Monthly Precipitation Forecasts Using Wavelet Neural Networks Models in a Semiarid Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
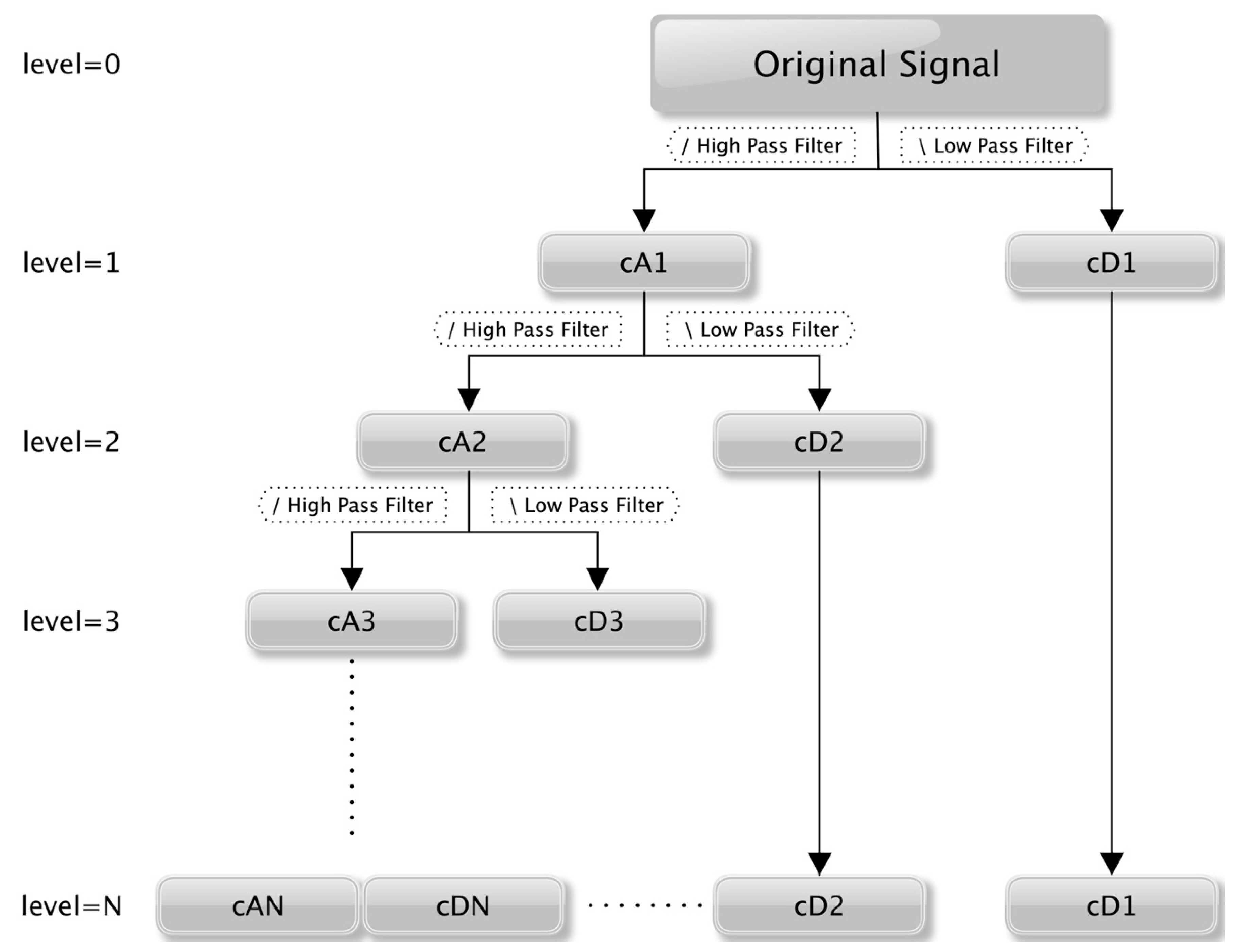
1.1. Wavelet Multiscale Analysis
1.2. Availability of Short-Term Meteorological Series
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Data
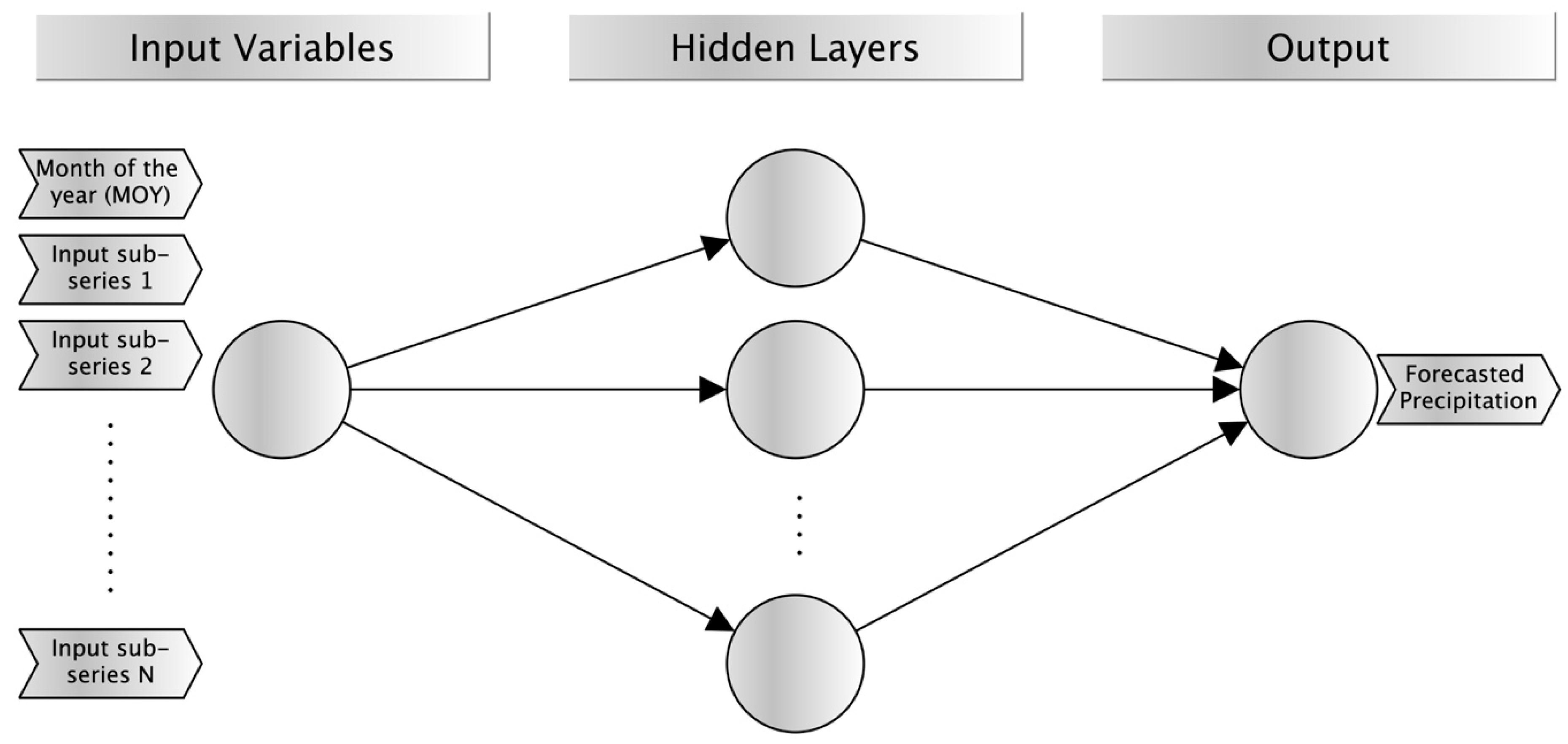
2.2. Development of Wavelet Neural Network (WNN) Models
2.3. Statistical Analysis and Performance Criteria
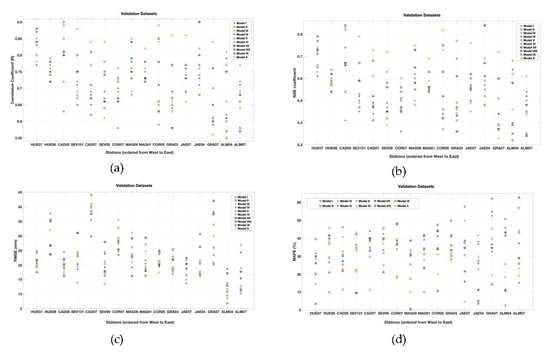
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pre-Processing Input Datasets
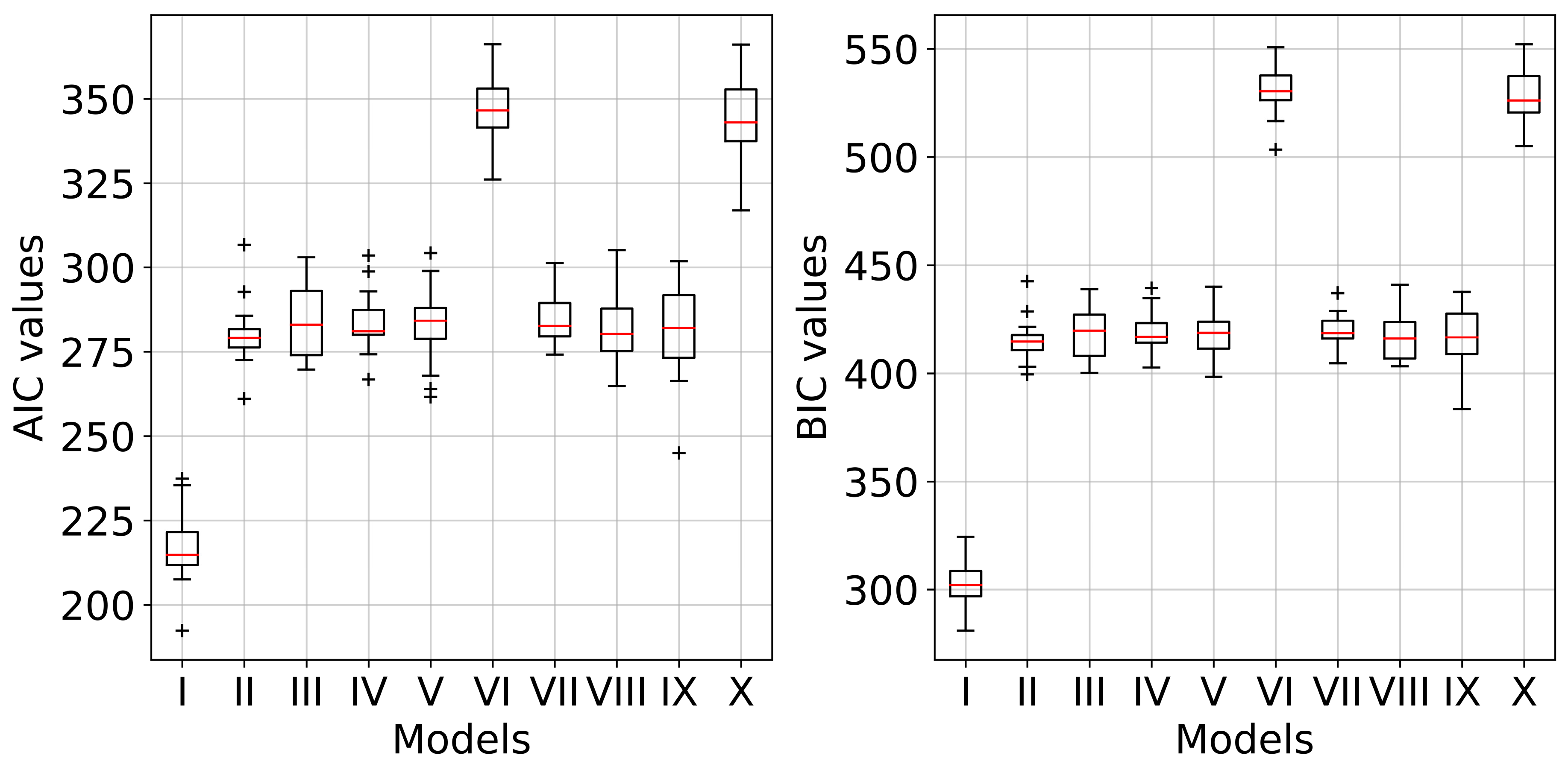
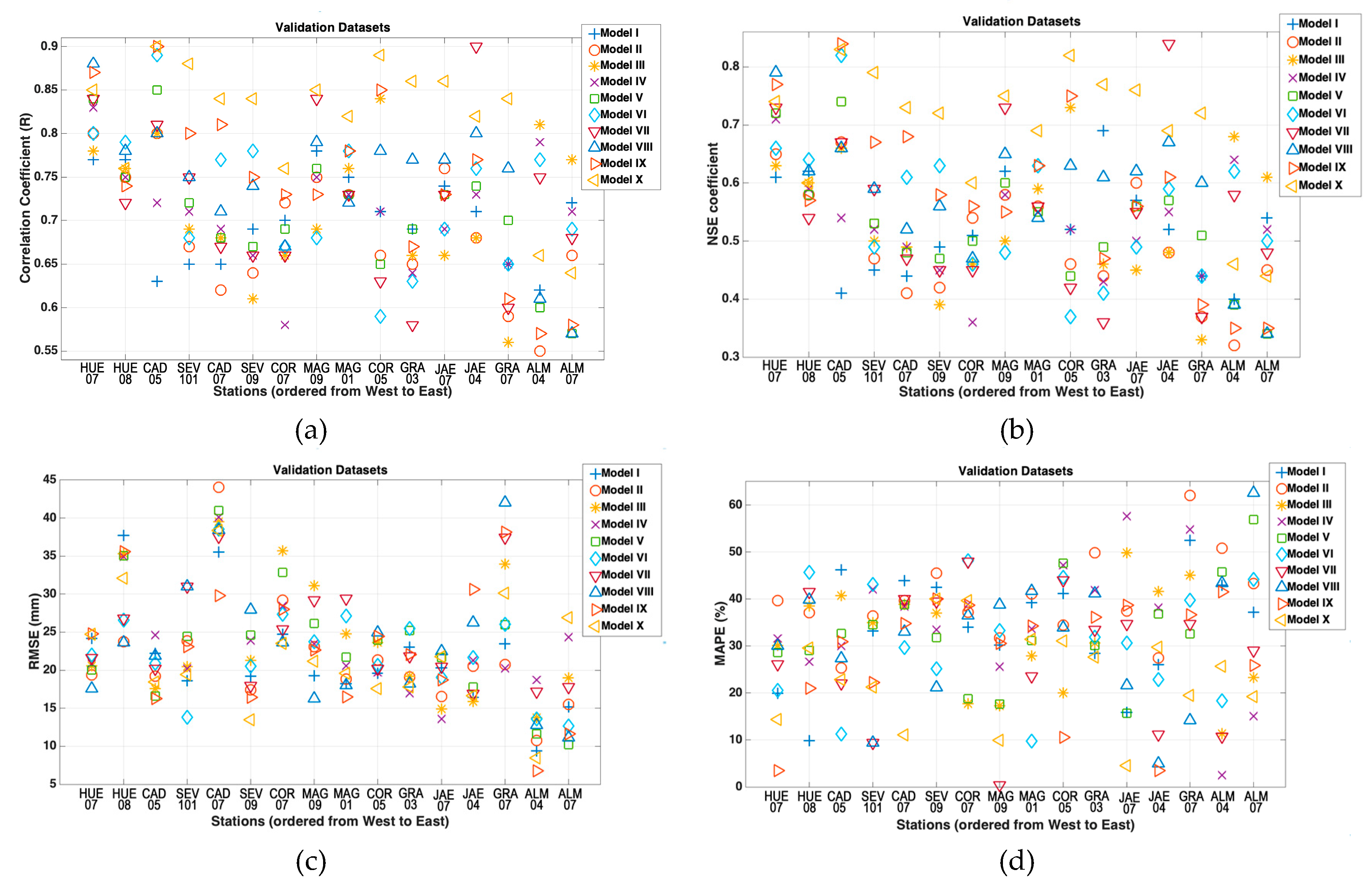
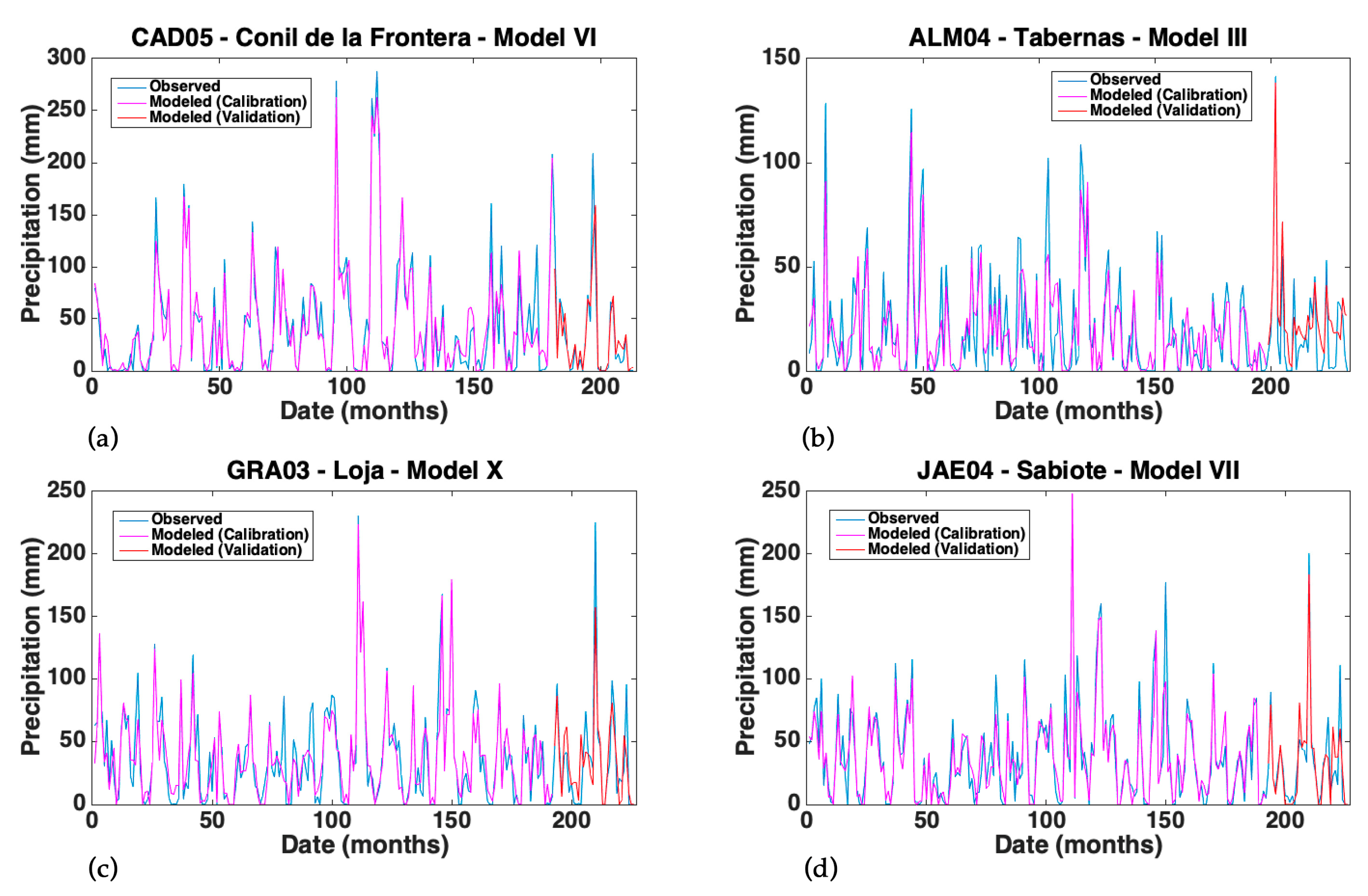
3.2. Performance of the Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Linnerud, K.; Mideksa, T.K.; Eskeland, G.S. The impact of climate change on nuclear power supply. Energy J. 2011, 32, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wu, J. Hybrid PSO and GA for neural network evolutionary in monthly rainfall forecasting. In Asian Conference on Intelligent Information and Database Systems; Selamat, A., Nguyen, N.T., Haron, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 7802, pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Zou, Y.; Liu, X.; Linge, N. A survey on rainfall forecasting using artificial neural network. Int. J. Embed. Syst. 2019, 11, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, A.; Bae, D.-H. Application of artificial neural networks for accuracy enhancements of real-time flood forecasting in the Imjin Basin. Water 2018, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, K.; Ghumman, A.R.; Haider, H.; Ghazaw, Y.M.; Shafiquzzaman, M. Future predictions of rainfall and temperature using GCM and ANN for arid regions: A case study for the Qassim Region, Saudi Arabia. Water 2018, 10, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghim, S.; Bras, R.L. Bias correction of climate modeled temperature and precipitation using artificial neural networks. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1867–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S.; Xu, X.; Braithwaite, D.; Verbist, K.M. Bias adjustment of satellite-based precipitation estimation using Gauge Observations—A case study in Chile. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 3790–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crochemore, L.; Ramos, M.H.; Pappenberger, F. Bias correcting precipitation forecasts to improve the skill of seasonal streamflow forecasts. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3601–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, M.C.V.; de Campos Velho, H.F.; Ferreira, N.J. Artificial neural network technique for rainfall forecasting applied to the São Paulo region. J. Hydrol. 2005, 301, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darji, M.; Dabhi, V.; Prajapati, H. Rainfall forecasting using neural network: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Advances in Computer Engineering and Applications (IEEE), Ghaziabad, India, 19–20 March 2015; pp. 706–707. [Google Scholar]
- Nanda, S.K.; Tripathy, D.P.; Nayak, S.K.; Mohapatra, S. Prediction of rainfall in India using Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2013, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, G.; Selvaraj, R.S. Prediction of monthly rainfall in Chennai using back propagation neural network model. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2011, 3, 211–213. [Google Scholar]
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.R.; Dandy, G.C. The use of artificial neural networks for the prediction of water quality parameters. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, M.; Krajewski, W.; Cuykendall, R. Rainfall forecasting in space and time using a neural network. J. Hydrol. 1992, 137, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.; Sudheer, K.; Jain, S.; Agarwal, P. Rainfall-runoff modelling using artificial neural networks: Comparison of network types. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 1277–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, D.A.K.; Jayawardena, A.W. Runoff forecasting using RBF networks with OLS algorithm. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1998, 3, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, C.; Wilby, R. An artificial neural network approach to rainfall-runoff modeling. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1998, 43, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.I.; Kim, Y.-O. Rainfall-runoff models using artificial neural networks for ensemble streamflow prediction. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 3819–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riad, S.; Mania, J.; Bouchaou, L.; Najjar, Y. Predicting catchment flow in a semi-arid region via an artificial neural network technique. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 2387–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birikundavyi, S.; Labib, R.; Trung, H.T.; Rousselle, J. Performance of neural networks in daily streamflow forecasting. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2002, 7, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.; Loucks, P.; Stedinger, J. Artificial neural network models of watershed nutrient loading. Water Res. Manag. 2012, 26, 2781–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, I.; Bai, C.-G. Application of artificial neural network for water quality management. Lowl. Technol. Int. 2003, 5, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Nourani, V.; Mousavi, S. Spatiotemporal groundwater level modeling using hybrid artificial intelligence-meshless method. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talei, A.; Chua, L.H.C.; Wong, T.S. Evaluation of rainfall and discharge inputs used by Adaptive Network-based Fuzzy Inference Systems (ANFIS) in rainfall–runoff modeling. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Lineros, M.; Estévez, J.; Giráldez, J.V.; Madueño, A. A new quality control procedure based on non-linear autoregressive neural network for validating raw river stage data. J. Hidrol. 2014, 510, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciuto, G.; Bonaccorso, B.; Cancelliere, A.; Rossi, G. Quality control of daily rainfall data with neural networks. J. Hydrol. 2009, 364, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, R. Artificial Neural Networks in hydrology. II: Hydrologic applications. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2000, 5, 124–137. [Google Scholar]
- Govindaraju, R. Artificial neural networks in hydrology. I: Preliminary concepts. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2000, 5, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Oyebode, O.; Stretch, D. Neural network modeling of hydrological systems: A review of implementation techniques. Nat. Resour. Model. 2019, 32, e12189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, N.Q.; Babel, M.S.; Weesakul, S.; Tripathi, N. An artificial neural network model for rainfall forecasting in Bangkok, Thailand. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustris, K.P.; Larissi, I.K.; Nastos, P.T.; Paliatsos, A.G. Precipitation forecast using artificial neural networks in specific regions of Greece. Water Res. Manag. 2011, 25, 1979–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, C.G.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, N.W.; Kim, H. Application of artificial neural networks to rainfall forecasting in the Geum River basin, Korea. Water 2018, 10, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbot, J.; Marohasy, J. Forecasting of medium-term rainfall using Artificial Neural Networks: Case studies from Eastern Australia. In Engineering and Mathematical Topics in Rainfall; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, Y. Using the back propagation neural network approach to bias correct TMPA data in the arid region of Northwest China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hongxing, C.; Flitman, A.; Fengying, W.; Guolin, F. Forecasting monsoon precipitation using artificial neural networks. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 18, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, N.; Kumar, A. Comparative analysis of backpropagation and RBF neural network on monthly rainfall prediction. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Coimbatore, India, 26–27 August 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Manek, A.; Singh, P. Comparative study of neural network architectures for rainfall prediction. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Technological Innovations in ICT for Agriculture and Rural Development (TIAR), Chennai, India, 15–16 July 2016; pp. 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, M. Monthly rainfall prediction using wavelet regression and neural network: An analysis of 1901–2002 data, Assam, India. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 118, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, N.; Shrivastava, N.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Mohanty, U.C. Development of an artificial neural network based multi-model ensemble to estimate the northeast monsoon rainfall over south peninsular India: An application of extreme learning machine. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Marín, A.P.; Estévez, J.; Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Ayuso, J.; Flammini, A. Assessing inhomogeneities in extreme annual rainfall data series by multifractal approach. Water 2020, 12, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlinger, P.; Sorteberg, A.; Liu, C.; Rasmussen, R.; Sodemann, H.; Ogawa, F. Multiscale characteristics of an extreme precipitation event over Nepal. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Cobo, M.; García-Marín, A.P.; Estévez, J.; Jiménez-Hornero, F.; Ayuso, J. Obtaining homogeneous regions by determining the generalized fractal dimensions of validated daily rainfall data sets. Water Res. Manag. 2017, 31, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Cobo, M.T.; García-Marín, A.P.; Estévez, J.; Ayuso-Muñoz, J.L. The identification of an appropriate Minimum Inter-event Time (MIT) based on multifractal characterization of rainfall data series. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 3507–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Marín, A.P.; Estévez, J.; Medina-Cobo, M.T.; Ayuso, J. Delimiting homogeneous regions using the multifractal properties of validated rainfall data series. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, J.M.; Sivapalan, M. A comparative modeling analysis of multiscale temporal variability of rainfall in Australia. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W07401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, J.; García-Marín, A.P.; Benitez, J.B.; Castillo, M.C.C.; Telesca, L. Introduction to the special issue on “hydro-meteorological time series analysis and their relation to climate change”. Acta Geophys. 2018, 66, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, A.; Morlet, J. Decomposition of Hardy functions into square integrable wavelets of constant shape. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 1984, 15, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.-F. A review on the applications of wavelet transform in hydrology time series analysis. Atmos. Res. 2013, 122, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswaran, R.; Khosa, R. Comparative study of different wavelets for hydrologic forecasting. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 46, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamowski, J.; Chan, H.F. A wavelet neural network conjunction model for groundwater level forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2011, 407, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddoo, T.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Andam-Akorful, S. Rainfall variability in the Huangfuchuang Watershed and its relationship with ENSO. Water 2015, 7, 3243–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Pan, Y.; Fan, Z. Modeling daily and monthly water quality indicators in a canal using a hybrid wavelet-based support vector regression structure. Water 2020, 12, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I. Ten Lectures on Wavelets; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães-Santos, C.A.; Silva, G.B.L.D. Daily streamflow forecasting using a wavelet transform and artificial neural network hybrid models. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalley, D.; Adamowski, J.; Khalil, B. Using discrete wavelet transforms to analyze trends in streamflow and precipitation in Quebec and Ontario (1954–2008). J. Hydrol. 2012, 475, 204–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaouda, D.; Murtagh, F.; Starck, J.L.; Renaud, O. Wavelet-based nonlinear multiscale decomposition model for electricity load forecasting. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO. Guide to Instruments and Methods of Observations; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Paola, F.; Giugni, M. Coupled spatial distribution of rainfall and temperature in USA. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 19, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, J.; Padilla, F.L.; Gavilán, P. Evaluation and regional calibration of solar radiation prediction models in southern Spain. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccel, E. Estimating air humidity from temperature and precipitation measures for modelling applications. Meteorol. Appl. 2012, 19, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) Observed Climate Change Impacts Database; Version 2.01; NASA Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC): Palisades, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, G.; Ge, J.; Sun, X.; Hirano, T.; Saigusa, N.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Temperature and precipitation control of the spatial variation of terrestrial ecosystem carbon exchange in the Asian region. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 182, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.; Fowler, H.; Alexander, L.; Dunn, R.; McClean, F.; Barbero, R.; Guerreiro, S.; Xiao-Feng, L.; Blenkinsop, S. GSDR: A global sub-daily rainfall dataset. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 4715–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strigaro, D.; Cannata, M.; Antonovic, M. Boosting a weather monitoring system in low income economies using open and non-conventional systems: Data quality analysis. Sensors 2019, 19, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Yang, H.; Song, J.; Abbaspour, K.; Xu, Z. A wavelet-neural network hybrid modelling approach for estimating and predicting river monthly flows. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, R.V.; Krishna, B.; Kumar, S.R.; Pandey, N.G. Monthly rainfall prediction using wavelet neural network analysis. Water Res. Manag. 2013, 27, 3697–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chau, K.; Li, Y. Methods to improve neural network performance in daily flows prediction. J. Hydrol. 2009, 372, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, V.; Alami, M.T.; Aminfar, M.H. A combined neural-wavelet model for prediction of Ligvanchai watershed precipitation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intel. 2009, 22, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Zotano, J.; Alcántara-Manzanares, J.; Olmedo-Cobo, J.A.; Martínez-Ibarra, E. La sistematización del clima mediterráneo: Identificación, clasificación y caracterización climática de Andalucía (España). Rev. Geogr. Norte Gd. 2015, 61, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, J.; Gavilán, P.; Giráldez, J.V. Guidelines on validation procedures for meteorological data from automatic weather stations. J. Hydrol. 2011, 402, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, J.; Gavilán, P.; García-Marín, A.P.; Zardi, D. Detection of spurious precipitation signals from automatic weather stations in irrigated areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, J.; Gavilán, P.; García-Marín, A.P. Spatial regression test for ensuring temperature data quality. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 131, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, V.; Elkiran, G.; Abdullahi, J. Multi-station artificial intelligence based ensemble modeling of reference evapotranspiration using pan evaporation measurements. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.T.; Shen, S.; Yang, S.; Hu, Z.; Chu, R. Assessing recent impacts of climate change on design water requirement of Boro rice season in Bangladesh. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 138, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, Y. Continuous daily evapotranspiration estimation at the field-scale over heterogeneous agricultural areas by fusing aster and modis data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, J.; García-Marín, A.P.; Morábito, J.A.; Cavagnaro, M. Quality assurance procedures for validating meteorological input variables of reference evapotranspiration in mendoza province (Argentina). Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 172, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Van Gelder, P.H.; Vrijling, J.; Ma, J. Forecasting daily streamflow using hybrid ANN models. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, L.; Ojha, C.S.P.; Chandniha, S.K.; Kumar, A. Regional scale analysis of trends in rainfall using nonparametric methods and wavelet transforms over a semi-arid region in India. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 2737–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Shamseldin, A.Y.; Melville, B.W. Comparative study of different wavelet based neural network models for rainfall–runoff modeling. J. Hydrol. 2014, 515, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Zhao, Y.; Lei, J. The incorrect usage of singular spectral analysis and discrete wavelet transform in hybrid models to predict hydrological time series. J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, H.; Dahamsheh, A. Artificial neural network models for forecasting monthly precipitation in Jordan. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2009, 23, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissanen, J. Modeling by shortest data description. Automatica 1978, 14, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, V.; Komasi, M. A geomorphology-based ANFIS model for multi-station modeling of rainfall-runoff process. J. Hydrol. 2013, 490, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laio, F.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Montanari, A. Model selection techniques for the frequency analysis of hydrological extremes. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W07416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, C.; Wilby, R. Hydrological modelling using artificial neural networks. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2001, 25, 80–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegeskorte, N. Crossvalidation, in Brain Mapping; Toga, A.W., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, UK, 2015; pp. 635–639. [Google Scholar]
- Kalteh, A.M. Enhanced monthly precipitation forecasting using artificial neural network and singular spectrum analysis conjunction models. INAE Lett. 2017, 2, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
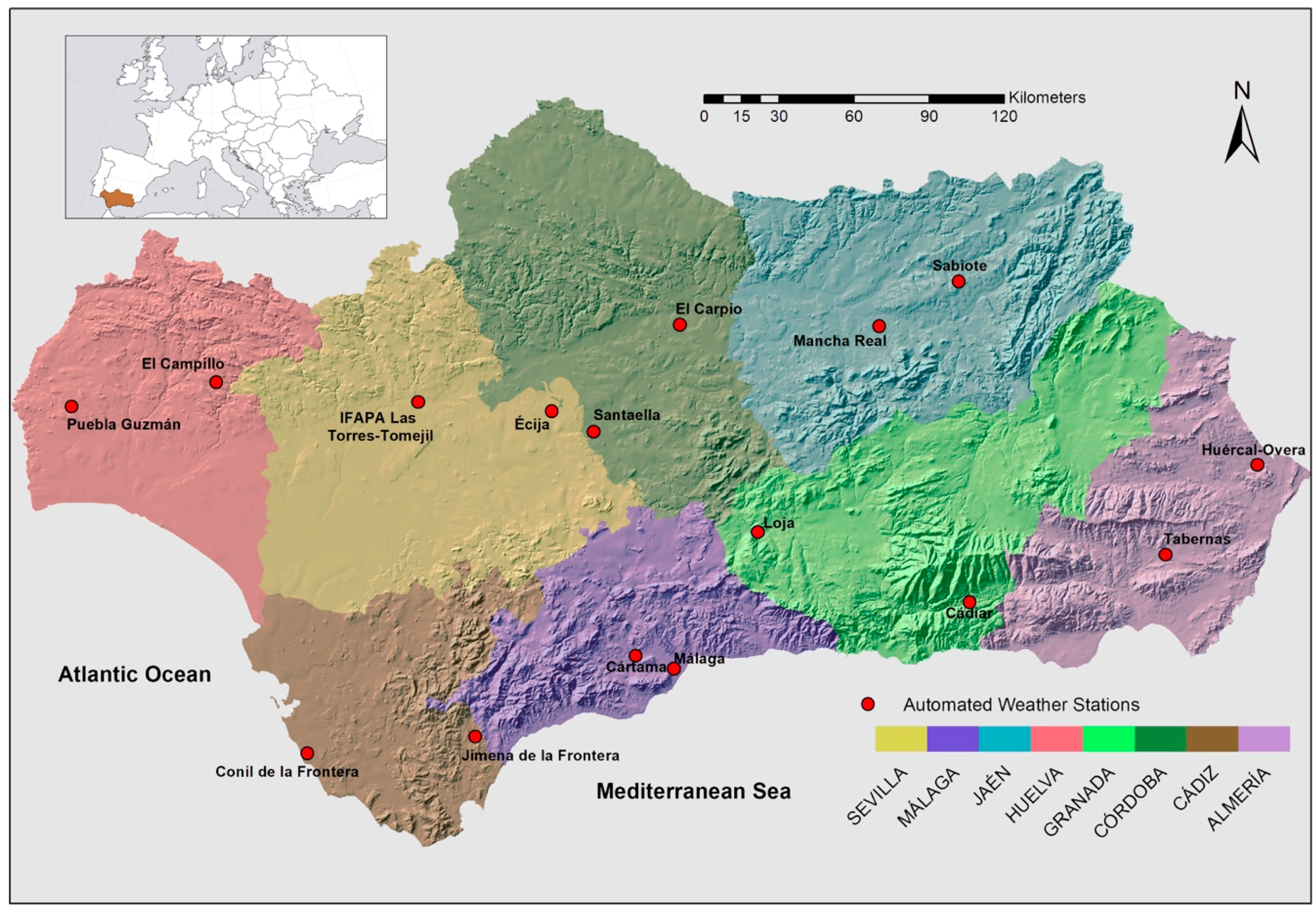
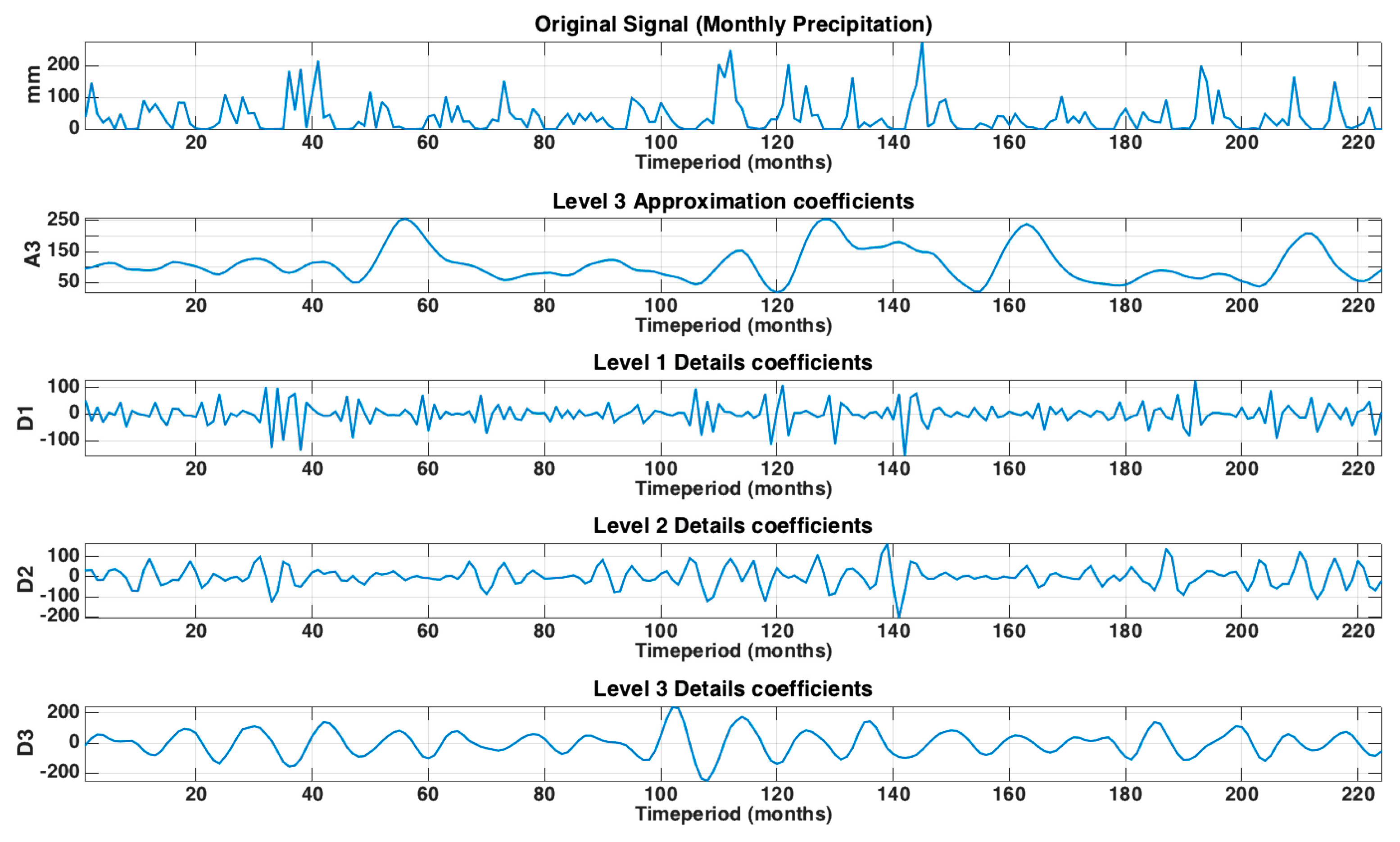
| Station Name | Province | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Elevation (m) | Time Period (Calibration) Time Period (Validation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tabernas (ALM04) | Almería | 37.0925 N | 2.3011 W | 435 | March 2000–August 2016 September 2016–July 2019 |
| Huércal Overa (ALM07) | Almería | 37.4133 N | 1.8831 W | 317 | February 2000–August 2016 September 2016–July 2019 |
| Conil Frontera (CAD05) | Cádiz | 36.3372 N | 6.1306 W | 26 | November 2000–November 2016 December 2016–July 2019 |
| Jimena Frontera (CAD07) | Cádiz | 36.4136 N | 5.3844 W | 53 | January 2001–September 2016 October 2016–July 2019 |
| El Carpio (COR05) | Córdoba | 37.9150 N | 4.5025 W | 165 | December 2000–September 2016 November 2016–July 2019 |
| Santaella (COR07) | Córdoba | 37.5236 N | 4.8842 W | 207 | November 2000–November 2016 December 2016–July 2019 |
| Loja (GRA03) | Granada | 37.1706 N | 4.1369 W | 487 | October 2000–September 2016 October 2016–July 2019 |
| Cádiar (GRA07) | Granada | 36.9242 N | 3.1825 W | 950 | October 2000–September 2016 October 2016–July 2019 |
| Puebla Guzmán (HUE07) | Huelva | 37.5533 N | 7.2469 W | 288 | December 2000–September 2016 November 2016–July 2019 |
| El Campillo (HUE08) | Huelva | 37.6622 N | 6.5981 W | 406 | December 2000–September 2016 November 2016–July 2019 |
| Mancha Real (JAE04) | Jaén | 37.9175 N | 3.5950 W | 436 | October 2000–September 2016 October 2016–July 2019 |
| Sabiote (JAE07) | Jaén | 38.0806 N | 3.2342 W | 822 | October 2000–September 2016 October 2016–July 2019 |
| Málaga (MAG01) | Málaga | 36.7575 N | 4.5364 W | 68 | November 2000–November 2016 December 2016–July 2019 |
| Cártama (MAG09) | Málaga | 36.7181 N | 4.6769 W | 95 | August 2001–October 2016 November 2016–July 2019 |
| Écija (SEV07) | Sevilla | 37.5942 N | 5.0756 W | 125 | December 2000–September 2016 November 2016–July 2019 |
| IFAPA Las Torres-Tomejil (SEV101) | Sevilla | 37.4008 N | 5.5875 W | 75 | November 2001–November 2016 December 2016–July 2019 |
| Sites | Datasets | Precipitation (mm) | Maximum Temperature (°) | Minimum Temperature (°) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std | Max | Min | Mean | Std | Max | Min | Mean | Std | Max | Min | ||
| Tabernas (ALM04) | All | 19.95 | 25.56 | 141.40 | 0.00 | 29.85 | 6.59 | 42.55 | 15.53 | 4.69 | 6.40 | 17.18 | −8.20 |
| Validation | 18.77 | 27.25 | 141.40 | 0.00 | 29.13 | 6.49 | 41.70 | 17.68 | 4.44 | 6.09 | 15.10 | −5.30 | |
| Calibration | 20.17 | 25.30 | 128.40 | 0.00 | 29.98 | 6.62 | 42.55 | 15.53 | 4.74 | 6.47 | 17.18 | −8.20 | |
| Huércal-Overa (ALM07) | All | 22.49 | 31.94 | 247.80 | 0.00 | 29.89 | 6.02 | 43.58 | 17.03 | 4.54 | 6.46 | 17.18 | −8.85 |
| Validation | 19.57 | 34.37 | 186.80 | 0.00 | 29.90 | 5.87 | 40.76 | 18.57 | 4.37 | 6.12 | 15.19 | −6.00 | |
| Calibration | 23.02 | 31.55 | 247.80 | 0.00 | 29.88 | 6.06 | 43.58 | 17.03 | 4.58 | 6.53 | 17.18 | −8.85 | |
| Conil de la Frontera (CAD05) | All | 42.71 | 54.32 | 287.60 | 0.00 | 28.72 | 6.45 | 41.37 | 16.04 | 6.53 | 5.02 | 15.80 | −5.38 |
| Validation | 37.95 | 55.09 | 208.60 | 0.00 | 28.00 | 6.80 | 40.30 | 18.96 | 5.91 | 4.72 | 15.80 | −1.03 | |
| Calibration | 43.58 | 54.28 | 287.60 | 0.00 | 28.86 | 6.39 | 41.37 | 16.04 | 6.65 | 5.07 | 15.37 | −5.38 | |
| Jimena de la Frontera (CAD07) | All | 61.05 | 75.03 | 441.00 | 0.00 | 30.18 | 6.74 | 46.57 | 18.64 | 5.99 | 5.26 | 16.02 | −3.88 |
| Validation | 63.22 | 86.12 | 371.40 | 0.00 | 29.86 | 5.90 | 42.28 | 19.62 | 5.73 | 5.05 | 14.70 | −1.51 | |
| Calibration | 60.66 | 73.11 | 441.00 | 0.00 | 30.23 | 6.89 | 46.57 | 18.64 | 6.04 | 5.31 | 16.02 | −3.88 | |
| El Carpio (COR05) | All | 41.23 | 48.84 | 317.60 | 0.00 | 31.38 | 8.59 | 47.10 | 15.42 | 4.89 | 6.58 | 17.93 | −9.54 |
| Validation | 38.12 | 48.55 | 260.20 | 0.00 | 31.54 | 8.56 | 47.10 | 19.61 | 4.32 | 6.50 | 15.40 | −6.15 | |
| Calibration | 41.78 | 48.99 | 317.60 | 0.00 | 31.35 | 8.61 | 46.94 | 15.42 | 4.99 | 6.60 | 17.93 | −9.54 | |
| Santaella (COR07) | All | 44.27 | 50.85 | 310.80 | 0.00 | 30.64 | 8.15 | 45.69 | 17.36 | 6.08 | 6.05 | 17.27 | −8.25 |
| Validation | 42.47 | 54.85 | 277.80 | 0.00 | 29.96 | 7.94 | 44.91 | 18.69 | 6.21 | 5.64 | 16.10 | −3.05 | |
| Calibration | 44.60 | 50.25 | 310.80 | 0.00 | 30.76 | 8.20 | 45.69 | 17.36 | 6.06 | 6.14 | 17.27 | −8.25 | |
| Loja (GRA03) | All | 36.96 | 39.12 | 230.60 | 0.00 | 29.87 | 7.53 | 45.94 | 16.92 | 4.05 | 6.01 | 15.37 | −9.45 |
| Validation | 35.66 | 44.21 | 225.40 | 0.00 | 29.97 | 7.90 | 45.94 | 16.92 | 4.08 | 5.94 | 14.70 | −5.80 | |
| Calibration | 37.20 | 38.25 | 230.60 | 0.00 | 29.86 | 7.48 | 42.85 | 17.08 | 4.05 | 6.04 | 15.37 | −9.45 | |
| Cádiar (GRA07) | All | 43.46 | 56.88 | 423.60 | 0.00 | 27.11 | 7.02 | 42.63 | 14.17 | 5.03 | 6.06 | 18.38 | −13.30 |
| Validation | 42.55 | 61.55 | 317.00 | 0.00 | 26.26 | 7.03 | 41.20 | 16.11 | 4.43 | 6.37 | 15.90 | −13.30 | |
| Calibration | 43.62 | 56.18 | 423.60 | 0.00 | 27.26 | 7.03 | 42.63 | 14.17 | 5.14 | 6.02 | 18.38 | −8.13 | |
| Puebla Guzmán (HUE07) | All | 46.69 | 53.29 | 296.80 | 0.00 | 29.21 | 7.84 | 43.63 | 15.42 | 6.60 | 5.09 | 16.38 | −4.02 |
| Validation | 43.36 | 50.38 | 197.80 | 0.00 | 29.24 | 7.62 | 42.18 | 18.65 | 6.82 | 4.68 | 15.50 | −0.73 | |
| Calibration | 47.29 | 53.90 | 296.80 | 0.00 | 29.21 | 7.89 | 43.63 | 15.42 | 6.56 | 5.17 | 16.38 | −4.02 | |
| El Campillo (HUE08) | All | 60.51 | 69.67 | 389.80 | 0.00 | 29.51 | 7.63 | 43.07 | 15.41 | 6.95 | 4.81 | 16.39 | −2.39 |
| Validation | 56.16 | 66.43 | 351.00 | 0.00 | 29.48 | 7.61 | 42.74 | 18.92 | 6.78 | 4.58 | 15.40 | −1.37 | |
| Calibration | 61.28 | 70.38 | 389.80 | 0.00 | 29.51 | 7.65 | 43.07 | 15.41 | 6.98 | 4.86 | 16.39 | −2.39 | |
| Mancha Real (JAE04) | All | 37.28 | 38.43 | 248.20 | 0.00 | 27.79 | 7.96 | 41.91 | 13.40 | 5.02 | 6.30 | 18.08 | −10.24 |
| Validation | 32.12 | 38.83 | 200.20 | 0.00 | 27.97 | 8.30 | 41.91 | 14.75 | 4.67 | 5.92 | 16.70 | −6.62 | |
| Calibration | 38.22 | 38.38 | 248.20 | 0.00 | 27.76 | 7.92 | 41.62 | 13.40 | 5.09 | 6.38 | 18.08 | −10.24 | |
| Sabiote (JAE07) | All | 32.65 | 33.43 | 192.00 | 0.00 | 30.36 | 8.20 | 45.25 | 15.84 | 6.08 | 6.77 | 19.96 | −8.64 |
| Validation | 28.96 | 36.93 | 192.00 | 0.00 | 30.18 | 8.51 | 45.25 | 17.60 | 5.92 | 6.44 | 18.20 | −5.06 | |
| Calibration | 33.32 | 32.81 | 174.20 | 0.00 | 30.39 | 8.16 | 44.23 | 15.84 | 6.11 | 6.85 | 19.96 | −8.64 | |
| Málaga (MAG01) | All | 38.10 | 50.99 | 272.70 | 0.00 | 30.09 | 6.38 | 42.78 | 18.44 | 7.66 | 5.92 | 19.10 | −4.27 |
| Validation | 38.18 | 54.26 | 199.40 | 0.00 | 29.60 | 5.88 | 39.60 | 21.14 | 7.28 | 5.35 | 19.10 | −0.85 | |
| Calibration | 38.09 | 50.53 | 272.70 | 0.00 | 30.17 | 6.47 | 42.78 | 18.44 | 7.73 | 6.03 | 18.75 | −4.27 | |
| Cártama (MAG09) | All | 39.77 | 54.17 | 266.00 | 0.00 | 30.69 | 6.46 | 43.13 | 18.92 | 7.08 | 5.66 | 17.73 | −2.60 |
| Validation | 36.60 | 50.64 | 177.40 | 0.00 | 30.31 | 6.38 | 40.48 | 21.30 | 6.58 | 5.58 | 17.20 | −1.38 | |
| Calibration | 40.33 | 54.89 | 266.00 | 0.00 | 30.76 | 6.49 | 43.13 | 18.92 | 7.17 | 5.69 | 17.73 | −2.60 | |
| Écija (SEV07) | All | 40.40 | 48.05 | 292.40 | 0.00 | 31.33 | 8.31 | 46.05 | 16.77 | 5.54 | 6.39 | 18.20 | −9.09 |
| Validation | 38.42 | 45.95 | 217.20 | 0.00 | 31.06 | 8.29 | 46.05 | 19.61 | 5.28 | 6.11 | 16.20 | −3.78 | |
| Calibration | 40.76 | 48.52 | 292.40 | 0.00 | 31.38 | 8.34 | 45.96 | 16.77 | 5.59 | 6.45 | 18.20 | −9.09 | |
| IFAPA C. Torres-T (SEV101) | All | 41.46 | 48.12 | 282.00 | 0.00 | 31.42 | 8.16 | 53.12 | 18.05 | 5.43 | 6.11 | 16.72 | −9.82 |
| Validation | 37.10 | 46.22 | 203.40 | 0.00 | 30.85 | 8.31 | 44.85 | 18.88 | 5.16 | 5.83 | 16.10 | −3.99 | |
| Calibration | 42.25 | 48.54 | 282.00 | 0.00 | 31.52 | 8.15 | 53.12 | 18.05 | 5.48 | 6.17 | 16.72 | −9.82 | |
| Models | Output | Input Variables | Nº Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | P (m + 1) | MOY, P{decomposed} (m) | 5 |
| II | P (m + 1) | MOY, P{decomposed} (m), P{decomposed} (m−1) | 9 |
| III | P (m + 1) | MOY, P{decomposed} (m), DTRm {decomposed} (m) | 9 |
| IV | P (m + 1) | MOY, P{decomposed} (m), DTRx {decomposed} (m) | 9 |
| V | P (m + 1) | MOY, P{decomposed} (m), DTRn {decomposed} (m) | 9 |
| VI | P (m + 1) | MOY, P{decomposed} (m), DTRx {decomposed} (m), DTRn {decomposed} (m) | 13 |
| VII | P (m + 1) | MOY, P{decomposed} (m), MTR {decomposed} (m) | 9 |
| VIII | P (m + 1) | MOY, P{decomposed} (m), Tx{decomposed} (m) | 9 |
| IX | P (m + 1) | MOY, P{decomposed} (m), Tn{decomposed} (m) | 9 |
| X | P (m + 1) | MOY, P{decomposed} (m), Tx{decomposed}, Tn{decomposed} (m) | 13 |
| Models | Datasets | R | RMSE (mm) | MAPE (%) | NSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max/Mean/Min | Min/Mean/Max | Min/Mean/Max | Max/Mean/Min | ||
| I | Validation | 0.78/0.70/0.62 | 9.39/21.69/37.74 | 9.82/33.94/52.52 | 0.62/0.51/0.40 |
| Calibration | 0.83/0.74/0.65 | 11.75/20.67/29.60 | 9.86/16.07/22.57 | 0.81/0.72/0.63 | |
| II | Validation | 0.80/0.69/0.55 | 10.73/31.55/44.03 | 25.34/39.93/62.02 | 0.67/0.50/0.32 |
| Calibration | 0.98/0.92/0.79 | 11.89/16.18/29.21 | 1.86/7.84/22.99 | 0.96/0.85/0.63 | |
| III | Validation | 0.84/0.71/0.56 | 13.75/24.17/39.53 | 11.39/31.57/49.86 | 0.73/0.54/0.33 |
| Calibration | 0.95/0.92/0.87 | 11.33/17.59/26.97 | 4.92/8.63/15.91 | 0.91/0.84/0.75 | |
| IV | Validation | 0.83/0.71/0.58 | 13.61/23.25/40.12 | 2.50/34.84/57.58 | 0.71/0.52/0.36 |
| Calibration | 0.92/0.85/0.74 | 11.12/16.84/24.50 | 4.11/8.21/17.00 | 0.91/0.85/0.73 | |
| V | Validation | 0.85/0.71/0.57 | 10.20/23.68/41.00 | 15.73/33.04/56.89 | 0.74/0.53/0.34 |
| Calibration | 0.97/0.93/0.85 | 11.54/15.66/24.80 | 1.58/6.50/16.68 | 0.94/0.87/0.73 | |
| VI | Validation | 0.89/0.73/0.59 | 12.64/22.48/38.51 | 9.80/31.19/48.17 | 0.82/0.55/0.37 |
| Calibration | 0.97/0.95/0.91 | 7.79/13.96/18.28 | 0.12/5.05/11.89 | 0.95/0.90/0.82 | |
| VII | Validation | 0.90/0.72/0.58 | 16.95/24.44/37.55 | 0.40/28.02/47.94 | 0.84/0.55/0.36 |
| Calibration | 0.97/0.95/0.92 | 8.48/14.65/23.19 | 1.67/4.46/9.58 | 0.95/0.90/0.85 | |
| VIII | Validation | 0.88/0.75/0.57 | 11.16/22.86/42.04 | 4.96/32.37/62.61 | 0.79/0.58/0.34 |
| Calibration | 0.98/0.94/0.91 | 7.67/15.34/25.52 | 0.02/4.23/9.05 | 0.96/0.89/0.83 | |
| IX | Validation | 0.90/0.74/0.57 | 6.79/22.84/38.17 | 3.45/28.05/41.50 | 0.84/0.58/0.35 |
| Calibration | 0.97/0.94/0.88 | 8.02/15.03/21.22 | 1.67/5.09/11.15 | 0.94/0.89/0.77 | |
| X | Validation | 0.90/0.82/0.64 | 8.49/21.49/38.39 | 4.57/23.61/40.04 | 0.83/0.69/0.44 |
| Calibration | 0.98/0.94/0.90 | 9.61/14.61/20.88 | 2.45/5.71/11.40 | 0.96/0.89/0.81 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Estévez, J.; Bellido-Jiménez, J.A.; Liu, X.; García-Marín, A.P. Monthly Precipitation Forecasts Using Wavelet Neural Networks Models in a Semiarid Environment. Water 2020, 12, 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071909
Estévez J, Bellido-Jiménez JA, Liu X, García-Marín AP. Monthly Precipitation Forecasts Using Wavelet Neural Networks Models in a Semiarid Environment. Water. 2020; 12(7):1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071909
Chicago/Turabian StyleEstévez, Javier, Juan Antonio Bellido-Jiménez, Xiaodong Liu, and Amanda Penélope García-Marín. 2020. "Monthly Precipitation Forecasts Using Wavelet Neural Networks Models in a Semiarid Environment" Water 12, no. 7: 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071909
APA StyleEstévez, J., Bellido-Jiménez, J. A., Liu, X., & García-Marín, A. P. (2020). Monthly Precipitation Forecasts Using Wavelet Neural Networks Models in a Semiarid Environment. Water, 12(7), 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071909