Microspheres as Surrogate Helminth Eggs: A Comparative Labscale Sedimentation Study for Tap- and Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
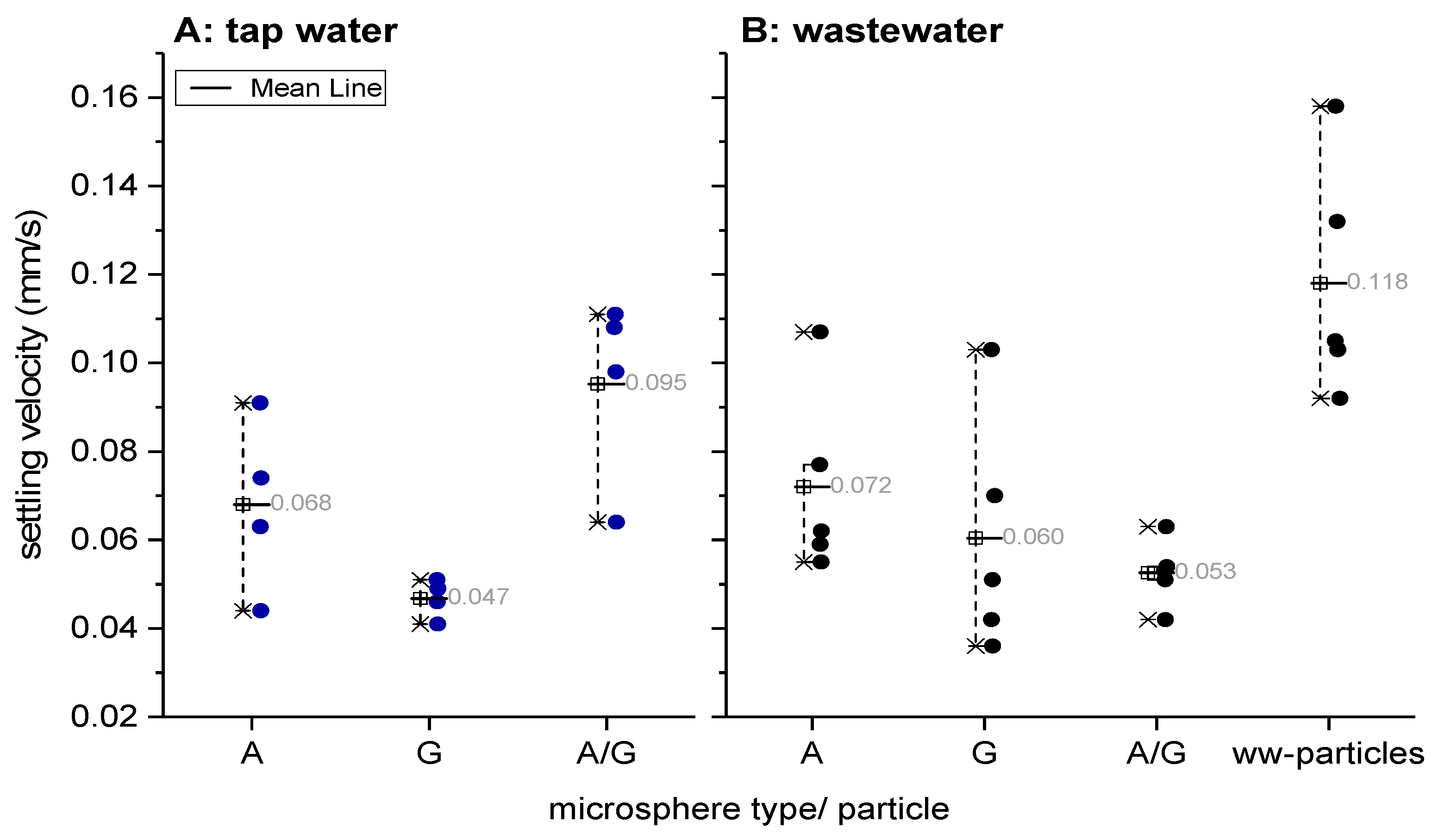
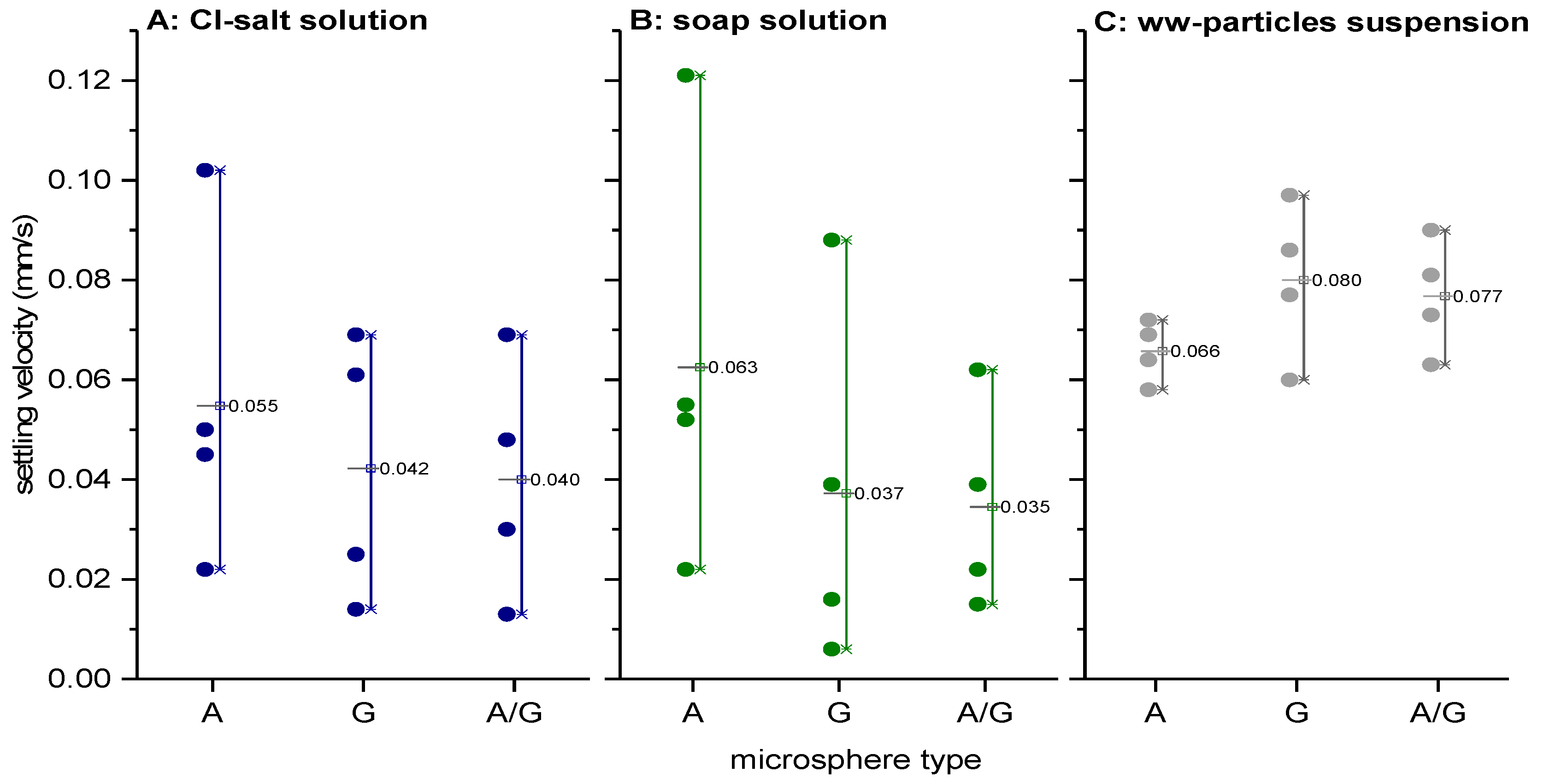
- Interaction between eggs and bulk sediment manifested in an increased settling velocity of suspended eggs when sediment was present in the suspension as compared to the situation of settling in clean water.
- Also, incorporation into the sediment bed and aggregation with sediment particles decreased the mobility of both helminthes egg types.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microspheres
- Protein A: surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus.
- Protein G: an immunoglobulin-binding protein expressed in group C and G Streptococcal bacteria much like Protein A, but with differing specificities.
- Protein A/G: recombinant fusion protein that combines IgG-binding domains of both Protein A and Protein G. This fusion protein is expressed in E. coli.
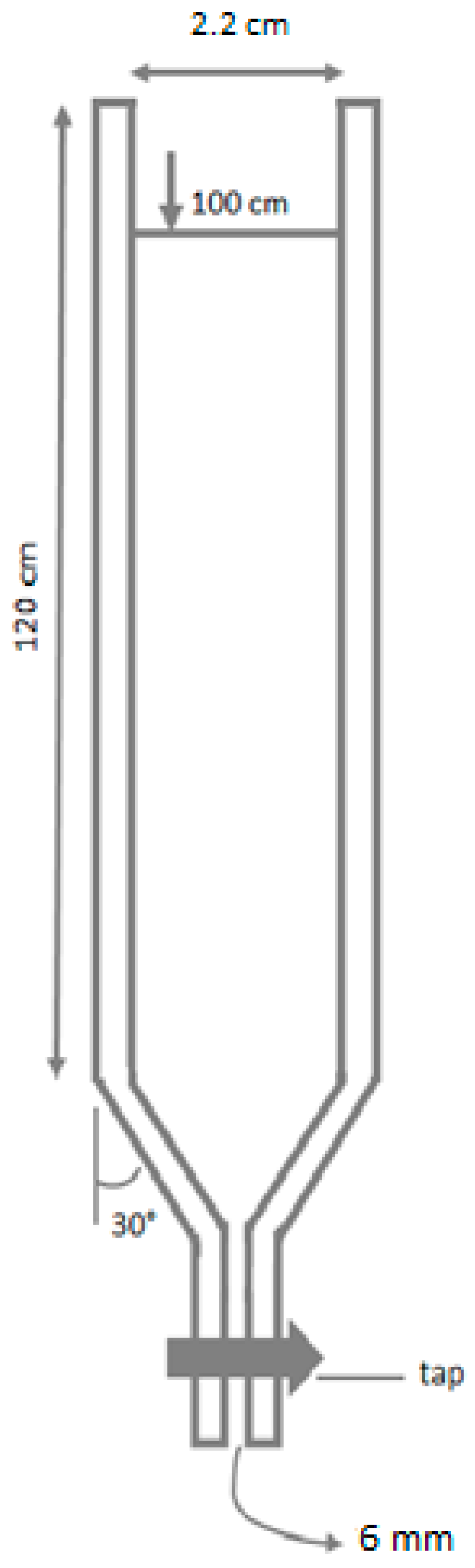
2.2. Sedimentation
2.3. Experimental Settling Velocity of Microspheres and Statistical Analyses
2.4. Theoretical Settling Velocity of Microspheres
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Settling Velocities of Microspheres in Tap- and Wastewater
3.2. Theoretical Settling Velocity in Tap Water
3.3. Comparative Analyses of Microspheres with Real Helminth Eggs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rivera, F.; Warren, A.; Curds, C.R.; Robles, E.; Gutierrez, A.; Gallegos, E.; Calderon, A. The application of the root zone method for the treatment and reuse of high-strength abattoir waste in Mexico. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya, C.; Torner-Morales, F.J.; Lucario, E.S.; Hernández, E.; Jiménez, B. Viability of six species of larval and non-larval helminth eggs for different conditions of temperature, pH and dryness. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4770–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Integrated Guide to Sanitary Parasitology; WHO-EM/CEH/121E; Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean, Regional Center for Environmental health Activities, WHO: Amman, Jordan, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Keraita, B.; Jimenez, B.; Drechsel, P. Extent and implications of agricultural reuse of untreated, partly treated and diluted wastewater in developing countries. CAB Rev. Perspect. Agric. Vet. Sci. Nutr. Nat. Resour. 2008, 3, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Eliminating Soil-transmitted Helminthiasis as a Public Health Problem in Children: Progress Report 2001–2010 and Strategic Plan 2011–2020; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; ISBN 978-92-4-150312-9. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections. Available online: http://www.whhttp//www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/soil-transmitted-helminth-infections (accessed on 6 June 2018).
- Jiménez, B.; Maya, C.; Velásquez, G.; Torner, F.; Arambula, F.; Barrios, J.A.A.; Velasco, M. Identification and quantification of pathogenic helminth eggs using a digital image system. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 166, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Riet, E.; Wuhrer, M.; Wahyuni, S.; Retra, K.; Deelder, A.M.; Tielens, A.G.M.; Van Der Kleij, D.; Yazdanbakhsh, M. Antibody responses to Ascaris-derived proteins and glycolipids: The role of phosphorylcholine. Parasite Immunol. 2006, 28, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, B. Helminth ova removal from wastewater for agriculture and aquaculture reuse. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2007, 55, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakam, K.K.; Thamsborg, S.M.; Dalsgaard, A.; Kyvsgaard, N.C.; Mejer, H. Environmental contamination and transmission of Ascaris suum in Danish organic pig farms. Parasite Vectors 2016, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dold, C.; Holland, C.V. Helminth-Nematode: Ascaris. Encycl. Food Saf. 2014, 2, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Henze, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Ekama, G.A.; Brdjanovic, D. Biological Wastewater Treatment—Principles, Modelling and Design; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lübken, M.; Wichern, M.; Bischof, F.; Prechtl, S.; Horn, H. Development of an empirical mathematical model for describing and optimizing the hygiene potential of a thermophilic anaerobic bioreactor treating faeces. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kereita, B.; Drechsel, P.; Klutse, A.; Cofie, O. On-Farm Treatment Options of Wastewater, Greywater and Fecal Sludge with Special Reference to West Africa; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka; CGIAR Research Program on Water, Land and Ecosystems (WLE): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mara, D.D.; Horan, N.J. (Eds.) Handbook of Water and Wastewater Microbiology; Academic Press: London, UK, 2003; ISBN 0-12-470100-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, M.E.; Thamsborg, S.M.; Andersen, T.J.; Olsen, A.; Dalsgaard, A. Sedimentation of helminth eggs in water. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4651–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, M.E.; Andersen, T.J.; Dalsgaard, A.; Olsen, A.; Thamsborg, S.M. Resuspension and settling of helminth eggs in water: Interactions with cohesive sediments. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3903–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, R.A. A study of eggs of Ascaris lumbricoides var suum with the electron microscope. J. Parasitol. 1956, 42, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahnak, A.; Dabagh, N. Adhesion of Cercaria (Larva of helminth parasites) to host by Lectins-carbohydrates bonds as a model for evaluation of Schistosoma entrance mechanisms in Cercarial Dermatitis. Iran. J. Public Health 2008, 37, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Emelko, M.B.; Huck, P.M. Microspheres as surrogates for Cryptosporidium filtration. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2004, 96, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.M.; Suttle, C.A. Grazing by marine nanoflagellates on viruses and virus-sized particles: Ingestion and digestion. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 94, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, R.W.; Kinner, N.E.; MacDonald, D.; Metge, E.W.; Bunn, A. Role of physical heterogeneity in the interpretation of small scale laboratory and field observations of bacteria, microbial-sized microsphere, and bromide transport through aquifer sediments. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 2713–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metge, D.W.; Harvey, R.W.; Anders, R.; Rosenberry, D.O.; Seymour, D.; Jasperse, J. Use of carboxylated microspheres to assess transport potential of Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts at the Russian River water supply facility, Sonoma County, California. Geomicrobiol. J. 2007, 24, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passmore, J.M.; Rudolph, D.L.; Mesquita, M.M.F.; Cey, E.E.; Emelko, M.B. The utility of microspheres as surrogates for the transport of E. coli RS2g in partially saturated agricultural soil. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aybay, C. Differential binding characteristics of protein G and protein A for Fc fragments of papain-digested mouse IgG. Immunol. Lett. 2003, 85, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, L.R.; Orihel, T.C. Atlas of Human Parasitology, 5th ed.; American Society for Clinical Pathology Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2007; 540p, ISBN 0-89189-1676. [Google Scholar]
- Arizono, N.; Yamada, M.; Tegoshi, T.; Onishi, K. Molecular Identification of Oesophagostomum and Trichuris Eggs Isolated from Wild Japanese Macaques. Korean J. Parasitol. 2012, 50, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeibig, E.A. Clinical Parasitology: A Practical Approach, 2nd ed.; Saunders Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, M.W. Determination of Settling Velocities of Cohesive Muds; HR Wallingford: Wallingford, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Huisman, L. Sedimentation and Flotation and Mechanical Filtration, 2nd ed.; Faculty of Civil Engineering, Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- McCave, I.N.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Principles and methods of geological particle size analysis. In Principles, Methods, and Application of Particle Size Analysis; Syvitski, J.P., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 3–21. ISBN 0-521-36472-8. [Google Scholar]
- Covert, P.A. An Examination of the Form and Variability of Manganese Oxide in Columbia River Suspended Material; Oregon State University: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dereszewska, A.; Cytawa, S.; Tomczak-Wandzel, R.; Medrzycka, K. The effect of anionic surfactant concentration on activated sludge condition and phosphate release in biological treatment plant. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaya-Beas, R.-E. Bio-Filtration of Helminth Eggs and Coliforms from Municipal Sewage for Agricultural Reuse in Peru; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, C.D. Some factors influencing sedimentation. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1926, 18, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutilier, L.; Jamieson, R.; Gordon, R.; Lake, C.; Hart, W. Adsorption, sedimentation, and inactivation of E. coli within wastewater treatment wetlands. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4370–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanson, G.T. Immobilization of Ligands on Chromatography Supports in. In Bioconjugate Techniques; Academic Press: London, UK, 2013; pp. 589–740. [Google Scholar]
- McDowell-Boyer, L.; Hunt, J.R.; Sitar, N. Particle Transport Through Porous Media. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 1901–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, J.P.; Bansal, V. Studies of the mobility of pesticides by soil thin layer chromatography. Soil Sci. 1978, 126, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R. Fate and behaviour of parasites in wastewater treatment systems. In Handbook of Water and Wastewater Microbiology; Mara, D.D., Horan, N.J., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2003; p. 610. ISBN 0-12-470100-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ayres, R.M.; Mara, D.D. Analysis of Wastewater for Use in Agriculture—A Laboratory Manual of Parasitological and Bacteriological Techniques; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
| Species | Shape | Diameter (µm) | Surface |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ascaris lumbricoides | Elliptical | 45–75 × 35–50 | Protein coated |
| Trichuris trichiura | Barrel shaped; Hyaline polar plug at each end | 50–55 × 22–24 | smooth; yellow-brown color |
| Taenia solium | Spherical | 31–43 | |
| Toxocara canis | Nearly spherical | 80–85 × 75 | |
| Oesophagostomum | Ovoid | 69–78 × 41–48 | Thin-shelled |
| p-Value (2-Tailed) | |
|---|---|
| ww particles vs. microsphere A | 0.0216 ** |
| ww particles vs. microsphere G | 0.0040 * |
| ww particles vs. microsphere A/G | 0.0013 * |
| Parasite Egg/Cyst | Average Size (µm) | Relative Density | Velocity (m/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ascaris–fertile | 60 × 45 | 1.11 | 0.77(=0.214 mm/s) |
| Ascaris–infertile | 90 × 40 | 1.2 | 3.15(=0.875 mm/s) |
| Trichuris | 50 × 22 | 1.15 | 0.73(=0.203 mm/s) |
| Parasite Egg | A | G | A/G |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water: | |||
| Ascaris | 0.540 * | 0.007 | 0.051 * |
| Trichuris | 0.004 | 0.00002 | 0.016 |
| Oesophagostomum | 0.010 | 0.00005 | 0.064 * |
| Wastewater: | |||
| Ascaris | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.00001 |
| Trichuris | 0.199 * | 0.096 * | 0.0005 |
| Oesophagostomum | 0.023 | 0.019 | 0.0001 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arthur, B.K.; Nettmann, E.; Rademacher, A.; Lübken, M.; Marschner, B.; Wichern, M. Microspheres as Surrogate Helminth Eggs: A Comparative Labscale Sedimentation Study for Tap- and Wastewater. Water 2018, 10, 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091192
Arthur BK, Nettmann E, Rademacher A, Lübken M, Marschner B, Wichern M. Microspheres as Surrogate Helminth Eggs: A Comparative Labscale Sedimentation Study for Tap- and Wastewater. Water. 2018; 10(9):1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091192
Chicago/Turabian StyleArthur, Barbara K., Edith Nettmann, Andrea Rademacher, Manfred Lübken, Bernd Marschner, and Marc Wichern. 2018. "Microspheres as Surrogate Helminth Eggs: A Comparative Labscale Sedimentation Study for Tap- and Wastewater" Water 10, no. 9: 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091192
APA StyleArthur, B. K., Nettmann, E., Rademacher, A., Lübken, M., Marschner, B., & Wichern, M. (2018). Microspheres as Surrogate Helminth Eggs: A Comparative Labscale Sedimentation Study for Tap- and Wastewater. Water, 10(9), 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091192







