Detection of Cover Collapse Doline and Other Epikarst Features by Multiple Geophysical Techniques, Case Study of Tarimba Cave, Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Site Description and Geology of the Area
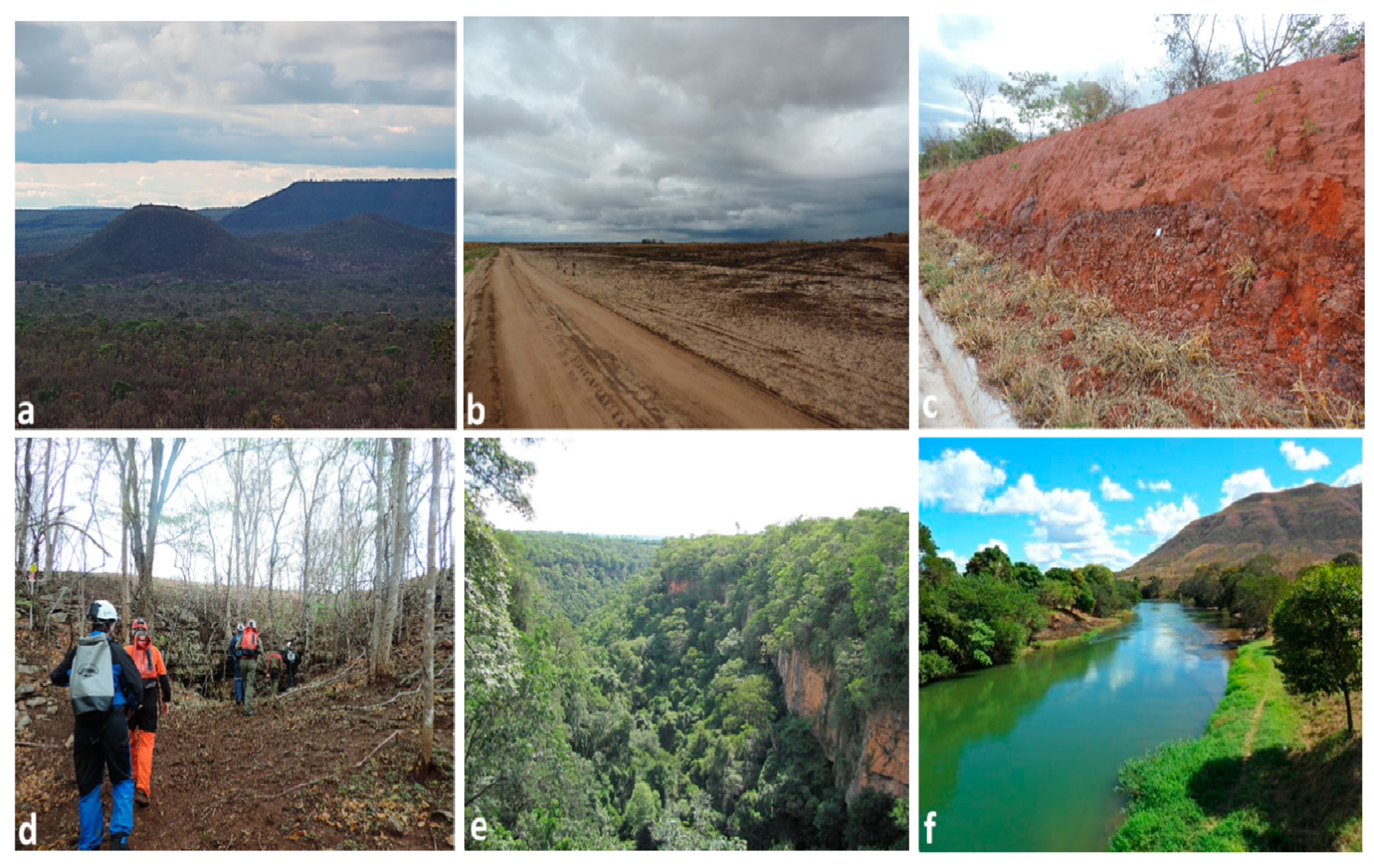
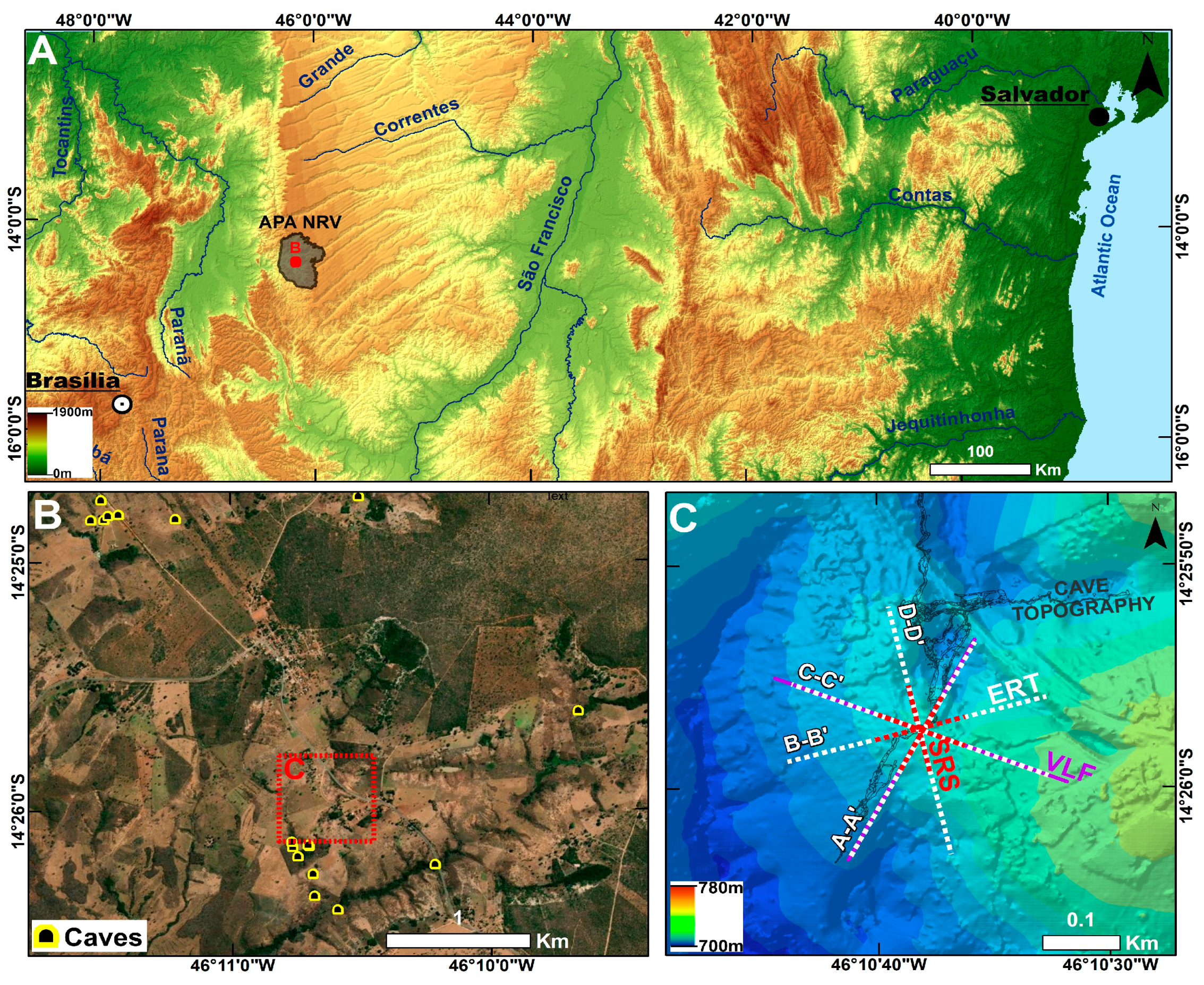
2.1. Study Area
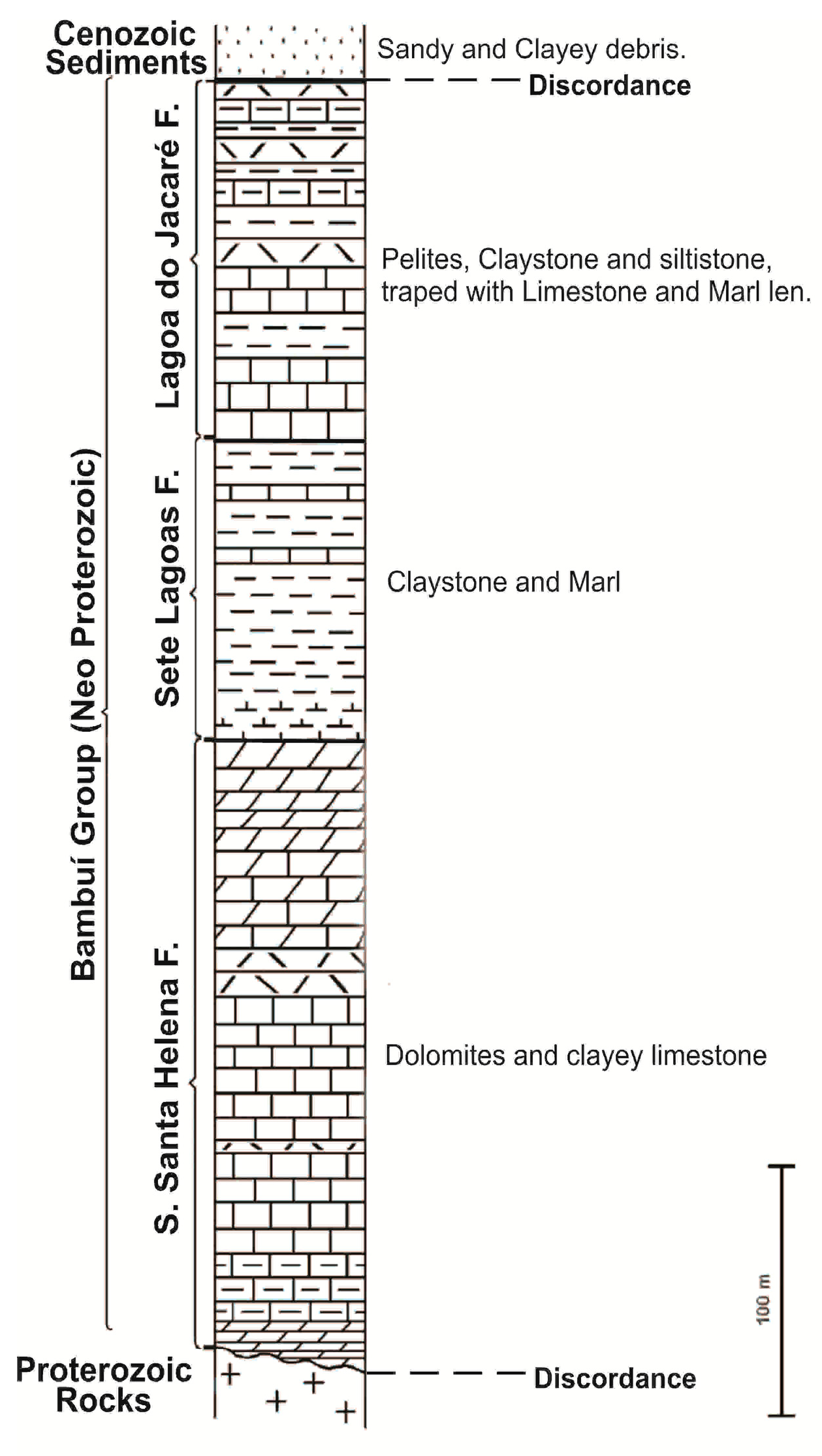
2.2. Geology and Geomorphology
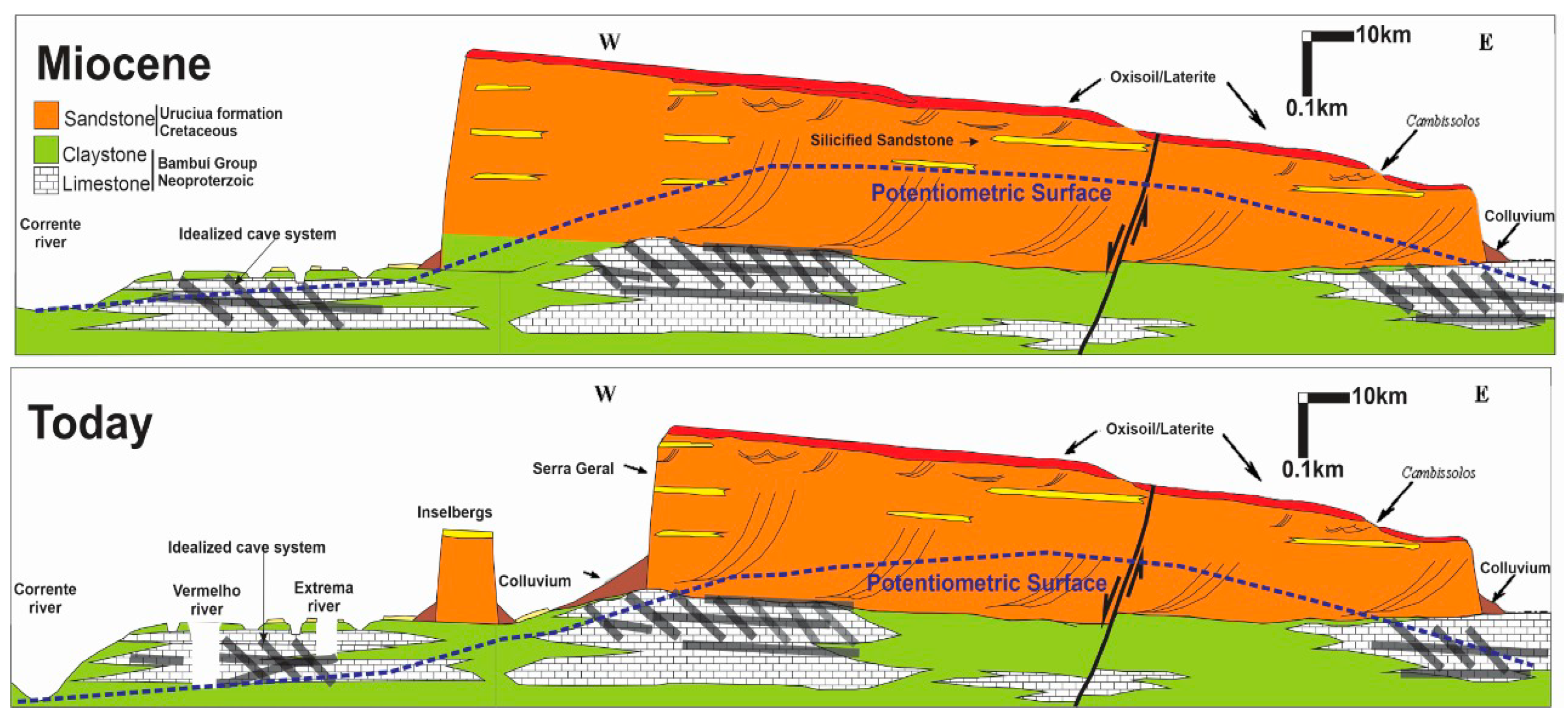
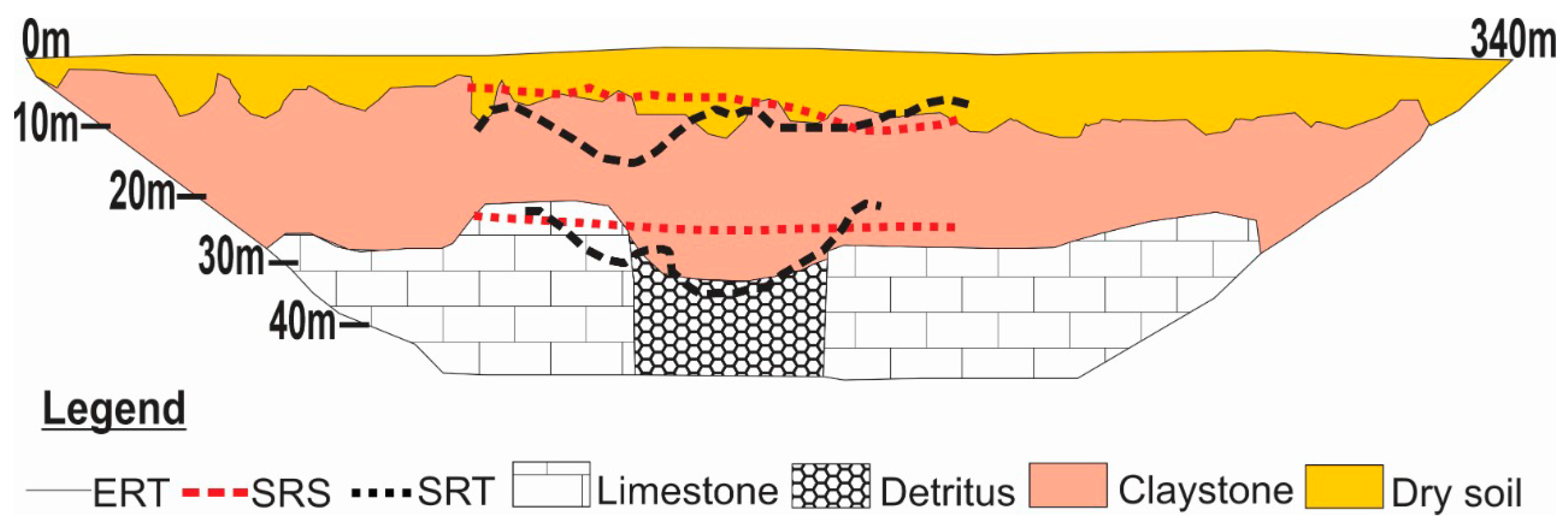
2.3. Cover-Collapse Doline & Perched Aquifer
3. Methodology
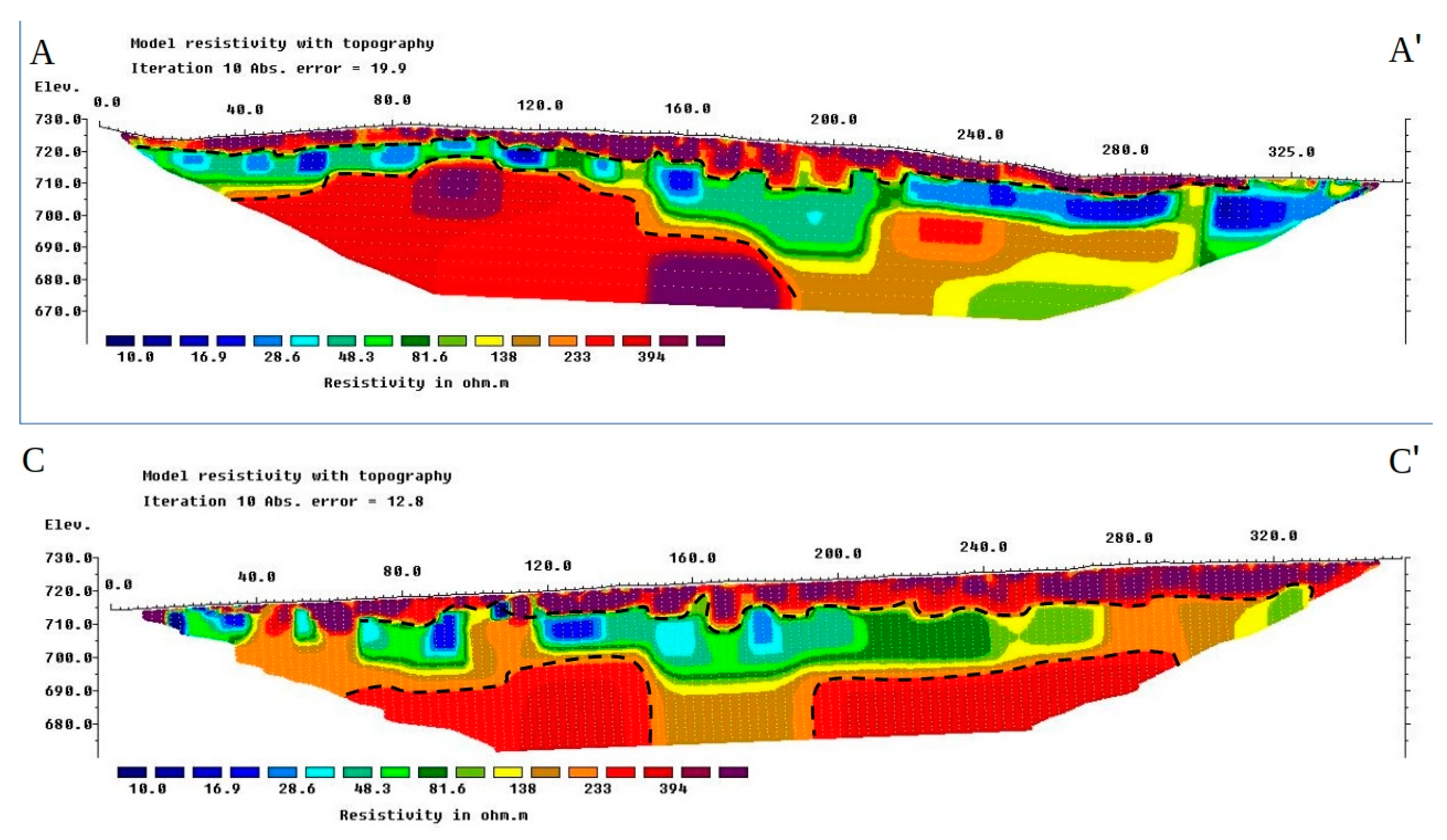
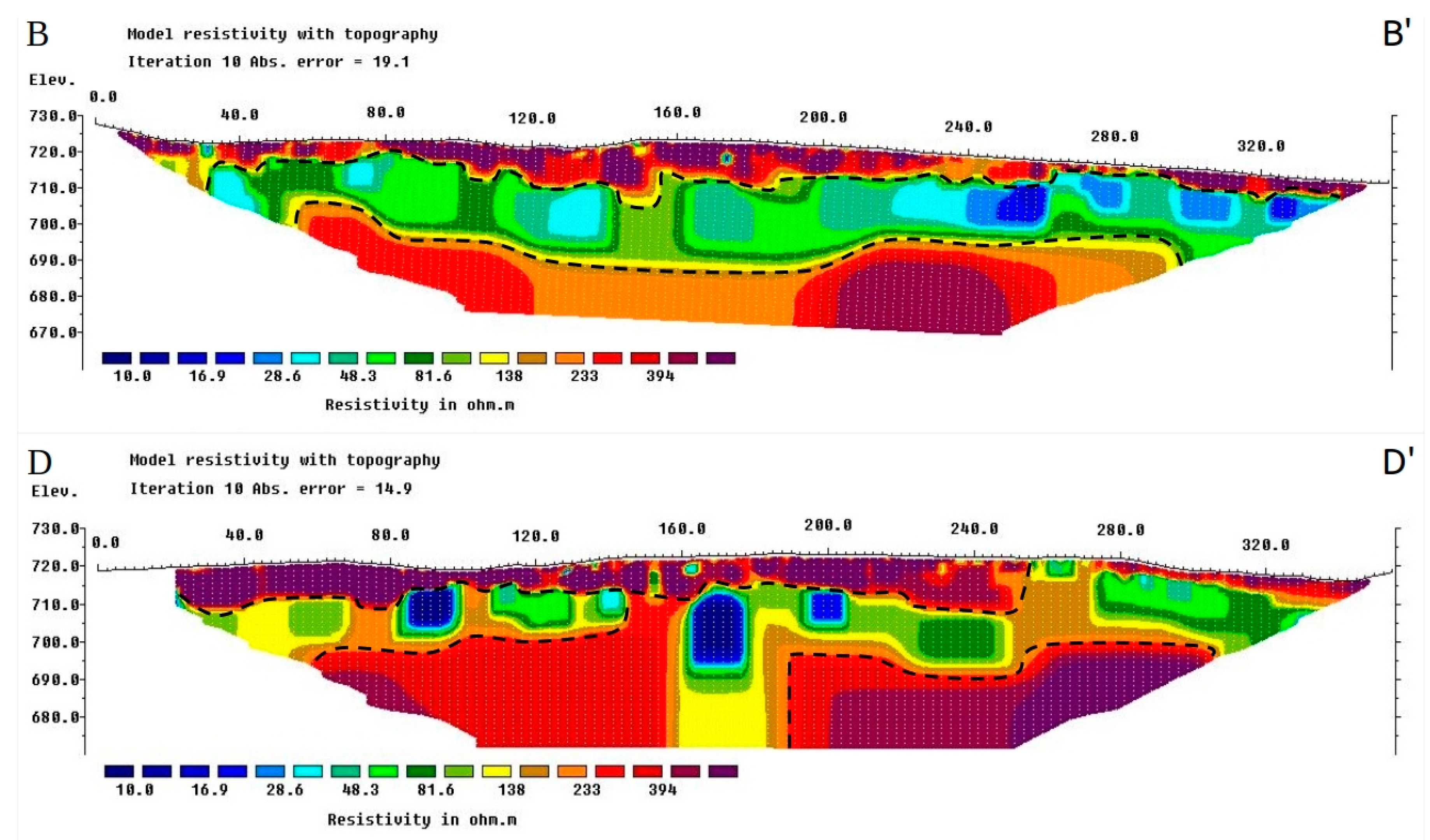
3.1. Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT)
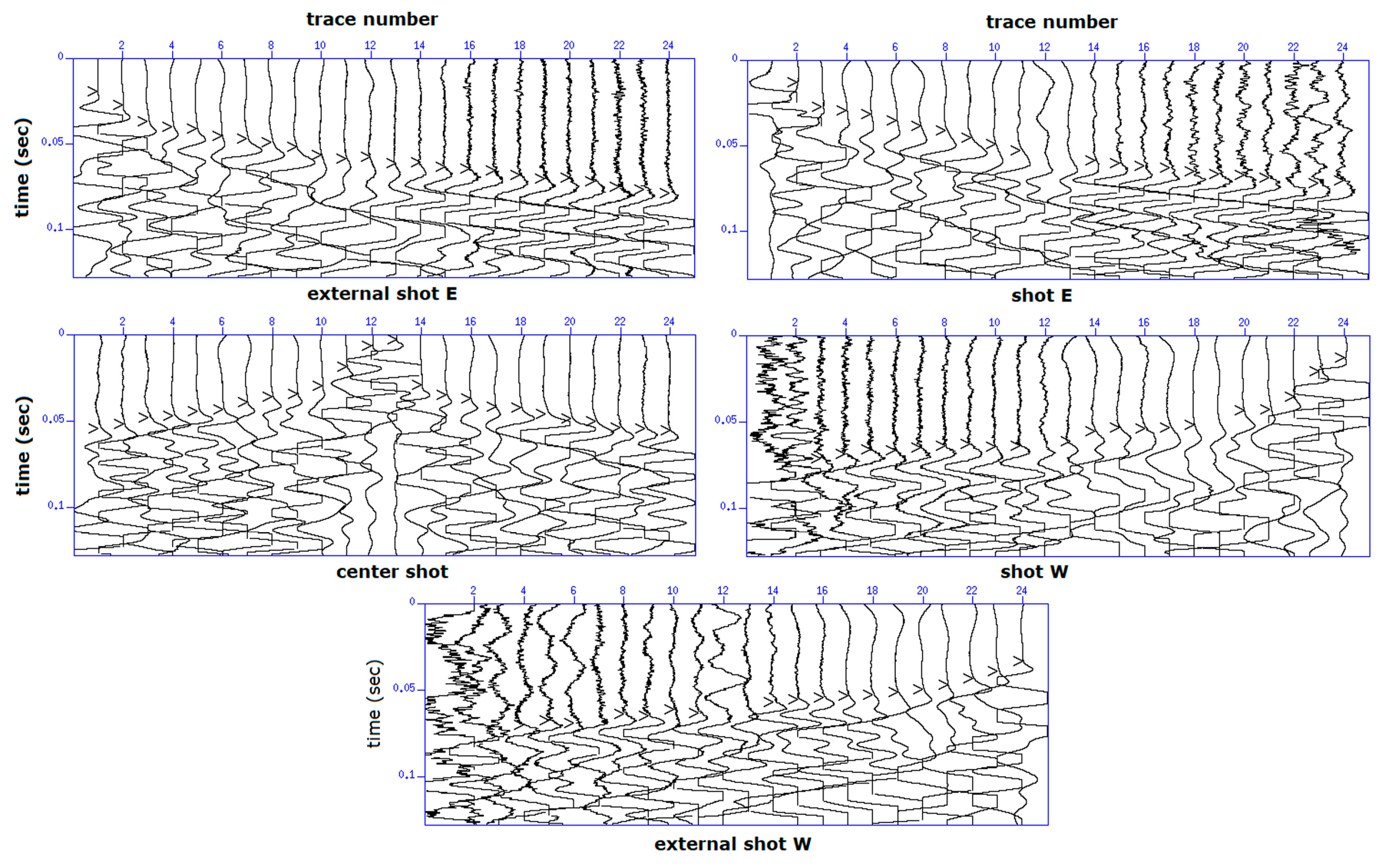
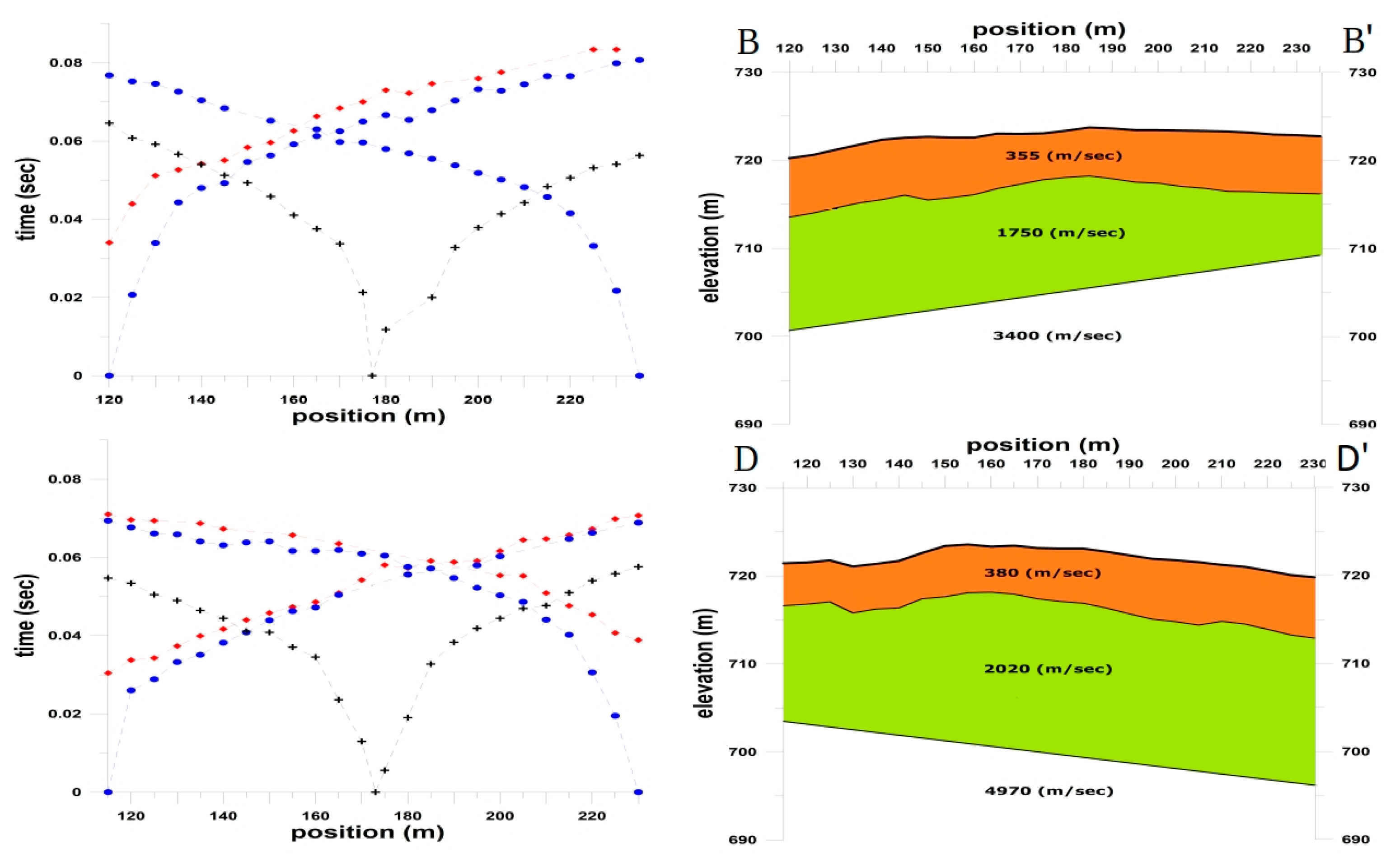
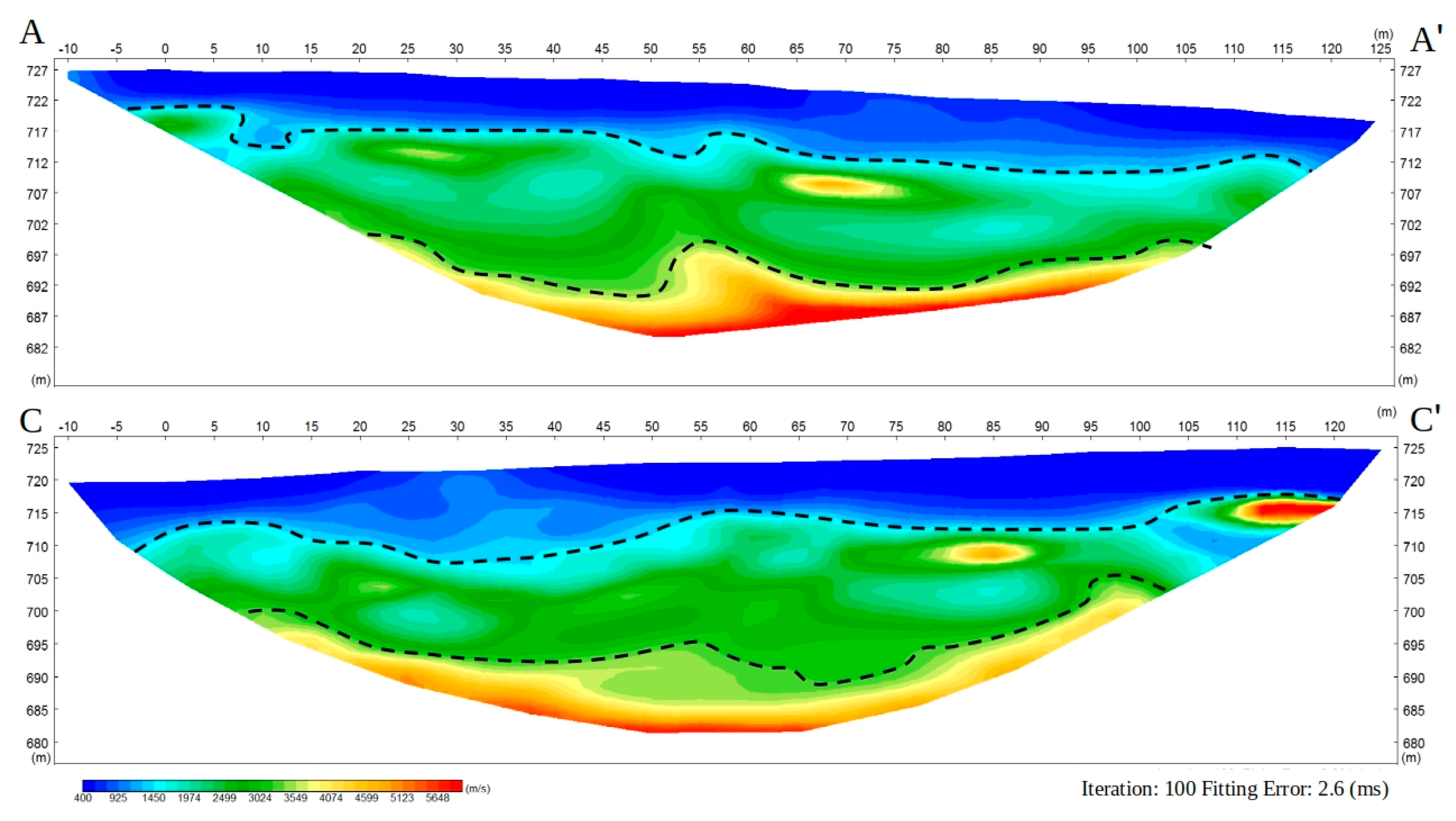
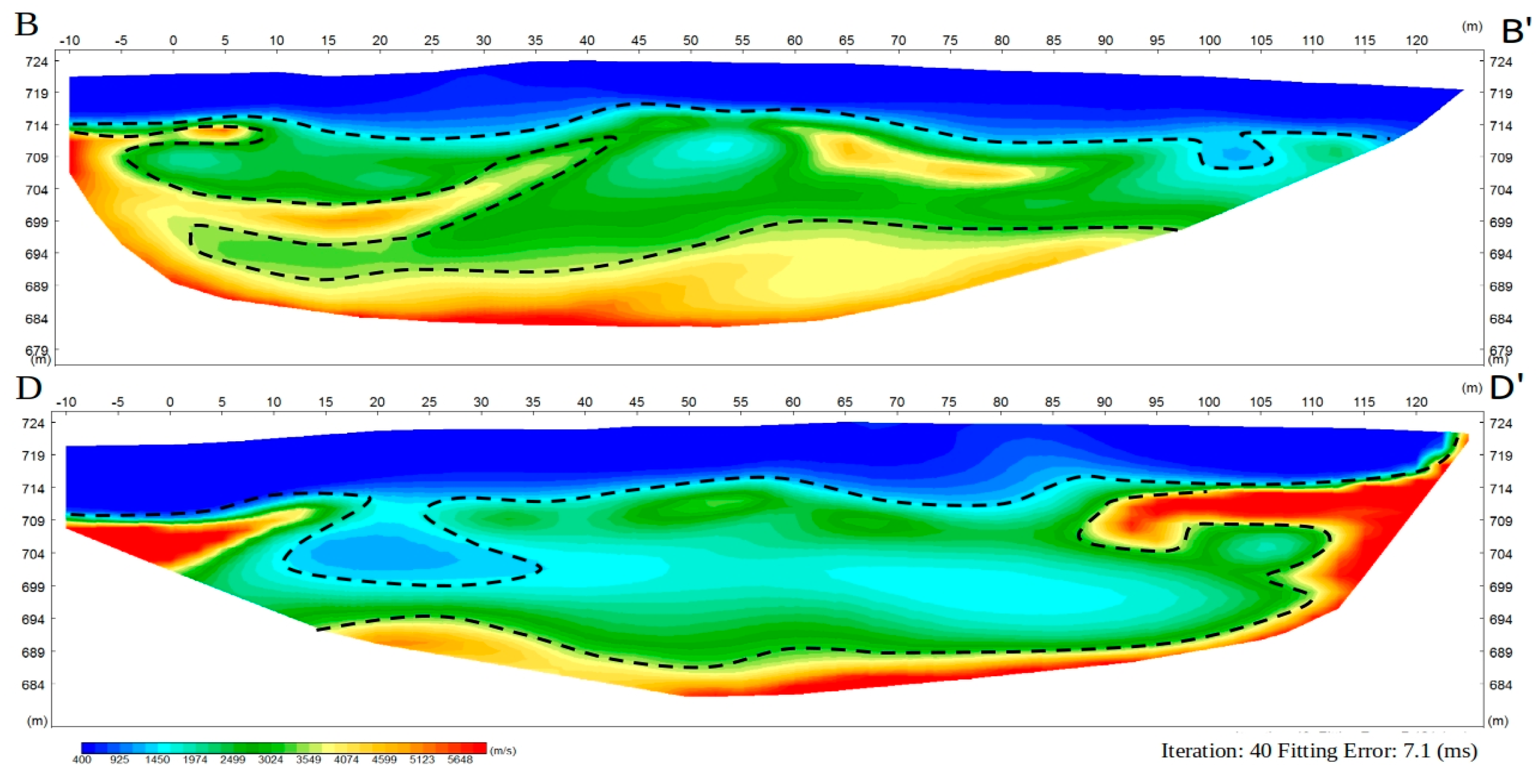
3.2. Seismic Refraction Survey (SRS)
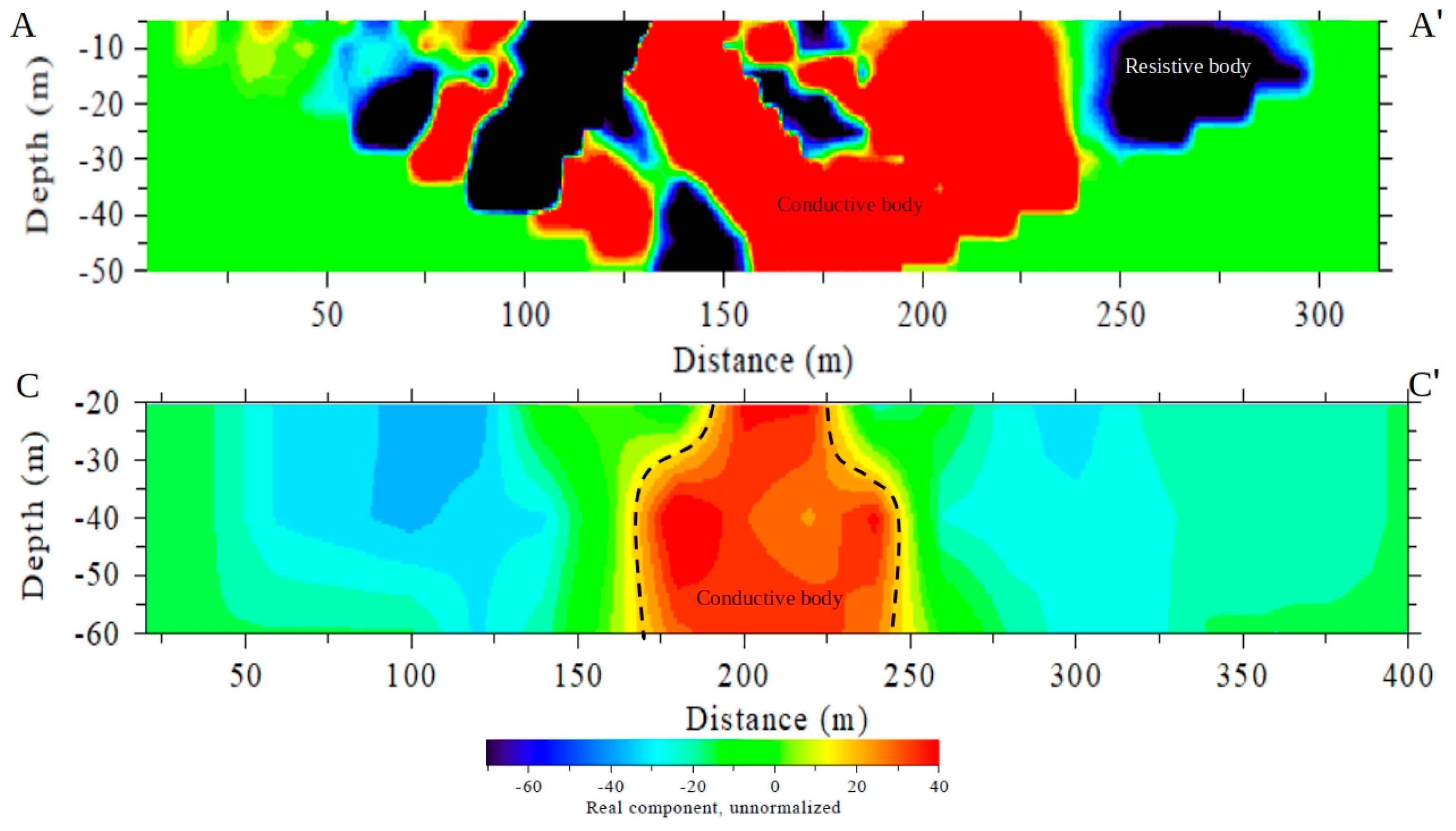
3.3. Very Low-Frequency Electromagnetic (VLF-EM)
4. Results, Analysis and Discussion
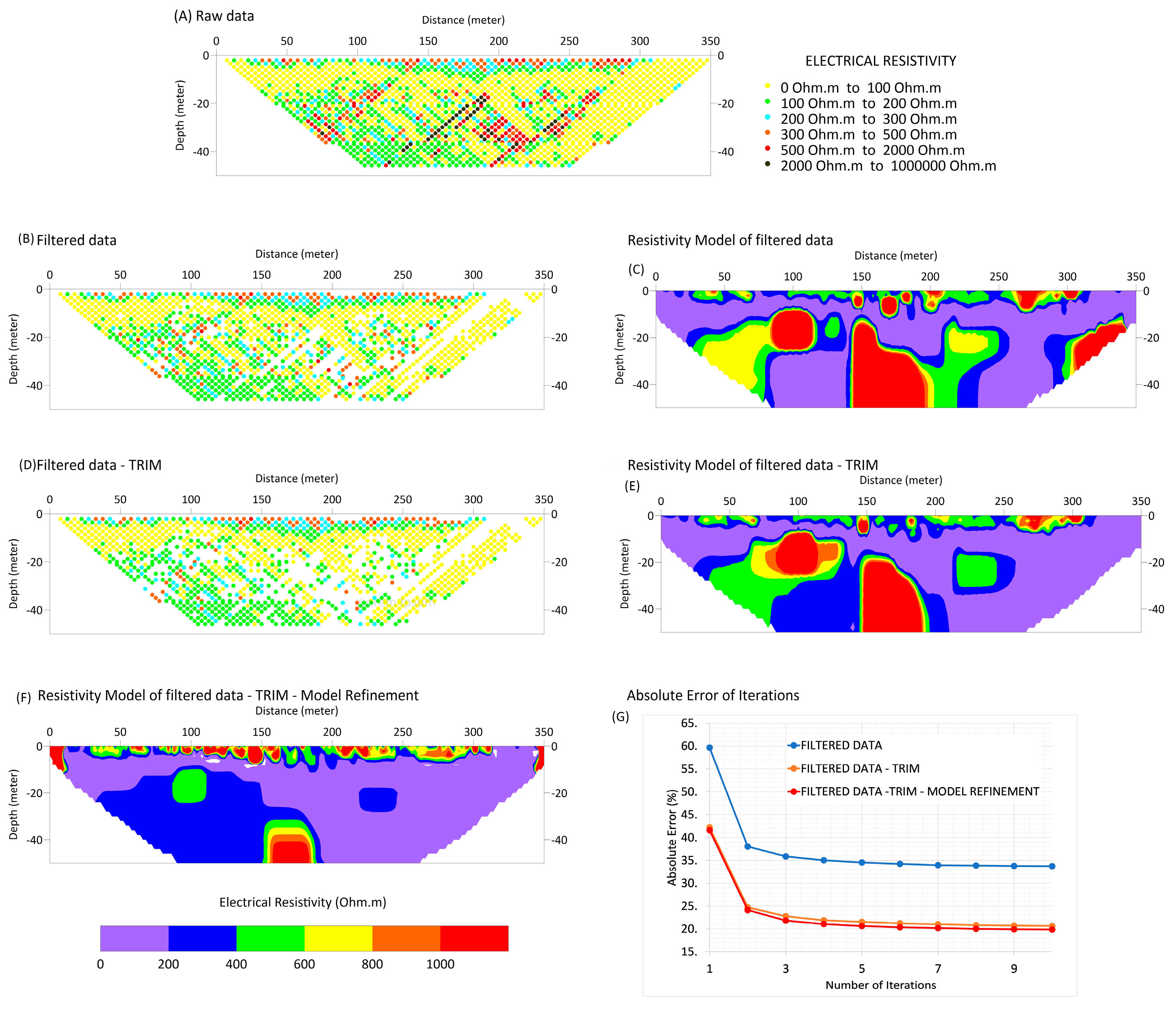
4.1. Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT)
4.2. Seismic Refraction Survey (SRS)
4.3. Very Low-Frequency Electromagnetic (VLF-EM)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abidi, A.; Demehati, A.; Banouni, H.; El Qandil, M. The Importance of Underground Cavities Detection in the Choice of Constructible Areas: Case of the Agglomeration of Fez (Morocco); Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, Y.; Uagoda, R.; Borges, W.; Nunes, J.; Hamza, O.; Condori, C.; Aslam, K.; Dou, J.; Cárdenas-Soto, M. The potential use of geophysical methods to identify cavities, sinkholes and pathways for water infiltration. Water 2020, 12, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valois, R.; Camerlynck, C.; Dhemaied, A.; Guerin, R.; Hovhannissian, G.; Plagnes, V.; Robain, H. Assessment of doline geometry using geophysics on the Quercy plateau karst (South France). Earth Surf. Process. Landfor. 2011, 36, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, G.; Romanov, D.; Nielbock, R. Cave detection using multiple geophysical methods: Unicorn cave, Harz Mountains, Germany. Geophysics 2011, 76, B71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.E.; El-Hussain, I.; Deif, A.; Araffa, S.A.S.; Mansour, K.; Al-Rawas, G. Integrated GPR, ERT and MASW for detecting near-surface caverns at Duqm area, Sultanate of Oman. Near Surf. Geophys. 2019, 17, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, N.; Al-Wardi, M.; Raef, A. Integration of micro-gravity and very low frequency (VLF) electromagnetic (em) data analyses to outline hazardous cavities and low rock-strength: Coastal carbonates, Wadi Shab, Oman. In Proceedings of the Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems, Austin, TX, USA, 22–26 March 2015; pp. 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Parise, M. Karst Geo-hazard: Causal factors and management issues. Acta Carsologica 2015, 44, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizman, C.; Thieme, D.M. Karst within the confining unit of the Floridan Aquifer: A geophysical investigation. J. Geogr. Geol. 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, F.; Parise, M.; de Waele, J.; Jourde, H. A review on natural and human-induced geohazards and impacts in karst. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Moreno, F.J.; Pedrera, A.; Ruano, P.; Galindo-Zaldívar, J.; Martos-Rosillo, S.; González-Castillo, L.; Marín-Lechado, C. Combined microgravity, electrical resistivity tomography and induced polarization to detect deeply buried caves: Algaidilla cave (Southern Spain). Eng. Geol. 2013, 162, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, N.; Narasimhachary, M.; Nandakumar, G.; Srinivas, Y. VES and VLF an application to ground water exploration, Khammam, India. Lead. Edge 2007, 26, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalikakis, K.; Plagnes, V.; Guerin, R.; Valois, R.; Bosch, F.P. Contribution of geophysical methods to karst-system exploration: An overview. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzi, V.; Ceccatelli, M.; Gracchi, T.; Masi, E.B.; Fanti, R. Assessing subsoil void hazards along a road system using H/V measurements, ERTs and IPTs to support local decision makers. Near Surf. Geophys. 2018, 16, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalikakis, K. Geophysical Methods Applied to Water Exploration and Protection in Karst Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, Paris, France, 2006; p. 217. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, D.C.; Williams, P.W. Karst Geomorphology and Hydrology; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 601. [Google Scholar]
- Oladotun, A.O.; Oluwagbemi, J.E.; Lola, A.M.; Maxwell, O.; Sayo, A. Predicting dynamic geotechnical parameters in near surface coastal environment. Cog. Eng. 2019, 6, 1588081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdet, C.; Colette, S.; Antoine, M.; Joëlle, R.; Portais, J.C. Detection of undercover karst features by geophysics (ERT) Lascaux cave hill. Geomorphology 2020, 360, 107177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaojun, Z.; Huang, J.; Song, L.; Chen, Y. Application of Ground penetrating Radar (GPR) exploration in Karst mountain areas. In Proceedings of the XIII Internarional Conference on Ground Penetrating Radar, IEEE, Lecce, Italy, 21–25 June 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Solbakk, T.; Fichler, C.; Wheeler, W.H.; Lauritzen, S.E.; Ringrose, P. Detecting Multiscale Karst Features Including Hidden Caves Using Microgravimetry in a Caledonian Nappe Setting; Mefjell Massif: Norsk Geologisk Forening, Norway, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Guérin, R.; Baltassat, J.M.; Boucher, M.; Chalikakis, K.; Galibert, P.Y.; Girard, J.F.; Plagnes, V.; Valois, R. Geophysical characterisation of karstic networks-application to the Ouysse system (Poumeyssen, France). C.R. Geosci. 2009, 341, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valois, R.; Bermejo, L.; Guérin, R.; Hinguant, S.; Pigeaud, R.; Rodet, J. Karstic morphologies identified with geophysics around Saulges caves (Mayenne, France). Archaeol. Prospect. 2010, 17, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billi, A.; de Filippis, L.; Poncia, P.P.; Sella, P.; Faccenna, C. Hidden sinkholes and karst cavities in the travertine plateau of a highly-populated geothermal seismic territory (Tivoli, central Italy). Geomorphology 2016, 255, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto, M.; Olona, J.; Fernández-Viejo, G.; Pando, L.; López-Fernández, C. Karst-induced sinkhole detection using an integrated geophysical survey: A case study along the Riyadh Metro Line 3 (Saudi Arabia). Near Surf. Geophys. 2018, 16, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez, R.E.; Tejero-Andrade, A.; Cifuentes, G.; Argote-Espino, D.L.; Hernández-Quintero, E. Karst detection beneath the pyramid of El Castillo, Chichen Itza, Mexico, by non-invasive ERT-3D methods. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermejo, L.; Ortega, A.I.; Guérin, R.; Benito-Calvo, A.; Pérez-González, A.; Parés, J.M.; Carbonell, E. 2D and 3D ERT imaging for identifying karst morphologies in the archaeological sites of Gran Dolina and Galería Complex (Sierra de Atapuerca, Burgos, Spain). Quat. Int. 2017, 433, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, E.S.; Silva, R.W.; Sampaio, E.E. Analysis of the risk of karst collapse in Lapão, Bahia, Brazil. Explor. Geophys. 2012, 43, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Queiroz, S.L.; Galvão, P.; Leal, L.R.B.; de Araujo Pereira, R.G.F.; da Purificação, C.G.C.; Laureano, F.V. Evaluation of susceptibility for terrain collapse and subsidence in karst areas, municipality of Iraquara, Chapada Diamantina (BA), Brazil. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.L.; Galvão, P.; Lucon, T.; Fujaco, M.A. Adapting the EPIK method to Brazilian Hydro (geo) logical context of the São Miguel watershed to assess karstic aquifer vulnerability to contamination. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2019, 90, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, I.; Sebastião, C.S.; Ferreira, M.L.; Lima, H.M.D.; Gama, M.F.P. Physical stability of iron ore caves: Geomechanical studies of a shallow underground cave in SE Brazil. REM Int. Eng. J. 2019, 72, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, G.P.; Grohmann, C.H. DEM-based geomorphological mapping and landforms characterization of a tropical karst environment in southeastern Brazil. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2019, 93, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranhão, D.D.; Pereira, M.G.; Collier, L.S.; dos Anjos, L.H.; Azevedo, A.C.; de Souza Cavassani, R. Pedogenesis in a karst environment in the Cerrado biome, northern Brazil. Geoderma 2020, 365, 114169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, H.A.S.; Bichuette, M.; Hardt, R.; de Souza Martinelli, R.; Bruno Filho, F.G.; Gallão, J.; Calvo, E.M. Preliminary Environmental Characterization and Conservation Proposal to Gruta da Tarimba Karst System—Goiás State, Brazil; Brazilian Society of Speleology: São Paulo, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gaspar, M.T.P.; Campos, J.E.G.O. Sistema aquífero urucuia. Rev. Bras. Geociênc. 2007, 37, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengala, C.V. Detalhamento da Geologia das Unidades Carbonáticas do Grupo Bambuí na Região de Alvorada do Norte, Goiás. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Brasília, Brasília, Brasil, March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dardenne, M.A. Síntese sobre a estratigrafia do Grupo Bambuí no Brasil Central. SBG Congr. Bras. Geol. 1978, 2, 507–510. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, M.; Uhlein, A. Estratigrafia do grupo bambuí e coberturas fanerozoicas no vale do rio São Francisco, norte de Minas Gerais. Rev. Bras. Geociênc. 2009, 39, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltham, T.; Waltham, A.C.; Bell, F.G.; Culshaw, M.G. Sinkholes and Subsidence: Karst and Cavernous Rocks in Engineering and Construction; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, W.C.; Stewart, J.W.; Knutilla, R.L.; Gilboy, A.E.; Miller, R.L. Types, Features, and Occurrence of Sinkholes in the Karst of West-Central Florida; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1985.
- Redhaounia, B.; Ilondo, B.O.; Gabtni, H.; Sami, K.; Bédir, M. Electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) applied to Karst carbonate aquifers: Case study from Amdoun, northwestern Tunisia. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2016, 173, 1289–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrofan, H.; Povară, I.; Mafteiu, M. Geoelectrical investigations by means of resistivity methods in karst areas in Romania. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Qady, G.; Hafez, M.; Abdalla, M.A.; Ushijima, K. Imaging subsurface cavities using geoelectric tomography and ground-penetrating radar. J. Cave Karst Stud. 2005, 67, 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, O.; Deceuster, J. Detection and mapping of ghost-rock features in the Tournaisis area through geophysical methods—An overview. Geol. Belg. 2014, 17, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gambetta, M.; Armadillo, E.; Carmisciano, C.; Stefanelli, P.; Cocchi, L.; Tontini, F.C. Determining geophysical properties of a near surface cave through integrated microgravity vertical gradient and electrical resistivity tomography measurements. J. Cave Karst Stud. 2011, 73, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pánek, T.; Šilhán, K.; Tábořík, P.; Hradecký, J.; Smolková, V.; Lenart, J.; Pazdur, A. Catastrophic slope failure and its origins: Case of the May 2010 Girová Mountain long-runout rockslide (Czech Republic). Geomorphology 2011, 130, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H. Tutorial: 2-D and 3-D Electrical Imaging Surveys; Geotomo Software: Penang, Malasya, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, Y. Resolution of resistivity tomography inferred from numerical simulation. Geophys. Prospect. 1992, 54, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, G.; Lapenna, V.; Loperte, A.; Perrone, A.; Telesca, L. 2D electrical resistivity tomographies for investigating recent activation landslides in Basilicata Region (Southern Italy). Ann. Geophys. 2008, 51, 275–285. [Google Scholar]
- Lapenna, V.; Lorenzo, P.; Perrone, A.; Piscitelli, S.; Rizzo, E.; Sdao, F. 2D electrical resistivity imaging of some complex landslides in Lucanian Apennine chain, southern Italy. Geophysics 2005, 70, B11–B18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebl, S.; Gemail, K.S.; Attwa, M.; Soliman, S.A.; Azab, A.; Farag, M.H. Utilizing shallow seismic refraction in defining the geotechnical properties of the foundation materials: A case study at New Minia City, Nile Valley, Egypt. Egypt. J. Pet. 2019, 28, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwa, M.; El-Shinawi, A. An integrative approach for preliminary environmental engineering investigations amidst reclaiming desert-land: A case study at East Nile Delta, Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClymont, A.; Bauman, P.; Johnson, E.; Pankratow, L. Geophysical applications to construction engineering projects. CSEG Rec. 2016, 41, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Prekopová, M.; Janočko, J.; Budinský, V.; Friedmanová, M. Integration of seismic and sedimentological methods for analysis of Quaternary alluvial depositional systems. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrukh, M.; Soupios, P.; Papadopoulos, N.; Sarris, A. Geophysical investigations at the Istron archaeological site, eastern Crete, Greece using seismic refraction and electrical resistivity tomography. J. Geophys. Eng. 2012, 9, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brixová, B.; Mosná, A.; Putiška, R. Applications of shallow seismic refraction measurements in the Western Carpathians (Slovakia): Case studies. Contrib. Geophys. Geod. 2018, 48, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azwin, I.N.; Saad, R.; Nordiana, M. Applying the seismic refraction tomography for site characterization. APCBEE Proc. 2013, 5, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jug, J.; Grabar, K.; Strelec, S.; Dodigović, F. Investigation of dimension stone on the Island Brač-Geophysical approach to rock mass quality assessment. Geosciences 2020, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagedoorn, J.G. The plus-minus method of interpreting seismic refraction sections. Geophys. Prospect. 1959, 7, 158–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, R.V.; Ram, S.; Sundararajan, N. Modeling and inversion of magnetic and VLF-EM data with an application to basement fractures: A case study from Raigarh, India. Geophysics 2007, 72, B133–B140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tarazi, E.; Abu Rajab, J.; Al-Naqa, A.; El-Waheidi, M. Detecting leachate plumes and groundwater pollution at Ruseifa municipal landfill utilizing VLF-EM method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2008, 65, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, M.; Rathor, B.S. VLF survey of the weathered layering southern India Geophys. Prospect 1983, 315, 24–37. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Oufi, A.; Mustafa, H.A.; Al-Tarazi, E.; Abu Rajab, J. Exploration of the extension of two lava tubes, faults and dikes using very low frequency-electromagnetic technique in NE Jordan. Acta Geophys. 2008, 56, 466–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindi, E. An assessment of the performance of the geophysical methods as a tool for the detection of zones of potential subsidence in the area southwest of Nakuru town, Kenya. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3643–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, D.C. Contouring of VLF-EM data. Geophysics 1969, 34, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, N.K.; Osazuwa, I.B. Geophysical imaging of municipal solid waste contaminant pathways. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilvy, R.D.; Lee, A.C. Interpretation of VLF-EM in-phase data using current density pseudosections 1. Geophys. Prospect. 1991, 39, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eluwole, A.B. An Interactive Manual on Qualitative and Computer Assisted Interpretation of Very Low Frequency Electromagnetic (VLF-EM) Data; Obafemi Awolowo University: Ife, Nigeria, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Y.; Ullah, S.F.; Hussain, M.B.; Aslam, A.Q.; Akhter, G.; Martinez-Carvajal, H.; Cárdenas-Soto, M. Modelling the vulnerability of groundwater to contamination in an unconfined alluvial aquifer in Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, Y.; Uagoda, R.; Borges, W.; Prado, R.; Hamza, O.; Cárdenas-Soto, M.; Havenith, H.-B.; Dou, J. Detection of Cover Collapse Doline and Other Epikarst Features by Multiple Geophysical Techniques, Case Study of Tarimba Cave, Brazil. Water 2020, 12, 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102835
Hussain Y, Uagoda R, Borges W, Prado R, Hamza O, Cárdenas-Soto M, Havenith H-B, Dou J. Detection of Cover Collapse Doline and Other Epikarst Features by Multiple Geophysical Techniques, Case Study of Tarimba Cave, Brazil. Water. 2020; 12(10):2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102835
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Yawar, Rogerio Uagoda, Welitom Borges, Renato Prado, Omar Hamza, Martín Cárdenas-Soto, Hans-Balder Havenith, and Jie Dou. 2020. "Detection of Cover Collapse Doline and Other Epikarst Features by Multiple Geophysical Techniques, Case Study of Tarimba Cave, Brazil" Water 12, no. 10: 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102835
APA StyleHussain, Y., Uagoda, R., Borges, W., Prado, R., Hamza, O., Cárdenas-Soto, M., Havenith, H.-B., & Dou, J. (2020). Detection of Cover Collapse Doline and Other Epikarst Features by Multiple Geophysical Techniques, Case Study of Tarimba Cave, Brazil. Water, 12(10), 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102835