Phosphorus Adsorption on Blast Furnace Slag with Different Magnetism and Its Potential for Phosphorus Recovery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Adsorption Material and Chemicals
2.2. Batch Adsorption Experiment
2.2.1. Adsorption Isotherm
2.2.2. Adsorption Kinetics
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Column Adsorption Experiment
2.4.1. Column Adsorption Device
2.4.2. Influence Factors
2.4.3. Thomas Models
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorption Isotherm
3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
3.3. Mechanism of P Adsorption on BFS
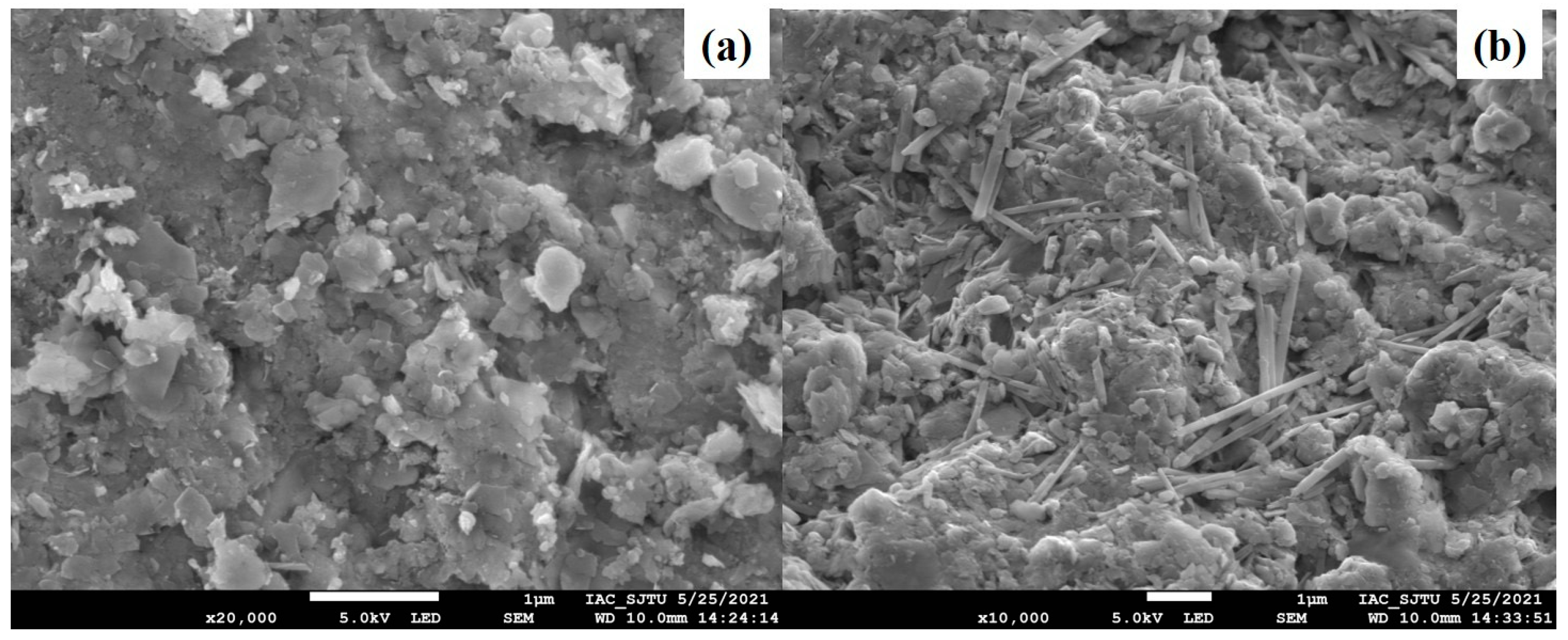
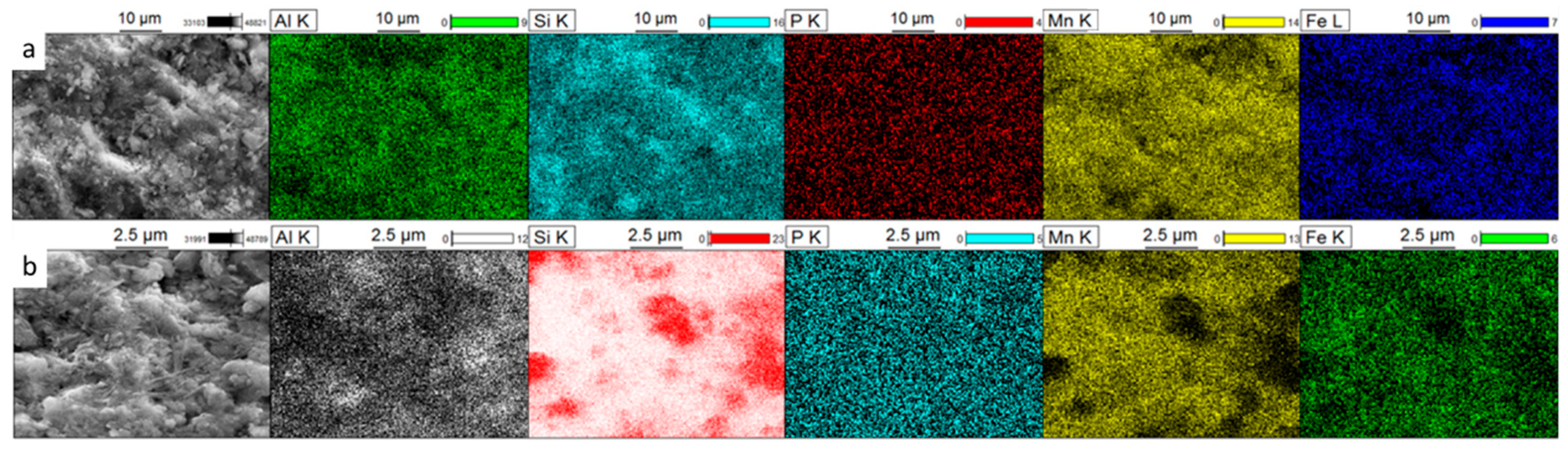
3.3.1. SEM-EDS Characterization
3.3.2. XRF Characterization
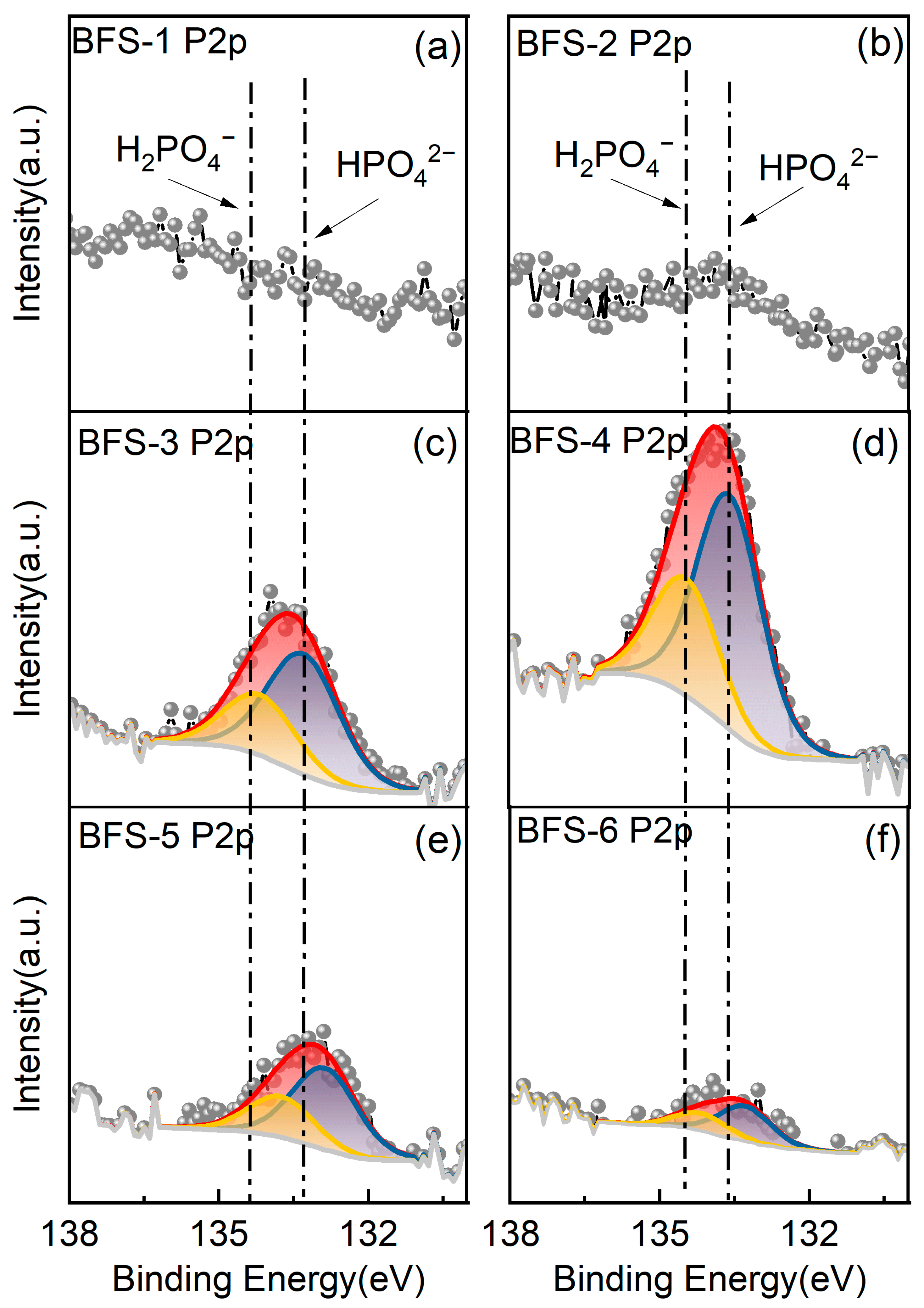
3.3.3. XPS Characterization
3.4. Optimization of Column Adsorption
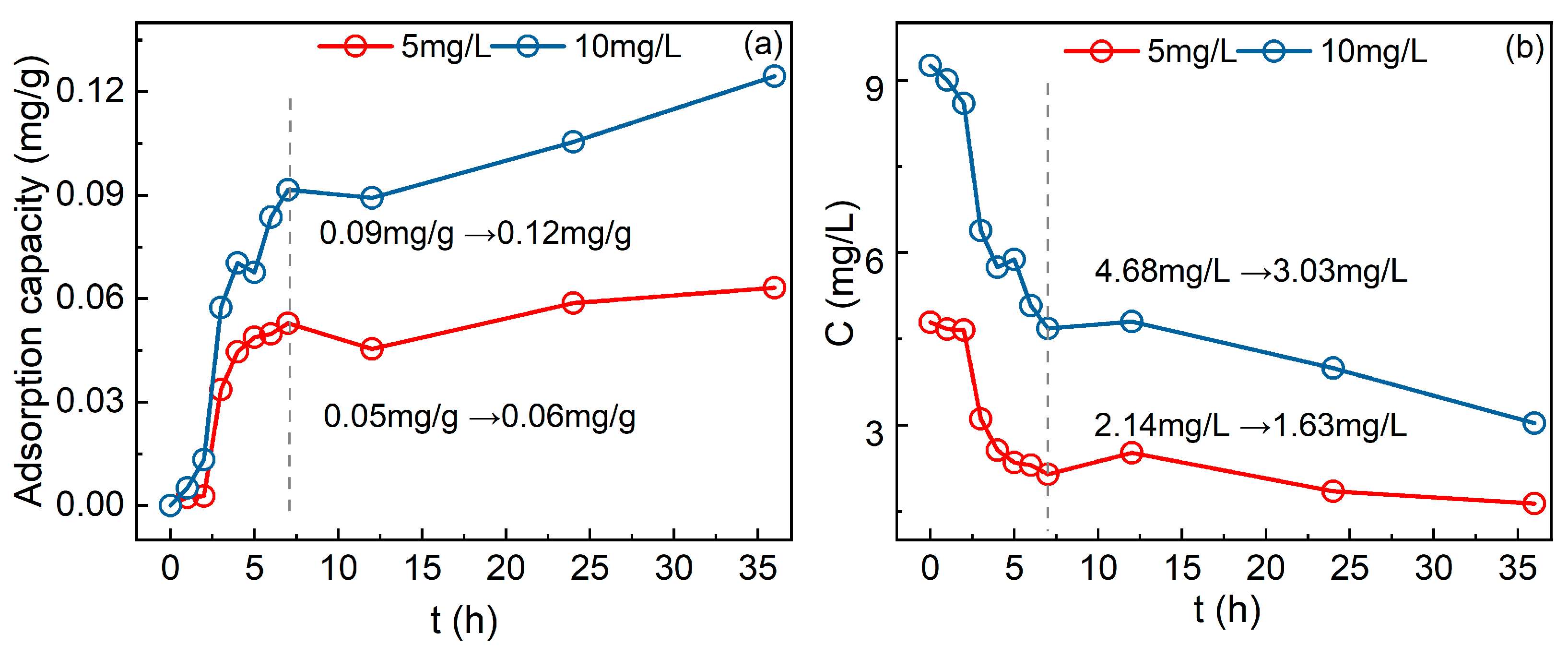
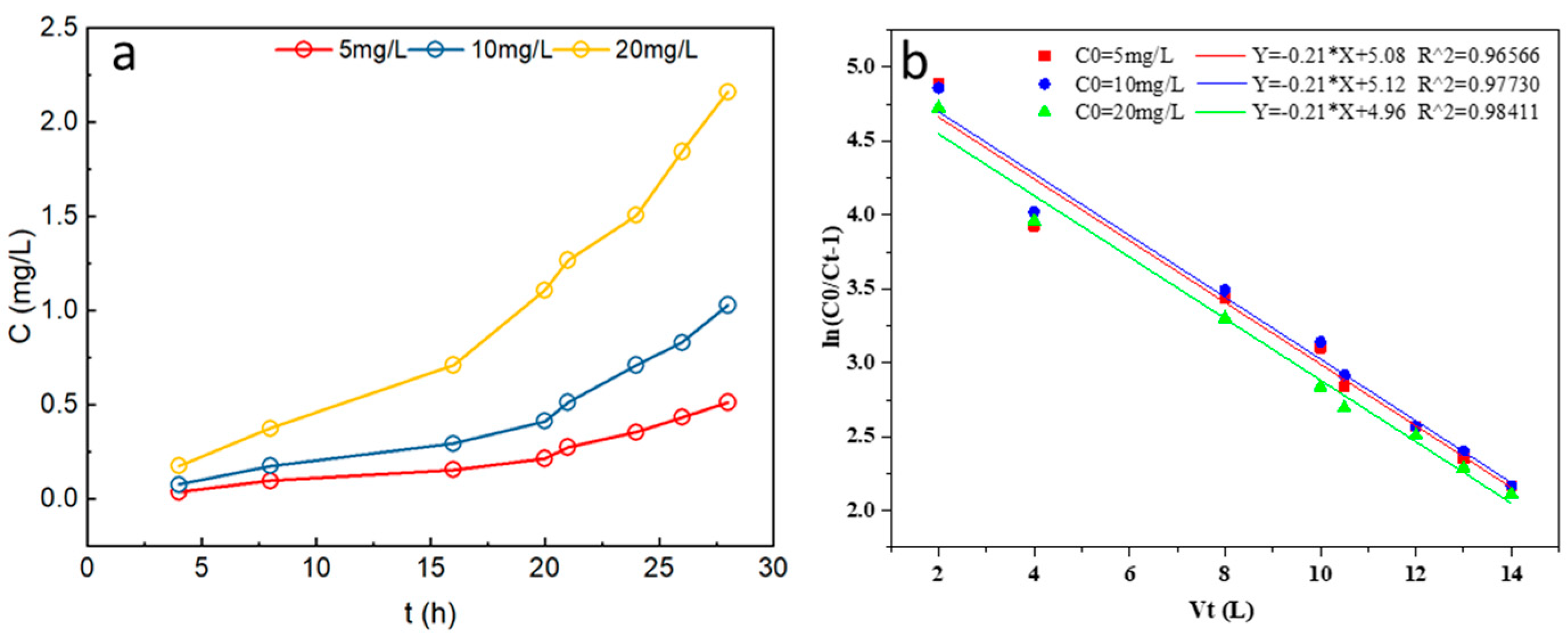
3.4.1. Effects of Initial P Concentration on P Adsorption
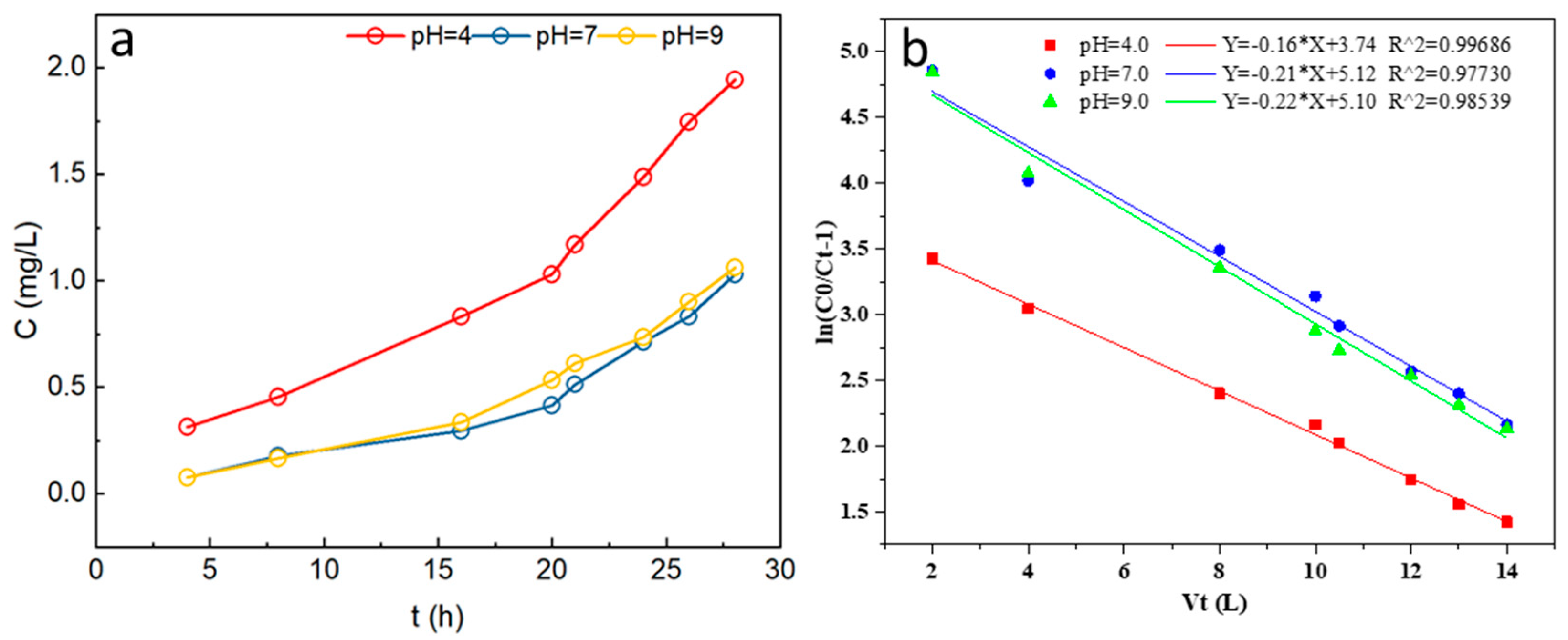
3.4.2. Effects of pH on P Adsorption
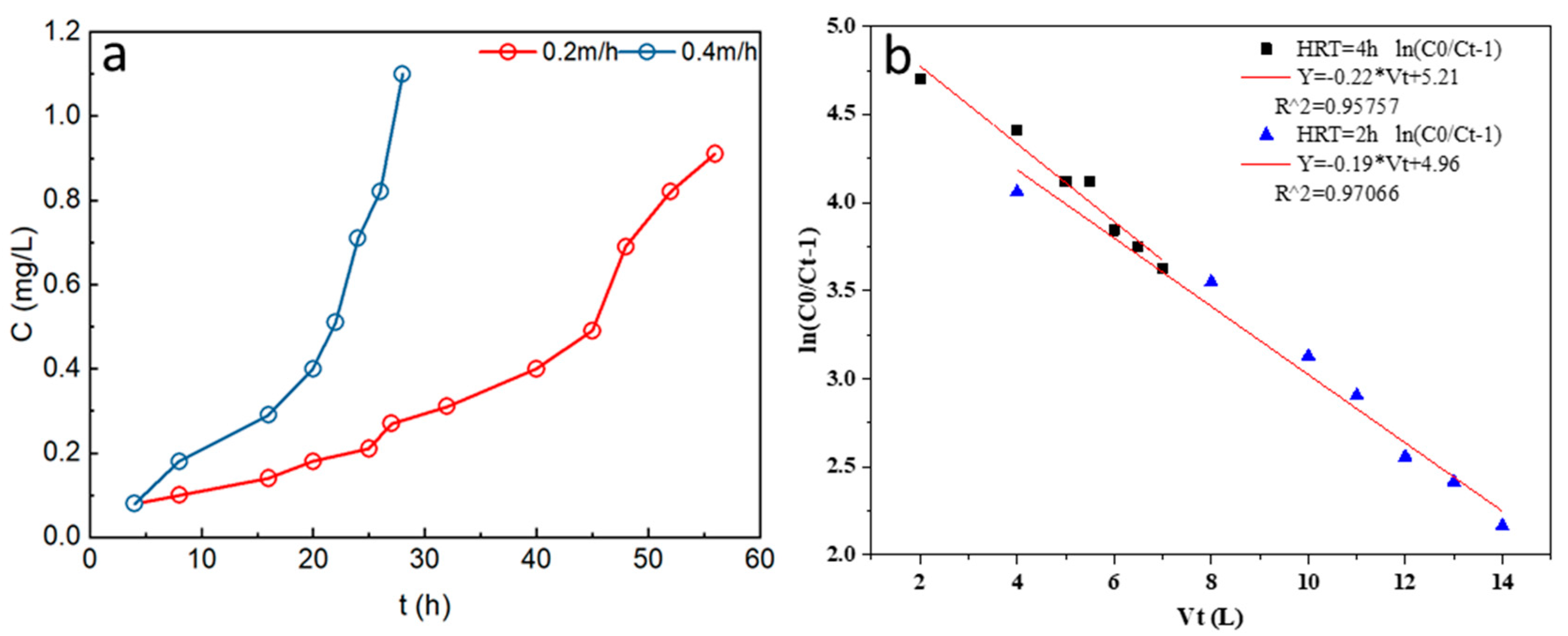
3.4.3. Effects of HRT on P Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bacelo, H.; Pintor, A.M.; Santos, S.C.; Boaventura, R.A.; Botelho, C.M. Performance and prospects of different adsorbents for phosphorus uptake and recovery from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, D.; Rosemarin, A.; Schröder, J.; Smit, A. Towards global phosphorus security: A systems framework for phosphorus recovery and reuse options. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z. Selection of chemical phosphorus removal scheme based on Analytic Hierarchy Process. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 245, 03073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, C.; Rong, H.; Cao, Y. Research progress and application prospect of anaerobic biological phosphorus removal. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özacar, M. Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution onto alunite. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huang, H.M.; Boiarkina, I.; Yu, W.; Huang, Y.F.; Wang, G.Q.; Young, B.R. Phosphorus recovery through struvite crystallisation: Recent developments in the understanding of operational factors. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yoo, I.; Park, B.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.; Chang, D.; Sunwoo, Y.; Shin, H.; Eo, Y.; Hong, K. Alternative technique for removal of phosphorus in wastewater using chemically surface-modified silica filter. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Korving, L.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Witkamp, G.-J. Adsorption as a technology to achieve ultra-low concentrations of phosphate: Research gaps and economic analysis. Water Res. X 2019, 4, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Lin, D.; Li, J.; Zeng, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, F. Ecological treatment technology for agricultural non-point source pollution in remote rural areas of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 40075–40087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 380, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, H.; Rains, M.; Taşcı, Y.; Zhang, J.-Z.; Trout, K.; Lewis, D.; Das, A.; Dalton, R. Why is calcite a strong phosphorus sink in freshwater? Investigating the adsorption mechanism using batch experiments and surface complexation modeling. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Zhu, X.; Ma, M.; Ouyang, Y.; Dong, M.; Zhu, W.; Luo, S. Phosphorus Sorption Capacities and Physicochemical Properties of Nine Substrate Materials for Constructed Wetland. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 55, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loganathan, P.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Bolan, N.S. Removal and Recovery of Phosphate from Water Using Sorption. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 847–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babatunde, A.; Zhao, Y. Equilibrium and kinetic analysis of phosphorus adsorption from aqueous solution using waste alum sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, S.P.; Guo, X.C.; Ren, Y.X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. A promising approach of reject water treatment using a tidal flow constructed wetland system employing alum sludge as main substrate. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 2367–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L. Blast furnace slag as phosphorus sorbents—column studies. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 229, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S. A comprehensive review on recent developments in bentonite-based materials used as adsorbents for wastewater treatment. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 1091–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Deng, T.; Liu, J.; Peng, W. Study on the phosphate removal from aqueous solution using modified fly ash. Fuel 2010, 89, 3668–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, I.; Molle, P.; de Miera, L.E.S.; Ansola, G. Basic Oxygen Furnace steel slag aggregates for phosphorus treatment. Evaluation of its potential use as a substrate in constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2016, 89, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhu, S. Characteristics and mechanisms of phosphate adsorption onto basic oxygen furnace slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Vilar, V.J.; Botelho, C.M.; Boaventura, R.A. A review of the use of red mud as adsorbent for the removal of toxic pollutants from water and wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haynes, R.J. Use of Industrial Wastes as Media in Constructed Wetlands and Filter Beds—Prospects for Removal of Phosphate and Metals from Wastewater Streams. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 1041–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Ye, S.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ni, J.; Chen, Y. Preparation of a new sorbent with hydrated lime and blast furnace slag for phosphorus removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongwei, C.; Lin, L.; Jie, Z.; Xiangxun, P.; Dewu, Z. Characteristics of adsorption of arsenic by red soil from sandstone weathering. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering, Nanjing, China, 24–26 June 2011; pp. 3910–3912. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, N.; Sundaram, M.M. Kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue by adsorption on various carbons—a comparative study. Dye. Pigment. 2001, 51, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidmohammadi, A.; Asgari, G.; Dargahi, A.; Leili, M.; Vaziri, Y.; Hayati, B.; Shekarchi, A.; Mobarakian, A.; Bagheri, A.; Khanghah, S.B.N.; et al. A Comparative Study for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Solution by Novel Activated Carbon Based Adsorbents. Prog. Color Colorants Coat. 2019, 12, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Huang, L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, F.; Xing, H.; Ma, S. Dynamics and Model Research on the Electrosorption by Activated Carbon Fiber Electrodes. Water 2021, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, D.; Lahtinen, M.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A comparative study for the removal of methylene blue dye by N and S modified TiO2 adsorbents. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 207, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, A.; Samarghandi, M.R.; Shabanloo, A.; Mahmoudi, M.M.; Nasab, H.Z. Statistical modeling of phenolic compounds adsorption onto low-cost adsorbent prepared from aloe vera leaves wastes using CCD-RSM optimization: Effect of parameters, isotherm, and kinetic studies. Biomass- Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Shang, Y.; Xiao, W.; Dou, C.; Han, R. Adsorption of Congo red from solution using cationic surfactant modified wheat straw in column model. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuić, I.; Trgo, M.; Perić, J.; Medvidović, N.V. Analysis of breakthrough curves of Pb and Zn sorption from binary solutions on natural clinoptilolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 167, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostura, B.; Huczala, R.; Leško, J.; Ritz, M. Retention of phosphates from aqueous solutions with in sol–gel-derived amorphous CaO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2 system as a model of blast furnace slag. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostura, B.; Kulveitová, H.; Leško, J. Blast furnace slags as sorbents of phosphate from water solutions. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1795–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, M.T.; Nguyen, L.N.; Johir, A.H.; Ngo, H.H.; Skidmore, C.; Fontana, A.; Galway, B.; Bustamante, H.; Nghiem, L.D. Phosphorus removal from aqueous solution by steel making slag—Mechanisms and performance optimisation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, L.I.; Jarvis, A.P.; Younger, P.; Johnson, K.L. Phosphorus Removal from Waste Waters Using Basic Oxygen Steel Slag. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2476–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koilraj, P.; Kannan, S. Phosphate uptake behavior of ZnAlZr ternary layered double hydroxides through surface precipitation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 341, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. Utilization of agro-industrial and municipal waste materials as potential adsorbents for water treatment—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, P.; McManamon, C.; Hanrahan, J.P.; Copley, M.; Holmes, J.; Morris, M.A. Development of chemically engineered porous metal oxides for phosphate removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
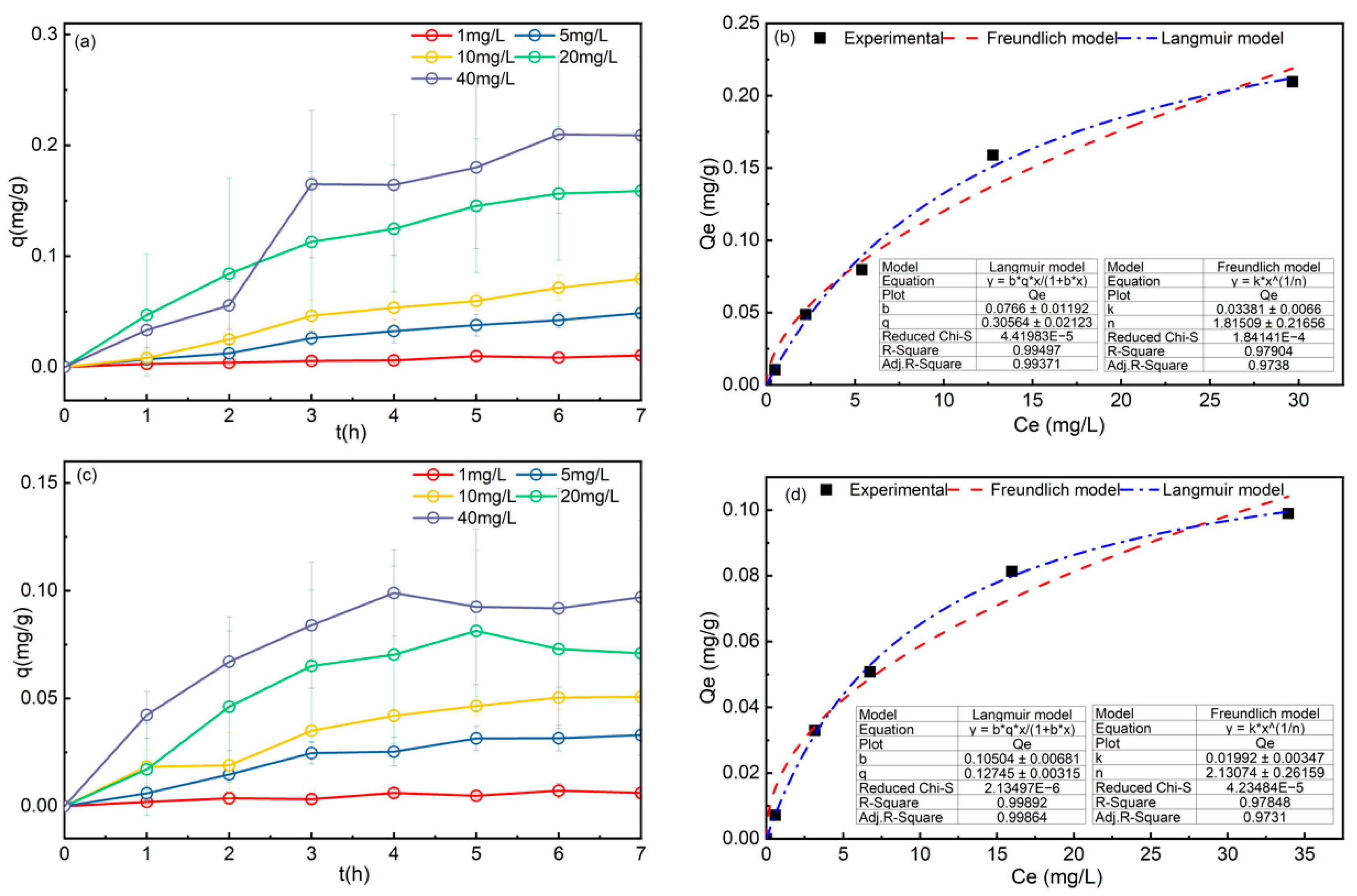
| Sample | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q0 (mg g−1) | B (L mg−1) | R2 | n | k | R2 | |
| BFS1 | 0.3058 | 0.0766 | 0.9937 | 1.8151 | 0.0338 | 0.9738 |
| BFS2 | 0.1275 | 0.1050 | 0.9986 | 2.1307 | 0.0199 | 0.9731 |
| Sample | Quasi-First-Order Dynamics Model | Quasi-Second Order Dynamics Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg g−1) | k1 (min−1) | R2 | qe (mg g−1) | k2 (g·mg−1 ·min−1) | R2 | |
| BFS1 | 0.2311 | −0.6367 | 0.9080 | 0.3015 | 0.6206 | 0.9965 |
| BFS2 | 0.1068 | −0.5658 | 0.9785 | 0.1217 | 2.5766 | 0.9986 |
| Element | Al | Si | P | Mn | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFS1—Before | 11.03 | 48.3 | 1.17 | 36.01 | 3.49 |
| BFS1—After | 14.72 | 35.90 | 1.40 | 39.88 | 7.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Zhan, R.; Liu, L.; Lan, J.; Zhao, N.; Wang, Z. Phosphorus Adsorption on Blast Furnace Slag with Different Magnetism and Its Potential for Phosphorus Recovery. Water 2022, 14, 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162452
Wu X, Zhan R, Liu L, Lan J, Zhao N, Wang Z. Phosphorus Adsorption on Blast Furnace Slag with Different Magnetism and Its Potential for Phosphorus Recovery. Water. 2022; 14(16):2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162452
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xiaoxin, Rui Zhan, Lili Liu, Jinjing Lan, Ning Zhao, and Zhiping Wang. 2022. "Phosphorus Adsorption on Blast Furnace Slag with Different Magnetism and Its Potential for Phosphorus Recovery" Water 14, no. 16: 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162452






