Prediction of the Discharge Flow in a Small Hydropower Station without Hydrological Data Based on SWAT Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
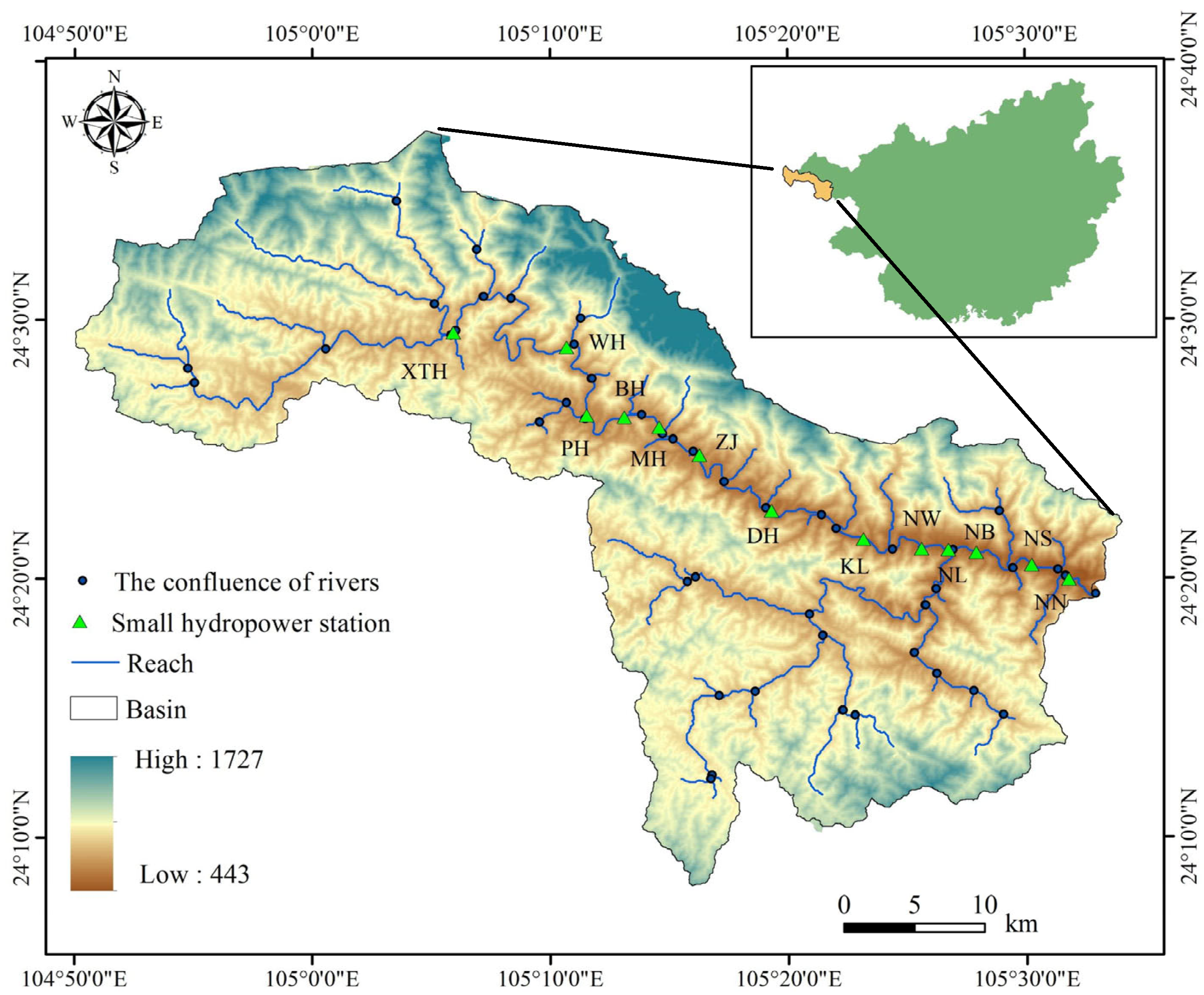
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Data Sources
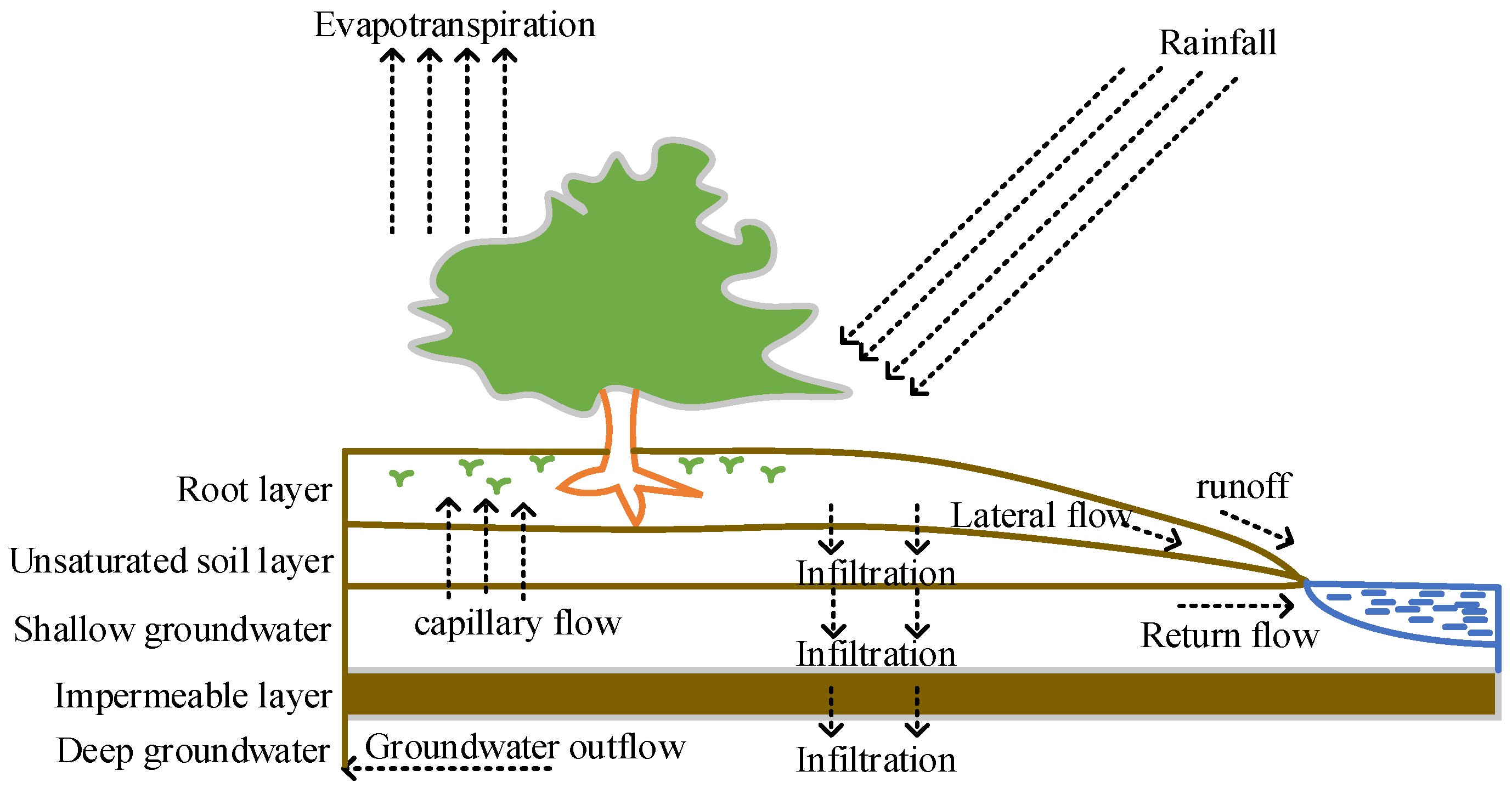
2.3. SWAT Model
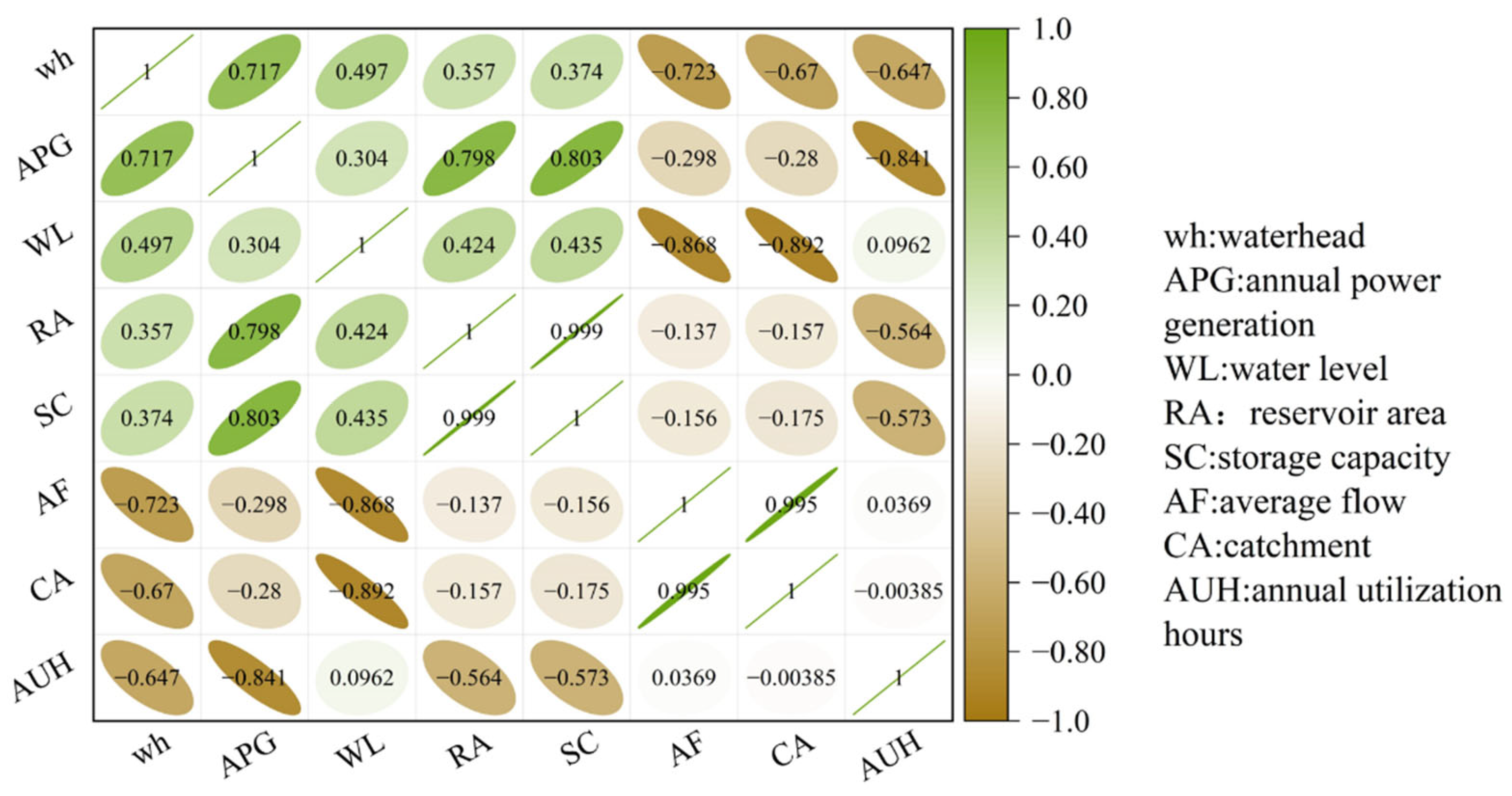
2.4. Correlation Analysis
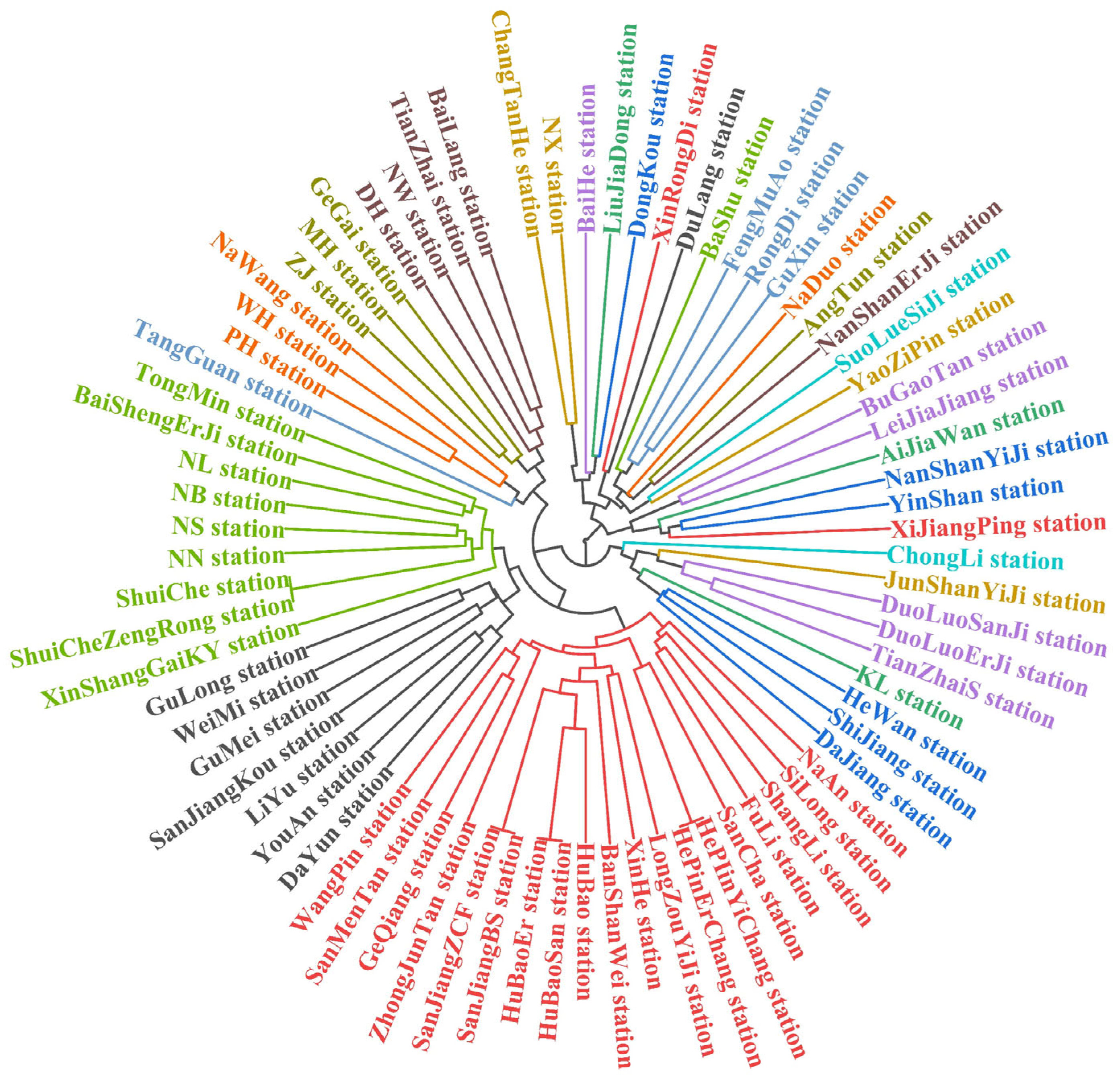
2.5. Clustering Analysis
2.6. Construction of SWAT Model
2.6.1. Watershed Delineation
2.6.2. Land Use
2.6.3. Soil Data
2.6.4. HRU Analysis
2.6.5. Weather Data Definition
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
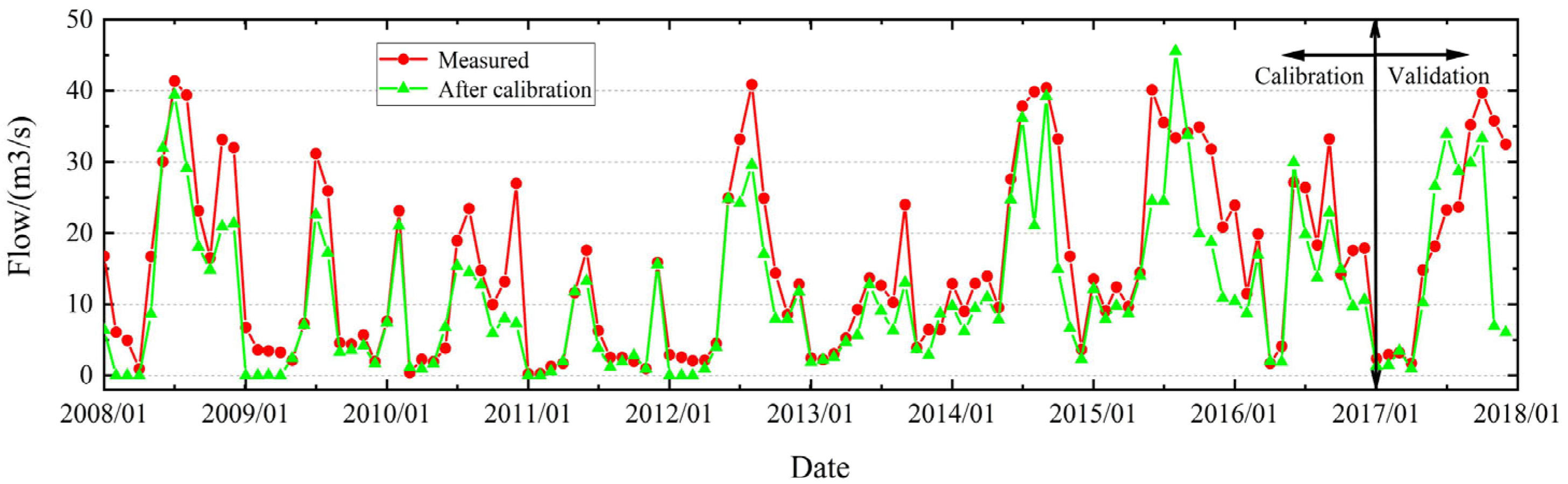
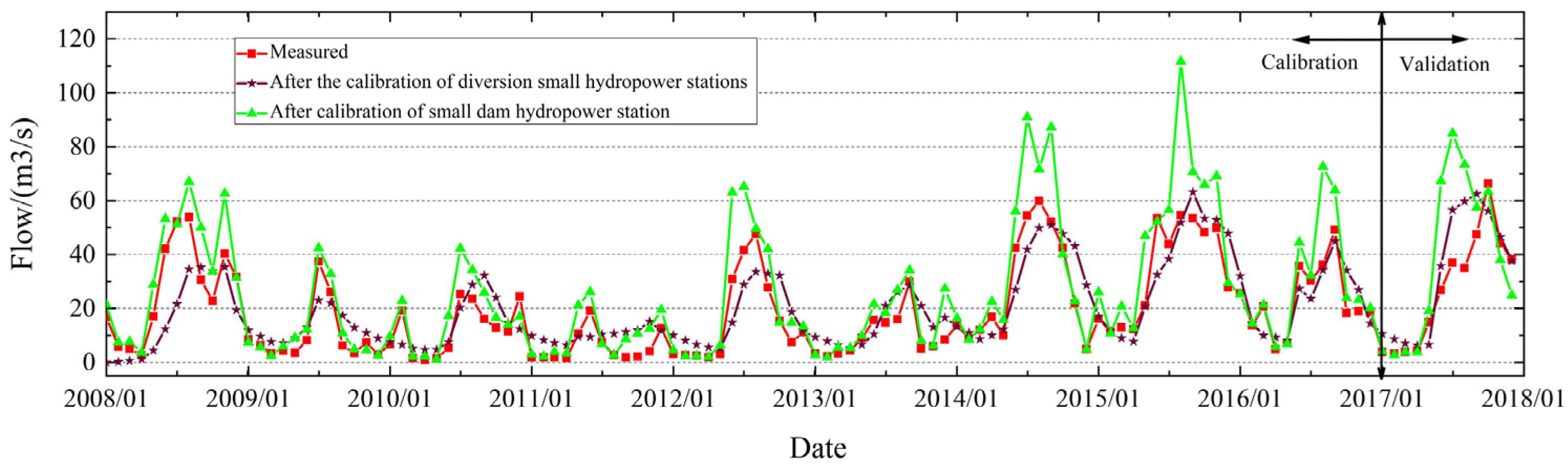
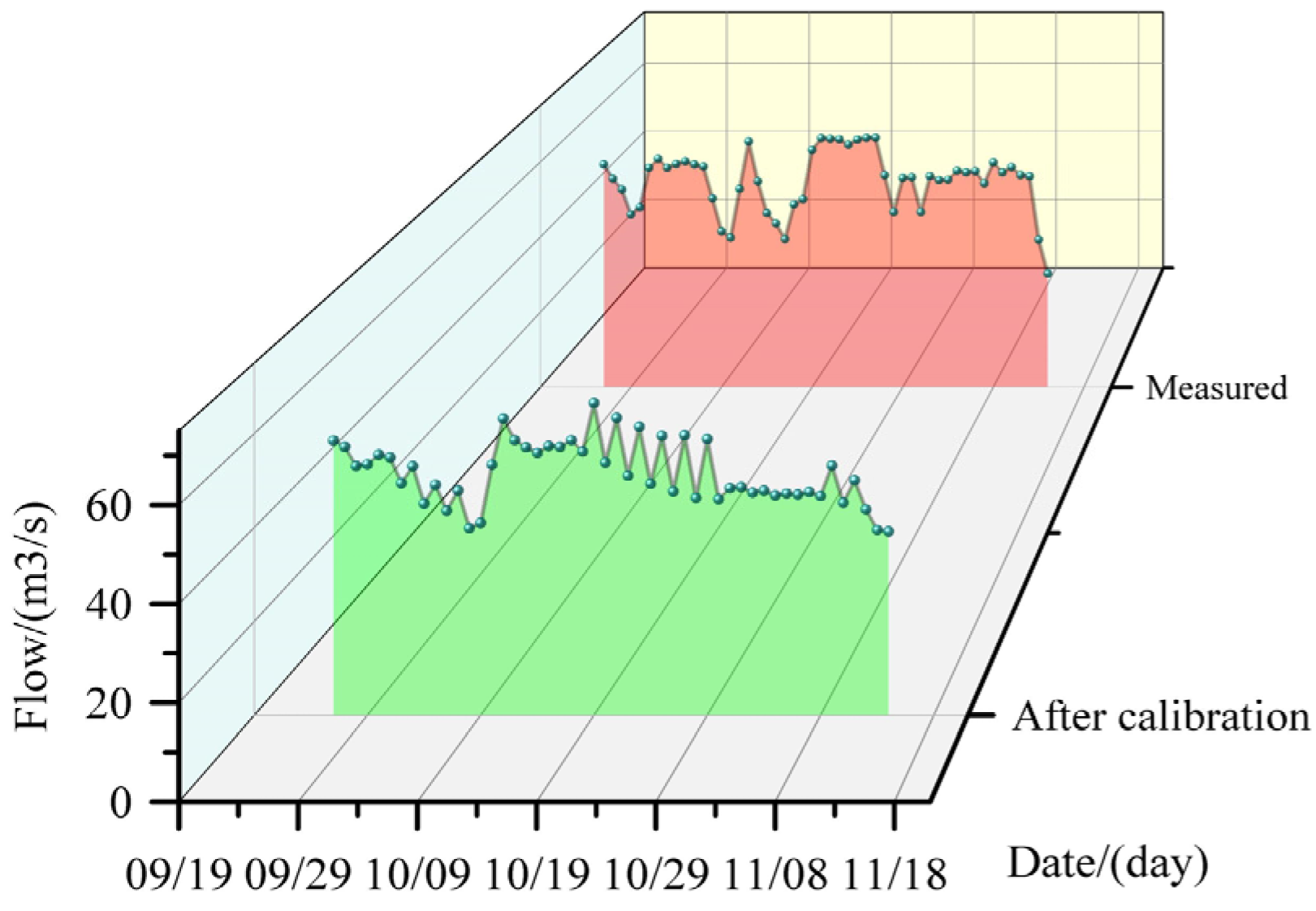
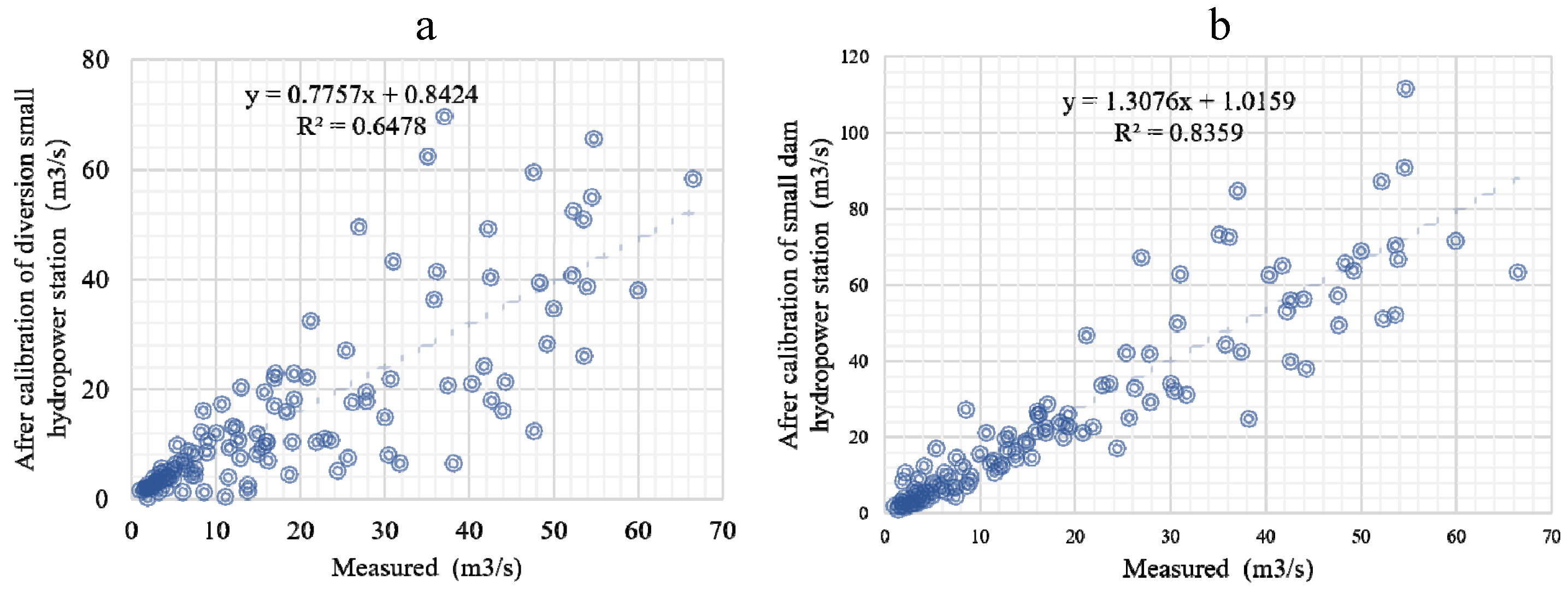
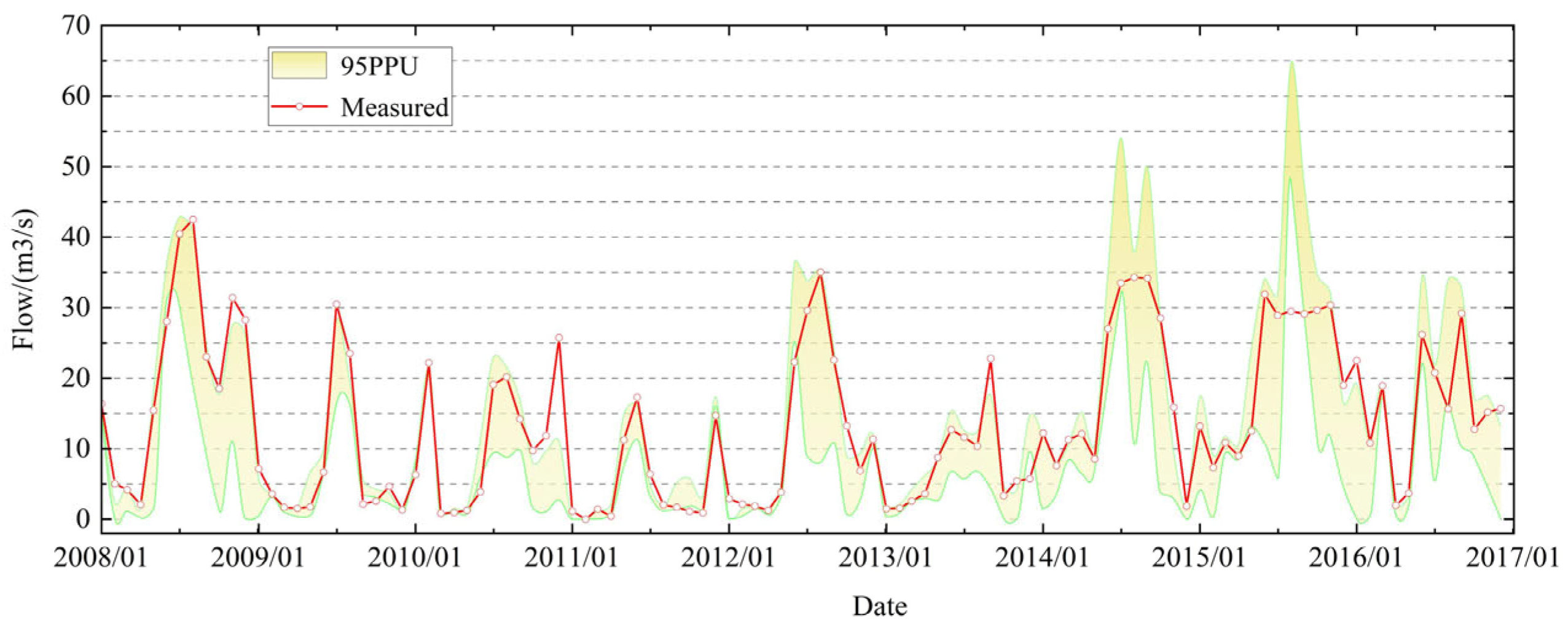
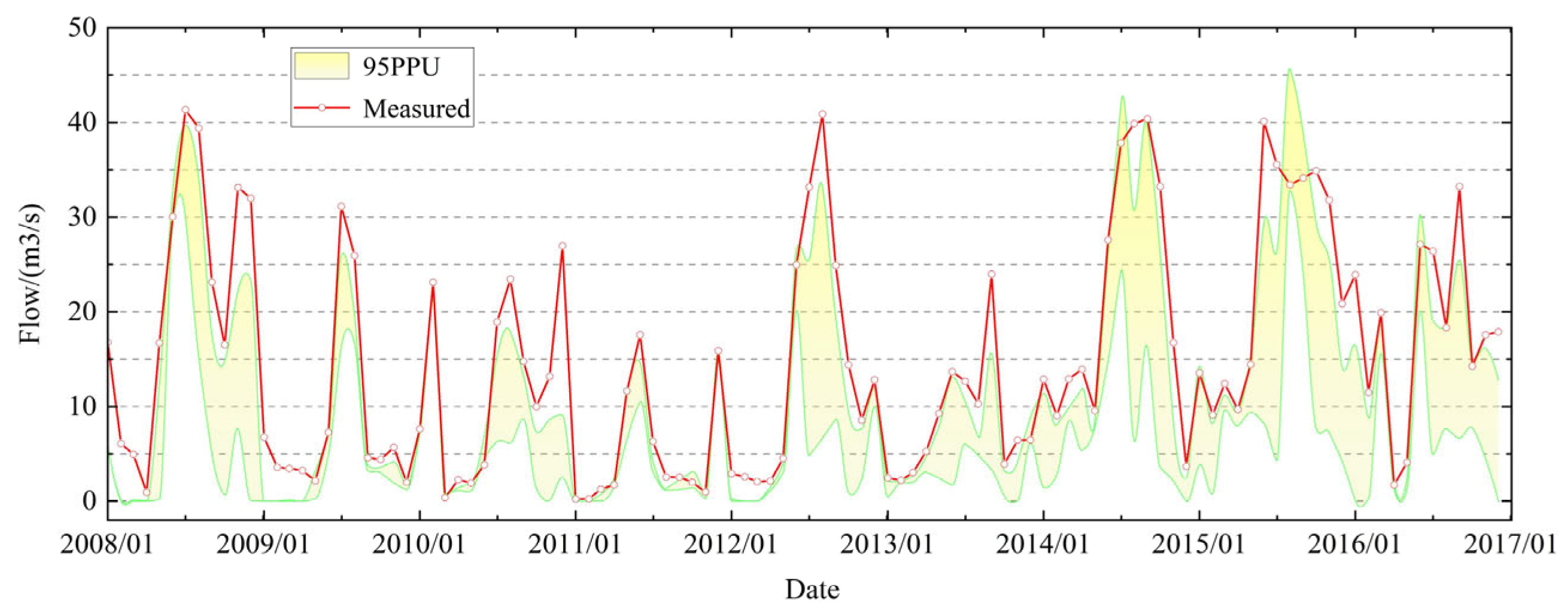
3.2. SWAT Model Calibration and Results Analysis
3.3. Uncertainty Analysis
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ugwu, C.O.; Ozor, P.A.; Mbohwa, C. Small hydropower as a source of clean and local energy in Nigeria: Prospects and challenges. Fuel Commun. 2022, 10, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paish, O. Small hydro power: Technology and current status. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2002, 6, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Silva, D.F.; Galvão Filho, A.R.; Carvalho, R.V.; de Souza, L.; Ribeiro, F.; Coelho, C.J. Water Flow Forecasting Based on River Tributaries Using Long Short-Term Memory Ensemble Model. Energies 2021, 14, 7707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yan, L.; Hang, T.; Feng, J. Stream-Flow Forecasting of Small Rivers Based on LSTM. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.05681v1. [Google Scholar]
- Zaini, N.; Malek, M.A.; Yusoff, M.; Mardi, N.H.; Norhisham, S. Daily River Flow Forecasting with Hybrid Support Vector Machine—Particle Swarm Optimization. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 140, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimeno-Sáez, P.; Senent-Aparicio, J.; Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Pulido-Velazquez, D. A Comparison of SWAT and ANN Models for Daily Runoff Simulation in Different Climatic Zones of Peninsular Spain. Water 2018, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razavi, T.; Coulibaly, P. Improving streamflow estimation in ungauged basins using a multi-modelling approach. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 2668–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horlacher, H.-B.; Cullmann, J.; Awulachew, S.B.; Saliha, A.H. Estimation of flow in ungauged catchments by coupling a hydrological model and neural networks: Case study. Hydrol. Res. 2011, 42, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cao, L.; Feng, R. Hydrological Similarity-Based Parameter Regionalization under Different Climate and Underlying Surfaces in Ungauged Basins. Water 2021, 13, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, R.; Tian, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Duan, Z. Evaluation of TMPA Satellite Precipitation in Driving VIC Hydrological Model over the Upper Yangtze River Basin. Water 2020, 12, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidegger, J.M.; Jackson, C.R.; Muddu, S.; Tomer, S.K.; Filgueira, R. Integration of 2D Lateral Groundwater Flow into the Variable Infiltration Capacity (VIC) Model and Effects on Simulated Fluxes for Different Grid Resolutions and Aquifer Diffusivities. Water 2021, 13, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Guo, J.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D. Future hydropower generation prediction of large-scale reservoirs in the upper Yangtze River basin under climate change. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koycegiz, C.; Buyukyildiz, M. Calibration of SWAT and Two Data-Driven Models for a Data-Scarce Mountainous Headwater in Semi-Arid Konya Closed Basin. Water 2019, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Vaghefi, S.A.; Yang, H.; Srinivasan, R. Global soil, landuse, evapotranspiration, historical and future weather databases for SWAT Applications. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayakrishnan, R.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Arnold, J.G. Advances in the application of the SWAT model for water resources management. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Z.; Nie, Z.; Liu, M. Hydrological Modeling of Karst Watershed Containing Subterranean River Using a Modified SWAT Model: A Case Study of the Daotian River Basin, Southwest China. Water 2021, 13, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonov, Y.A.; Semenova, N.K.; Khristoforov, A.V. Short-Range Streamflow Forecasting of the Kama River Based on the HBV Model Application. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2021, 46, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Li, L.; Xia, J.; Gippel, C.J. A hydrological model modified for application to flood forecasting in medium and small-scale catchments. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.D.; Griensven, A.V.; Liew, M.; et al. SWAT: Model Use, Calibration, and Validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, P.W.; Sadeghi, A.M.; Srinivasan, R. Applications of the SWAT Model Special Section: Overview and Insights. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, K.; Nischal, S. Hydrological Modelling of Small Gauged and Ungauged Mountainous Watersheds Using SWAT—A Case of Western Ghats in India. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2021, 13, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanishka, G.; Eldho, T.I. Streamflow estimation in ungauged basins using watershed classification and regionalization techniques. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 129, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, H.; Lei, X.; Cai, S.; Wu, H.; Ji, X. Hydrological Modeling in the Manas River Basin Using Soil and Water Assessment Tool Driven by CMADS. Teh. Vjesn. Tech. Gaz. 2017, 24, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, J.; Guo, S.; Deng, L.; Yin, J.; Pan, Z.; He, S.; Li, Q. Adaptive optimal allocation of water resources response to future water availability and water demand in the Han River basin, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large Area Hydrologic Modeling And Assessment Part I: Model Development1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kavian, A.; Golshan, M.; Abdollahi, Z. Flow discharge simulation based on land use change predictions. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee Rodgers, J.; Nicewander, W.A. Thirteen Ways to Look at the Correlation Coefficient. Am. Stat. 1988, 42, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudose, N.; Marin, M.; Cheval, S.; Ungurean, C.; Davidescu, S.; Tudose, O.; Alin Lucian, M.; Davidescu, A. SWAT Model Adaptability to a Small Mountainous Forested Watershed in Central Romania. Forests 2021, 12, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Dias, V.; da Pereira Luz, M.; Medero, G.M.; Tarley Ferreira Nascimento, D.; de Nunes Oliveira, W.; de Rodrigues Oliveira Merelles, L. Historical Streamflow Series Analysis Applied to Furnas HPP Reservoir Watershed Using the SWAT Model. Water 2018, 10, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data | Source | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| DEM | Geospatial Data | 30 m × 30 m |
| land use | CAS | 1 km |
| Land cover | HWSD | 1 km |
| Meteorological data | CMADS | Month/day |
| Parameter | Meaning | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| the final soil water content | mm | |
| the initial soil water content | mm | |
| daily rainfall | mm | |
| daily evapotranspiration | mm | |
| daily surface runoff | mm | |
| daily percolation | mm | |
| daily lateral flow | mm |
| Name and Code | Area (Hectare) | Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Forest land (FRST) | 57,803.52 | 37.24 |
| Cultivated land (AGRL) | 78,128.10 | 50.34 |
| Grassland (PAST) | 18,865.81 | 12.16 |
| Residential land (URBN) | 268.25 | 0.17 |
| Waters (WATR) | 132.46 | 0.09 |
| Parameter | Meaning | Initial Range | Modification Method | Optimal Parameter | p-Value | t-Stat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN2 | Initial SCS runoff curve number for moisture condition II | 35–98 | v | 96.24 | 0 | 27.73 |
| CANMX | Maximum canopy storage | 0–100 | v | 98.40 | 0 | 3.86 |
| SQL_AWC | Available water capacity of the soil layer | 0–1 | r | 0.02 | 0.37 | 0.88 |
| ESCO | Soil evaporation compensation factor | 0–1 | v | 0.72 | 0.57 | 0.56 |
| REVAPMN | Threshold depth of water in the shallow aquifer for “revap” or percolation to the deep aquifer to occur | 0–500 | v | 253.51 | 0.61 | 0.50 |
| ALPHA_BF | Base flow alpha factor | 0–1 | v | 0.52 | 0.28 | −1.07 |
| EPCO | Plant uptake compensation factor | 0–1 | v | 0.18 | 0.21 | −1.24 |
| GWQMN | Threshold depth of water in the shallow aquifer required for return flow to occur | 0–4500 | v | 3139.44 | 0.16 | −1.40 |
| GW_REVAP | Ground water “revap” coefficient | 0.02–0.2 | r | 0.09 | 0.05 | −1.90 |
| Station | NSE | |
|---|---|---|
| MH | 0.74 | 0.84 |
| NW | 0.73 | 0.78 |
| Station | p-Factor | r-Factor |
|---|---|---|
| MH | 0.30 | 0.55 |
| NW | 0.68 | 0.75 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, S.; Zhu, Y. Prediction of the Discharge Flow in a Small Hydropower Station without Hydrological Data Based on SWAT Model. Water 2022, 14, 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132011
Xie S, Zhu Y. Prediction of the Discharge Flow in a Small Hydropower Station without Hydrological Data Based on SWAT Model. Water. 2022; 14(13):2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132011
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Shenghuo, and Yun Zhu. 2022. "Prediction of the Discharge Flow in a Small Hydropower Station without Hydrological Data Based on SWAT Model" Water 14, no. 13: 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132011
APA StyleXie, S., & Zhu, Y. (2022). Prediction of the Discharge Flow in a Small Hydropower Station without Hydrological Data Based on SWAT Model. Water, 14(13), 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132011





