The Impact of Mountain Range Geographic Orientation on the Altitude Effect of Precipitation δ18O in the Upper Reaches of the Heihe River Basin in the Qilian Mountains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
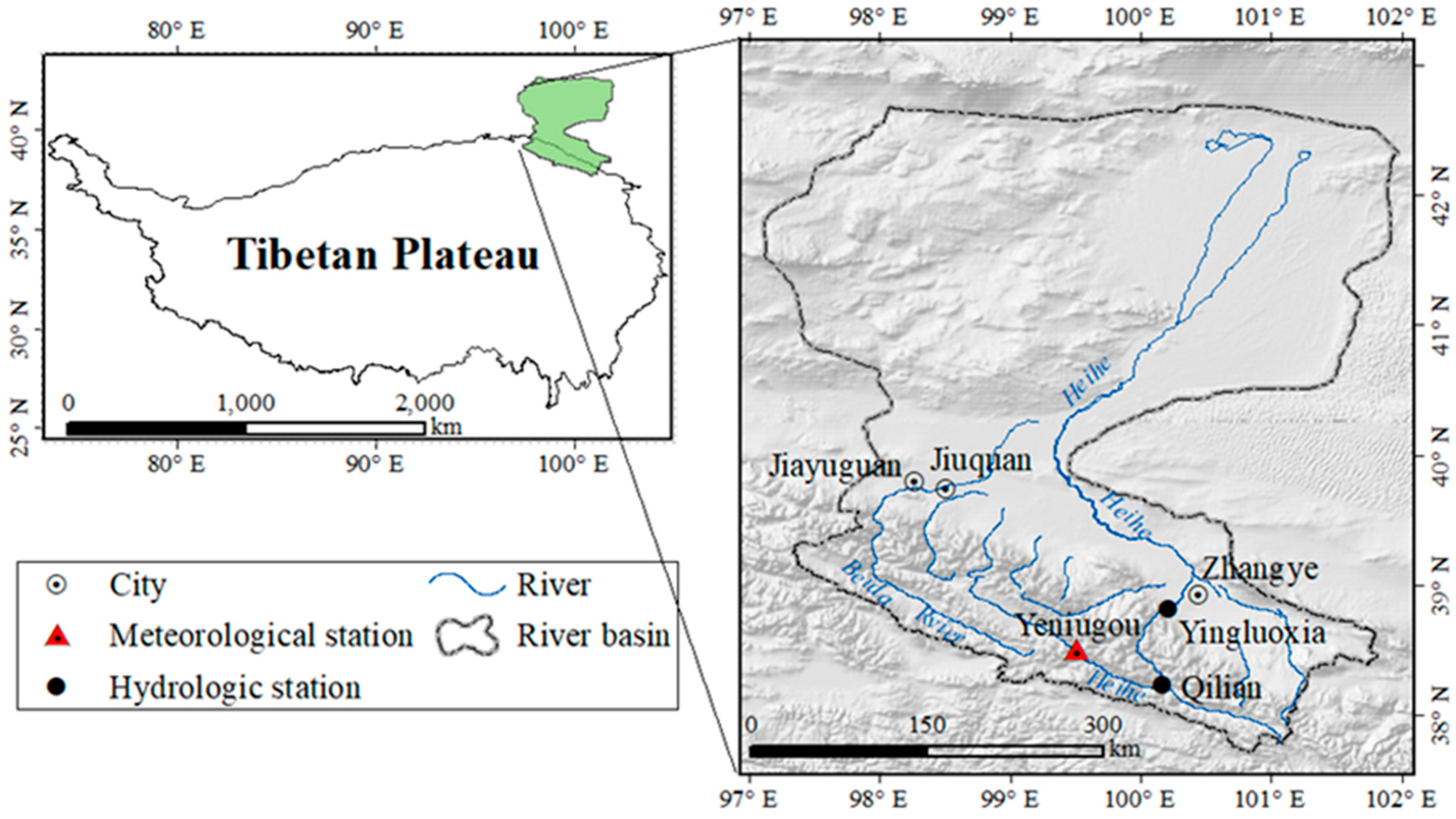
2. Study Area and Precipitation Sampling
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Precipitation Sampling
3. Results
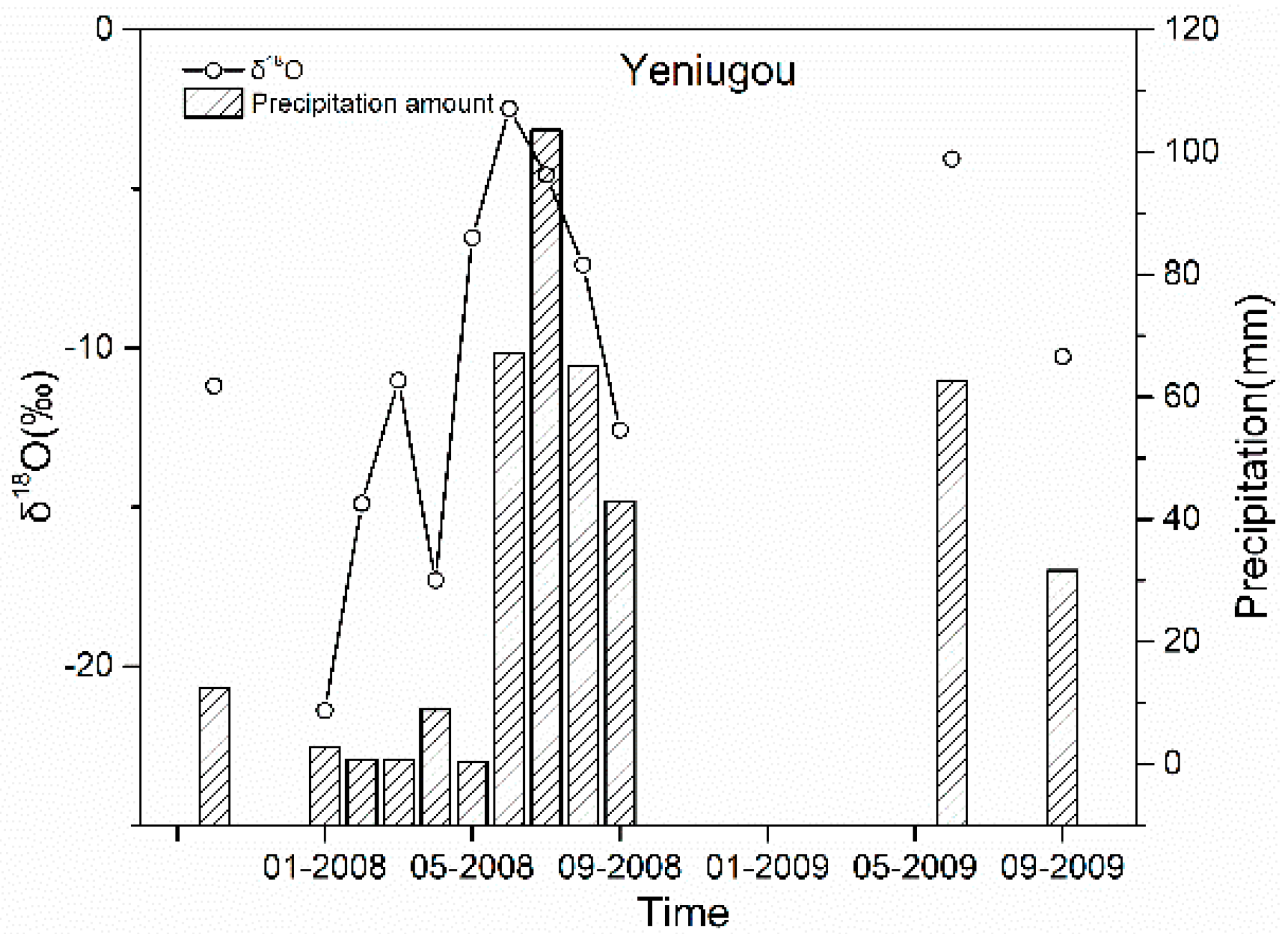
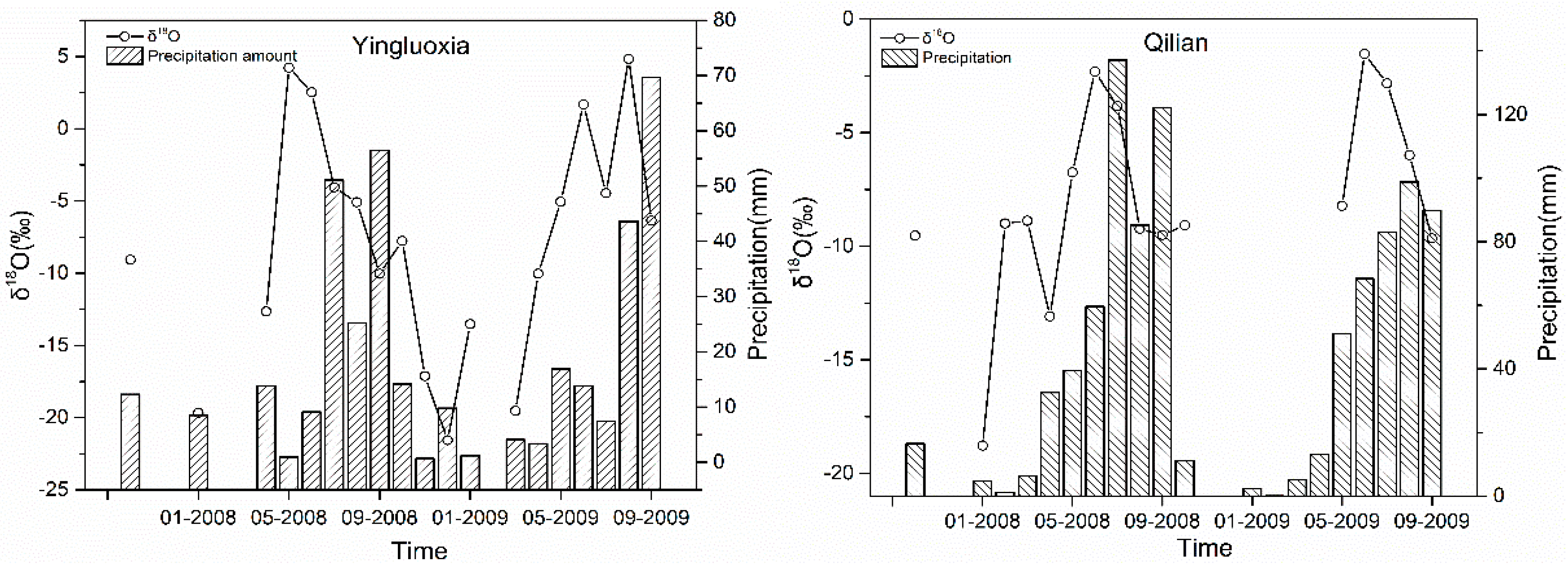
3.1. The Seasonal Variation of Precipitation δ18O
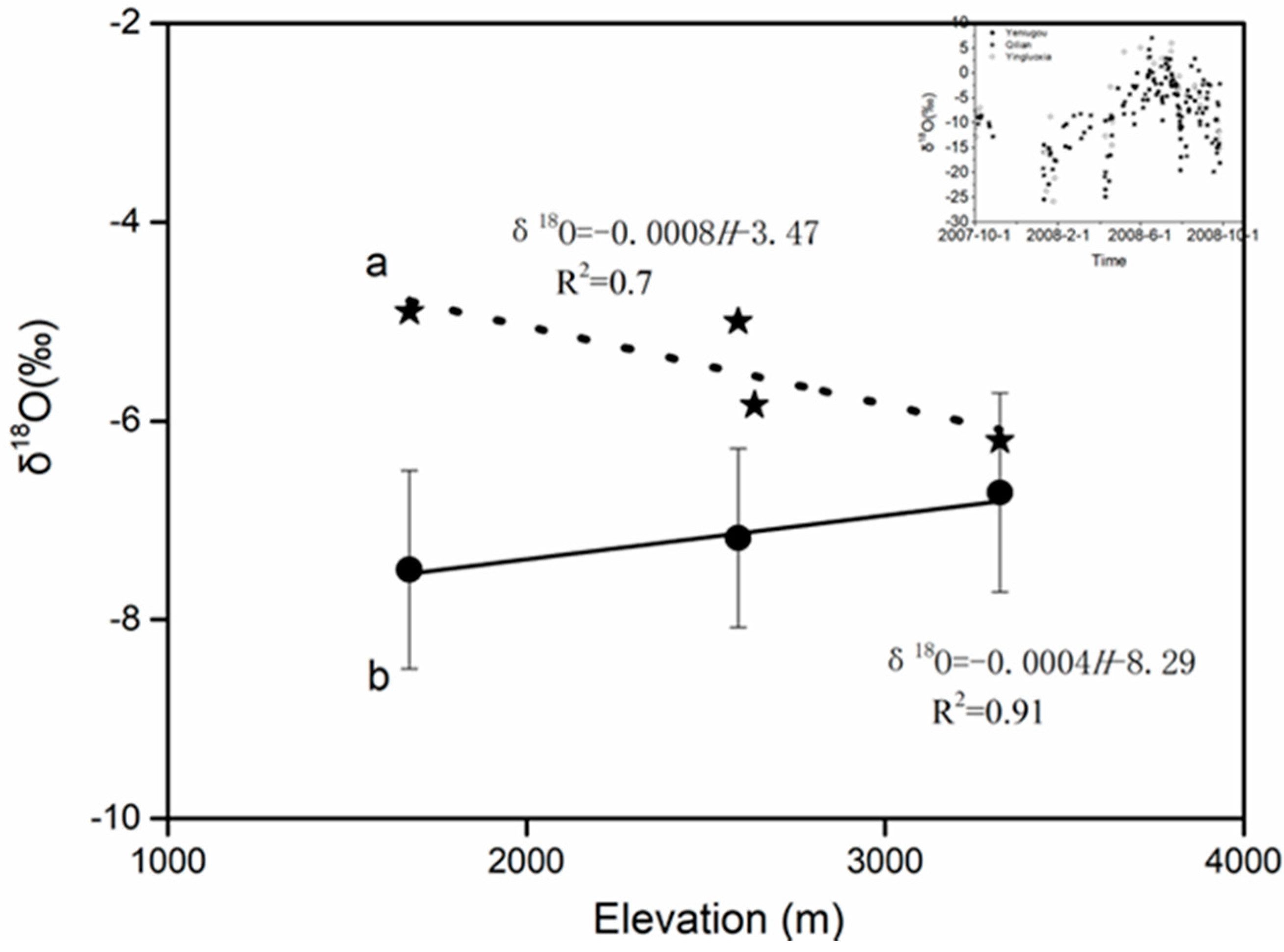
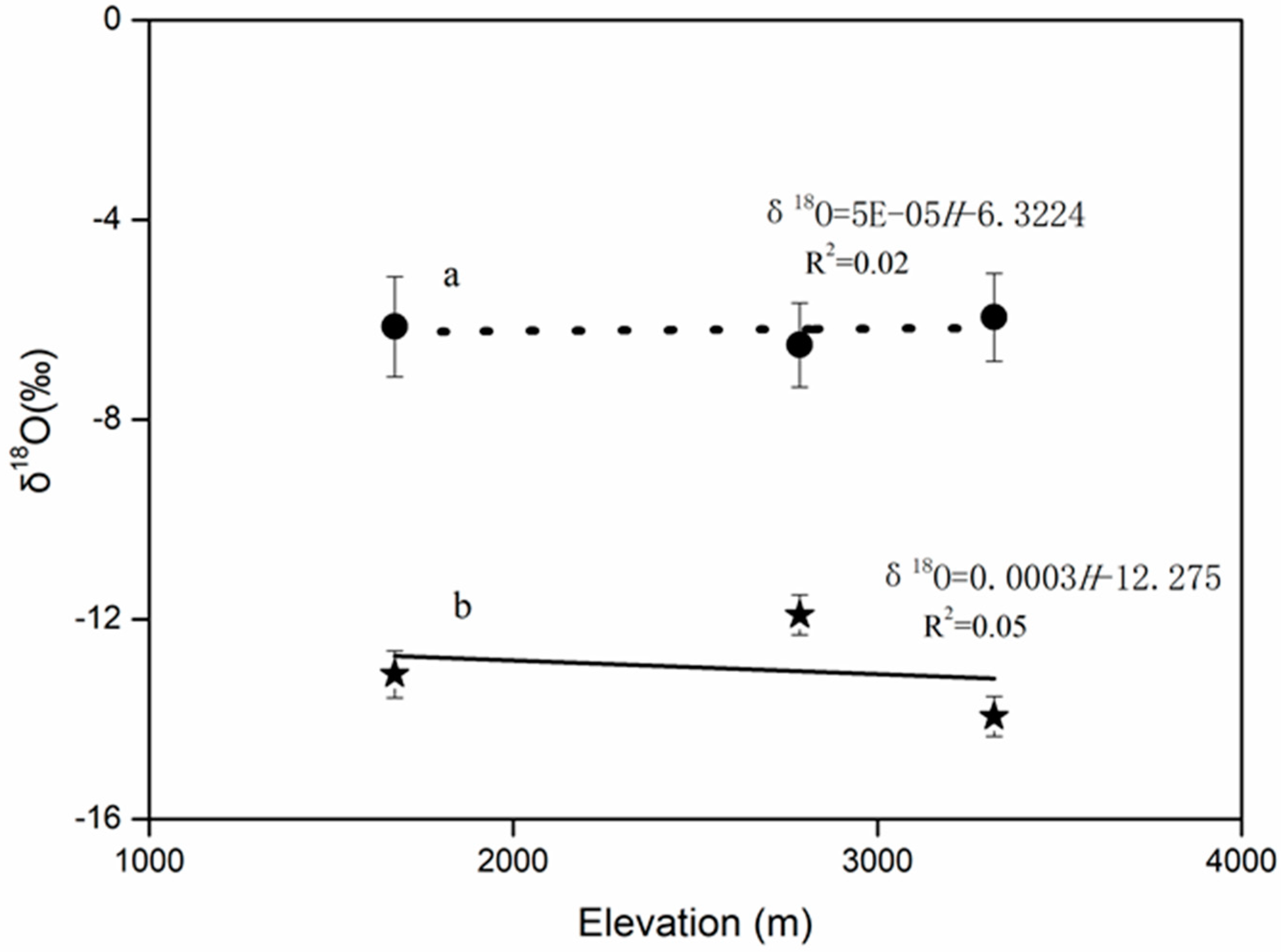
3.2. The Precipitation δ18O-Elevation Gradient
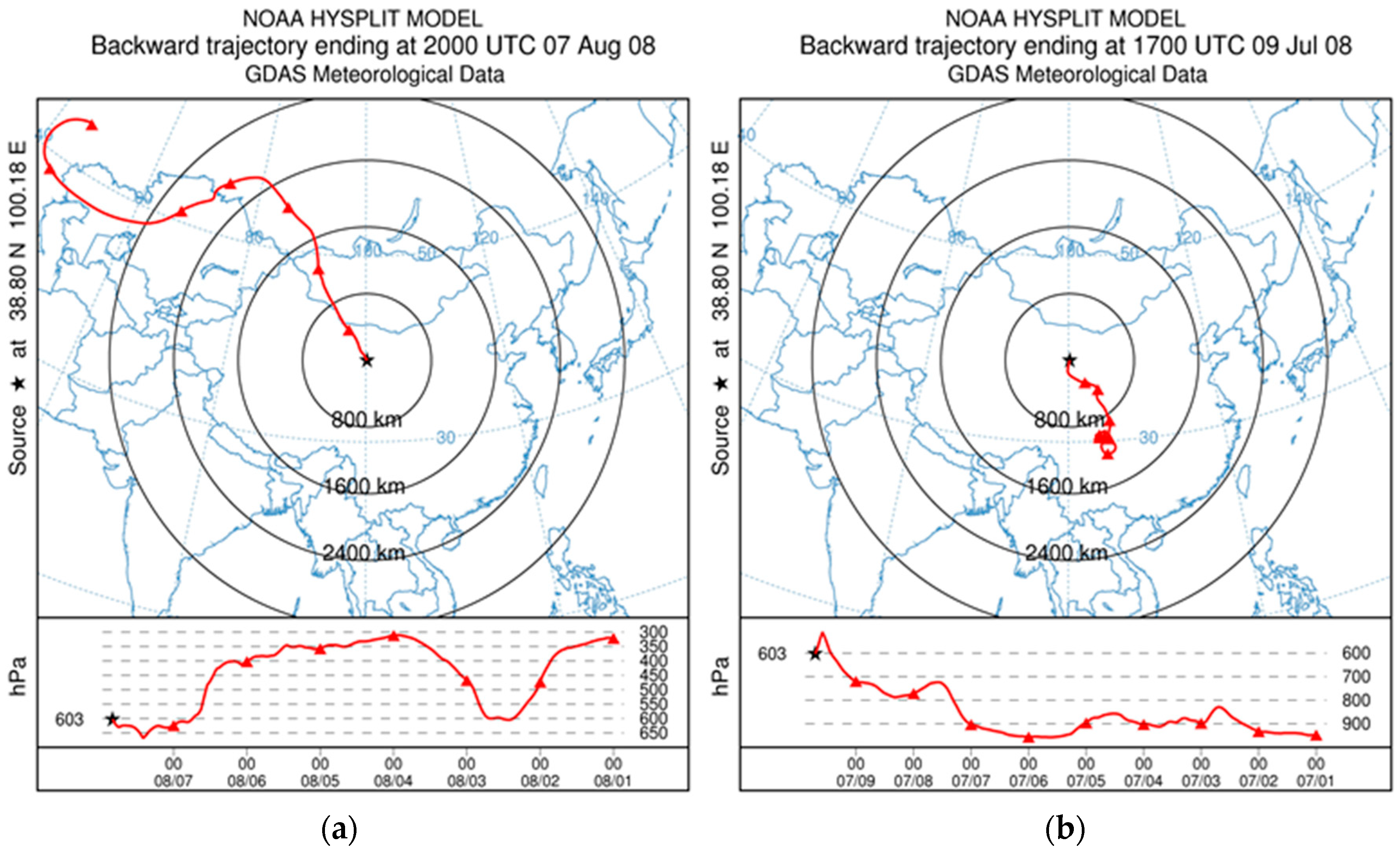
3.3. Trajectory Analysis of the Atmospheric Water Vapor
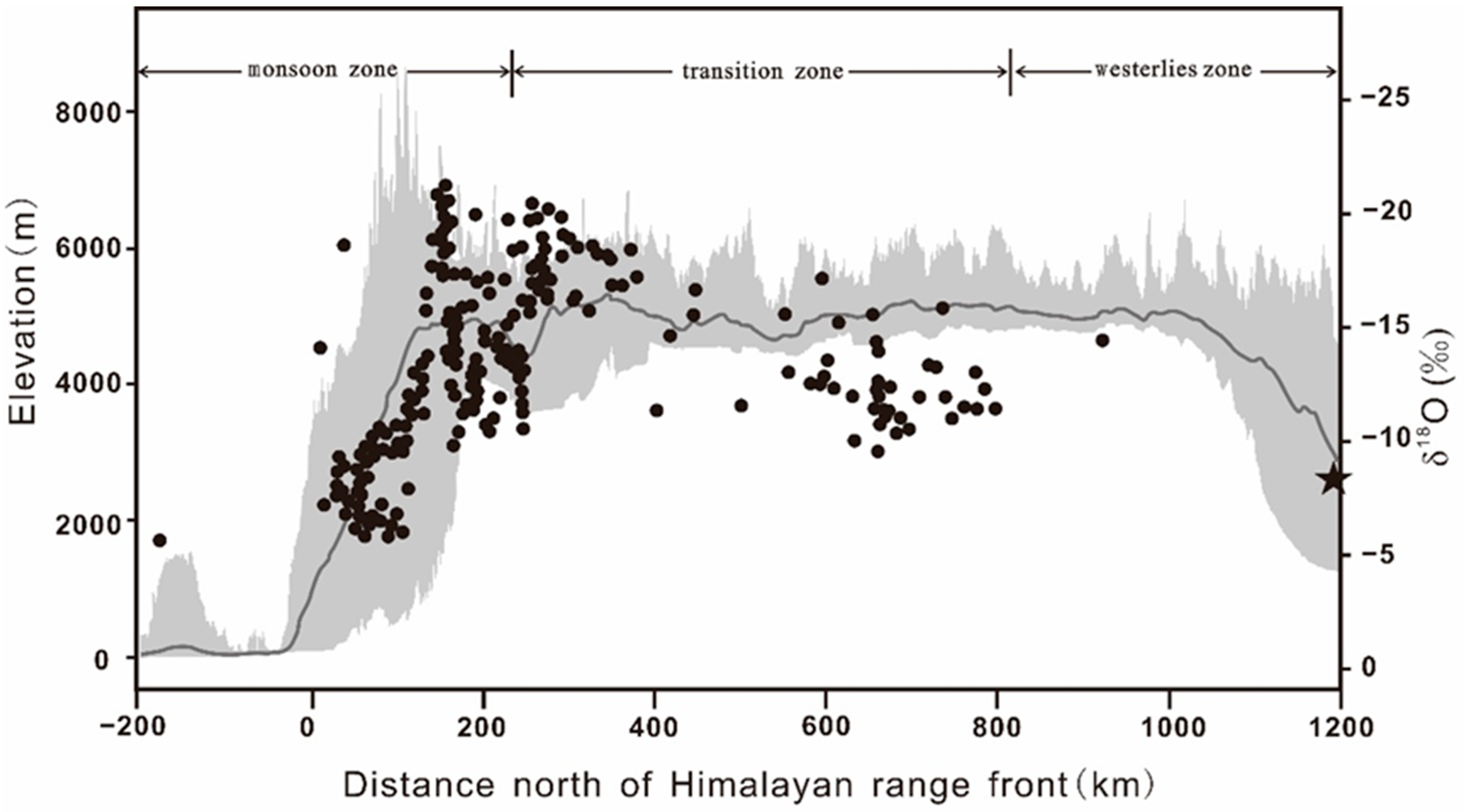
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lechler, A.R.; Niemi, N.A. The influence of snow sublimation on the isotopic composition of spring and surface waters in the southwestern united states: Implications for stable isotope-based paleoaltimetry and hydrologic studies. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2012, 124, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, D.B.; Currie, B.S. Palaeo-altimetry of the late eocene to miocene lunpola basin, central tibet. Nature 2006, 439, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poage, M.A.; Chamberlain, C.P. Empirical relationships between elevation and the stable isotope composition of precipitation and surface waters: Considerations for studies of paleoelevation change. Am. J. Sci. 2001, 301, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyr, A.J.; Currie, B.S.; Rowley, D.B. Geochemical evaluation of fenghuoshan group lacustrine carbonates, north-central tibet: Implications for the paleoaltimetry of the eocene tibetan plateau. J. Geol. 2005, 113, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, D.B.; Pierrehumbert, R.T.; Currie, B.S. A new approach to stable isotope-based paleoaltimetry: Implications for paleoaltimetry and paleohypsometry of the high himalaya since the late miocene. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 188, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCelles, P.G.; Quade, J.; Kapp, P.; Fan, M.; Dettman, D.L.; Ding, L. High and dry in central tibet during the late oligocene. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 253, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quade, J.; Breecker, D.O.; Daeron, M.; Eiler, J. The paleoaltimetry of tibet: An isotopic perspective. Am. J. Sci. 2011, 311, 77–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; Lewis: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.S.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhao, X.; Shen, X.f.; Gu, W.Z.; Chen, L.; Su, Z.G. Study of groundwater supply of the confined cquifers in the ejin basin based on isotopic methods. Geol. Rev. 2004, 6, 649–658. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, R.; Tian, L.D.; Wong, Y.B.; Liu, Z.F.; Zhao, Z.P. The altitide effect of δ18o in precipitation and river water in the southern himalayas. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.X.; Xu, B.Q.; Yang, W.; Qu, D.M.; Lin, P.N. The indian monsoonal influence on altitude effect of δ18o in surface water on southeast tibetan plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 42, 747–754. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.Y.; Yang, D.; Lai, Q.Z.; Huang, F.X.; Shi, R.D. Regional variation of river water oxygen isotope and empirical elevation prediction models in Tibetan plateau. Quat. Sci. 2009, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Wan, L.; Nie, Z.L.; Shen, J.M.; Chen, J.S. Idetification of groundwater recharge in the heihe basin using environmental isotopes. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2006, 6, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Z.L.; Chen, Z.Y.; Shen, J.M.; Zhang, G.H.; Cheng, X.X. Environmental isotopes as tracers of hydrological cycle in the recharge area of the heihe river. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2005, 21, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.L.; Zhang, S.B.; He, J.Q.; Pu, J.C.; Wu, X.B.; Jiang, X. Tracing the major source area if the mountainous runoff generation of the heihe river in northwest ching using stable isotope technique. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 2148–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wu, Y.Q. Characteristics of the δ18o in precipitation in theupper and middle reaches of heihe river. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2007, 29, 440–445. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.J.; Yin, L.; Xiao, H.L.; Cheng, G.D.; Zhou, M.X.; Yang, Y.G.; Li, C.Z.; Zhou, J. Isotopic evidence for the moisture origin and composition of surface runoff in the headwaters of the heihe river basin. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.L.; Zhang, S.B.; Pu, J.C.; He, J.Q.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.B. Seasonal variation of δ18o in river water in the upper reaches of heihe river basin and its influence factors. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2008, 30, 914–920. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wu, Y.Q. Variation of δ18o in water in heihe river basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2007, 18, 864–870. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.W. The neoteetonics in the qilian montainsregion. Northwest. Geol. 1984, 4, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.F.; Pan, B.T.; EIRBY, K.; Li, Q.Y.; Geng, H.P.; Chen, J.F. Spatial differences in rock uplift rates inferred from channel steepness indices along the northern flank of qikian mountain, northeast. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Q.Y.; Xue, W.X.; Guo, H.; Shi, Z.J. Characteristics of climate change in qilian mountains region in recent 50 years. Plateau Meteorol. 2009, 28, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, J.Y.; Bai, H.Z.; Zhao, J.H.; Xu, X.H. A study of atmospheric water cycle over the qilian mountains(i): Variation of annual water vapor transport. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2014, 36, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, A.; Wang, T.; Han, C.; Song, Y.; Theakstone, W.H. Can monsoon moisture arrive in the qilian mountains in summer? Quat. Int. 2015, 358, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.Q.; Song, G.J.; Jiang, X.; Li, Q.L.; Wu, X.B. Relation between glacial meltwater runoff and mountainous runoff in 2006 in four typical river basins of heihe river water system. J. Desert Res. 2008, 28, 1186–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.H.; Zou, S.B.; Xiao, H.L.; Yi, Z.L.; Lu, Z.X.; Liu, S.Y. Eco-hydrological ontology in inland river basin: Construction method and application. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2014, 36, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.P.; Li, M.; Tong, C.P.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, S.J. Public perception and selections of adaptation measures against glacier change and its impacts: Taking the hexi inland river basin as an example. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2015, 37, 70–79. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, W.Z. Isotope Hydrology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.Q.; Nakawom, S.; Keqin, D.; Jianchen, P. Water isotope variations in the snow pack and summer precipitation at july 1 glacier, qilian mountains in Northwest China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 2187–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.J.; Ye, B.S.; Zhou, W.J. Temporal and spatial precipitation distribution in the heihe catchment, northwest china, during the past 40 a. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 1999, 21, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.D.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.X. Indian monsoon influences altitude effect of δ18o in precipitation/river water on the tibetan plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 2124–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W. Vertical distribution of the transported quantity of material and energy by airflow. Desert Oasis Meteorol. 2009, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.L.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, H.Y. Atmospheric water vapor transport from westerly and monsoon over the Northwest China. Adv. Water Sci. 2005, 16, 432–438. [Google Scholar]
- Djebou, D.C.S.; Singh, V.P.; Frauenfeld, O.W. Analysis of watershed topography effects on summer precipitation variability in the southwestern united states. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C.; McDonnell, J.J. Isotope Tracers in Catchment Hydrology; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.D.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Gao, J.; Yu, W.S.; Yang, X.X.; Risi, C.; Sturm, C.; Werner, M.; Zhao, H.B.; He, Y.Q.; et al. A review of climatic controls on δ18o in precipitation over the tibetan plateau: Observations and simulations. Rev. Geophys. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Levene Statistic | df1 | df2 | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.042 | 2 | 207 | 0.354 |
| Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between Groups | 171.397 | 2 | 85.698 | 1.861 | 0.158 |
| Within Groups | 9533.468 | 207 | 46.055 | ||
| Total | 9704.865 | 209 |
| Source of Moisture | Yingluoxia | Qilian | Yeniugou | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Proportion in Total Rainfall during the Period (%) | n | Proportion in Total Rainfall during the Period (%) | n | Proportion in Total Rainfall during the Period (%) | |
| Westerly belt | 37 | 62.5 | 71 | 89.1 | 41 | 79.5 |
| Monsoon | 12 | 37.5 | 32 | 10.9 | 16 | 20.5 |
| Total | 49 | 100 | 103 | 100 | 57 | 100 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Y. The Impact of Mountain Range Geographic Orientation on the Altitude Effect of Precipitation δ18O in the Upper Reaches of the Heihe River Basin in the Qilian Mountains. Water 2018, 10, 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121797
He J, Zhang W, Wu Y. The Impact of Mountain Range Geographic Orientation on the Altitude Effect of Precipitation δ18O in the Upper Reaches of the Heihe River Basin in the Qilian Mountains. Water. 2018; 10(12):1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121797
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jianqiao, Wei Zhang, and Yuwei Wu. 2018. "The Impact of Mountain Range Geographic Orientation on the Altitude Effect of Precipitation δ18O in the Upper Reaches of the Heihe River Basin in the Qilian Mountains" Water 10, no. 12: 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121797
APA StyleHe, J., Zhang, W., & Wu, Y. (2018). The Impact of Mountain Range Geographic Orientation on the Altitude Effect of Precipitation δ18O in the Upper Reaches of the Heihe River Basin in the Qilian Mountains. Water, 10(12), 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121797





