The Quantitative Analysis of Water Mass during Winter on the East China Sea Shelf Using an Extended OMP Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
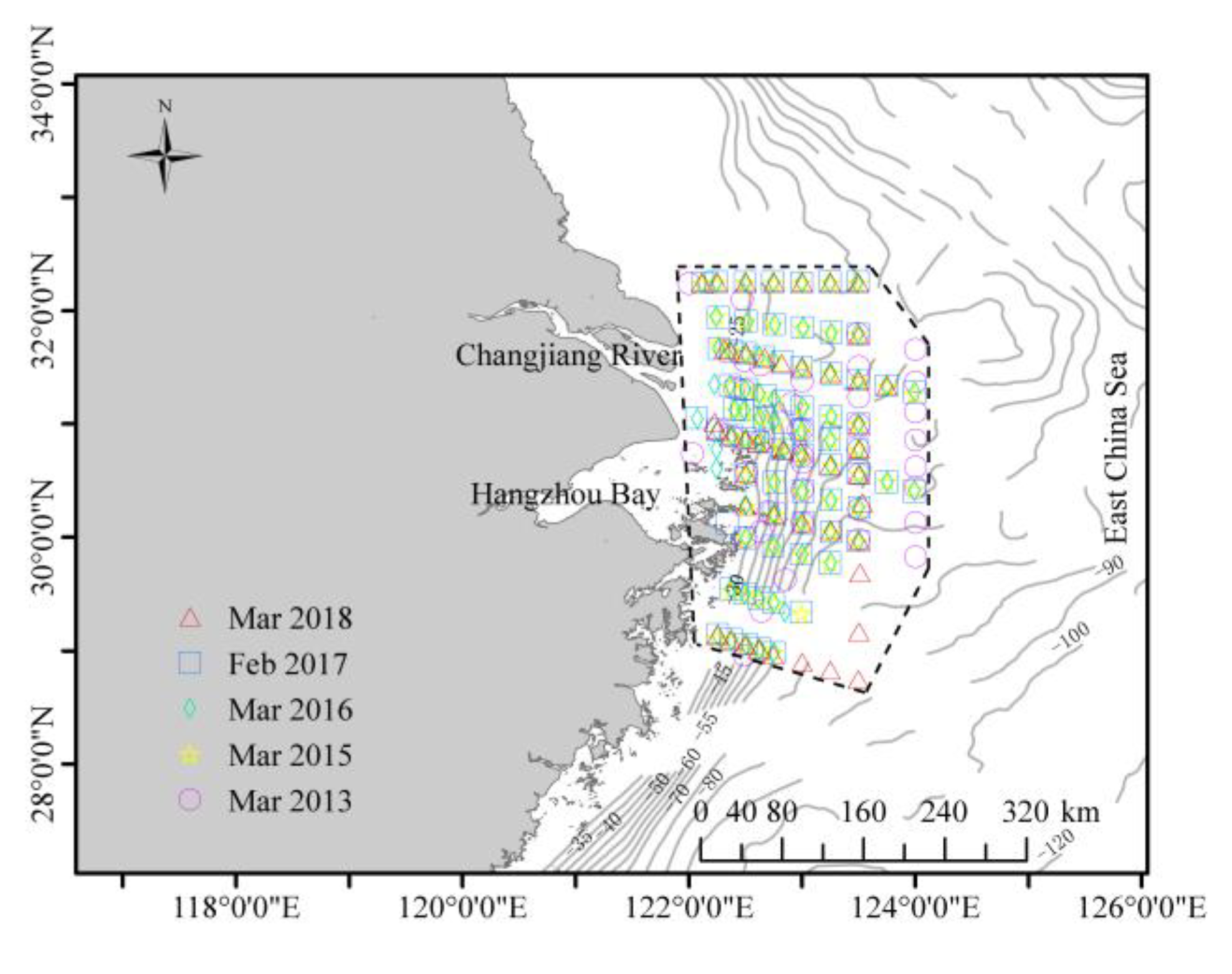
2.1. Biogeochemical Data
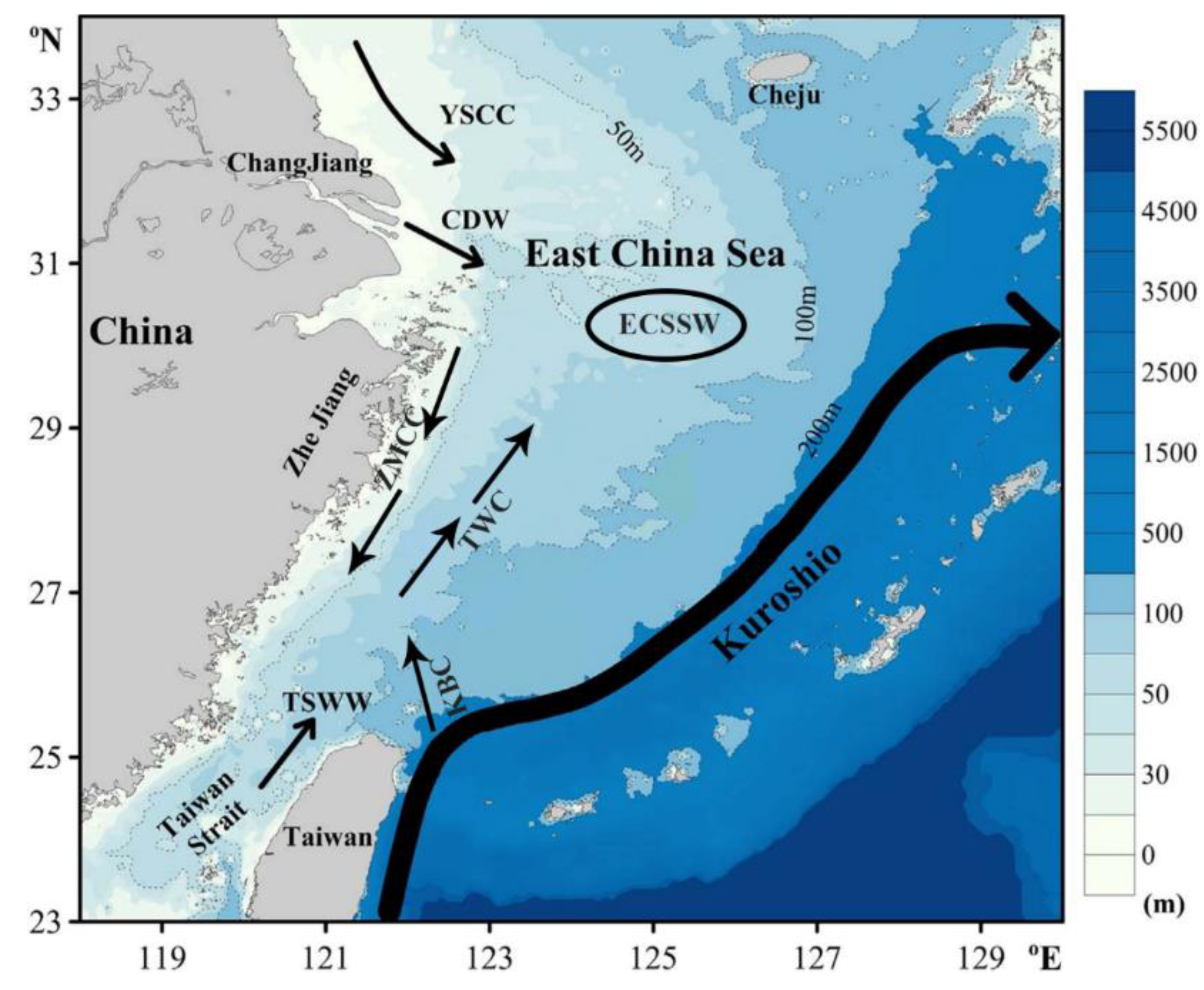
2.2. Spatial Distribution and Source Water Type Definition
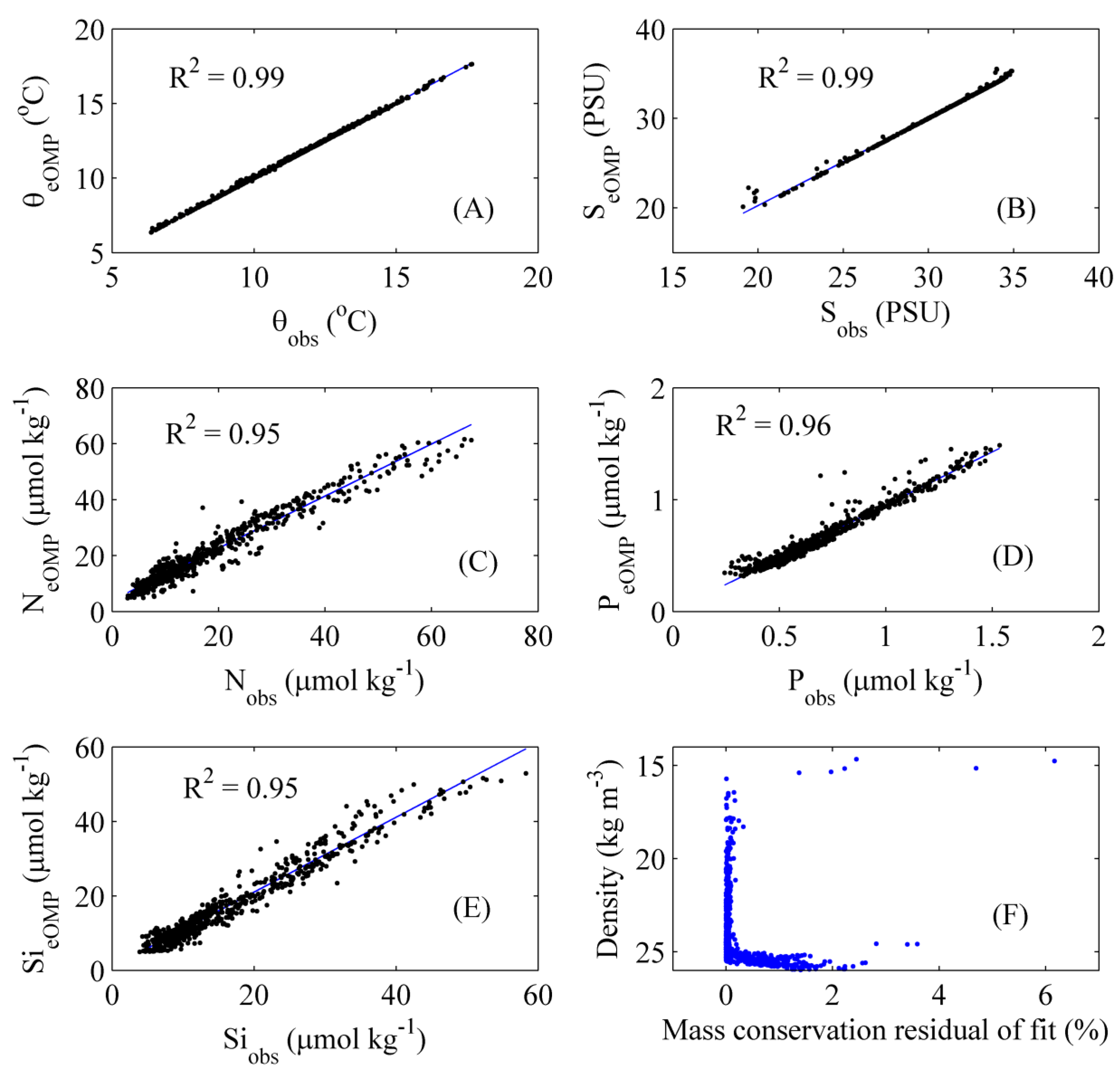
2.3. Optimum Multiparameter Analysis
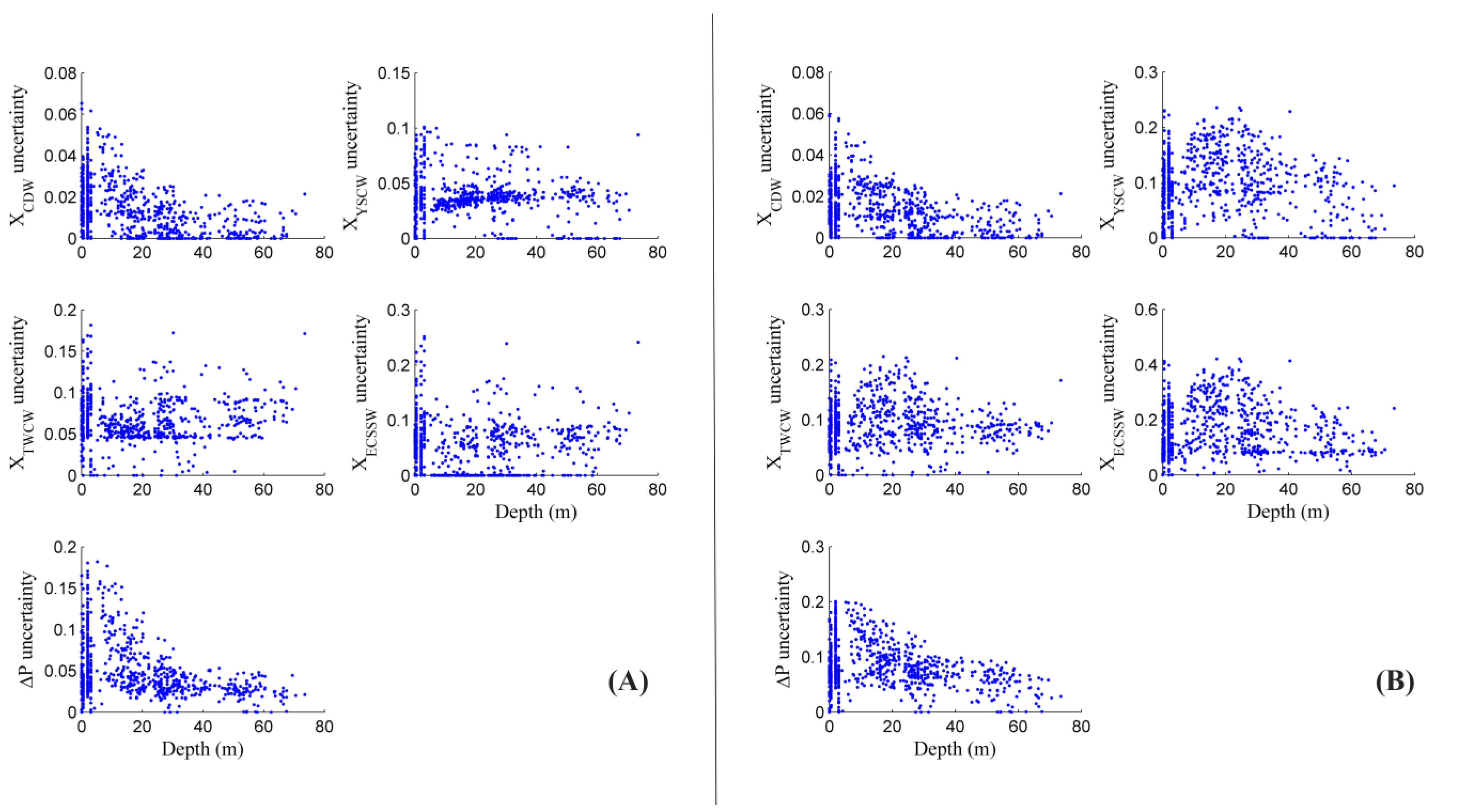
2.4. Uncertainty
3. Results and Discussion
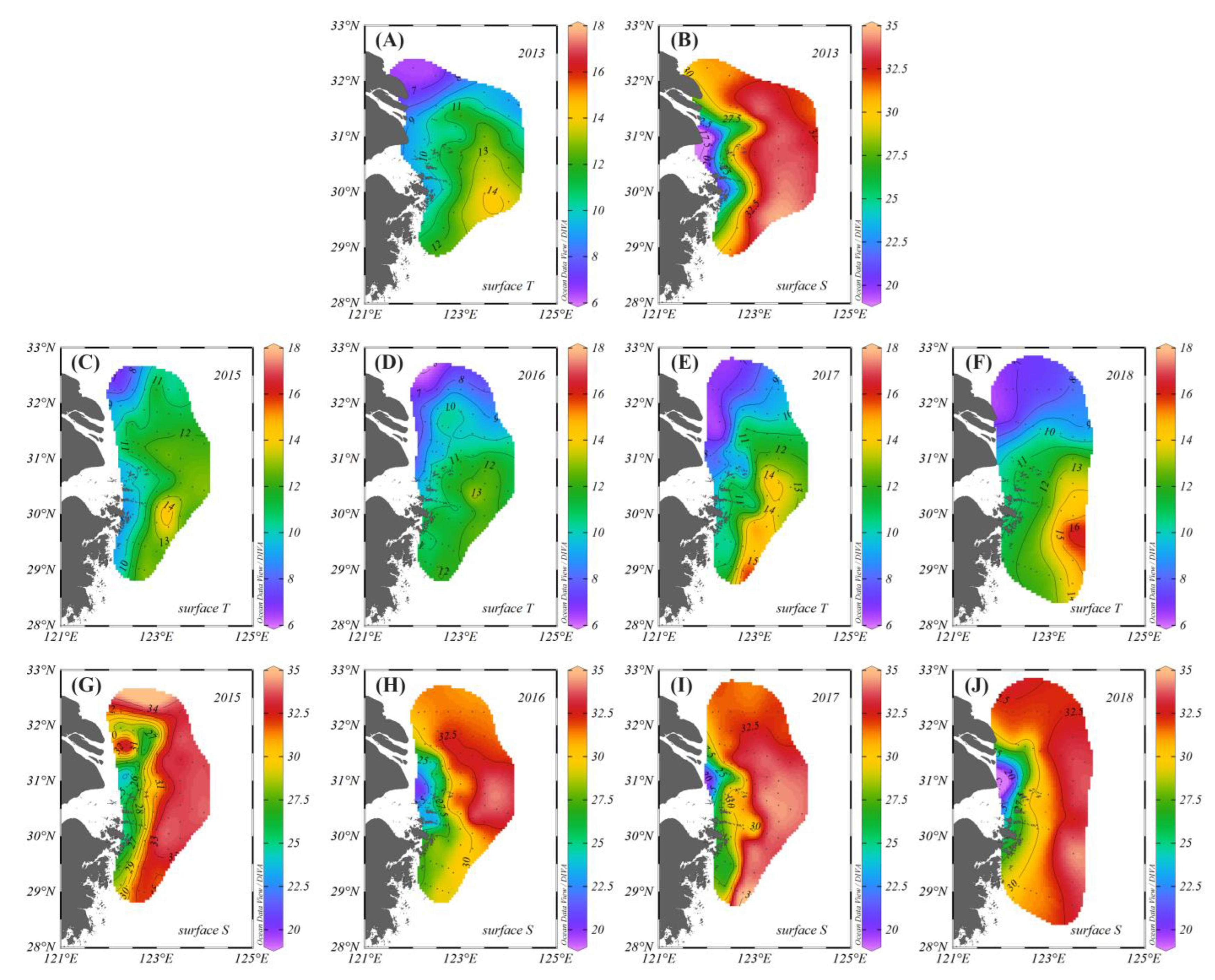
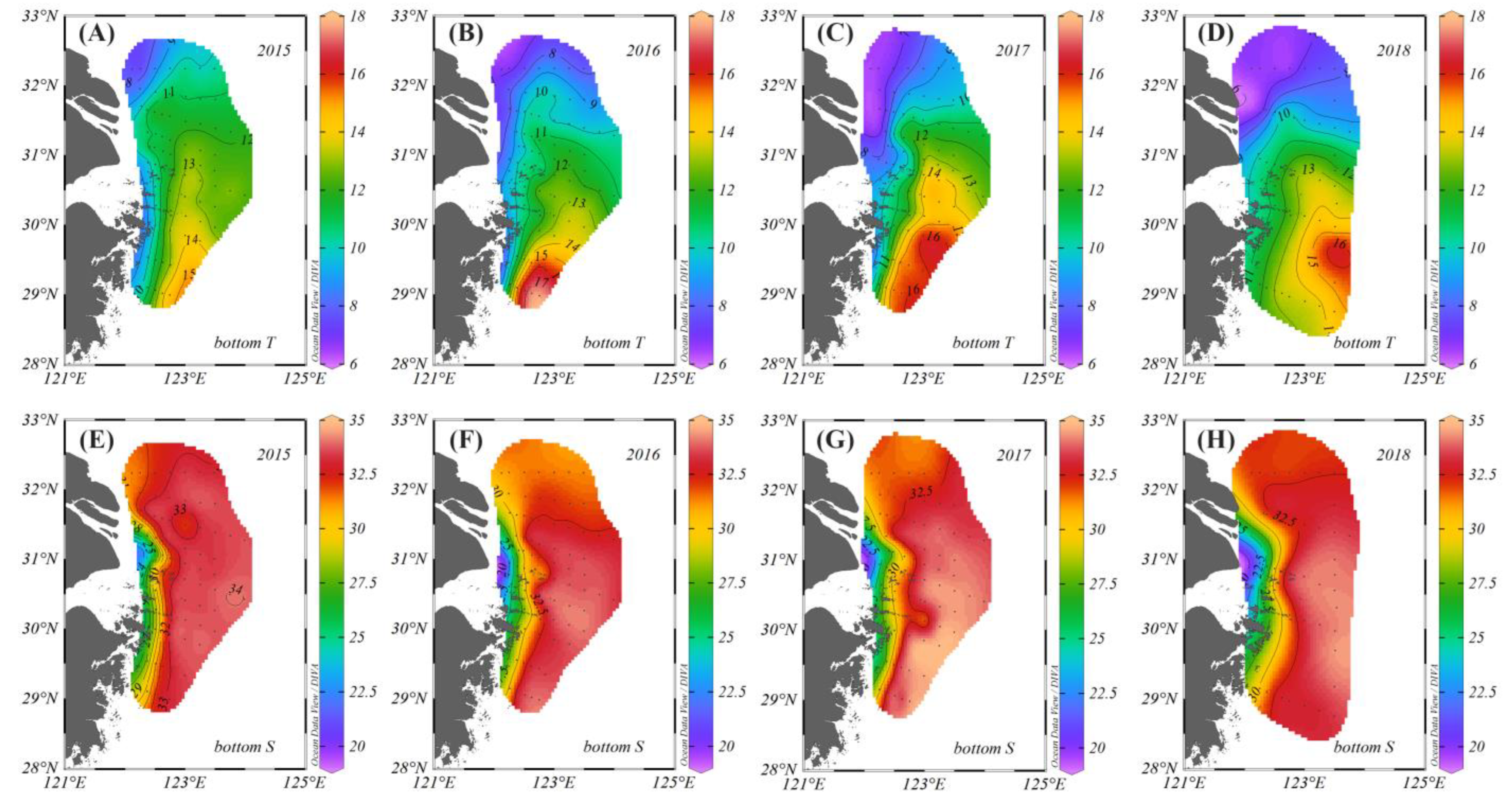
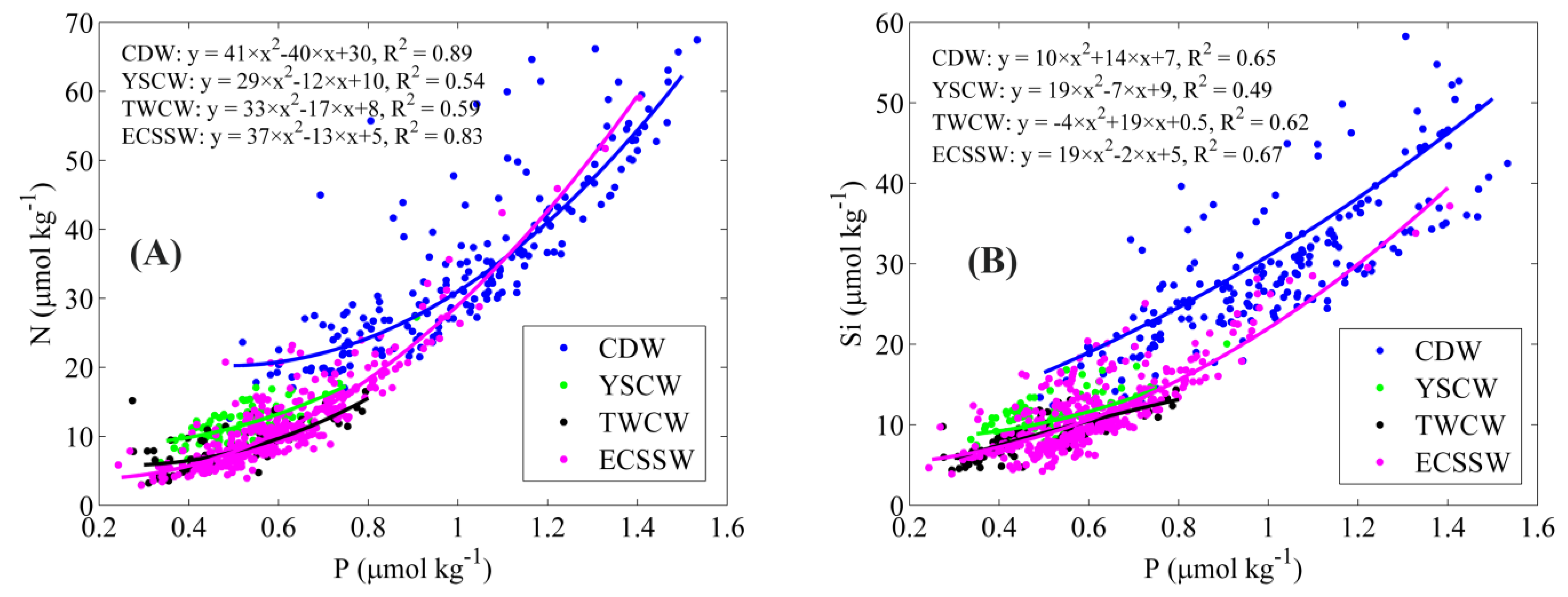
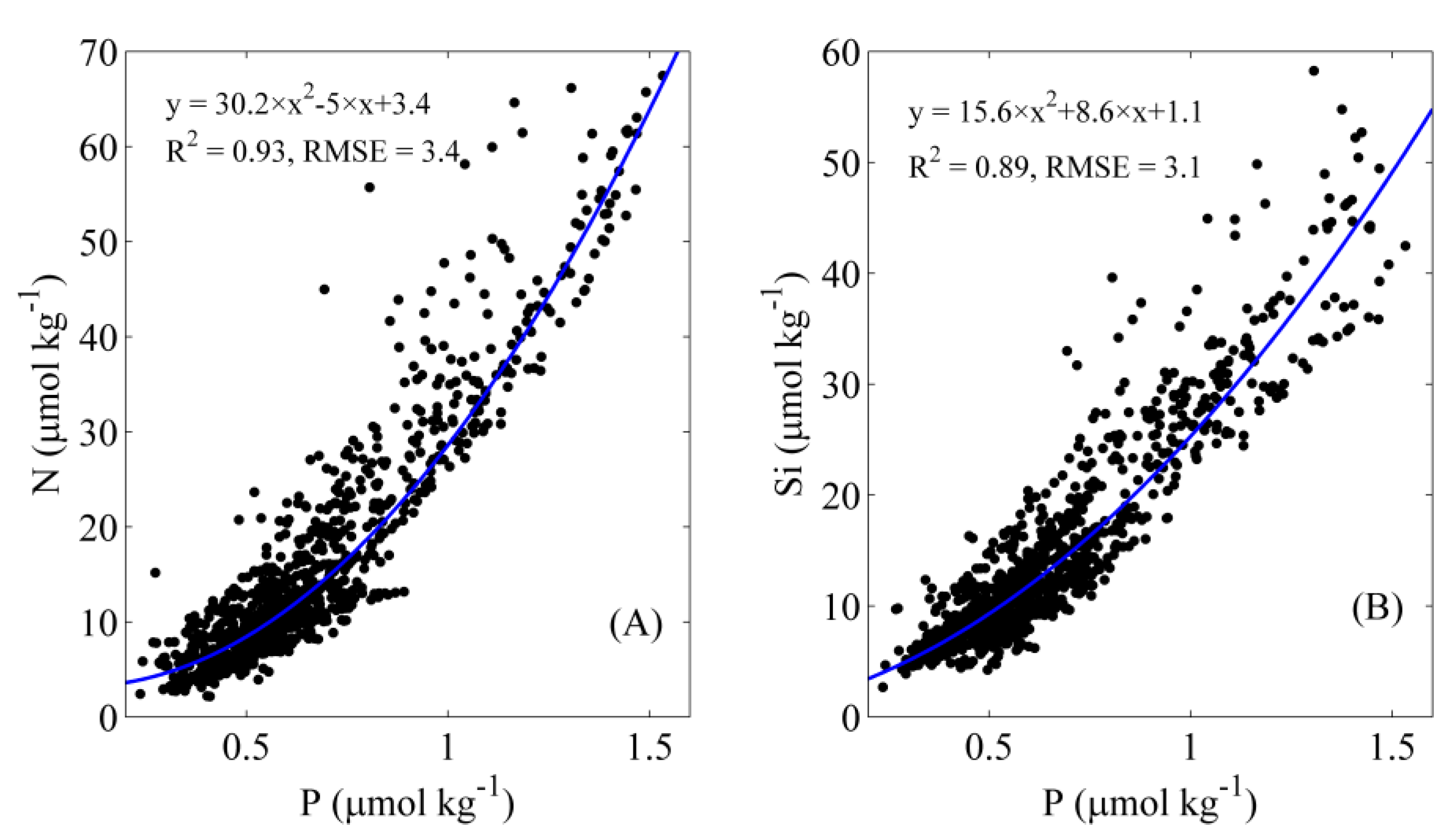
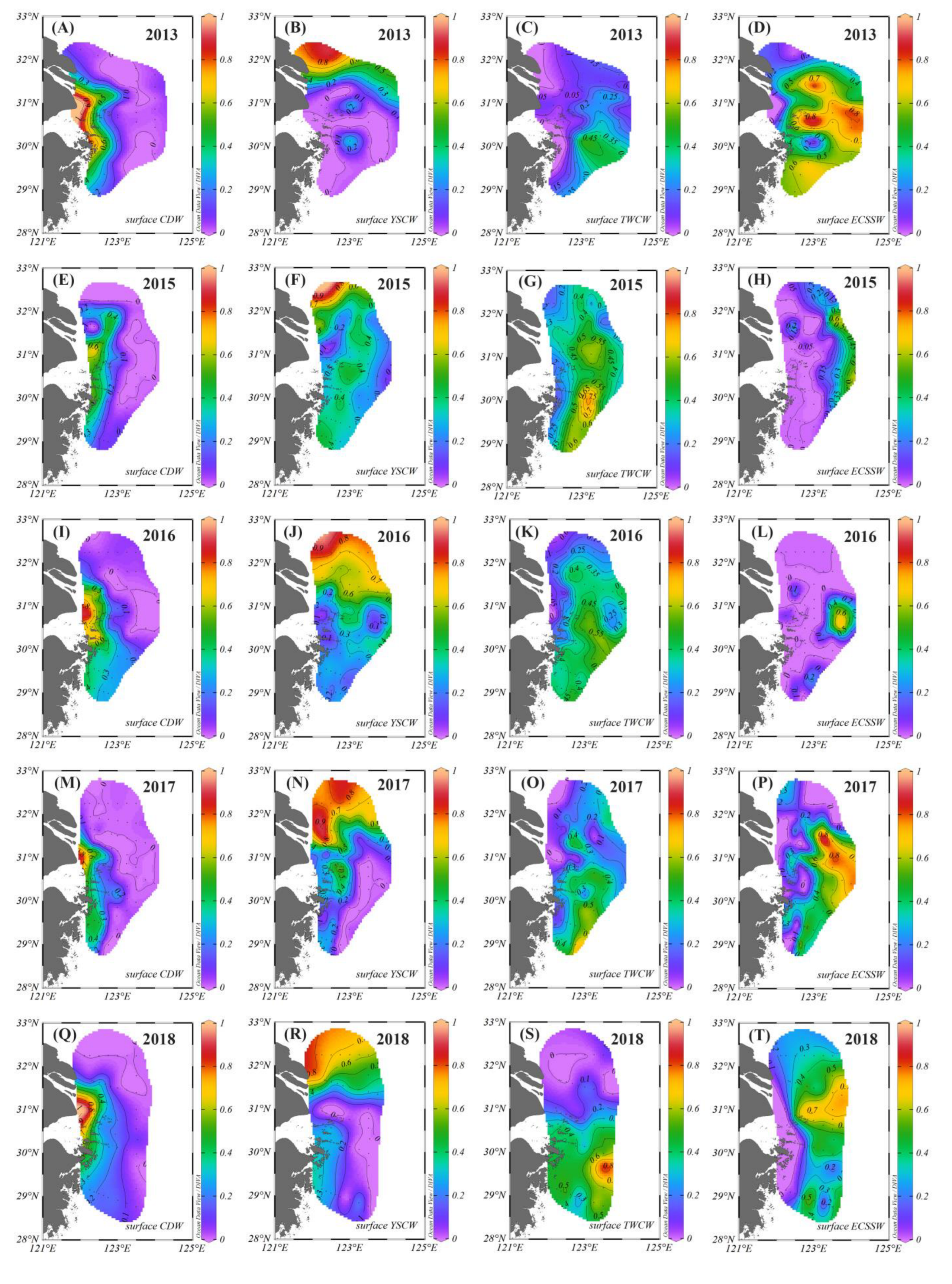
3.1. Contributions and Natural Boundaries of Source Water Masses
3.2. Comparison with Previous Studies
3.3. Interannual Variability of Source Water Masses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ichikawa, H.; Beardsley, R.C. The Current System in the Yellow and East China Seas. J. Oceanogr. 2002, 58, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, H.J.; Cho, C.H. Seasonal circulation patterns of the Yellow and East China Seas derived from satellite-tracked drifter trajectories and hydrographic observations. Prog. Oceanogr. 2016, 146, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Chao, S.Y. A climatological description of circulation in and around the East China Sea. Deep-Sea Res. Part II-Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2003, 50, 1065–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beardsley, R.C.; Limeburner, R.; Yu, H.; Cannon, G.A. Discharge of the Changjiang (Yangtze River) into the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 1985, 4, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.C.; Chen, Y.L.L.; Liu, K.K. Chemical hydrography and chlorophyll a distribution in the East China Sea in summer: Implications in nutrient dynamics. Cont. Shelf Res. 1996, 16, 1561–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.A. Chemical and physical fronts in the Bohai, Yellow and East China seas. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, 394–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Mao, X.; Yang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W. Seasonal Variations of Several Main Water Masses in the Southern Yellow Sea and East China Sea in 2011. J. Ocean Univ. China 2013, 12, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.X.; Han, X.B.; Yue, S.H.; Wen, G.Y.; Yang, R.M.; Kusky, T.M. Monthly variations of water masses in the East China Seas. Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26, 1954–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.M.; Ren, J.L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G.L. Nutrient gradients from the eutrophic Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary to the oligotrophic Kuroshio waters and re-evaluation of budgets for the East China Sea Shelf. Prog. Oceanogr. 2007, 74, 449–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Qin, S.; Yang, D.; Liu, Z. The study on seasonal characteristics of water masses in the western East China Sea shelf area. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 33, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yin, B.; Liu, Z.; Bai, T.; Qi, J.; Chen, H. Numerical study on the pattern and origins of Kuroshio branches in the bottom water of southern East China Sea in summer. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C02014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yin, B.; Chai, F.; Feng, X.; Xue, H.; Gao, G.; Yu, F. The onshore intrusion of Kuroshio subsurface water from February to July and a mechanism for the intrusion variation. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 167, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, C.; Ding, P.; Li, C.; Lin, H. Does the Taiwan warm current exist in winter? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L12302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.T.A.; Sheu, D.D. Does the Taiwan Warm Current originate in the Taiwan Strait in wintertime? J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, C04005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lian, E.; Yang, S.; Wu, H.; Yang, C.; Li, C.; Liu, J.T. Kuroshio subsurface water feeds the wintertime Taiwan Warm Current on the inner East China Sea shelf. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 4790–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hur, H.B.; Jacobs, G.A.; Teague, W.J. Monthly variations of water masses in the Yellow and East China Sea, November 6, 1998. J. Oceanogr. 1999, 55, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Hong, G.H.; Park, Y.; Zhang, H.F. Reevaluation of mixing among multiple water masses in the shelf: An example from the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Song, X.X.; Yuan, Y.Q.; Cao, X.H.; Wang, W.T.; Chi, L.B.; Yu, Z.M. Water Mass Analysis of the East China Sea and Interannual Variation of Kuroshio Subsurface Water Intrusion Through an Optimum Multiparameter Method. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 3723–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, M. A multi-parameter extension of temperature/salinity diagram techniques for the analysis of non-isopycnal mixing. Prog. Oceanogr. 1981, 10, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, M.; Large, D.G.B. Optimum Multiparameter Analysis of Mixing in the Thermocline of the Eastern Indian Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, R.; Tomczak, M. Optimum multiparameter analysis of the water mass structure in the Atlantic Ocean thermocline. Deep Sea Res. Part I 1999, 46, 1895–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, P.C.; Pérez, F.F.; Velo, A.; Gilcoto, M. Water masses distribution in the Southern Ocean: Improvement of an extended OMP (eOMP) analysis. Prog. Oceanogr. 2012, 103, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bashmachnikov, I.; Nascimento, A.; Neves, F.; Menezes, T.; Koldunov, N.V. Distribution of intermediate water masses in the subtropical northeast Atlantic. Ocean Sci. 2015, 11, 803–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Ibáñez, M.I.; Pardo, P.C.; Carracedo, L.I.; Mercier, H.; Lherminier, P.; Ríos, A.F.; Pérez, F.F. Structure, transports and transformations of the water masses in the Atlantic Subpolar Gyre. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 135, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dotto, T.S.; Kerr, R.; Mata, M.M.; Garcia, C.A.E. Multidecadal freshening and lightening in the deep waters of the Bransfield Strait, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 3741–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Carvalho Ferreira, M.L.; Kerr, R. Source water distribution and quantification of North Atlantic Deep Water and Antarctic Bottom Water in the Atlantic Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2017, 153, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.C. Quantifying Antarctic Bottom water and North Atlantic Deep Water volumes. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, C05027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| SWT | θ | S | NO3− | PO43− | SiO32− | Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°C) | (PSU) | (μmol kg−1) | (μmol kg−1) | (μmol kg−1) | ||
| CDW | 8.7 (±0.8) | 18.8 (±1.2) | 60 (±9) | 1.4 (±0.15) | 52 (±7) | 0.01 |
| YSCW | 5.5 (±0.5) | 31.2 (±0.3) | 9.0 (±0.9) | 0.35 (±0.04) | 8.0 (±0.9) | 0.04 |
| TWCW | 17.2 (±0.5) | 34.6 (±0.2) | 7.4 (±0.4) | 0.52 (±0.07) | 5.5 (±0.4) | 0.06 |
| ECSSW | 11.5 (±0.5) | 33.7 (±0.3) | 3.6 (±0.3) | 0.25 (±0.04) | 4.7 (±0.3) | 0.05 |
| Weight | 38.5 | 37.3 | 8.8 | 12.3 | 10.8 | |
| Ratio | N/A | N/A | 47 (±7) | 1 | 35 (±4) | |
| r2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.95 |
| Year | CDW | YSCW | TWCW | ECSSW | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | Bottom | Surface | Bottom | Surface | Bottom | Surface | Bottom | |
| 2015 | 7.7% | 4.3% | 6.2% | 11.4% | 26.2% | 37.1% | 3.1% | 12.9% |
| 2016 | 15.1% | 4.2% | 35.6% | 38.9% | 8.2% | 15.3% | 2.7% | 12.5% |
| 2017 | 5.6% | 2.9% | 29.6% | 30.4% | 7.0% | 21.7% | 29.6% | 27.5% |
| 2018 | 6.8% | 6.7% | 18.2% | 22.2% | 15.9% | 24.4% | 36.4% | 35.6% |
| STD | 3.7% | 1.4% | 11.2% | 10.2% | 7.7% | 7.9% | 15.2% | 9.9% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Wallhead, P.; Bellerby, R.G.J.; Liu, J.; Yang, A. The Quantitative Analysis of Water Mass during Winter on the East China Sea Shelf Using an Extended OMP Analysis. Water 2022, 14, 3214. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203214
Li X, Wallhead P, Bellerby RGJ, Liu J, Yang A. The Quantitative Analysis of Water Mass during Winter on the East China Sea Shelf Using an Extended OMP Analysis. Water. 2022; 14(20):3214. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203214
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaoshuang, Philip Wallhead, Richard Garth James Bellerby, Jing Liu, and Anqiang Yang. 2022. "The Quantitative Analysis of Water Mass during Winter on the East China Sea Shelf Using an Extended OMP Analysis" Water 14, no. 20: 3214. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203214





