The Impact of Land-Use on the Hierarchical Pore Size Distribution and Water Retention Properties in Loamy Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
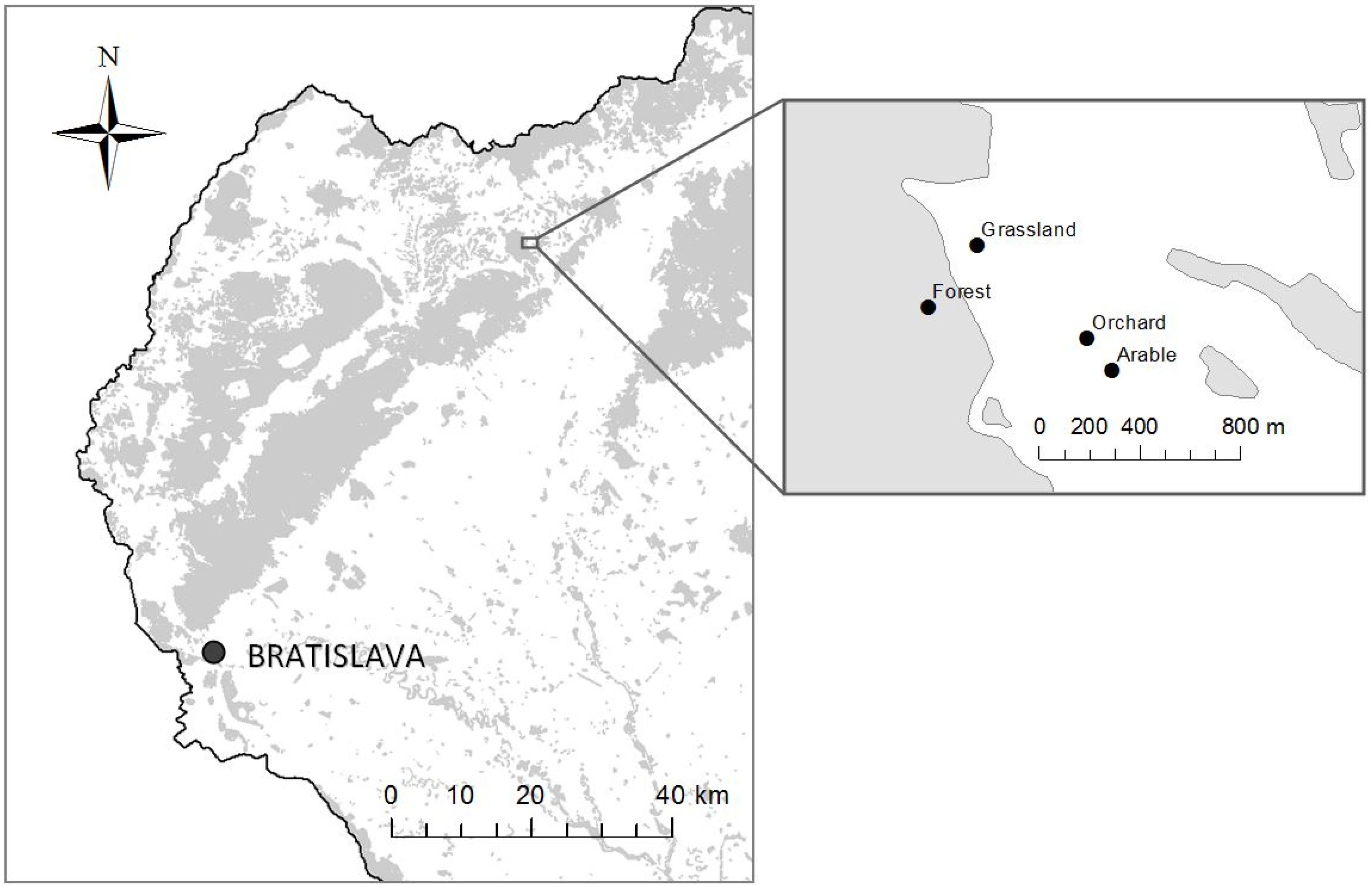
2.1. Study Sites and Soil Sampling
2.2. Laboratory Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
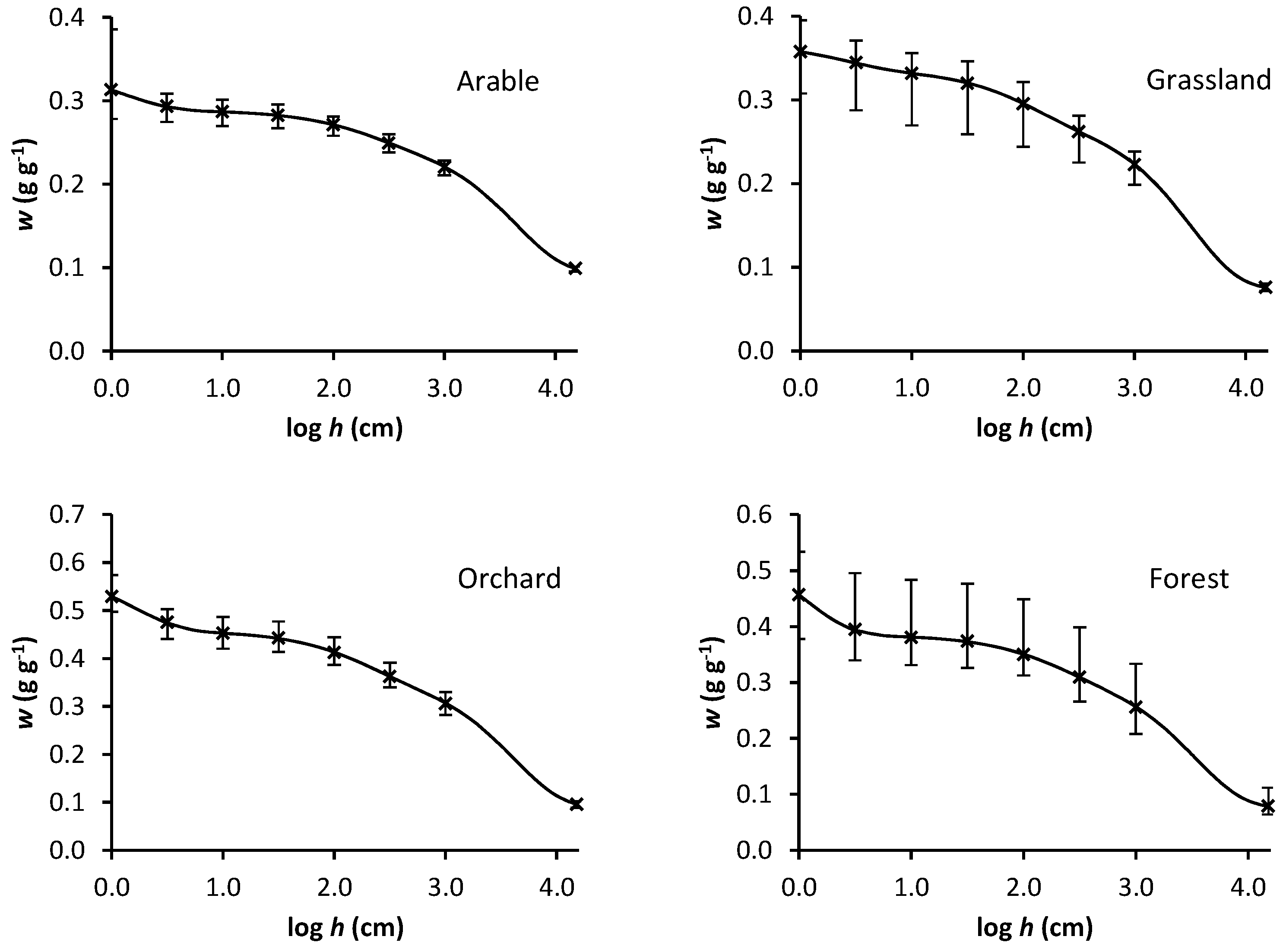
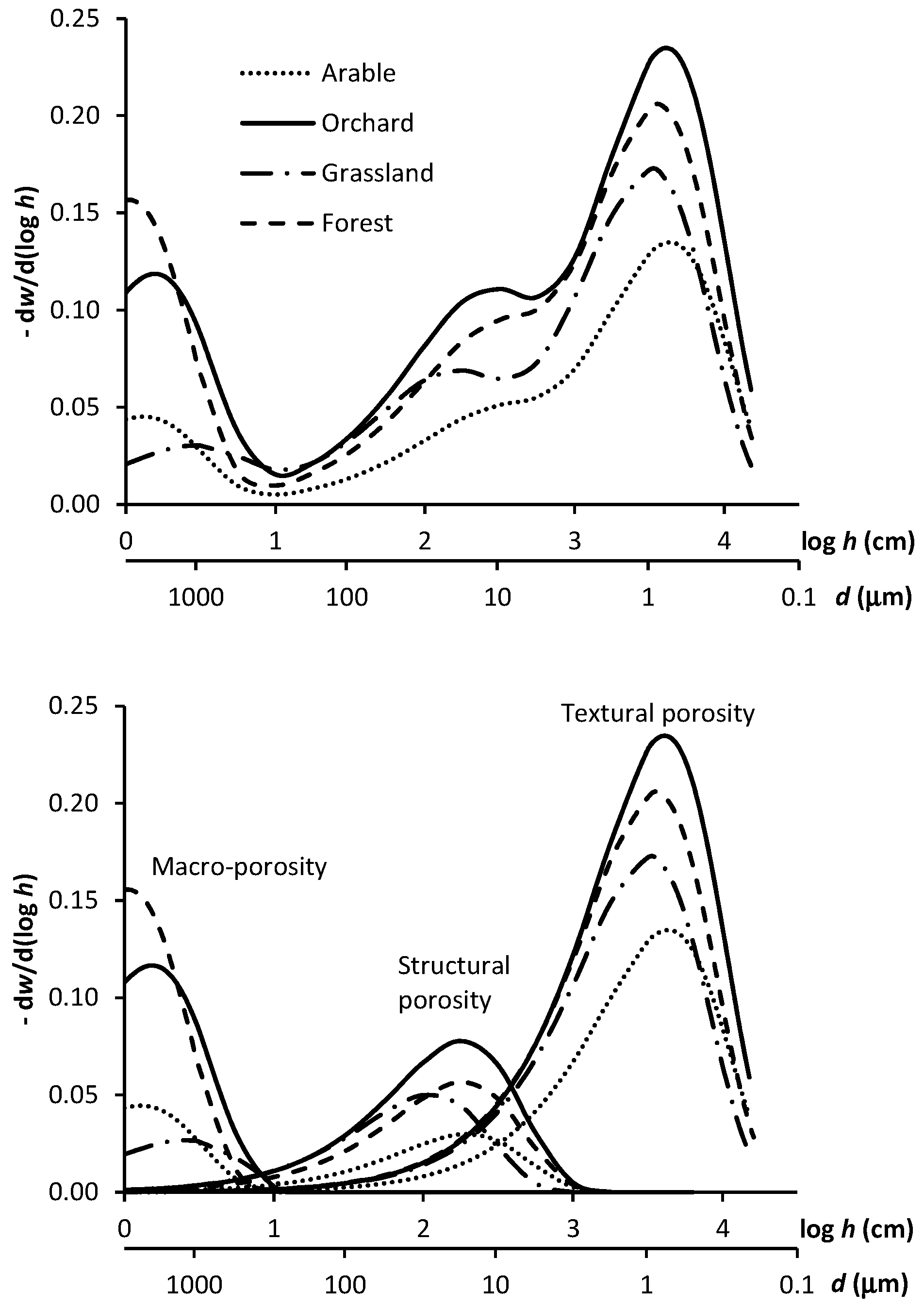
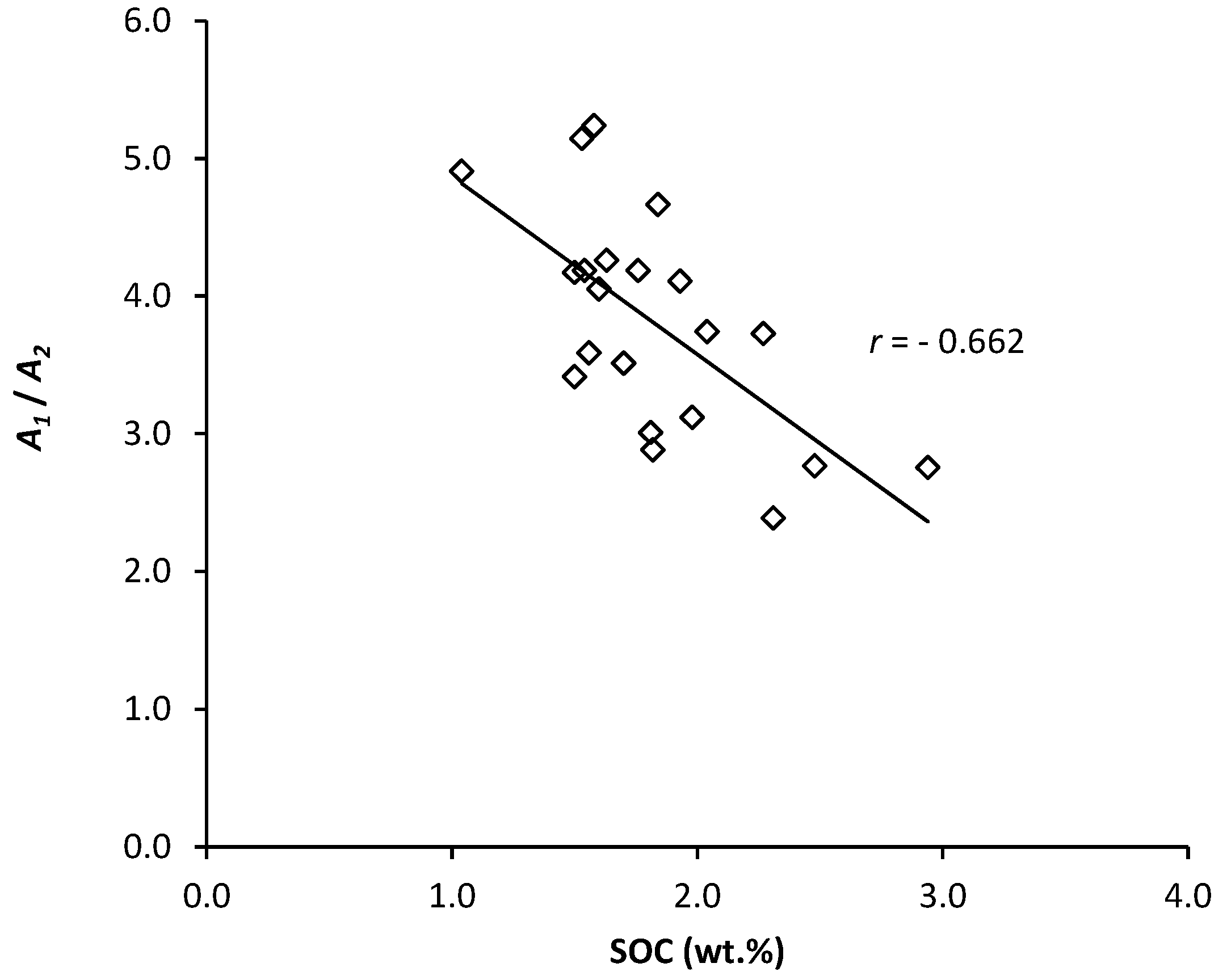
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dexter, A.R.; Richard, G. The saturated hydraulic conductivity of soils with n-modal pore size distributions. Geoderma 2009, 154, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durner, W. Hydraulic conductivity estimation for soils with heterogeneous pore structure. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, A.; Chun, H.-C.; Mazer, M.; Wang, W.; Rose, J.B.; Smucker, A.; Rivers, M. Relationships between intra-aggregate pore structures and distributions of Escherichia coli within soil macro-aggregates. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 63, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, R.H.; Corey, A.T. Hydraulic Properties of Porous Media; Hydrology Papers 3; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutílek, M.; Jendele, L.; Panayiotopoulos, K.P. The influence of uniaxial compression upon pore size distribution in bi-modal soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 86, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, A.R.; Czyz, E.A.; Richard, G.; Reszkowska, A. A user-friendly water retention function that takes account of the textural and structural pore spaces in soil. Geoderma 2008, 143, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solone, R.; Bittelli, M.; Tomei, F.; Morari, F. Errors in water retention curves determined with pressure plates: Effects on the soil water balance. J. Hydrol. 2012, 470–471, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.L.; Schjonning, P.; Watts, C.W.; Christensen, B.T.; Munkholm, L.J. Soil water retention: Uni-Modal models of pore-size distribution neglect impacts of soil management. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B. Estimating the water retention shape parameter from sand and clay content. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseling, J.G.; Stoof, C.R.; Ritsema, C.J.; Oostindie, K.; Dekker, L.W. The effect of soil texture and organic amendment on the hydrological behaviour of coarse textured soils. Soil Use Manag. 2009, 25, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereecken, H.; Maes, J.; Feyen, J.; Darius, P. Estimating the soil moisture retention characteristic from texture, bulk density, and carbon content. Soil Sci. 1989, 148, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otalvaro, I.F.; Neto, M.P.C.; Delage, P.; Caicedo, B. Relationship between soil structure and water retention properties in a residual compacted soil. Eng. Geol. 2016, 205, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormann, H.; Klaassen, K. Seasonal and land use dependent variability of soil hydraulic and soil hydrological properties of two Northern German soils. Geoderma 2008, 145, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, J.P.; Flury, M.; Bezdicek, D.F. Hydraulic properties in a Silt Loam Soil under Natural Prairie, conventional till, and no-till. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Deforestation and land-use effects on soil degradation and rehabilitation in western Nigeria. I. Soil physical and hydrological properties. Land Degrad. Dev. 1996, 7, 19–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffler, R.; Neill, C.; Krusche, A.V.; Elsebeer, H. Soil hydraulic response to land-use change associated with the recent soybean expansion at the Amazon agricultural frontier. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, B.; Elsenbeer, H.; De Moraes, J.M. The influence of land-use change on soil hydraulic properties: Implications for runoff generation. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2006, 222, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.L.; Wu, J.; You, W.H. Recovery of saturated hydraulic conductivity along a forest successional series from abandoned land to mature, evergreen broad-leaved forest in eastern China. Soil Res. 2012, 50, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Jia, Z. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil physical properties in the wind–water erosion region of the northern Loess Plateau of China. Clean Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Feger, K.-H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Schwärzel, K. Impact of land-use changes on soil hydraulic properties of Calcaric Regosols on the Loess Plateau, NW China. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, P.; Gao, X.; Tian, L.; Li, H. Changes of soil hydraulic properties under early-stage natural vegetation recovering on the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2014, 113, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankoviansky, M. Historical evolution of permanent gullies in the Myjava Hill Land, Slovakia. Catena 2003, 51, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlapa, P.; Chrenková, K.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Šimkovic, I. Soil profile improvement as aby-product of gully stabilization measures. Catena 2012, 92, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS) Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps Update 2015; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2015; 192p. [Google Scholar]
- Dexter, A.R. Soil physical quality. Part I. Theory, effects of soil texture, density, and organic matter, and effects on root growth. Geoderma 2004, 120, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle-Size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1—Physical and Mineralogical Methods, 2nd ed.; Klute, A., Ed.; Agronomy Series 9; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, G.R.; Hartge, K.H. Particle density. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1—Physical and Mineralogical Methods, 2nd ed.; Klute, A., Ed.; Agronomy Series 9; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3—Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Soltanpour, P.N., Tabatabai, M.A., Johnston, C.T., Sumner, M.E., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Pulido Moncada, M.; Gabriels, D.; Lobo, D.; De Beuf, K.; Figueroa, R.; Cornelis, W.M. A comparison of methods to assess susceptibility to soil sealing. Geoderma 2014, 226–227, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newville, M.; Otten, R.; Nelson, A.; Ingargiola, A.; Stensitzki, T.; Allan, D.; Fox, A.; Carter, F.; Michal; Pustakhod, D. lmfit/lmfit-py 0.9.14. 2019. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/3381550 (accessed on 24 September 2019).
- White, D.A., II; Welty-Bernard, A.; Rasmussen, C.; Schwartz, E. Vegetation controls on soil organic carbon dynamics in an arid, hyperthermic ecosystem. Geoderma 2009, 150, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.K.; Liang, W.J.; Jianf, Y.; Dai, G.H.; Wang, X.G.; Han, S.J. Distribution of soil organic carbon fractions along the altitudinal gradient in Changbai mountain, China. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiarree, S.; Chidthaisong, A.; Tangtham, N.; Polprasert, C.; Sarobol, E.; Tyler, S.C. Soil organic carbon loss and turnover resulting from forest conversion to maize fields in Eastern Thailand. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplot, V.; Bouahom, B.; Valentin, C. Soil organic carbon stocks in Laos: Spatial variations and controlling factors. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 16, 1380–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengiz, Q.; Saglam, M.; Turkman, F. Effects of soil types and land use—land cover on soil organic carbon density at Madendere watershed. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2015, 4, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenberger, G.; Zech, W.; Thomas, R.J. Lignin and carbohydrate alteration in particle size separates of an Oxisol under tropical pastures following native savanna. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1995, 27, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawls, W.J.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Ritchie, J.C.; Sobecki, T.M.; Bloodworth, H. Effect of soil organic carbon on soil water retention. Geoderma 2003, 116, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachepsky, Y.A.; Rawls, W.J. Accuracy and reliability of pedotransfer functions as affected by grouping soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 1748–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaverdiloo, H.; Homaee, M.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Dashtaki, S.G. Deriving and validating pedotransfer functions for some calcareous soils. J. Hydrol. 2011, 399, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Wendroth, O.; Matocha, C.; Edwards, D. Effect of macroporosity on pedotransfer function estimates at the field scale. Vadose Zone J. 2019, 18, 180151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliai, M.; Vignozzi, N.; Pellegrini, S. Soil structure and the effect of management practices. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oorts, K.; Bossuyt, H.; Labreuche, J.; Merckx, R.; Nicolardot, B. Carbon and nitrogen stocks in relation to organic matter fractions, aggregation and pore size distribution in no-tillage and conventional tillage in northern France. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 58, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosbellet, C.; Vidal-Beaudet, L.; Caubel, V.; Charpentier, S. Improvement of soil structure formation by degradation of coarse organic matter. Geoderma 2011, 162, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffar, M.; Lu, S.G. Pore size distribution of clayey soils and its correlation with soil organic matter. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, L.F.; Borges, J.A.; Rosa, J.A.; Cooper, M.; Heck, R.J.; Passoni, S.; Roque, W.L. Soil structure changes induced by tillage systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Steinbach, H.S. A review of the effects of tillage systems on some soil physical properties, water content, nitrate availability and crops yield in the Argentine Pampas. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 104, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Mooney, S.J.; Peng, X.H. Bimodal soil pore structure investigated by a combined soil water retention curve and X-ray Computed Tomography approach. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, L.R.; Fiedler, F.; Dunn, G.H.; Benjamin, J.G.; Garrison, A. Changes in soil water retention curves due to tillage and natural reconsolidation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clothier, B.E.; Green, S.R. Rootzone processes and the efficient use of irrigation water. Agric. Water Manag. 1994, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Zhang, G.L. Water infiltration in urban soils and its effects on the quantity and quality of runoff. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luxmoore, R.J.; Jardine, P.M.; Wilson, G.V.; Jones, J.R.; Zelszny, L.W. Physical and chemical controls of preferred path flow through a forested hillslope. Geoderma 1990, 46, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.F.; Lin, H.; Schmidt, J. Quantitative relationships between soil macropore characteristics and preferential flow and transport. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, N.J. Near-saturated hydraulic properties of macroporous soils. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, N.; Koestel, J.; Messing, I.; Moeys, J.; Lindahl, A. Influence of soil, land use and climatic factors on the hydraulic conductivity of soil. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 5185–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipiec, J.; Hatano, R. Quantification of compaction effects on soil physical properties and crop growth. Geoderma 2003, 116, 107–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Nieber, J.L.; Gupta, S.C. Compaction effect on the gas diffusion coefficient in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezső, J.; Czigány, S.; Nagy, G.; Pirkhoffer, E.; Słowik, M.; Lóczy, D. Monitoring soil moisture dynamics in multilayered Fluvisols. Bull. Geogr. Phys. Geogr. Ser. 2019, 16, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhos, K.; Czigany, S.; Madarasz, B.; Ladanyi, M. Interpretation of soil quality indicators for land suitability assessment–A multivariate approach for Central European arable soils. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliai, M.; Vignozzi, N. The pore system as an indicator of soil quality. In Sustainable Land Management—Environmental Protection: A Soil Physical Approach; Advances in Geoecology 35; Pagliai, M., Jones, R., Eds.; Catena Verlag: Reiskirchen, Germany, 2002; pp. 71–82. [Google Scholar]
| Soil Properties | Arable | Orchard | Grassland | Forest | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand (wt.%) | Mean | 34.6 | 35.6 | 39.8 | 36.5 |
| SD | 2.3 | 4.4 | 0.9 | 2.4 | |
| Silt (wt.%) | Mean | 41.5 | 45.7 | 41.0 | 43.8 |
| SD | 4.3 | 6.1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | |
| Clay (wt.%) | Mean | 23.9 | 18.8 | 19.2 | 19.7 |
| SD | 4.1 | 2.7 | 1.0 | 2.0 | |
| SOC (wt.%) | Mean | 1.59 | 2.24 | 1.48 | 1.98 |
| SD | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.52 | |
| pH | Mean | 6.78 | 6.42 | 5.10 | 4.73 |
| SD | 0.19 | 0.76 | 0.11 | 0.55 | |
| StI (%) | Mean | 4.19 | 5.99 | 4.24 | 5.40 |
| SD | 0.27 | 0.81 | 0.74 | 1.62 | |
| BD (g cm−3) | Mean | 1.45 | 1.11 | 1.36 | 1.20 |
| SD | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.08 | |
| Research Plot | C (g g−1) | A1 (g g−1) | h1 (cm) | A2 (g g−1) | h2 (cm) | A3 (g g−1) | h3 (cm) | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arable | 0.094 | 0.159 | 4337 | 0.035 | 198 | 0.053 | 1.30 | 6.94 × 10−5 |
| SE | 0.001 | 0.001 | 271 | 0.002 | 15 | 0.001 | 0.04 | |
| Orchard | 0.088 | 0.277 | 4104 | 0.092 | 184 | 0.138 | 1.53 | 1.47 × 10−3 |
| SE | 0.003 | 0.005 | 523 | 0.007 | 22 | 0.004 | 0.07 | |
| Grassland | 0.074 | 0.203 | 3224 | 0.059 | 113 | 0.032 | 2.52 | 1.33 × 10−4 |
| SE | 0.000 | 0.001 | 80 | 0.001 | 5 | 0.001 | 0.17 | |
| Forest | 0.076 | 0.242 | 3374 | 0.067 | 186 | 0.184 | 1.06 | 4.55 × 10−4 |
| SE | 0.002 | 0.010 | 593 | 0.011 | 45 | 0.014 | 0.09 |
| Research | PWP (g g−1) | FC (g g−1) | TP (g g−1) | AWC (g g−1) | AC (g g−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plot | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| Arable | 0.099 | 0.003 | 0.248 | 0.008 | 0.313 | 0.038 | 0.149 | 0.010 | 0.065 | 0.037 |
| Orchard | 0.097 | 0.005 | 0.369 | 0.029 | 0.521 | 0.034 | 0.272 | 0.027 | 0.152 | 0.051 |
| Grassland | 0.076 | 0.003 | 0.260 | 0.019 | 0.356 | 0.030 | 0.184 | 0.021 | 0.095 | 0.015 |
| Forest | 0.079 | 0.017 | 0.307 | 0.046 | 0.457 | 0.058 | 0.228 | 0.030 | 0.150 | 0.031 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dlapa, P.; Hriník, D.; Hrabovský, A.; Šimkovic, I.; Žarnovičan, H.; Sekucia, F.; Kollár, J. The Impact of Land-Use on the Hierarchical Pore Size Distribution and Water Retention Properties in Loamy Soils. Water 2020, 12, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020339
Dlapa P, Hriník D, Hrabovský A, Šimkovic I, Žarnovičan H, Sekucia F, Kollár J. The Impact of Land-Use on the Hierarchical Pore Size Distribution and Water Retention Properties in Loamy Soils. Water. 2020; 12(2):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020339
Chicago/Turabian StyleDlapa, Pavel, Dávid Hriník, Andrej Hrabovský, Ivan Šimkovic, Hubert Žarnovičan, Frederik Sekucia, and Jozef Kollár. 2020. "The Impact of Land-Use on the Hierarchical Pore Size Distribution and Water Retention Properties in Loamy Soils" Water 12, no. 2: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020339
APA StyleDlapa, P., Hriník, D., Hrabovský, A., Šimkovic, I., Žarnovičan, H., Sekucia, F., & Kollár, J. (2020). The Impact of Land-Use on the Hierarchical Pore Size Distribution and Water Retention Properties in Loamy Soils. Water, 12(2), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020339






