Urban Surface Water Quality, Flood Water Quality and Human Health Impacts in Chinese Cities. What Do We Know?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background: Connections between Urban Surface Water, Floods and Human Health
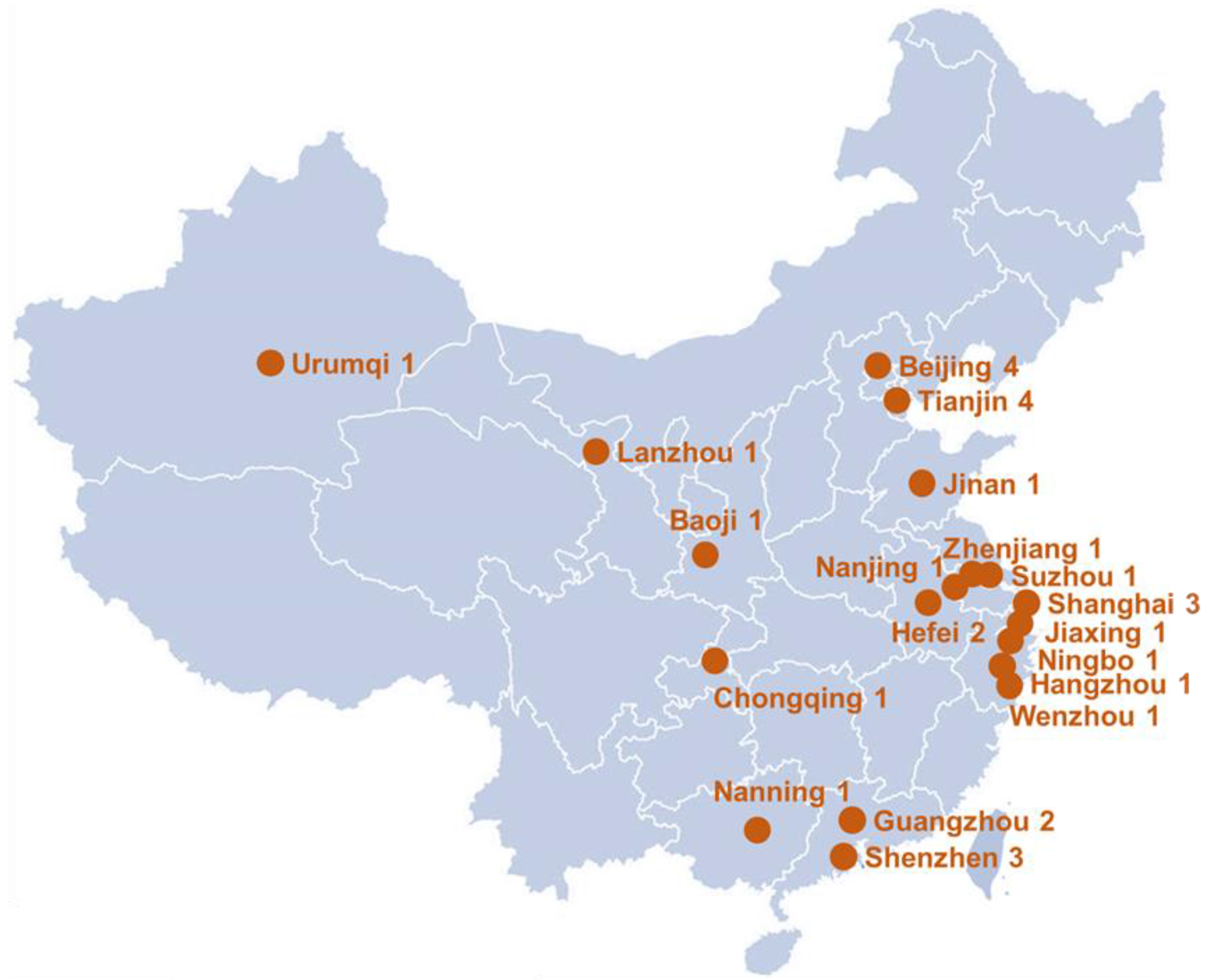
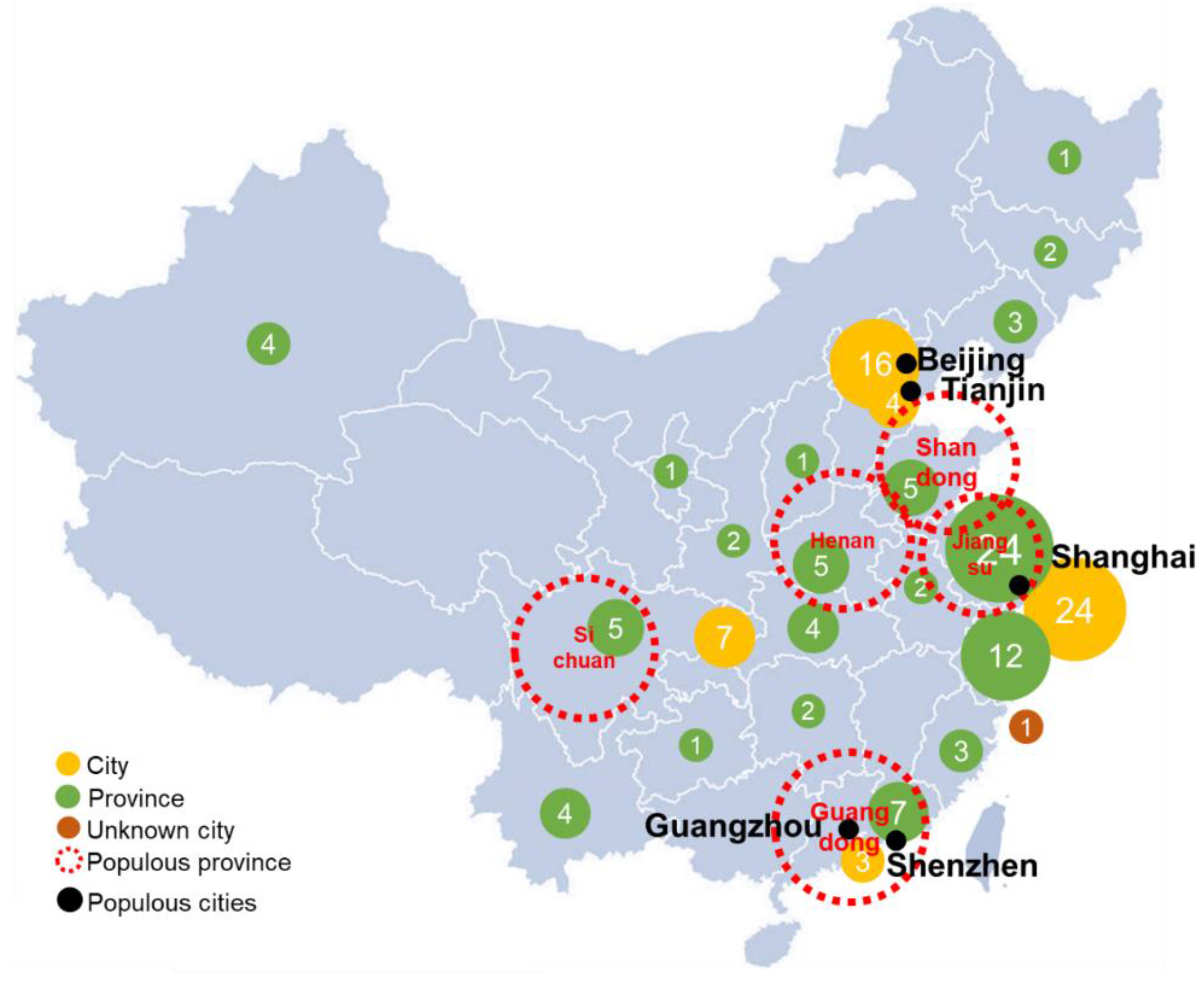
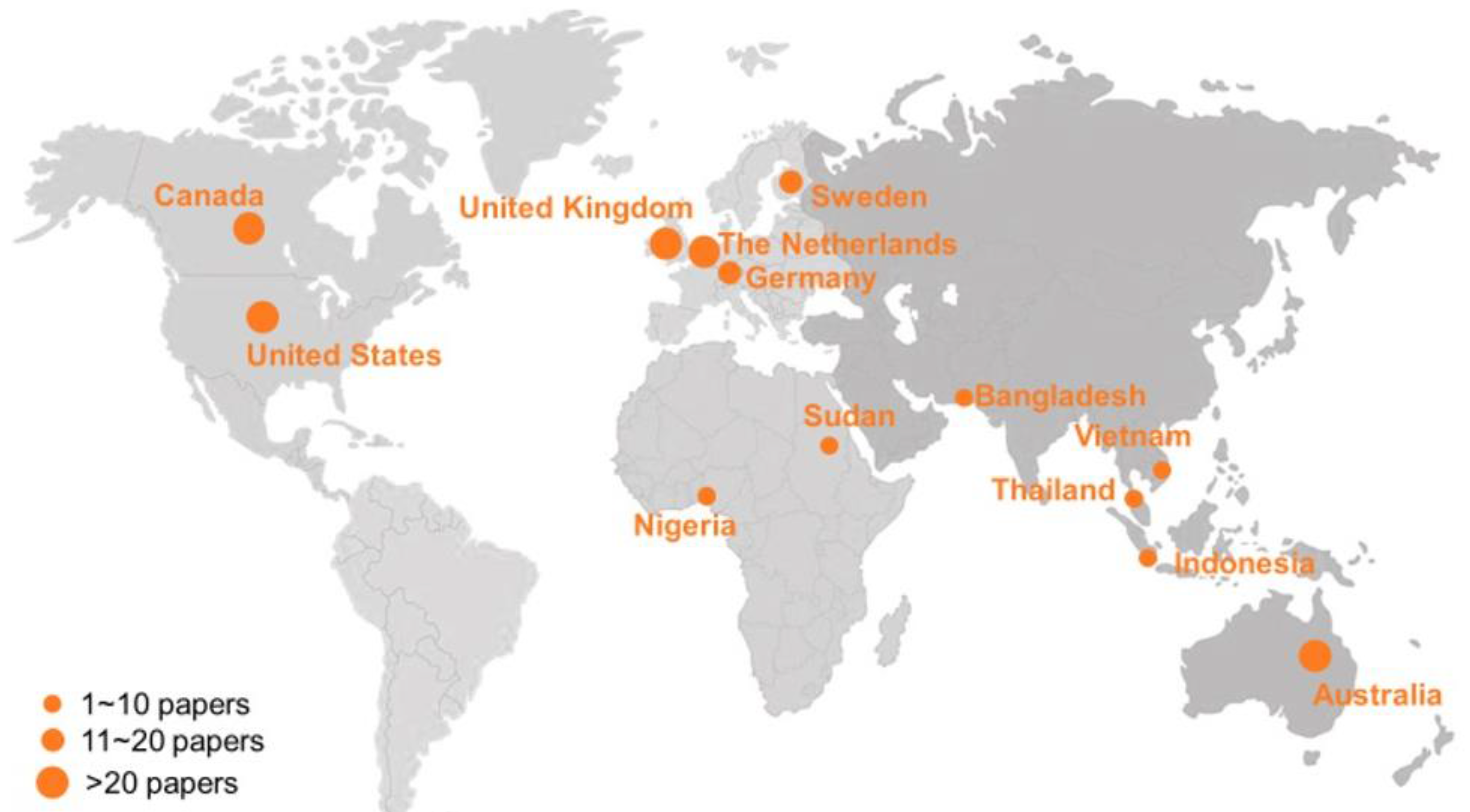
3. Methodology/Approach
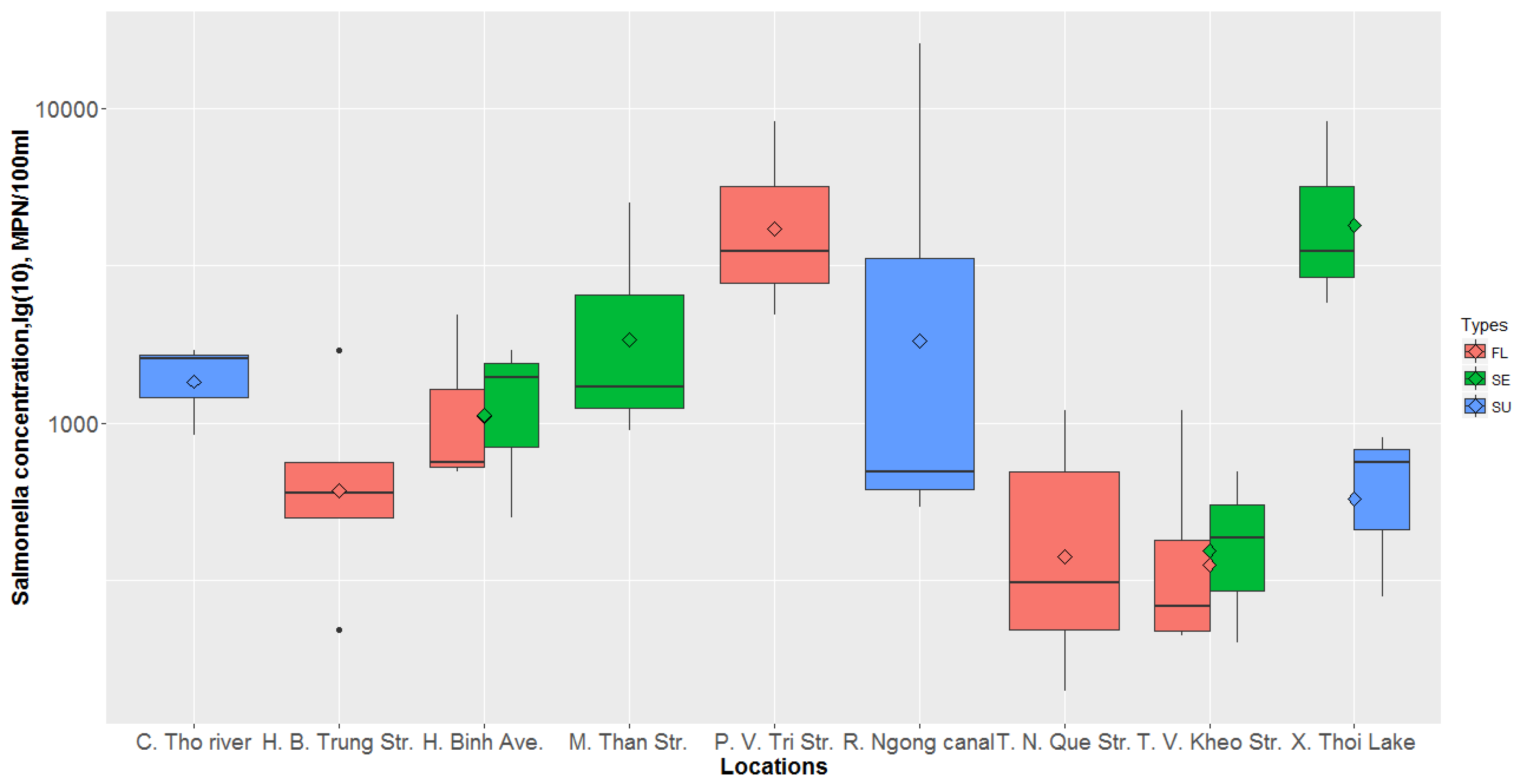
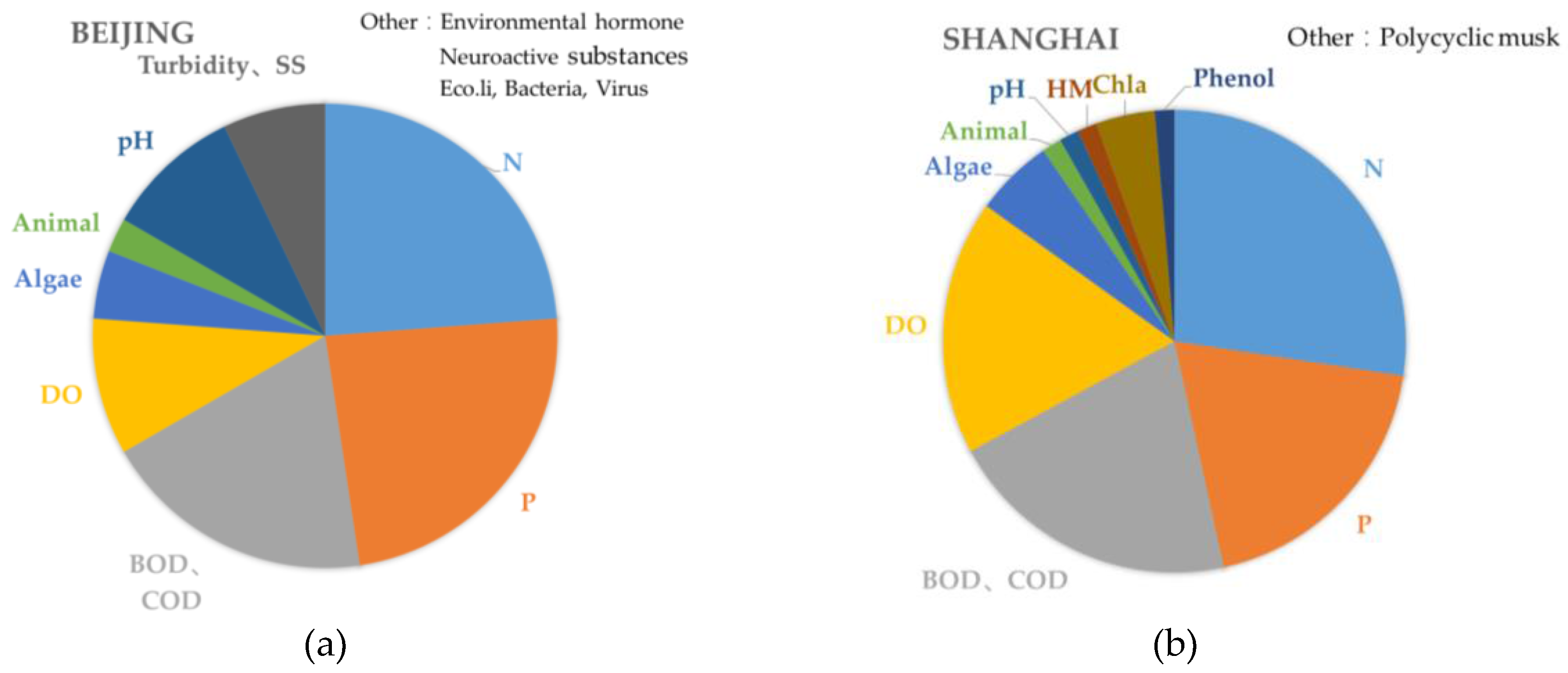
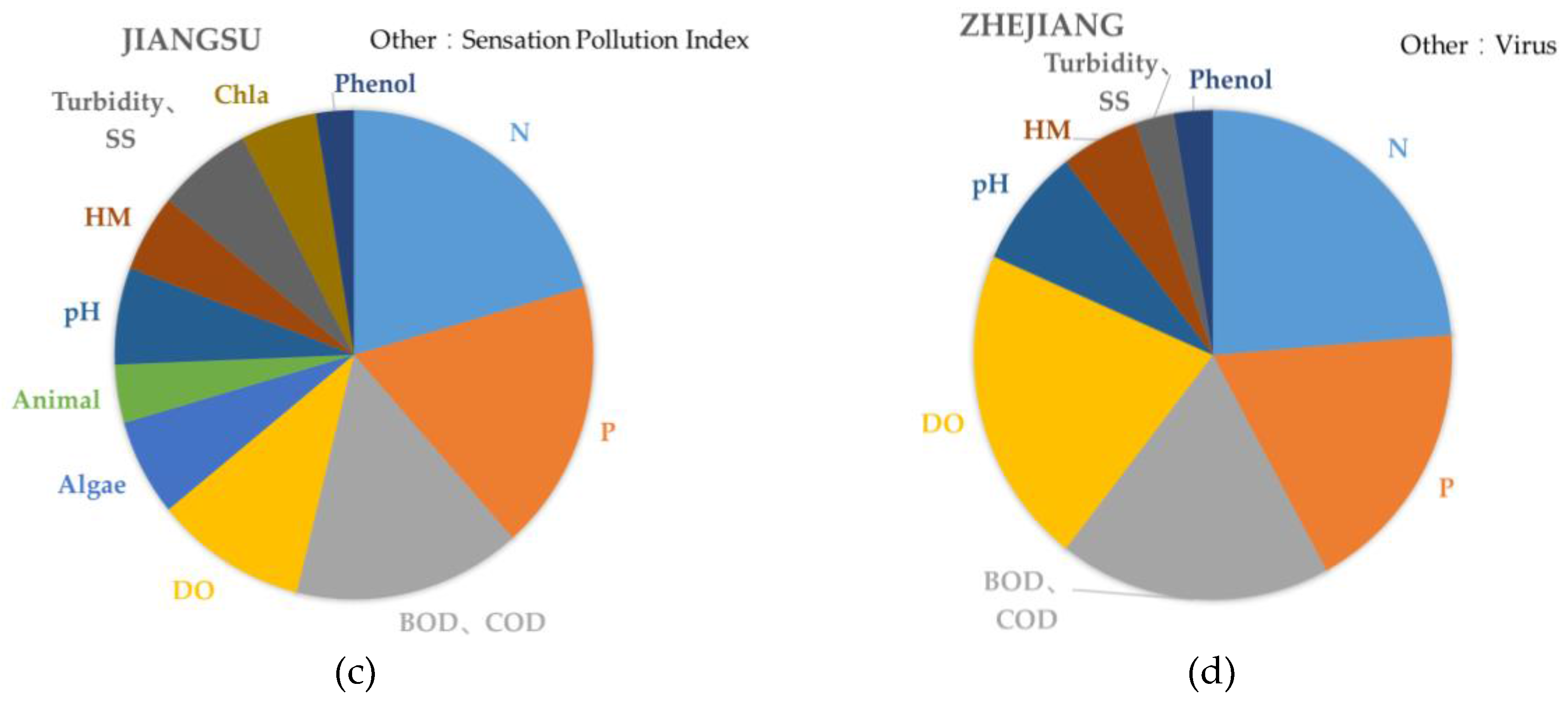
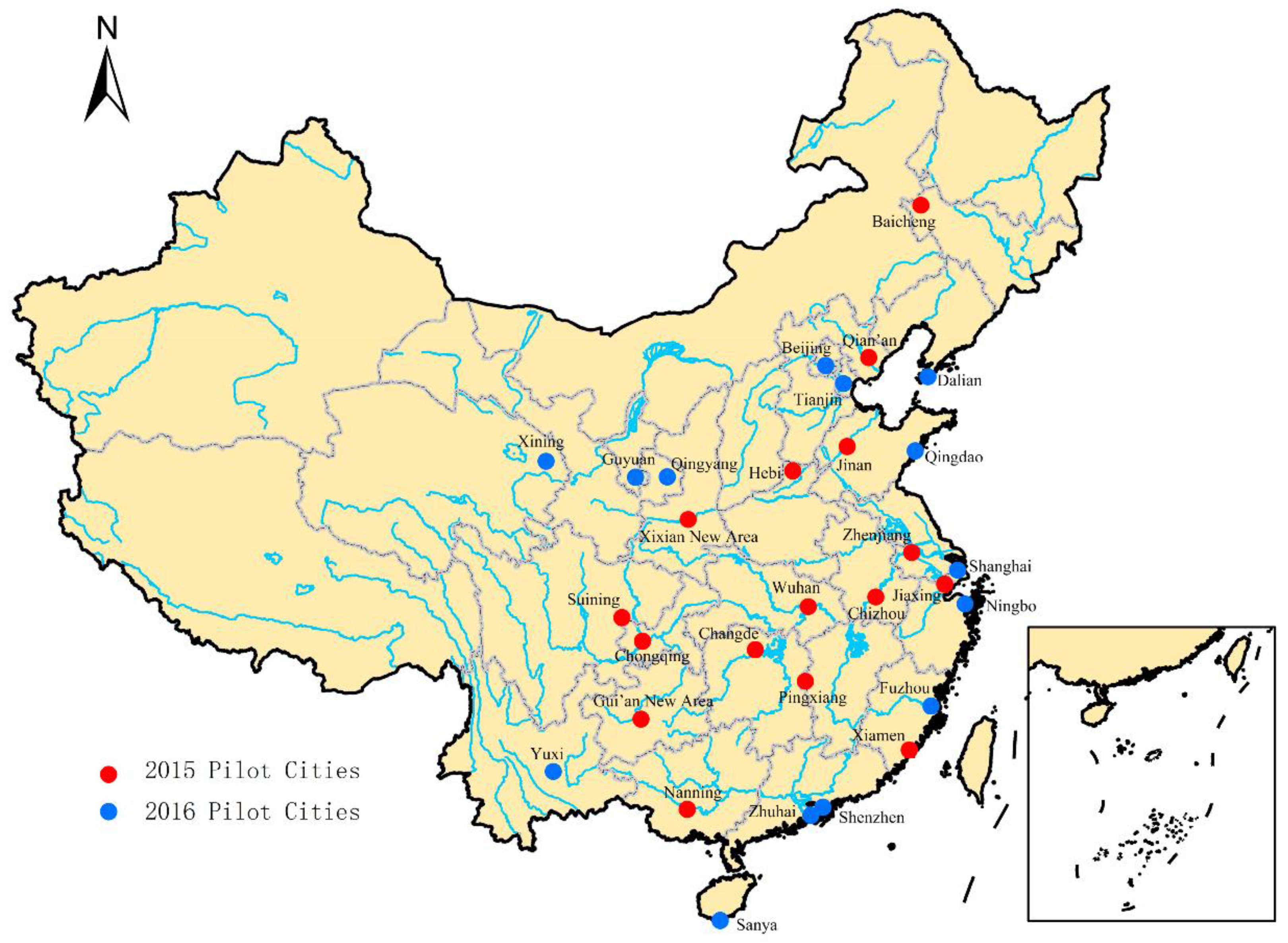
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konrad, C.P. Effects of Urban Development on Floods. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/fs07603/ (acccessed on 21 February 2018).
- Zhang, C.-L.; Chen, F.; Miao, S.G.; Li, Q.C.; Xuan, C.Y. Influences of urbanization on precipitation and water resources in the metropolitan Beijing area. In Proceedings of the 21st American Metrological Society Conference on Hydrology, San Antonio, TX, USA, 17 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Huong, H.T.L.; Pathirana, A. Urbanization and climate change impacts on future urban flood risk in Can Tho city, Vietnam. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.; Du, G.; Zhou, J. Urban flood risk warning under rapid urbanization. Environ. Res. 2015, 139, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, A.S.; Zhou, Q.; Linde, J.J.; Arnbjergnielsen, K. Comparing Methods of Calculating Expected Annual Damage in Urban Pluvial Flood Risk Assessments. Water 2015, 7, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament; Council of the European Union. Directive 2007/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2007 on the Assessment and Management of Flood Risks (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2007/60/oj (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- European Parliament; Council of the European Union. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32000L0060 (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Horton, R. Extreme rain, flooding, and health. Lancet 2017, 390, 1005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D. Water supply: China’s sponge cities to soak up rainwater. Nature 2016, 537, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotny, V. Water Quality: Diffuse Pollution and Watershed Management; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Alderman, K.; Turner, L.R.; Tong, S. Floods and human health: A systematic review. Environ. Int. 2012, 47, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiew, F.H.S.; Mcmahon, T.A. Modelling runoff and diffuse pollution loads in urban areas. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.L.; Sun, X.; Chen, Q.K.; Yang, L.Y. Effect of ammonia in the tailwater from wastewater treatment plant on the growth of myriophyllum spicatum. Chin. J. Ecol. 2015, 34, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar]
- Nabelkova, J.; Kominkova, D.; Jirak, J. The impact of highway runoff on the chemical status of small urban streams. Urban Environ. 2012, 19, 297–306. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, H.; Tasaki, M.; Uchiyama, N.; Morita, M. Water quality and pollution load during flood and non-flood periods in an urban tidal river. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 69, I_1723–I_1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nábelková, J.; Stastná, G.; Komínková, D. Flood impact on water quality of small urban streams. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karlavičienė, V.; Švedienė, S.; Marčiulionienė, D.E.; Randerson, P.; Rimeika, M.; Hogland, W. The impact of storm water runoff on a small urban stream. J. Soils Sediment. 2008, 9, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Bi, J.L.; Wang, L.S.; Tang, W.Z.; Shan, B.Q.; Yang, L.; Chen, J. Effect of storm runoff on the water quality of urban rivers with unconventional water sources. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2015, 35, 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, H.Y.; Zhuo, M.N.; Li, D.Q.; Zhou, Y.Z. The water quality characteristics of runoff on urban road in Guangzhou. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2006, 15, 969–973. [Google Scholar]
- Floresrodrîguez, J.; Bussy, A.L.; Thevenot, D. Toxic metals in urban runoff: Physico-chemical mobility assessment using speciation schemes. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 29, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zehetner, F.; Rosenfellner, U.; Mentler, A.; Gerzabek, M.H. Distribution of Road Salt Residues, Heavy Metals and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons across a Highway-Forest Interface. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 198, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, K.C. Flood plain management models for economic, environmental and ecological impact analysis. In Proceedings of the Conference on Ecological Modelling, Copenhagen, Denmark, 28 August–2 September 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Cash, R.A.; Halder, S.R.; Husain, M.; Islam, M.S.; Mallick, F.H.; May, M.A.; Rahman, M.; Rahman, M.A. Reducing the health effect of natural hazards in Bangladesh. Lancet 2013, 382, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cann, K.F.; Thomas, D.R.; Salmon, R.L.; Wyn-Jones, A.P.; Kay, D. Extreme water-related weather events and waterborne disease. Epidemiol. Infect 2013, 141, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ten Veldhuis, J.A.E.; Clemens, F.H.L.R.; Sterk, G.; Berends, B.R. Microbial risks associated with exposure to pathogens in contaminated urban flood water. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2910–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Huynh, T.T.N.; Baino-Salingay, M.L.; Ho, L.P.; Steen, P.V.D.; Pathirana, A. Water Quality Dynamics of Urban Water Bodies during Flooding in Can. Tho City, Vietnam. Water 2017, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cai, R.H.; He, J. A Guide to the Chinese Core Periodical; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ochoo, B.; Valcour, J.; Sarkar, A. Association between perceptions of public drinking water quality and actual drinking water quality: A community-based exploratory study in newfoundland (Canada). Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heibati, M.; Stedmon, C.A.; Stenroth, K.; Rauch, S.; Toljander, J.; Säve-Söderbergh, M.; Murphy, K.R. Assessment of drinking water quality at the tap using fluorescence spectroscopy. Water Res. 2017, 125, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abera, B.; Bezabih, B.; Hailu, D. Microbial quality of community drinking water supplies: A ten year (2004–2014) analyses in west amhara, ethiopia. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2017, 9–10, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgeman, J.; Baker, A.; Brown, D.; Boxall, J.B. Portable led fluorescence instrumentation for the rapid assessment of potable water quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emelko, M.B.; Silins, U.; Bladon, K.D.; Stone, M. Implications of land disturbance on drinking water treatability in a changing climate: Demonstrating the need for “ source water supply and protection” strategies. Water Res. 2011, 45, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storey, M.V.; Van, d.G.B.; Burns, B.P. Advances in on-line drinking water quality monitoring and early warning systems. Water Res. 2011, 45, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, H.G.; Sheridan, G.J.; Lane, P.N.J.; Nyman, P.; Haydon, S. Wildfire effects on water quality in forest catchments: A review with implications for water supply. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 170–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkandawire, T.; Banda, E. Assessment of drinking water quality of mtopwa village in bangwe township, blantyre. Desalination 2009, 248, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cidu, R.; Frau, F.; Tore, P. Drinking water quality: Comparing inorganic components in bottled water and italian tap water. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macova, M.; Toze, S.; Hodgers, L.; Mueller, J.F.; Bartkow, M.; Escher, B.I. Bioanalytical tools for the evaluation of organic micropollutants during sewage treatment, water recycling and drinking water generation. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4238–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, H.T.; Marcussen, H.; Hansen, H.C.; Le, G.T.; Duong, H.T.; Ta, N.T.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Hansen, S.; Strobel, B.W. Screening of inorganic and organic contaminants in floodwater in paddy fields of hue and thanh hoa in vietnam. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 7348–7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwonumara, N.; Okogwu, O. The impact of flooding on water quality, zooplankton composition, density and biomass in lake iyieke, cross river-floodplain, southeastern nigeria. Acta Zool. Litu. 2013, 23, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.I.; Elagib, N.A.; Horn, F.; Sag, S. Lessons learned from khartoum flash flood impacts: An integrated assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.; Burlando, P.; Priadi, C. The importance of integrated solutions to flooding and water quality problems in the tropical megacity of jakarta. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 20, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Hutchins, M. The impacts of urbanisation and climate change on urban flooding and urban water quality: A review of the evidence concerning the United Kingdom. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 12, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.; Stewart, L.; Hawdon, A.; Keen, R.; Karim, F.; Kemei, J. Flood water quality and marine sediment and nutrient loads from the tully and murray catchments in north queensland, australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 60, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcmillan, M.D.; Rahnema, H.; Romiluy, J.; Kitty, F.J. Effect of exposure time and crude oil composition on low-salinity water flooding. Fuel 2016, 185, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuch, G.; Serrao-Neumann, S.; Morgan, E.; Choy, D.L. Water in the city: Green open spaces, land use planning and flood management—An australian case study. Land Use Policy 2017, 63, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintern, A.; Leahy, P.J.; Heijnis, H.; Zawadzki, A.; Gadd, P.; Jacobsen, G.; Deletic, A.; Mccarthyad, D.T. Identifying heavy metal levels in historical flood water deposits using sediment cores. Water Res. 2016, 105, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dortch, M.S.; Zakikhani, M.; Kim, S.C.; Steevens, J.A. Modeling water and sediment contamination of lake pontchartrain following pump-out of hurricane katrina floodwater. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesiri, B.; Deilami, K.; Mcgree, J.; Goonetilleke, A. Use of surrogate indicators for the evaluation of potential health risks due to poor urban water quality: A bayesian network approach. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 233, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantine, K.; Massoud, M.; Alameddine, I.; El-Fadel, M. The role of the water tankers market in water stressed semi-arid urban areas: Implications on water quality and economic burden. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 188, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Wang, C.; Hou, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Yang, Y.Y.; You, G.X. Effect of inter-basin water transfer on water quality in an urban lake: A combined water quality index algorithm and biophysical modelling approach. Ecol. Indic. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazemi, A.; Madani, K. Urban water security: Emerging discussion and remaining challenges. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minomo, K.; Ohtsuka, N.; Nojiri, K.; Matsumoto, R. Influence of combustion-originated dioxins in atmospheric deposition on water quality of an urban river in japan. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 64, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.H.; Yin, H.L.; Xie, M. Development of integrated catchment and water quality model for urban rivers. Chin. J. Hydrodyn. B 2015, 27, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, S. Water governance in an urban age. Util. Policy 2016, 43, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, S.; Nam, K.; Kim, J.; Kwak, C. Development of urban runoff model ffc-qual for first-flush water-quality analysis in urban drainage basins. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 205, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosrati, K. Identification of a water quality indicator for urban roof runoff. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2017, 9–10, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.B.; Frost, P.C. Monitoring water quality in toronto’s urban stormwater ponds: Assessing participation rates and data quality of water sampling by citizen scientists in the freshwater watch. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Man, H.; van den Berg, H.H.J.L.; Leenen, E.J.T.M.; Schijven, J.F.; Schets, F.M.; van der Vliet, J.C.; van Knapen, F.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Quantitative assessment of infection risk from exposure to waterborne pathogens in urban floodwater. Water Res. 2014, 48, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardoulakis, S.; Dimitroulopoulou, C.; Thornes, J.; Lai, K.M.; Taylor, J.; Myers, I.; Heaviside, C.; Mavrogianni, A.; Shrubsole, C.; Chalabi, Z.; Davies, M.; et al. Impact of climate change on the domestic indoor environment and associated health risks in the UK. Environ. Int. 2015, 85 (Suppl. 1), 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picou, J.S.; Nicholls, K.; Guski, R. Environmental stress and health. Int. Encycl. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 12, 804–808. [Google Scholar]
- Chaturongkasumrit, Y.; Techaruvichit, P.; Takahashi, H.; Kimura, B.; Keeratipibul, S. Microbiological evaluation of water during the 2011 flood crisis in thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.F. Floodwater challenges. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 815–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, N.A.; Valsaraj, K.T.; Thibodeaux, L.J. Elevated in-home sediment contaminant concentrations—The consequence of a particle settling-winnowing process from hurricane katrina floodwaters. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigg, B.C.; Beyrouty, C.A.; Norman, R.J.; Gbur, E.E.; Hanson, M.G.; Wells, B.R. Rice responses to changes in floodwater and n timing in southern usa. Field Crops Res. 2000, 66, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modlmaier, M.; Kuhn, R.; Kaaden, O.R.; Pfeffer, M. Transmission studies of a european sindbis virus in the floodwater mosquito aedes vexans (diptera: Culicidae). Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 291 (Suppl. 33), 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.B.; Routray, J.K. Assessing factors affecting flood-induced public health risks in kassala state of sudan. Oper. Res. Health Care 2014, 3, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waroux, O.L.P.D. Floods as Human Health Risks. In Encyclopedia of Environmental Health; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Q.; Fang, T.; Huang, Y.; Dong, P.; Wang, H. Evaluation of bacterial pathogen diversity, abundance and health risks in urban recreational water by amplicon next-generation sequencing and quantitative pcr. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 57, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocker, W.; Maute, K.; Webb, C.; French, K. Mosquito assemblages associated with urban water bodies; implications for pest and public health threats. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 162, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renouf, M.A.; Serrao-Neumann, S.; Kenway, S.J.; Morgan, E.A.; Low, C.D. Urban water metabolism indicators derived from a water mass balance—Bridging the gap between visions and performance assessment of urban water resource management. Water Res. 2017, 122, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, J.L.; Maitre, D.C.L.; Roux, D.J.; Colvin, C.; Smith, J.S.; Smith-Adao, L.B.; Maherry, A.; Sitas, N. Strategic water source areas for urban water security: Making the connection between protecting ecosystems and benefiting from their services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Cui, Q.; Huang, Y.; Dong, P.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.T.; Ye, Q. Distribution comparison and risk assessment of free-floating and particle-attached bacterial pathogens in urban recreational water: Implications for water quality management. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 613–614, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrimann, S.; Pham-Duc, P.; Cissé, G.; Tram, N.T.; Ha, H.T.; Dung, D.T.; Ngoc, P.; Nguyen, H.; Anh Vuong, T.; Utzinger, J.; Schindler, C.; Winkler, M.S. Microbial contamination along the main open wastewater and storm water channel of hanoi, vietnam, and potential health risks for urban farmers. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Liang, M.; Wang, Z.; Hynds, P. Biofilm growth kinetics and nutrient (n/p) adsorption in an urban lake using reclaimed water: A quantitative baseline for ecological health assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völker, S.; Kistemann, T. Developing the urban blue: Comparative health responses to blue and green urban open spaces in germany. Health Place 2015, 35, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, M.D.S. Status of water use sanitation and hygienic condition of urban slums: A study on rupsha ferighat slum, khulna. Desalination 2009, 246, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanan, A.; Kandasamy, J.; Vigneswaran, S.; Sharma, D. A gradualist approach to address australia’s urban water challenge. Desalination 2009, 249, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.N.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.; Saint, C. Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2997–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.B.; Marsalek, J.; Chocat, B. Urban Water Quality; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Sales-Ortells, H.; Medema, G. Microbial health risks associated with exposure to stormwater in a water plaza. Water Res. 2015, 74, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruin, I.; Creutin, J.-D.; Anquetin, S.; Lutoff, C. Human exposure to flash floods–Relation between flood parameters and human vulnerability during a storm of September 2002 in Southern France. J. Hydrol. 2008, 361, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, K.; Sthiannopkao, S.; Kim, K.-W.; Wong, M.H.; Sao, V.; Hashim, J.H.; Yasin, M.S.M.; Aljunid, S.M. Health risk assessment of inorganic arsenic intake of Cambodia residents through groundwater drinking pathway. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5777–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, A.; Ray, I. Wastewater for agriculture: A reuse-oriented planning model and its application in peri-urban China. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moglia, M.; Gan, K.; Delbridge, N. Exploring methods to minimize the risk of mosquitoes in rainwater harvesting systems. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-J.; Ma, X.; Zhu, G.-F.; Xu, M.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, G.-A.; Shi, B.-J. Analysis of the breeding sources of overwintering Aedes albopictus and influencing factors in Ningbo city, 2016. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2017, 28, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Available online: http://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/syr/ (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Xu, Y.X.; Xu, R.Q.; Wang, S.Z. Investigation of the breeding place of mosquito larva in outdoor environmental seeper. Shanghai J. Prev. Med. 2004, 16, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, Q.-B.; Liu, W.-J.; Zhang, J.-F.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Yu, Q.-F. Characterization of Urban Roadway Runoff in Xi'an City. Water Sav. Irrig. 2013, 4, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Huang, Y.Q.; Wu, T.; Li, J.J.; Xu, M.L. Research on the Characteristics of Urban Runoff in Zhenjiang: Rainwater Utilization Demonstration Project. Environ. Eng. 2010, 28, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Tu, X.-J.; Qin, Y.-Q.; Huang, X.-Y.; Hu, Z.-B.; Wei, Q. Analysis of pollutants concentration of initial rainwater in nanning roads. Environ. Eng. 2017, 7, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, A.-P. Analysis on stormwater management project in Baoan District, Shenzhen City. China Water Wastewater 2010, 16, 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.M.; Mi, N.; Wang, X.T.; Cai, Z.W.; Di, W.Z. Analysis of Road Runoff Pollutants in Northern City Based on the Typical Rainfall. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 418–426. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.X.; Li, Q.Q.; Li, T.L.; Wang, W.; Jin, C.H.; Yang, Z.Z.; Cao, J.G. Study on the pollution status of rainfall runoff in Tianjin. China Water Wastewater 2015, 11, 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, F.; Chen, W. Probe to the Rainwater Utilization Scheme in Nanjing City Residential Area. China Water Wastewater 2003, 19, 95–97. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, G.X.; Wang, P.X.; Qiu, W.G. Rainwater quality monitoring and treatment in Shanghai City. Water Wastewater Eng. 2007, 33, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.R.; Nie, T.F. Characteristics and Load of Non-Point Source Pollution of Urban Rainfall Runoff in Guangzhou, China. J. South China Univ. Technol. Nat. Sci. Edit. 2012, 40, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.W.; Hua, L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Shan, W.J.; Shi, W.X.; Huang, Z.F.; Jiao, Z.Z. The Characteristics of Pollution in Urban Rainwater Pipe Network and Its Influence on the Water Quality of Receiving Water Body. Environ. Chem. 2012, 31, 208–215. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Liu, Z.Q.; Liu, H.H.; Tian, Y. Analysis and Research on the Rainwater Utilization on One Campus of Tianjin. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 2, 288–292. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, H.H.; Li, Y.; Fang, X.J.; Jiang, Z.H. Study on the water quality characteristics of the road stormwater runoff in Beijing City. Water Wastewater Eng. 2011, 37, 130–133. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.S.; Guo, L.C.; Luo, X.L.; Chen, F.R.; Zeng, Y.P. The Characteristics of Rainwater-Runoff-Flow Pollution Chain in Guangzhou. Environ. Chem. 2014, 33, 1040–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.X.; Wang, Y.J. Water Quality Analysis and Recycling Suggestions for a Campus in Lanzhou. Water Wastewater Eng. 2013, 39, 151–153. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Li, T.; Qian, J.; Peng, S.H.; Qian, L.P. Types of Detention Tank for Xinghua Drainage System in Hefei City. China Water Wastewater 2012, 28, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.F.; Li, T.; Li, H. Characteristics of Surface Runoff Pollution of Shanghai Urban Area. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 28, 1430–1434. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yu, X.J. The analysis of change trend of runoff water quality and recycling methods in Jinan. Environ. Pollut. Control 2008, 30, 98–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Zhao, L.J.; Li, T.L.; Jin, Z.H. Characteristics of pollution and monitoring of water quality in Tianjin. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2009, 18, 2127–2131. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, P.Q.; Ren, Y.F.; Wang, X.K.; Ouyang, Z.P.; Zhou, X.P. Research on Evaluation of Water Quality of Beijing Urban Stormwater Runoff. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Si, S.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zheng, K.B.; Sun, K.P. Study on control effects of permeable asphalt road and road retention on water quality and quantity of runoff. Water Wastewater Eng. 2015, 11, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.Q.; Li, T.L.; Liu, D.X.; Jin, Z.H. Pollution characteristics of runoff in different function area of Tianjin. Environ. Pollut. Control 2011, 33, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Wang, X.K.; Hao, L.L.; Hou, P.Q.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Characterization and Source Apportionment of Pollutants in Urban Roadway Runoff in Chongqing. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.F.; Li, T.; Gao, T.Y. Study on Pollution Load of Urban Surface Runoff in Shanghai. China Water Wastewater 2006, 22, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Che, W.; He, W.H.; Lu, C.Y. Pollution analysis and control countermeasures of rainwater runoff in Hangzhou. China Water Wastewater 2015, 17, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, W.; Wang, J.L.; Che, W. Analysis on characteristics of stormwater runoff flush on different land surfaces. Tech. Equip. Environ. Pollut. Control 2012, 6, 817–822. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.M.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.D.; Lin, H. Study on the Change Regularity and Treatment of Urban Rainwater Runoff. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 28, 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.H.; Lai, Q.Y.; Du, J.Y.; Bao, Y.S.; Zheng, W.W.; Ye, F.X. Analysis of water quality characteristics of different bedding surface rainfall runoff in ningbo city. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, S1, 312–316. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H.; Han, Y.; Peng, D.C. Analysis and characteristics of water quality of urban rain runoff. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 24, 84–85. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.J.; Li, T.; Ye, G.J.; Tang, X.Y. Study on the pollution characteristics of surface runoff in fengqiao industry park of Suzhou. Environ. Pollut. Control 2009, 31, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.R.; Hai, M.Y.; Zhao, L.L. Analysis on the characteristics of storm runoff water quality of different underlaying surfaces in urumqi. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2010, 17, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.R.; Hu, S.; Huang, H.; Li, H. Study on surface runoff pollution in the baimang river basin of shenzhen city. China Water Wastewater 2011, S1, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.J.; Liu, H.Q.; Sun, H.L.; Zhou, L.Z.; Zhang, M.H. Study on the characteristics of surface runoff pollution in different functional areas in Wenzhou. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, S1, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Gao, H.J.; Li, T. Pollution Characterization of Impermeability Surface Runoff in Typical Urban of Hefei. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Ren, R.; Wang, Z.J.; Lin, X.T.; Liu, L.L.; Wu, S.H.; Zhang, S.F.; Chen, S. Investigation on Status of Environmental Hormone Pollution in the Industrial Wastewater and Urban Sewage in Beijing. Res. Environ. Sci. 2007, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.T.; Guo, C.S.; Hua, Z.D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Pollution Status and Environmental Risks of Illicit Drugs in the Urban Rivers of Beijing. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 845–853. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wei, Y.S.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.W.; Yu, M.; Xiao, Q.C.; Yu, D.W.; Sun, C.; Yang, Y.; Gao, L.J.; et al. Investigation of microbial contamination in Wenyu River of Beijing. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2012, 32, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Mark, O.; Jørgensen, C.; Hammond, M.; Khan, D.; Tjener, R.; Erichsen, A.; Helwigh, B. A new methodology for modelling of health risk from urban flooding exemplified by cholera—Case Dhaka, Bangladesh. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, S28–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preparing for Extreme And Rare Events in COASTAL REGIONS (PEARL). Available online: http://www.pearl-fp7.eu/ (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- United States Geological Survey (USGS) Office of Water Quality. USGS Water-Quality Information. USGS Water-Quality Sampling of Flood Waters. Available online: https://water.usgs.gov/owq/floods/ (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Hawdon, A.; Keen, R.; Kemei, J.; Vleeshouwer, J.; Wallace, J. Design and application of automated flood water quality monitoring systems in the wet tropics. CSIRO Land Water Sci. Rep. 2007, 49, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.C.; Zhao, H.X.; Yin, J.; Zhang, W.J. An Analysis of Water Environment Factors and an Evaluation of Water Quality of Aiyi River. China Rural Water Hydropower 2014, 12, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.F.; Zhou, L.R.; He, Q.; Li, Y.W. Biotoxicity Analysis of the Gulin River Quality. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 7, 182–185. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Wu, S.H.; Dai, E.F.; Xu, Z.C. Flood loss analysis and quantitative risk assessment in China. Nat. Hazards 2012, 63, 737–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Ye, M.W.; Yin, Z.N.; Xu, S.Y. A review of advances in urban flood risk analysis over China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ding, L.Q.; Ren, M.L.; Li, C.Z.; Wang, H. Sponge City Construction in China: A Survey of the Challenges and Opportunities. Water 2017, 9, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjing Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: http://www.njhb.gov.cn/43462/43466/ (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Chongqing Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: www.cepb.gov.cn/ (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Beijing Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: www.bjepb.gov.cn/bjhrb/index/index.html (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Guangzhou Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: www.gzepb.gov.cn/ (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Shanghai Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: www.hzepb.gov.cn/ (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Hangzhou Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: www.hzepb.gov.cn/ (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- National Surface Water Quality Automatic Monitoring and Real-Time Data Release System. Available online: http://123.127.175.45:8082/ (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- AKVO Organization. Available online: https://akvo.org/blog/akvo-caddisfly-a-water-quality-testing-kit-for-sdg-monitoring/ (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Gironás, J.; Roesner, L.A.; Rossman, L.A.; Davis, J. A new applications manual for the Storm Water Management Model (SWMM). Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 813–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deltares Institution. Available online: http://oss.deltares.nl/web/delft-fews/about (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Juntunen, J.; Merilainen, P.; Simola, A. Public health and economic risk assessment of waterborne contaminants and pathogens in Finland. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment: Application for Water Safety Management, 1st ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, C.N.; Rose, J.B.; Gerba, C.P. Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]


| Keywords | Literature |
|---|---|
| Drinking/potable water quality | [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37] |
| Flood water quality | [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] |
| Urban water quality | [48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57] |
| Flood water & health | [58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67] |
| Urban water & health | [68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77] |
| Journal | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Health Risk | Flood & Health Risk | Direct Exposure to Flood Water | |
| Water Research | 2110 | 212 | 3 |
| Water Science and Technology | 398 | 51 | 0 |
| Environmental Monitoring and Assessment | 5706 | 747 | 0 |
| Journal of Hydrology | 406 | 224 | 1 |
| Water | 32 | 3 | 0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rui, Y.; Fu, D.; Do Minh, H.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Zevenbergen, C.; Pathirana, A. Urban Surface Water Quality, Flood Water Quality and Human Health Impacts in Chinese Cities. What Do We Know? Water 2018, 10, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10030240
Rui Y, Fu D, Do Minh H, Radhakrishnan M, Zevenbergen C, Pathirana A. Urban Surface Water Quality, Flood Water Quality and Human Health Impacts in Chinese Cities. What Do We Know? Water. 2018; 10(3):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10030240
Chicago/Turabian StyleRui, Yuhan, Dafang Fu, Ha Do Minh, Mohanasundar Radhakrishnan, Chris Zevenbergen, and Assela Pathirana. 2018. "Urban Surface Water Quality, Flood Water Quality and Human Health Impacts in Chinese Cities. What Do We Know?" Water 10, no. 3: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10030240
APA StyleRui, Y., Fu, D., Do Minh, H., Radhakrishnan, M., Zevenbergen, C., & Pathirana, A. (2018). Urban Surface Water Quality, Flood Water Quality and Human Health Impacts in Chinese Cities. What Do We Know? Water, 10(3), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10030240







