Water Budget, Biological Water Use, and the Soil Hydrological Cycle across Typical Ecosystems of the Heihe River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Location
2.2. Description of Datasets
2.3. Water Balance of the Terrestrial Ecosystem
2.4. Estimation of Potential ET
2.5. Estimation of Biological Water Use Fraction
2.6. Estimation of Soil Water Residence Time
3. Results
3.1. Seasonal Variations in the Observed Soil Water Profile and Water Budget Components in the HRB
3.2. Statistics of the Water Budget and Its Components across Ecosystems in the HRB
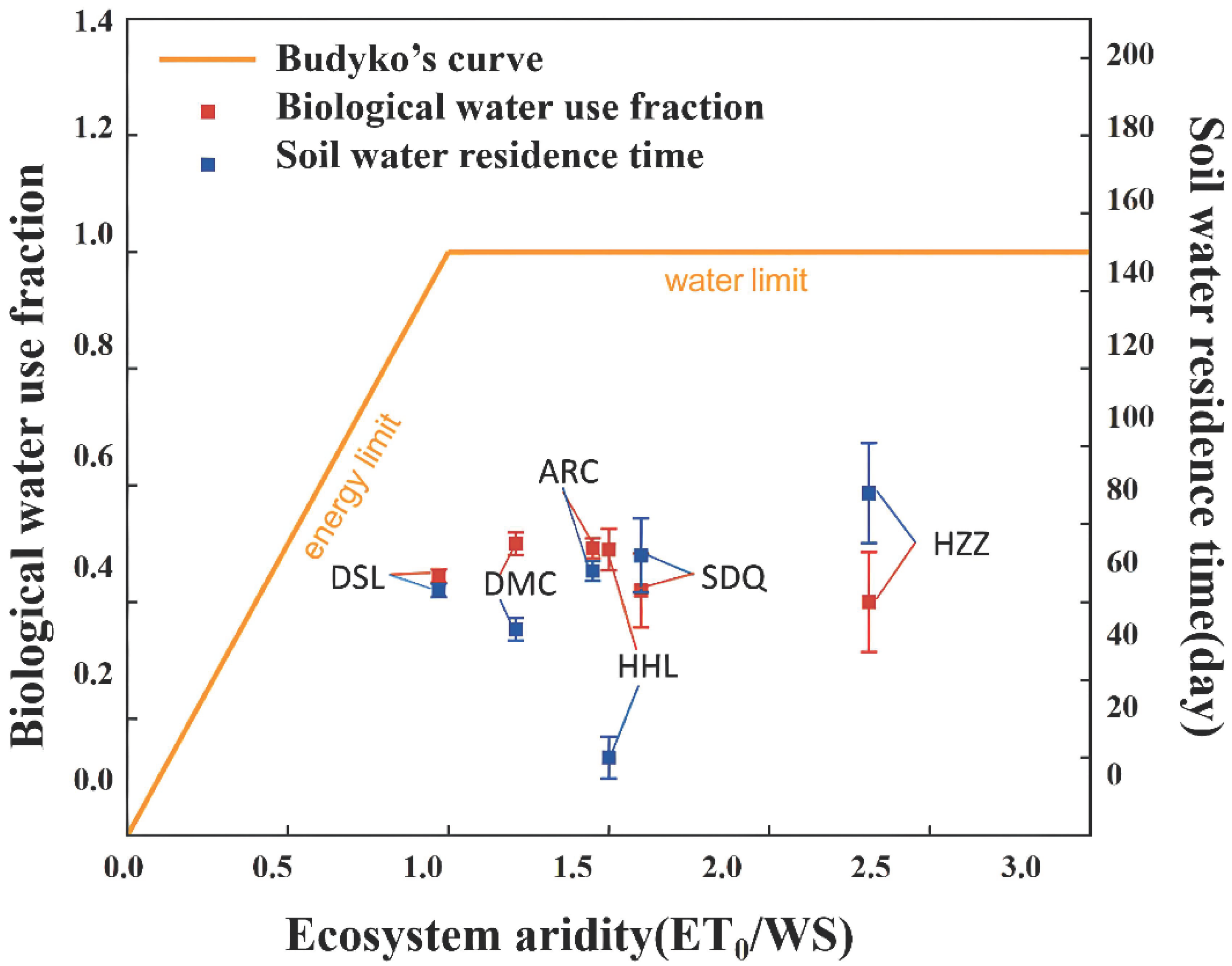
3.3. Biological Water Uses and Soil Water Residence among Ecosystems
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Budget across Different Ecosystems and Uncertainties
4.2. Differences in the Biological Water Use Fraction among Different Ecosystems
4.3. The Soil Water Residence Time and Soil Hydrological Cycle
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Model ET Partitioning and Estimation of Transpiration
= HV + lT,
= G + HG + lE,
Appendix A.2. Assessment of the Model Performance
| Site | Index | IE |
|---|---|---|
| ARC | R2 | 0.91 |
| I | 0.96 | |
| RMSE (W/m2) | 16.02 | |
| n | 711 | |
| DSL | R2 | 0.8 |
| I | 0.95 | |
| RMSE (W/m2) | 20.18 | |
| n | 724 | |
| DMC | R2 | 0.84 |
| I | 0.94 | |
| RMSE (W/m2) | 23.67 | |
| n | 669 | |
| HHL | R2 | 0.84 |
| I | 0.95 | |
| RMSE (W/m2) | 27.4 | |
| n | 673 | |
| SDQ | R2 | 0.78 |
| I | 0.89 | |
| RMSE (W/m2) | 38.61 | |
| n | 716 |
| Reference | Approach | Dominated Vegetation | T/ET | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growing Season | Whole Year | |||
| Su et al. [47] | Lysimeters | T. ramosissima | 0.37–0.50 | N/A |
| Zhao et al. [31] | Sap flow measurement | Calligonum L. | 0.64 | N/A |
| Zhou et al. [48] | uWUE | Alpine meadow | 0.55 | 0.51 |
| Cropland | 0.63 | 0.52 | ||
| P. euphratica | 0.55 | 0.53 | ||
| Tong et al. [46] | Two-source model | Alpine meadow | 0.79 ± 0.12 | 0.51 ± 0.26 |
| Alpine swamp meadow | 0.55 ± 0.23 | 0.31 ± 0.28 | ||
| Cropland | 0.80 ± 0.13 | 0.53 ± 0.26 | ||
| P. euphratica | 0.67 ± 0.07 | 0.52 ± 0.17 | ||
| T. ramosissima | 0.67 ± 0.06 | 0.50 ± 0.20 | ||
References
- Hostetler, S.W. Hydrological and Thermal Response of Lakes to Climate: Description and Modeling. In Physics and Chemistry of Lakes; Lerman, A., Imboden, D.M., Gat, J.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 63–82. ISBN 978-3-642-85132-2. [Google Scholar]
- Yapiyev, V.; Sagintayev, Z.; Inglezakis, V.; Samarkhanov, K.; Verhoef, A. Essentials of Endorheic Basins and Lakes: A Review in the Context of Current and Future Water Resource Management and Mitigation Activities in Central Asia. Water 2017, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Zheng, Y. Modeling Ecohydrological Processes and Spatial Patterns in the Upper Heihe Basin in China. Forests 2015, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R. Saving Iran’s great salt lake. Science 2015, 349, 1044–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.D.; Zhao, C.Y. An Integrated Study of Ecological and Hydrological Processes in the Inland River Basin of the Arid Regions, China. Adv. Earth Sci. 2008, 23, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.-F.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Liu, S.-M.; Ding, Z.-Y.; Ma, J.-Z.; Huang, C.-L.; Han, T.; He, J.-H. Evaluating the complementary relationship for estimating ET using the multi-site data across north China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 230, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, X.-Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Wu, X.; Ma, Y.-J. Numerical modeling the isotopic composition of ET in an arid artificial oasis cropland ecosystem with high-frequency water vapor isotope measurement. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 230, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, L.-H.; Wang, Y.-B.; Tian, J.; He, C.-S.; Liu, G.-H. Variations of Soil Moisture under Different Land Use and Land Cover Types in the Qilian Mountain, China. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 24, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, R.-S.; Song, Y.-X.; Liu, J.-F.; Han, C.-T.; Liu, Z.-W. Measurement and estimation of grassland ET in a mountainous region at the upper reach of Heihe River basin, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Gao, M.; Yi, S.; Zhao, C.; Ye, B.; Li, M.; Wang, S. Understanding the impact of mountain landscapes on water balance in the upper Heihe River watershed in northwestern China. J. Arid Land 2013, 5, 366–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Sun, F.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y. New interpretation of the role of water balance in an extended Budyko hypothesis in arid regions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Ge, Y.; Li, H.; Han, F.; Hu, X.; Tian, W.; Tian, Y.; Pan, X.; Nian, Y.; et al. Hydrological Cycle in the Heihe River Basin and Its Implication for Water Resource Management in Endorheic Basins. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 890–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, S.P.; Moore, G.W.; Miralles, D.G. A mesic maximum in biological water use demarcates biome sensitivity to aridity shifts. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1883–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Yang, B.; Sun, X.; Lee, X. ET partitioning through in-situ oxygen isotope measurements in an oasis cropland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 230, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R.E. A review of global terrestrial ET: Observation, modeling, climatology, and climatic variability: GLOBAL TERRESTRIAL ET. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Wang, N.-A.; Wang, P.-L.; Sun, Y.-M.; Dong, C.-Y. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics and Quantification of the Affects Factors for Reference ET in Heihe River Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2012, 27, 975–989. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.-D.; Xiao, H.-L.; Fu, B.-J.; Xiao, D.-N.; Zheng, C.-M.; Kang, S.-Z.; Yan, X.-D.; Wang, Y.; An, L.-Z.; Li, X.-B.; et al. Advances in Synthetic Research on the Eco-hydrological Process of the Heihe River Basin. Adv. Earth. Sci. 2014, 29, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Andrews, C.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, C. Role of groundwater in the dryland ecohydrological system: A case study of the Heihe River Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 6760–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Xu, Z.W.; Wang, W.Z.; Jia, Z.Z.; Zhu, M.J.; Bai, J.; Wang, J.M. A comparison of eddy-covariance and large aperture scintillometer measurements with respect to the energy balance closure problem. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1291–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Shi, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, T.; Wang, W.; Ma, M. Intercomparison of surface energy flux measurement systems used during the HiWATER-MUSOEXE: INTERCOMPARISON OF FLUX INSTRUMENTS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13140–13157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, M.; Falge, E.; Baldocchi, D.; Papale, D.; Aubinet, M.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Buchmann, N.; Gilmanov, T.; Granier, A.; et al. On the separation of net ecosystem exchange into assimilation and ecosystem respiration: Review and improved algorithm. Glob. Change Biol. 2005, 11, 1424–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ahmed, S.E.; Ma, L.Y. Influence diagnostics in the linear regression model with stochastic linear restrictions. Pak. J. Stat. 2009, 25, 647–662. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, C.; Sun, R.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Hao, L.; Jiang, G. A Study of Shelterbelt Transpiration and Cropland ET in an Irrigated Area in the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River in Northwestern China. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-J.; Zhang, F.-P.; Wang, H.-W.; Lei, S.-J.; Gao, Z. Analysis of the Spatio-Temporal Charateristics of Water Use Efficiency of Vegetation and Its Relationship with Climate in the Heihe River Basin. J. Desert Res. 2017, 37, 733–741. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Liang, S.; Wang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Song, J. Long-Time-Series Global Land Surface Satellite Leaf Area Index Product Derived From MODIS and AVHRR Surface Reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5301–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, T.; Kaihotsu, I.; Oyunbaatar, D.; Ganbold, T. Summertime soil hydrological cycle and surface energy balance on the Mongolian steppe. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 69, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Pei, D.; Sun, H. Improved Water Use Efficiency Associated with Cultivars and Agronomic Management in the North China Plain. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-X.; Chen, L.-H. A Study on Water Balance of PROTECTIVE Forest Ecosystem in Loess Area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1996, 16, 238–245. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Gao, B.; Jiao, Y.; Lei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Cong, Z. A distributed scheme developed for eco-hydrological modeling in the upper Heihe River. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, B.; Chang, X.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cleverly, J.; Eamus, D. ET partitioning, stomatal conductance, and components of the water balance: A special case of a desert ecosystem in China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 538, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Wang, Y.-B.; Gao, Z.-Y.; Liu, G.-H. Soil Hydrological Characteristics of the Degrading Meadow in Permafrost Regions in the Beiluhe River Basin. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2013, 35, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-S.; Yang, Y.; Han, C.-T.; Liu, J.-F.; Kang, E.-S.; Song, Y.-X.; Liu, Z.-W. Field Experimental Research on Hydrological Function over Several Typical Underlying Surfaces in the Cold Regions of Western China. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 29, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L. Land-Use and Land-Cover Change and Its Impacts on ET in Inland River Basin of Arid Region; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.-L.; Niu, J.-Y.; Wang, R.-Y.; Lv, X.-D. Impact of climate change on water requirement of main crops in irrigated oasis of Hexi corridor. Acta Pratac. Sin. 2011, 20, 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Wen, X.; Sun, X. Irrigation depth far exceeds water uptake depth inan oasis cropland in the middle reaches of Heihe River Basin. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geerts, S.; Raes, D. Deficit irrigation as an on-farm strategy to maximize crop water productivity in dry areas. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereres, E.; Soriano, M.A. Deficit irrigation for reducing agricultural water use. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 58, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S. Concept, Modeling, and Application of the Underlying Water Use Efficiency for Terrestrial Ecosystems. Ph.D. Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lupon, A.; Ledesma, J.L.J.; Bernal, S. Riparian ET shapes stream flow dynamics and water budgets in a Mediterranean catchment; Catchment hydrology/Modelling approaches. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.-F.; Luo, Y.; Shao, M.-A.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, X.-C. Evapotranspiration and its main controlling mechanism over the desert riparian forests in the lower Tarim River Basin. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.-F.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.-H.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhao, C.-Y. Evapotranspiration of a Populus euphratica Oliv. forest and its controlling factors in the lower Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Sci. Cold Arid. Reg. 2017, 9, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljedahl, A.K.; Hinzman, L.D.; Kane, D.L.; Oechel, W.C.; Tweedie, C.E.; Zona, D. Tundra water budget and implications of precipitation underestimation. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 6472–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, M.; Liu, X.-Q. Simulation of transpiration for typical xeromorphic plants in inland arid region of Northwestern China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 7751–7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yamanaka, T. Application of a two-source model for partitioning ET and assessing its controls in temperate grasslands in central Japan: A two-source model of et in temperate grasslands. Ecohydrology 2014, 7, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, X.-Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Shi, F.; Bai, Y.; Li, E.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Seasonality of the Transpiration Fraction and Its Controls Across Typical Ecosystems Within the Heihe River Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 1277–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Li, S.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, R.; Xie, T. Partitioning evapotranspiration of desert plants under different water regimes in the inland Heihe River Basin, Northwestern China. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2016, 30, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, G. Water use efficiency and evapotranspiration partitioning for three typical ecosystems in the Heihe River Basin, northwestern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 253, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
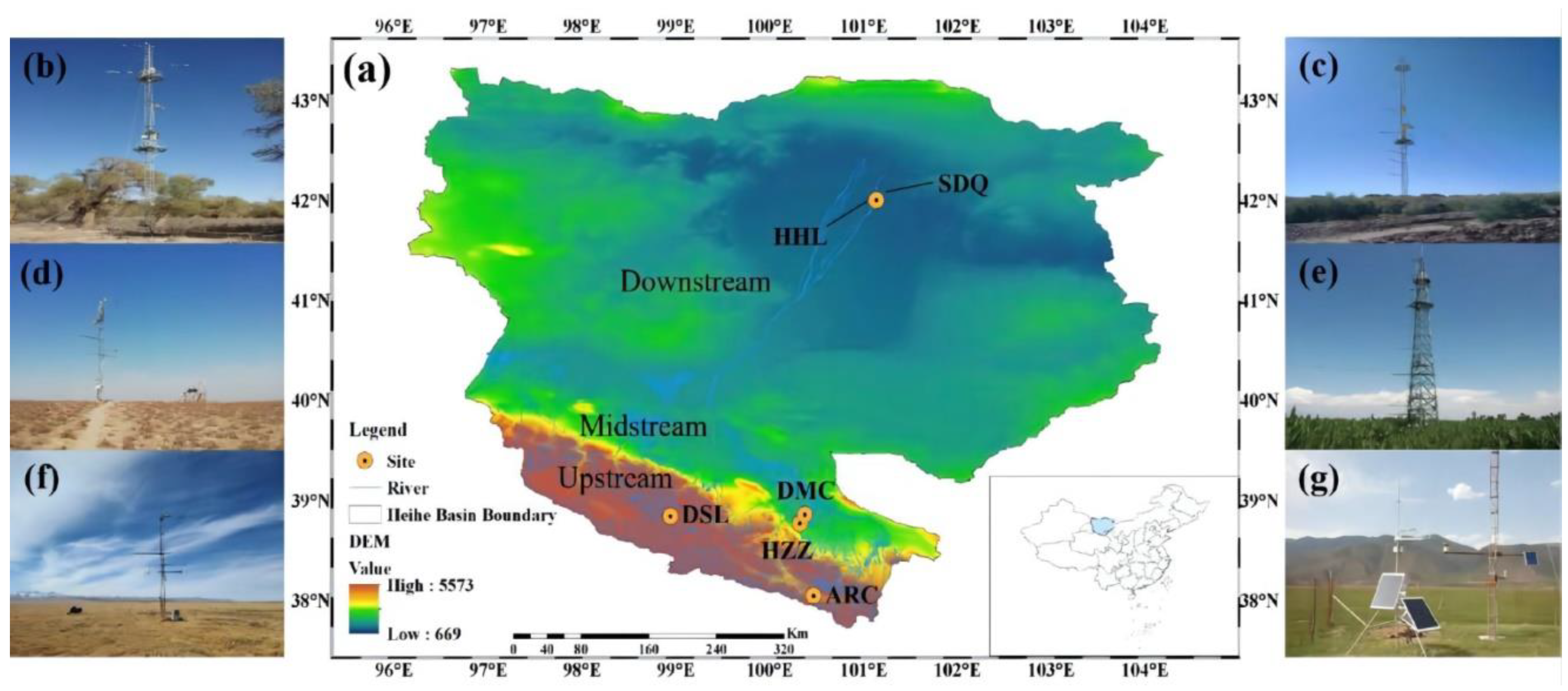
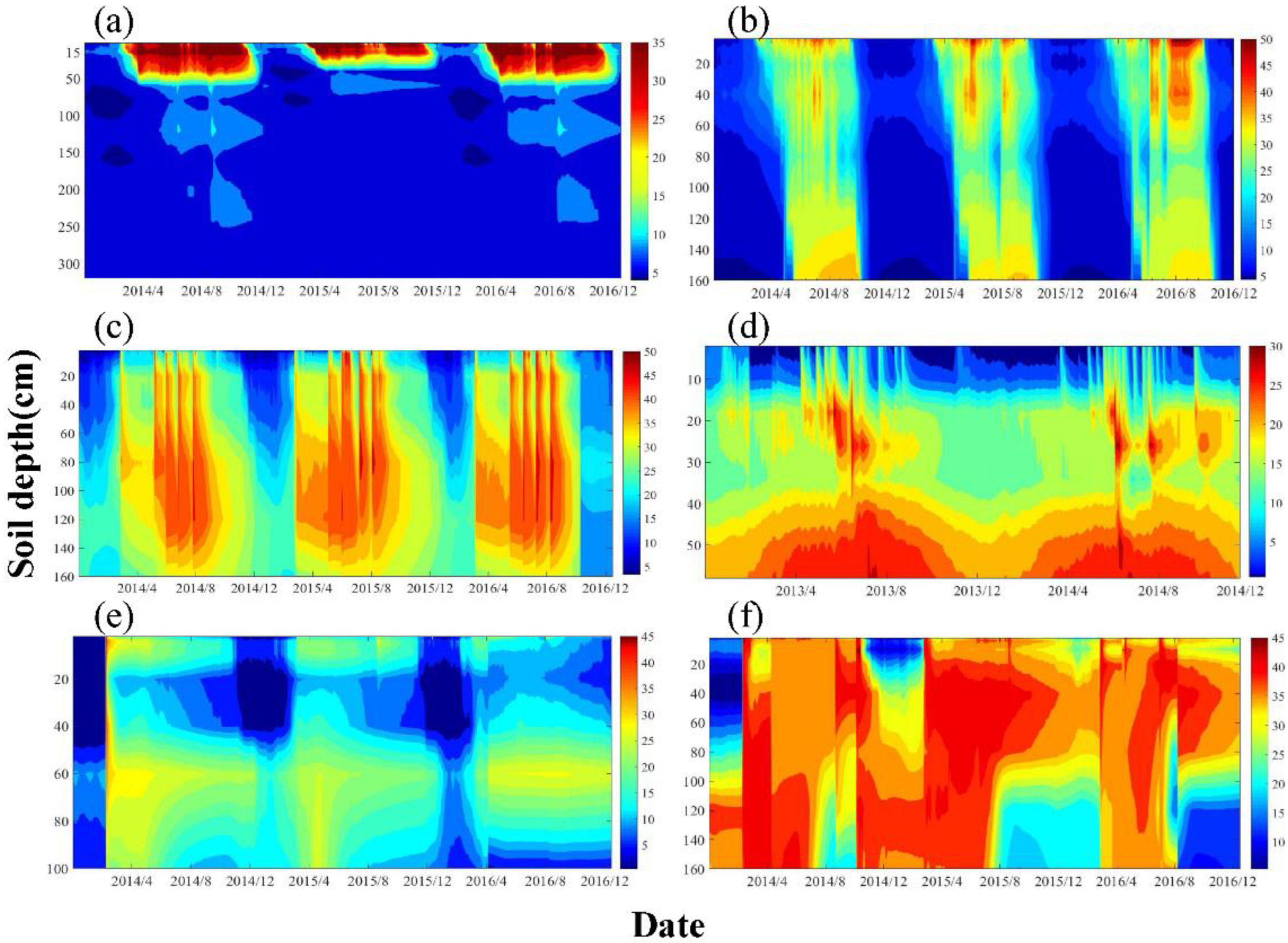
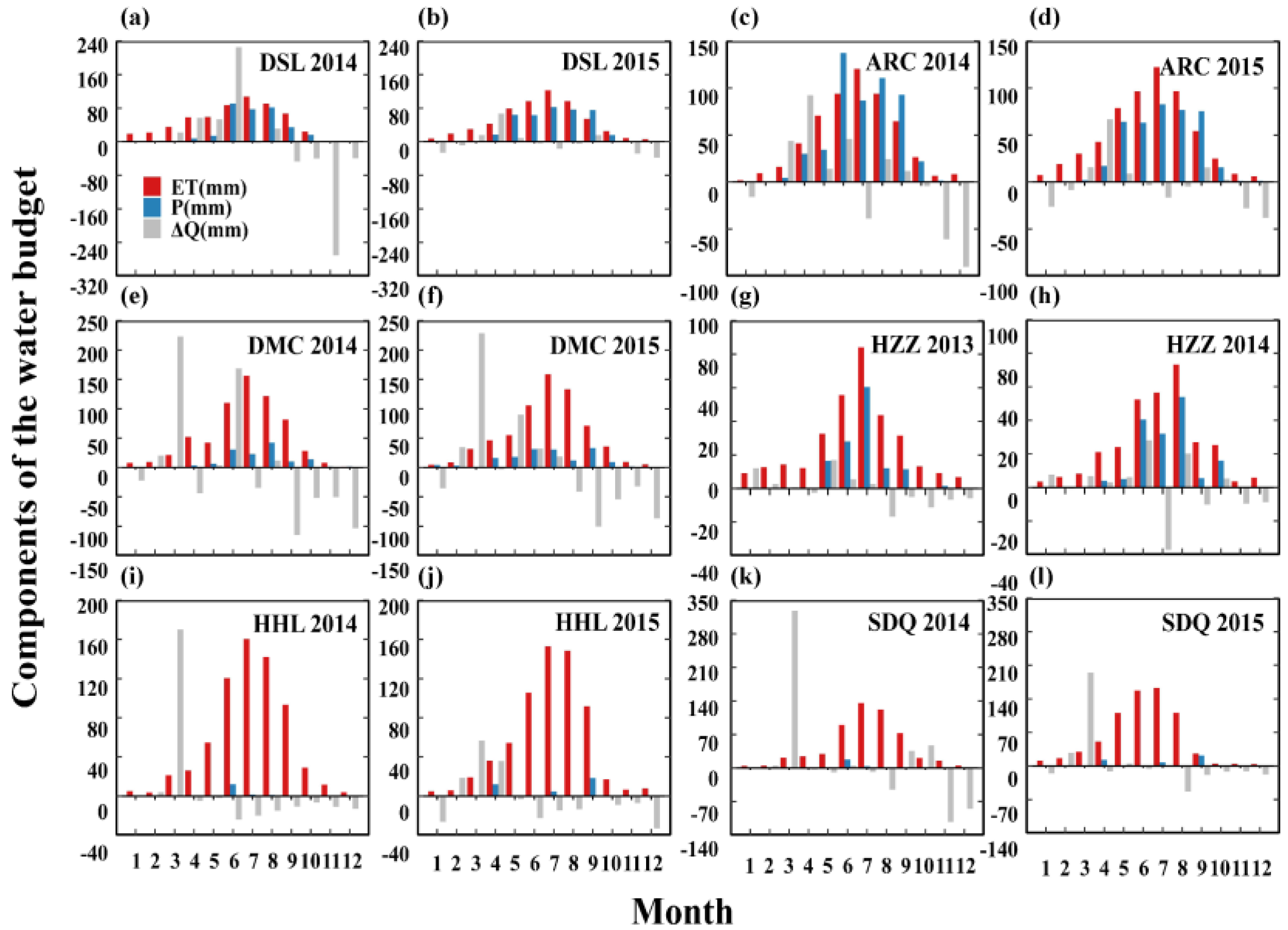
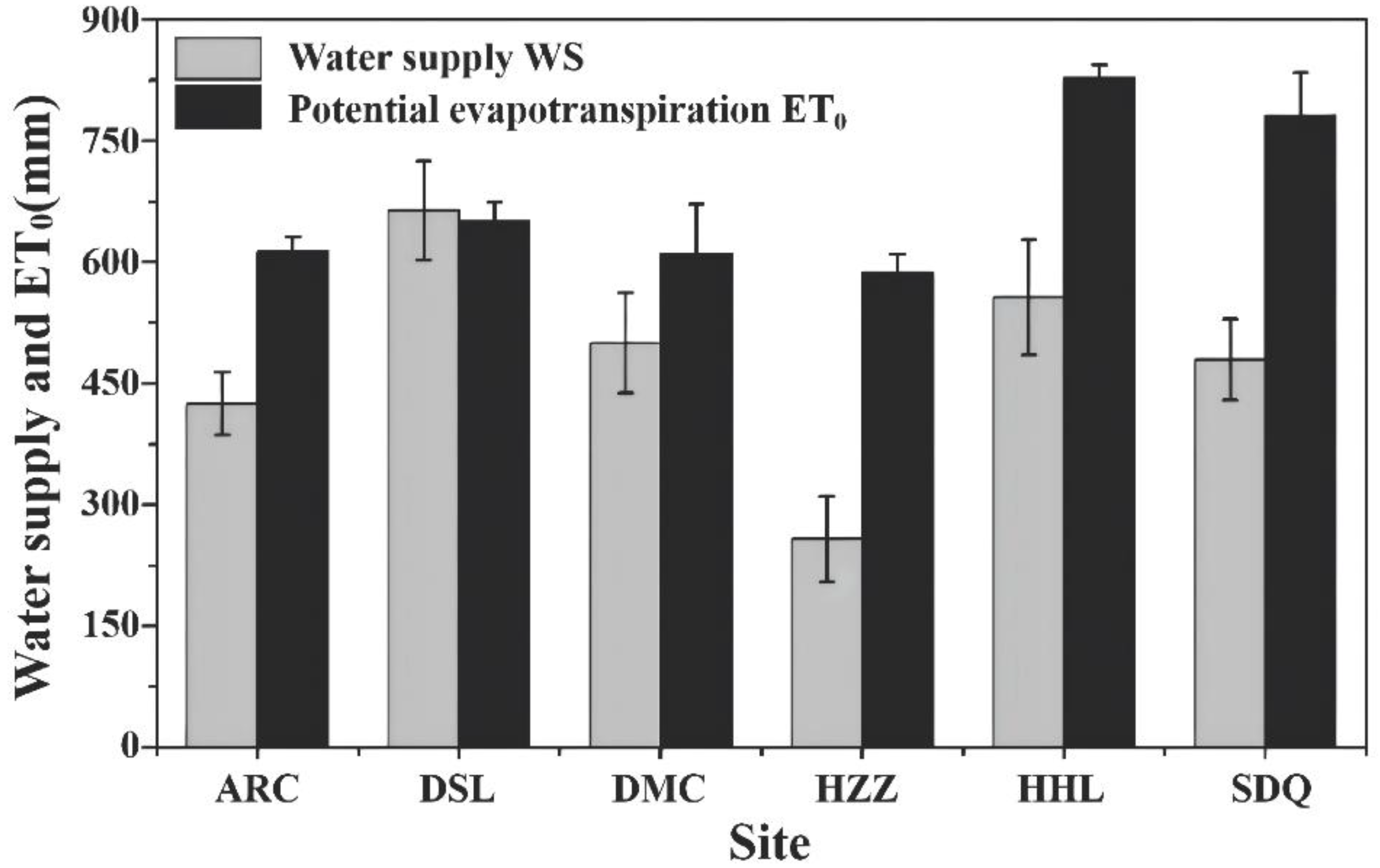
| Site | Lon | Lat | Altitude (m) | Soil Type | Climate Type | Vegetation Type/Dominate Species | APP (mm) | ATP (°C) | Time Span |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARC | 100.46° E | 38.05° N | 3044 | Chernozem | Dwc | Apline meadow | 322.3 | −0.41 | 2013–2016 |
| DSL | 98.94° E | 38.84° N | 3739 | Leptosol | ET | Apline swamp meadow | 211.87 | −1.97 | 2014–2016 |
| HZZ | 100.32° E | 38.77° N | 1731 | Calcisol | BWk | Kalidium foliatum | 143.5 | 8.57 | 2013/2014–2016 |
| DMC | 100.37° E | 38.86° N | 1556 | Cambisol | BWk | Maize | 147.25 | 7.46 | 2013–2016 |
| HHL | 101.13° E | 41.99° N | 874 | Solonchak | BWk | P. euphratica and T. ramosissima | 33.5 | 10.22 | 2014–2016 |
| SDQ | 101.14° E | 42.00° N | 873 | Solonchak | BWk | T. ramosissima | 26 | 10.46 | 2014–2016 |
| Site | Time Scale | Year | Precipitation (mm) | ET (mm) | Change of Soil Water Storage (mm) | Runoff (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ET | T | E | ΔQ | (ΔR) mm | ||||
| ARC | Yearly | 2013 | 392 | 492 | 241 | 251 | −6 | −94 |
| 2014 | 520 | 518 | 275 | 243 | 21 | −18 | ||
| 2015 | 401 | 551 | 292 | 259 | −16 | −134 | ||
| 2016 | 464 | 471 | 226 | 245 | 10 | −17 | ||
| Mean | 444 | 508 | 259 | 250 | 2 | −66 | ||
| May–Sep | 2013 | 323 | 330 | 274 | 56 | 10 | −17 | |
| 2014 | 427 | 342 | 287 | 55 | 43 | 42 | ||
| 2015 | 314 | 349 | 293 | 60 | −9 | −26 | ||
| 2016 | 393 | 314 | 257 | 63 | 46 | 33 | ||
| Mean | 364 | 334 | 278 | 59 | 23 | 8 | ||
| DSL | Yearly | 2014 | 325 | 472 | 212 | 336 | −5 | −142 |
| 2015 | 310 | 505 | 232 | 340 | 9 | −204 | ||
| 2016 | 388 | 470 | 202 | 268 | 1 | −83 | ||
| Mean | 341 | 482 | 215 | 315 | 2 | −143 | ||
| May–Sep | 2014 | 284 | 286 | 215 | 137 | 207 | −209 | |
| 2015 | 260 | 282 | 214 | 118 | 112 | −134 | ||
| 2016 | 341 | 316 | 228 | 88 | 189 | −164 | ||
| Mean | 295 | 295 | 219 | 114 | 169 | −169 | ||
| Site | Year | Precipitation (mm) | ET (mm) | Change of Soil Water Storage | Irrigation/Groundwater | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ET | T | E | ΔQ (mm) | I/GW (mm) | |||
| HZZ | 2013 | 129 | 247 | 127 | 120 | 3 | 122 |
| 2014 | 137 | 233 | 125 | 108 | 81 | 177 | |
| 2016 | 182 | 272 | 82 | 190 | 2 | 88 | |
| Mean | 149 | 251 | 111 | 139 | 29 | 129 | |
| DMC | 2013 | 136 | 703 | 373 | 330 | 30 | 597 |
| 2014 | 134 | 640 | 333 | 307 | 6 | 512 | |
| 2015 | 161 | 665 | 366 | 299 | 50 | 554 | |
| 2016 | 101 | 638 | 313 | 325 | 23 | 560 | |
| Mean | 133 | 662 | 346 | 315 | 27 | 556 | |
| SDQ | 2014 | 25 | 547 | 252 | 295 | 158 | 681 |
| 2015 | 42 | 650 | 312 | 338 | 98 | 741 | |
| 2016 | 33 | 617 | 284 | 333 | 156 | 523 | |
| Mean | 33 | 605 | 283 | 322 | 137 | 648 | |
| HHL | 2014 | 17 | 671 | 322 | 349 | 66 | 720 |
| 2015 | 35 | 691 | 346 | 346 | −17 | 633 | |
| 2016 | 49 | 720 | 382 | 338 | 31 | 695 | |
| Mean | 34 | 694 | 350 | 344 | 27 | 683 | |
| Site | Year | Precipitation (mm) | Transpiration (mm) | Irrigation/ Groundwater/Lateral Runoff | Biological Water Use Fraction (BWF) | Soil Water Storage | Soil Water Residence Time, τ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I/GW (mm) | T/WS | (mm Q) | (Day) | ||||
| Apline meadow | 2013 | 392 | 241 | 94 | 0.50 | 83.24 | 63 |
| 2014 | 520 | 275 | 18 | 0.51 | 99.36 | 67 | |
| 2016 | 464 | 226 | 17 | 0.47 | 98.94 | 75 | |
| mean | 459 | 247 | 43 | 0.49 | 93.85 | 68 | |
| Apline swamp meadow | 2014 | 325 | 212 | 142 | 0.45 | 80.30 | 63 |
| 2015 | 310 | 232 | 204 | 0.45 | 82.46 | 59 | |
| 2016 | 388 | 202 | 83 | 0.43 | 86.10 | 67 | |
| mean | 318 | 222 | 173 | 0.44 | 82.95 | 63 | |
| Kalidium Foliatum | 2013 | 129 | 127 | 122 | 0.51 | 64.41 | 94 |
| 2014 | 137 | 125 | 177 | 0.40 | 62.07 | 72 | |
| 2016 | 182 | 82 | 88 | 0.30 | 71.72 | 97 | |
| mean | 149 | 111 | 129 | 0.40 | 66.07 | 88 | |
| Cropland | 2013 | 136 | 373 | 597 | 0.51 | 95.47 | 48 |
| 2014 | 134 | 333 | 512 | 0.52 | 94.91 | 54 | |
| 2015 | 161 | 366 | 554 | 0.51 | 103.58 | 53 | |
| 2016 | 101 | 313 | 560 | 0.47 | 106.62 | 59 | |
| mean | 133 | 346 | 556 | 0.50 | 100.14 | 53 | |
| T. rmosissima | 2014 | 25 | 252 | 681 | 0.36 | 121.12 | 63 |
| 2015 | 42 | 312 | 741 | 0.40 | 133.63 | 62 | |
| 2016 | 33 | 284 | 523 | 0.51 | 137.92 | 91 | |
| mean | 33 | 283 | 648 | 0.42 | 130.89 | 72 | |
| P. euphratica | 2014 | 17 | 322 | 720 | 0.44 | 44.10 | 22 |
| 2015 | 35 | 346 | 633 | 0.52 | 43.92 | 24 | |
| 2016 | 49 | 382 | 695 | 0.51 | 29.22 | 14 | |
| mean | 34 | 350 | 683 | 0.49 | 39.08 | 20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, D.; Sun, H.; Wang, P. Water Budget, Biological Water Use, and the Soil Hydrological Cycle across Typical Ecosystems of the Heihe River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182895
Chen Q, Xing Y, Zhang D, Sun H, Wang P. Water Budget, Biological Water Use, and the Soil Hydrological Cycle across Typical Ecosystems of the Heihe River Basin. Water. 2022; 14(18):2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182895
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qi, Yuhua Xing, Dapeng Zhang, Haitao Sun, and Pei Wang. 2022. "Water Budget, Biological Water Use, and the Soil Hydrological Cycle across Typical Ecosystems of the Heihe River Basin" Water 14, no. 18: 2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182895
APA StyleChen, Q., Xing, Y., Zhang, D., Sun, H., & Wang, P. (2022). Water Budget, Biological Water Use, and the Soil Hydrological Cycle across Typical Ecosystems of the Heihe River Basin. Water, 14(18), 2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182895







