Hydrochemical Characteristics of Hot Springs in the Intersection of the Red River Fault Zone and the Xiaojiang Fault Zone, Southwest Tibet Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Geological Settings
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Techniques
3.2. Data Collection and Processing
4. Results and Discussion
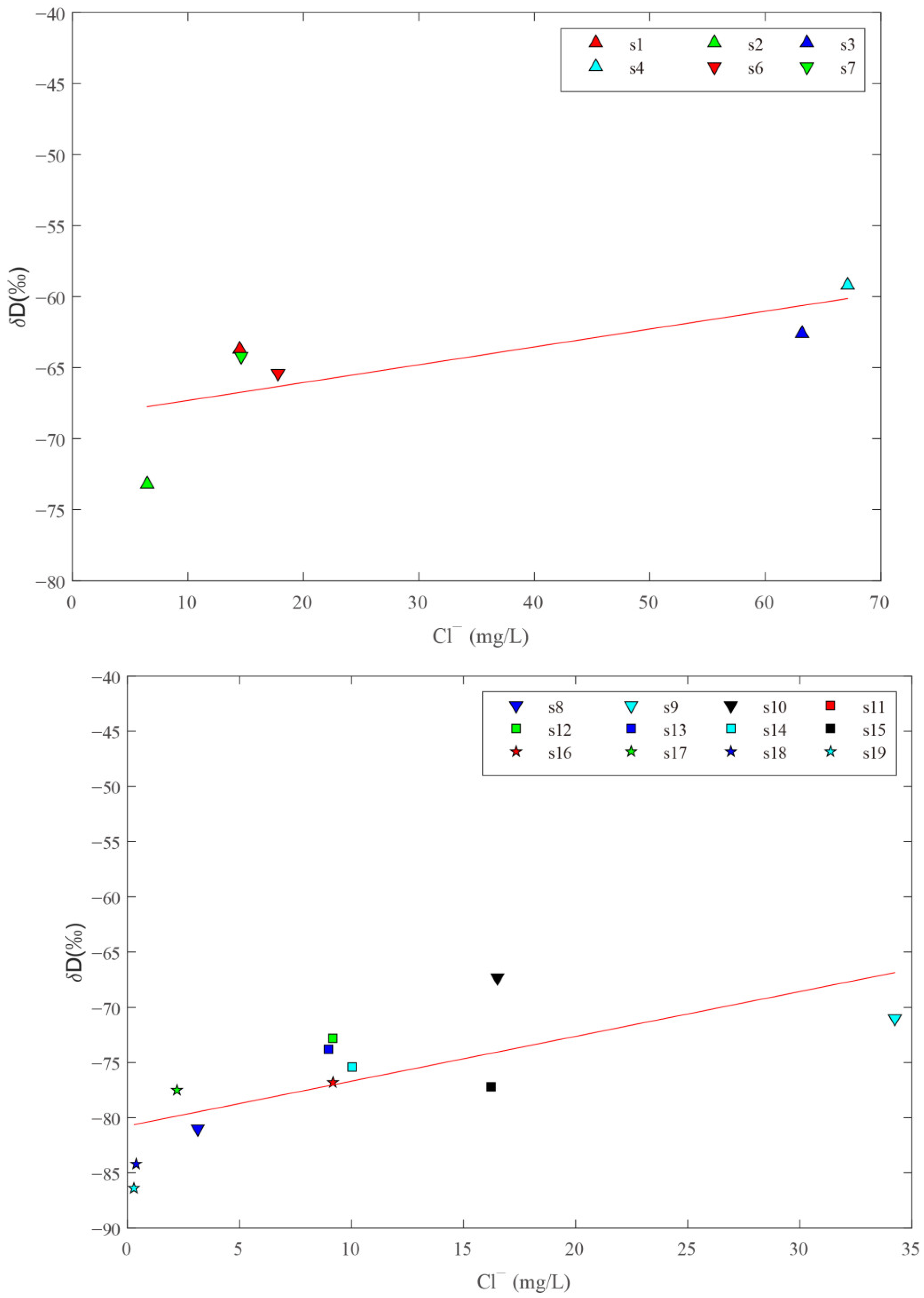
4.1. Recharge Sources of Hot Spring Water
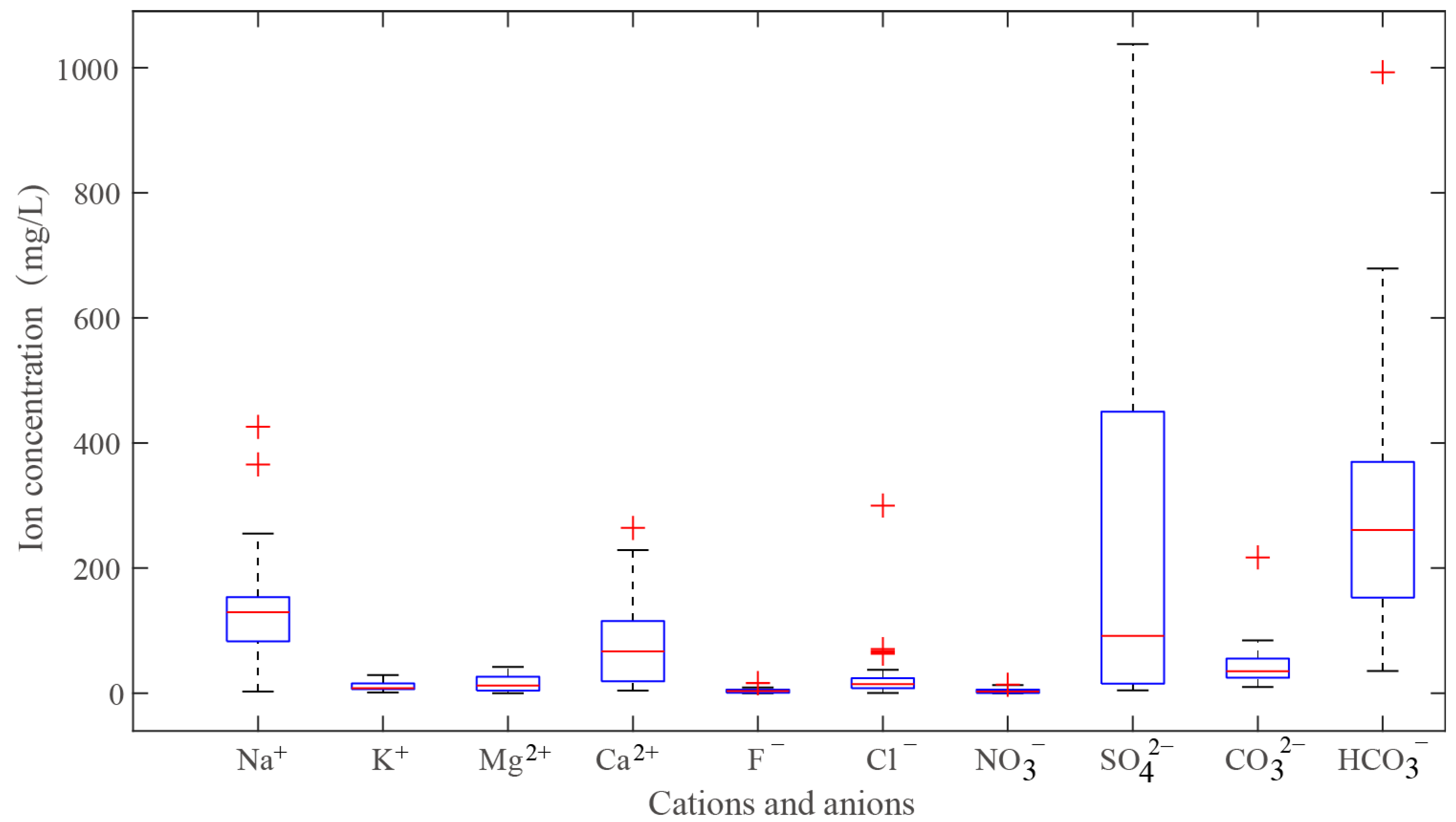
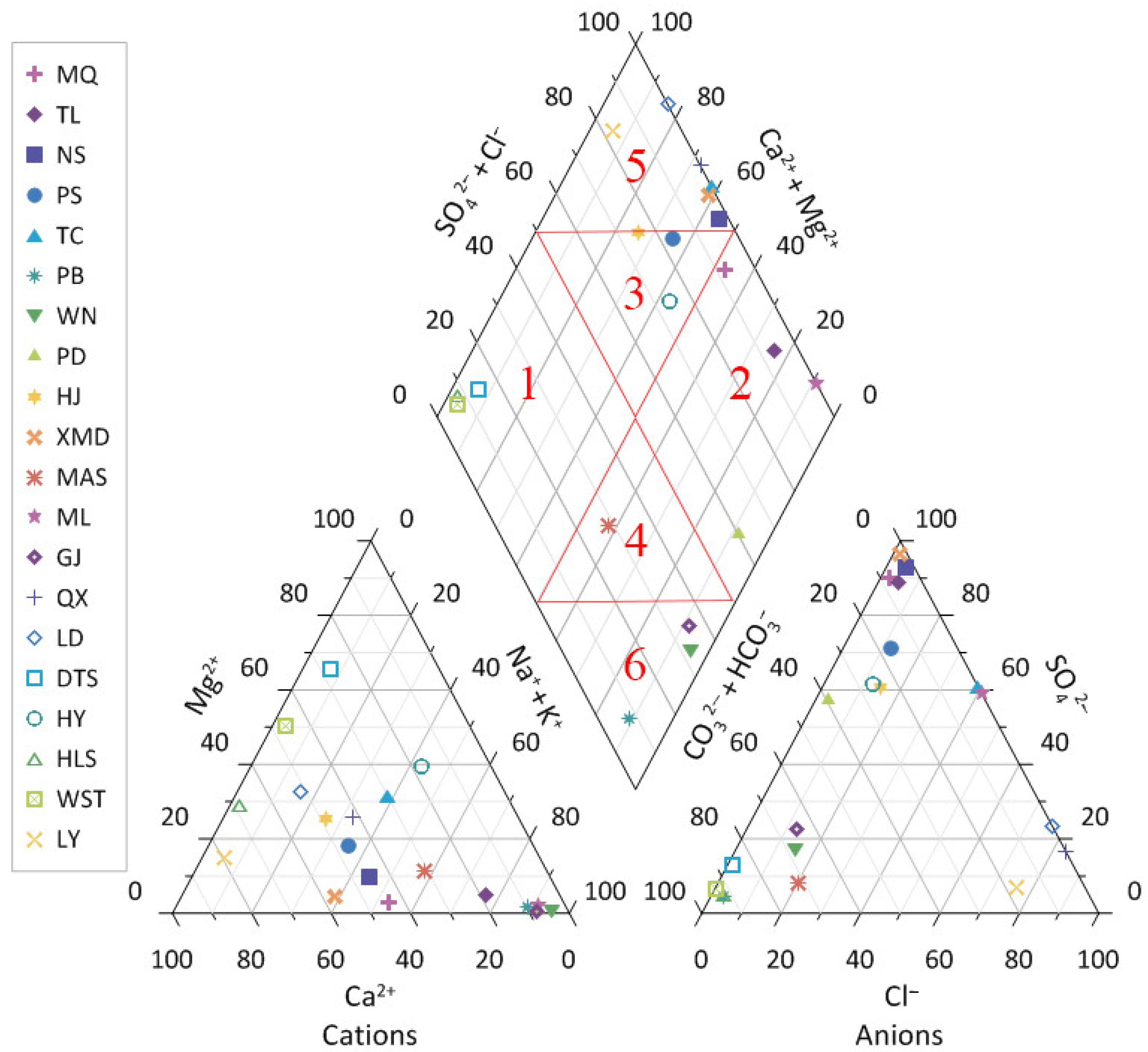
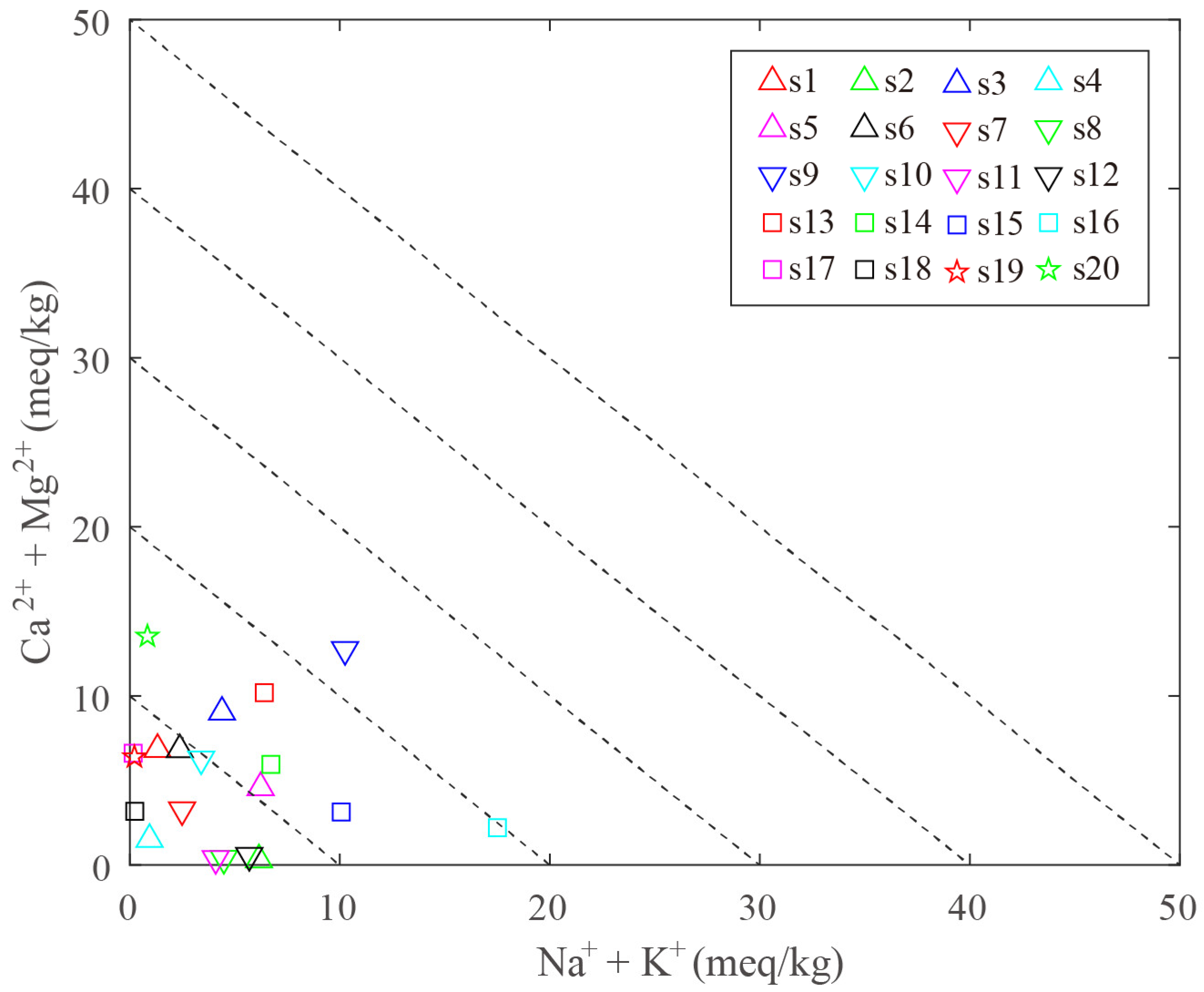
4.2. Origin of Water-Soluble Ions in Hot Spring
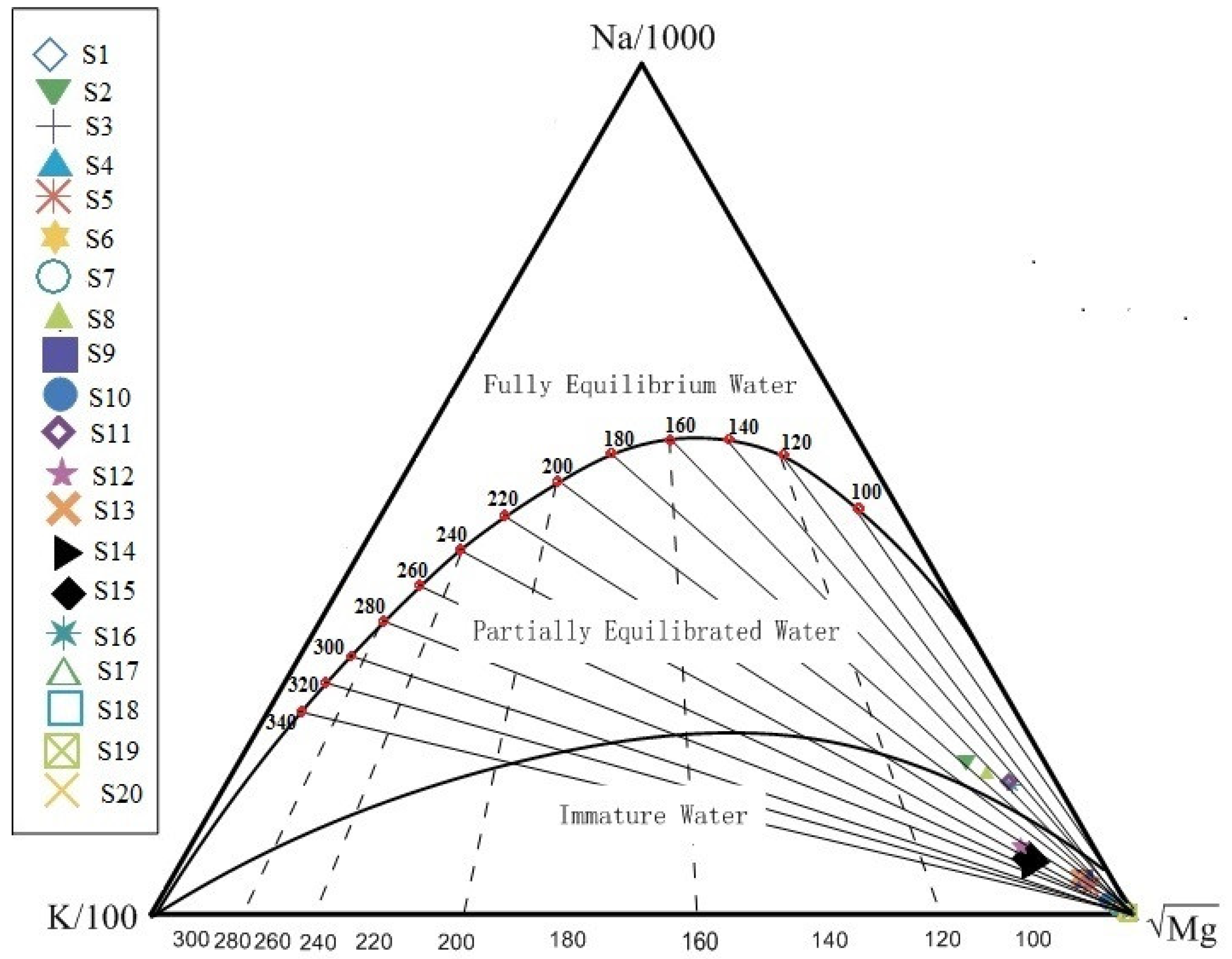
4.2.1. Origin of Major Elements
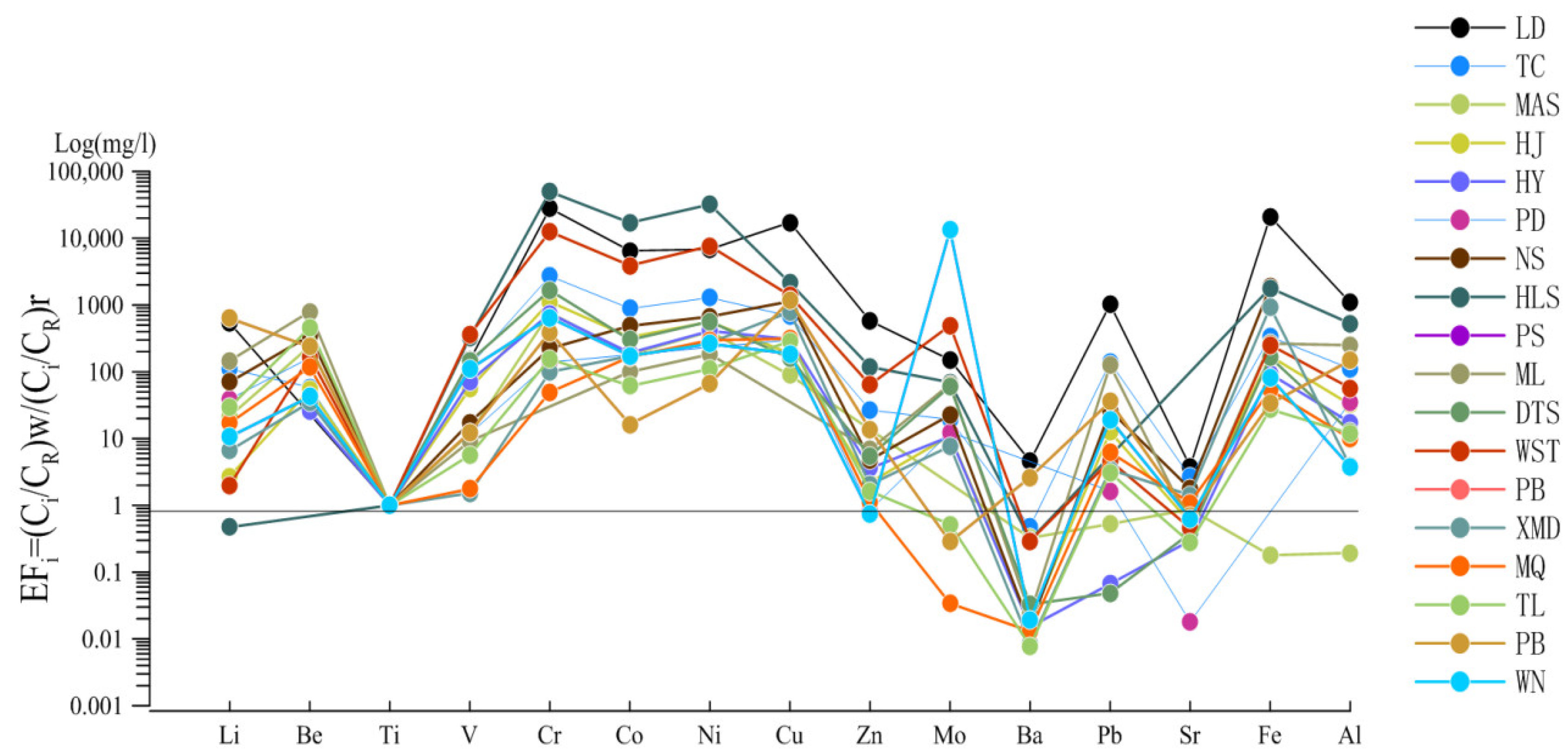
4.2.2. Origin of Trace Elements
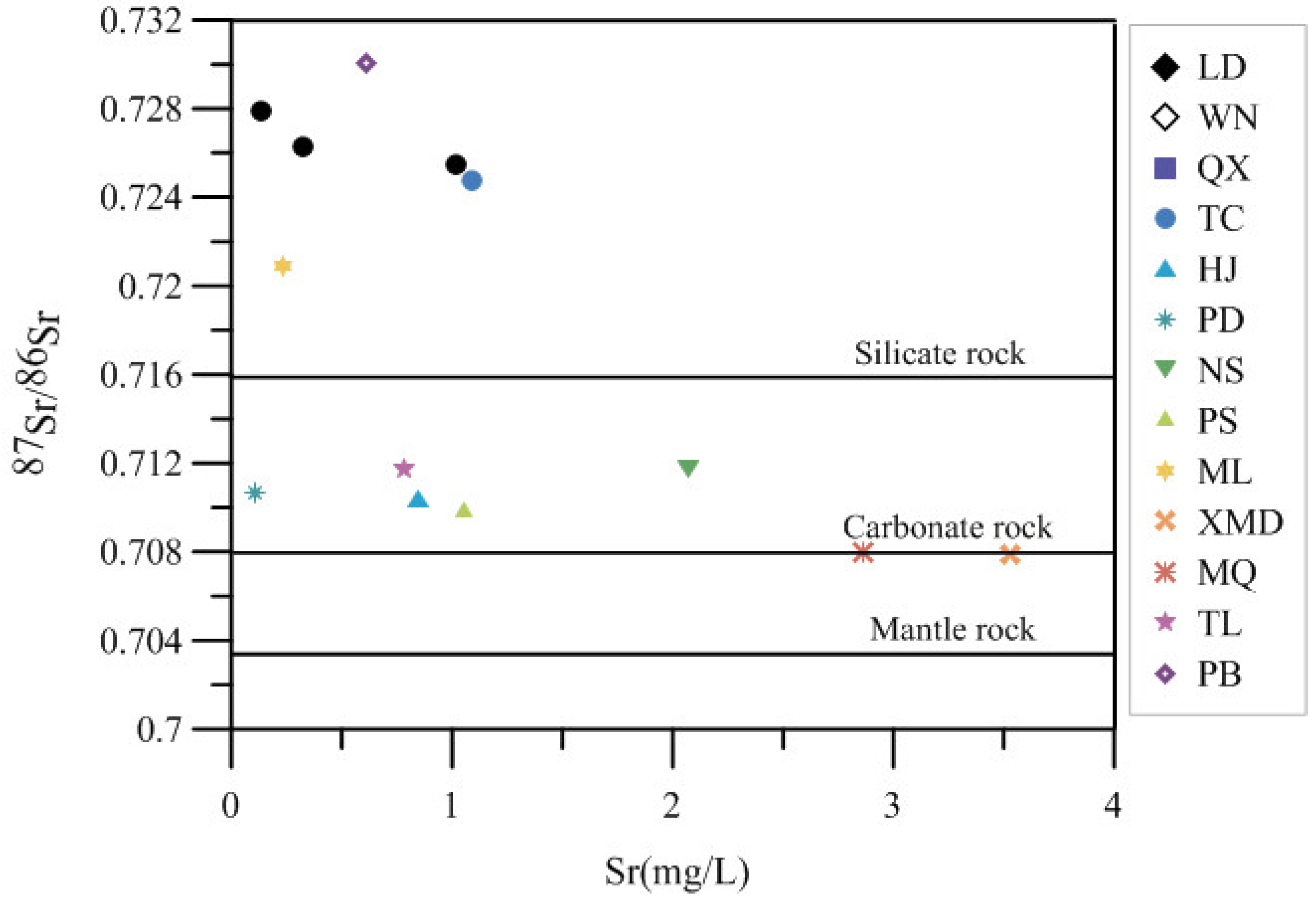
4.2.3. Strontium Isotope Analysis
4.3. Water Rock Interaction of Hot Springs
4.3.1. The Water–Rock Reaction Equilibrium
4.3.2. Mixing with Shallow Groundwater or Surface Water
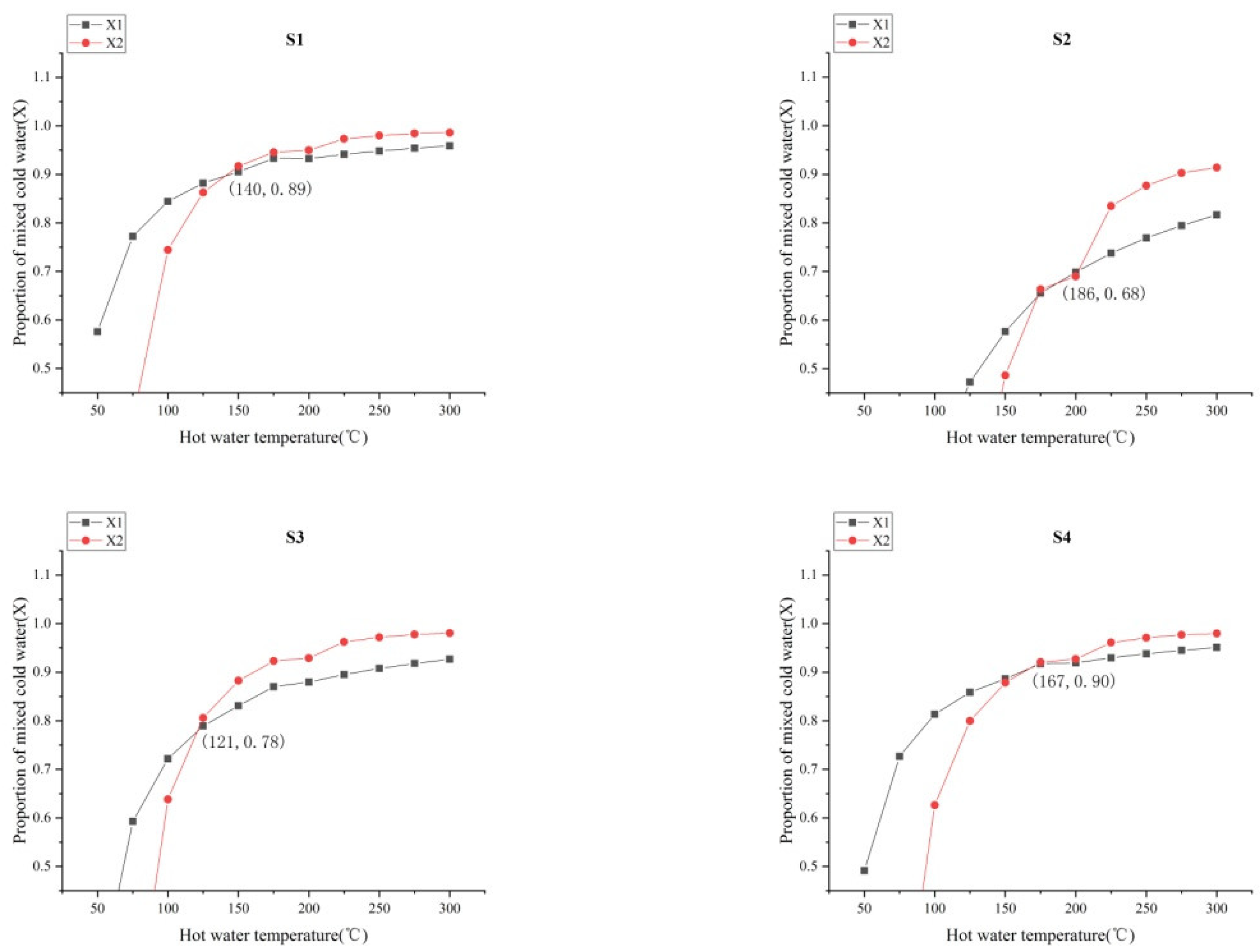
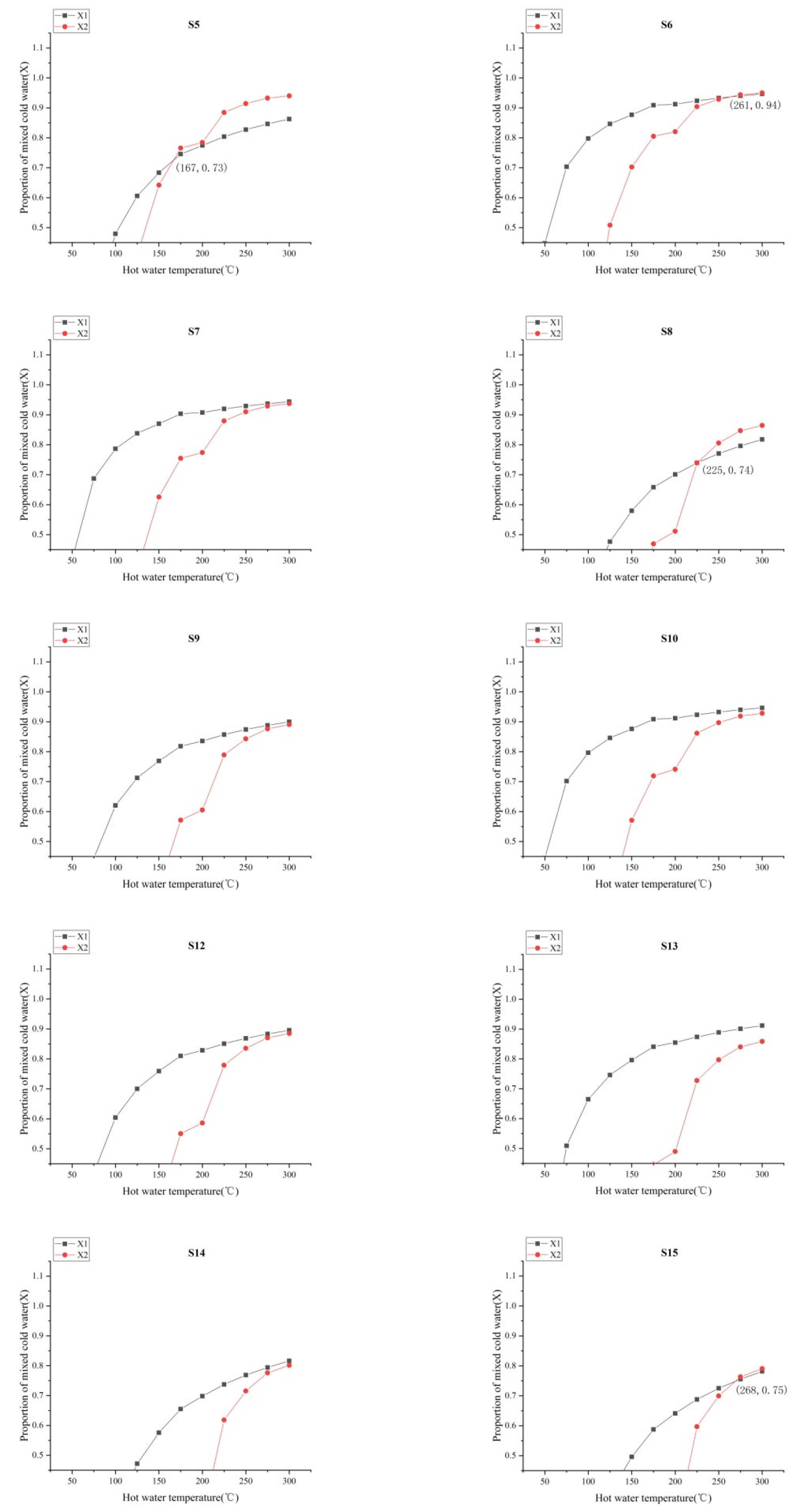
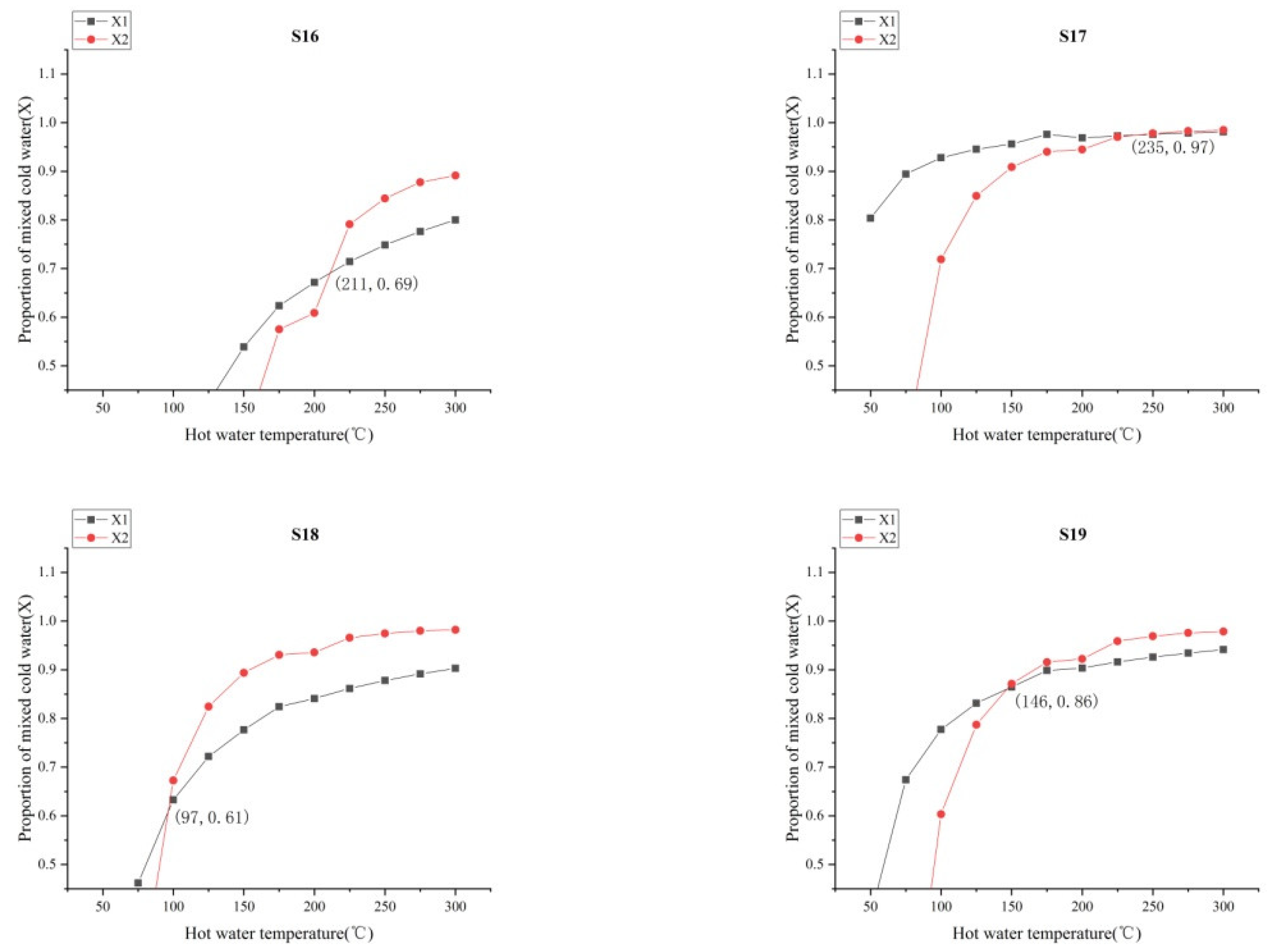
4.3.3. The Ratio of Cold and Hot Water
4.3.4. Geothermal Reservoir Temperature and Circulation Depth
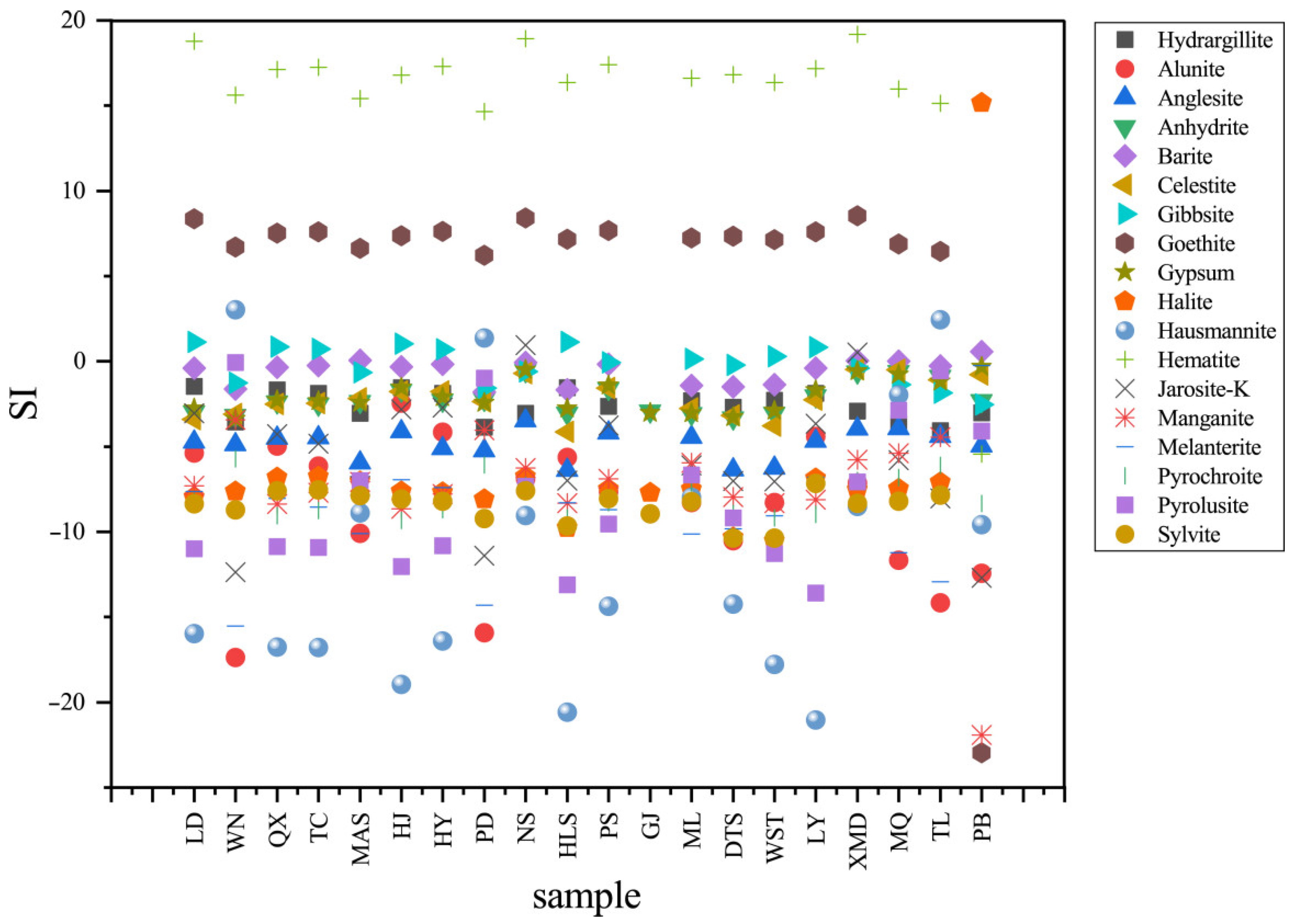
4.3.5. Mineral Saturation States
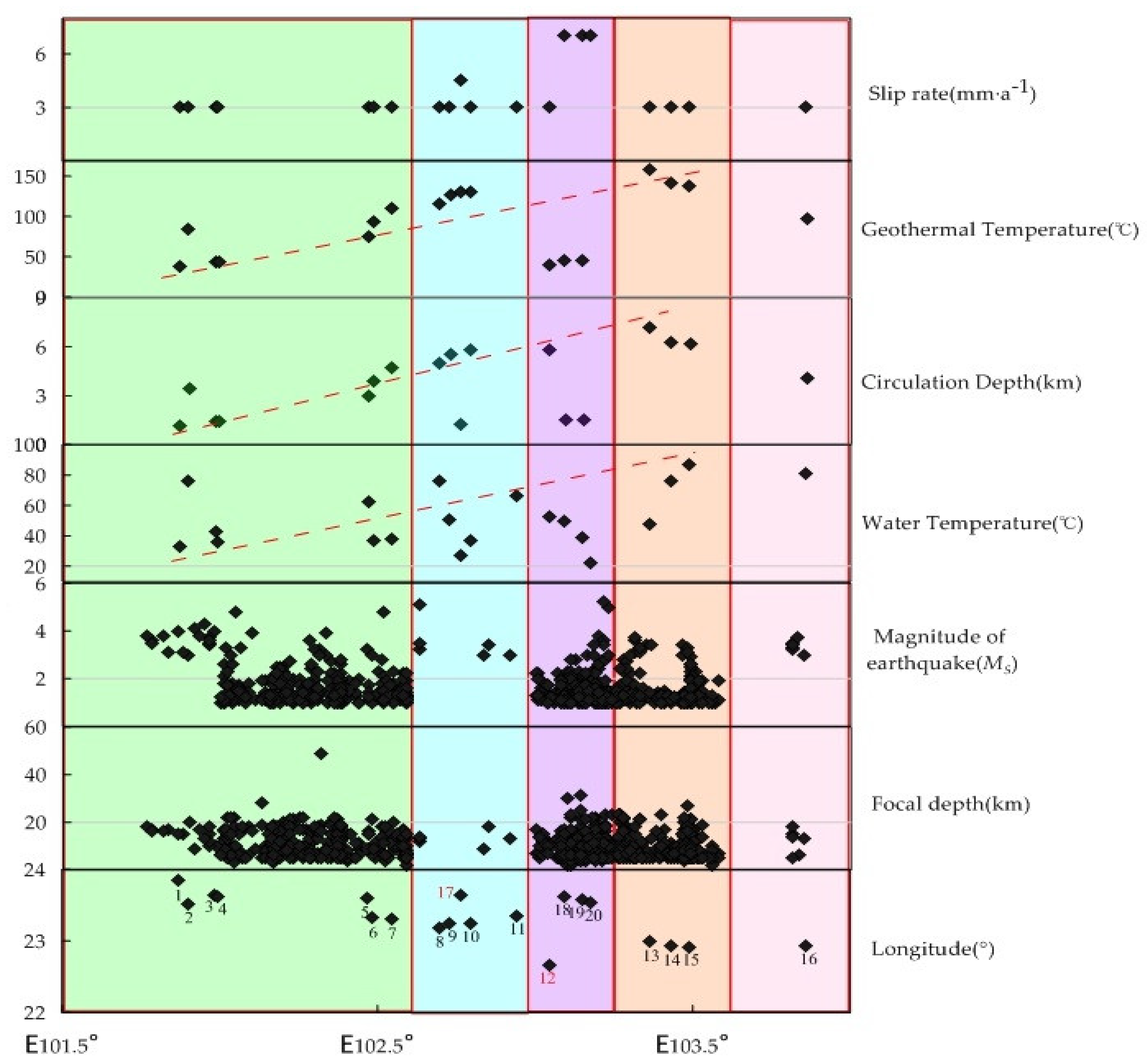
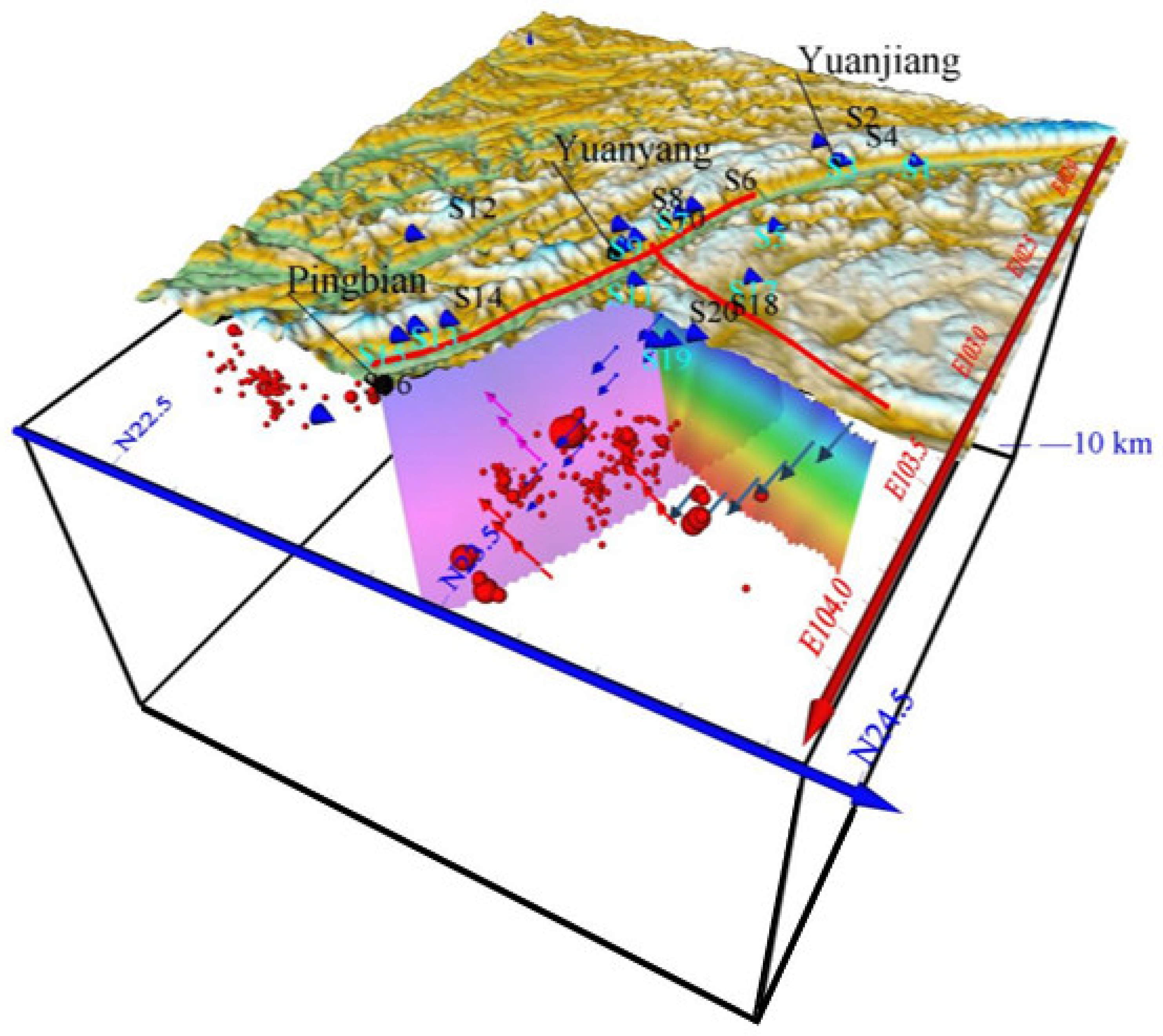
4.4. Relationship between Spatial Distribution of Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Seismicity at the Intersection of the RRF and the XJF
4.5. Hydrogeochemical Cycle Model
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The temperature of the recharge area ranged from 0.73 °C to 11.86 °C. The hot spring water intersection of the RRF and the XJF was recharged by atmospheric precipitation, recharged elevations ranged from 1.1 to 2 km, and it was positively correlated with the elevation of the hot spring sampling sites.
- (2)
- Hydrochemical types were mainly controlled by aquifer lithology, in which sodium bicarbonate and sulphuric acid water gathered mainly in the RRF, while calcium bicarbonate water gathered mainly in the XJF. The temperature range was inferred from an equation, based on the SiO2 concentration and chemical geothermal method, as 64.3–162.7 °C. The temperature range was inferred from an equation, based on the silicon–enthalpy equation method, as 97–268 °C, and the cold water mixing ratio was 61–97%. The circulation depths for springs were estimated in the range from 1.1 to 7.2 km. Our data showed that the circulation depth of the RRF was deeper than that of the XJF, and it was mainly concentrated in the second and fourth segments of the RRF.
- (3)
- It was speculated that the hot water intersection of the RRF and the XJF was obviously controlled by the fault and the cutting depth of granite.
- (4)
- Relationship discussed between geothermal anomaly and earthquake activity had a good correspondence, and it found that deep fluid has an important control action on the regional seismicity.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.S.; Zhang, Y.C.; Wu, M.L. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of the southern section of the North-South seismic belt and its relationship with earthquakes. J. Geomech. 2003, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanikawa, W.; Sakaguchi, M.; Tadai, O.; Hirose, T. Influence of fault slip rate on shear-induced permeability. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115, B07412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L. Chemical and isotopic characteristics and origin of spring waters in the Lanping Simao Basin, Yunnan, Southwestern China. Geochemistry 2015, 75, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, T.; Zpab, C.; Ywab, C.; Qi, G.D. Fluid geochemistry of the Cuopu high temperature geothermal system in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis with implication on its genesis. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 110, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woith, H.; Wang, R.J.U.; Maiwald, U.; Pekdeger, A.; Zschau, J. On the origin of geochemical anomalies in groundwaters induced by the Adana 1998 earthquake. Chem. Geol. 2012, 339, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Hua, Y. Tottori earthquakes and Daisen volcano: Effects of fluids, slab melting and hot mantle upwelling. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 485, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, T.; Zhao, D.; Huang, Z.; Wang, L. Structural heterogeneity in source zones of the 2018 Anchorage intraslab earthquake and the 1964 Alaska megathrust earthquake. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2020, 21, e2019GC008812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, M.K.; Zhao, D. 3-D seismic structure of Kii Peninsula in southwest Japan: Evidence for slab dehydration in the forearc. Tectonophysics 2003, 364, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhao, D.; Qiu, X. The 2007 Niigata earthquake: Effect of arc magma and fluids. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2008, 166, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hariri, M.; Abercrombie, R.E.; Rowe, C.A.; Do Nascimento, A.F. The role of fluids in triggering earthquakes: Observations from reservoir induced seismicity in Brazil. Geophys. J. Int. 2010, 181, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becken, M.; Ritter, O.; Bedrosian, P.A.; Weckmann, U. Correlation between deep fluids, tremor and creep along the central San Andreas fault. Nature 2011, 480, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C. Genesis of the high conductivity layer in the inner crust and upper mantle of mainland China and the mechanism of the Tangshan earthquake. Earth Sci. Front. 2003, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.D.; Zhang, P.Z.; Ran, Y.K.; Yang, X.P.; Min, W.; Chu, Q.Z. Active tectonics and seismicity in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2003, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.W.; Wen, X.Z.; Zhen, R.Z.; Ma, W.T.; Song, F.M.; Yu, G.H. Latest tectonic variation patterns and dynamic sources of active blocks in Sichuan-Yunnan region. Sci. China (Ser. D) 2003, 32, 151–162. [Google Scholar]
- Tapponnier, P.; Peltzer, G.; Le Dain, A.Y.L.; Armijo, R.; Cobbold, P. Propagation extrusion tectonics in Asia: Newinsights from simple experiments with plasticine. Geology 1982, 10, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Liu, Z.; Nan, D.; Sun, H.; Haoting, L.I.; Zhao, H. The characteristics and reservoir temperatures of hot springs in Jueyong, Chamdo, Xizang (Tibet). Geol. Rev. 2020, 66, 499–509. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ran, Y.K.; Chen, L.C.; Wang, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Xie, Y.Q. Holocene seismic activity evidence of the southern segment of the Red River fault zone. Seismol. Geol. 2016, 38, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.Z.; Du, F.; Long, F.; Fan, J.; Zhu, H. Relationship between tectonic dynamics and strong earthquake sequences of Xiaojiang and Qujiang-Shiping fault systems. Sci. China: Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.K. Geometry and deformation features of the most recent co-seismic surface ruptures along the Xiaojiang Fault and its tectonic implications for the Tibetan Plateau. J. Asia Earth Sci. 2013, 77, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.D.; Qin, J.Z. Analysis of strong earthquake risk in Xiaojiang fault zone and its surrounding area. J. Seismol. Res. 2009, 31, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.H.; Zhang, J.G.; Mao, Y.; Zhen, D.C.; Pang, W.D.; Liu, X.W. Characteristics of tectonic stress field in Xiaojiang fault zone and its surrounding area. J. Yunnan Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2012, 34, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Lü, J.; Wang, M.; Bürgmann, R. Contemporary crustal deformation around the southeast borderland of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2005, 110, B11409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, E.N.; Shen, Z.K. Inversion of Present Activity Rate of Main Faults in Sichuan-Yunnan Area Based on GPS Data. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2008, 38, 582–597. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.Z. Rupture segmentation and assessment of probabilities of seismic potential on the Xiaojiang fault zone. Acta Seismol. Sin. 1993, 3, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.M.; Wang, Y.P. China Active Fault Research Album Xiaojiang Active Fault Zone; Seismological Press: Beijing, China, 1998; ISBN 7-5028-1593-7. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbohm, L.M.; Burchfiel, B.C.; Chen, L. Propagation of surface uplift, lower crustal flow, and Cenozoic tectonics of the southeast margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Geology 2006, 34, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Long, C.X.; Fan, T.Y.; Zhou, C.J.; Feng, H.; Yang, Z.Y. Dynamic characteristics and mechanism of arcuate torsional active tectonic system in southeastern margin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geol. Bull. China 2015, 34, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.C.; Yuan, D.X.; Ding, T.P.; Li, Y.H.; Le, G.L.; Lin, Y.S. Heterogeneity of HE isotope distribution and tectonic genesis of CO2 emission points in southwest China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2007, 81, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Leloup, P.H.; Arnaud, N.; Lacassin, R.; Kienast, J.R.; Tapponnier, P. New constraints on the structure, thermochronology, and timing of the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone, SE Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 6683–6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.P.; Liu, J.S.; Li, X.B.; Zhang, X.L. Genetic relationships between granites and Sn, Ag, Cu, Pb, Zn polymetallic deposits in southeast Yunnan. Discuss. Geol. Prospect. 2006, 21, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.K.; Mo, X.X.; Yu, X.H.; Li, Y.; He, W.Y. Geochemical characteristics and geodynamic significance of Cenozoic basalts from Maguan and Pingbian, southeastern Yunnan. Prov. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2013, 29, 1325–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Yan-hui, Z.; Liang-sheng, Z.; Yang, C. Determining Trace Elements in Rock Samples Containing Refractory Minerals by Pressurize-microwave Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Uranium. Geol. 2018, 34, 105–111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.T.; Wang, X.M.; Cui, J.Y.; Liu, Y.A. Method improvement of selective dissolution of carbonate minerals in whole rock samples and determination of strontium isotopic ratio. World Nucl. Geosci. 2015, 32, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, G.; Pozzi, A.; Michetti, A.M.; Noble, P.J.; Rosen, M.R. Towards the Understanding of Hydrogeochemical Seismic Responses in Karst Aquifers: A Retrospective Meta-Analysis Focused on the Apennines (Italy). Minerals 2020, 10, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.D.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, E.; Wang, D. Discussion on the stable isotope time-space distribution law of China atmospheric precipitation. Editor. Off. Site Investig. Sci. Technol. 1997, 3, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Shi, H.; Chao, C.; Zeng, L.; Sun, F.; Jing, L.; Chen, Z.; Dan, H.; Du, J. Spatial-temporal Variations of H2 Concentration in Soil Gas in the Seismic Fault Zone Produced by the Wenchuan MS8.0 Earthquake. Adv. Earth Ence 2017, 32, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.S.; Li, Y.S. Isotope Geochemistry in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1997; pp. 21–82. ISBN 7-03-005653-1. [Google Scholar]
- Long, G.; Zhou, X.; Li, T.; Wang, X.C.; Tang, L.W.; Chen, T.; Guo, S. Characteristics and genesis of songshan Hot spring in Yanqing County. Beijing Mod. Geol. 2014, 28, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.C.; Jia, T.; Gang, S.T.; Deng, Y.; Liu, W.P.; Peng, X. Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in Hamatong Basin. Yangtze River 2017, 48, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.R. Chemical and Isotopic Characteristics and Genesis of Some Hot Spring Water in Xishuangbanna, Yunnan; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos Trans. 1944, 25, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollaro, C.; Vespasiano, G.; De Rosa, R.; Marini, L. Use of mean residence time and flowrate of thermal waters to evaluate the volume of reservoir water contributing to the natural discharge and the related geothermal reservoir volume. Application to Northern Thailand hot springs. Geothermics 2015, 58, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loska, K.; Cebula, J.; Pelczar, J.; Wiechula, D.; Kwapulinski, J. Use of enrichment and eontamination factors together rithgeoaccumulation indexes to evaluate the content of Cd, Cu, and Ni in the Rybink water reserboir in Poland. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1997, 93, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinann, C.; Caritat, P.D. Intrinsic flaw of element enrichment factors (EFs) in environmental geochemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 5084–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, N. Water-granite interaction: Clues from strontium, neodymium and rare earth elements in soil and waters. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 1432–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giggenbach, W.F. Geothermal solute equilibria: Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2749–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespasiano, G.; Marini, L.; Muto, F.; Auqué, L.F.; Cipriani, M.; De Rosa, R.; Critelli, S.; Gimeno, M.; Blasco, M.; Dotsika, E.; et al. Chemical, isotopic and geotectonic relations of the warm and cold waters of the Cotronei (Ponte Coniglio), Bruciarello and Repole thermal areas,(Calabria-Southern Italy). Geothermics 2021, 96, 102228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Study on Geochemical Characteristics of Geothermal Fluids in Southeast Yunnan; Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, R.O.; Truesdell, A.H. Geochemical indicators of subsurface temperature Part, estimate of temperature and fractions of hot water mixed with cold water. J. Res. USA Geol. Surv. 1974, 2, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Cioni, R.; Marini, L. A Thermodynamic Approach to Water Geothermometry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Z.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Fan, Z.C. Calculation of reservoir temperature using a SiO2 mixing model, Zhangzhou geothermal-field, SE China. Chin. Sci. Bull 1990, 35, 1360–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ran, H.; Li, Q.L.; Zhao, C.L.; Liu, Y.W. Study on characteristics of thermal storage temperature field and seismic activity in west Yunnan. Int. Seism. Trends 2018, 8, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, T.; Chen, X.B.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, P.J.; Dong, Z.Y.; Cui, T.F.; Jiang, F.; Cai, J.T.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. A magnetotelluric study of 3D electrical resistivity structure underneath the southern segment of the Red River fault zone. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 225, 105056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammanco, S.; Palano, M.; Scaltrito, A.; Scarfì, L.; Sortino, F. Possible role of fluid overpressure in the generation of earthquake swarms in active tectonic areas: The case of the Peloritani Mts (Sicily, Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2008, 178, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terakawa, T.; Hashimoto, C.; Matsu, M. Changes in seismic activity following the 2011 Tohoku-oki earthquake: Effects of pore fluid pressure. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 365, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tang, J.; Dong, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Zhan, Y. Deep electrical conductivity structure of the southern area in Yunnan Province. Chin. J. Geophys. 2014, 57, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Unsworth, M.; Wang, X.B.; Li, D.W.; Wang, E.C.; Li, R.H.; Hu, Y.B.; Cai, X.L. New insights into crustal and mantle flow beneath the red river fault zone and adjacent areas on the southern margin of the Tibetan plateau revealed by a 3-D magnetotelluric study. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2020JB019396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, M.; Bedrosian, P.A. On the geoelectric structure of major strike-slip faults and shear zones. Earth Planets Space 2004, 56, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.C.; Wang, W.L.; Li, L.W.; Hou, J.M.; Xing, L.T.; Li, Z.P.; Shi, Y.Y.; Yan, Y.C. Geochemical characteristics of hot spring gas in jinshajiang-Honghe fault zone. Acta Petrol. 2020, 36, 18. [Google Scholar]
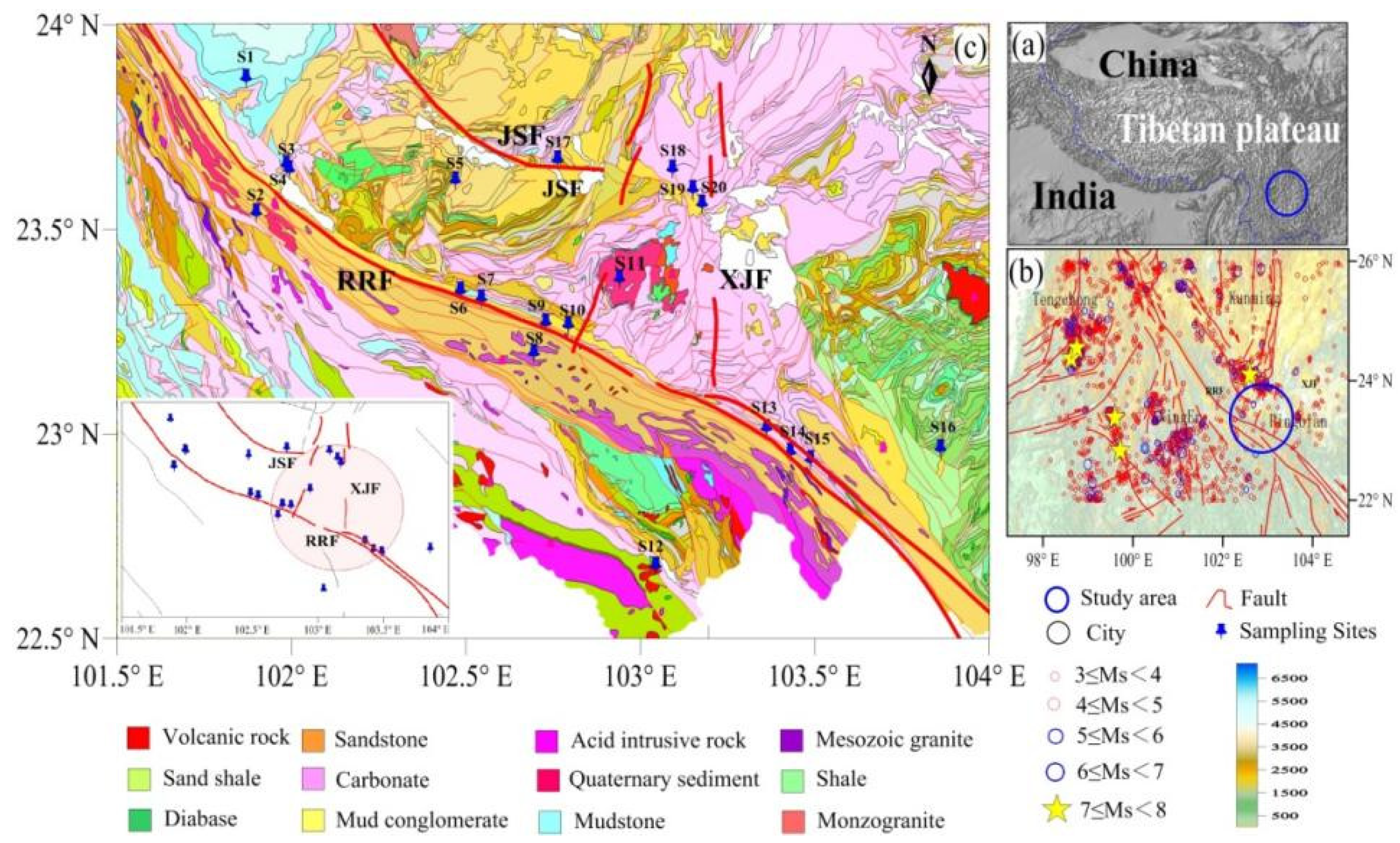
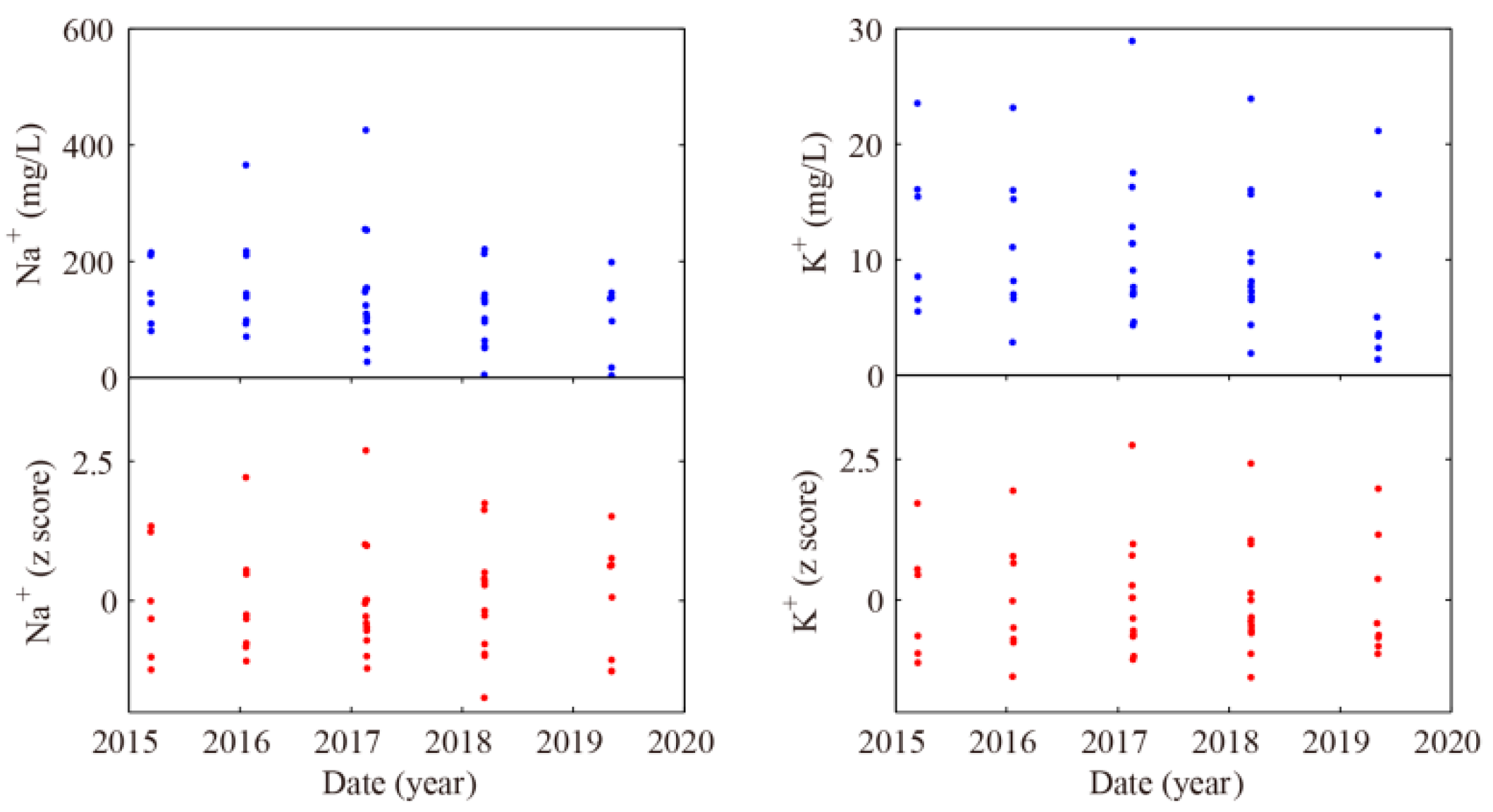
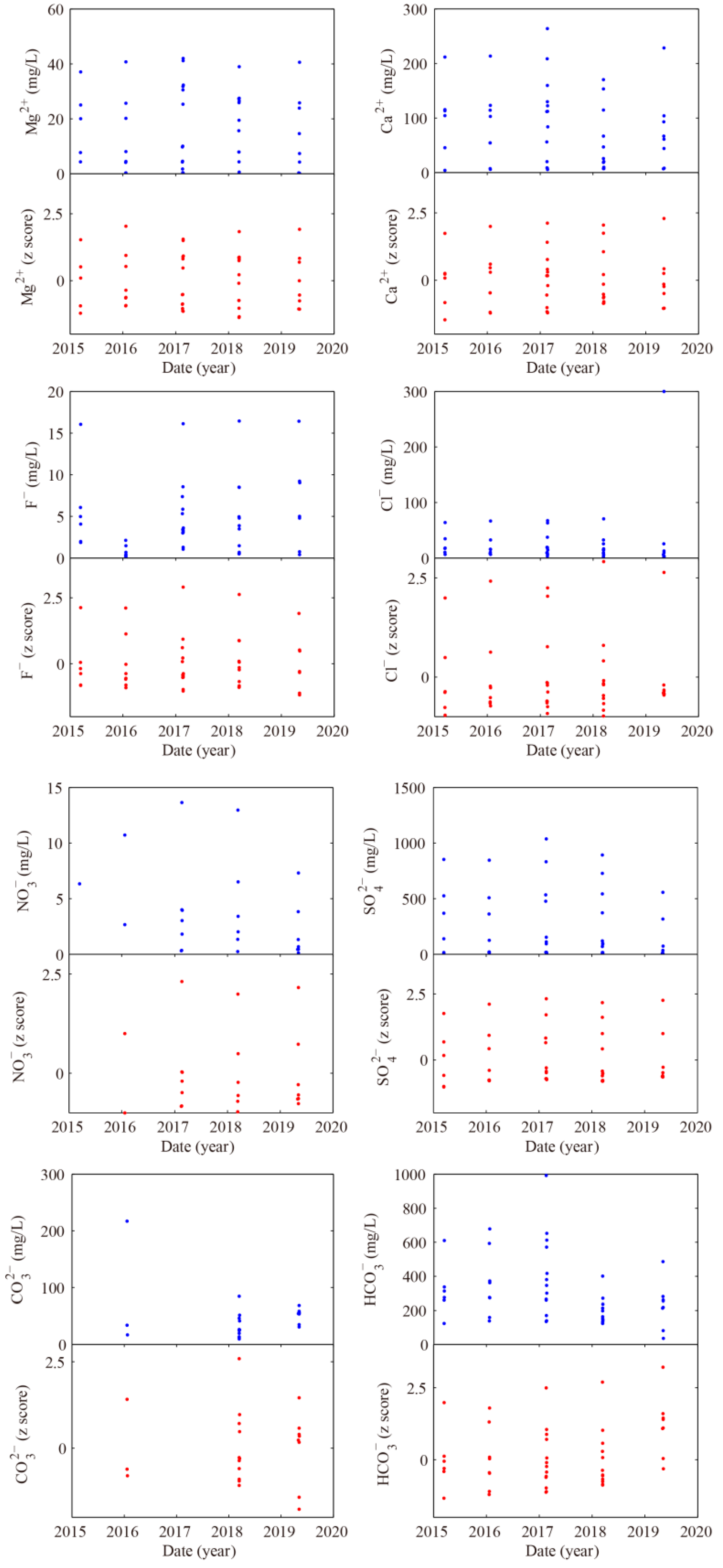
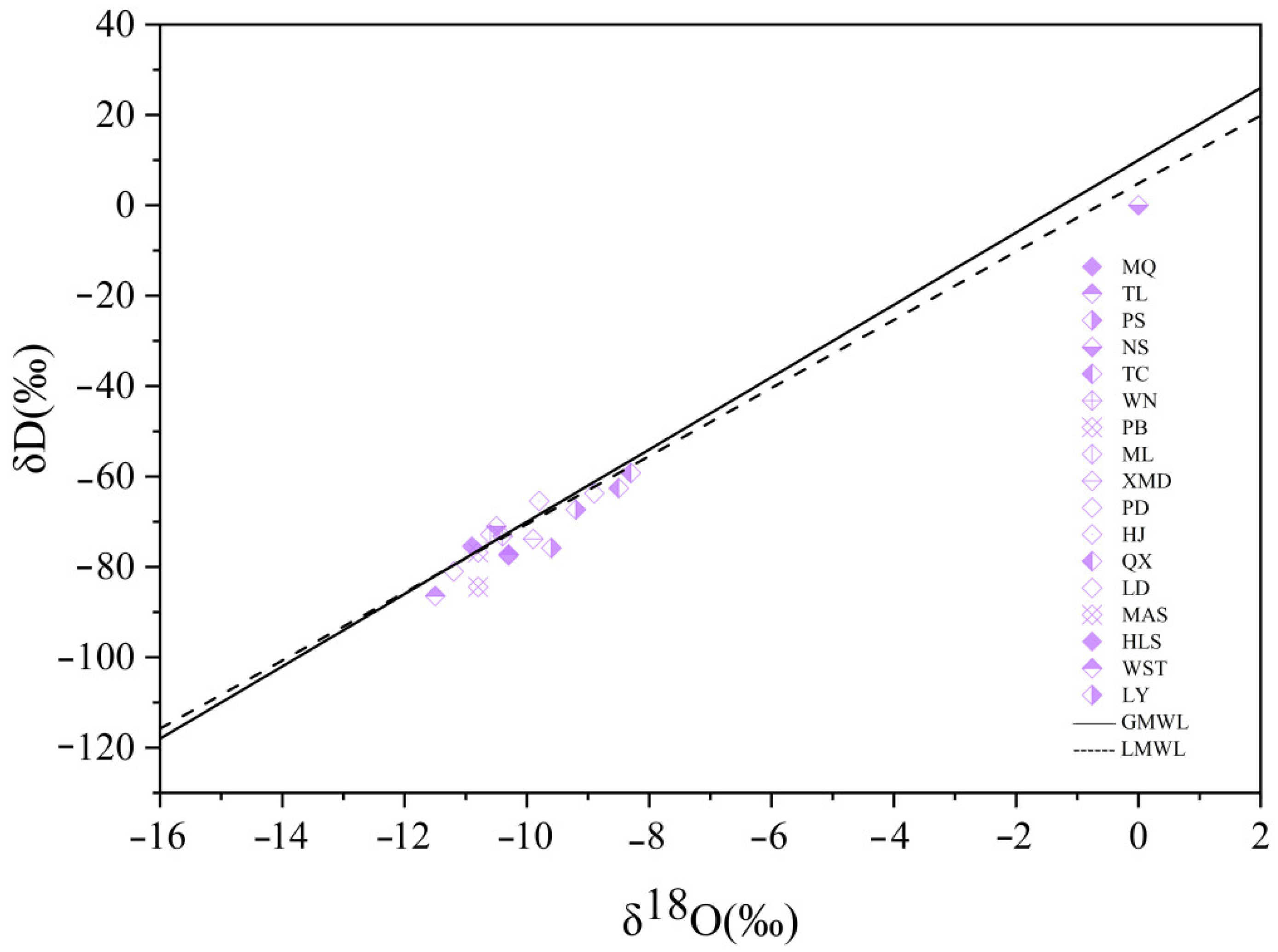
| No. | Spring Name | Longitude | Latitude | Altitude | Belongs to Fracture | Outcropped Lithology * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°) | (°) | (m) | ||||
| S1 | Lei Da | 101.8694 | 23.84618 | 445 | RRF | carbonate |
| S2 | Wa Na | 101.8983 | 23.51716 | 941 | Triassic Ganbatang metamorphic sandstone and phyllite | |
| S3 | Qi Xia | 101.9847 | 23.63402 | 413 | sandstone, carbonate | |
| S4 | Tian Cheng | 101.9937 | 23.6226 | 374 | sandstone, carbonate | |
| S5 | Ma Anshan | 102.4693 | 23.59537 | 1052 | carbonate, limestone | |
| S6 | Hu Jie | 102.4851 | 23.32551 | 414 | Ailaoshan group schist, marble, mixed rock | |
| S7 | Hong Yuan | 102.5441 | 23.30633 | 297 | metamorphic rock | |
| S8 | Po Duo | 102.6953 | 23.17386 | 1144 | Ailaoshan group schist, marble, mixed rock | |
| S9 | Nan Shan | 102.729 | 23.24808 | 514 | sandstone, metamorphic rock, carbonate | |
| S10 | Pai Shan | 102.7938 | 23.24111 | 286 | sandstone, metamorphic rock, carbonate | |
| S11 | Ge Jiu | 102.9396 | 23.35529 | 886 | Jurassic granite | |
| S12 | Meng La | 103.0441 | 22.65327 | 432 | DDFF | carbonate, limestone |
| S13 | Xiao Madian | 103.3615 | 22.99038 | 320 | RRF | Ailaoshan group schist, marble, mixed rock |
| S14 | Meng Qiao | 103.4294 | 22.93215 | 240 | Ailaoshan group schist, marble, mixed rock | |
| S15 | Teng Long | 103.4884 | 22.91374 | 136 | Ailaoshan group schist, marble, mixed rock | |
| S16 | Pin Bian | 103.8604 | 22.94037 | 274 | MZ-NXHF | sandstone, volcanic rock |
| S17 | Huang Longsi | 102.7625 | 23.64655 | 1334 | XJF | limestone |
| S18 | Da Tianshan | 103.0921 | 23.62381 | 1194 | carbonate, limestone | |
| S19 | Wen Shuitang | 103.1497 | 23.57432 | 1168 | carbonate, limestone | |
| S20 | Long Yuan | 103.1765 | 23.53867 | 1183 | carbonate, limestone |
| No. | δD | δ18O | SiO2 | Sr | Sr86/Sr87 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (‰) | (mg/L) | (μg/L) | (‰) | ||
| S1 | −63.7 | −8.9 | 20.46 | 0.323 | 0.7263 |
| S2 | −73.2 | −10.4 | 69.55 | 0.13484 | 0.727911 |
| S3 | −62.6 | −8.5 | 24.40 | 1.01 | 0.72548 |
| S4 | −59.2 | −8.3 | 24.82 | 1.09 | 0.724765 |
| S5 | −83.4 | −10.9 | 51.79 | - | - |
| S6 | −65.4 | −9.8 | 44.94 | 0.8485 | 0.710358 |
| S7 | −64.2 | −8.9 | 53.71 | - | - |
| S8 | −81 | −11.2 | 103.36 | 0.11033 | 0.710651 |
| S9 | −71 | −10.5 | 85.60 | 2.073 | 0.711759 |
| S10 | −67.3 | −9.2 | 59.92 | 1.05175 | 0.709807 |
| S11 | - | - | - | - | - |
| S12 | −72.8 | −10.6 | 89.24 | 0.233 | 0.720928 |
| S13 | −73.8 | −9.9 | 107.43 | 3.5335 | 0.707867 |
| S14 | −75.4 | −10.9 | 146.16 | 2.85975 | 0.707932 |
| S15 | −77.2 | −10.3 | 153.65 | 0.78525 | 0.71177 |
| S16 | −76.8 | −10.8 | 84.96 | 0.611 | 0.730016 |
| S17 | −77.5 | −10.3 | 21.40 | - | - |
| S18 | −84.2 | −11.3 | 23.11 | - | - |
| S19 | −86.4 | −11.5 | 25.68 | - | - |
| S20 | −75.8 | −9.6 | - | - | - |
| Temperature/°C | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 | 300 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enthalpy/(4.1868J/g) | 50 | 75 | 100.1 | 125.4 | 151 | 177 | 203.6 | 230.9 | 259.2 | 289 | 321 |
| SiO2 Content/(mg/L) | 13.5 | 26.6 | 48 | 80 | 125 | 185 | 265 | 365 | 486 | 614 | 692 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Q.; Yan, Y.; He, M.; Li, J.; Dong, J.; Tian, J.; Ding, F.; Li, Y.; et al. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Hot Springs in the Intersection of the Red River Fault Zone and the Xiaojiang Fault Zone, Southwest Tibet Plateau. Water 2022, 14, 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162525
Li Z, Zhou X, Xu Q, Yan Y, He M, Li J, Dong J, Tian J, Ding F, Li Y, et al. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Hot Springs in the Intersection of the Red River Fault Zone and the Xiaojiang Fault Zone, Southwest Tibet Plateau. Water. 2022; 14(16):2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162525
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zirui, Xiaocheng Zhou, Qiulong Xu, Yucong Yan, Miao He, Jingchao Li, Jinyuan Dong, Jiao Tian, Fenghe Ding, Ying Li, and et al. 2022. "Hydrochemical Characteristics of Hot Springs in the Intersection of the Red River Fault Zone and the Xiaojiang Fault Zone, Southwest Tibet Plateau" Water 14, no. 16: 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162525
APA StyleLi, Z., Zhou, X., Xu, Q., Yan, Y., He, M., Li, J., Dong, J., Tian, J., Ding, F., Li, Y., Ma, C., Wang, X., & Luo, Z. (2022). Hydrochemical Characteristics of Hot Springs in the Intersection of the Red River Fault Zone and the Xiaojiang Fault Zone, Southwest Tibet Plateau. Water, 14(16), 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162525






