Integrating In Situ and Ocean Color Data to Evaluate Ecological Quality under the Water Framework Directive
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
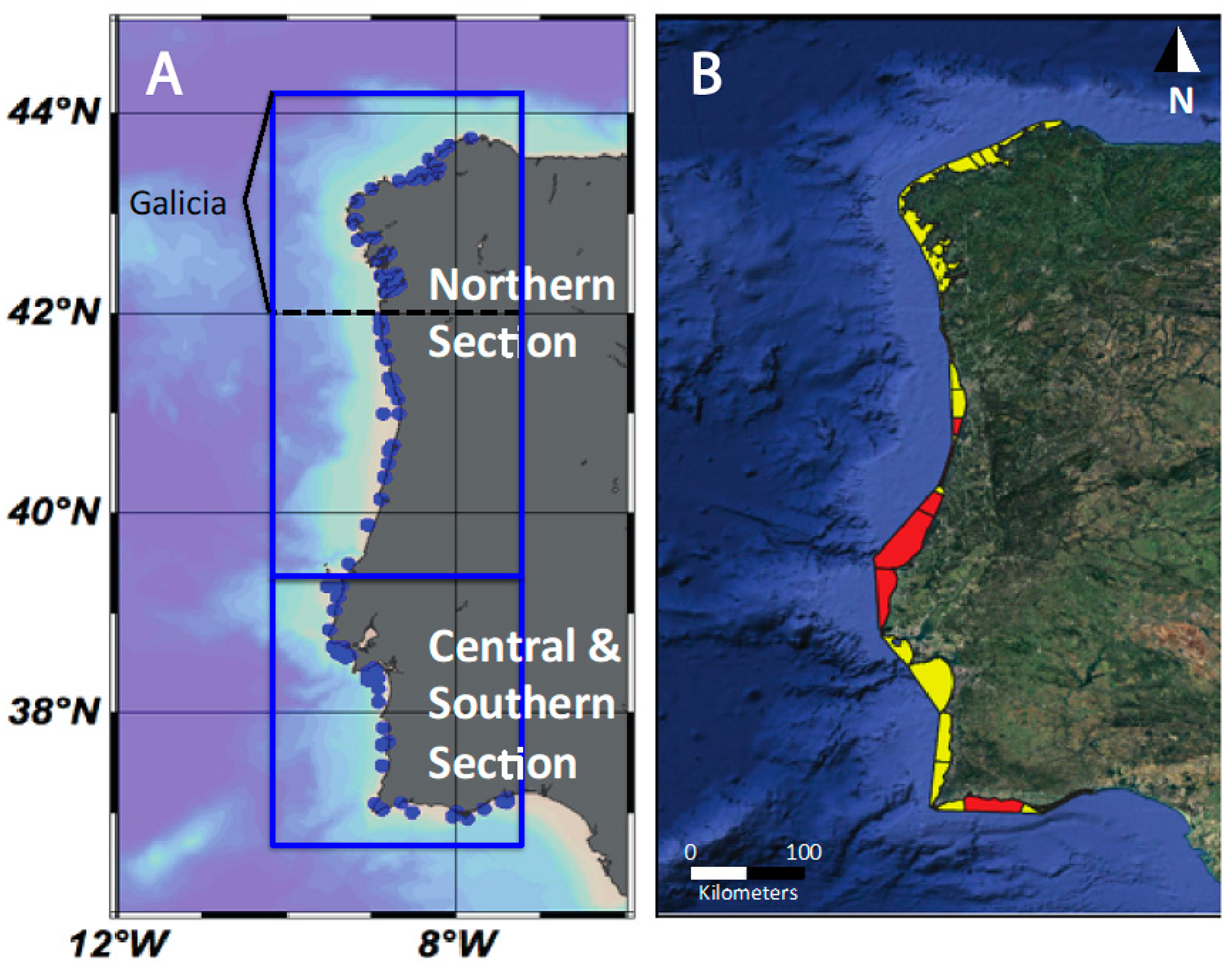
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Database
2.2.1. In Situ Dataset
Environmental Data
Phytoplankton Data (Chl a)
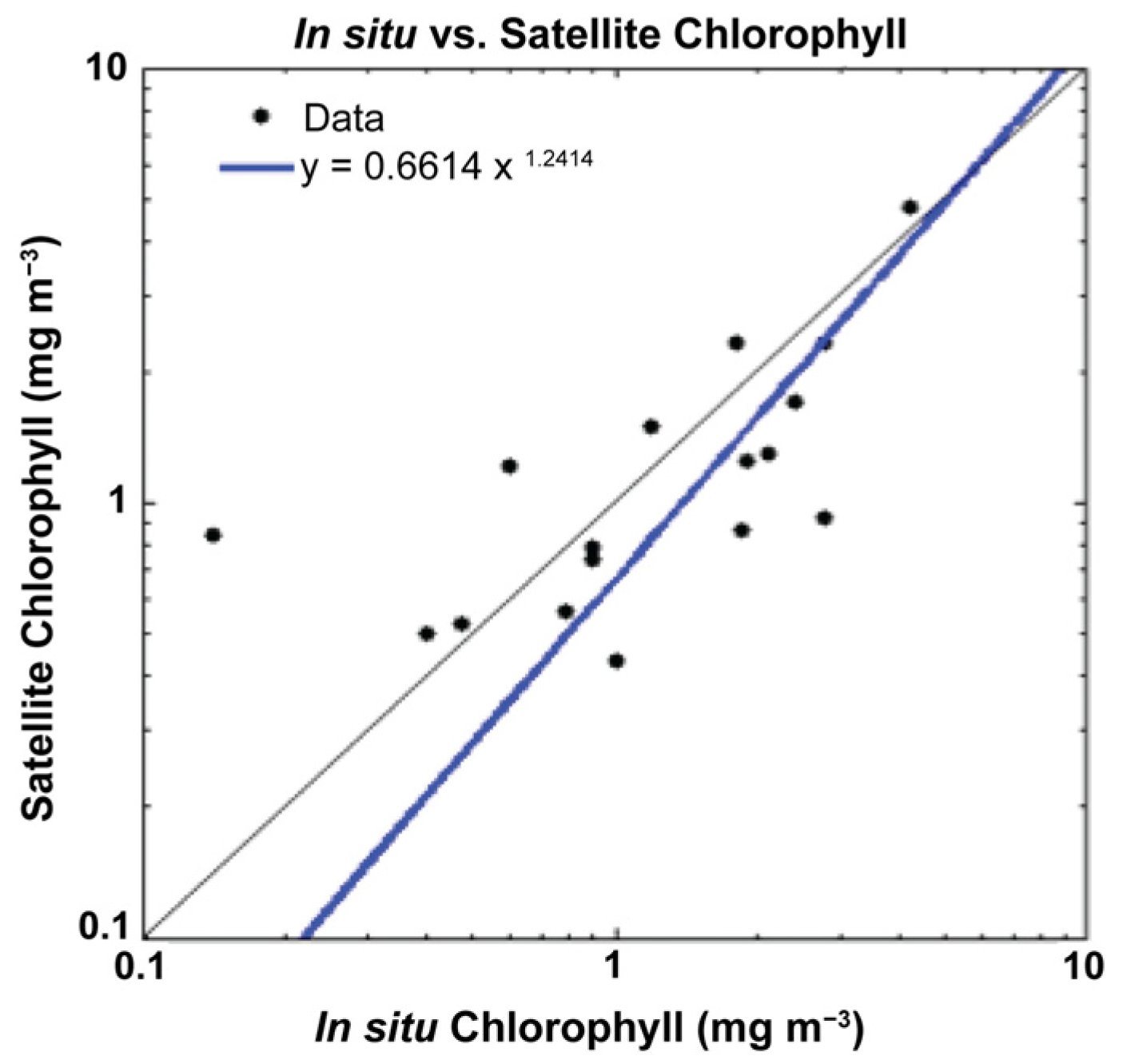
2.2.2. Satellite Dataset
2.3. Anthropogenic Pressure–LUSI Index
2.4. TRIX Trophic Index
2.5. Assessment of Ecological Quality
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
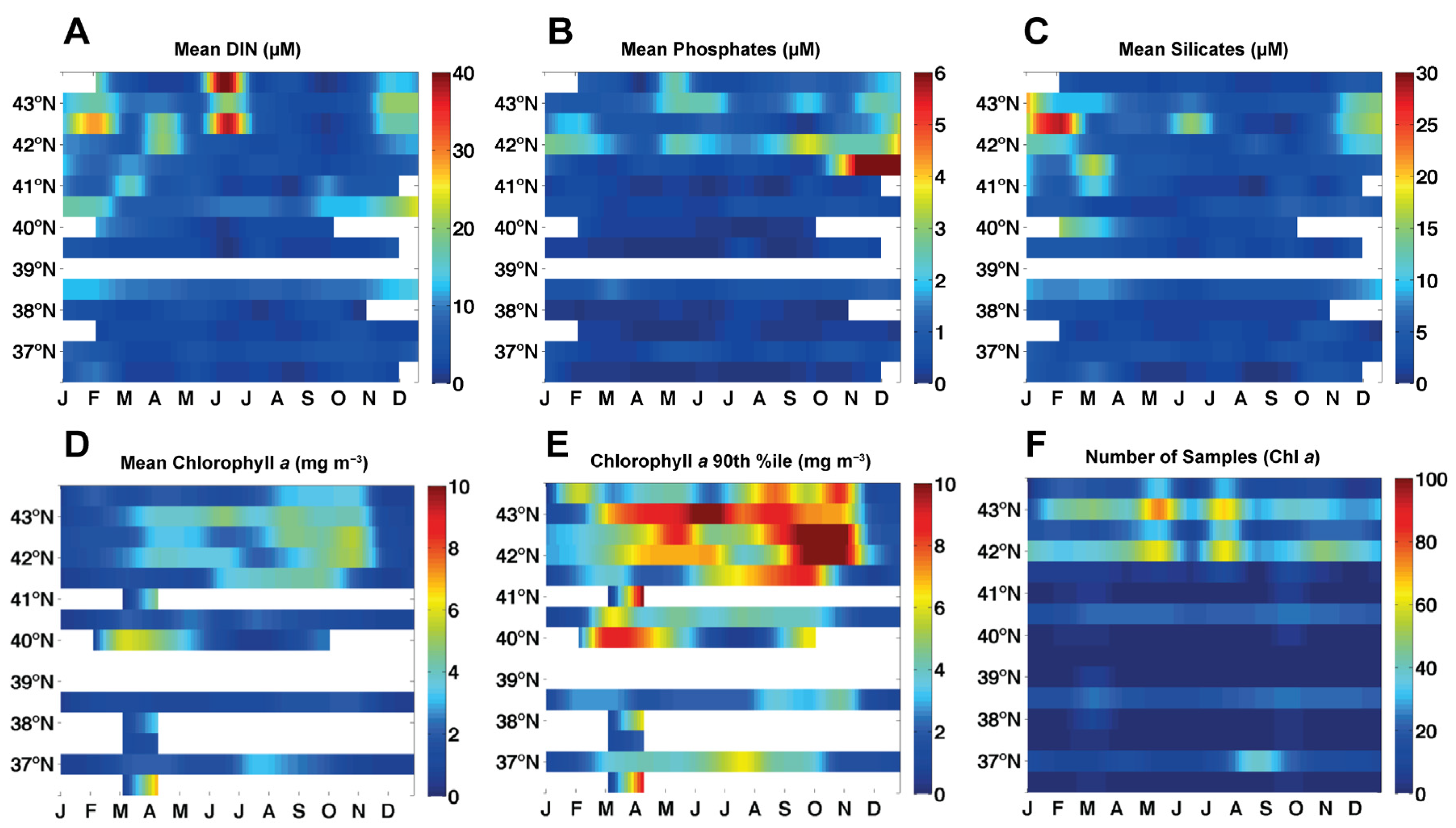
3.1. Chl a Variability in the Western Iberia Coast (WIC)
3.2. Assessing Anthropogenic Pressure
3.2.1. Winter Nutrient Concentrations
3.2.2. LUSI Index
3.3. TRIX Trophic Index
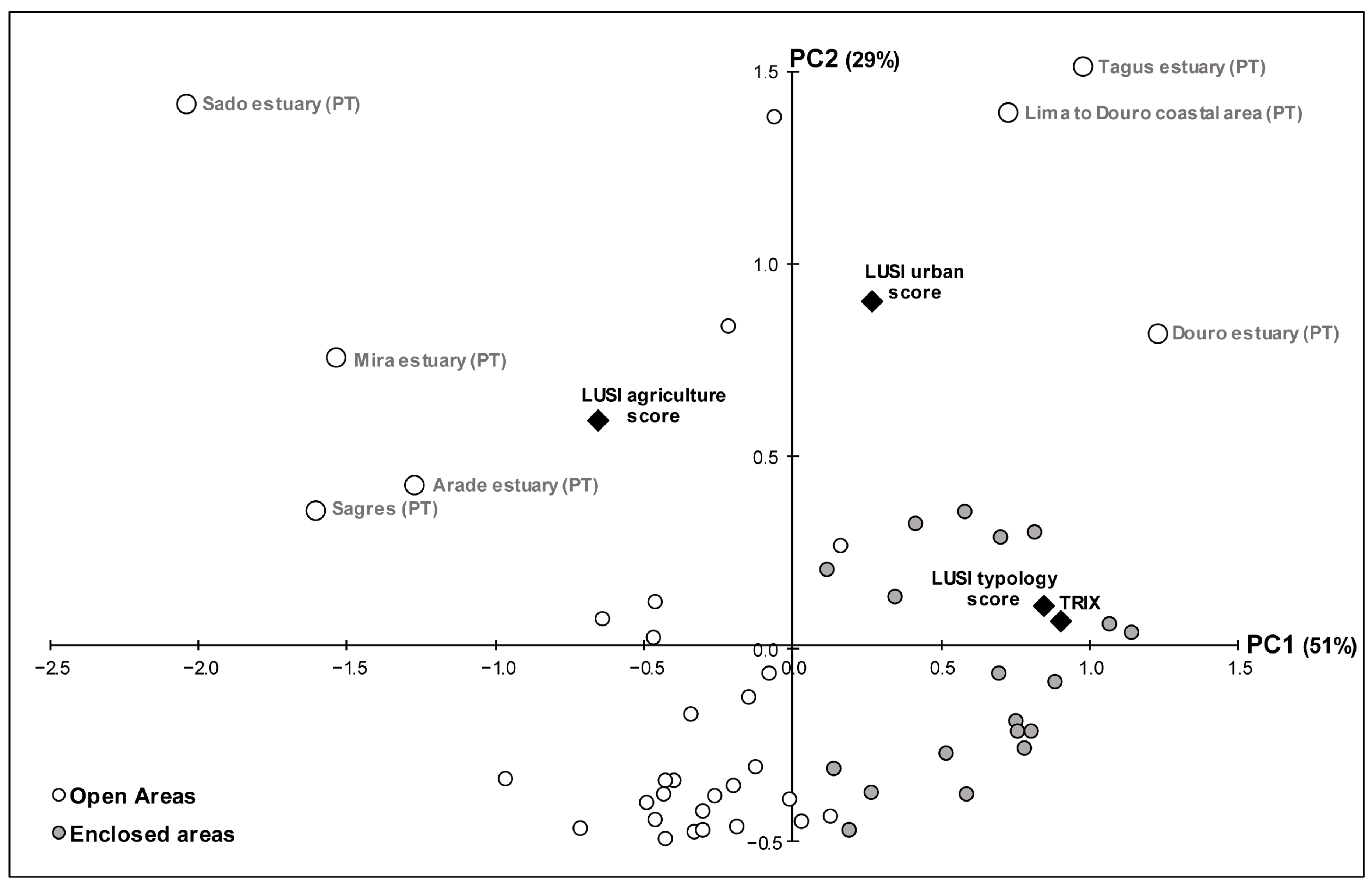
3.4. Relationship between LUSI and TRIX
3.5. Use of Pressure Indicators to Understand Eutrophication
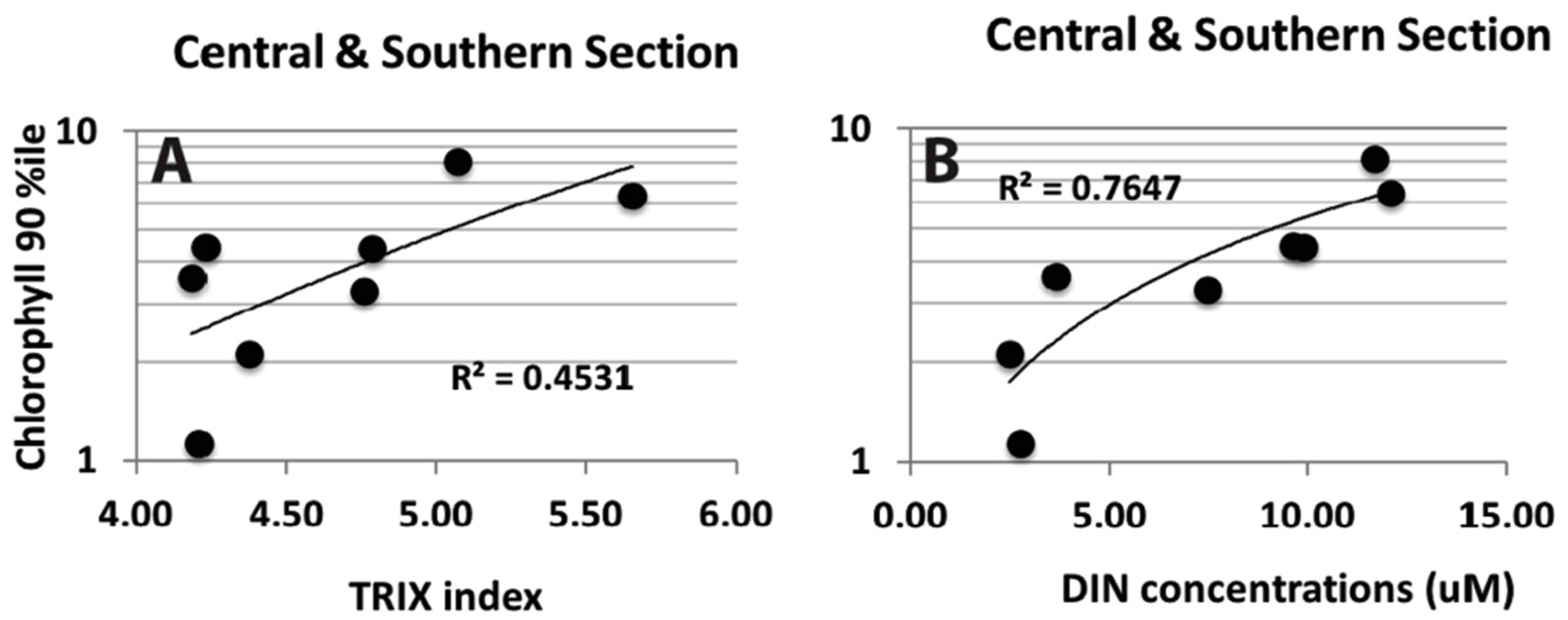
3.5.1. Phytoplankton Response to Dissolved Nutrients
3.5.2. Relationship between Phytoplankton and LUSI
3.5.3. Relationship between Phytoplankton and TRIX
3.6. Ecological Quality of Coastal Water Bodies (CWBs)
4. Discussion
4.1. Eutrophication Indicators for Coastal Waters in the WIC
4.2. Phytoplankton Response to Anthropogenic Pressures
4.3. Trophic Level and Ecological Quality Status (EQS)
4.4. Future Advances for Operational Monitoring
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stachowicz, J.J.; Whitlatch, R.B.; Osman, R.W. Species diversity and invation resistance in marine ecosystem. Science 1999, 286, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snelgrove, P.; Berghe, E.V.; Miloslavich, P.; Archambault, P.; Bailly, N.; Brandt, A.; Bucklin, A.; Clark, M.; Dahdouh-Guebas, F.; Halpin, P.; et al. Global patterns in Marine Biodiversity. In First Global Integrated Marine Assessment (First World Ocean Assessment); UN General Assembly; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Chapter 34; p. 37. [Google Scholar]
- EUROSTAT. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Archive:Coastal_regions_-_population_statistics (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Socolow, R.H. Nitrogen management and the future of food: Lessons from the management of energy and carbon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6001–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, B.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Zimmermann, J.; Nicholls, R.J. Future coastal population growth and exposure to sea-level rise and coastal flooding- a global assessment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.H.; Conley, D.J. Eutrophication in coastal marine ecosystems: Towards better understanding and management strategies. Hydrobiologia 2009, 629, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moal, M.; Gascuel-Odoux, C.; Ménesguen, A.; Souchon, Y.; Étrillard, C.; Levain, A.; Moatar, F.; Pannard, A.; Souchu, P.; Lefebvre, A.; et al. Eutrophication: A new wine in an old bottle? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrita, M.T.; Silva, A.; Oliveira, P.; Angélico, M.M.; Nogueira, M. Assessing eutrophication in the Portuguese continental exclusive economic zone within the European Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norring, N.P.; Jorgensen, E. Eutrophication and agroculture in Denmark: 20 years of experience and prospects for the future. Hydrobiologia 2009, 629, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.D.; Rask, N.; Madsen, H.B.; Jorgensen, O.T.; Petersen, S.E.; Nielsen, S.V.K.; Pedersen, C.B.; Jensen, M.H. Odense Pilot River Basin: Implementation of the EU Water Framework Directive in a shallow eutrophic estuary (Odense Fjord, Denmark) and its upstream catchment. Hydrobiologia 2009, 629, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Humborg, C.; Rahm, L.; Savchuk, O.P.; Wulff, F. Hypoxia in the Baltic Sea and basin-scale changes in phosphorus biogeochemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 5315–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, A.; Dauer, D.; Elliott, M.; Simenstad, C. Medium- and Long-term Recovery of Estuarine and Coastal Ecosystems: Patterns, Rates and Restoration Effectiveness. Estuaries Coast 2010, 33, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesch, D.F. Barriers and Bridges in Abating Coastal Eutrophication. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Valdes, L.; Pinckney, J.; Piehler, M.; Dyble, J.; Moisander, P. Phytoplankton photopigments as indicators of estuarine and coastal eutrophication. BioScience 1997, 53, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Dennis, R.L.; Whitall, D.R. Atmospheric Deposition of Nitrogen: Implication for nutrient over-enrichment of coastal waters. Estuaries 2002, 25, 677–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Cao, H.; Xy, J.; Yan, Y.; Lin, X.; Huang, J. Characteristics of Atmospheric Deposition during the period of algal bloom formation in urban water bodies. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, E.; Michalak, A.M.; Balaji, V. Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science 2017, 357, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, R.G.; Walker, P.J.; Andersen, E.J.; Barron, R.J.; Bord, R.J.; Gibson, J.R.; Kennedy, V.S.; Knight, C.G.; Megonigal, J.P.; O’Connor, E.R.; et al. The potential impacts of climate change on mid-Atlantic coastal region. Clim. Res. 2000, 14, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J.E. Our evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 210, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.; Rosenberg, R. Marine benthic hypoxia: A review of its ecological effects and behavioural response of benthoc macrofauna. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2015, 33, 245–303. [Google Scholar]
- Nixon, S.W. Eutrophication and the macroscope. In Eutrophication in Coastal Ecosystems. Developments in Hydrobiology; Andersen, J.H., Conley, D.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 207, pp. 5–19. [Google Scholar]
- Howarth, R.; Marino, R. Nitrogen as the limiting nutrient for eutrophication in coastal marine ecosystems: Evolving views over three decades. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Castensen, J.; Vaquer-Sunyer, R.; Duarte, C.M. Ecosystem thresholds with hypoxia. In Eutrophication in Coastal Ecosystems. Developments in Hydrobiology; Andersen, J.H., Conley, D.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 207, pp. 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, C.M. Coastal eutrophication research: A new awareness. Hydrobiologia 2009, 629, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaanus, A.; Toming, K.; Hallfors, S.; Kaljurand, K.; Lips, I. Potential phytoplankton indicator species for monitoring Baltic coastal waters in the summer period. In Eutrophication in Coastal Ecosystems. Developments in Hydrobiology; Andersen, J.H., Conley, D.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 207, pp. 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, M.; Best, M.; Coates, D.; Bresnan, E.; O’Boyle, S.; Park, R.; Silke, J.; Cusack, C.; Skeats, J. Establishing boundary classes for the classification of the UK marine waters using phytoplankton communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 55, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla, M.; Franco, J.; Bald, J.; Borja, A.Å.L.; Laza, A.; Seoane, S.; Valencia, V. Assessment of the phytoplankton ecological status in the Basque coast (northern Spain) according to the European Water Framework Directive. J. Sea Res. 2009, 61, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.G.; Andersen, J.H.; Borja, A.; Bricker, S.; Camp, J.; Silva, M.C.; Garcés, E.; Heiskanen, A.S.; Humborg, C.; Ignatiades, L.; et al. Overview of eutrophication indicators to assess environmental status within the European Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, F.; Teixeira, H. WFD Intercalibration Data Archives: Coastal and Transitional Waters; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; p. 91. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, A.C.; Brotas, V.; Caetano, M.; Coutinho, T.P.; Bordalo, A.; Icely, J.; Neto, J.; Serôdio, J.; Moita, T. Defining phytoplankton class boundaried in Portuguese transitional waters: An evaluation of the ecological quality status according to the Water Framework Directive. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 19, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birk, S.; Bonne, W.; Borja, A.; Brucet, S.; Courrat, A.; Poikane, S.; Solimini, A.; Van de Bund, W.; Zampoukas, N.; Hering, D. Three hundred ways to assess Europe’s surface waters: An almost complete overview of biological methods to implement the Water Framework Directive. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.L.; Tao, S.; Dawson, R.W.; Li, B.G. A GIS-based method of lake eutrophication assessment. Ecol. Model. 2001, 144, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollenweider, R.; Giovanardi, F.; Montanari, G.; Rinaldi, A. Characterization of the trophic conditions of marine coastal waters with special reference to the NW Adriatic Sea: Proposal for a trophic scale, turbidity and generalized water quality index. Environmentrics 1998, 9, 329–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flo, E.; Camp, J.; Garcés, E. Assessment of pressure methodology for biological quality element phytoplankton: Land Uses Simplified Index (LUSI). In Mediterranean Geographical Intercalibration Group-Coastal Waters-Biological Quality Element Phytoplankton-France and Spain; Water Framework Directive Intercalibration Phase 2: Milestone 5 report; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2011; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Flo, E. Opening the Black Box of Coastal Inshore Waters in the NW Mediterranean Sea: Environmental Quality Tools and Assessment. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vascetta, M.; Kauppila, P.; Furman, E. Aggregate indicators in coastal policy making: Potentials of the Trophic Index TRIX for sustainable considerations of eutrophication. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 16, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, F.; Teixeira, H.; Marcos, C.; Marques, J.C.; Pérez-Ruzafa, A. Applicability of the trophic index TRIX in two transitional ecosystems: The Mar Menor lagoon (Spain) and the Modengo estuary (Portugal). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1442–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carletti, A.; Heinskanen, A.S. Water Framework Directive Intercalibration Technical Report Part 3: Coastal and Transitional Waters; EUR 23838 EN/3; Publication Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Saraiva, S.; Pina, P.; Martins, F.; Santos, M.; Braunschweig, F.; Neves, R. Modelling the influence of nutrient loads on Portuguese estuaries. Hydrobiologia 2007, 587, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, A.; Newton, A.; Tett, P.; Fernandes, T. Sediment-water interactions in a coastal shallow lagoon, Ria Formosa (Portugal): Implications within the Water Framework Directive. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peliz, A.; Rosa, T.; Santos, M.; Pissarra, J. Fronts, jets, and counter-flows in the Western Iberian upwelling system. J. Mar. Syst. 2002, 35, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.; Peliz, A.; Dubert, J.; Oliveira, P.B.; Angélico, M.; Ré, P. Impact of a winter upwelling event on the distribution and transport of sardine (Sardina pilchardus) eggs and larvae off western Iberia: A retention mechanism. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, A.; Alvarez, M.; Ruíz-Villarreal, M.; Varela, M. Changes in phytoplankton production and upwelling intensity off A Coruna (NW Spain) for the last 28 years. Ocean Dyn. 2019, 69, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, I.; Lorenzo, M.N.; de Castro, M. Analysis of chlorophyll a concentration along the Galicias coast: Seasonal variability and trends. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 69, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiuza, A. Hidrologia e Dinâmica das Águas Costeiras de Portugal (Hydrology and Dynamics of the Portuguese Coastal Waters). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Lisbon, Lisbon, Portugal, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Gago, J.; Miguez, B.M.; Gilcoto, M.; Pérez, F. Surface waters of the NW Iberian Margin: Upwelling on the shelf versus outwelling of upwelled waters from the Rias Baixas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 51, 821–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, I.; de Castro, M.; Prego, R.; Gómez-Gesteira, M. Hydrographic characterization of a Winter-upwelling event in the Ria of Pontevedra (NW Spain). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 56, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, I.; Ospina-Alvarez, N.; Pazos, Y.; de Castro, M.; Bernardez, P.; Campos, M.J.; Gomez-Gesteira, J.L.; Alvarez-Ossorio, M.T.; Varela, M.; Gomez-Gesteira, M.; et al. A Winter upwelling event in the Northern Galician Rias: Frequency and oceanographic implications. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.C.; Mendes, R.; Alvarez, I.; Vaz, N.; Gomez-Gesteira, M.; Dias, J.M. Unusual circulation patterns of the Rias Baixas induced by Minho Freshwater intrusion (NW of the Iberian Peninsula). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC (European Commission). Commission Decision 2018/229 of 12 February 2018 establishing, pursuant to Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, the values of the Member State monitoring system classifications as a result of the intercalibration exercise and repealing Commission Decision 2013/480/EU. Off. J. Eur. Union 2018, 47, 1–91. [Google Scholar]
- Grasshoff, K.; Ehrhardt, M.; Kremling, K. Methods of Seawater Analysis, 2nd ed.; Verlag Chemie Weinhein: New York, NY, USA, 1983; p. 419. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, L.W. Die Bestimmung des in Wasser gelosten Sauerstoffen. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1888, 21, 2843–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyendranath, S.; Grant, M.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Brockmann, C.; Brotas, V.; Chuprin, A.; Doerfffer, R.; Dowell, M.; Farman, A.; Groom, S.; et al. ESA Ocean Colour Climate Change Initiative (Ocean_Colour_cci): Version 3.1 Data; Centre for Environmental Data Analysis: Didcot, UK, 4 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gohin, F.; Saulquin, B.; Oger-Jeanneret, H.; Lozac’h, L.; Lampert, L.; Lefebvre, A.; Riou, P.; Bruchon, F. Towards a better assessment of the ecological status of coastal waters using satellite-derived chlorophyll-a concentrations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3329–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lee, Z.; Franz, B.A. Chlorophyll-a algorithms for oligotrophic oceans: A novel approach based on three-band reflectance difference. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C01011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, C.; D’Alimonte, D.; Brito, A.C.; Kajiyama, T.; Mendes, C.R.; Vitorino, J.; Oliveira, P.B.; da Silva, J.; Brotas, V. Validation of standard and alternative satellite ocean-color chlorophyll products off Western Iberia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, K.G.; Ovidio, F.; Rijkeboer, M. Atmospheric correction of SeaWiFS imagery for turbid coastal and inland waters. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, B.; Kiselev, V.; Zibordi, G. Adjacency effects in satellite radiometric products from coastal waters: A theoretical analysis for the northern Adriatic Sea. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 854–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa, S.; Doxaran, D.; Ody, A.; Vanhellemont, Q.; Lafon, V.; Lubac, B.; Gernez, P. Atmospheric corrections and multi-conditional algorithm for multi-sensor remote sensing of suspended particulate matter in low-to-high turbidity levels coastal waters. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flo, E.; Garcés, E.; Camp, J. Land Uses Simplified Index (LUSI): Determining Land Pressures and their link with coastal eutrophication. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, I.; Pachés, M.; Martínez-Guijarro, R.; Ferrer, J. Glophymed: An index to establish the ecological status for the Water Framework Directive based on phytoplankton in coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 75, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, B.; Capellacci, S.; Ricci, F. The influence of the Pro River discharge phytoplankton bloom dynamics along the coastline of Pesaro (Italy) in the Adriatic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.; Garrido-Amador, P.; Brito, A.C. Disentangling environmental drivers of phytoplankton biomass off Western Iberia. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, a44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohin, F.; Zande, D.; Tilstone, G.; Eleveld, M.; Lefebvre, A.; Andrieux-Loyer, F.; Blauw, A.; Bryère, P.; Devreker, D.; Garnesson, P.; et al. Twenty years of satellite data and in-situ observations of surface chlorophyll-a from the northern Bay of Biscay to the eastern English Channel. Is the water quality improving? Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terauchi, G.; Maure, E.R.; Yu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Lee, C.; Kachur, V.; Ishizaka, J. Assessment of eutrophication using remotely sensed chlorophyll-a in the Northwest Pacific region. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing of the Ocean and Coastal Ocean and Inland Waters, Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–26 September 2018; Volume 10778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J. The relative importance of light and nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth: A simple indez of coastal ecosystem sensitivity to nutrient enrichment. Aquat. Ecol. 1999, 33, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, S.; Icely, J.; Newton, A. Enrichment experiments and primary production at Sagres (SW Portugal). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 359, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrenz, S.; Fahnenstiel, G.; Redalje, D.; Lang, G.; Dagg, M.; Whitledge, T.; Dortch, Q. Nutrients, irradiance, and mixing as factors regulating primary production in coastal waters impacted by the Mississippi River plume. Cont. Shelf Res. 1999, 19, 1113–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmendia, M.; Borja, A.; Franco, J.; Revilla, M. Phytoplankton composition indicators for the assessment of eutrophication in marine waters: Present state and challenges within the European Directives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 66, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninčević-Gladan, N.; Bužančić, M.; Kušpilić, G.; Grbec, B.; Matijević, S.; Skejić, S.; Marasović, I.; Morović, M. The response of phytoplankton community to anthropogenic pressure gradient in the coastal waters of the eastern Adriatic Sea. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 56, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAMAOT. Estratégia Marinha para a subdivisão da plataforma Continental Estendida. In Directiva Quadro Estratégia Marinha; Ministério da Agricultura, do Mar, do Ambiente e do Ordenamento do Território: Lisboa, Portugal, 2012; p. 896. [Google Scholar]
- Ansper, A.; Alikas, K. Retrieval of Chlorophyll a from sentinel-2 MSI data for the European Union Water Framework Directive Reporting Purposes. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toming, K.; Kutser, T.; Uiboupin, R.; Arikas, A.; Vahter, K.; Paavel, B. Mapping water quality parameters with Sentinel-3 Ocean and Land Colour Instrument Imagery in the Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; DiGiacomo, P.M. Detecting phytoplankton diatom fraction based on the spectral shape of satellite-derived algal light absorption coefficient. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 63, S85–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T.; Morales, J.; Stuart, V.; Forget, M.H.; Devred, E.; Bouman, H. Remote sensing of phytoplankton functional types. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3366–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, A.; Sá, C.; Brotas, V.; Brewin, B.; Silva, T.; Vitorino, J.; Platt, T.; Sathyendranath, S. Effect of phytoplankton size classes on bio-optical properties of phytoplankton in the western Iberian coast: Application of models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longphuirt, S.N.; McDermott, G.; O’Boyle, S.; Wilkes, R.; Stengel, D.B. Decoupling Abundance and Biomass of Phytoplankton Communities under different environmental controls: A New Multi-Metric Index. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasopoulou, E.; Simis, S. Satellite-assisted monitoring of water quality to support the implementation of the Water Framework Directive. EOMORES White Paper 2019, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Karger, F.; Hestir, E.; Ade, C.; Turpie, K.; Roberts, D.; Siegel, D.; Miller, R.J.; Humm, D.; Izenberg, N.; Keller, M.; et al. Satellite sensor requirements for monitoring essential biodiversity variables of coastal ecosystems. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 28, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
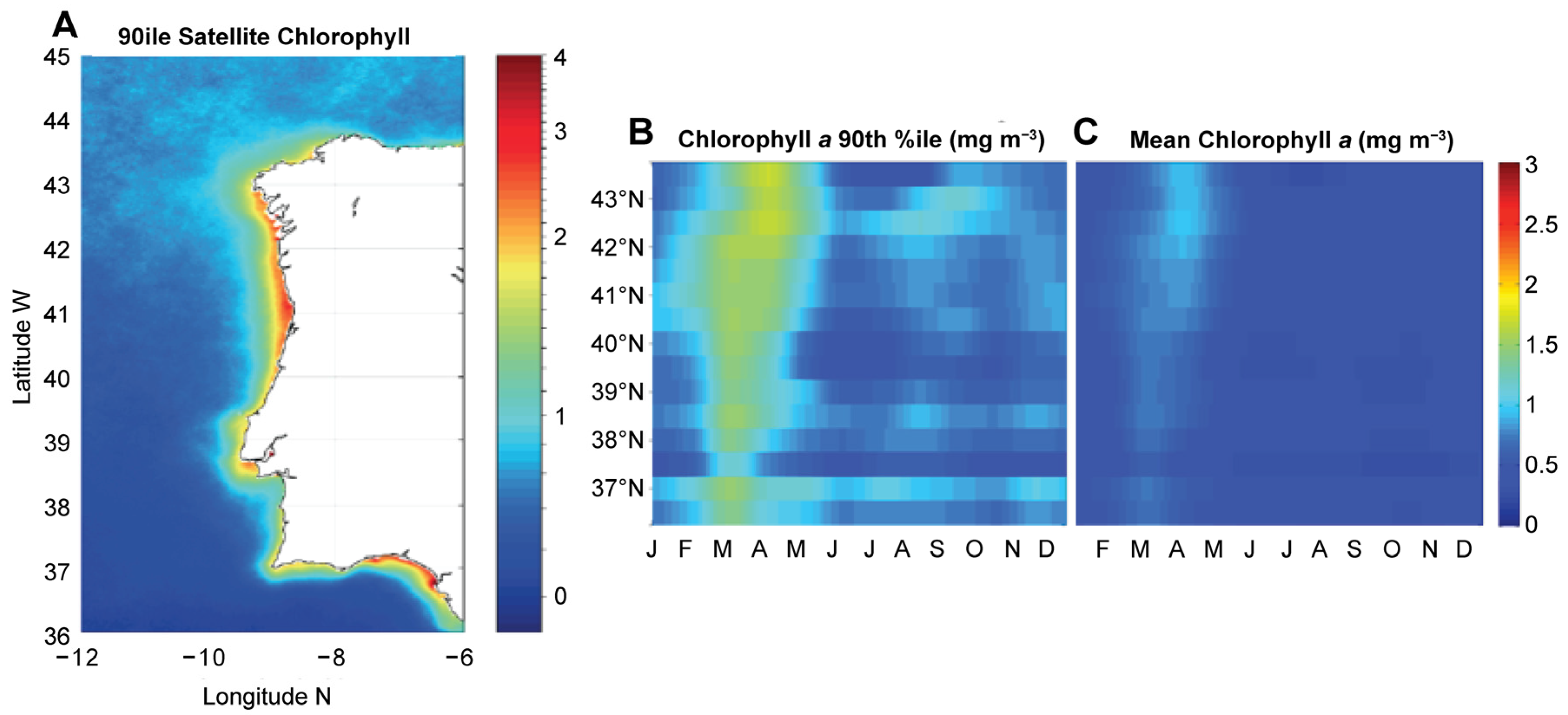
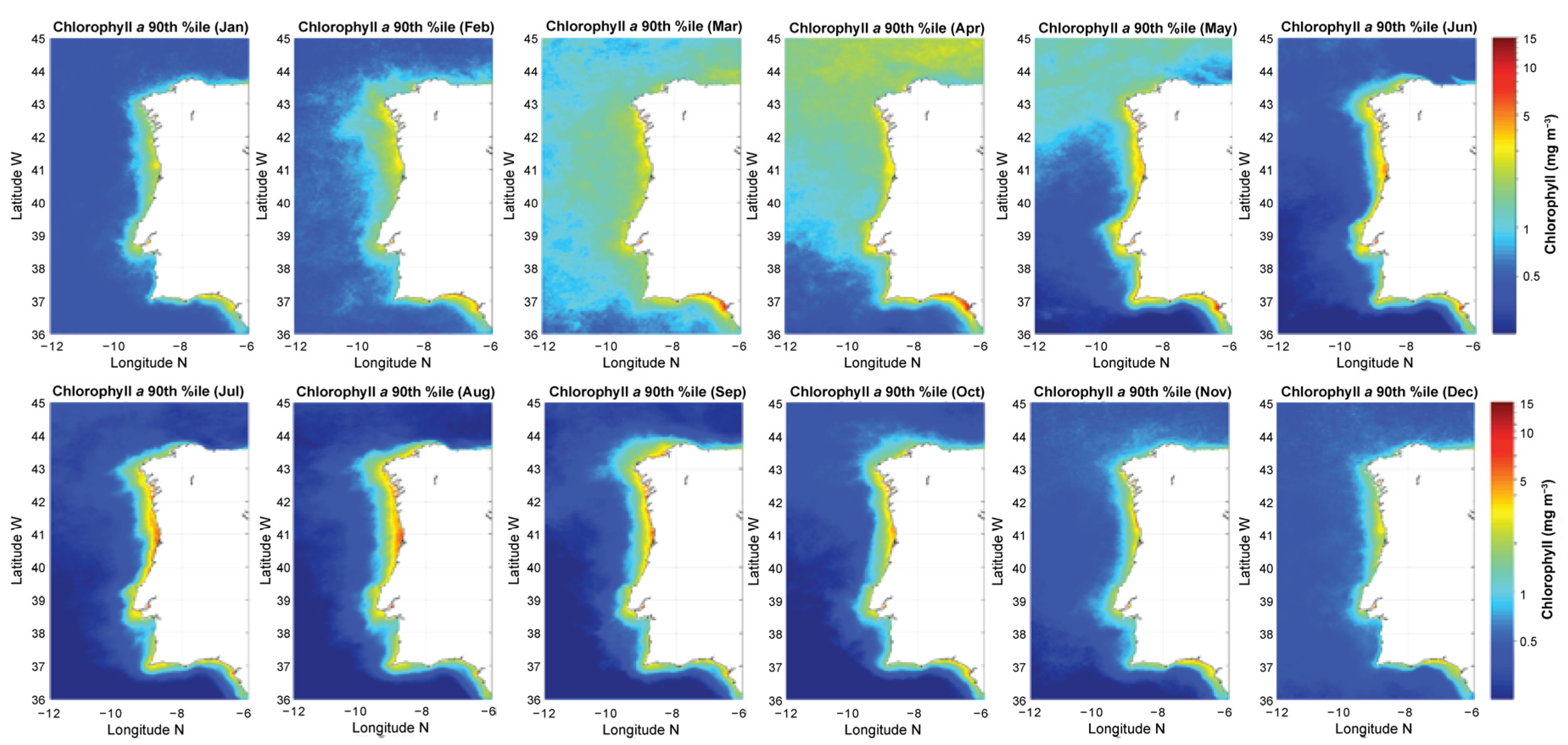

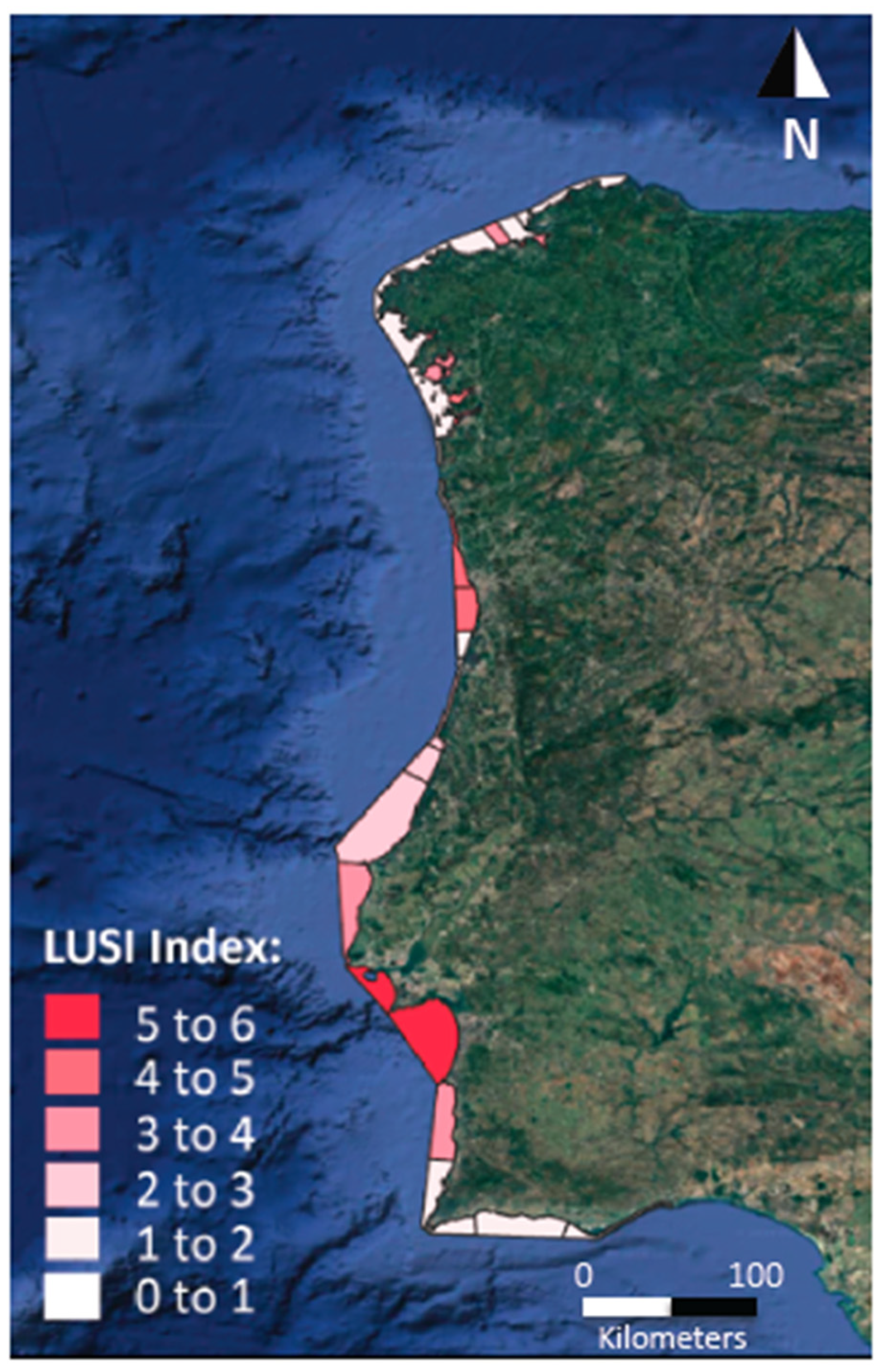
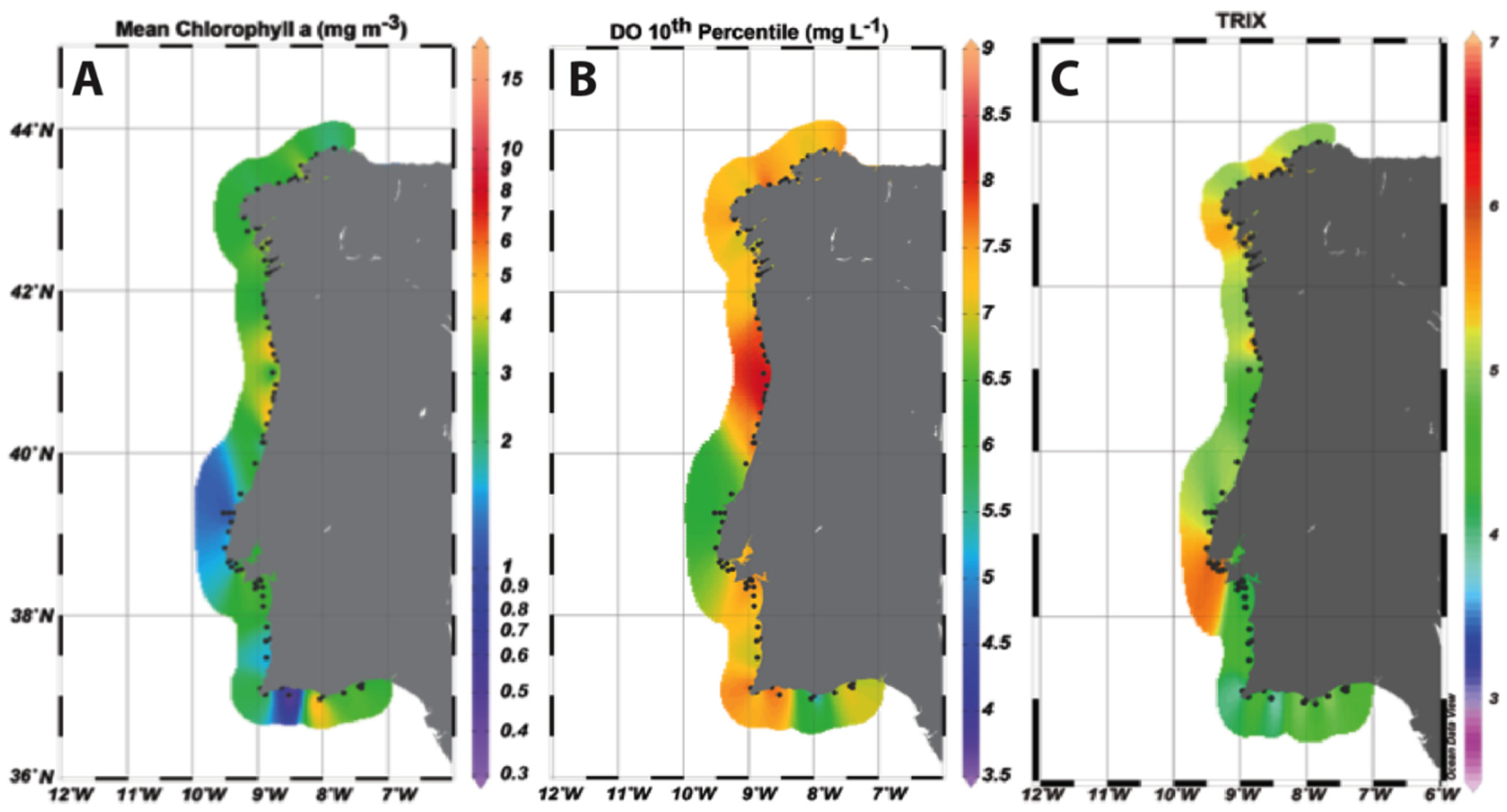
| Parameter | Period | N | Max | Min | Average | 90th %ile | 50th %ile | 10th %ile | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity | 1995–2014 | 1533 | 37.10 | 21.32 | 34.42 | 35.83 | 35.17 | 32.18 | 0.05 |
| In situ Chl a (mg m−3) | 2001–2014 | 1785 | 19.35 | 0.03 | 2.22 | 4.82 | 1.40 | 0.46 | 0.05 |
| In situ and Sat Chl a (mg m−3) | 1998–2014 | 1842 | 19.35 | 0.03 | 2.18 | 4.77 | 1.40 | 0.46 | 0.05 |
| DIN (µM) | 1995–2014 | 1732 | 332.79 | 0.04 | 8.46 | 16.41 | 4.61 | 0.69 | 0.04 |
| Winter DIN (µM) | 1995–2013 | 388 | 332.79 | 0.08 | 14.56 | 23.71 | 8.95 | 2.71 | 2.83 |
| Phosphate (µM) | 1995–2014 | 1410 | 54.60 | 0.01 | 0.97 | 1.81 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Winter phosphate (µM) | 1995–2013 | 326 | 31.68 | 0.01 | 1.37 | 2.62 | 0.58 | 0.18 | 0.30 |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg L−1) | 2002–2014 | 1151 | 16.59 | 0.38 | 8.27 | 9.74 | 8.19 | 6.95 | 0.04 |
| Distance | N | r2 | Bias | RMSE | RPD (%) | APD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 km | 17 | 0.642 | −0.034 | 0.282 | 21.2 | 62.9 |
| Sub-Typology | Chl a P90 (mg m−3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| High/Good Boundary | Good/Moderate Boundary | ||
| NEA 1/26e | 1. Portugal–strong upwelling | 8.00 | 12.00 |
| 2.. Portugal–upwelling | 4.50 | 8.20 | |
| 3. Spain–upwelling coast | 6.00 | 9.00 | |
| 4. Spain–upwelling coast-Rias | 8.00 | 12.00 | |
| Sections | WBs | Population (×106) | Utilized Agric. Area (UAA, ×108 m2) | Salinity | DO (mg L−1) | Urban Score | Agric. Score | Typ. Score | LUSI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | <10 km from coast | Regional averages | ||||||||
| Northern | Galicia | 19 | 1.67 | 9.03 | 34.67 | 7.35 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 1.61 | 2.00 |
| Northern PT | 9 | 3.23 | 15.57 | 33.99 | 7.45 | 0.83 | 0.24 | 1.77 | 2.89 | |
| Central and Southern | Central PT | 4 | 1.65 | 43.57 | 35.44 | 6.84 | 0.95 | 1.49 | 1.27 | 4.14 |
| Southern PT | 4 | 0.45 | 6.41 | 35.58 | 6.67 | 0.26 | 0.22 | 1.22 | 1.60 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brito, A.C.; Garrido-Amador, P.; Gameiro, C.; Nogueira, M.; Moita, M.T.; Cabrita, M.T. Integrating In Situ and Ocean Color Data to Evaluate Ecological Quality under the Water Framework Directive. Water 2020, 12, 3443. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123443
Brito AC, Garrido-Amador P, Gameiro C, Nogueira M, Moita MT, Cabrita MT. Integrating In Situ and Ocean Color Data to Evaluate Ecological Quality under the Water Framework Directive. Water. 2020; 12(12):3443. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123443
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrito, Ana C., Paloma Garrido-Amador, Carla Gameiro, Marta Nogueira, Maria Teresa Moita, and Maria Teresa Cabrita. 2020. "Integrating In Situ and Ocean Color Data to Evaluate Ecological Quality under the Water Framework Directive" Water 12, no. 12: 3443. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123443
APA StyleBrito, A. C., Garrido-Amador, P., Gameiro, C., Nogueira, M., Moita, M. T., & Cabrita, M. T. (2020). Integrating In Situ and Ocean Color Data to Evaluate Ecological Quality under the Water Framework Directive. Water, 12(12), 3443. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123443






