Tetracycline Degradation by Peroxydisulfate Activated by Waste Pulp/Paper Mill Sludge Biochars Derived at Different Pyrolysis Temperature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Characterization of Biochar
2.3. Catalytic Degradation Experiments
2.4. Experiments for Mechanism Exploration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of SBCs
3.2. Degradation Performance
3.3. Mechanisms on PDS Activation by SBCs
3.3.1. Free Radical Pathway
3.3.2. Non-Radical Pathway
3.4. Optimum Conditions for Degradation of TC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xing, X.J.; Huang, L.; Zhao, S.J.; Xiao, J.F.; Lan, M.H. S,N-Doped carbon dots for tetracyclines sensing with a fluorometric spectral response. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aga, D.S.; Seamus, O.C.; Steve, E.; José, P.O.; Daniel, S.; David, T. Determination of the persistence of tetracycline antibiotics and their degradates in manure-amended soil using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7165–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.L.; Chen, T.H.; Chen, D.; Zou, X.H.; Li, M.X.; Huang, F.J.; Sun, F.W.; Wang, C.; Shu, D.B.; Liu, H.B. Sulfurized oolitic hematite as a heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst for tetracycline antibiotic degradation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 260, 118203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, N.A.; Holst, S.V.; Schmitt, H.; Zaan, B.M.V.D.; Gerritsen, H.W.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Langenhoff, A.A.M. Fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes during conventional and additional treatment technologies in wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Evolution of antibiotic resistance at non-lethal drug concentrations. Drug Resist. Update 2012, 15, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Huang, F.L.; Zeng, G.M.; Huang, D.L.; Qin, L.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, C.; Li, B.S.; Yi, H.; Liu, S.Y.; et al. Fabrication of novel magnetic MnFe2O4/biochar composite and heterogeneous photo-Fenton degradation of tetracycline in near neutral pH. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.S.; Liu, G.C.; Ma, X.H.; Gong, J.X.; Ma, B.R.; Yan, Q.H.; Chen, Q.H.; Ma, D.; Zhang, G.S.; Gao, M.C.; et al. High efficiency heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst biochar modified CuFeO2 for the degradation of tetracycline: Economical synthesis, catalytic performance and mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 280, 119386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.M.; Peng, Z.L.; Wang, W.; Cai, Y.C.; Tan, F.T.; Wang, X.Y.; Qiao, X.L. Facile preparation of MgO-loaded SiO2 nanocomposites for tetracycline removal from aqueous solution. Powder Technol. 2019, 347, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Gómez-Pacheco, C.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; López-Peñalver, J.J. Kinetic study of tetracycline adsorption on sludge-derived adsorbents in aqueous phase. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 213, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Ma, Y.L.; Li, C.E.; Xu, M. Removal of tetracycline residue from pharmaceutical wastewater by using 3D composite film. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.M.; Peng, Z.L.; Wang, W.; Cai, Y.C.; Tan, F.T.; Wang, X.Y.; Qiao, X.L.; Wong, P.K. Enhanced dark adsorption and visible-light-driven photocatalytic properties of narrower-band-gap Cu2S decorated Cu2O nanocomposites for efficient removal of organic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 384, 121302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.L.; Yue, Q.Y.; Kong, J.J.; Zhao, P.; Gao, Y.; Fu, K.F.; Gao, B.Y. Microbial diversity in combined UAF–UBAF system with novel sludge and coal cinder ceramic fillers for tetracycline wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.L.; He, J.Y.; Zhang, K.S.; Liu, T.; Xu, W.; Huang, X.J.; Kong, L.T.; Liu, J.H. Morphology-tunable WMoO nanowire catalysts for the extremely efficient elimination of tetracycline: Kinetics, mechanisms and intermediates. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Q.; He, X.X.; Fu, Y.S.; Dionysiou, D.D. Degradation kinetics and mechanism of oxytetracycline by hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.G.; Sun, H.Q.; Shao, Z.P.; Wang, S.B. Nonradical reactions in environmental remediation processes: Uncertainty and challenges. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 224, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmez-Hanci, T.; Arslan-Alaton, I. Comparison of sulfate and hydroxyl radical based advanced oxidation of phenol. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 224, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, R.; Tlili, S.; Chiron, S.; Barbati, S. Removal of carbamazepine from urban wastewater by sulfate radical oxidation. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2011, 9, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, J.; Chen, H.; Sun, H. Persulfate activation with sawdust biochar in aqueous solution by enhanced electron donor-transfer effect. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Astruc, D. The recent development of efficient Earth-abundant transition-metal nanocatalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 816–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, S.; Zuo, X.; Huang, Y.; Cai, T.; Ding, D. Biochar modification significantly promotes the activity of Co3O4 towards heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsanam, P.; Peeters, E.; Makshina, E.V.; Parvulescu, V.I.; Sels, B.F. Advances in porous and nanoscale catalysts for viable biomass conversion. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2366–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H. Burgeoning prospects of biochar and its composite in persulfate-advanced oxidation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhong, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H.; Cao, X. Roles of the mineral constituents in sludge-derived biochar in persulfate activation for phenol degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mian, M.M.; Liu, G. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by chemically modified sludge biochar for the removal of organic pollutants: Understanding the role of active sites and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 392, 123681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.L.; Guo, W.Q.; Wang, H.Z.; Du, J.S.; Wu, Q.L.; Chang, J.S.; Ren, N.Q. Singlet oxygen-dominated peroxydisulfate activation by sludge-derived biochar for sulfamethoxazole degradation through a nonradical oxidation pathway: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liao, Z.W.; Ifthikar, J.; Shi, L.R.; Du, Y.N.; Zhu, J.Y.; Xi, S.; Chen, Z.Q.; Chen, Z.L. Treatment of refractory contaminants by sludge-derived biochar/persulfate system via both adsorption and advanced oxidation process. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.C.; Jiang, J.; Huang, G.X.; Yu, H.Q. Sludge biochar-based catalysts for improved pollutant degradation by activating peroxymonosulfate. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 8978–8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Duan, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Ren, N.; Ho, S.H. Graphitic biochar catalysts from anaerobic digestion sludge for nonradical degradation of micropollutants and disinfection. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Preparation, modification and environmental application of biochar: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 1002–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluchamy, C.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Enhancement of hydrolysis of lignocellulose waste pulp and paper mill sludge through different heating processes on thermal pretreatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Z.; Huang, D.L.; Liu, Y.G.; Zhang, C.; Lai, C.; Wang, X.; Zeng, G.M.; Gong, X.M.; Duan, A.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Recent advances in biochar-based catalysts: Properties, applications and mechanisms for pollution remediation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 380–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, G.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ok, Y.S.; An, T. Persistent free radicals in carbon-based materials on transformation of refractory organic contaminants (ROCs) in water: A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 137, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, R.; Deng, R.; Luo, H.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, C. Mn doped magnetic biochar as persulfate activator for the degradation of tetracycline. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatalo, S.; Repo, E.; Makila, E.; Salonen, J.; Vakkilainen, E.; Sillanpaa, M. Adsorption behavior of hydrothermally treated municipal sludge & pulp and paper industry sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, R.N.; Calisto, V.; Ferreira, C.I.A.; Esteves, V.I.; Otero, M. Removal of pharmaceuticals from municipal wastewater by adsorption onto pyrolyzed pulp mill sludge. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 3611–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devi, P.; Saroha, A.K. Synthesis of the magnetic biochar composites for use as an adsorbent for the removal of pentachlorophenol from the effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisto, V.; Ferreira, C.I.A.; Santos, S.M.; Gil, M.V.; Otero, M.; Esteves, V.I. Production of adsorbents by pyrolysis of paper mill sludge and application on the removal of citalopram from water. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaukura, N.; Murimba, E.C.; Gwenzi, W. Synthesis, characterisation and methyl orange adsorption capacity of ferric oxide–biochar nano-composites derived from pulp and paper sludge. Appl. Water Sci. 2016, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.X.; Zhao, B.W.; Ma, F.F.; Duan, K.X.; Philippe, B.; Liu, H. Adsorption characteristics and mechanism of tetracycline on paper sludge biochar. Chinese Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 3821–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Oh, W.D.; Lim, T.T. Graphene- and CNTs-based carbocatalysts in peroxysulfates activation: Material design and catalytic mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 941–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.X.; Wang, L.; Ma, X.L.; Lian, R.; Huang, J.W.; She, H.D.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, Q.Z. Construction of hierarchical ZnIn2S4@PCN-224 heterojunction for boosting photocatalytic performance in hydrogen production and degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 284, 119762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Lin, H.; Zhao, J.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by sewage sludge biochar-based catalyst for efficient removal of bisphenol A: Performance and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 272, 118909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.D.; Harris, W. Properties of dairy-manure-derived biochar pertinent to its potential use in remediation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5222–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazetta, A.L.; Zhang, T.; Silva, T.L.; Almeida, V.C.; Asefa, T. Bone char-derived metal free N- and S-co-doped nanoporous carbon and its effificient electrocatalytic activity for hydrazine oxidation. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2018, 225, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cao, X.D.; Masek, O.; Zimmerman, A. Heterogeneity of biochar properties as a function of feed stock sources and production temperatures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 256–257, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, Y.; Chen, C.S.; Tu, Y.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Zhang, H. Heterogeneous degradation of organic pollutants by persulfate activated by CuO-Fe3O4: Mechanism, stability, and effects of pH and bicarbonate ions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6838–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Li, M.Q.; Wang, C.H.; Zhang, M.; Khan, M.A.N.; Sun, X.Y.; Shen, J.Y.; Han, W.Q.; Wang, L.J.; Li, J.S. Singlet oxygen-dominated non-radical oxidation process for efficient degradation of bisphenol A under high salinity condition. Water Res. 2019, 148, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chen, T.; Huang, Q.X.; Zhan, M.X.; Li, X.D.; Yan, J.H. Activation of persulfate by CO2-activated biochar for improved phenolic pollutant degradation: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Ghanbari, F. Combination of UVC-LEDs and ultrasound for peroxymonosulfate activation to degrade synthetic dye: Influence of promotional and inhibitory agents and application for real wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 6003–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Bai, S.W.; Li, R.X.; Su, G.Y.; Duan, X.G.; Wang, S.B.; Ren, N.Q.; Ho, S.H. Magnetic biochar catalysts from anaerobic digested sludge: Production, application and environment impact. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.G.; Sun, H.Q.; Wang, S.B. Metal-free carboncatalysis in advanced oxidation reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.F.; Tang, L.; Pang, Y.; Zeng, G.M.; Wang, J.J.; Deng, Y.C.; Liu, Y.N.; Feng, H.P.; Chen, S.; Ren, X.Y. Magnetic nitrogen-doped sludge-derived biochar catalysts for peroxydisulfate activation: Internal electron transfer mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 364, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.S.; Huang, X.C.; Ma, F.; Wang, L.; Duan, X.G.; Wang, S.B. Catalytic removal of aqueous contaminants on N-doped graphitic biochars: Inherent roles of adsorption and nonradical mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8649–8658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Jin, P. A new application pattern for sldge-derived biochar adsorbent: Ideal persulfate activator for the high-efficiency mineralization of pollutants. J. Hazad. Mater. 2021, 419, 126343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.; Lo, S.L.; Kuo, J.; Huang, C.P. Promoted degradation of perfluorooctanic acid by peroxydisulfate when adding activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Z.J.; Li, X.M.; Wang, D.B.; Xu, Q.X.; Tao, Z.; Huang, X.D.; Yao, F.B.; Wu, Y.; He, L.; Yang, Q. Persulfate activation by oxidation biochar supported magnetite particles for tetracycline removal: Performance and degradation pathway. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
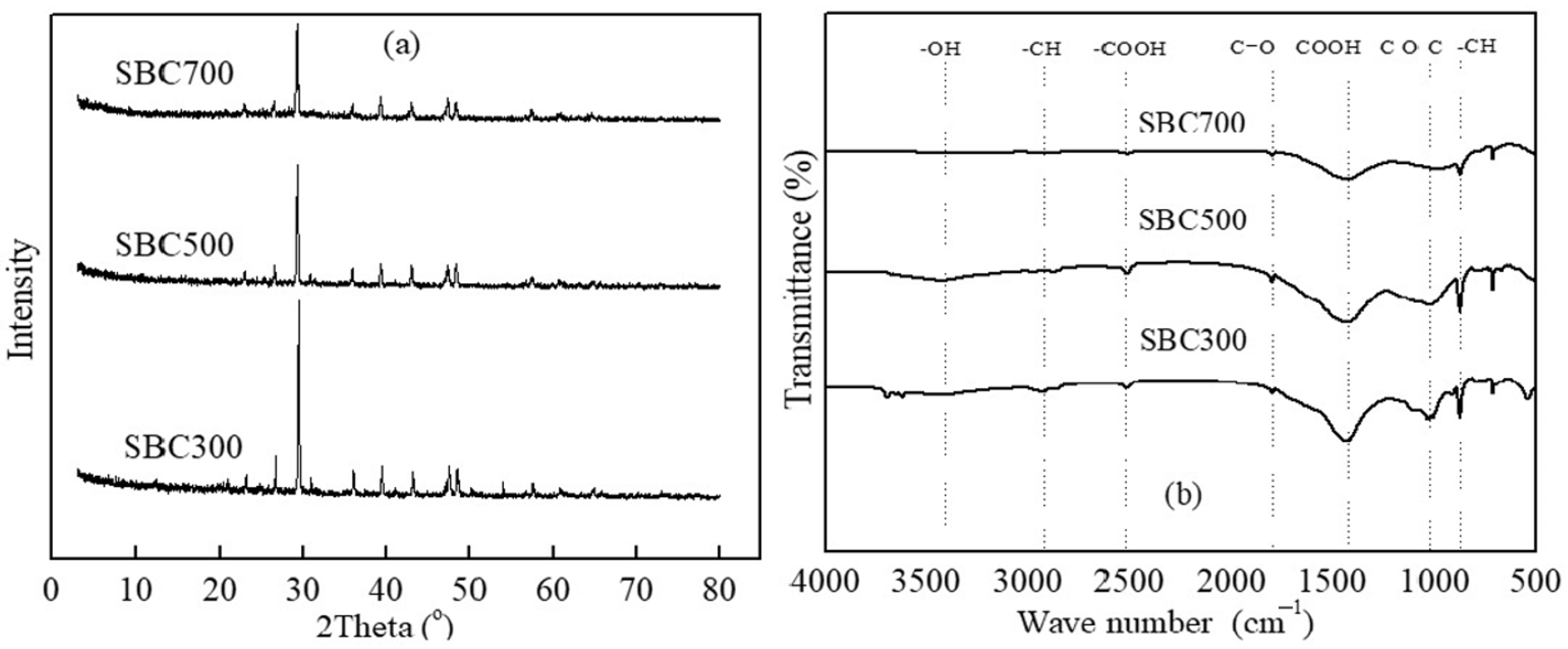
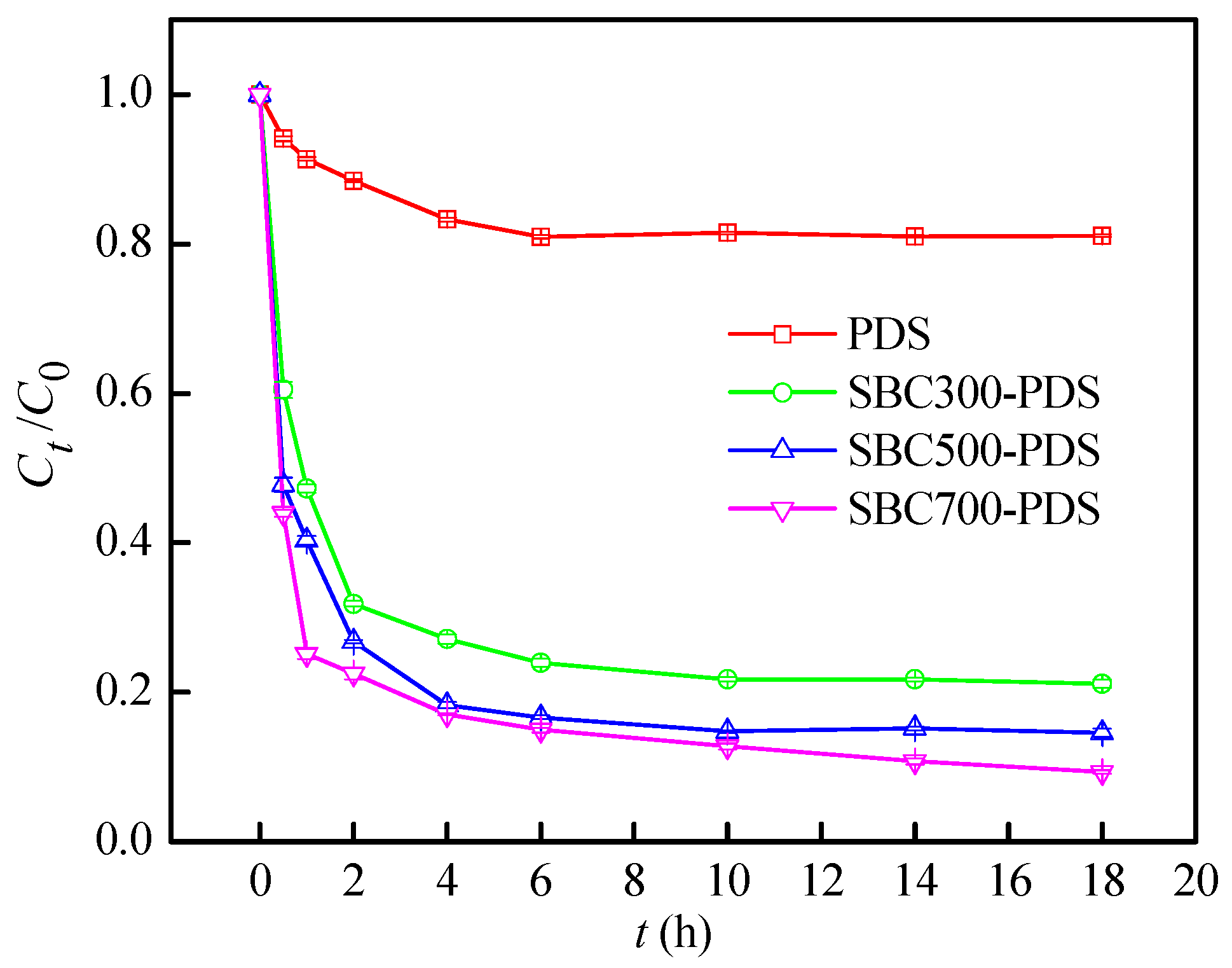

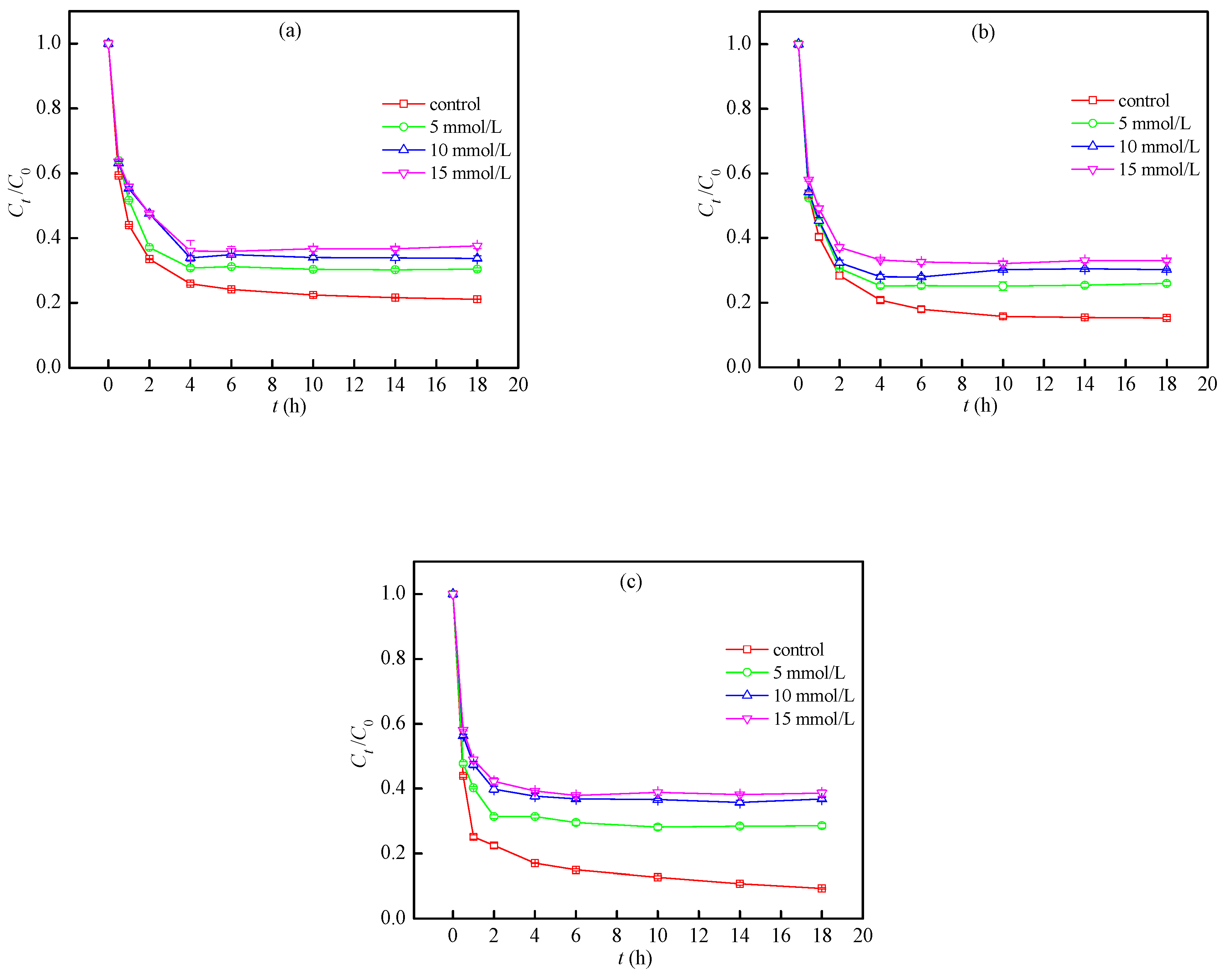
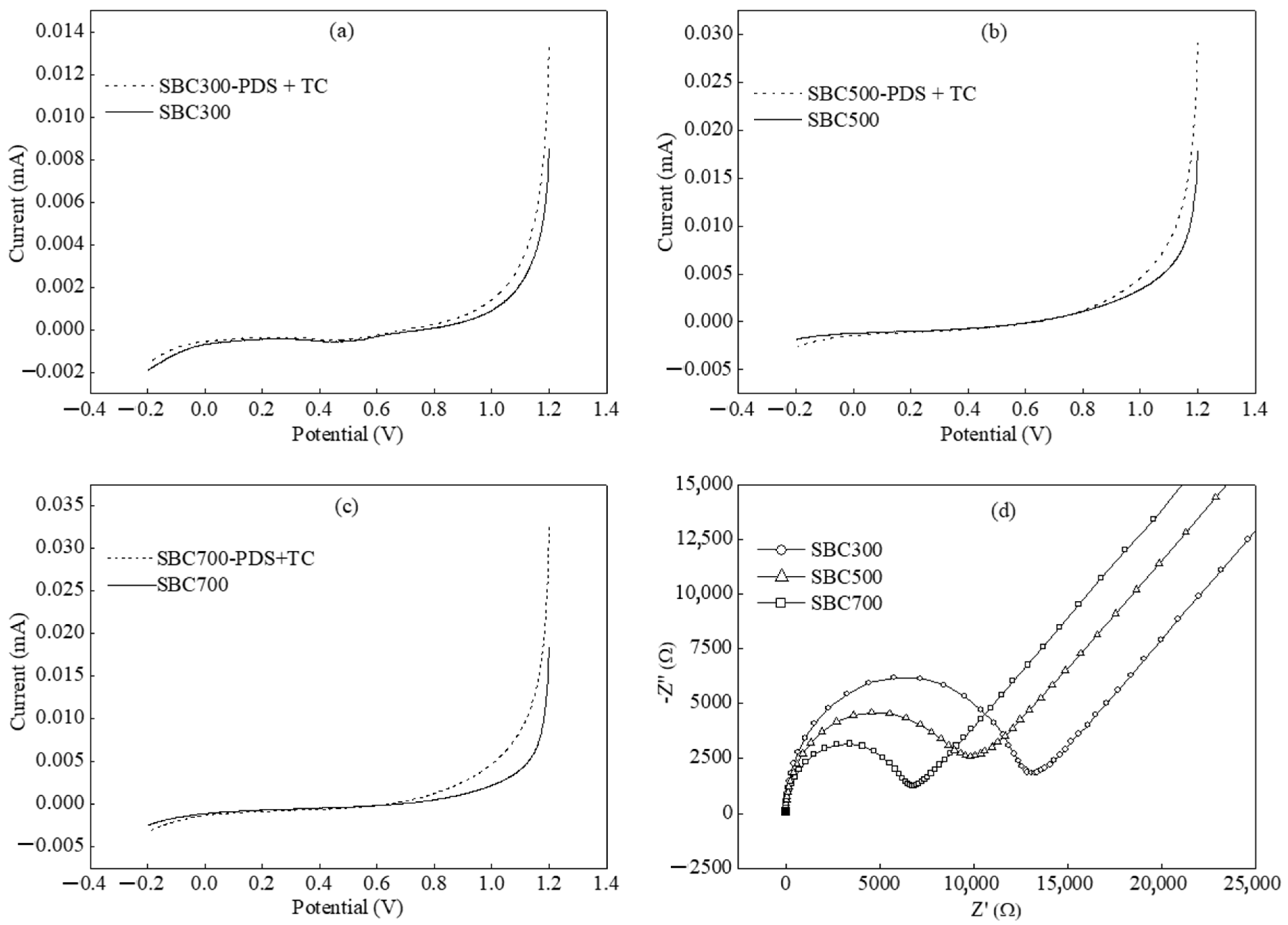
| Biochar | Elemental Composition (wt%) | H/C | O/C | (N+O)/C | pHpzc | Specific Area (m2/g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | H | O | ||||||
| SBC300 | 19.98 | 1.64 | 1.95 | 19.84 | 1.17 | 0.74 | 0.82 | 7.98 | 7.12 |
| SBC500 | 15.96 | 0.67 | 0.43 | 19.93 | 0.32 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 9.25 | 32.82 |
| SBC700 | 14.11 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 15.99 | 0.25 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 9.87 | 37.80 |
| Condition | SBC300-PDS | SBC500-PDS | SBC700-PDS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar dosage (g/L) | 0.5 | 62.2 ± 0.97 | 72.8 ± 1.21 | 76.0 ± 0.32 |
| 1.0 | 78.9 ± 0.54 | 85.7 ± 0.96 | 90.7 ± 0.23 | |
| 2.0 | 80.6 ± 0.23 | 87.6 ± 0.09 | 92.5 ± 0.41 | |
| 3.0 | 82.6 ± 0.31 | 89.8 ± 0.18 | 95.9 ± 0.64 | |
| PDS dosage (nPDS: nTC) | 50:1 | 66.6 ± 0.39 | 74.2 ± 0.79 | 83.8 ± 0.23 |
| 100:1 | 78.9 ± 0.54 | 85.7 ± 0.96 | 90. 7 ± 0.23 | |
| 200:1 | 80.4 ± 0.47 | 86.8 ± 0.55 | 91.7 ± 0.55 | |
| 300:1 | 79.3 ± 0.54 | 86.8 ± 0.55 | 91.8 ± 0.41 | |
| Initial pH value | 3 | 82.8 ± 0.77 | 87.9 ± 0.70 | 94.1 ± 0.67 |
| 5 | 79.7 ± 0.54 | 83.1 ± 0.55 | 88.2 ± 0.54 | |
| 7 | 78.9 ± 0.54 | 85.7 ± 0.96 | 90.7 ± 0.11 | |
| 9 | 78.0 ± 0.23 | 84.3 ± 0.67 | 87.6 ± 0.41 | |
| 11 | 59.2 ± 0.41 | 71.9 ± 0.81 | 83.8 ± 0.64 | |
| Biochar reuse (run) | 1 | 79.5 ± 0.87 | 86.6 ± 0.79 | 89.4 ± 0.72 |
| 2 | 74.2 ± 0.76 | 82.5 ± 0.69 | 84.7 ± 0.77 | |
| 3 | 66.4 ± 0.58 | 72.1 ± 0.32 | 76.9 ± 0.96 | |
| 4 | 52.8 ± 0.77 | 63.5 ± 0.55 | 71.5 ± 0.69 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, B.; Zhang, J. Tetracycline Degradation by Peroxydisulfate Activated by Waste Pulp/Paper Mill Sludge Biochars Derived at Different Pyrolysis Temperature. Water 2022, 14, 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14101583
Zhao B, Zhang J. Tetracycline Degradation by Peroxydisulfate Activated by Waste Pulp/Paper Mill Sludge Biochars Derived at Different Pyrolysis Temperature. Water. 2022; 14(10):1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14101583
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Baowei, and Juanxiang Zhang. 2022. "Tetracycline Degradation by Peroxydisulfate Activated by Waste Pulp/Paper Mill Sludge Biochars Derived at Different Pyrolysis Temperature" Water 14, no. 10: 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14101583
APA StyleZhao, B., & Zhang, J. (2022). Tetracycline Degradation by Peroxydisulfate Activated by Waste Pulp/Paper Mill Sludge Biochars Derived at Different Pyrolysis Temperature. Water, 14(10), 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14101583






