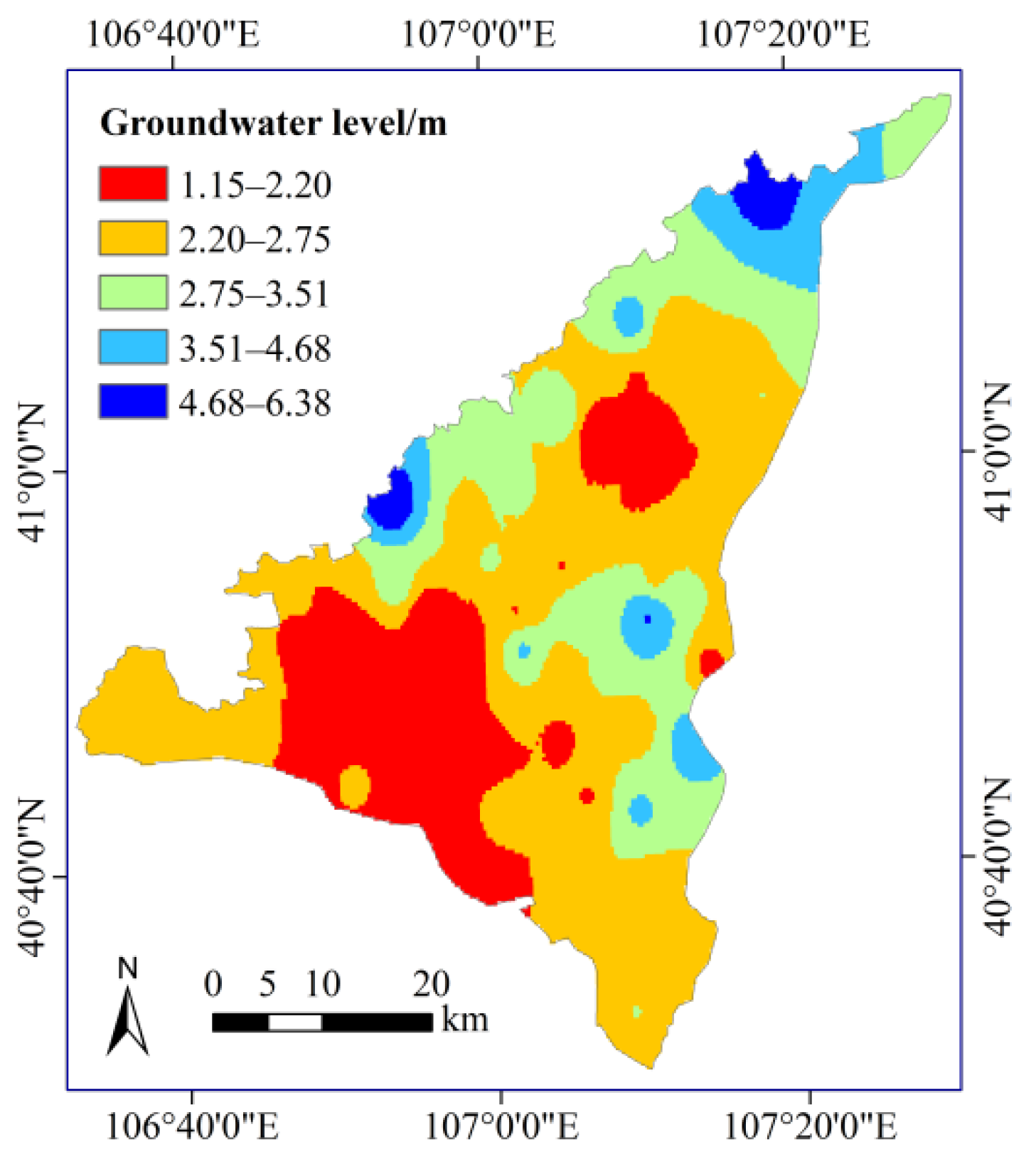
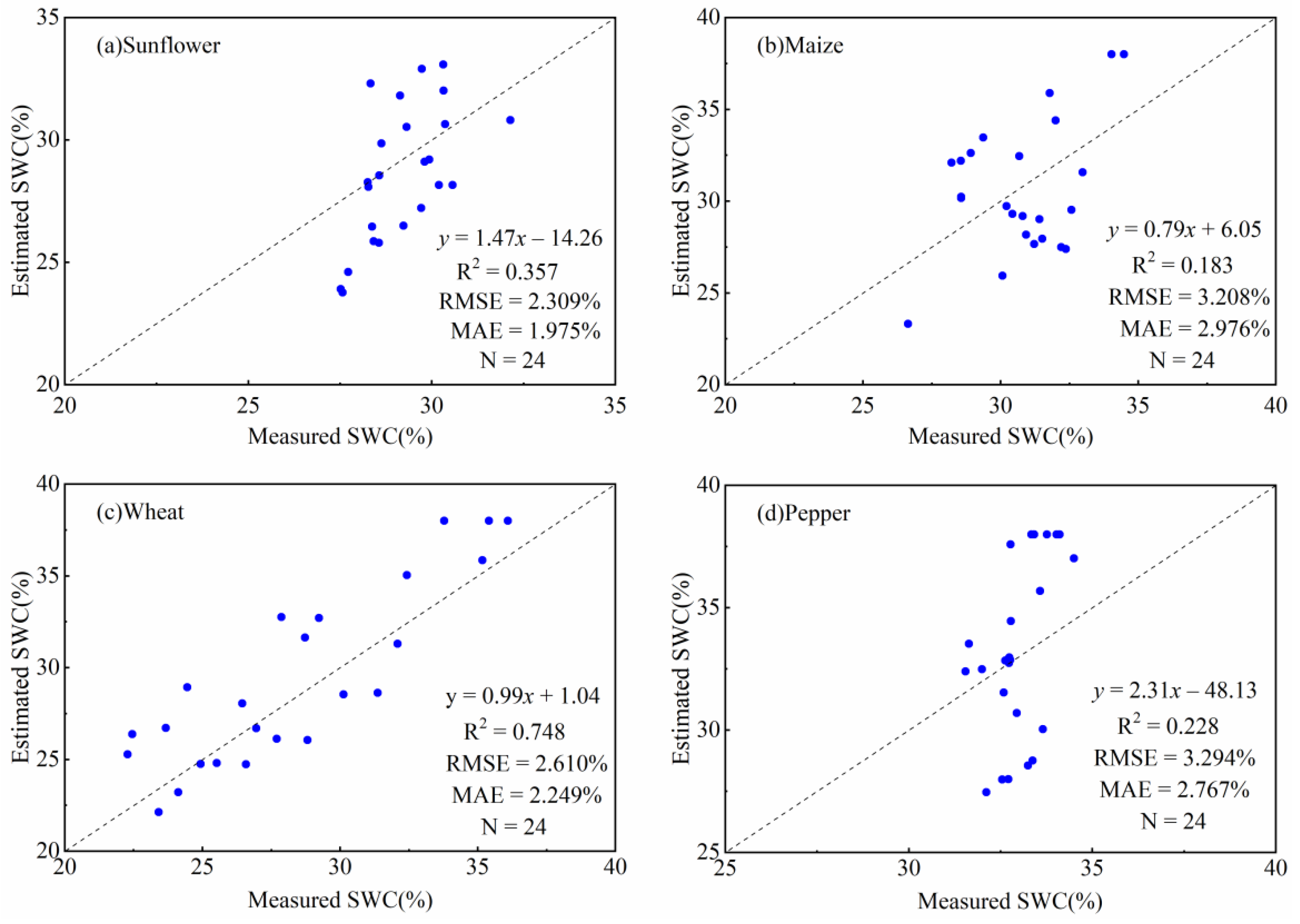
3.3. Spatial Distribution of the SWC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture–climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobriyal, P.; Qureshi, A.; Badola, R.; Hussain, S.A. A review of the methods available for estimating soil moisture and its implications for water resource management. J. Hydrol. 2012, 458–459, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Farahmand, A.; Melton, F.S.; Teixeira, J.; Anderson, M.C.; Wardlow, B.D.; Hain, C.R. Remote sensing of drought: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 452–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, D.A.; Campbell, C.S.; Hopmans, J.W.; Hornbuckle, B.K.; Jones, S.B.; Knight, R.; Ogden, F.; Selker, J.; Wendroth, O. Soil Moisture Measurement for Ecological and Hydrological Watershed-Scale Observatories: A Review. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 358–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Otkin, J.A.; Kustas, W.P. A climatological study of evapotranspiration and moisture stress across the continental United States based on thermal remote sensing: 2. Surface moisture climatology. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D11112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Loew, A.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Niesel, J. Spatial Downscaling of Satellite Soil Moisture Data Using a Vegetation Temperature Condition Index. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Lin, L.; Wu, S.; Kwal Deng, K.A.; Petropoulos, G.P. Surface soil moisture retrievals over partially vegetated areas from the synergy of Sentinel-1 and Landsat 8 data using a modified water-cloud model. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 72, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Bai, L.; Yan, L.; Zhang, C.; Yang, W.; Lei, H.; Quan, J.; Meng, X.; Shi, C. Generation of spatially complete and daily continuous surface soil moisture of high spatial resolution. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abowarda, A.S.; Bai, L.; Zhang, C.; Long, D.; Li, X.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Z. Generating surface soil moisture at 30 m spatial resolution using both data fusion and machine learning toward better water resources management at the field scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 255, 112301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Jiao, X.; Li, B.; Yu, X.; Shao, M.; Jin, X. Long time series of daily evapotranspiration in China based on the SEBAL model and multisource images and validation. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3995–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, W.H.; Steppe, K. Estimating evapotranspiration and drought stress with ground-based thermal remote sensing in agriculture: A review. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 4671–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, N.; Walker, J.P.; Guerschman, J.; Ryu, D.; Gurney, R.J. Standing water effect on soil moisture retrieval from L-band passive microwave observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Jones, S.B.; Philpot, W.D. A linear physically-based model for remote sensing of soil moisture using short wave infrared bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, G.; Qu, Z.; Pereira, L.S. Assessing the groundwater dynamics and impacts of water saving in the Hetao Irrigation District, Yellow River basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Qin, Z.; Shi, J.; Gong, P. A practical split-window algorithm for retrieving land-surface temperature from MODIS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 26, 3181–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Yang, D.; Huang, J.; Chen, D. Evaluation of MODIS surface reflectance products for wheat leaf area index (LAI) retrieval. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Schmugge, T.; Kustas, W.P.; Massman, W.J. An Evaluation of Two Models for Estimation of the Roughness Height for Heat Transfer between the Land Surface and the Atmosphere. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2001, 40, 1933–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Li, X.; Cao, Q.; Hao, R.; Qiao, J. Impacts of climate variability and landscape pattern change on evapotranspiration in a grassland landscape mosaic. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 34, 1035–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Bali, K.M.; Light, S.; Hessels, T.; Kisekka, I. Evaluation of remote sensing-based evapotranspiration models against surface renewal in almonds, tomatoes and maize. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 238, 106228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yujiao, W.; Lin, Z.; Xinyu, C.; Wenke, W.; Jianshi, G.; Huilin, Y.; Dan, M. A downscaling study of evapotranspiration in Nanjing based on the ESTARFM model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 6287–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.D.; Idso, S.B.; Reginato, R.J.; Pinter, P.J., Jr. Canopy temperature as a crop water stress indicator. Water Resour. Res. 1981, 17, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhangzhong, L.; Yu, J.; Shi, K.; Yao, L. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of Reference Evapotranspiration in Shandong Province from 1980 to 2019. Water 2020, 12, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Suo, L. Water requirement model for crop under the condition of water-saving irrigation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 1, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judeh, T.; Bian, H.; Shahrour, I. GIS-Based Spatiotemporal Mapping of Groundwater Potability and Palatability Indices in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas. Water 2021, 13, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, Z. Rapid Diagnosis of Nitrogen Nutrition Status in Summer Maize over Its Life Cycle by a Multi-Index Synergy Model Using Ground Hyperspectral and UAV Multispectral Sensor Data. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, A.; Mondal, P. Synergistic Use of Radar and Optical Satellite Data for Improved Monsoon Cropland Mapping in India. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veloso, A.; Mermoz, S.; Bouvet, A.; Le Toan, T.; Planells, M.; Dejoux, J.-F.; Ceschia, E. Understanding the temporal behavior of crops using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2-like data for agricultural applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbick, N.; Chowdhury, D.; Salas, W.; Qi, J. Monitoring Rice Agriculture across Myanmar Using Time Series Sentinel-1 Assisted by Landsat-8 and PALSAR-2. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, W.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, J.; Yuan, Y. Application of a parallel spectral–spatial convolution neural network in object-oriented remote sensing land use classification. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, V.; Talebi, A.; Shirmohammadi, B. Producing a landslide inventory map using pixel-based and object-oriented approaches optimized by Taguchi method. Geomorphology 2014, 204, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Franklin, S.E.; Guo, X.; Stenhouse, G.B. Object-oriented classification of multi-resolution images for the extraction of narrow linear forest disturbance. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 2, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnes, M.L.; Yoder, L.; Khodaee, M. Detecting Winter Cover Crops and Crop Residues in the Midwest US Using Machine Learning Classification of Thermal and Optical Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Ciara, H.; Xiang, M.; Tang, H.; Wu, W. In-Season Crop Mapping with GF-1/WFV Data by Combining Object-Based Image Analysis and Random Forest. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Du, X. Long Time Series Land Cover Classification in China from 1982 to 2015 Based on Bi-LSTM Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haoran, S.; Lei, W.; Rencai, L.; Zhen, Z.; Baozhong, Z. Mapping Plastic Greenhouses with Two-Temporal Sentinel-2 Images and 1D-CNN Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Csillik, O. Sentinel-2 cropland mapping using pixel-based and object-based time-weighted dynamic time warping analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, C.; Manoli, G.; Martello, M.; Chemin, Y.; Pons, D.; Teatini, P.; Piccoli, I.; Morari, F. Mapping Maize Evapotranspiration at Field Scale Using SEBAL: A Comparison with the FAO Method and Soil-Plant Model Simulations. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safa, B.; Mehrez, Z.; Mohammad, E.H.; Nicolas, B.; Zohra, L.-C.; Qi, G.; Pascal, F. Soil Moisture and Irrigation Mapping in A Semi-Arid Region, Based on the Synergetic Use of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Q.; Zribi, M.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Baghdadi, N. Synergetic Use of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data for Soil Moisture Mapping at 100 m Resolution. Sensors 2017, 17, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| ID | Site Number | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Elevation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 53420 | 107.13 | 40.90 | 1056.7 |
| 2 | 53324 | 107.02 | 41.45 | 1576.8 |
| 3 | 53231 | 106.40 | 41.40 | 1509.6 |
| 4 | 53513 | 107.42 | 40.75 | 1039.3 |
| 5 | 53419 | 107.00 | 40.33 | 1055.1 |
| 6 | 53512 | 106.82 | 39.68 | 1091.6 |
| 7 | 53522 | 107.85 | 40.05 | 1184.3 |
| 8 | 53336 | 108.52 | 41.57 | 1288.2 |
| 9 | 53337 | 108.27 | 41.10 | 1022.7 |
| 10 | 53433 | 108.65 | 40.73 | 1020.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Wei, Z.; Lin, R.; Cai, J.; Han, C. Estimation of Evapotranspiration and Soil Water Content at a Regional Scale Using Remote Sensing Data. Water 2022, 14, 3283. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203283
Chen H, Wei Z, Lin R, Cai J, Han C. Estimation of Evapotranspiration and Soil Water Content at a Regional Scale Using Remote Sensing Data. Water. 2022; 14(20):3283. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203283
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, He, Zheng Wei, Rencai Lin, Jiabing Cai, and Congying Han. 2022. "Estimation of Evapotranspiration and Soil Water Content at a Regional Scale Using Remote Sensing Data" Water 14, no. 20: 3283. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203283
APA StyleChen, H., Wei, Z., Lin, R., Cai, J., & Han, C. (2022). Estimation of Evapotranspiration and Soil Water Content at a Regional Scale Using Remote Sensing Data. Water, 14(20), 3283. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203283






