Stable-Isotope-Aided Investigation of the Effect of Redox Potential on Nitrous Oxide Emissions as Affected by Water Status and N Fertilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Material
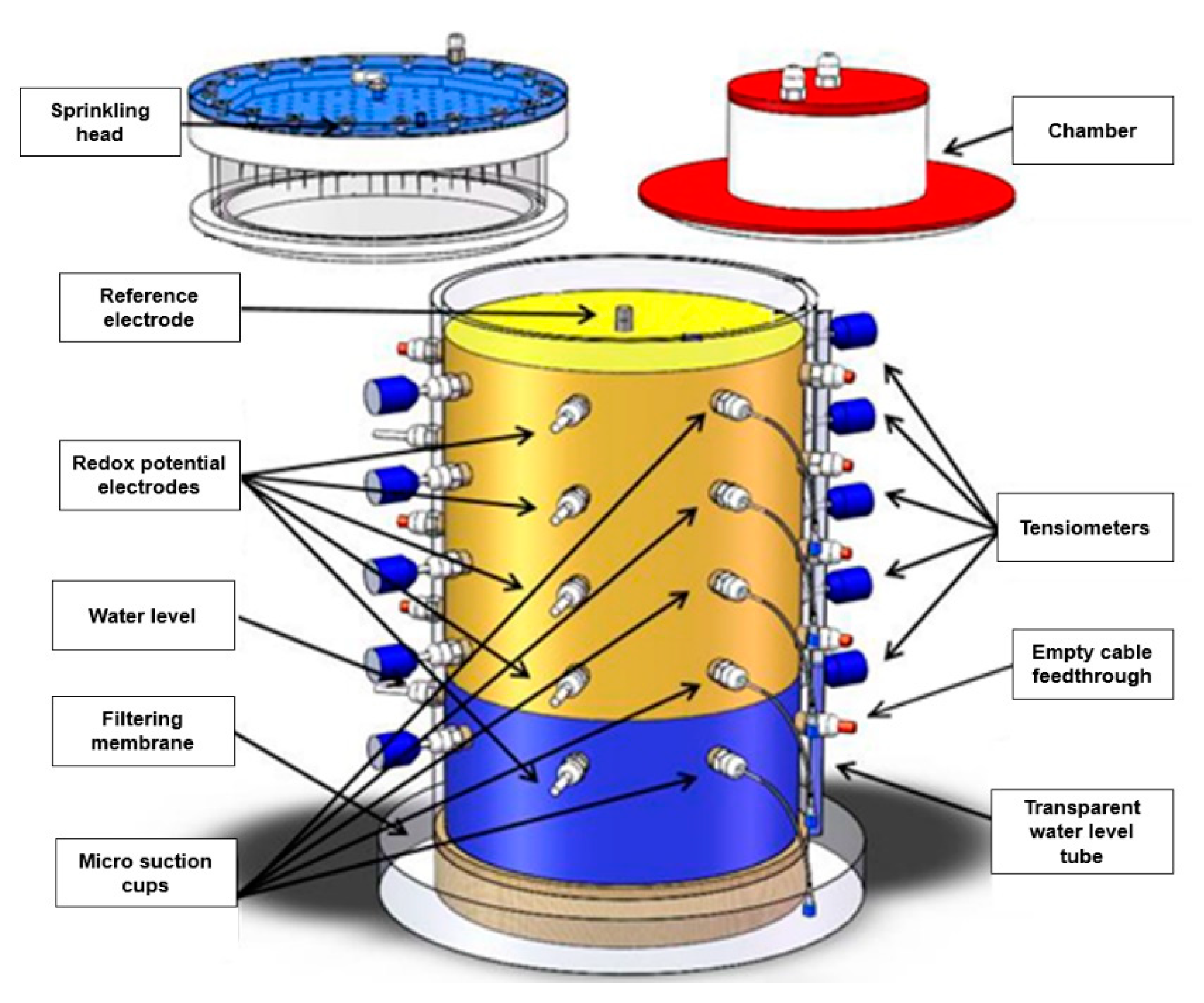
2.2. Soil Lysimeter Experimental Setup
2.3. Experimental Procedures
2.4. N2O Flux Measurements
2.5. Isotope-Ratio Measurements
2.6. Eh Measurements
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
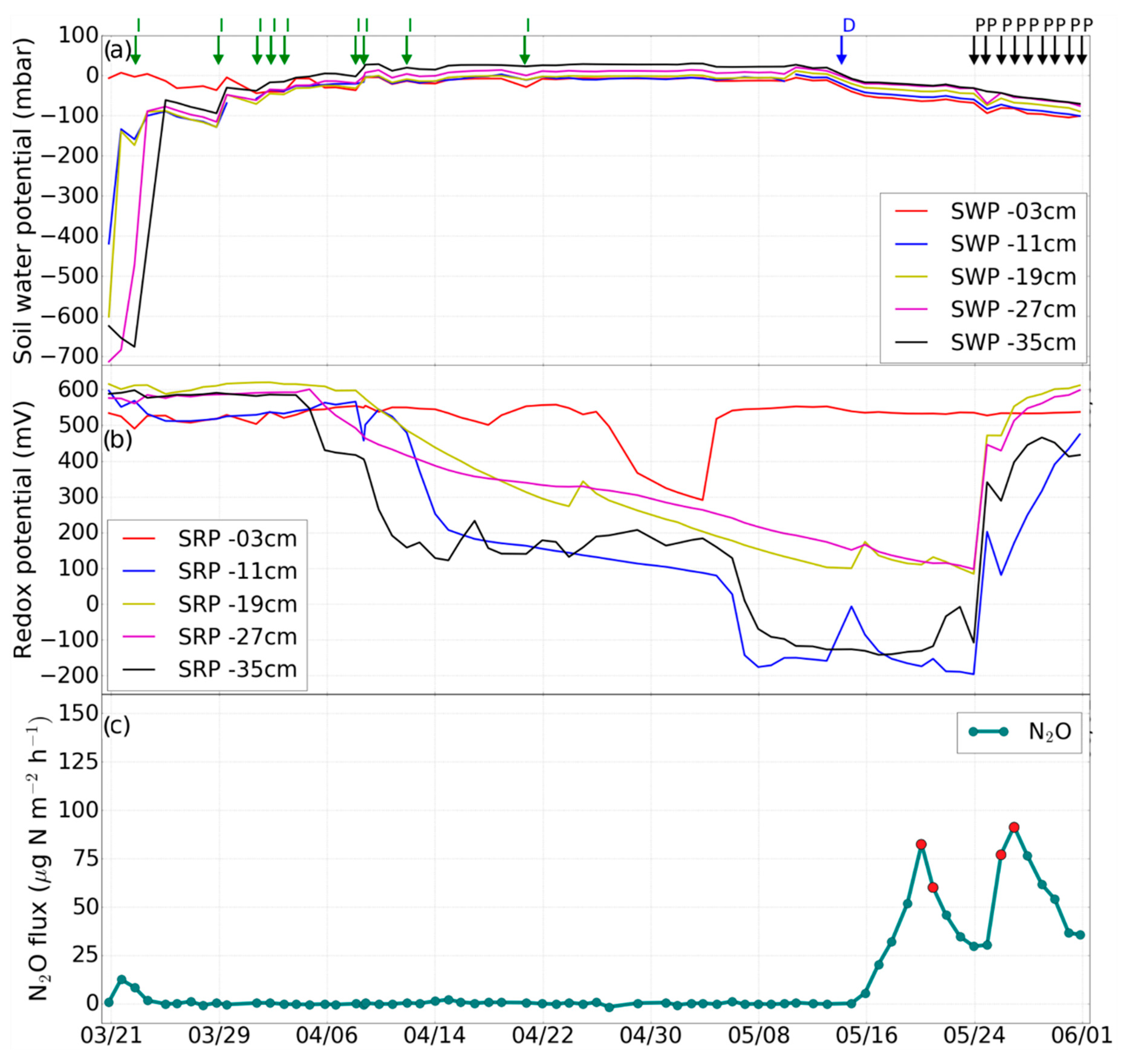
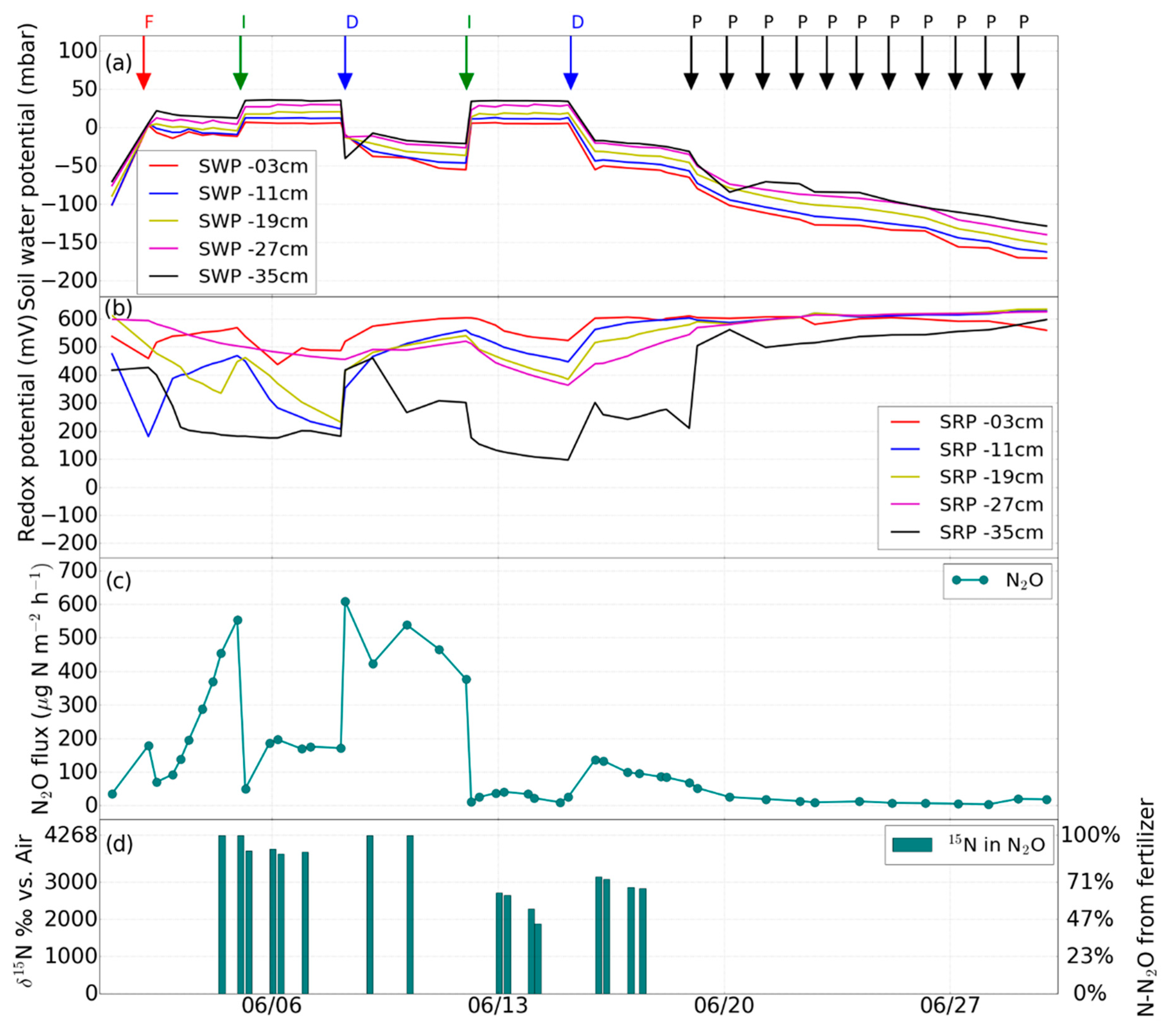
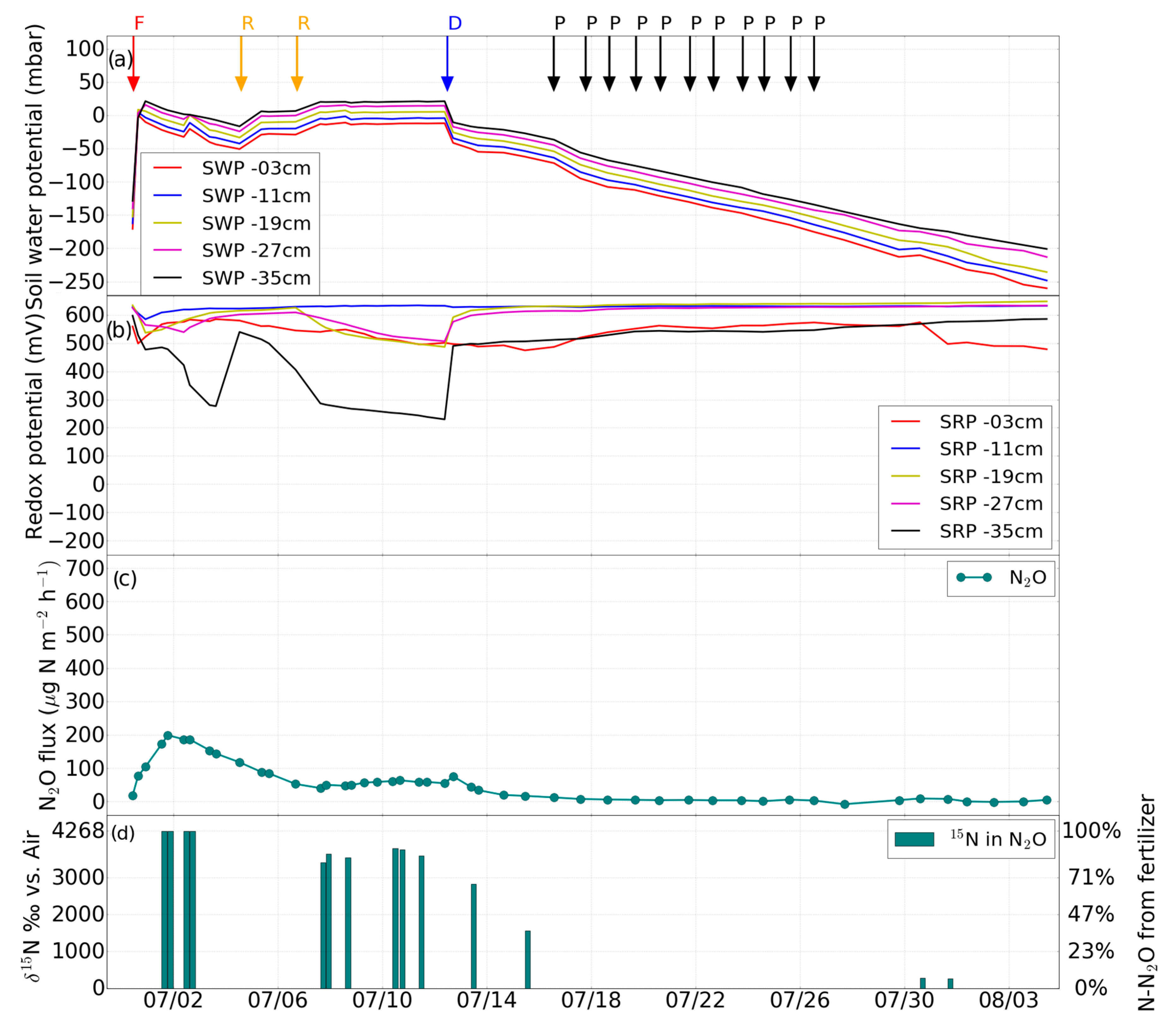
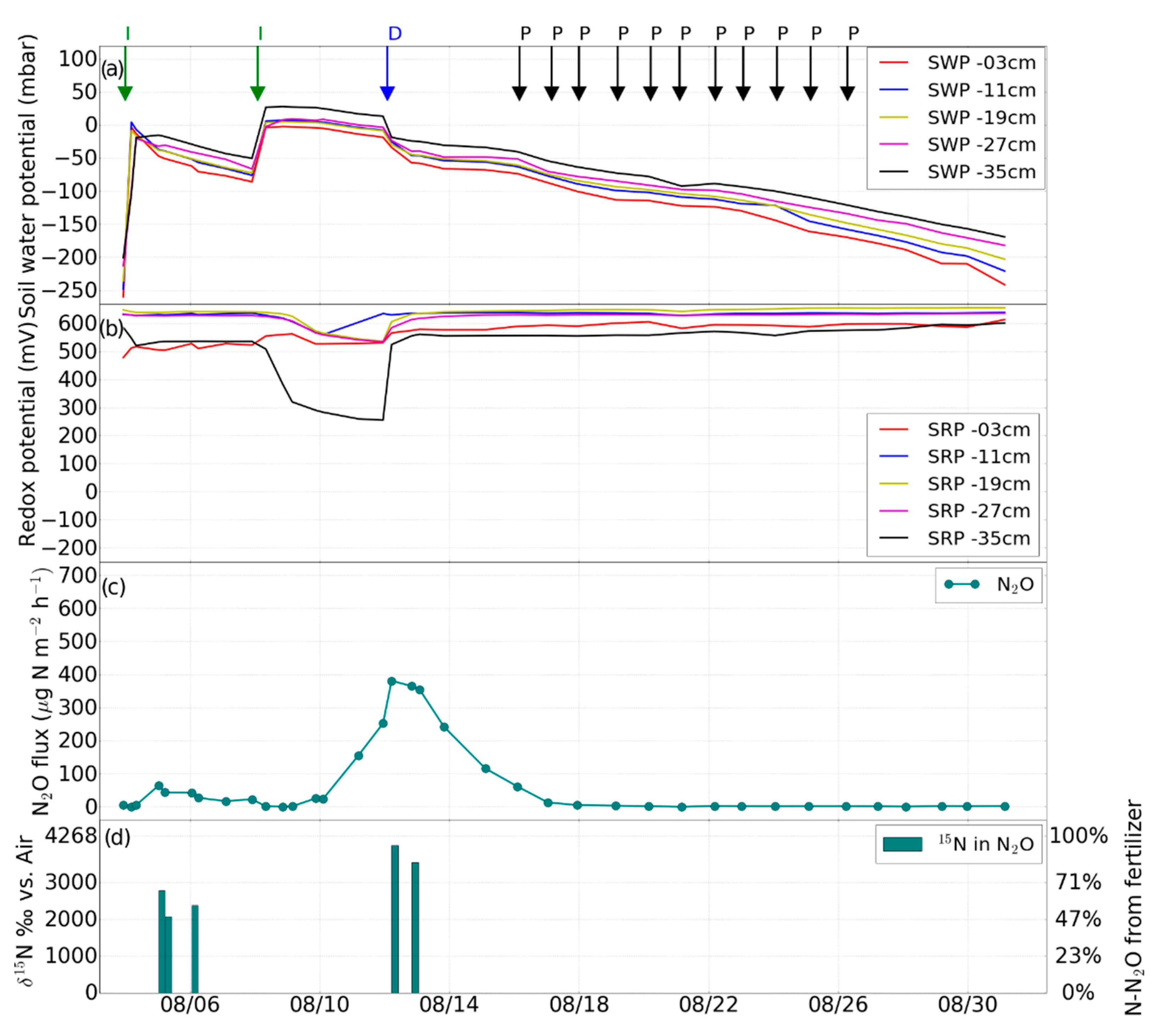
3.1. Impact of Hydrological Events on Soil Water Potential and Eh
3.2. Impact of Hydrological Events on N2O Emissions
3.3. Variations of δ15Nbulk, 15N SP and δ18O of N2O Emissions
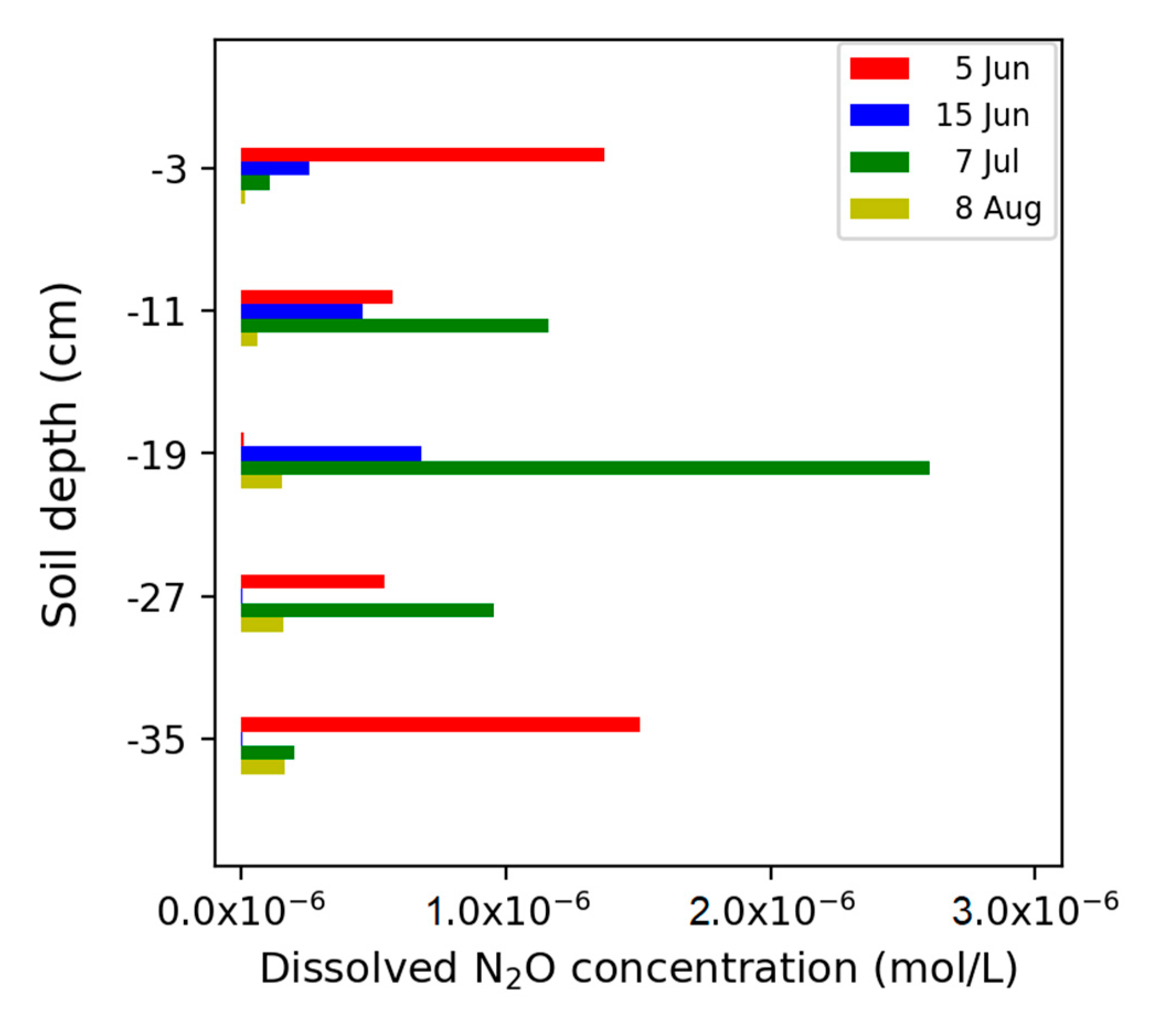
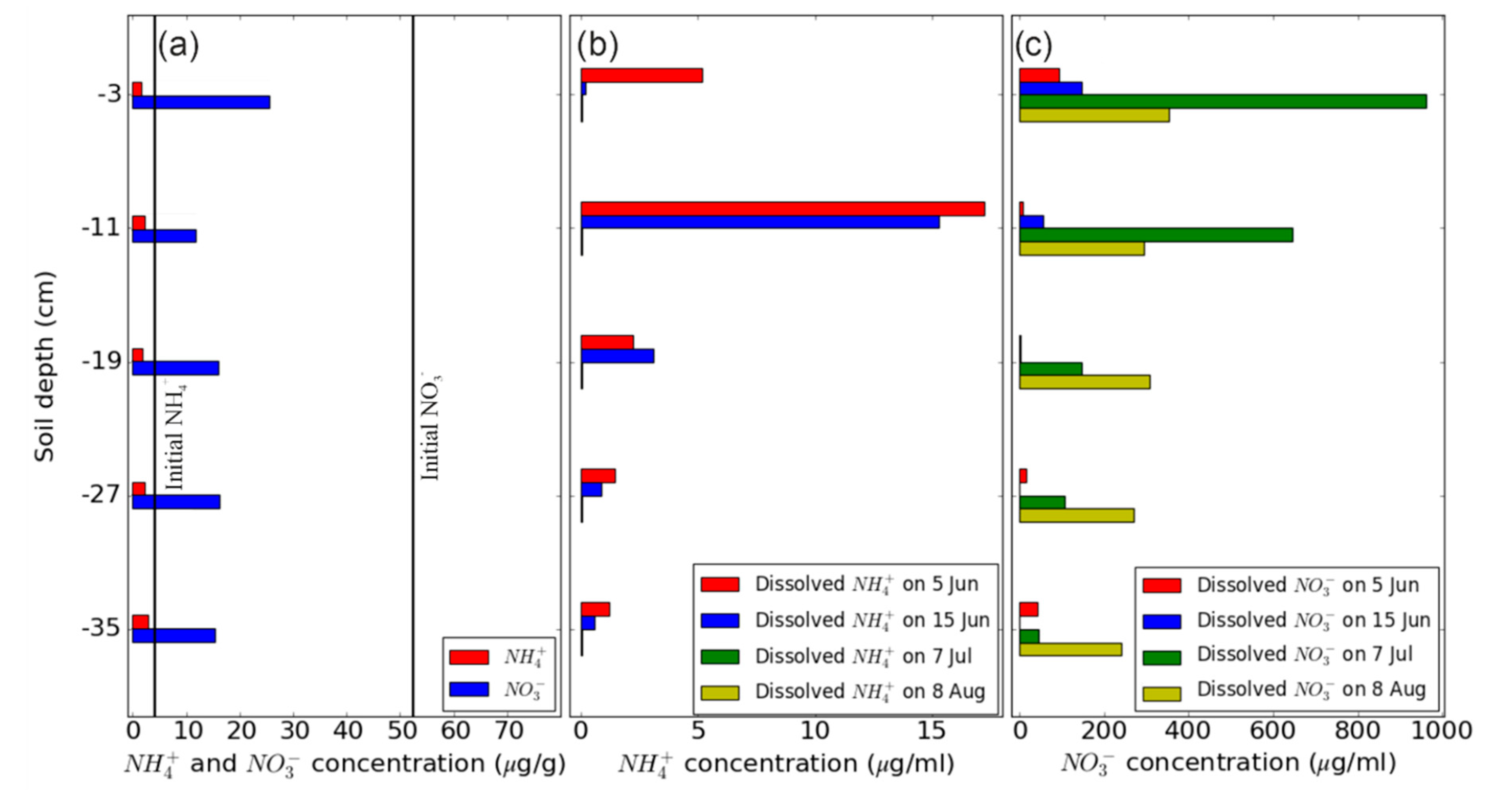
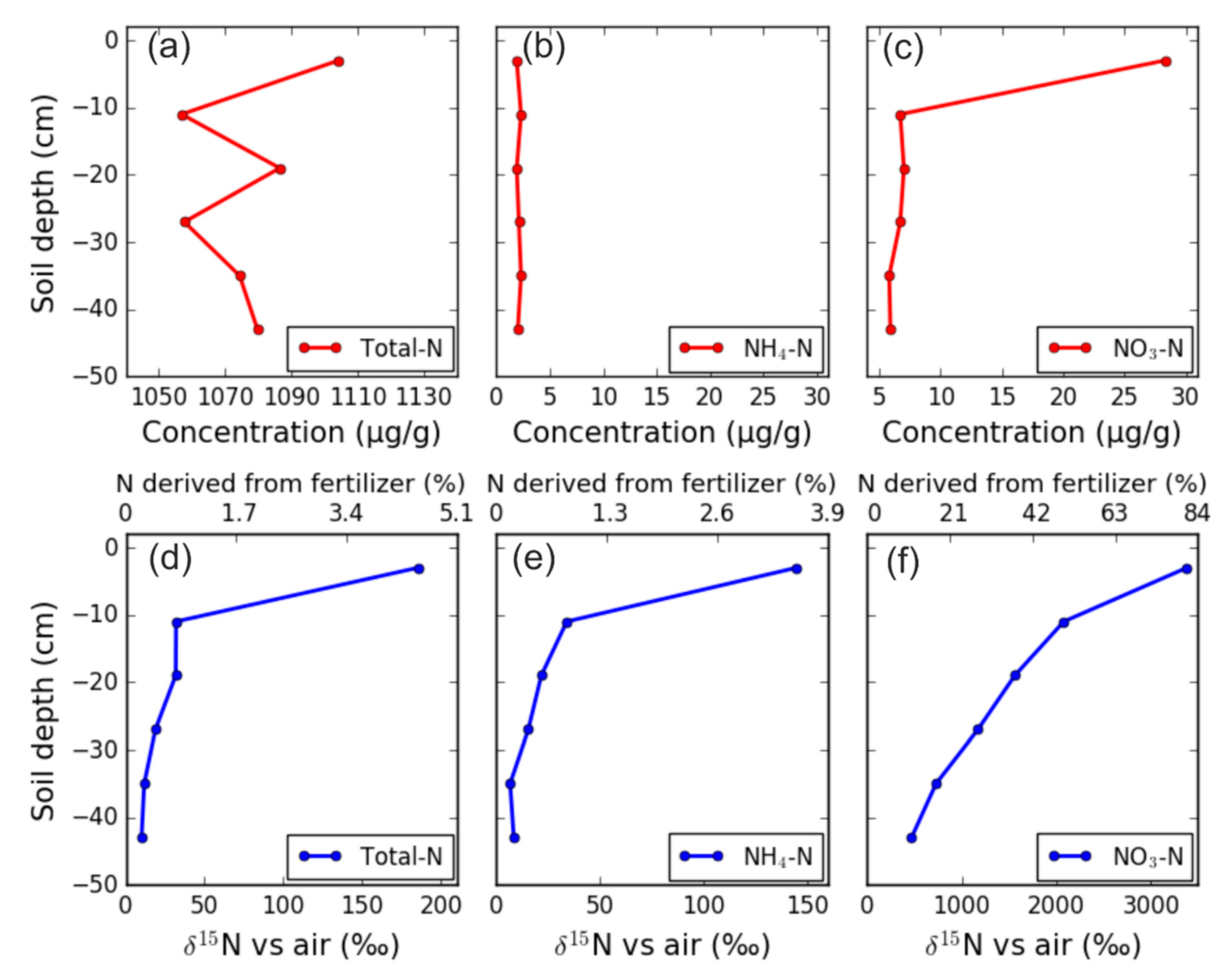
3.4. Impact of Different Hydrological Events on Mineral N and Dissolved N2O Concentrations along the Soil Profile
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Soil Hydrological Conditions on Eh and Dissolved N
4.2. Changes in N2O Emissions in Response to Changes in Soil Water Potential, Eh, and Available N
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. The Physical Science Basis: Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 468–479. [Google Scholar]
- Kutsch, W.L.; Bahn, M.; Heinemeyer, A. Soil Carbon Dynamics: An Integrated Methodology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 49–69. [Google Scholar]
- Nieder, R.; Benbi, D.K. Carbon and Nitrogen in the Terrestrial Environment; Springer Science and Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 430. [Google Scholar]
- Schaufler, G.; Kitzler, B.; Schindlbacher, A.; Skiba, U.; Sutton, M.A. Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. Greenhouse gas emissions from European soils under different land use: Effects of soil moisture and temperature. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 61, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Andrews, J.A. Soil respiration and the global carbon cycle. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Bustamante, M.; Ahammad, H.; Clark, H.; Dong, H.; Elsiddig, E.A.; Haberl, H.; Harper, R.; House, J.; Jafari, M. Agriculture, Forestry and Other Land Use (AFOLU); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 816–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay, D.S.; Davidson, E.A.; Smith, K.A.; Smith, P.; Melillo, J.M.; Dentener, F.; Crutzen, P.J. Global agriculture and nitrous oxide emissions. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Martino, D.; Cai, Z.; Gwary, D.; Janzen, H.; Kumar, P.; McCarl, B.; Ogle, S.; O’Mara, F.; Rice, C.; et al. Agriculture. In Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Metz, B., Davidson, O.R., Bosch, P.R., Dav, R., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 498–532. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Mitigation of Climate Change: Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Baggs, E.M.; Dannenmann, M.; Kiese, R.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. Nitrous oxide emissions from soils: How well do we understand the processes and their controls? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 2013, 368, 20130122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggs, E.M.; Rees, R.; Smith, K.; Vinten, A. Nitrous oxide emission from soils after incorporating crop residues. Soil Use Manag. 2000, 16, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Moncrieff, J.B. The dependence of soil CO2 efflux on temperature. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minick, K.J.; Pandey, C.B.; Fox, T.R.; Subedi, S. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium and N2O flux: Effect of soil redox potential and N fertilization in loblolly pine forests. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertel, C.; Matschullat, J.; Zurba, K.; Zimmermann, F.; Erasmi, S. Greenhouse gas emissions from soils—A review. Chem. Erde 2016, 76, 327–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruser, R.; Flessa, H.; Russow, R.; Schmidt, G.; Buegger, F.; Munch, J.C. Emission of N2O, N2 and CO2 from soil fertilized with nitrate: Effect of compaction, soil moisture and rewetting. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubol, S.; Silver, W.L.; Bellin, A. Hydrologic control on redox and nitrogen dynamics in a peatland soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, G.S.; Bajita-Locke, J.B.; Hue, N.V.; Strand, D. Manganese solubility and phytotoxicity affected by soil moisture, oxygen levels, and green manure additions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2004, 35, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Schimel, J.P.; Holden, P.A. Variations in microbial community composition through two soil depth profiles. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yao, S.; You, M.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Zou, W.; Han, X.; Zhang, B. Contrasting development of soil microbial community structure under no-tilled perennial and tilled cropping during early pedogenesis of a Mollisol. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 77, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flessa, H.; Beese, F. Effects of sugarbeet residues on soil redox potential and nitrous oxide emission. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995, 59, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunting, E.R.; Kampfraath, A.A. Contribution of bacteria to redox potential (Eh) measurements in sediments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz, E.; Urban, D. Soil redox potential and its impact on microorganisms and plants of wetlands. J. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 16, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bogena, H.R.; Vereecken, H.; Brüggemann, N. Characterizing redox potential effects on greenhouse gas emissions induced by water-level changes. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Patrick, W.H. Redox range with minimum nitrous oxide and methane production in a rice soil under different pH. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 1952–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masscheleyn, P.H.; DeLaune, R.D.; Patrick, W.H., Jr. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from laboratory measurements of rice soil suspension: Effect of soil oxidation-reduction status. Chemosphere 1993, 26, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, S.; Vepraskas, M.J.; Richardson, J.L. Soil redox potential: Importance, field measurements, and observations. Adv. Agron. 2007, 94, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.C.A.; Caravelli, A.H.; Zaritzky, N.E. Nitrification and aerobic denitrification in anoxic–aerobic sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Wang, J.; Cai, Z.C.; Wang, S.Q. Soil pH is a good predictor of the dominating N2O production processes under aerobic conditions. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lang, M. Gross nitrogen transformations and related N2O emissions in uncultivated and cultivated black soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, D.M.; Doran, J.W. Effect of water-filled pore space on carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide production in tilled and nontilled soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.S.; Tiedje, J.M. Phases of denitrification following oxygen depletion in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1979, 11, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Clough, T.J.; Elberling, B. Flooding-induced N2O emission bursts controlled by pH and nitrate in agricultural soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 69, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunting, E.R.; Van der Geest, H.G. Predictability of bacterial activity and denitrification in aquatic sediments with continuous measurements of redox potential. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 8, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogena, H.R.; Montzka, C.; Huisman, J.A.; Graf, A.; Schmidt, M.; Stockinger, M.; Von Hebel, C.; Hendricks-Franssen, H.J.; Van der Kruk, J.; Tappe, W.; et al. The TERENO-Rur Hydrological Observatory: A Multiscale Multi-Compartment Research Platform for the Advancement of Hydrological. Science. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korres, W.; Reichenau, T.G.; Fiener, P.; Koyama, C.N.; Bogena, H.R.; Cornelissen, T.; Baatz, R.; Herbst, M.; Diekkrüger, B.; Vereecken, H.; et al. Spatio-temporal soil moisture patterns—A meta-analysis using plot to catchment scale data. J. Hydrol. 2015, 520, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, T.B.; Venterea, R.T. USDA-ARS GRACEnet Project Protocols: Chamber-Based Trace Gas Flux Measurements. Sampling Protocols; USDA-ARS: Washington, WA, USA, 2010; Chapter 3; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Han, L.; Luo, X.; Liu, Z.; Han, S. Effects of nitrogen addition on dissolved N2O and CO2, dissolved organic matter, and inorganic nitrogen in soil solution under a temperate old-growth forest. Geoderma 2009, 151, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraim, E.; Wolf, B.; Harris, E.; Gasche, R.; Wei, J.; Yu, L.; Kiese, R.; Eggleston, S.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Zeeman, M.; et al. Attribution of N2O sources in a grassland soil with laser spectroscopy based isotopocule analysis. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 3247–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, J.; Liu, S.; Vereecken, H.; Brueggemann, N. Abiotic nitrous oxide production from hydroxylamine in soils and their dependence on soil properties. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 84, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Amelung, W.; Lehndorff, E.; Schloter, M.; Vereecken, H.; Brüggemann, N. N2O and NOx emissions by reactions of nitrite with soil organic matter of a Norway spruce forest. Biogeochemistry 2017, 132, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decock, C.; Six, J. How reliable is the intramolecular distribution of 15N in N2O to source partition N2O emitted from soil? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, S.; Yoshida, N.; Koba, K. Isotopocule analysis of biologically produced nitrous oxide in various environments. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2017, 36, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nason, G.E.; Myrold, D.D. 15N in soil research: Appropriate application of rate estimation procedures. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1991, 34, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvaney, R.L.; Khan, S.A.; Stevens, W.B.; Mulvaney, C.S. Improved diffusion methods for determination of inorganic nitrogen in soil extracts and water. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1997, 24, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, B.; Bernasconi, S.M.; Pannatier, E.G.; Luster, J. A simple method for the removal of dissolved organic matter and δ15N analysis of NO3- from freshwater. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Reichel, R.; Islam, M.S.; Wissel, H.; Amelung, W.; Brüggemann, N. Chemical composition of high organic carbon soil amendments affects fertilizer-derived N2O emission and nitrogen immobilization in an oxic sandy loam. Front Environ Sci. 2020, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsch, W.J.; Gosselink, J.G. Wetlands, 4th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; p. 736. [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda, S.; Yoshida, O.; Yamagishi, H.; Fujii, A.; Yoshida, N.; Watanabe, S. Identifying the origin of nitrous oxide dissolved in deep ocean by concentration and isotopocule analyses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Klein, C.A.; Monaghan, R.M. The effect of farm and catchment management on nitrogen transformations and N2O losses from pastoral systems—Can we offset the effects of future intensification? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Saggar, S.; Bhandral, R.; Bolan, N.; Ledgard, S.; Lindsey, S.; Sun, W. Effects of irrigating dairy-grazed grassland with farm dairy effluent on nitrous oxide emissions. Plant Soil 2008, 309, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiba, U.; Sheppard, L.; Pitcairn, C.E.R.; Leith, I.; Crossley, A.; Van Dijk, S.; Fowler, D. Soil nitrous oxide and nitric oxide emissions as indicators of elevated atmospheric N deposition rates in seminatural ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 102, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorau, K.; Luster, J.; Mansfeldt, T. Soil aeration: The relation between air-filled pore volume and redox potential. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Olmedo, M.; Ortiz, M.; Sellés, G. Effects of transient soil waterlogging and its importance for rootstock selection. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 75, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshki, S.R. Wetland plant responses to soil flooding. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2001, 46, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralova, M.; Masscheleyn, P.H.; Patrick, W.H., Jr. Redox potential as an indicator of electron availability for microbial activity and nitrogen transformations in aerobic soil. Zentralbl. Mikrobiol. 1992, 147, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgin, A.J.; Yang, W.H.; Hamilton, S.K.; Silver, W.L. Beyond carbon and nitrogen: How the microbial energy economy couples elemental cycles in diverse ecosystems. Front Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buresh, R.J.; Patrick, W.H., Jr. Nitrate reduction to ammonium and organic nitrogen in an estuarine sediment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1981, 13, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buresh, R.J.; Patrick, W.H., Jr. Nitrate reduction to ammonium in anaerobic soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1978, 42, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Horwath, W.R. Nitrous oxide uptake in rewetted wetlands with contrasting soil organic carbon contents. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 100, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martikainen, P.J.; Nykänen, H.; Crill, P.; Silvola, J. Effect of a lowered water table on nitrous oxide fluxes from northern peatlands. Nature 1993, 366, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regina, K.; Nykänen, H.; Silvola, J.; Martikainen, P.J. Fluxes of nitrous oxide from boreal peatlands as affected by peatland type, water table level and nitrification capacity. Biogeochemistry 1996, 35, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Tsuruta, H.; Watanabe, T. N2O and NO emissions from soils after the application of different chemical fertilizers. Chemosphere 2000, 2, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comfort, S.D.; Kelling, K.A.; Keeney, D.R.; Converse, J.C. Nitrous oxide production from injected liquid dairy manure. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husson, O. Redox potential (Eh) and pH as drivers of soil/plant/microorganism systems: A transdisciplinary overview pointing to integrative opportunities for agronomy. Plant Soil 2013, 362, 389–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Włodarczyk, T.; Stępniewski, W.; Brzezińska, M. Dehydrogenase activity, redox potential, and emissions of carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide from Cambisols under flooding conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 36, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Redox Potential | N2O | ||||||
| −3 cm | −11 cm | −19 cm | −27 cm | −35 cm | All | Fluxes (μg·N·m−2·h−1) | |
| Experiment 1: Before fertilization (n = 72) | |||||||
| Mean | 516.2 | 175.3 | 376.5 | 374.7 | 229.5 | 334.4 | 12.1 |
| Max | 558.5 | 597.9 | 621.1 | 601.6 | 598.9 | 583.0 | 91.7 |
| Min | 291.7 | −195.4 | 85.4 | 98.6 | −141.1 | 83.6 | 0.0 |
| Range | 266.8 | 793.3 | 535.7 | 503.0 | 740.0 | 499.4 | 91.7 |
| SD | 61.2 | 228.2 | 196.8 | 165.0 | 247.4 | 164.9 | 23.3 |
| CV (%) | 11.9 | 130.1 | 52.3 | 44.0 | 107.8 | 49.3 | 192.4 |
| Experiment 2: 1st fertilization (n = 28) | |||||||
| Mean | 570.3 | 510.5 | 513.3 | 531.6 | 352.2 | 495.6 | 137.8 |
| Max | 608.1 | 627.4 | 634.1 | 624.4 | 579.3 | 608.6 | 539.4 |
| Min | 451.0 | 214.5 | 295.8 | 367.9 | 99.3 | 340.2 | 4.1 |
| Range | 157.1 | 412.9 | 338.3 | 256.5 | 480.0 | 268.4 | 535.3 |
| SD | 42.6 | 121.4 | 99.3 | 73.4 | 161.0 | 87.1 | 158.5 |
| CV (%) | 7.5 | 23.8 | 19.3 | 13.8 | 45.7 | 17.6 | 115.1 |
| Experiment 3: 2nd fertilization (n = 35) | |||||||
| Mean | 537.7 | 629.3 | 611.2 | 603.6 | 480.1 | 572.4 | 38.4 |
| Max | 582.2 | 634.2 | 647.6 | 634.4 | 585.4 | 609.8 | 187.4 |
| Min | 475.3 | 607.2 | 495.9 | 514.7 | 241.9 | 476.7 | 0.6 |
| Range | 106.9 | 27.0 | 151.7 | 119.7 | 343.4 | 133.0 | 186.8 |
| SD | 32.9 | 5.8 | 43.9 | 33.8 | 109.5 | 37.5 | 51.0 |
| CV (%) | 6.1 | 0.9 | 7.2 | 5.6 | 22.8 | 6.5 | 131.9 |
| Experiment 4: Post-fertilization saturation phase (n = 29) | |||||||
| Mean | 574.1 | 632.0 | 639.3 | 622.8 | 531.3 | 599.9 | 50.2 |
| Max | 616.5 | 640.3 | 658.2 | 637.8 | 603.2 | 631.2 | 360.2 |
| Min | 503.6 | 565.0 | 545.6 | 542.1 | 260.3 | 496.3 | 0.2 |
| Range | 112.9 | 75.3 | 112.6 | 95.7 | 342.9 | 134.9 | 360.0 |
| SD | 32.6 | 14.7 | 27.2 | 23.7 | 87.7 | 33.6 | 95.2 |
| CV (%) | 5.7 | 2.3 | 4.3 | 3.8 | 16.5 | 5.6 | 189.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Bogena, H.R.; Vereecken, H.; Brüggemann, N. Stable-Isotope-Aided Investigation of the Effect of Redox Potential on Nitrous Oxide Emissions as Affected by Water Status and N Fertilization. Water 2020, 12, 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102918
Wang J, Bogena HR, Vereecken H, Brüggemann N. Stable-Isotope-Aided Investigation of the Effect of Redox Potential on Nitrous Oxide Emissions as Affected by Water Status and N Fertilization. Water. 2020; 12(10):2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102918
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jihuan, Heye R. Bogena, Harry Vereecken, and Nicolas Brüggemann. 2020. "Stable-Isotope-Aided Investigation of the Effect of Redox Potential on Nitrous Oxide Emissions as Affected by Water Status and N Fertilization" Water 12, no. 10: 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102918
APA StyleWang, J., Bogena, H. R., Vereecken, H., & Brüggemann, N. (2020). Stable-Isotope-Aided Investigation of the Effect of Redox Potential on Nitrous Oxide Emissions as Affected by Water Status and N Fertilization. Water, 12(10), 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102918






