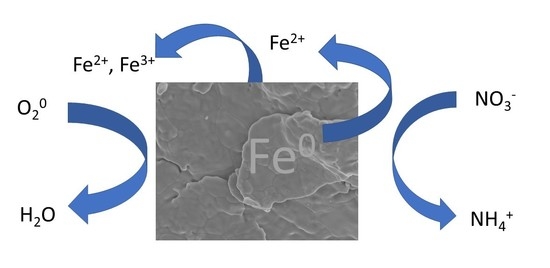
Reactivity of Nitrate with Zero-Valent Iron
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Stirred-Batch Anoxic and Oxic Reactions
2.3. Analytical Techniques
3. Results
3.1. Stoichiometry of Nitrate Reduction by Zero-Valent Iron
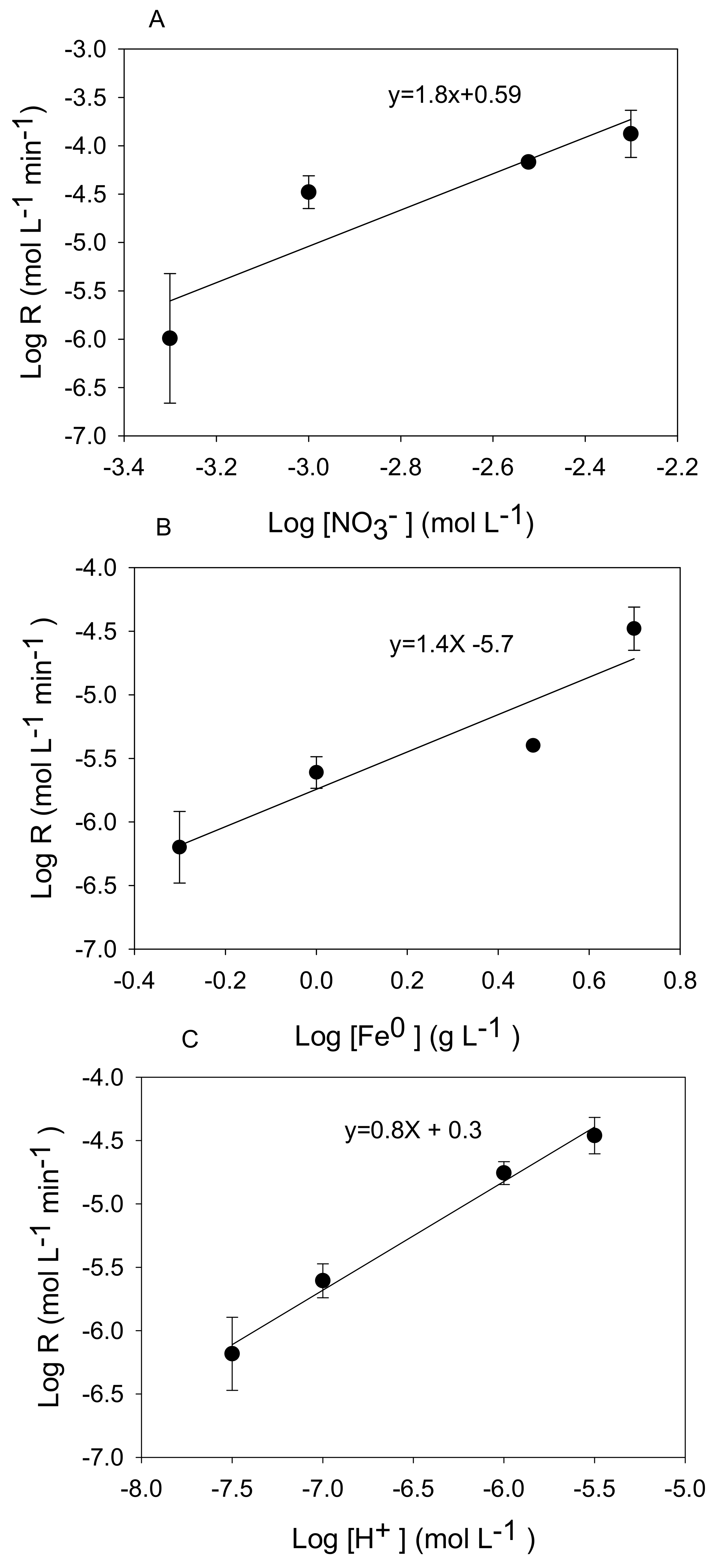
3.2. Kinetic Analysis

3.3. Nitrate Reduction under Oxic Conditions
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adyasari, D.; Oehler, T.; Afiati, N.; Moosdorf, N. Groundwater nutrient inputs into an urbanized tropical estuary system in Indonesia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eick, M.J.; Brady, W.D.; Lynch, C.K. Charge Properties and Nitrate Adsorption of Some Acid Southeastern Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 1999, 28, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; Verspagen, J.M.; Lürling, M.; Van Donk, E.; Visser, P.M.; Huisman, J. The ecological stoichiometry of toxins produced by harmful cyanobacteria: An experimental test of the carbon-nutrient balance hypothesis. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sar, C.; Mwenya, B.; Pen, B.; Takaura, K.; Morikawa, R.; Tsujimoto, A.; Kuwaki, K.; Isogai, N.; Shinzato, I.; Asakura, Y.; et al. Effect of ruminal administration of Escherichia coli wild type or a genetically modified strain with enhanced high nitrite reductase activity on methane emission and nitrate toxicity in nitrate-infused sheep. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 94, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathod, S.K.; Velmurugan, S.; Ahluwalia, A. A ‘green’diet-based approach to cardiovascular health? Is inorganic nitrate the answer? Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Cheng, Y.; Oswald, R.; Behrendt, T.; Trebs, I.; Meixner, F.X.; Andreae, M.O.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, Y.; Pöschl, U. Soil Nitrite as a Source of Atmospheric HONO and OH Radicals. Science 2011, 333, 1616–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Horn, M.A.; Behrendt, T.; Müller, S.; Li, J.; Cole, J.A.; Xie, B.; Ju, X.; Li, G.; Ermel, M.; et al. Soil HONO emissions at high moisture content are driven by microbial nitrate reduction to nitrite: Tackling the HONO puzzle. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugaoen, H.; Garcia-Segura, S.; Hristovski, K.; Westerhoff, P. Challenges in photocatalytic reduction of nitrate as a water treatment technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 1524–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y. An overview of in-situ remediation for nitrate in groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 804, 149981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siantar, D.P.; Schreier, C.G.; Chou, C.-S.; Reinhard, M. Treatment of 1,2-dibromo-3-chloropropane and nitrate-contaminated water with zero-valent iron or hydrogen/palladium catalysts. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2315–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-P.; Wang, H.-W.; Chiu, P.-C. Nitrate reduction by metallic iron. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2257–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alowitz, J.M.; Scherer, M.M. Kinetics of nitrate, nitrite, and Cr (VI) reduction by iron metal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A.D.; Demond, A.H. Long-Term Performance of Zero-Valent Iron Permeable Reactive Barriers: A Critical Review. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2007, 24, 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepong-Tsindé, R.; Ndé-Tchoupé, A.I.; Noubactep, C.; Nassi, A.; Ruppert, H. Characterizing a Newly Designed Steel-Wool-Based Household Filter for Safe Drinking Water Provision: Hydraulic Conductivity and Efficiency for Pathogen Removal. Processes 2019, 7, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakari, O.; Njau, K.N.; Noubactep, C. Fe0-Supported Anaerobic Digestion for Organics and Nutrients Removal from Domestic Sewage. Water 2022, 14, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hu, R.; Ndé-Tchoupé, A.I.; Gwenzi, W.; Ruppert, H.; Noubactep, C. Designing the Next Generation of Fe0-Based Filters for Decentralized Safe Drinking Water Treatment: A Conceptual Framework. Processes 2020, 8, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Zhang, T.C. Kinetics of Nitrate Reduction by Iron at Near Neutral pH. J. Environ. Eng. 2002, 128, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Maroto, J.; García-Herruzo, F.; García-Rubio, A.; Gómez-Lahoz, C.; Vereda-Alonso, C. Kinetics of the chemical reduction of nitrate by zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, I.; Muftikian, R.; Fernando, Q.; Korte, N. Reduction of nitrate to ammonia by zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 1997, 35, 2689–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L. Kinetics of Soil Chemical Processes; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lasaga, A.C. 1. Rate Laws of Chemical Reactions. In Kinetic Theory in the Earth Sciences; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, P.; James, J. Nitrate removal in zero-valent iron packed columns. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1818–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginner, J.L.; Alvarez, P.J.; Smith, S.L.; Scherer, M.M. Nitrate and nitrite reduction by Fe0: Influence of mass transport, temperature, and denitrifying microbes. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2004, 21, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.C.; Oh, S.-Y.; Cha, D.K. Enhanced reduction of nitrate by zero-valent iron at elevated temperatures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.; Cha, D.K. Effect of low temperature on abiotic and biotic nitrate reduction by zero-valent Iron. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 754, 142410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luther, G.W., III. Inorganic Chemistry for Geochemistry and Environmental Sciences: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Atwood, J.D. Inorganic and Organometallic Reaction Mechanisms; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, R.M.; Puls, R.W.; Hightower, S.K.; Sabatini, D.A. Coupled Iron Corrosion and Chromate Reduction: Mechanisms for Subsurface Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.C.; Lee, H.-L. Chemical reduction of nitrate by nanosized iron: Kinetics and pathways. Water Res. 2005, 39, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Zhang, T.C. Effects of low pH on nitrate reduction by iron powder. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2631–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stookey, L.L. Ferrozine—A new spectrophotometric reagent for iron. Anal. Chem. 1970, 42, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Zhang, T.C.; Shea, P.J.; Comfort, S.D. Effects of Oxide Coating and Selected Cations on Nitrate Reduction by Iron Metal. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, Y.; Kim, J.-W.; Watkins, J.; Wilkin, R.T. Formation of Ferrihydrite and Associated Iron Corrosion Products in Permeable Reactive Barriers of Zero-Valent Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 5469–5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Huang, Y.H.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, Z. Reductive removal of selenate by zero-valent iron: The roles of aqueous Fe2+ and corrosion products, and selenate removal mechanisms. Water Res. 2014, 67, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, E.; Wehrli, B.; Stumm, W. The coordination chemistry of weathering: III. A generalization on the dissolution rates of minerals. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 1969–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriver, D.; Atkins, P.; Langford, C.H. Inorganic Chemistry; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1994; p. 790. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A. Standard Potentials in Aqueous Solution; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nakata, K.; Kayama, Y.; Shimazu, K.; Yamakata, A.; Ye, S.; Osawa, M. Surface-enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopic studies of adsorbed nitrate, nitric oxide, and related compounds 2: Nitrate ion adsorption at a platinum electrode. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4358–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.-E.; Stewart, A.K.L.; Gewirth, A.A. Nitrate Adsorption and Reduction on Cu(100) in Acidic Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10171–10180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Puls, R.W. Nitrate Reduction by Zerovalent Iron: Effects of Formate, Oxalate, Citrate, Chloride, Sulfate, Borate, and Phosphate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2715–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, G.M.; Limonti, C.; Siciliano, A.; Kabdaşlı, I. Nitrate Removal by Zero-Valent Metals: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wagner, K.M.; Karathanasis, T.; Matocha, C.J. Reactivity of Nitrate with Zero-Valent Iron. Water 2022, 14, 2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182796
Wagner KM, Karathanasis T, Matocha CJ. Reactivity of Nitrate with Zero-Valent Iron. Water. 2022; 14(18):2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182796
Chicago/Turabian StyleWagner, Katie M., Tasios Karathanasis, and Christopher J. Matocha. 2022. "Reactivity of Nitrate with Zero-Valent Iron" Water 14, no. 18: 2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182796
APA StyleWagner, K. M., Karathanasis, T., & Matocha, C. J. (2022). Reactivity of Nitrate with Zero-Valent Iron. Water, 14(18), 2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182796