Abstract
An apparent proliferation of filamentous algal blooms (FABs) in pristine lakes around the world is a source of concern. However, little is known about the predominant drivers and effects of such FABs on lake ecosystems. We observed FABs in a large clear-water lake (Bear Lake, UT/ID, USA) and analyzed long-term lake monitoring data and algal stable isotopes for changes in climate, food webs and anthropogenic nutrient loading, respectively, as potential local drivers of FAB formation. Furthermore, we quantified in situ metabolism rates on rocks with and without FABs at two locations. Long-term monitoring data revealed increasing summer water temperatures (2009 to 2020) and decreasing winter ice cover (1923 to 2021). The FABs had δ15N values that were higher than 0 ‰, indicating a potential nutrient influx to Bear Lake from livestock or human waste. Climate change and anthropogenic nutrients may thus have facilitated FAB occurrence. Contrary to expectation, the FABs exhibited significantly lower gross primary production rates compared to low-biomass periphyton communities, indicating potentially negative effects of FAB proliferations on lake food webs. Our results highlight the need for expanding lake monitoring programs to include littoral zones to detect and mitigate changes occurring in lakes.
1. Introduction
Eutrophication has been a lasting critical challenge for societies that wish to interact with aquatic environments in a way that minimizes their deleterious effects on water quality. Historically, eutrophication was considered to be the effect of nutrient loading (typically phosphorus and/or nitrogen) into waterways, resulting in large phytoplankton-dominated algal blooms [1]. Such algal blooms can include cyanotoxin-releasing cyanobacteria, making them “Harmful Algal Blooms” (HABs), often with severe consequences for ecosystem functioning [2,3,4]. We now understand that HAB formation in lakes may also be exacerbated by rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns that are associated with climate change [5,6]. Meanwhile, nutrient concentrations have been trending upwards, even in lakes in remote catchments lacking direct anthropogenic drivers [7], which is generally attributed to catchment chemistry shifts [8,9] or increased nutrient loading from dust deposition [10]. Altogether, our understanding of the causes and effects of eutrophication in lakes is continuing to evolve. One phenomenon that has received increasing attention in recent years is the apparent rise of filamentous (attached) algal blooms (FABs) in clear-water “pristine” lakes and streams around the world [11].
As FABs may be comprised of various green algae and/or cyanobacteria assemblages, they can result from a wide range of diverse and potentially interacting environmental and anthropogenic drivers. For instance, drivers (reviewed by [11]) may include groundwater nutrient enrichment [12,13]; warming water temperatures [14]; altered lake stratification [11]; chronic changes in nitrogen: phosphorus ratios in surface waters [15]; and declines of key grazers via pesticides or food web interactions [16]. In the Laurentian Great Lakes, an increase in FABs (predominantly Cladophora glomerata) in recent decades is believed to be the result of invasive dreissenid mussels increasing water transparency and transporting nutrients from pelagic to benthic realms [17,18]. This broad range of potential drivers makes it difficult to predict where, when, and why FABs occur, and impedes research into broader studies of their ecological consequences in affected lakes and streams.
There are several reasons to believe that FABs may have negative ecological consequences on aquatic systems. Specifically, some FABs release toxins [19], or accumulate harmful concentrations of Escherichia coli [20]. The formation of FABs can also be seen as a fundamental shift in the allocation and cycling of carbon, but the net effect of this shift on food supply to the aquatic food web may be difficult to predict. Periphyton (benthic algae) production has been established as an important source of organic carbon for freshwater food webs [21]. Although the increases in periphyton biomass that are evident in FAB formation may reasonably indicate an increase in the resources that are available to lake consumers [22], the relationship between biomass and gross primary production in periphyton mats is poorly constrained [23]. Studies of phytoplankton communities in lakes have suggested that self-shading from high biomass accumulation can result in lower rates of net primary production (i.e., the rates of autochthonous organic matter supply that is available to consumers [24]). It has also been noted that periphyton may represent the base of an “inverted trophic pyramid”, whereby intensive grazing keeps periphyton biomass low and production rates high, and biomass accumulation resulting from a release from grazing also results in lower-quality periphyton being made available to consumers, due to higher carbon-to-nutrient ratios [16]. Once algal filaments have matured, they tend to be avoided by grazers [25]. Thus, FAB formation may potentially result in reductions in both water quality and autochthonous food web support.
In January 2005, and again between Fall 2019 and Spring 2021 (the period of this study) we observed the occurrence of FABs in the littoral zone of a large, oligotrophic lake—Bear Lake (UT/ID, USA). We considered climate change, anthropogenic nutrient pollution, and changes in the food web to be the potential drivers of FAB formation in the lake. We therefore analyzed long-term monitoring data for the lake, as well as stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen in collected periphyton tissues from FAB and non-FAB sites. Given the lake’s hydrological link to an agriculture-heavy watershed, we hypothesized that anthropogenic nutrient enrichment could be a driver of the FABs, but that Bear Lake would also be experiencing the effects of climate change, as indicated by increasing surface water temperatures and decreasing ice cover periods [26]. To measure the potential consequences of FABs for the lake ecosystem, we carried out in situ experiments to determine the primary production rates of FAB and non-FAB sites. We hypothesized that rocks with FABs would be generally more productive than rocks without FABs [22], but that the productive efficiency of the algae (i.e., measured per mg chl a on a rock surface) would be lower with FABs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
Bear Lake (42° N, 111°20′ W) is a large (280 km2) and deep (mean depth = 29 m, maximum depth = 63 m) lake of tectonic origin (Figure 1). Although its contemporary nutrient concentrations are low (total phosphorus = 4.7 ± 2.7 μg L−1, total inorganic nitrogen = 0.044 ± 0.018 mg L−1; 2001–2007 surface water means with standard deviations, from Bear Lake Regional Commission; BLRC, Garden City, UT, USA), it has historically been classified as an oligo-mesotrophic lake [27]. High calcium concentrations (29.9 ± 1.5 mg L−1; 2004–2007 surface water means with standard deviations, BLRC) result in frequent calcite precipitation events, keeping phytoplankton biomass low (mean surface chl a concentrations are 1.6 ± 1.2 μg L−1; 2001–2007 surface water means with standard deviations, BLRC), and water clarity high (mean ZSecchi from 2009 to 2020 = 6.8 ± 1.9 m). Bear Lake features a high degree of fish endemism (four endemic species) due to its great age (sediment cores have been dated to 250,000 years [28]) and historical periods of hydrological isolation. However, in 1911, the Bear River was linked to Bear Lake by damming the river, constructing a man-made channel for inflow to the lake, and constructing an additional outlet channel that was supplemented by a large, electric pump for outflow, allowing the Bear Lake basin to be used to store excess water and regulate its supply for downstream agriculture. More recently, research on Bear Lake has raised concerns that extreme water level drawdown in the lake may be imperiling some endemic fish species that rely upon littoral locations for spawning [29]. The primary community near Bear Lake is Garden City, UT, located on the western shore (population ~550 in 2019, with tourism populations surging to ~30,000 during summer months). Nearshore housing units surround many parts of Bear Lake. On the southern (Utah) side, these residences are on a sewage system, and on the northern (Idaho) side, they are on septic systems.
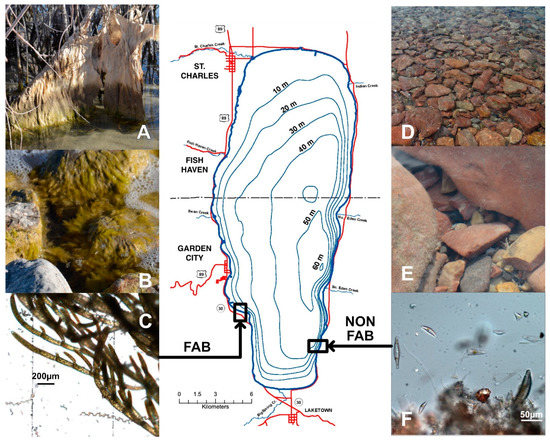
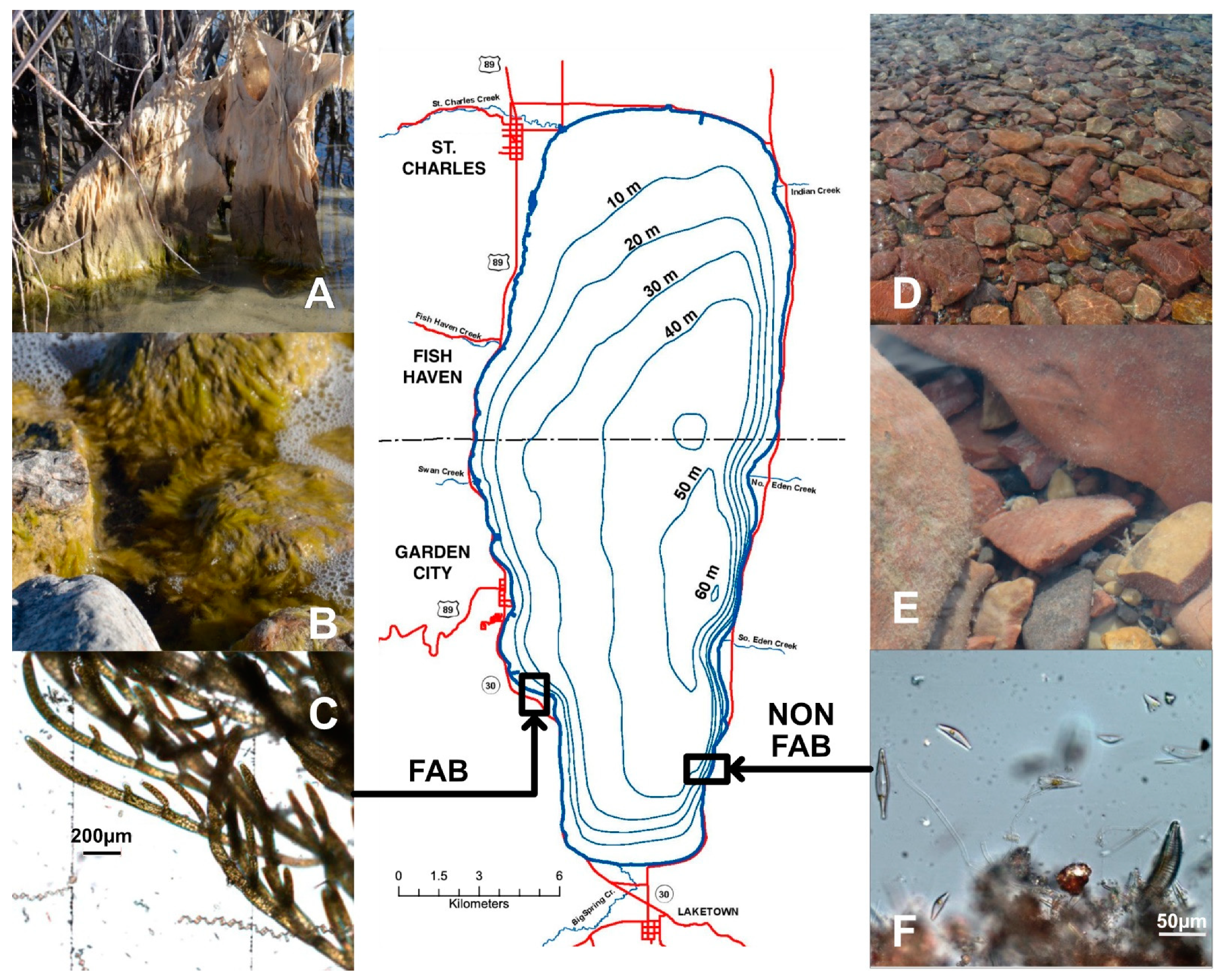
Figure 1.
Bear Lake at the border of Idaho (ID) and Utah (UT) with infrastructure (red), major tributaries, and sampling locations of filamentous algae blooms at the western shore (FAB site) and non-filamentous algae at the eastern shore (non-FAB site). At the FAB site, aquatic plants (A) and rocks (B) were densely covered by filamentous algae during all sampling campaigns (October 2019; June, July, and October 2020; and June 2021), which mainly comprised Cladophora glomerata (microscope image (C)). Periphyton on the rocky substrate at the non-FAB site (D,E) were dominated by various diatoms (Epithemia, Gomphonema, Cymbella; (F)). Photos by Soren Brothers (non-FAB), Sabine Hilt (FAB) and Katrin Preuß (microscope).
2.2. Long-Term Data on Ice Cover and Water Temperature
To determine whether the lake was warming due to climate change, we analyzed monitoring data from the lake, collected by the Utah Division of Wildlife Resources. The longest time series that was available for analysis was the annual ice period data (i.e., the number of days of ice cover each year), available from 1923 to 2021. Bear Lake was considered to be frozen when there was no open water present on the entire lake surface. This was determined either by viewing Bear Lake from above, when there were no clouds/fog present, from the Bear Lake Overlook Rest Area on U.S. Highway 89 (immediately to the west of the lake), or by driving around the perimeter of the lake and viewing the lake surface with binoculars. The ice-off date was considered when the surface of Bear Lake changed from frozen to open water. This happened within a matter of hours and was always accompanied by a strong wind event in the spring. More recent monitoring data (spring and summer surface water temperatures and Secchi depths) were available from 2009 to 2020 and these were included in our analysis as well. The surface water temperatures were measured in the top 10 cm of the water column with a YSI Model 2030 Pro (Yellow Springs Instruments, Yellow Springs, OH, USA) hand-held multi-parameter meter from a boat at an established site, approximately 1 km east of the Bear Lake State Park marina.
2.3. Stable Isotope Analyses
We analyzed and presented data from two separate sets of field campaigns: one that was focused on retrieving periphyton biomass samples for a stable isotope analysis, and another that was focused on measuring in situ GPP rates in FAB and non-FAB communities (described below in Section 2.4). Periphyton sample collection for the stable isotope analysis occurred in October 2019 (from the FAB site) and June 2021 (from both the FAB and non-FAB sites). The samples were stored in plastic Falcon tubes and shipped immediately to a laboratory in Berlin, Germany, where they also underwent species identification. In October 2019, FABs were sampled from four different substrates that were found at the FAB site (two types of rocks, reed, submerged macrophytes), while the samples in June 2021 were all scraped from rocks (four replicates per site). The samples were dried at 60 °C and ground to a fine powder. The bulk elemental content and stable isotope analyses of carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) were conducted by elemental analysis–continuous flow isotope ratio mass spectrometry (e.g., [30]), using a Flash IRMS elemental analyzer, coupled via a Conflo IV interface to a Delta V Advantage mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, Bremen, Germany). The results are expressed in the δ notation, using ratios of samples and isotope standards issued by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), on the Vienna Pee Dee Belemnite (V-PDB) for δ13C, and atmospheric nitrogen (air-N2) scale for δ15N. The analytical error (mean SD from repeat measurements of in-house standards) for each run was always smaller than 0.3 ‰ for δ13C and δ15N.
2.4. Gross Primary Production
Three sampling campaigns to quantify rates of FAB and non-FAB gross primary production (GPP) were carried out in 2020 (in June, July, and October). Our first campaign (June) focused on the site where the FABs had first been identified and retrieved in 2019 (FAB; 41°54.942′ N, 111°23.453′ W), while subsequent campaigns sampled the FAB site, as well as a second site where minimal FAB occurrence was observed (non-FAB; 41°53.345′ N, 111°17.468′ W, Figure 1). Both sites are on the Utah side of the lake (featuring sewage systems, thus unlikely to have direct groundwater eutrophication from septic tanks), and both are far from the north end, where the lake is connected to the Bear River. During each field campaign, rocks and water samples were collected manually in the near-shore zone (from depths of ~0.1 to 0.15 m below the surface), minimizing physical disturbance to the rock surface (or filamentous algae growth on the rock). During each campaign, subsamples of filamentous algae from each site were also collected in plastic Falcon tubes and viewed under a microscope to identify the periphyton species present at a given site (permitting taxonomic comparisons with samples shipped to Berlin for stable isotope analyses, as described in Section 2.3).
There is no universal standardized protocol for the measurement of GPP in benthic periphyton communities. All methods for measuring aquatic metabolism rates are associated with some errors [31,32], and research focusing on benthic metabolism in particular has generally been more recent than research on planktonic dynamics [33]. Nevertheless, in situ measurements of changes in oxygen concentrations in sealed transparent benthic chambers or domes are a common method for assessing periphyton metabolism rates both in marine [34] and freshwater [35,36] environments. We thus measured oxygen dynamics in sealed clear and dark chambers containing rocks with attached FAB (Cladophora) or non-FAB periphyton assemblages and exposed in the lake (in situ), as this general approach has also been applied to determine periphyton metabolism rates in other large lakes [37,38]. This approach permits the direct measurement of benthic GPP for rocky littoral areas, and captures the effects of self-shading in dense FAB mats, which can play an important role in their seasonal growth patterns [39].
All the rocks (n = 12 in the first campaign; n = 6 per site in the second campaign; and n = 12 at the FAB and 6 at the non-FAB site in the third campaign) were incubated in the nearshore lake zone at ambient lake temperatures in 3 L watertight plastic (polycarbonate) chambers to undergo light–dark metabolism experiments, in order to measure the rates of gross primary production (GPP), net ecosystem production (NEP), and community respiration (CR) using changes in dissolved oxygen (DO) concentrations, following standard methods [30]. Each rock underwent both a light and dark treatment. Briefly, the rate of change in DO for a chamber that was exposed to ambient/full sunlight (in chambers that were exposed at the same near-shore depth that the rocks were collected from, ~10 to 15 cm below the water surface) represented NEP (the sum of GPP and CR). The rate of change in DO for containers that were stored in dark chambers (also placed in the near-shore water to minimize changes to ambient water temperatures) represented CR, which we report as a negative number, given that it is a rate of decline in DO. Light incubations that are exposed for too long may form bubbles when oxygen leaves the dissolved state (resulting in a dampened DO measurement in light incubations). We therefore adapted our sampling periods in the field to avoid this. Specifically, we found that incubation periods of 30–60 min for rocks were appropriate for measuring substantial metabolic rates in both light and dark treatments, while minimizing bubble formation.
Gross primary production was calculated as NEP minus (negative) CR. Changes in the DO concentration were measured using a Yellow Springs Instruments (YSI) DO probe, calibrated prior to each deployment. The metabolic rates that were measured in each chamber were calculated according to the water volume (measured carefully with a graduated cylinder, accounting for displacement by the rocks), and converted from volumetric to surface area rates by multiplying the total rates by the upper-exposed surface area of each incubated rock. This was calculated by wrapping the upper-exposed surface of each rock in aluminum foil and weighing the dried foil in our laboratory, and finally comparing the weight of that foil with the weight of the aluminum foil of the known surface area. The metabolic rates are furthermore converted to carbon units assuming photosynthetic and respiratory quotients (PQ and RQ) of 1. Although the lake PQ and RQ values may vary between lakes, they are often close to 1 [40,41].
To correct for phytoplankton production in the lake water during the rock incubation experiments, we deployed two “control” chambers containing only lake water, in order to measure the water-column aquatic metabolism rates. Given the lower rates of aquatic metabolism, longer incubation periods of 1–2 h were adopted in the water-only treatments. However, as the water column concentrations of chl a in Bear Lake tend to be extremely low, we anticipated that incubation experiments of water alone might not provide suitable data for calculating water-column metabolism rates via changes in dissolved oxygen. Therefore, we collected one liter of water from each site and sampling campaign, which we filtered and analyzed in the laboratory to determine the ambient water chl a concentrations at our sampling sites. The chl a concentrations were measured in 95% ethanol using a Turner 10AU fluorometer [42], either within 24 h of sampling, or else within two weeks if the samples were immediately frozen. Phytoplankton production (P, mg C m−3 d−1) was subsequently estimated as 10.3 x chl a (mg m−3)1.19 [43]. As we expected differences in GPP between the FAB and non-FAB communities to be primarily apparent as GPP rates that were expressed relative to periphyton chl a concentrations on rocks, we took additional steps to measure the rock periphyton chl a concentrations. Immediately following the incubation experiments, periphyton was scrubbed from each rock using a metal periphyton brush, transferred to a glass-fiber filter, and transported to our laboratory in a dark cooler with ice packs for analyzing the chl a concentrations (following the same method described above).
We recognized that the irregular sampling structure (including separate campaigns for stable isotope analysis measurements and GPP measurements) introduced potential uncertainties in precisely matching the GPP rates to the results of stable isotope analyses. We also recognize that asymmetries within the GPP-specific campaigns (with unmatched sampling frequencies of FAB and non-FAB sites) are not ideal for comparing aquatic metabolism rates in these two communities. However, we have decided to analyze and present all available data, as we believe that each of these measures from periphyton communities (stable isotope signatures and GPP rates) are of significant interest on their own, and assessing them alongside one another presents a potentially compelling case for future research efforts. Considering the asymmetrical measurements of the FAB and non-FAB GPP rates, our analysis explicitly considers that only two of the three sampling campaigns measured both communities on the same date, and we have adopted statistical tests (described below, in Section 2.5) that are appropriate for the sample size of these groups.
2.5. Statistics
Data were checked for normal distribution using Kolmogorov–Smirnov tests. Periphyton chl a data were not normally distributed and thus compared between the FAB and non-FAB sites using a Mann–Whitney U test. All other data were normally distributed. The means of the metabolism values were compared between the FAB and non-FAB sites using t-tests. Long-term trends in the number of ice days and water temperature were analyzed using linear curve fits. The stable isotope signatures of δ13C and δ15N were compared between the FAB site in 2019 and 2021 and the non-FAB site in 2021 using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a subsequent Tukey’s post hoc test. The statistical analyses were carried out using Origin 2016G.
3. Results
3.1. Occurrence of FABs in Bear Lake
FAB occurrence was observed in January 2005; October 2019; June, July, and October 2020; and June 2021 at both the eastern and western shores of Bear Lake (Figure 1). Microscope analyses on samples that were retrieved in 2019 and 2021 indicated that the FABs appeared to be generally dominated by the filamentous green alga Cladophora glomerata (Figure 1A–C), while various diatoms dominated at the non-FAB sites (Figure 1D–F).
3.2. Potential Causes of FAB Occurrence
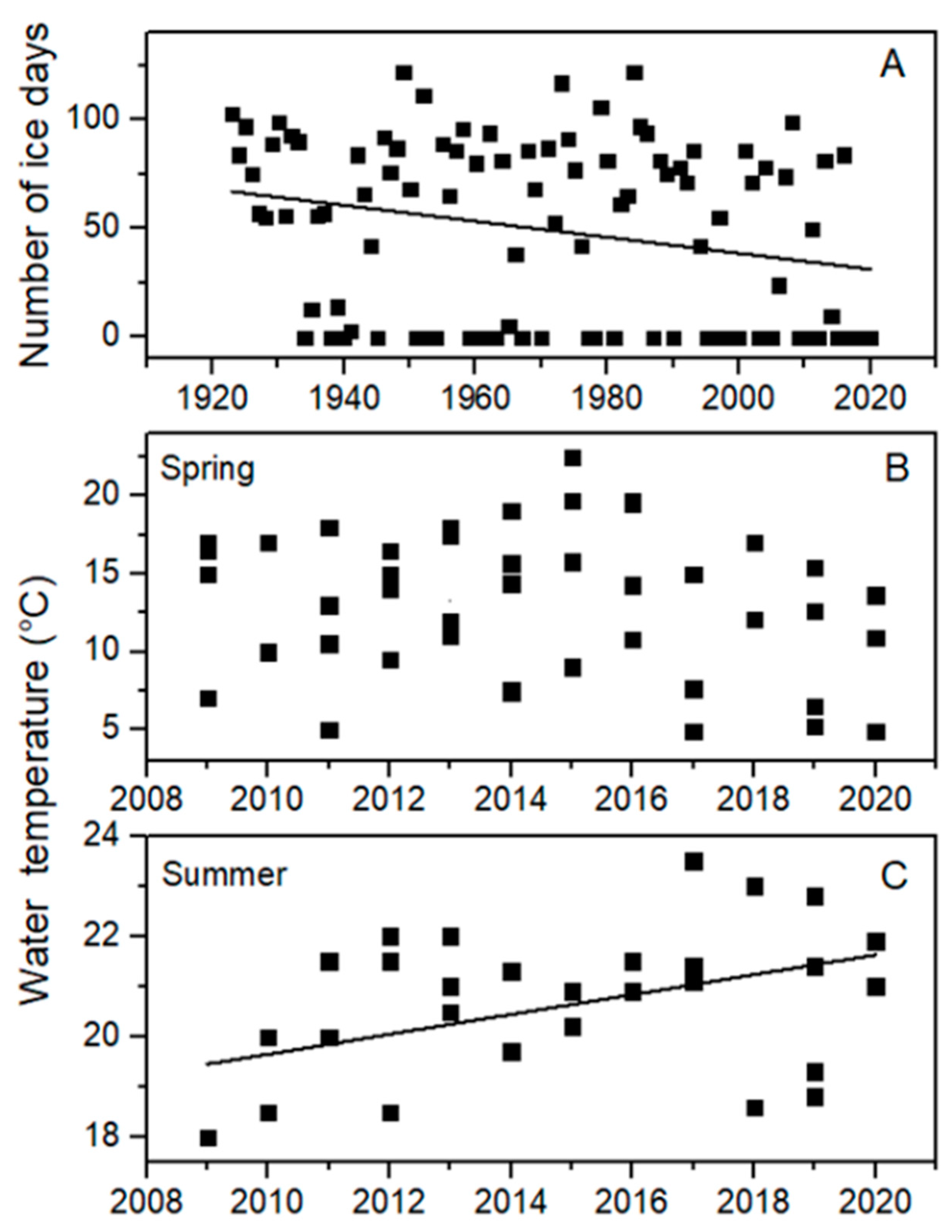
The lake monitoring data show that Bear Lake is warming, as evidenced by both a long-term decrease in ice period from 1923 to 2021 (Figure 2A, linear curve fit: y = −0.368x + 774, R2 = 0.06, p = 0.011), and a recent (2009 to 2020) significant increase in summer water temperatures (Figure 2C, linear curve fit: y = 0.198x − 378, R2 = 0.18, p = 0.0096), with no significant change in springtime water temperatures (Figure 2B, p = 0.51). Specifically, long-term ice cover data indicated that Bear Lake had last frozen over in the winter of 2016–2017, meaning that the lake had (as of winter 2020–2021) experienced four consecutive ice-free winters. The longest prior run of consecutive ice-free winters since 1923 had been three years, which occurred fairly recently (1998–2000). Prior to 1998, there were only two instances in which the lake did not freeze over for two consecutive years (1953–1956, and 1977–1978).
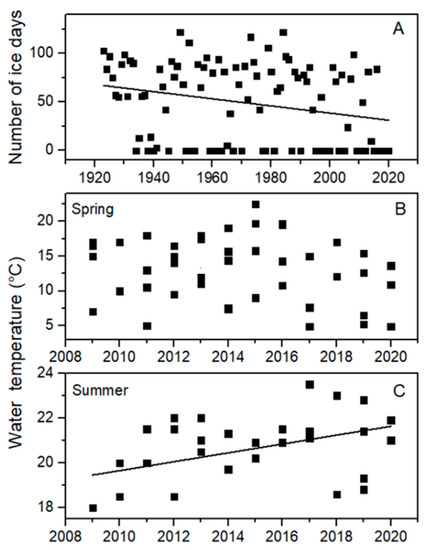
Figure 2.
(A) Number of ice days, (B) surface water temperature in spring (April–June) and (C) surface water temperature in summer (July–August) in Bear Lake. Trends were significant for numbers of ice days (linear curve fit: y = −0.368x + 774, R2 = 0.06, p = 0.011) and water temperature in summer (linear curve fit: y = 0.198x − 378, R2 = 0.18, p = 0.0096).
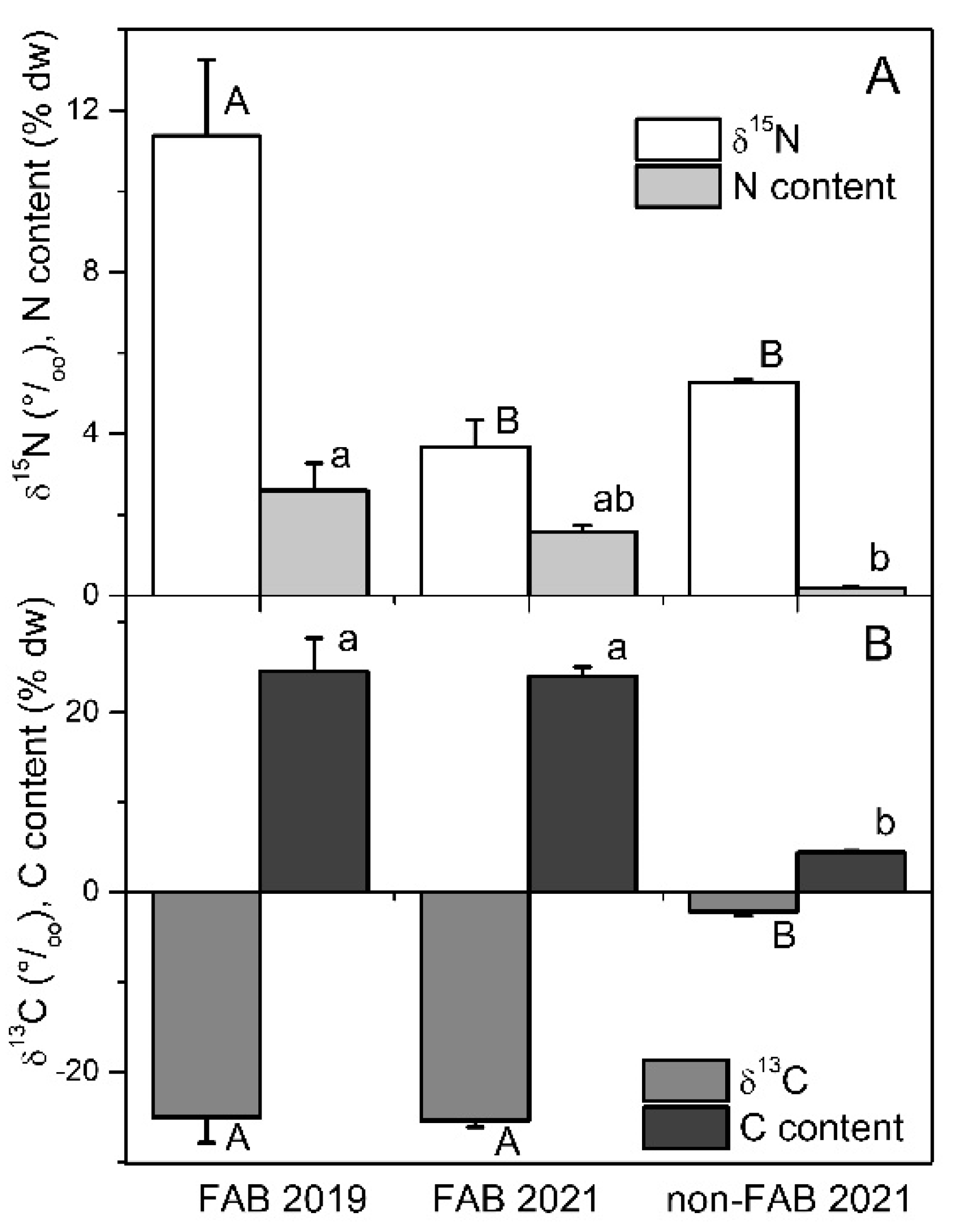
Analyses of stable isotopes from FAB and non-FAB materials that were collected in June 2021 indicated that the δ15N values were not significantly different between the sites (Figure 3, one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post hoc test at p < 0.05). In October 2019, the δ15N values of the FABs that were collected at the west site were significantly higher than in 2021 (Figure 3, one-way ANOVA, p = 0.006). However, the N content in periphyton tissues was significantly higher in the FABs than in the non-FABs (Figure 3, one-way ANOVA, p = 0.015). The δ15C values of the FABs were significantly lower than those of the non-FABs (Figure 3, one-way ANOVA, p < 0.0001). Similarly, the C content of the FABs was significantly higher than that of the non-FAB tissues (Figure 3, one-way ANOVA, p < 0.0001).
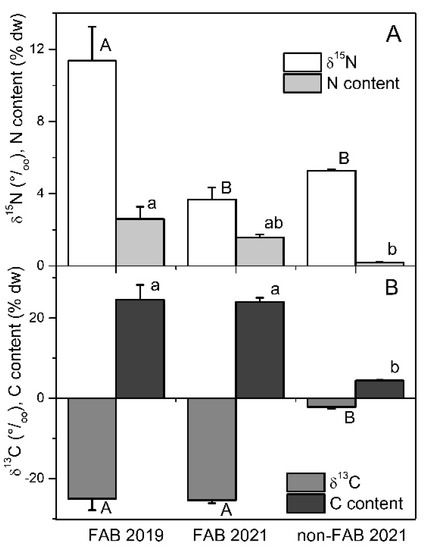
Figure 3.
δ15N signature and N content (A) and δ13C signature and C content ((B), n = 4) of filamentous algae blooms (FAB) at the western shore and non-FAB at the eastern shore of Bear Lake in October 2019 and June 2021 (+standard error). Different letters indicate significant differences among FAB 2019, FAB 2021 and non-FAB 2021 values (one way ANOVA, p < 0.05, Tukey’s post hoc test).
3.3. Effects on Primary Production
A total of 14 rock measurements at the FAB site (of 30 total) and five measurements at the non-FAB site (of 12 total) resulted in negative GPP values, meaning that, in these cases, DO concentrations declined more rapidly under light vs. dark conditions. These were excluded from further analyses. Regarding CR, three measurements from the FAB site and one from the non-FAB site produced positive values and were therefore also not included in the associated analyses. All but one water-only incubation provided negative GPP values, and phytoplankton GPP (used to correct for lake water GPP in rock incubations) was therefore estimated from the water chl a concentrations.
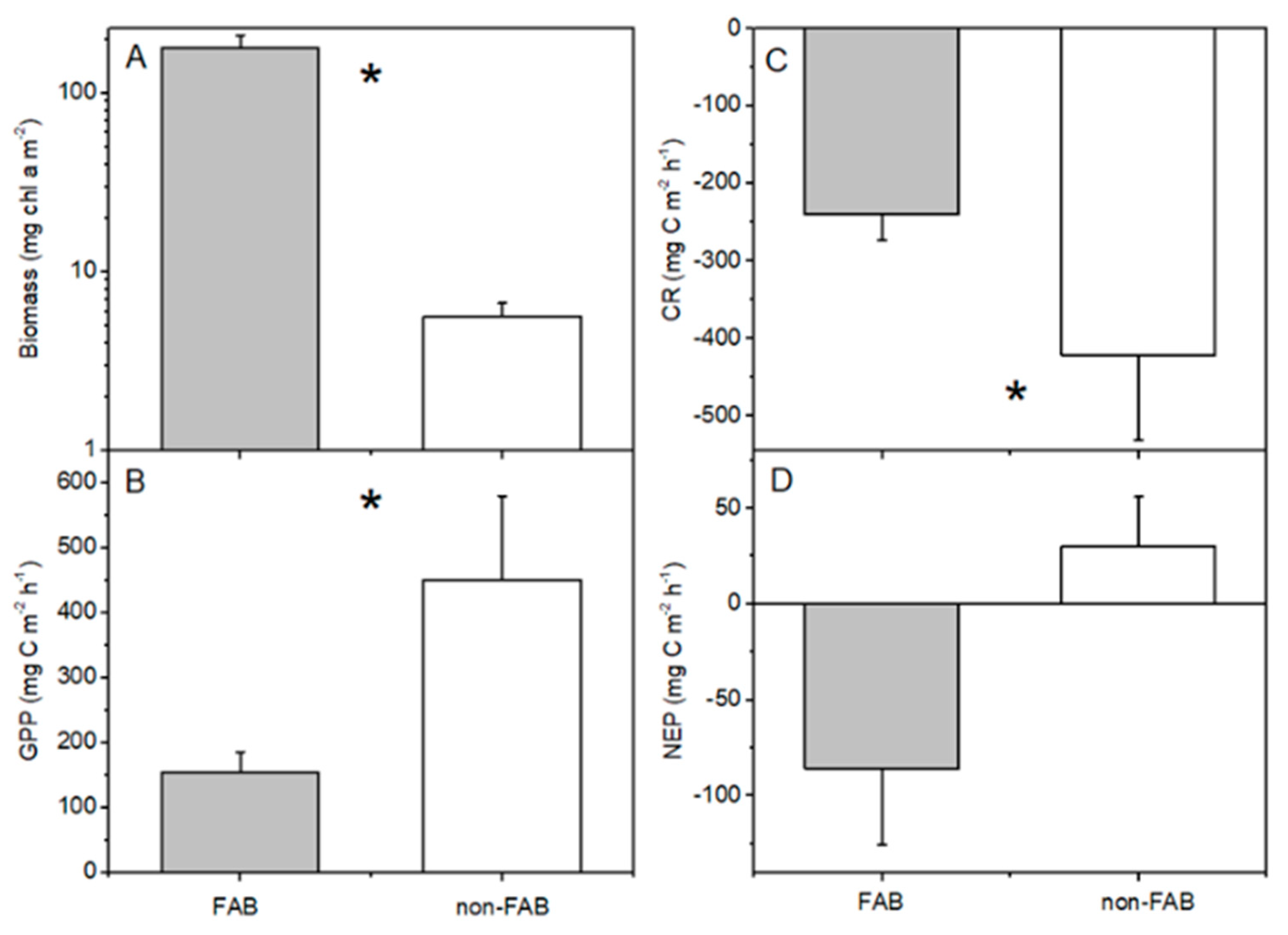
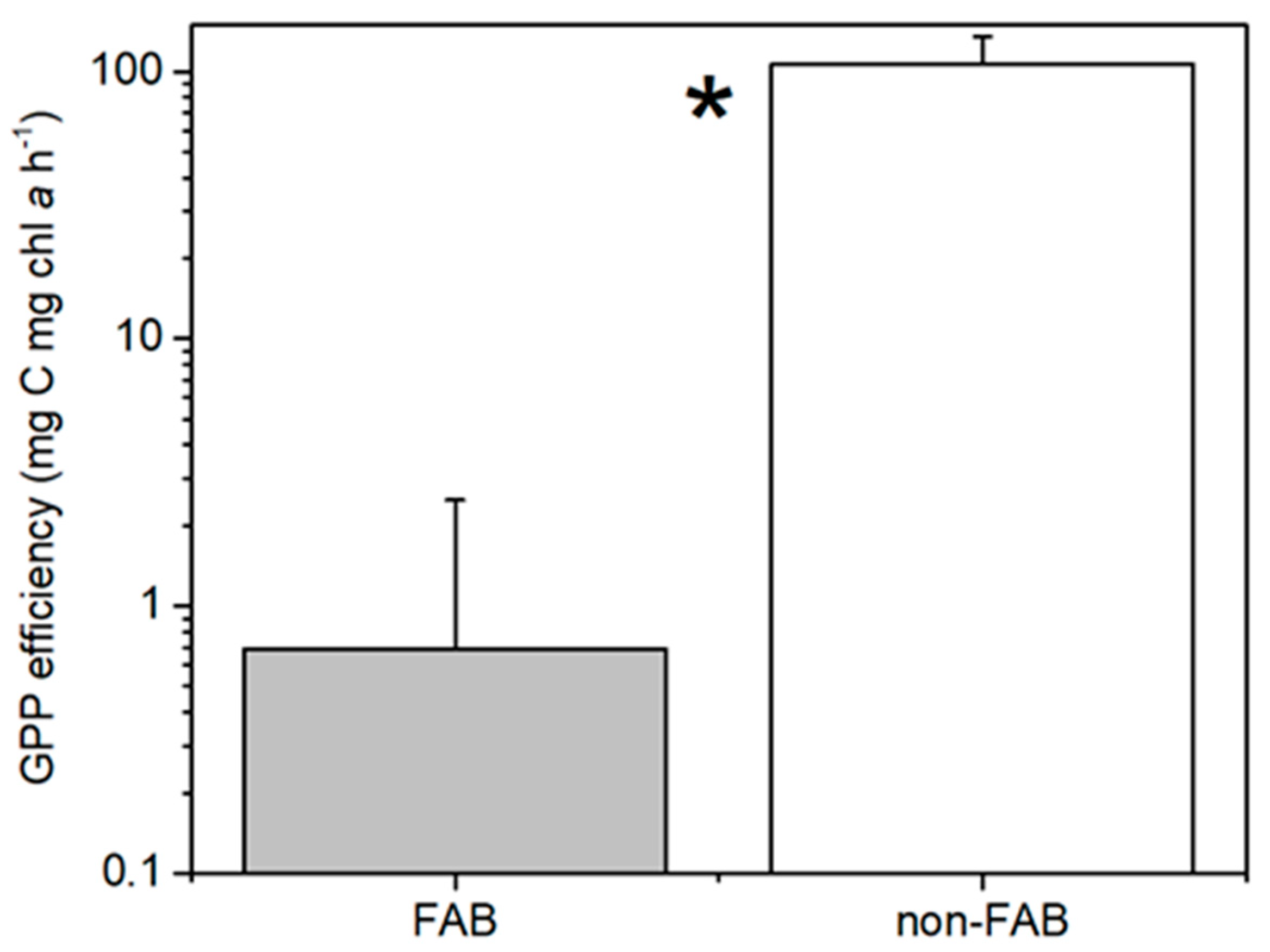
The periphyton biomass on rocks that was sampled at the FAB site was significantly greater than that at the non-FAB site (Mann–Whitney U test, p < 0.05, Figure 4A). Despite much higher periphyton biomasses present at the FAB site, the measured total GPP rates from rocks on the non-FAB site were significantly greater than the rates that were measured at the FAB site (t-test, p = 0.005, Figure 4B). This difference remains significant if one high GPP outlier is removed from the non-FAB site, as well as if only the two months during which both sites were sampled are compared. This difference also remains significant if zero-values are applied to the negative GPP rates that were removed from the analyses (as discussed in Methods). Calculated per mg chl a (i.e., considering the productive efficiency of periphyton on rocks), this difference between sites is substantially greater (t-test, p = 0.00001, Figure 5). The non-FAB sites had significantly lower values of CR (t-test p = 0.048, Figure 4C), while there were no significant differences between the FAB and non-FAB site NEP (t-test, p = 0.08, Figure 4D) measured rates. The statistical significance of the differences that were observed between the sites was not affected by the inclusion or exclusion of the June sampling campaign (for which only the data from the FAB site was available).
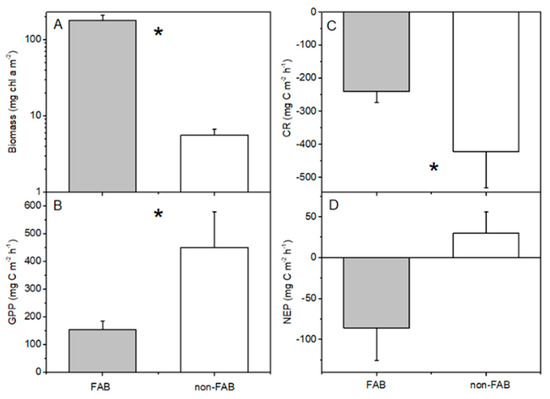
Figure 4.
(A) Periphyton biomass, (B) gross primary production (GPP), (C) community respiration (CR), and (D) net ecosystem production (NEP) at FAB (filamentous algae blooms) and non-FAB sites in Bear Lake (June, July, October for FAB, n = 16; just July/October for non-FAB, n = 7, +standard error). Asterisks indicate significant differences between FAB and non-FAB values (t-tests, p < 0.05).
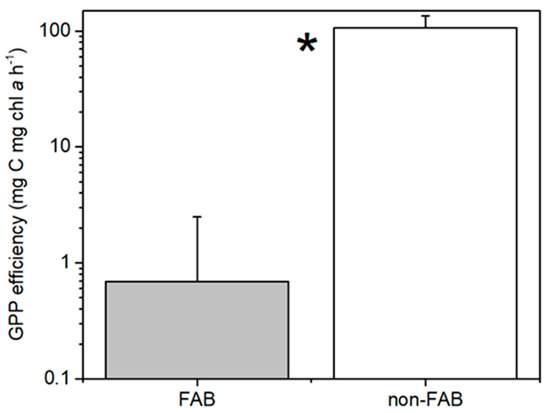
Figure 5.
Periphyton gross primary production (GPP) efficiency at FAB (filamentous algae blooms) and non-FAB sites in Bear Lake (June, July, October for FAB, n = 16; just July/October for non-FAB, n = 7. +standard error). * significant difference between FAB and non-FAB values (t-test, p < 0.05).
Although the lake water chl a concentrations were higher in the FAB site (30 ± 7 μg L−1, n = 5) compared to the non-FAB site (7 ± 10 μg L−1, n = 3), the resulting planktonic GPP rates in both sites were minor compared to the overall measured rates (FAB mean = 25 ± 7 mg C m−3 h−1; non-FAB mean = 4 ± 10 mg C m−3 h−1). All measurements are means ± standard error).
4. Discussion
Similar to observations in many other clear lakes globally [11], FABs occurred at several littoral shallow areas around Bear Lake. They were dominated by Cladophora glomerata, the most widely distributed macroalga throughout the world’s freshwater ecosystems [44]. While no long-term data on the spatial and temporal dynamics of FAB occurrence were available for Bear Lake, a declining number of ice days, increasing surface water temperatures and anthropogenic nutrient enrichment indicated from stable isotope signatures may facilitate FAB proliferation. Rocks with FABs accumulated a higher biomass, yet their GPP during the investigated period was lower than that of the rocks without FABs, contrary to our expectations. As predicted, however, the productive efficiency of the FABs was lower than that of the non-FAB periphyton. In the following, we discuss these findings and their implications for the lake ecosystem.
4.1. Potential Causes of FAB Occurrence
An apparent recent rise in FABs has been linked to a variety of drivers in lakes around the world, including climate change, eutrophication (including groundwater pollution), and food web effects [11]. We considered that climate may have played some role in the occurrence of FABs in Bear Lake, as periphyton production can respond positively to warming [14,45]. C. glomerata, the dominant species in Bear Lake FABs, has its photosynthesis temperature optimum at 28–31 °C [46] and modelling predicted an earlier spring growth with surface water warming [47]. Furthermore, ice cover period may be an important measure for considering recent FAB formation developments, as littoral ice may physically scrape periphyton (and associated nutrient matrices) from nearshore rocks, resetting periphyton colonization on rocks and thus physically reducing FAB formation. Coupled with the recent increase in summertime temperatures, there is a plausible mechanism whereby the climate warming of Bear Lake assists the development of FABs.
C. glomerata often dominates the benthic flora of eutrophic waters and it has become a nuisance on lake shores worldwide as a result of anthropogenic eutrophication ([48] and references therein). Elevated concentrations of soluble phosphate that were associated with cultural eutrophication were considered to be responsible for the Cladophora bloom occurrences in the lower North American Great Lakes in the 1950s to 1980s [44], and are still responsible for their current nuisance development [49]. While not yet considered a nuisance in Bear Lake, its presence there may potentially indicate local eutrophication [13]. All the δ15N values that were measured were higher than 0 ‰ and thus may indicate an influence of livestock or human waste on nearshore littoral areas [50,51,52], although within-group variability of δ15N can be high [52,53]. While livestock numbers in the area are in decline, and there has been no upward trend in local flood irrigation that could wash terrestrial nutrients to the lake’s littoral zone, tourism and associated construction has risen in recent decades (pers. obs.). Eutrophication via lacustrine groundwater discharge [54] may also provide nutrients directly to the sediment–water interface, thus promoting FABs [12], and it is possible that a highly variable but generally declining trend in Bear Lake’s water levels [29] may be have exposed local groundwater discharge to areas that are closer to shore, making the occurrence of FABs more readily visible. Such locally and temporary increased nutrient availability, however, is difficult to directly measure from monitoring the nutrient concentrations in the water. Tissue nutrient concentrations of benthic primary producers such as macrophytes or filamentous algae that integrate over longer periods are therefore a useful measure for detecting such hidden nutrient inputs. In June 2021, the tissue N contents of filamentous algae from the FAB site were significantly higher than those from the non-FAB site (Figure 5), which could also indicate a higher N availability at the FAB site, although it may also be an effect of a higher proportion of inorganic material in the dry weight of the non-FABs.
We also considered that top-down controls can play a role in FAB occurrence in lakes [11]. Specifically, the disappearance of periphyton grazers such as snails may release periphyton from biotic controls on their biomass [55]. Alternatively, the selective grazing of epiphytic diatoms growing on Cladophora mats could potentially promote Cladophora growth [16,56]. Indeed, the effects of herbivore grazing of periphyton have previously been associated with increased periphyton biomass-specific productivity through fecal fertilization and increased light supply to periphyton [16,57]. Two fish species in Bear Lake rely upon benthic macroinvertebrates during various times of the year—the Bear Lake sculpin (Cottus extensus), and the Bonneville whitefish (Prosopium spilonotus), and might reduce populations of periphyton grazers during these periods. However, state government fish monitoring data using catch-per-effort and gill-net surveys (data not shown) indicate no trends in either sculpin or Bonneville whitefish populations, indicating that they are unlikely cause the occurrence of FABs in Bear Lake. Studies in Lake Tahoe (CA/NV, USA) have shown that periphyton production can also be stimulated or inhibited by low or high crayfish population densities, respectively [58]. Crayfish have likewise been observed to have an inhibitory effect on Cladophora mat formation in Michigan streams [59]. Although Bear Lake historically featured a plentiful native population of crayfish, they appeared to be entirely absent from the lake after 1992 for approximately a decade, and are now only sparsely observed in the lake (ST, pers. obs.), possibly coinciding with a recent establishment of invasive crayfish populations in the lake [60].
We cannot fully disentangle the effects of climate change, nutrient enrichment, and food web controls as causal factors promoting FAB formation in Bear Lake. However, it is apparent that recent lake changes in ice cover, water temperature, and introduced crayfish may be affecting the lake in a way that could promote FABs. However, our analyses also indicate that nutrient enrichment may be critical for the current occurrence of the FABs that are observed in Bear Lake. In this case, nutrient enrichment may be associated with a localized decline in primary production rates. It is also possible that these stressors (climate, nutrients and food web controls) are interacting to promote FABs. For instance, phenological shifts between periphyton and grazers permitted critical FAB biomass accumulation to occur earlier in the year, allowing periphyton assemblages to grow to an apex size that precluded grazing by the local herbivore community [16,61].
4.2. Consequences of FAB Occurrence for Primary Production and Lake Food Web
Our measured rates of periphyton GPP are within the range that has been described previously for mesotrophic and oligotrophic lakes ([36] and references therein). However, contrary to the findings of a previous study that focused on FAB blooms by Spirogyra sp. in a Japanese lake [22], we measured the highest rates of both total and chl a-specific GPP on non-FAB rocks in Bear Lake. Several measurements at both the FAB and non-FAB sites showed negative GPP values that were excluded from the analyses (as discussed in Methods). This approach did not affect our results, as such cases occurred at approximately the same frequency at both sites. Higher δ13C signatures of periphyton at the non-FAB site support our findings of a higher productivity because they indicate a greater shortage in CO2, either due to higher photosynthetic rates [57] or a thicker boundary layer [62].
Filamentous green algae such as Spirogyra and Mougeotia can exhibit rates of net photosynthesis up to ten times higher than those of C. glomerata (7.7 mg O2 g−l h−l) [63], which are highest at 300 µmol photons m−2 s−1 [64]. The light intensity at our nearshore Bear Lake sampling sites would have been higher than this, potentially leading to an unfavorable energy balance for this species. Low chl a concentrations and low maximal rates of photosynthesis are physiological acclimations to high-light environments in C. glomerata [65]. It is thus possible that light conditions would have been preferable for C. glomerata at greater lake depths, although the cobble substrate on which we observed FAB growth is largely limited in Bear Lake to the shallow nearshore zone [29]. Our chamber measurements excluded the effects of waves on GPP, but this does not explain the lower GPP values of the FABs, as periphyton biomass accumulation is often lower in nearshore zones where wave action suppresses production [66,67].
Although seasonal analyses of GPP are limited due to small sample sizes, the measured GPP rates did not differ significantly between months at either the FAB or non-FAB site. While the mean GPP rates at the FAB site declined steadily from June (217 ± 44 mg C m−2 h−1) to July (145 ± 58 mg C m−2 h−1) to October (75 ± 52 mg C m−2 h−1), they remained substantially lower than the measured rates at the non-FAB site (overall mean = 451 ± 129 mg C m−2 h−1). It is therefore possible that earlier springtime GPP rates were higher at the FAB site than those that were measured in our three campaigns, but there is no evidence to indicate that they could have been high enough to influence the overall differences in the GPP rates that were observed between the FAB and non-FAB sites. Assuming constant non-FAB GPP rates, the springtime FAB GPP would need to surpass 1400 mg C m−2 h−1, which is an order of magnitude higher than the mean June-measured GPP rates, as well as far above the range of rates that are typically reported in the literature ([67] and references therein).
The implications of lower GPP by FABs for the food web of Bear Lake are yet unclear. Littoral-benthic resources are an important support for aquatic food webs [21,67,68], including those in Bear Lake, where phytoplankton production is minimal [69]. Elevated CR rates in the non-FAB treatment compared to the FAB treatment (Figure 4C) indicate that a large fraction of the carbon fixation in these assemblages likely fuels microbial production and respiration, although it cannot be taken for granted that such carbon is effectively transferred up the food web to higher trophic levels [70], as variable bacterial growth efficiencies can also result in a loss of carbon as respiration to the water column ([32] and references therein, [71]). However, during these sampling periods, the measured NEP tended to be positive at the non-FAB site and negative at the FAB site (Figure 4D), indicating that an active surplus of organic matter at non-FAB rocks may be available to benthic consumers at higher trophic levels. We recognize that a period of positive NEP would have been required to accumulate the biomass that was observed on the FAB rocks; we also note that our earliest FAB sampling campaign (June 2020) features a similar number of positive (n = 5) and negative (n = 7) NEP values, with a mean NEP that is much closer to zero (data not shown). Likewise, the consistently negative measured NEP rates on these rocks later in the year are not entirely surprising, as C. glomerata FABs may experience summertime collapses due to self-shading [39], or even modelled declines in biomass extending later into the season [72]. Nevertheless, data from other systems indicate that, once formed, these FABs likely make an undesirable food source for grazers in the lake ([16] and references therein).
5. Conclusions
Our study underlines the difficulty of determining a definitive attribution of biotic ecosystem changes, such as the global rising occurrence of FABs [11], to singular causes, especially when multiple stressors (in this case, climate change, invasive species and anthropogenic eutrophication) co-occur, with cumulative effects on ecosystems. Our results indicate that high-biomass, low-productivity FABs can have substantial negative consequences to lake ecosystems because low-biomass, high-productivity periphyton assemblages are known as an essential resource for lake food webs [16,21]. Understanding these dynamics is important, as the littoral zones of lakes are hotspots of both biodiversity [73] and anthropogenic impacts [74]. Addressing and better assessing the multiple stressors impacting inland waters is thus essential for future mitigation of the threat of FABs to aquatic food webs around the world.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.P., S.H. and S.B.; methodology, S.H., T.G., S.T. and S.B.; formal analysis, M.P., S.H., T.G. and S.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.P.; writing—review and editing, M.P., S.H., T.G., S.T. and S.B.; supervision, S.B.; funding acquisition, M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially funded by a Utah State University Undergraduate Research and Creative Opportunities Grant.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request.
Acknowledgments
This study was motivated by a workshop at Lake Tahoe in 2019, and we thank the organizers (Yvonne Vadeboncoeur, Sudeep Chandra) and funders (National Science Foundation through DEB grant no. 1939502, Royal Society of New Zealand) of that workshop. We also thank Katrin Preuß (IGB Berlin) for periphyton species determination and photographs, Mitch Poulsen (Bear Lake Regional Commission) for providing lake nutrient data, and Utah Division of Wildlife Resources technicians who assisted with temperature and Secchi depth collections on Bear Lake.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Dodds, W.K. Nutrients, Eutrophication and Harmful Algal Blooms along the Freshwater to Marine Continuum. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2019, 6, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M. Eutrophication, Harmful Algae and Biodiversity—Challenging Paradigms in a World of Complex Nutrient Changes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilt, S.; Brothers, S.; Jeppesen, E.; Veraart, A.J.; Kosten, S. Translating Regime Shifts in Shallow Lakes into Changes in Ecosystem Functions and Services. Bioscience 2017, 67, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.B.G.; Hilt, S.; Kosten, S.; de Klein, J.J.M.; Paerl, H.W.; Van de Waal, D.B. Shifting States, Shifting Services: Linking Regime Shifts to Changes in Ecosystem Services of Shallow Lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 66, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daloğlu, I.; Cho, K.H.; Scavia, D. Evaluating Causes of Trends in Long-Term Dissolved Reactive Phosphorus Loads to Lake Erie. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10660–10666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate: Blooms like It Hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddard, J.L.; Van Sickle, J.; Herlihy, A.T.; Brahney, J.; Paulsen, S.; Peck, D.V.; Mitchell, R.; Pollard, A.I. Continental-Scale Increase in Lake and Stream Phosphorus: Are Oligotrophic Systems Disappearing in the United States? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3409–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopáček, J.; Hejzlar, J.; Kaňa, J.; Norton, S.A.; Stuchlík, E. Effects of Acidic Deposition on In-Lake Phosphorus Availability: A Lesson from Lakes Recovering from Acidification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2895–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopáček, J.; Kaňa, J.; Bičárová, S.; Brahney, J.; Navrátil, T.; Norton, S.A.; Porcal, P.; Stuchlík, E. Climate Change Accelerates Recovery of the Tatra Mountain Lakes from Acidification and Increases Their Nutrient and Chlorophyll a Concentrations. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 81, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahney, J.; Mahowald, N.; Ward, D.S.; Ballantyne, A.P.; Neff, J.C. Is Atmospheric Phosphorus Pollution Altering Global Alpine Lake Stoichiometry? Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2015, 29, 1369–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadeboncoeur, Y.; Moore, M.V.; Stewart, S.D.; Chandra, S.; Atkins, K.S.; Baron, J.S.; Bouma-Gregson, K.; Brothers, S.; Francoeur, S.N.; Genzoli, L.; et al. Blue Waters, Green Bottoms: Benthic Filamentous Algal Blooms Are an Emerging Threat to Clear Lakes Worldwide. Bioscience 2021, 71, 1011–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timoshkin, O.A.; Moore, M.V.; Kulikova, N.N.; Tomberg, I.V.; Malnik, V.V.; Shimaraev, M.N.; Troitskaya, E.S.; Shirokaya, A.A.; Sinyukovich, V.N.; Zaitseva, E.P.; et al. Groundwater Contamination by Sewage Causes Benthic Algal Outbreaks in the Littoral Zone of Lake Baikal (East Siberia). J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, E.E.; Hampton, S.E.; Fradkin, S.C.; Kennedy, B.P. Effects of Shoreline Development on the Nearshore Environment in Large Deep Oligotrophic Lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 1673–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNicola, D.M. Periphyton Responses to Temperature at Different Ecological Levels. In Algal Ecology: Freshwater Benthic Ecosystems; Stevenson, R.J., Bothwell, M.L., Lowe, R.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 149–181. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, U. Nutrient Competition Experiments with Periphyton from the Baltic Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 140, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadeboncoeur, Y.; Power, M.E. Attached Algae: The Cryptic Base of Inverted Trophic Pyramids in Freshwaters. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2017, 48, 255–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczynski, A.; Auer, M.T.; Brooks, C.N.; Grimm, A.G. The Cladophora Resurgence in Lake Ontario: Characterization and Implications for Management. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 73, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, M.T.; Tomlinson, L.M.; Higgins, S.N.; Malkin, S.Y.; Howell, E.T.; Bootsma, H.A. Great Lakes Cladophora in the 21st Century: Same Algae-Different Ecosystem. J. Great Lakes Res. 2010, 36, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Evans, W.R.; Yin, Q.Q.; Bell, P.; Moczydlowski, E. Evidence for Paralytic Shellfish Poisons in the Freshwater Cyanobacterium Lyngbya Wollei (Farlow Ex Gomont) Comb. Nov. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3104–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitman, R.L.; Shively, D.A.; Pawlik, H.; Nevers, M.B.; Byappanahalli, M.N. Occurrence of Escherichia Coli and Enterococci in Cladophora (Chlorophyta) in Nearshore Water and Beach Sand of Lake Michigan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4714–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Zanden, M.J.; Vadeboncoeur, Y.; Chandra, S. Fish Reliance on Littoral-Benthic Resources and the Distribution of Primary Production in Lakes. Ecosystems 2011, 14, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, K. Abrupt Change in Primary Productivity in a Littoral Zone of Lake Biwa with the Development of a Filamentous Green-Algal Community. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulch, H.M.; Turner, M.A.; Findlay, D.L.; Vinebrooke, R.D.; Donahue, W.F. Benthic Algal Biomass—Measurement and Errors. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 66, 1989–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blindow, I.; Hargeby, A.; Meyercordt, J.; Schubert, H. Primary Production in Two Shallow Lakes with Contrasting Plant Form Dominance: A Paradox of Enrichment? Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 2711–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Gudder, D.A. The Ecology of Cladophora. J. Phycol. 1992, 28, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Kraemer, B.M.; Lenters, J.D.; Merchant, C.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Global Lake Responses to Climate Change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarra, V.A.; Adams, V.D.; Thomas, C.; Herron, R.; Birdsey, P.; Kollock, V.; Pitts, M. A Historical Perspective and Present Water Quality Conditions in Bear Lake, Utah-Idaho. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1984, 1, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, D.S.; Bright, J.; Dean, W.E.; Rosenbaum, J.G.; Moser, K.; Anderson, R.S.; Colman, S.M.; Heil, C.W.; Jiménez-Moreno, G.; Reheis, M.C.; et al. A Quarter-Million Years of Paleoenvironmental Change at Bear Lake, Utah and Idaho. Spec. Pap. Geol. Soc. Am. 2009, 450, 311–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassic, H.C.; Gaeta, J.W. Littoral Habitat Loss Caused by Multiyear Drought and the Response of an Endemic Fish Species in a Deep Desert Lake. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C.; Silva, S.R.; Kelly, V.J. Carbon and Nitrogen Isotopic Compositions of Particulate Organic Matter in Four Large River Systems across the United States. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 1301–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehr, P.A.; Testa, J.M.; Kemp, W.M.; Cole, J.J.; Sand-Jensen, K.; Smith, S.V. The Metabolism of Aquatic Ecosystems: History, Applications, and Future Challenges. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 74, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brothers, S.; Vadeboncoeur, Y. Shoring up the Foundations of Production to Respiration Ratios in Lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 2762–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadeboncoeur, Y.; Vander Zanden, M.J.; Lodge, D.M. Putting the Lake Back Together: Reintegrating Benthic Pathways into Lake Food Web Models. Bioscience 2002, 52, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrer, A.M.; Thrush, S.F.; Hewitt, J.E.; Kraan, C. The Up-Scaling of Ecosystem Functions in a Heterogeneous World. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep10349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puts, I.C.; Bergström, A.-K.; Verheijen, H.A.; Norman, S.; Ask, J. An Ecological and Methodological Assessment of Benthic Gross Primary Production in Northern Lakes. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozersky, T.; Barton, D.R.; Hecky, R.E.; Guildford, S.J. Dreissenid Mussels Enhance Nutrient Efflux, Periphyton Quantity and Production in the Shallow Littoral Zone of a Large Lake. Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 2799–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althouse, B.; Higgins, S.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Benthic and Planktonic Primary Production along a Nutrient Gradient in Green Bay, Lake Michigan, USA. Freshw. Sci. 2014, 33, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, L. Diversity and Function of Algal Biofilms in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Ph.D. Thesis, Wright State University, Dayton, OH, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, S.N.; Hecky, R.E.; Guildford, S.J. The Collapse of Benthic Macroalgal Blooms in Response to Self-Shading. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 2557–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggren, M.; Lapierre, J.F.; Del Giorgio, P.A. Magnitude and Regulation of Bacterioplankton Respiratory Quotient across Freshwater Environmental Gradients. ISME J. 2012, 6, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachon, D.; Sadro, S.; Bogard, M.J.; Lapierre, J.; Baulch, H.M.; Rusak, J.A.; Denfeld, B.A.; Laas, A.; Klaus, M.; Karlsson, J.; et al. Paired O2–CO2 Measurements Provide Emergent Insights into Aquatic Ecosystem Function. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2020, 5, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilati, A.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A. Importance of Zooplankton for the Persistence of a Deep Chlorophyll Layer: A Limnocorral Experiment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Giorgio, P.A.; Peters, R.H. Balance between Phytoplankton Production and Respiration in Lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.N.; Malkin, S.Y.; Todd Howell, E.; Guildford, S.J.; Campbell, L.; Hiriart-Baer, V.; Hecky, R.E. An Ecological Review of Cladophora Glomerata (Chlorophyta) in the Laurentian Great Lakes. J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 839–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazanjian, G.; Velthuis, M.; Aben, R.; Stephan, S.; Peeters, E.T.H.M.; Frenken, T.; Touwen, J.; Xue, F.; Kosten, S.; Van De Waal, D.B.; et al. Impacts of Warming on Top-down and Bottom-up Controls of Periphyton Production. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, W.W.; Adams, M.S.; Farmer, A.M. Effects of Light and Temperature on Photosynthesis of the Nuisance Alga Cladophora Glomerata (L.) Kutz from Green Bay, Lake Michigan. New Phytol. 1988, 109, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, S.Y.; Guildford, S.J.; Hecky, R.E. Modeling the Growth Response of Cladophora in a Laurentian Great Lake to the Exotic Invader Dreissena and to Lake Warming. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 1111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, D.; Maberly, S.C.; Parker, J.E. Phosphorus and Nitrogen Relationships of Cladophora Glomerata in Two Lake Basins of Different Trophic Status. Freshw. Biol. 1996, 35, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, M.T.; McDonald, C.P.; Kuczynski, A.; Huang, C.; Xue, P. Management of the Phosphorus-Cladophora Dynamic at a Site on Lake Ontario Using a Multi-Module Bioavailable P Model. Water 2021, 13, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhlke, J.K. Sources, Transport, and Reaction of Nitrate in Ground Water. In Residence Times and Nitrate Transport in Ground Water Discharging to Streams in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed: U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 03-4035; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, D.; Botte, J.; De Baets, B.; Accoe, F.; Nestler, A.; Taylor, P.; Van Cleemput, O.; Berglund, M.; Boeckx, P. Present Limitations and Future Prospects of Stable Isotope Methods for Nitrate Source Identification in Surface- and Groundwater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J.E.; Canuel, E.A.; Harris, D. Stable Carbon and Nitrogen Isotope Composition of Aquatic and Terrestrial Plants of the San Francisco Bay Estuarine System. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 713–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whorley, S.B.; Wehr, J.D. Periphyton C and N Stable Isotopes Detect Agricultural Stressors in Low-Order Streams. Freshw. Sci. 2022, 41, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périllon, C.; Pöschke, F.; Lewandowski, J.; Hupfer, M.; Hilt, S. Stimulation of Epiphyton Growth by Lacustrine Groundwater Discharge to an Oligo-Mesotrophic Hard-Water Lake. Freshw. Sci. 2017, 36, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brönmark, C.; Klosiewski, S.P.; Stein, R.A. Indirect Effects of Predation in a Freshwater, Benthic Food Chain. Ecology 1992, 73, 1662–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, S.Y.; Sorichetti, R.J.; Wiklund, J.A.; Hecky, R.E. Seasonal Abundance, Community Composition, and Silica Content of Diatoms Epiphytic on Cladophora Glomerata. J. Great Lakes Res. 2009, 35, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liess, A.; Hillebrand, H. Invited Review: Direct and Indirect Effects in Herbivore—Periphyton Interactions. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2004, 159, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, R.W.; Goldman, C.R. The Effects of a Benthic Grazer on the Primary Productivity of the Littoral Zone of Lake Tahoe. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1975, 20, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creed, R.P.J. Direct and Indirect Effects of Crayfish Grazing in a Stream Community. Ecology 1994, 75, 2091–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, E.R.; Egly, R.M.; Williams, B.W. New Records of the Non-Native Virile Crayfish Faxonius Virilis (Hagen, 1870) from the Upper Snake River Drainage and Northern Bonneville Basin of the Western United States. BioInvasions Rec. 2018, 7, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahney, J.; Bothwell, M.L.; Capito, L.; Gray, C.A.; Null, S.E.; Menounos, B.; Curtis, P.J. Glacier Recession Alters Stream Water Quality Characteristics Facilitating Bloom Formation in the Benthic Diatom Didymosphenia Geminata. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- France, R.L. Carbon-13 Enrichment in Benthic Compared to Planktonic Algae: Foodweb Implications. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 124, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.M.; Arancibia-Avila, P.; Graham, L.E. Physiological Ecology of a Species of the Filamentous Green Alga Mougeotia under Acidic Conditions: Light and Temperature Effects on Photosynthesis and Respiration. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.M.; Auer, M.T.; Canale, R.P.; Hoffmann, J.P. Ecological Studies and Mathematical Modeling of Cladophora in Lake Huron: 4. Photosynthesis and Respiration as Functions of Light and Temperature. J. Great Lakes Res. 1982, 8, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.S.; Nilsson, J.; Pedersén, M.; Snoeijs, P. Photosynthesis, Carbon Uptake and Antioxidant Defence in Two Coexisting Filamentous Green Algae under Different Stress Conditions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 2005, 292, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stokes, L.W.; Olson, T.A. The Photosynthetic Pigments of Lake Superior Periphyton and Their Relation to Primary Productivity; Water Resources Research Center: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Brothers, S.; Vadeboncoeur, Y.; Sibley, P. Benthic Algae Compensate for Phytoplankton Losses in Large Aquatic Ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 3865–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierszen, M.E.; Hrabik, T.R.; Stockwell, J.D.; Cotter, A.M.; Hoffman, J.C.; Yule, D.L. Depth Gradients in Food-Web Processes Linking Habitats in Large Lakes: Lake Superior as an Exemplar Ecosystem. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 2122–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.; Hawkins, C. Trophic Interactions Between Fish and Invertebrates in Bear Lake, Utah-Idaho; Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Lischke, B.; Mehner, T.; Hilt, S.; Attermeyer, K.; Brauns, M.; Brothers, S.; Grossart, H.P.; Köhler, J.; Scharnweber, K.; Gaedke, U. Benthic Carbon Is Inefficiently Transferred in the Food Webs of Two Eutrophic Shallow Lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 1693–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Giorgio, P.A.; Cole, J.J. Bacterial Growth Efficiency in Natural Aquatic Systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1998, 29, 503–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczynski, A.; Bakshi, A.; Auer, M.T.; Chapra, S.C. The Canopy Effect in Filamentous Algae: Improved Modeling of Cladophora Growth via a Mechanistic Representation of Self-Shading. Ecol. Modell. 2020, 418, 108906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadeboncoeur, Y.; McIntyre, P.B.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Borders of Biodiversity: Life at the Edge of the World’s Large Lakes. Bioscience 2011, 61, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D.; McIntyre, P.B.; Smith, S.D.P.; Halpern, B.S.; Boyer, G.L.; Buchsbaum, A.; Burton, G.A.; Campbell, L.M.; Chadderton, W.L.; Ciborowski, J.J.H.; et al. Joint Analysis of Stressors and Ecosystem Services to Enhance Restoration Effectiveness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).