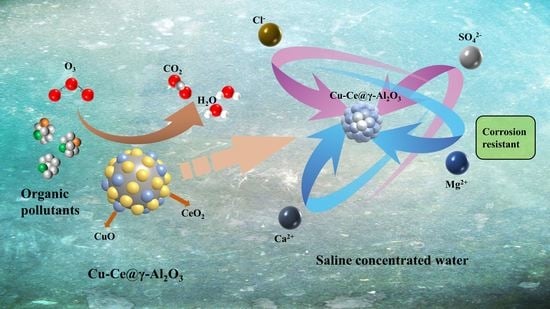
Preparation of Cu-Ce@γ-Al2O3 and Study on Catalytic Ozone Oxidation for the Treatment of RO Concentrate Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Catalyst Preparation Process
2.3. Methods for Catalyst Characterization
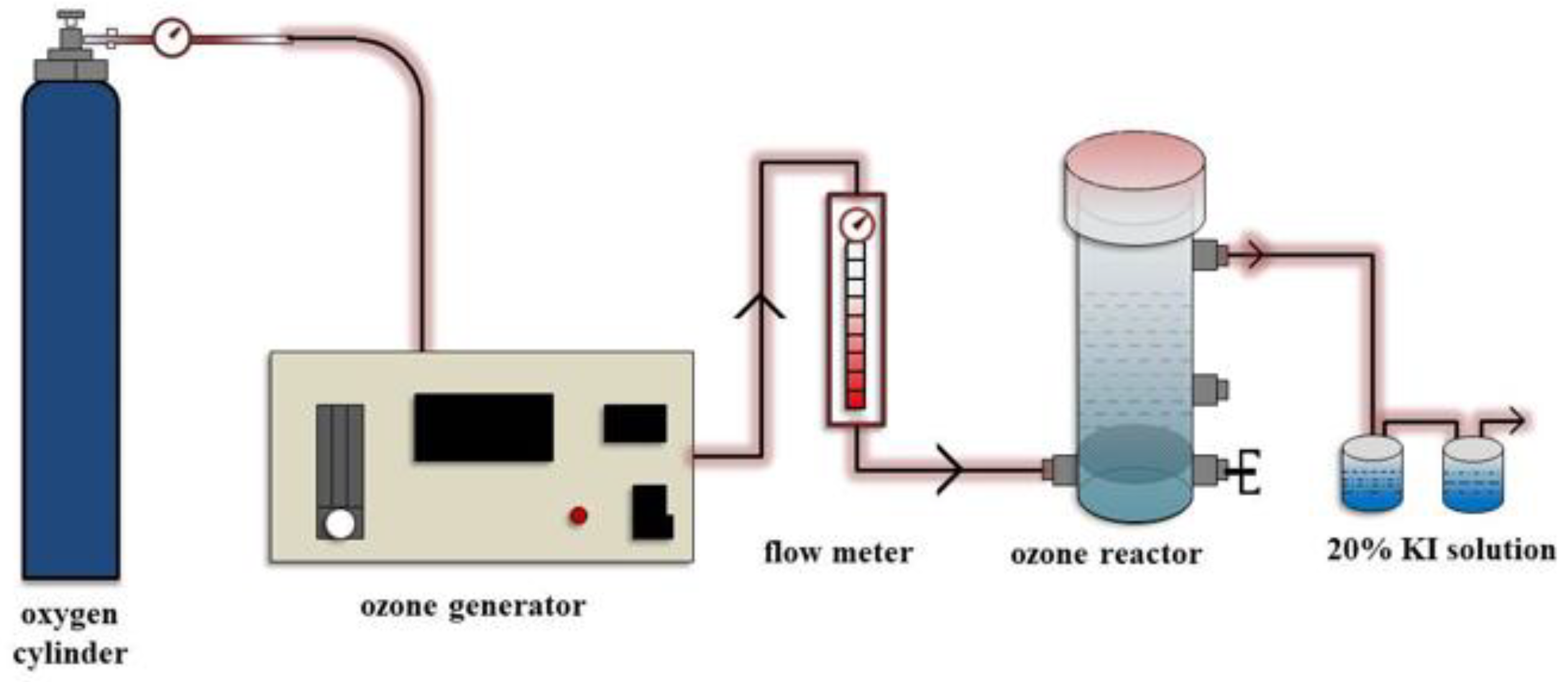
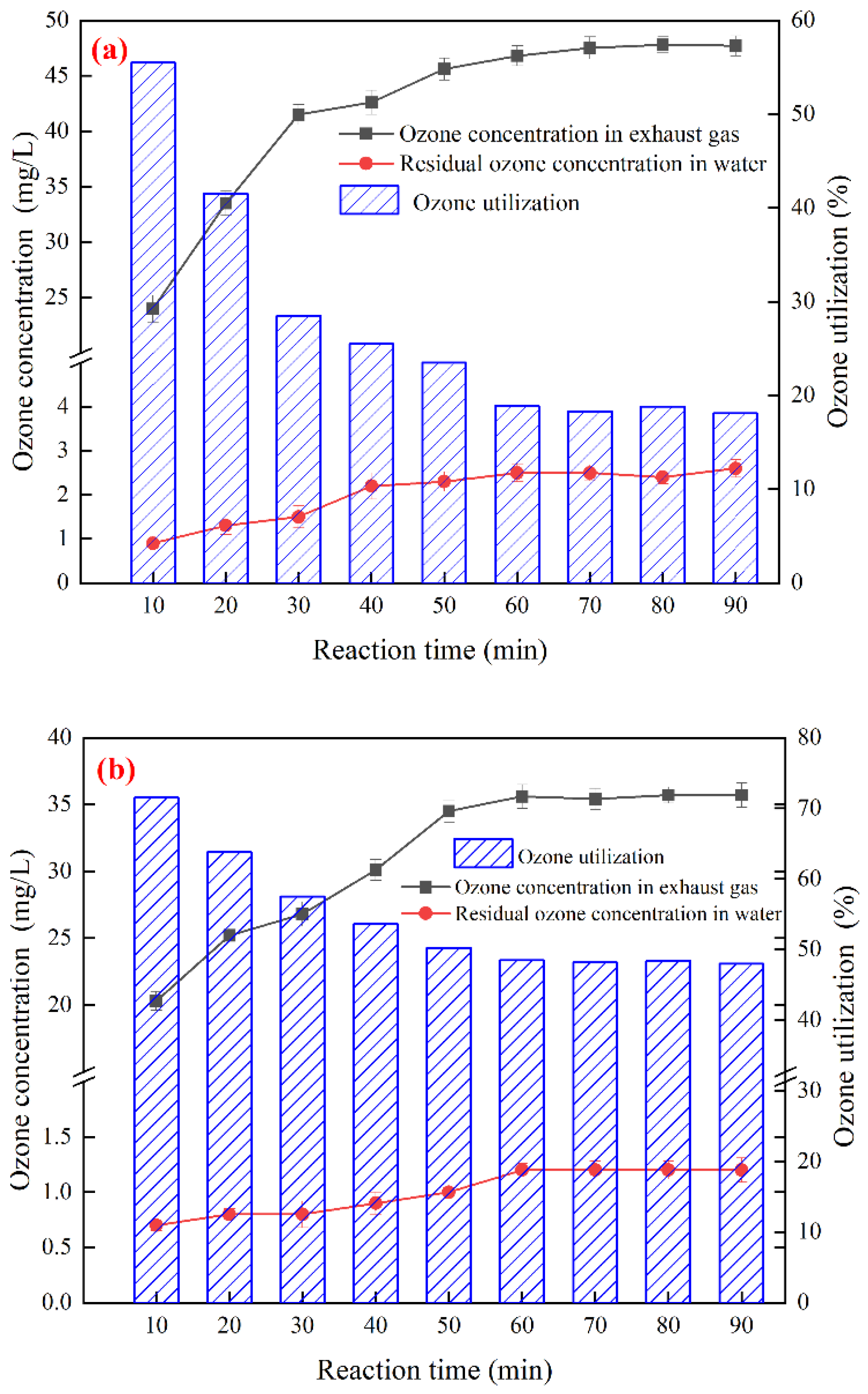
2.4. Ozone Catalytic Oxidation Experiment
2.5. Water Quality Analysis Method
2.6. Multilevel-Fuzzy Analysis Evaluation Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Optimization of Cu-Ce@γ-Al2O3 Catalyst
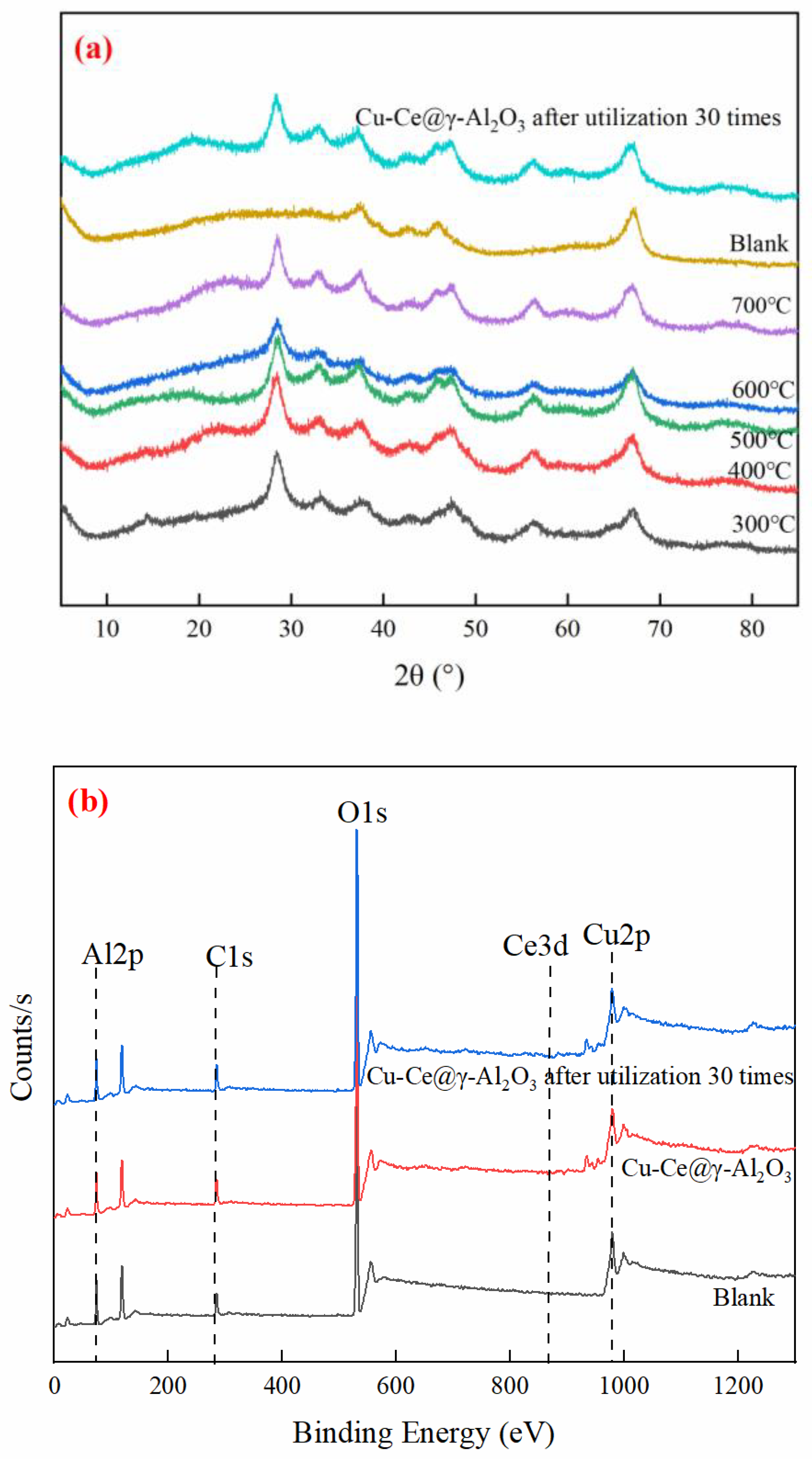
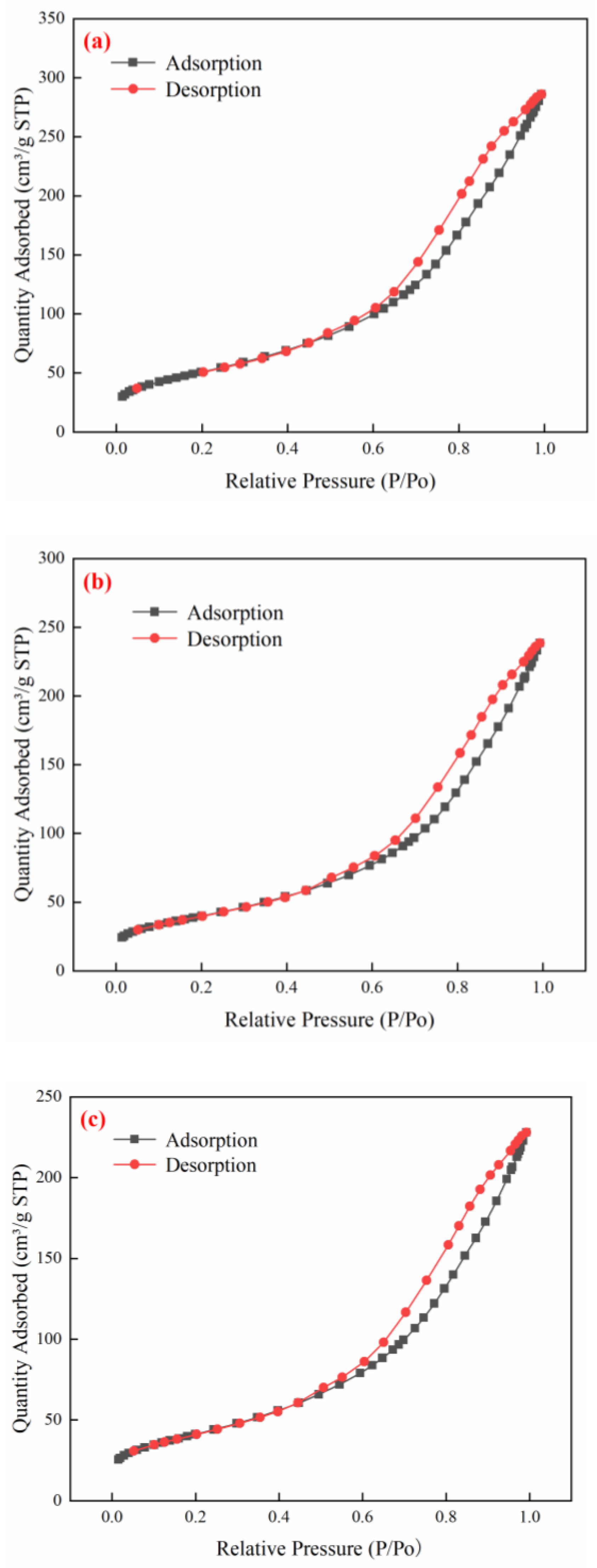
3.2. Characterization and Analysis of Cu-Ce@γ-Al2O3 Catalysts
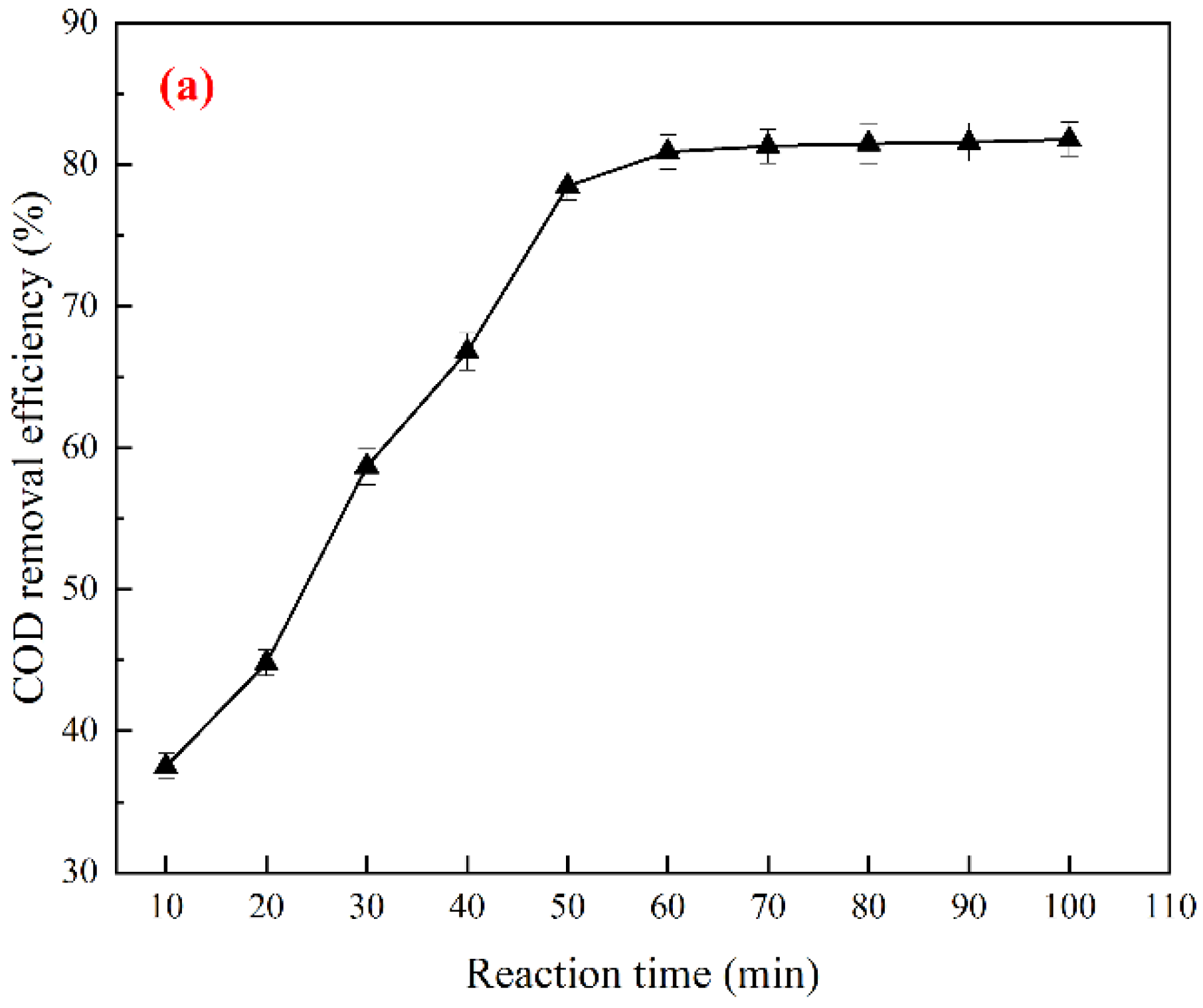
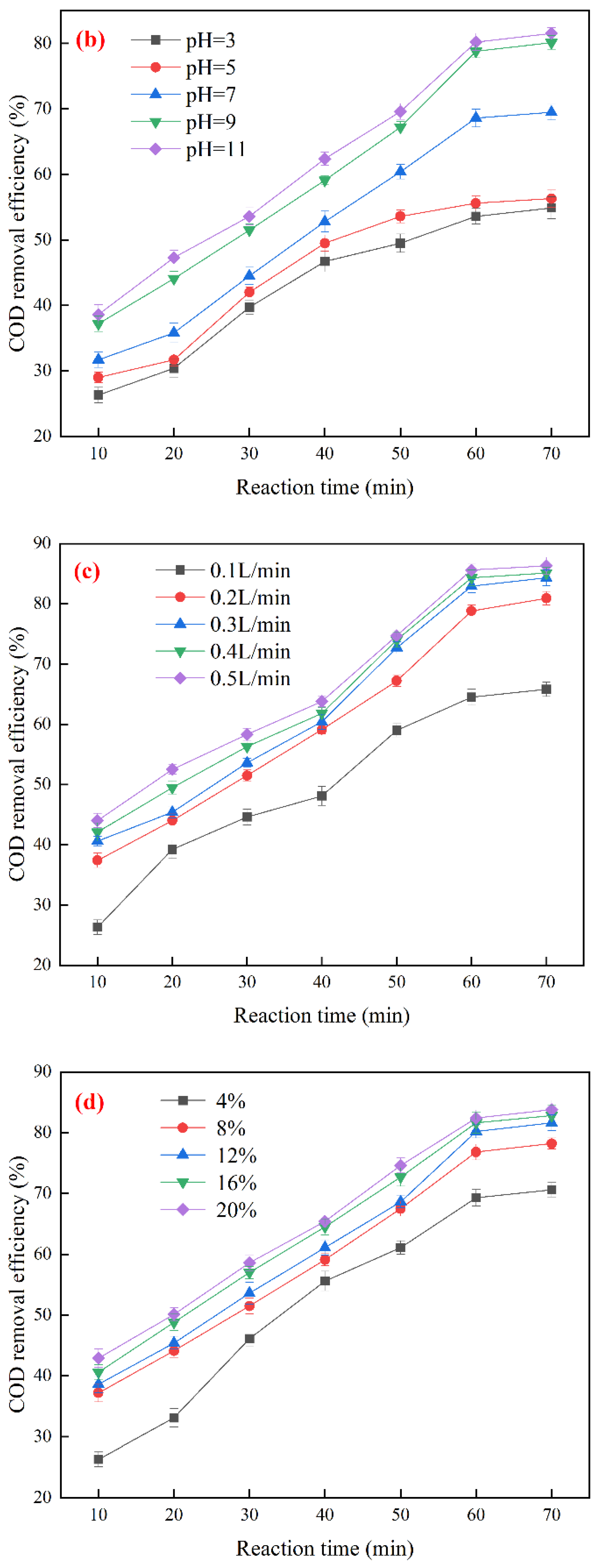
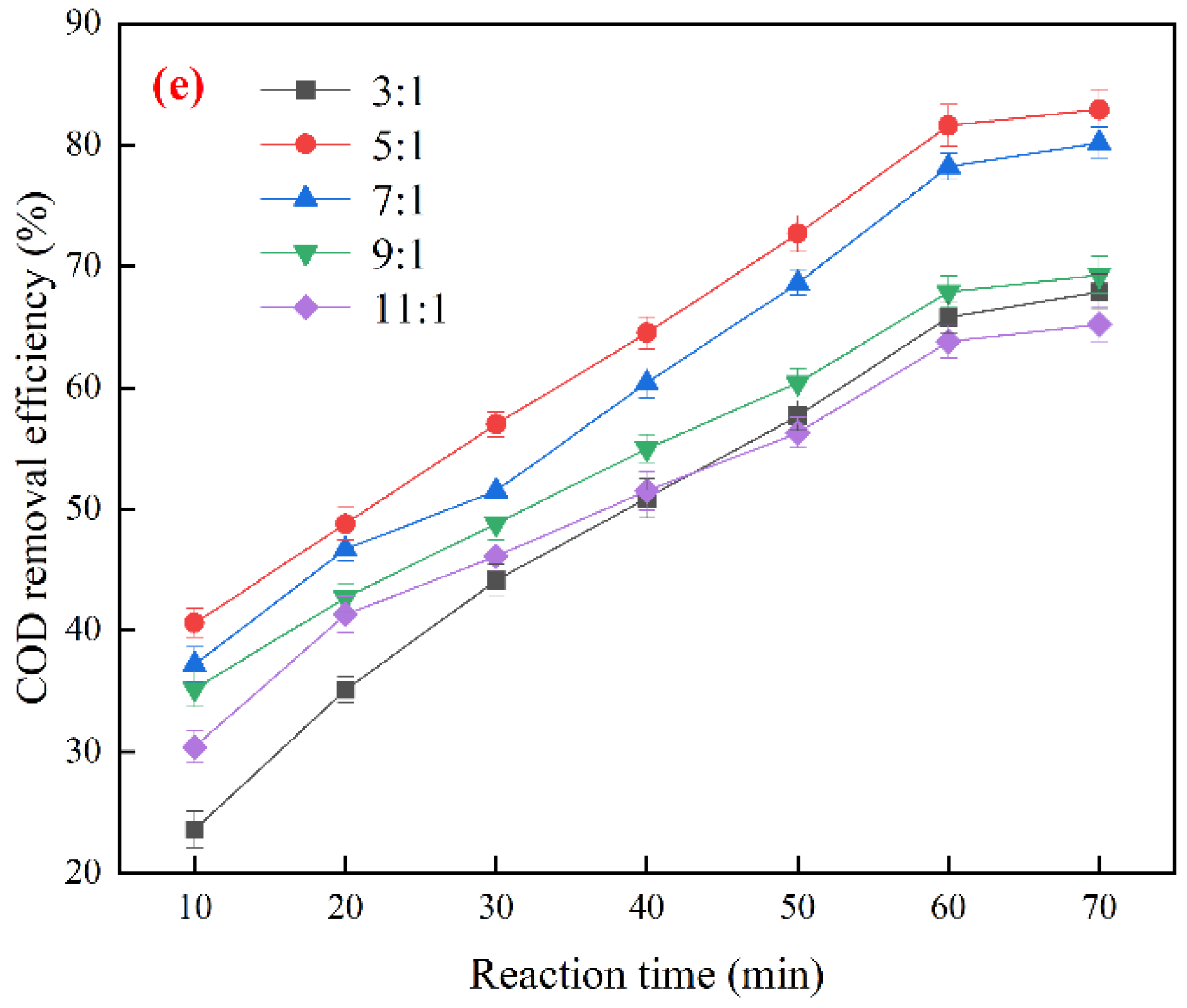
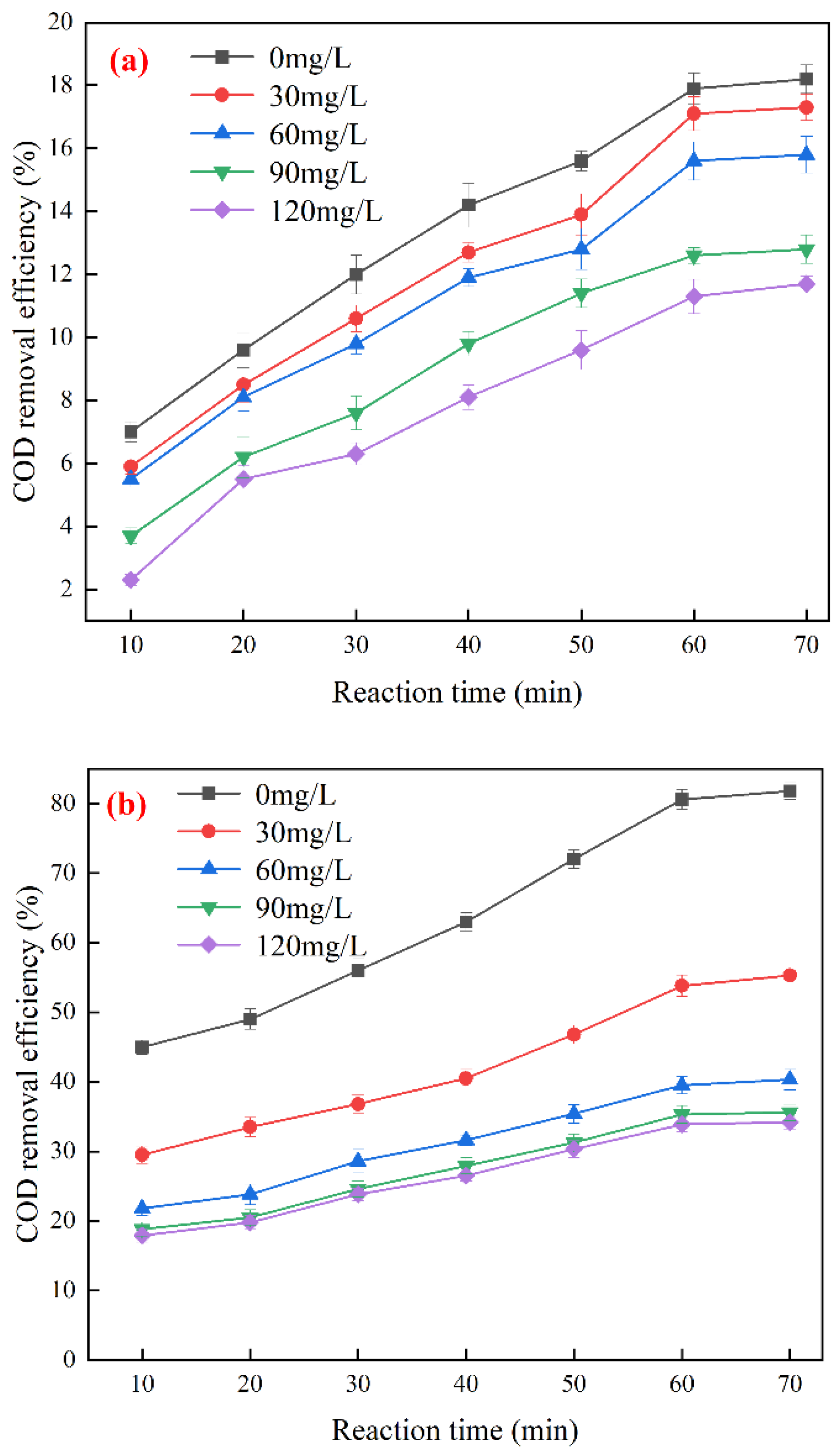
3.3. Optimization of Ozone Catalytic Oxidation Conditions
3.4. Effects of Free Radical Quenchers on Ozone Catalytic Oxidation
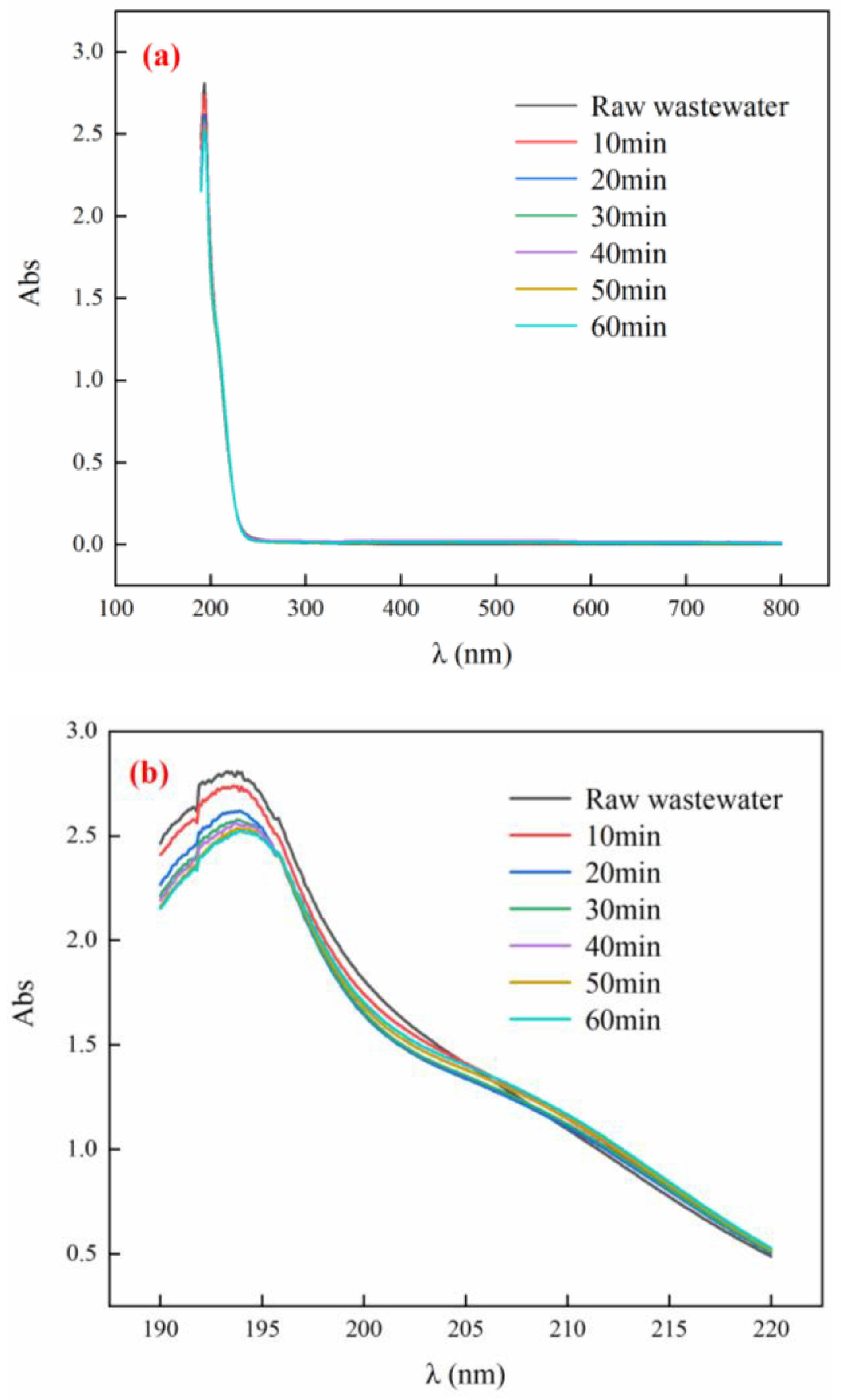
3.5. UV Absorption Peak of Tail Water
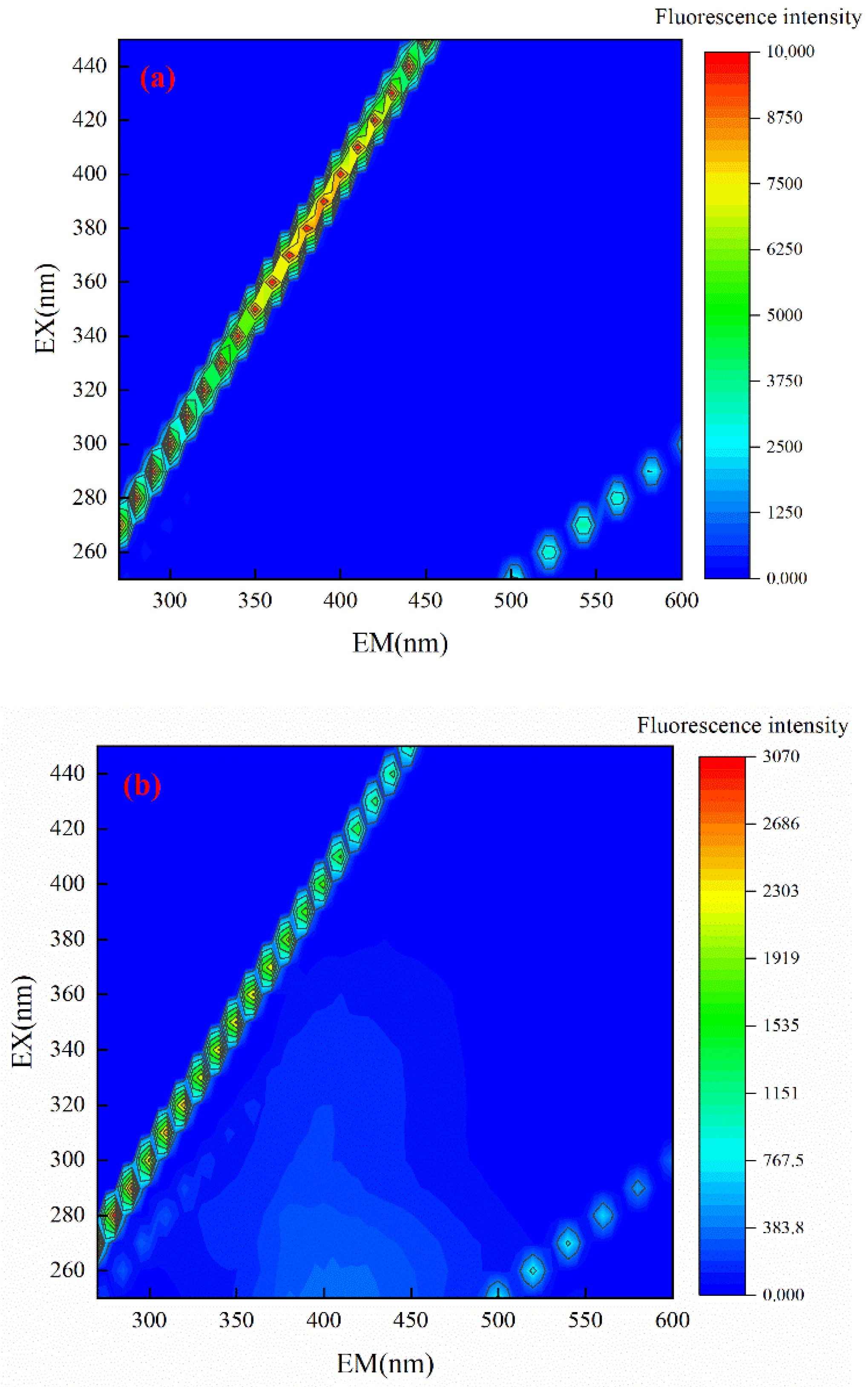
3.6. 3D-EEM Spectrum Analysis of Tail Water
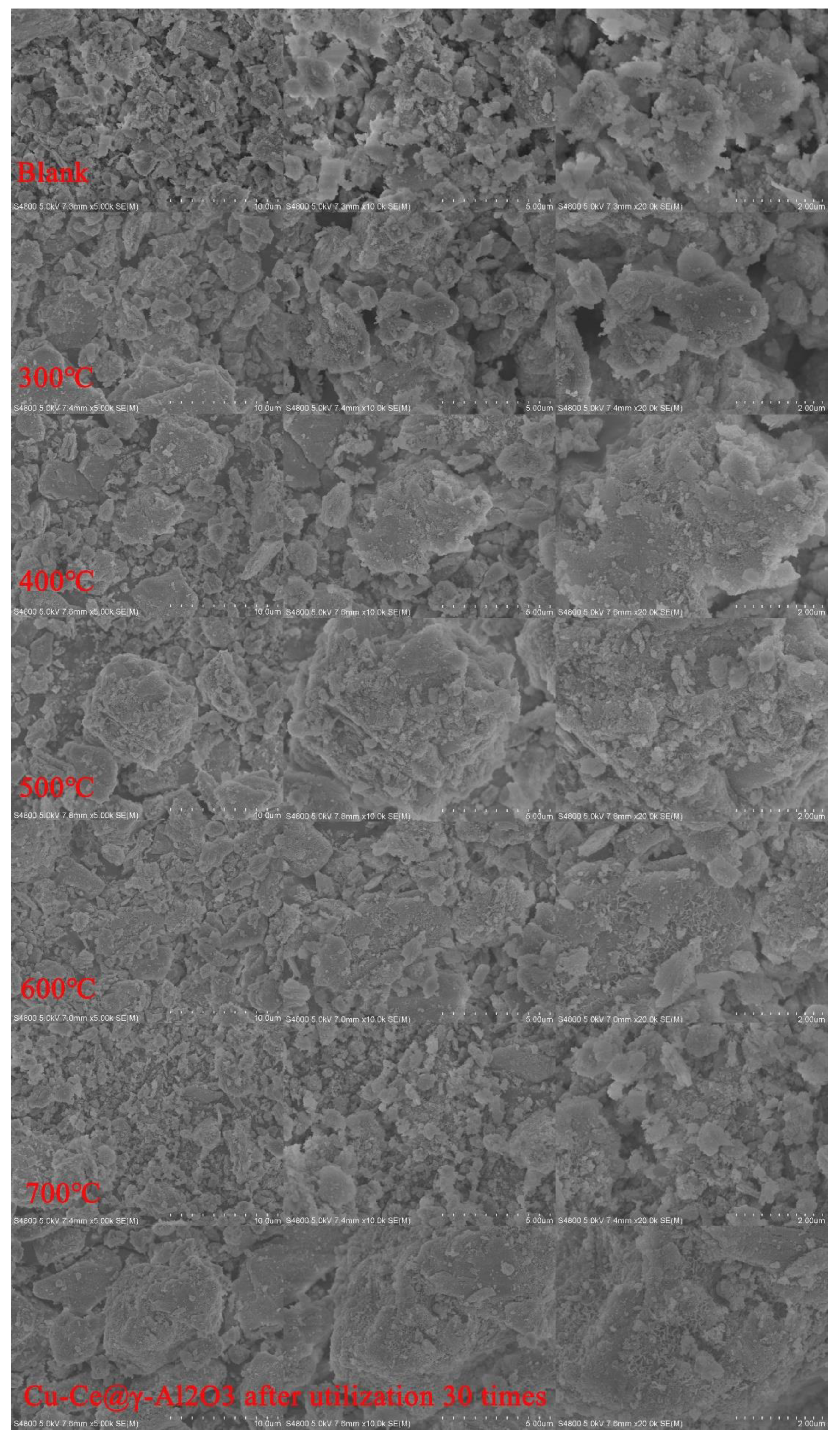
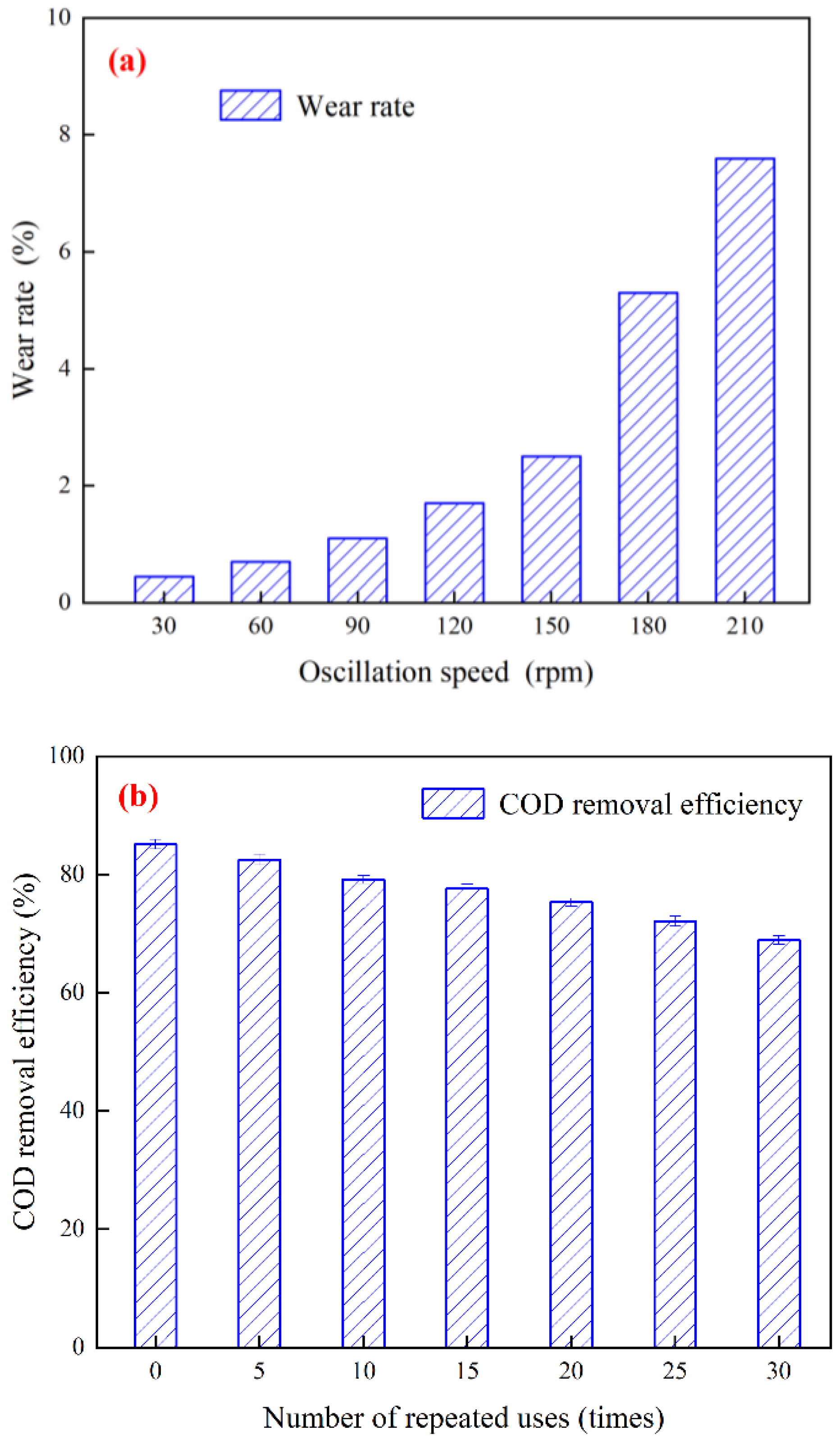
3.7. Cu-Ce@γ-Al2O3 Catalyst Stability
3.8. Multilevel-Fuzzy Analysis Evaluation Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, J. Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of organics and formation of disinfection byproducts in reverse osmosis concentrate. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lokare, O.R.; Gusa, A.V.; Vidic, R.D. Pretreatment of brackish water reverse osmosis (BWRO) concentrate to enhance water recovery in inland desalination plants by direct contact membrane distillation (DCMD). Desalination 2021, 508, 115050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, N.; Ding, S.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.; Lu, J.; Ding, J. Nanofiltration desalination of reverse osmosis concentrate pretreated by advanced oxidation with ultrafiltration: Response surface optimization and exploration of membrane fouling. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, W.; Bai, J.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, T.; Guan, X.; Zhou, B. Highly efficient removal of total nitrogen and dissolved organic compound in waste reverse osmosis concentrate mediated by chlorine radical on 3D Co3O4 nanowires anode. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xia, J.; Ding, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Shang, Z.; Lu, J.; Ding, J. Removing organic matters from reverse osmosis concentrate using advanced oxidation-biological activated carbon process combined with Fe3+/humus-reducing bacteria. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2020, 203, 110945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, M.; Roddick, F.; Fan, L. Effect of coagulation on treatment of municipal wastewater reverse osmosis concentrate by UVC/H2O2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 266, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Ren, X.; Han, J.; Wu, Y.; Gou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, P. Toxicity reduction of reverse osmosis concentrates from petrochemical wastewater by electrocoagulation and Fered-Fenton treatments. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Mo, S.; Fu, M.; Chen, L.; Ye, D. Ozone-enhanced deep catalytic oxidation of toluene over a platinum-ceria-supported BEA zeolite catalyst. Mol Catal. 2018, 460, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Tan, Q.; Wang, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Oturan, N.; Oturan, M.A. Degradation of organics in reverse osmosis concentrate by electro-Fenton process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215–216, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Ziolek, M.; Nawrocki, J. Catalytic ozonation and methods of enhancing molecular ozone reactions in water treatment. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 46, 639–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Sun, Z.; Ma, J. Novel relationship between hydroxyl radical initiation and surface group of ceramic honeycomb supported metals for the catalytic ozonation of nitrobenzene in aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4157–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wen, X. Novel catalytic ceramic membranes anchored with MnMe oxide and their catalytic ozonation performance towards atrazine degradation. J. Membrane Sci. 2022, 648, 120362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlaq, A.; Brown, D.R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Catalytic ozonation for the removal of organic contaminants in water on alumina. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Miao, R.; Wang, P.; Sun, F.; Li, X. Bi-metal oxide-modified flat-sheet ceramic membranes for catalytic ozonation of organic pollutants in wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Dacquin, J.; Royer, S.; Zhang, H. Mechanism and kinetics of catalytic ozonation for elimination of organic compounds with spinel-type CuAl2O4 and its precursor. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, L.; Fan, C.; Shao, L.; Song, K.; Yi, J.; Cai, X.; Wang, J.; Kang, M.; Li, T. The Ce doping Cu/ZSM-5 as a new superior catalyst to remove NO from diesel engine exhaust. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 253, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Ma, W.; Guo, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q.X. Mn-Fe-Mg-Ce loaded Al2O3 catalyzed ozonation for mineralization of refractory organic chemicals in petroleum refinery wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 183, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati Sani, O.; Navaei Fezabady, A.A.; Yazdani, M.; Taghavi, M. Catalytic ozonation of ciprofloxacin using γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles in synthetic and real wastewaters. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Xie, Y.; Cao, H. Organic pollutants removal in wastewater by heterogeneous photocatalytic ozonation. Chemosphere 2015, 121, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Xu, B.; Chen, Z.; Feng, L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, D. Catalytic ozonation of 2-isopropyl-3-methoxypyrazine in water by γ-AlOOH and γ-Al2O3: Comparison of removal efficiency and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Tang, Y.; Li, L. Relationship between the structure of Fe-MCM-48 and its activity in catalytic ozonation for diclofenac mineralization. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Ke, P.; Xu, J.; Guan, B. γ-Al2O3 doped with cerium to enhance electron transfer in catalytic ozonation of phenol. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.; He, H. Detrimental role of residual surface acid ions on ozone decomposition over Ce-modified γ-MnO2 under humid conditions. J. Environ. Sci.-China 2020, 91, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Lai, L.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, W.; Lai, B. Catalytic ozonation of succinic acid in aqueous solution using the catalyst of Ni/Al2O3 prepared by electroless plating-calcination method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 195, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Ma, W.; Han, H.; Han, Y.; Ma, W. Catalytic ozonation of quinoline using nano-MgO: Efficacy, pathways, mechanisms and its application to real biologically pretreated coal gasification wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Lu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhu, L.; Ma, Z.; Wu, Y. Catalytic ozonation of sulfosalicylic acid over manganese oxide supported on mesoporous ceria. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Yin, X.; Liu, Y. The role of Mn-doping for catalytic ozonation of phenol using Mn/γ-Al2O3 nanocatalyst: Performance and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3415–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataee, A.; Rad, T.S.; Fathinia, M. The role of clinoptilolite nanosheets in catalytic ozonation process: Insights into the degradation mechanism, kinetics and the toxicity. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 2017, 77, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jiang, F.; Sun, D.; Qiu, B. Catalytic ozonation for advanced treatment of incineration leachate using (MnO2-Co3O4)/AC as a catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 325, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Han, H. Effect of catalytic ozonation coupling with activated carbon adsorption on organic compounds removal treating RO concentrate from coal gasification wastewater. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, A.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, B.; Xia, Y.; Tan, Y. Catalytic ozonation of thymol in reverse osmosis concentrate with core/shell Fe3O4@SiO2@Yb2O3 catalyst: Parameter optimization and degradation pathway. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sheng, M.; Li, Y.; Xue, W.; Li, K.; Cao, G. A hybrid process of Fe-based catalytic ozonation and biodegradation for the treatment of industrial wastewater reverse osmosis concentrate. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Garg, S.; Chen, G.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Yuan, Y.; Waite, T.D. Coal chemical industry membrane concentrates: Characterisation and treatment by ozonation and catalytic ozonation processes. Environ Chem. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, H.; Luo, H.; Xu, P. Photocatalytic treatment of desalination concentrate using optical fibers coated with nanostructured thin films: Impact of water chemistry and seasonal climate variations. Photochem. Photobiol. 2016, 92, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zheng, H. Catalytic activity and evaluation of Fe-Mn@Bt for ozonizing coal chemical biochemical tail water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 239, 116524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Index | Unit | Content | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| COD | mg/L | 146.6 | Potassium dichromate method |
| Ammonia nitrogen | mg/L | 2.5 | Nessler’s reagent colorimetry |
| pH | / | 7.49 | pH meter |
| Turbidity | mg/L | 0.25 | Turbidimeter |
| Chroma | NTU | 1.5 | Colorimeter |
| Total nitrogen | mg/L | 10.2 | UV spectrophotometry |
| Total phosphorus | mg/L | 0.95 | UV spectrophotometry |
| Conductivity | us/cm | 1695 | Conductivity meter |
| Sample | γ-Al2O3 | Cu-Ce@γ-Al2O3 | Cu-Ce@γ-Al2O3 after Utilization 30 Times | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Weight percent (%) | Atomic percent (%) | Weight percent (%) | Atomic percent (%) | Weight percent (%) | Atomic percent (%) |
| OK | 44.48 | 59.82 | 42.58 | 56.83 | 45.21 | 60.73 |
| AlK | 44.18 | 38.42 | 40.32 | 35.19 | 38.08 | 33.75 |
| CK | 10.13 | 1.85 | 9.24 | 3.81 | 8.39 | 3.62 |
| CuK | / | / | 3.42 | 1.16 | 3.23 | 1.04 |
| CeK | / | / | 3.92 | 0.60 | 3.59 | 0.54 |
| Sample | Na2O | Al2O3 | SiO2 | CaO | Fe2O3 | SO3 | CuO | CeO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| γ-Al2O3 (%) | 0.33 | 98.93 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.07 | / | / |
| Cu-Ce@γ-Al2O3 (%) | 0.11 | 87.29 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 6.25 | 6.44 |
| Cu-Ce@γ-Al2O3 after utilization 30 times (%) | 0.29 | 85.53 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.02 | 0.50 | 5.85 | 6.36 |
| Serial Number | Environmental Impact T1 | Resource Consumption T2 | Energy Consumption T3 | Overall Score | Scoring Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0661 | 0.1626 | 0.1634 | 0.3921 | 17 |
| 2 | 0.2007 | 0.1626 | 0.0812 | 0.4444 | 14 |
| 3 | 0.3726 | 0.1626 | 0.0403 | 0.5755 | 10 |
| 4 | 0.3846 | 0.1626 | 0.0200 | 0.5672 | 11 |
| 5 | 0.0908 | 0.1495 | 0.0403 | 0.2805 | 22 |
| 6 | 0.1025 | 0.1535 | 0.0403 | 0.2963 | 21 |
| 7 | 0.2196 | 0.1603 | 0.0403 | 0.4202 | 16 |
| 8 | 0.4055 | 0.1718 | 0.0403 | 0.6176 | 8 |
| 9 | 0.4164 | 0.1912 | 0.0403 | 0.6179 | 3 |
| 10 | 0.1834 | 0.2055 | 0.0403 | 0.4292 | 15 |
| 11 | 0.4437 | 0.1519 | 0.0403 | 0.6359 | 6 |
| 12 | 0.4604 | 0.1401 | 0.0403 | 0.6408 | 4 |
| 13 | 0.4880 | 0.1331 | 0.0403 | 0.6615 | 2 |
| 14 | 0.1873 | 0.2284 | 0.0403 | 0.4561 | 13 |
| 15 | 0.4604 | 0.1383 | 0.0403 | 0.6390 | 5 |
| 16 | 0.4653 | 0.1185 | 0.0403 | 0.6241 | 7 |
| 17 | 0.4703 | 0.1068 | 0.0403 | 0.6173 | 9 |
| 18 | 0.1685 | 0.1537 | 0.0403 | 0.3626 | 18 |
| 19 | 0.5396 | 0.1422 | 0.0403 | 0.7221 | 1 |
| 20 | 0.3553 | 0.1353 | 0.0403 | 0.5309 | 12 |
| 21 | 0.1694 | 0.1313 | 0.0403 | 0.3410 | 19 |
| 22 | 0.1516 | 0.1289 | 0.0403 | 0.3208 | 20 |
| Wastewater Type | Index | Method | Initial Concentration (mg/L) | Removal Efficiency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RO concentrate | COD | Catalytic ozonation by Cu-Ce@γ-Al2O3 catalyst | 146.6 | 85.2% | This study |
| RO concentrate | TOC | Catalytic ozonation coupling with activated carbon adsorption | 66 | 58% | [30] |
| RO concentrate | COD | Catalytic ozonation with core/shell Fe3O4@SiO2@Yb2O3 catalyst | 100 (thymol) | 57% | [31] |
| RO concentrate | COD | A hybrid process of Fe-based catalytic ozonation and biodegradation | 108 | 63% | [32] |
| RO concentrate | DOC | Catalytic ozonation by Fe-oxide@Al2O3 catalyst | 30 | 47% | [33] |
| RO concentrate | Rh B | Photocatalytic by Fe-TiO2 mixed-phase nanocomposite thin films | 4.1 | 69% | [34] |
| Coal chemical biochemical tail water | TOC | Catalytic ozonation by Fe-Mn@Bt | 210 | 53.5% | [35] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, W.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ding, L.; Zhou, J. Preparation of Cu-Ce@γ-Al2O3 and Study on Catalytic Ozone Oxidation for the Treatment of RO Concentrate Water. Water 2022, 14, 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182881
Sun W, Xiao Z, Sun Y, Ding L, Zhou J. Preparation of Cu-Ce@γ-Al2O3 and Study on Catalytic Ozone Oxidation for the Treatment of RO Concentrate Water. Water. 2022; 14(18):2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182881
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Wenquan, Zhiqiang Xiao, Yongjun Sun, Lei Ding, and Jun Zhou. 2022. "Preparation of Cu-Ce@γ-Al2O3 and Study on Catalytic Ozone Oxidation for the Treatment of RO Concentrate Water" Water 14, no. 18: 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182881
APA StyleSun, W., Xiao, Z., Sun, Y., Ding, L., & Zhou, J. (2022). Preparation of Cu-Ce@γ-Al2O3 and Study on Catalytic Ozone Oxidation for the Treatment of RO Concentrate Water. Water, 14(18), 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182881