The Current State-Of-Art of Copper Removal from Wastewater: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Copper (Cu) as a Pollutant in Wastewater
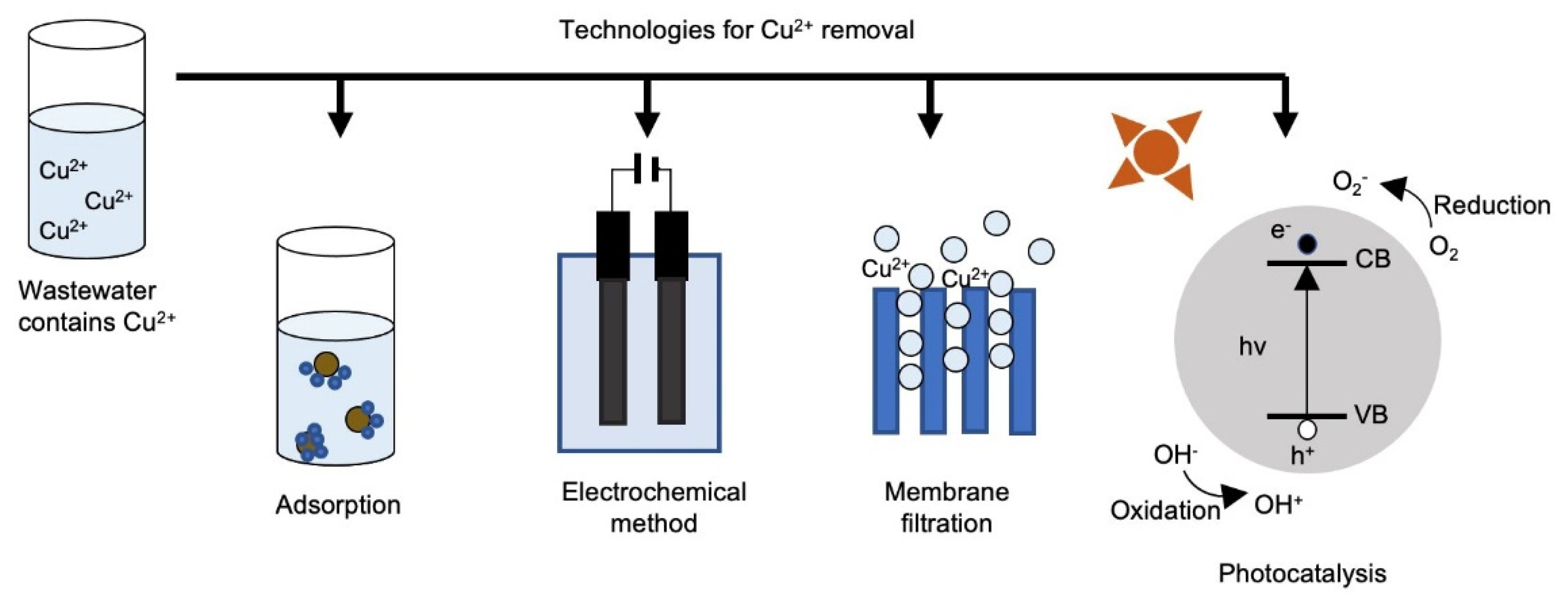
3. Copper Removal Techniques
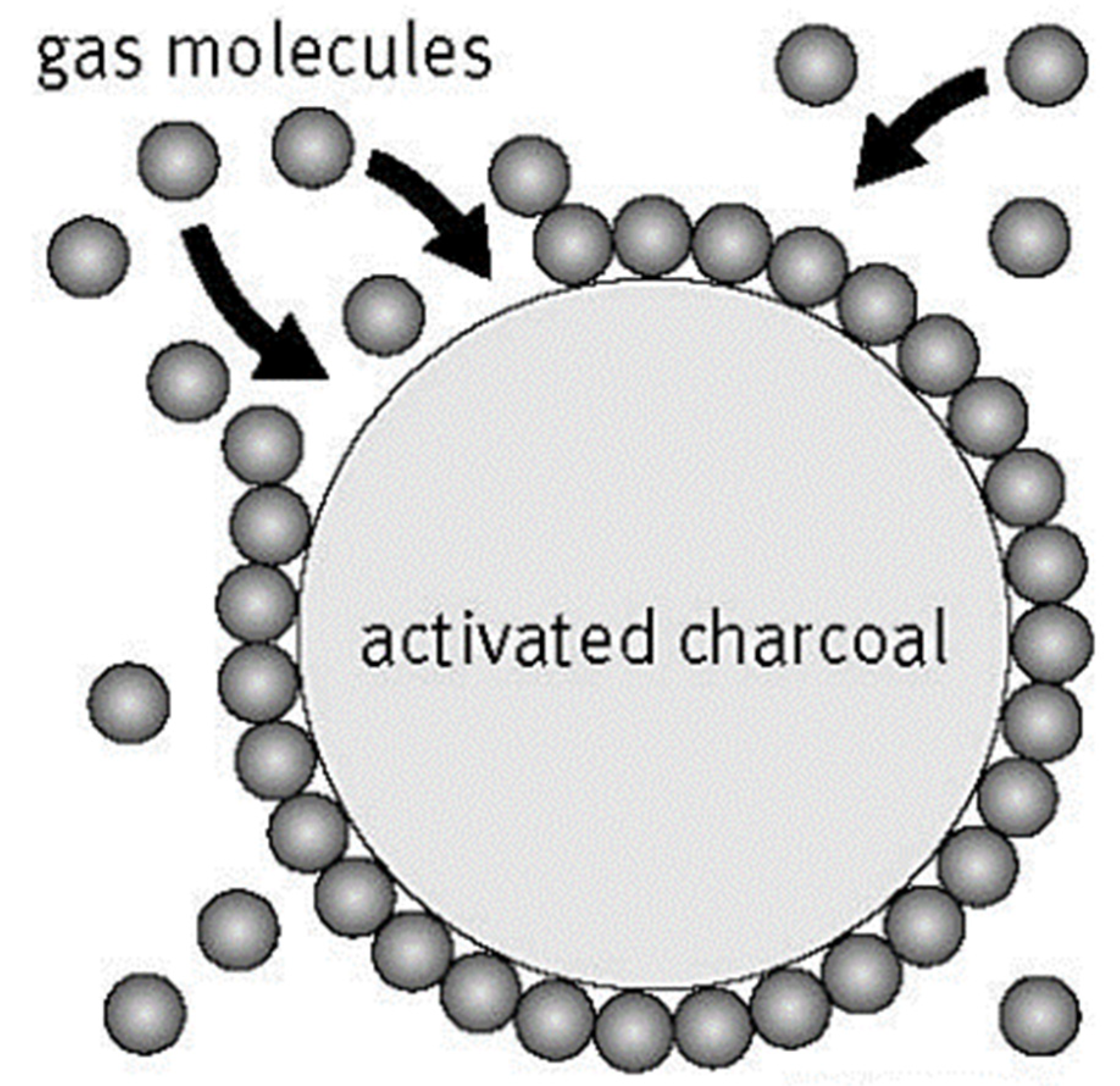
3.1. Adsorption
3.1.1. Natural Materials as Adsorbents
3.1.2. Modified Biopolymers as Adsorbents
3.1.3. Low-Cost Bio Sorbents as Adsorbents
3.1.4. Nanomaterials as Adsorbents
3.2. Cementation
3.3. Membrane Filtration
3.3.1. Ultrafiltration (UF)
3.3.2. Nanofiltration
3.3.3. Reverse Osmosis
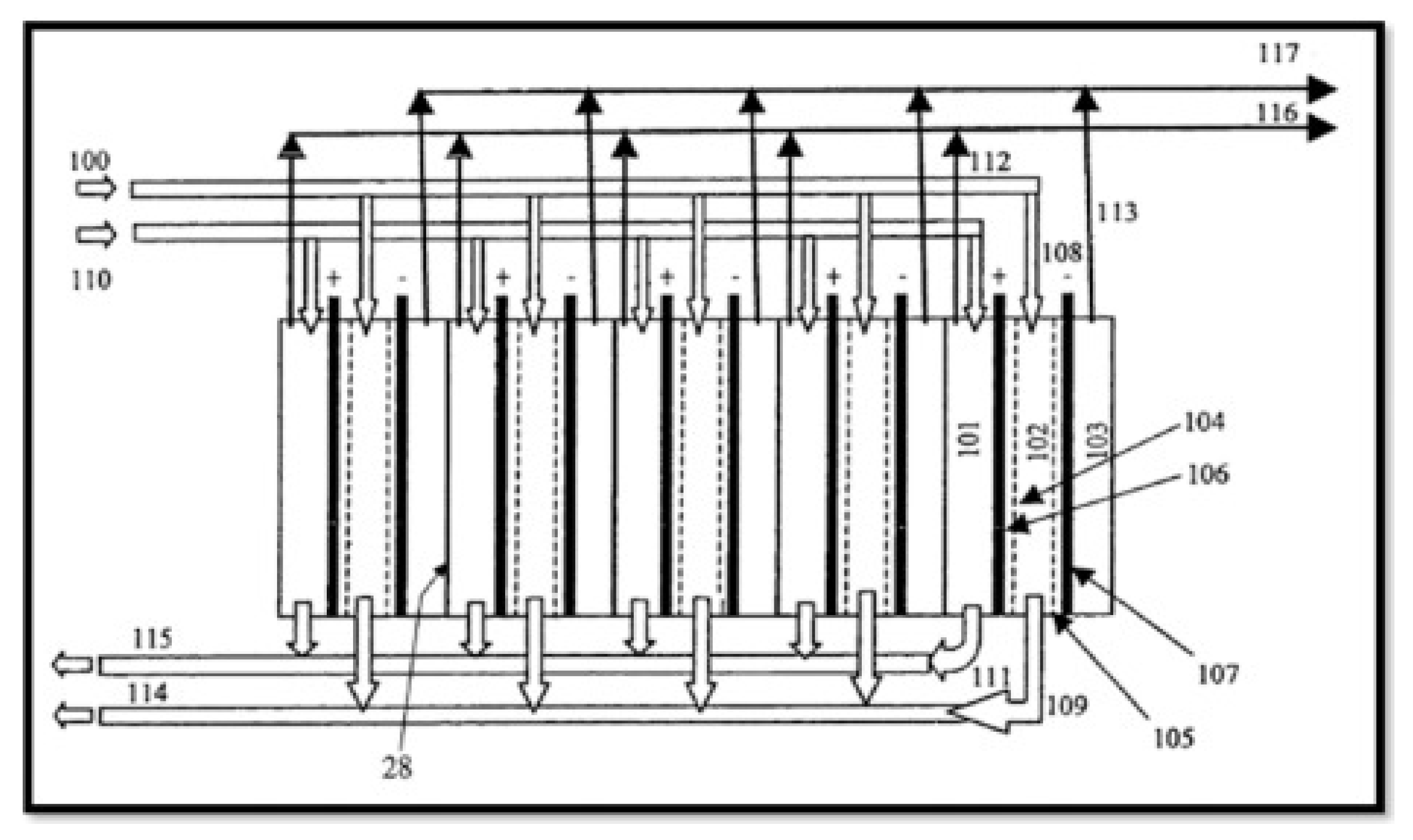
3.4. Electrochemical Methods
3.5. Photocatalysis
3.6. Comparison of Copper Removal Processes
4. Challenges of Copper Removal
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Saydeh, S.A.; El-Naas, M.H.; Zaidi, S.J. Copper removal from industrial wastewater: A comprehensive review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 56, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstkotte, B.; Alexovič, M.; Maya, F.; Duarte, C.M.; Andruch, V.; Cerdá, V. Automatic determination of copper by in-syringe dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of its bathocuproine-complex using long path-length spectrophotometric detection. Talanta 2012, 99, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doebrich, J.L. Copper: A Metal for the Ages; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Reston, VI, USA, 2009.
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy metals in contaminated soils: A review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2011, 2011, 402647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevin, R. Understanding international crime trends: The legacy of preschool lead exposure. Environ. Res. 2007, 104, 315–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexovič, M.; Balogh, I.S.; Škrlíková, J.; Andruch, V. A dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction procedure for UV-Vis spectrophotometric determination of chromium (VI) in water samples. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husak, V. Copper and copper-containing pesticides: Metabolism, toxicity and oxidative stress. J. Vasyl Stefanyk Precarpathian Natl. Univ. Ser. Soc. Hum. Sci. 2015, 2, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.Q.; Chinnappan, A.; Lee, J.K.Y.; Loc, N.H.; Tran, L.T.; Wang, G.; Kumar, V.V.; Jayathilaka, W.; Ji, D.; Doddamani, M. 3D printing of highly pure copper. Metals 2019, 9, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortella, G.; Pieretti, J.; Rubilar, O.; Fernández-Baldo, M.; Benavides-Mendoza, A.; Diez, M.; Seabra, A. Silver, copper and copper oxide nanoparticles in the fight against human viruses: Progress and perspectives. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.; Madhuri, S. Heavy metals causing toxicity in animals and fishes. Res. J. Anim. Vet. Fish. Sci. 2014, 2, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Huster, D. Wilson disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 24, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouyyok, W.; Shin, Y.; Davidson, J.; Samuels, W.D.; LaFemina, N.H.; Rutledge, R.D.; Fryxell, G.E.; Sangvanich, T.; Yantasee, W. Selective removal of copper (II) from natural waters by nanoporous sorbents functionalized with chelating diamines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6390–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, S.A.; Baldwin, D.H.; Mebane, C.A.; Hawkes, T.; Gross, S.J.; Scholz, N.L. An Overview of Sensory Effects on Juvenile Salmonids Exposed to Dissolved Copper: Applying a Benchmark Concentration Approach to Evaluate Sublethal Neurobehavioral Toxicity; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hirotsu, K.E.; Chen, J.K. Metals in Coins. In Metal Allergy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Da̧browski, A.; Hubicki, Z.; Podkościelny, P.; Robens, E. Selective removal of the heavy metal ions from waters and industrial wastewaters by ion-exchange method. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Gupta, S.S. Adsorptive accumulation of Cd(II), Co(II), Cu(II), Pb(II), and Ni(II) from water on montmorillonite: Influence of acid activation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, A. A review on copper pollution and its removal from water bodies by pollution control technologies. Indian, J. Environ. Prot. 2009, 29, 552–560. [Google Scholar]
- Alila, S.; Costa, A.I.; Vieira Ferreira, L.F.; Boufi, S. Modified biopolymer adsorbent for the removal of dissolved organic pollutants. Int. J. Environ. Technol. Manag. 2010, 12, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Garduño, O.; Martínez, M.E.; Gimeno, M.; Tecante, A.; Beristain-Cardoso, R.; Shirai, K. Copper removal from wastewater by a chitosan-based biodegradable composite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 28527–28535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, M.; Kaykioglu, G.; Belgiorno, V.; Lofrano, G. Removal of emerging contaminants from water and wastewater by adsorption process. In Emerging Compounds Removal from Wastewater; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 15–37. [Google Scholar]
- Nordin, A.H.; Ahmad, K.; Xin, L.K.; Syieluing, W.; Ngadi, N. Efficient adsorptive removal of methylene blue from synthetic dye wastewater by green alginate modified with pandan. Mater. Today: Proc. 2021, 39, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucaci, A.R.; Bulgariu, D.; Popescu, M.-C.; Bulgariu, L. Adsorption of Cu(II) Ions on Adsorbent Materials Obtained from Marine Red Algae Callithamnion corymbosum sp. Water 2020, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Lu, Q.; Chen, R.; Duan, Y.; Wang, L.; Gao, L.; Pan, S. Synthesis of a novel flocculant on the basis of crosslinked Konjac glucomannan-graft-polyacrylamide-co-sodium xanthate and its application in removal of Cu2+ ion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçekus, H.; Türker, U.; LaMoreaux, J.W. Survival and Sustainability: Environmental Concerns in the 21st Century; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, R. Advances in application of natural clay and its composites in removal of biological, organic, and inorganic contaminants from drinking water. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 2011, 872531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Hamid, S.; Shahadat, M.; Ballinger, B.; Azha, S.F.; Ismail, S.; Ali, S.W.; Ahammad, S.Z. Role of clay-based membrane for removal of copper from aqueous solution. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Hu, J.C.; Liu, W.L.; Nie, F.M. Application of biopolymer-based adsorbents in removal of heavy metals. In Proceedings of the Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd: Bach, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 373–377. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Gibb, S.W. Copper removal from wastewater using spent-grain as biosorbent. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larous, S.; Meniai, A. Removal of copper (II) from aqueous solution by agricultural by-products-sawdust. Energy Procedia 2012, 18, 915–923. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, A.; Das, S.; Seth, S.; Maulik, S.; Bhargava, B.; Rao, V. Role of modifying genes on the severity of rare mutation of MYH7 gene in hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Exp. Cardiol. 2012, 3, 1000225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Díaz, I.; López, F.A.; Alguacil, F.J. Carbon nanofibers: A new adsorbent for copper removal from wastewater. Metals 2018, 8, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassef, E.; El-Taweel, Y.A. Removal of copper from wastewater by cementation from simulated leach liquors. J. Chem. Eng. Process Technol. 2015, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panão, A.S.; De Carvalho, J.M.; Correia, M.J. Copper Removal from Sulphuric Leaching Solutions by Cementation; Centre of Chemical Processes, Technical University of Lisbon: Lisbon, Portugal, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gunatilake, S. Methods of removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Methods 2015, 1, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Molinari, R.; Poerio, T.; Argurio, P. Selective separation of copper (II) and nickel (II) from aqueous media using the complexation–ultrafiltration process. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.; Schmidt, E. Polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration process for heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater. Desalination 2010, 256, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarillo, R.; Llanos, J.; García-Fernández, L.; Pérez, Á.; Canizares, P. Treatment of copper (II)-loaded aqueous nitrate solutions by polymer enhanced ultrafiltration and electrodeposition. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 70, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rashdi, B.; Johnson, D.; Hilal, N. Removal of heavy metal ions by nanofiltration. Desalination 2013, 315, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbal, F.; Camcı, S. Copper, chromium and nickel removal from metal plating wastewater by electrocoagulation. Desalination 2011, 269, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Fang, Z.; Hou, J.; Ma, X.; Huang, Y.; Huang, L. Effects of heavy metal wastewater on the anoxic/aerobic-membrane bioreactor bioprocess and membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rashdi, B.; Somerfield, C.; Hilal, N. Heavy metals removal using adsorption and nanofiltration techniques. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2011, 40, 209–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh-sik, K. Removal of Heavy Metals in Wastewater Using a Nano-Filtration Membrane Technology; Korea Environmental Industry and Technology Institute: Seoul, Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, A.T.; Zhang, Y.; Jullok, N.; Meesschaert, B.; Pinoy, L.; Van der Bruggen, B. RO concentrate treatment by a hybrid system consisting of a pellet reactor and electrodialysis. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 79, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yanjun, W.; Xiaoyan, Q.; Zhenshan, L.; Jinren, N. Mechanism of combination membrane and electro-winning process on treatment and remediation of Cu2+ polluted water body. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cséfalvay, E.; Pauer, V.; Mizsey, P. Recovery of copper from process waters by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis. Desalination 2009, 240, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudilovskiy, P.; Kagramanov, G.; Kolesnikov, V. Use of RO and NF for treatment of copper containing wastewaters in combination with flotation. Desalination 2008, 221, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprarescu, S.; Purcar, V.; Sarbu, A.; Radu, A.-L.; Ghiurea, M.; Maior, I. The use of electrodialysis for Cu2+ removal from wastewater. Rev Roum Chim 2014, 59, 639–644. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, K.B.; Ottosen, L.M.; Jensen, P.E.; Lejon, T. Comparison of 2-compartment, 3-compartment and stack designs for electrodialytic removal of heavy metals from harbour sediments. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 181, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G. Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 38, 11–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañizares, P.; Jiménez, C.; Martínez, F.; Sáez, C.; Rodrigo, M.A. Study of the electrocoagulation process using aluminum and iron electrodes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 6189–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, A.A. Investigation of the electro-coagulation treatment process for the removal of total suspended solids and turbidity from municipal wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhoum, N.; Monser, L.; Bellakhal, N.; Belgaied, J.-E. Treatment of electroplating wastewater containing Cu2+, Zn2+ and Cr (VI) by electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 112, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, C.A.; Bhadrinarayana, N.; Anantharaman, N.; Begum, K.M.S. Heavy metal removal from copper smelting effluent using electrochemical cylindrical flow reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, J.; Mahvi, A.; Bazrafshan, E. Application of electrocoagulation process in removal of zinc and copper from aqueous solutions by aluminum electrodes. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2010, 4, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Khelifa, A.; Moulay, S.; Naceur, A. Treatment of metal finishing effluents by the electroflotation technique. Desalination 2005, 181, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, P.K.; Barton, G.W.; Wark, M.; Mitchell, C.A. A quantitative comparison between chemical dosing and electrocoagulation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 211, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vunain, E.; Mishra, A.; Mamba, B. Dendrimers, mesoporous silicas and chitosan-based nanosorbents for the removal of heavy-metal ions: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 570–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, S.; Jalali, M.; Afkhami, A. Heavy metals removal from aqueous solutions using TiO2, MgO, and Al2O3 nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2013, 200, 448–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, F.O.; Musonge, P.; Bakare, B.F. Adsorption of Copper and Lead Ions in a Binary System onto Orange Peels: Optimization, Equilibrium, and Kinetic Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, R.; Patel, A.K.; Nguyen, T.-B.; Singhania, R.R.; Chen, C.-W.; Dong, C.-D. Adsorption of copper (II) in aqueous solution using biochars derived from Ascophyllum nodosum seaweed. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 328, 124829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishkin, A.; Mironovs, V.; Vu, H.; Novak, P.; Baronins, J.; Polyakov, A.; Ozolins, J. Cavitation-dispersion method for copper cementation from wastewater by iron powder. Metals 2018, 8, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrivar, E.; Karamoozian, M.; Gharabaghi, M. Modeling and optimization of oxide copper cementation kinetics. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Lawless, D.; Feng, X. Removal of heavy metals from water using polyvinylamine by polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration and flocculation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 158, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.-P.; Gao, J.; Sun, S.-P.; Zhang, S.; Chung, T.-S. Poly (amidoamine) dendrimer (PAMAM) grafted on thin film composite (TFC) nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes for heavy metal removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 487, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-K.; Chiu, K.-F.; Lin, C.-Y.; Leu, H.-J. Electrochemical treatment of wastewater: Selectivity of the heavy metals removal process. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 27741–27748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikame, S.S.; Mungray, A.A.; Mungray, A.K. Modification of anode electrode in microbial fuel cell for electrochemical recovery of energy and copper metal. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 275, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakaraju, D.; Ravichandar, S.; Lim, Y.C. Combined effects of adsorption and photocatalysis by hybrid TiO2/ZnO-calcium alginate beads for the removal of copper. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 55, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Pan, Z.; Li, H.; Bai, B.; Guan, W. Effect of different type of scavengers on the photocatalytic removal of copper and cyanide in the presence of TiO2@ yeast hybrids. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 6399–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, M.; Nosrati, A.; Kaur, S.; Wagner, J.; Baus, U.; Nydén, M. Copper removal from acid mine drainage-polluted water using glutaraldehyde-polyethyleneimine modified diatomaceous earth particles. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maarof, H.I.; Daud, W.M.A.W.; Aroua, M.K. Recent trends in removal and recovery of heavy metals from wastewater by electrochemical technologies. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2017, 33, 359–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| UF Type | Membrane Type | Surfactant Agent | Initial Conc. | Ideal pH | Removal Efficiency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEUF | Polyethersulfone | PEI | 50 mg/L | pH > 6 | 94% | [36] |
| PEUF | Polyethersulfone | Carboxy methyl cellulose | 10 mg/L | pH = 7 | 97.6% | [37] |
| PEUF | Ceramic | Poly (acylic acid) sodium | 160 mg/L | pH = 5.5 | 98–99.5% | [38] |
| Membrane Types | Initial Concentration | Removal Efficiency | Operation Circumstance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NF | 0.01 M | 47–66% | Transmembrane pressure 1–3 bar | [42] |
| NF | 0.47 M | 96–98% | Pressure = 20 bars | [43] |
| RO | 7.86 × 10−3 M | 98–99.5% | Pressure = 5 bars | [44] |
| RO | Between 4.7 × 10−4 and 1.57 × 10−3 M | 70–90% | Low pressure RO | [45] |
| RO+NF | 2 M | More than 95% | Pressure = 35 bars | [46] |
| RO+NF | 0.015 M | 95–99% | Pressure = 3.8 bars | [47] |
| Reactor | Current Density | Conductivity (mS/cm) | Expenditure of Energy | Ideal pH | Electrode Component | Removal Rate | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous | 4.8 A/dm3 | - | - | 4 | Al-Al | 99% | [54] |
| 5 A | - | 10.99 kWh/kg | 0.64 | Ss-Ti | 98.8% | [55] | |
| Batch | 5 A | 1600 | 35.63 kWh/g | 7 | Fe-Fe | 99.99% | [56] |
| 5 A | 1600 | 35.06 kWh | 7 | Al-Al | 99.9% | [56] | |
| 0.3 A | 0.634 | - | 5 | RO-Ti-Ss | 99% | [57] | |
| 100 A/m2 | 2 | 10.07 kWh/m3 | 3 | Fe-Al | 100% | [28] | |
| 33 A/m2 | 20 | - | 9 | Al-Al | >50% | [58] |
| Removal Technique | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption using inexpensive adsorbents |
|
|
| Cementation |
|
|
| Membrane filtration |
|
|
| Electrochemical methods |
|
|
| Photocatalysis |
|
|
| Removal Technique | Type of Material | Operating Condition | Removal Efficiency | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorption using inexpensive adsorbents |
| Initial concentration of 100 mg/L, adsorbent dosage of 1 g, reaction time of 120 min, pH 5. | 86.3% | [61] |
| Initial concentration of 500 mg/L, adsorbent dosage of 0.2 mg, reaction time of 6 h, pH 5. | 99.0% | [62] | ||
| Cementation |
| Initial concentration of 750 mg/L, reaction time of 7 min, pH 2.95, linear speed of 24.13 m/s. | 95% | [63] |
| Initial concentration of 3 g/L, reaction time of 10 min, pH 1, rotational speed of 500 rpm. | 90% | [64] | ||
| Membrane filtration |
| Initial concentration of 25 mg/L, Pressure of 200 kPa, pH 6 | 90% | [65] |
| Initial concentration of 1000 mg/L, Pressure of 1000 kPa, pH 8 | 99% | [66] | ||
| Electrochemical methods |
| Initial concentration of 0.06 M, pH 6.6, energy supply 10 V, 20 h | 70% | [67] |
| Initial concentration of 100 mg/L, pH 7.0, energy supply 0.6 V, 96 h | 82.8% | [68] | ||
| Photocatalysis |
| Initial concentration of 20 mg/L, reaction time of 2 h, pH 7 | 98.9% | [69] |
| Initial concentration of 10−4 mol/L, reaction time of 30 min, pH 5 | 70% | [70] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ab Hamid, N.H.; bin Mohd Tahir, M.I.H.; Chowdhury, A.; Nordin, A.H.; Alshaikh, A.A.; Suid, M.A.; Nazaruddin, N.‘I.; Nozaizeli, N.D.; Sharma, S.; Rushdan, A.I. The Current State-Of-Art of Copper Removal from Wastewater: A Review. Water 2022, 14, 3086. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193086
Ab Hamid NH, bin Mohd Tahir MIH, Chowdhury A, Nordin AH, Alshaikh AA, Suid MA, Nazaruddin N‘I, Nozaizeli ND, Sharma S, Rushdan AI. The Current State-Of-Art of Copper Removal from Wastewater: A Review. Water. 2022; 14(19):3086. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193086
Chicago/Turabian StyleAb Hamid, Nur Hafizah, Muhamad Iqbal Hakim bin Mohd Tahir, Amreen Chowdhury, Abu Hassan Nordin, Anas Abdulqader Alshaikh, Muhammad Azwan Suid, Nurul ‘Izzah Nazaruddin, Nurul Danisyah Nozaizeli, Shubham Sharma, and Ahmad Ilyas Rushdan. 2022. "The Current State-Of-Art of Copper Removal from Wastewater: A Review" Water 14, no. 19: 3086. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193086
APA StyleAb Hamid, N. H., bin Mohd Tahir, M. I. H., Chowdhury, A., Nordin, A. H., Alshaikh, A. A., Suid, M. A., Nazaruddin, N. ‘I., Nozaizeli, N. D., Sharma, S., & Rushdan, A. I. (2022). The Current State-Of-Art of Copper Removal from Wastewater: A Review. Water, 14(19), 3086. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193086









