Application of Artificial Neural Networks for Accuracy Enhancements of Real-Time Flood Forecasting in the Imjin Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
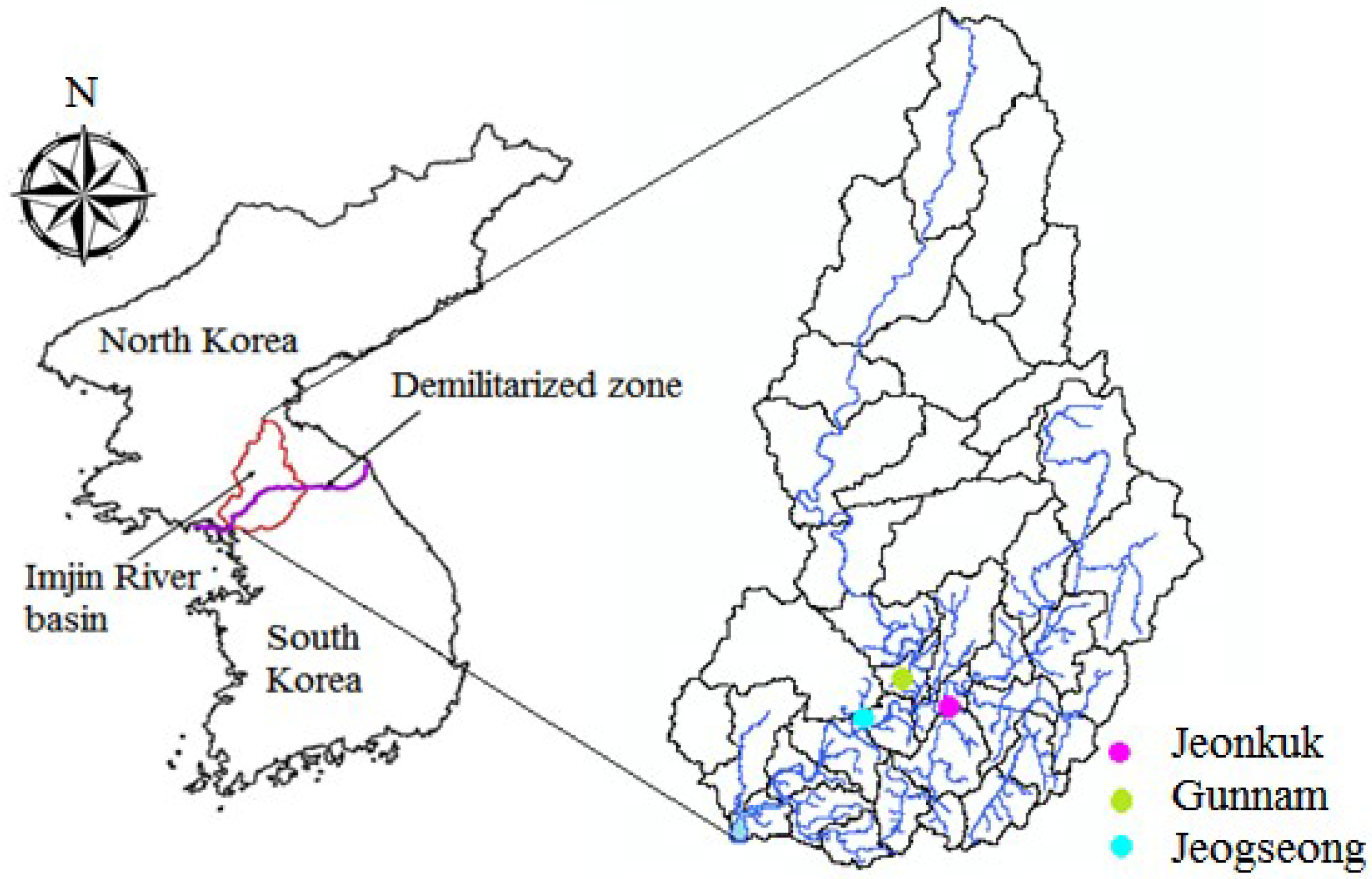
2.1. Imjin Basin
2.2. Hydrological and Meteorological Data
3. Methodology
3.1. WRF Model
3.2. Sejong University Rainfall-Runoff (SURR) Model
3.3. Bias Correction of Real-Time Forecasts
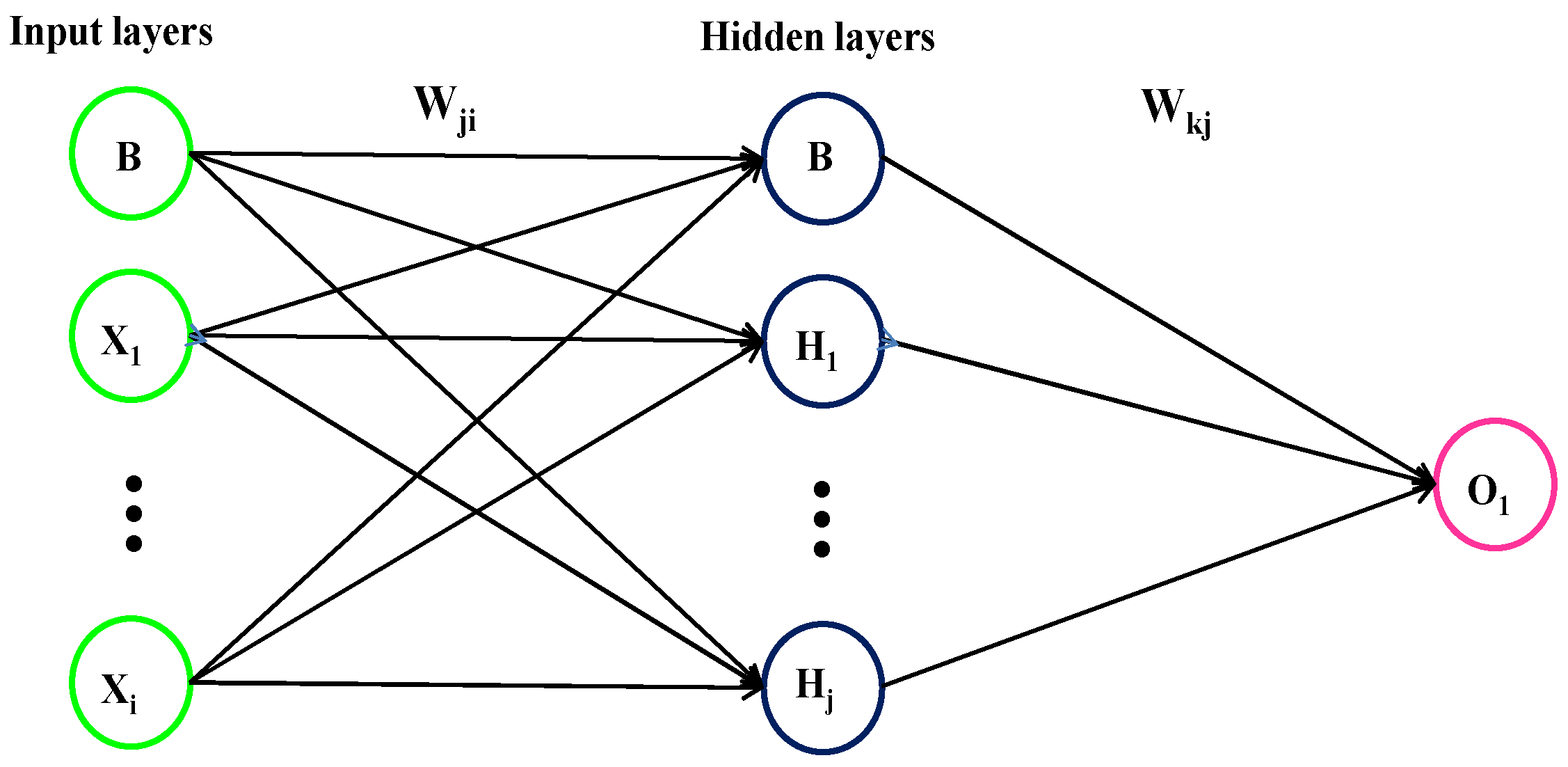
3.3.1. Description of ANN
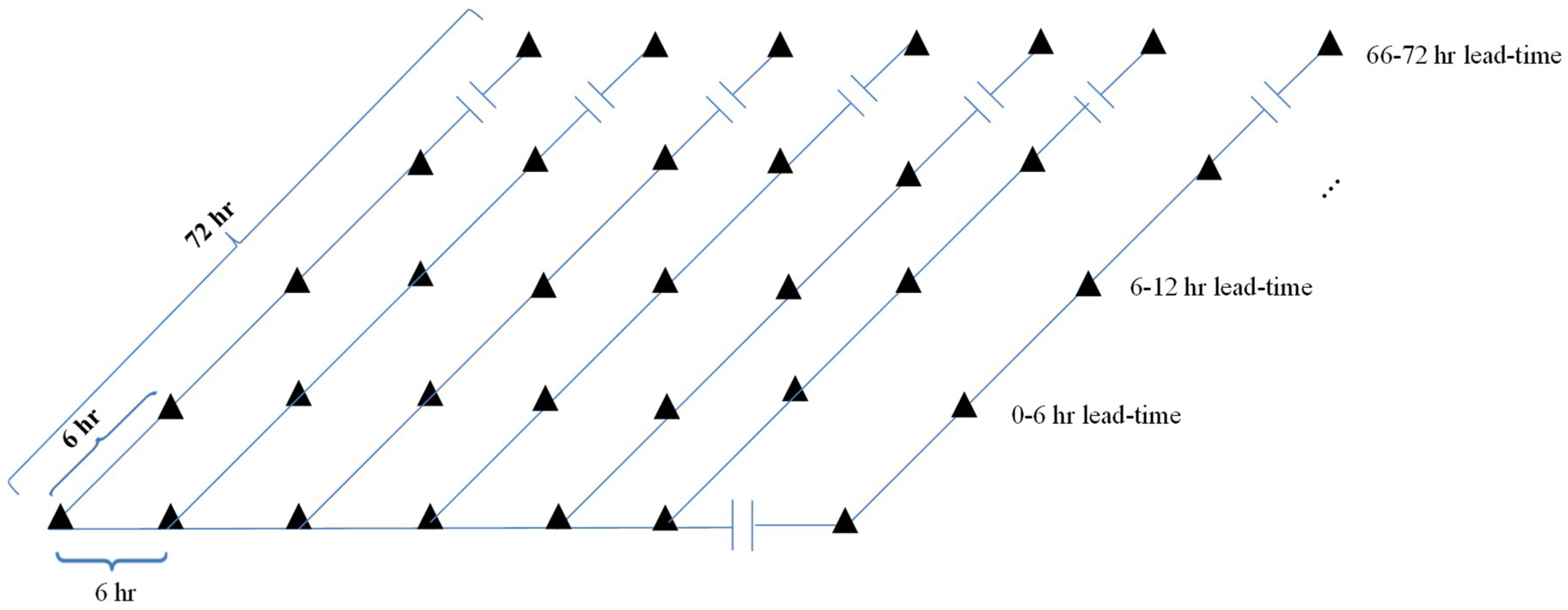
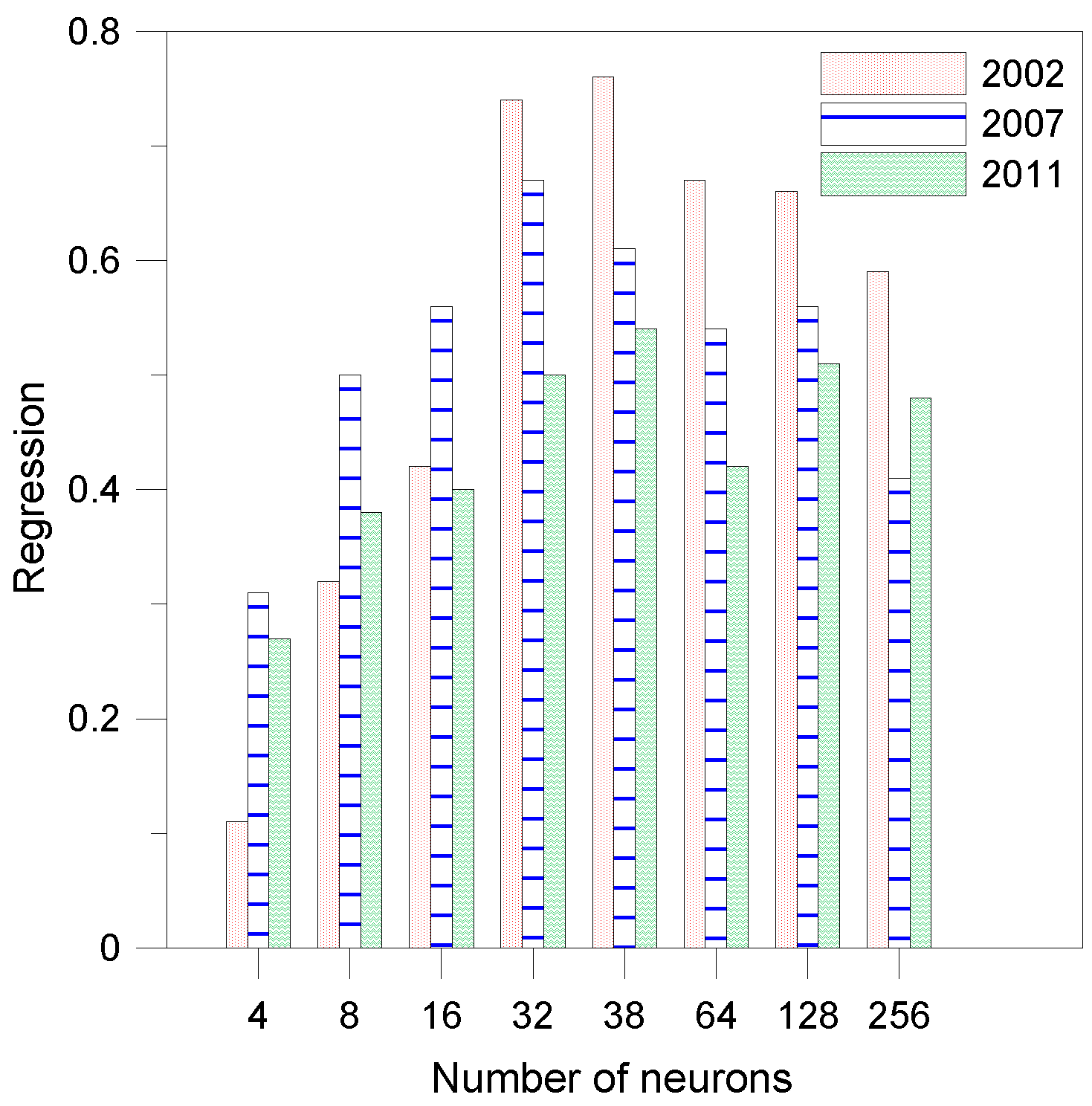
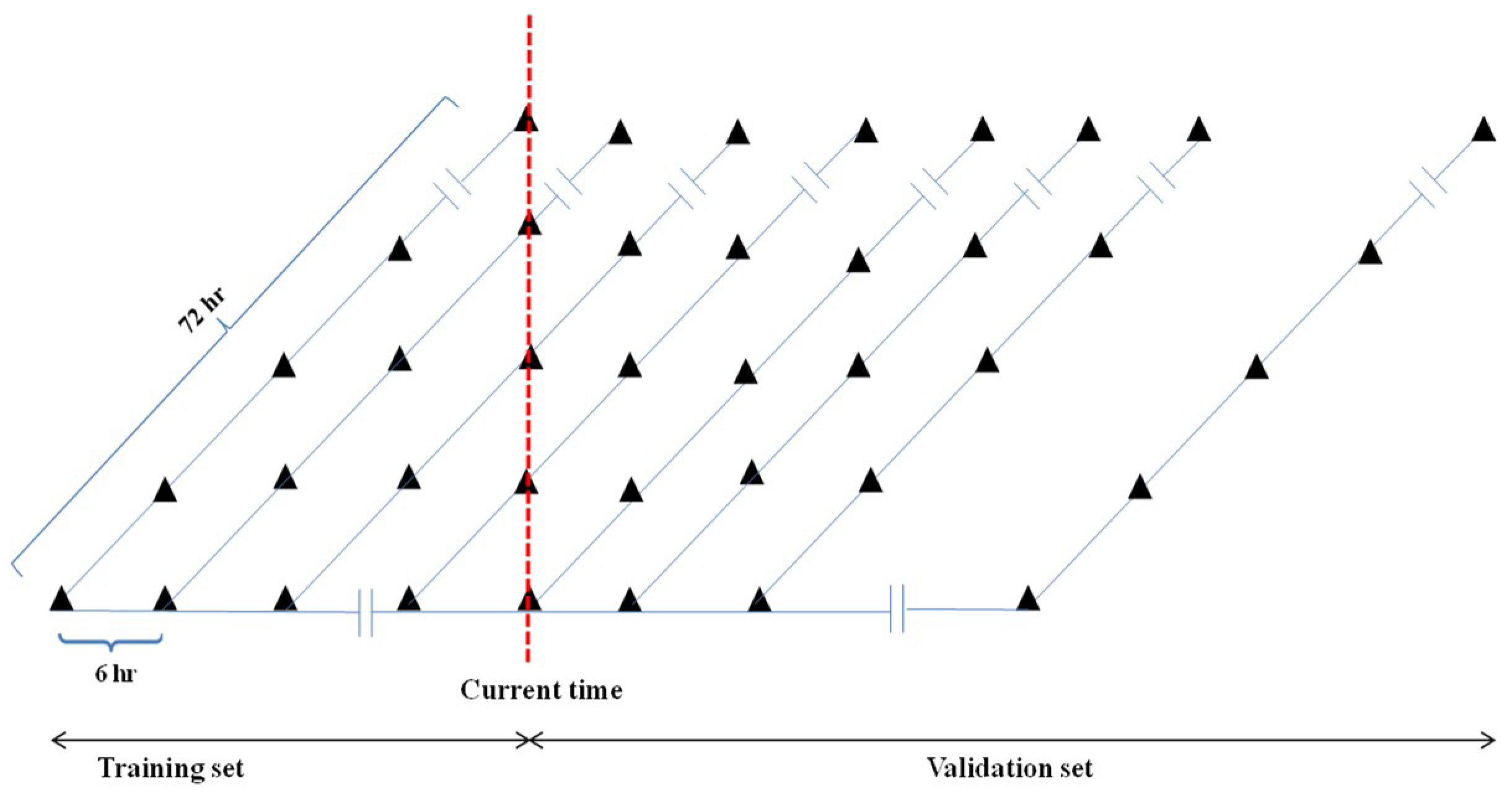
3.3.2. Application of ANN for Real-Time Bias Correction
4. Results
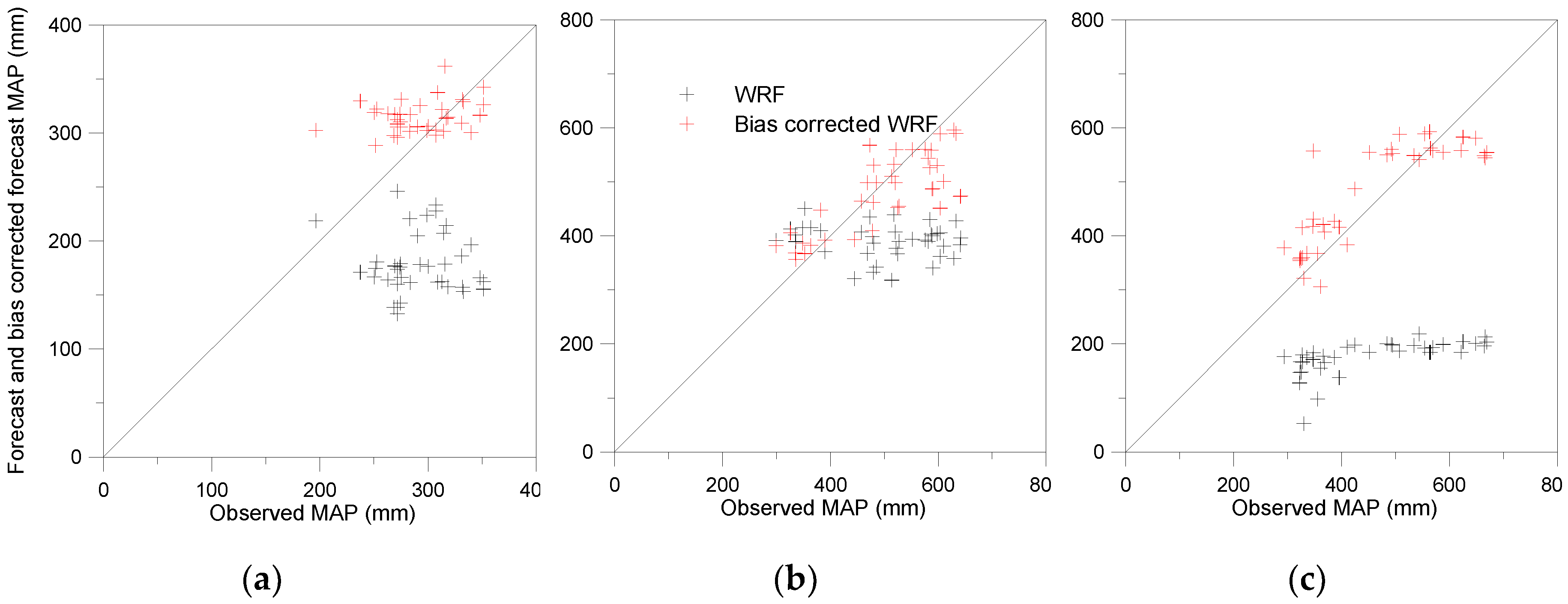
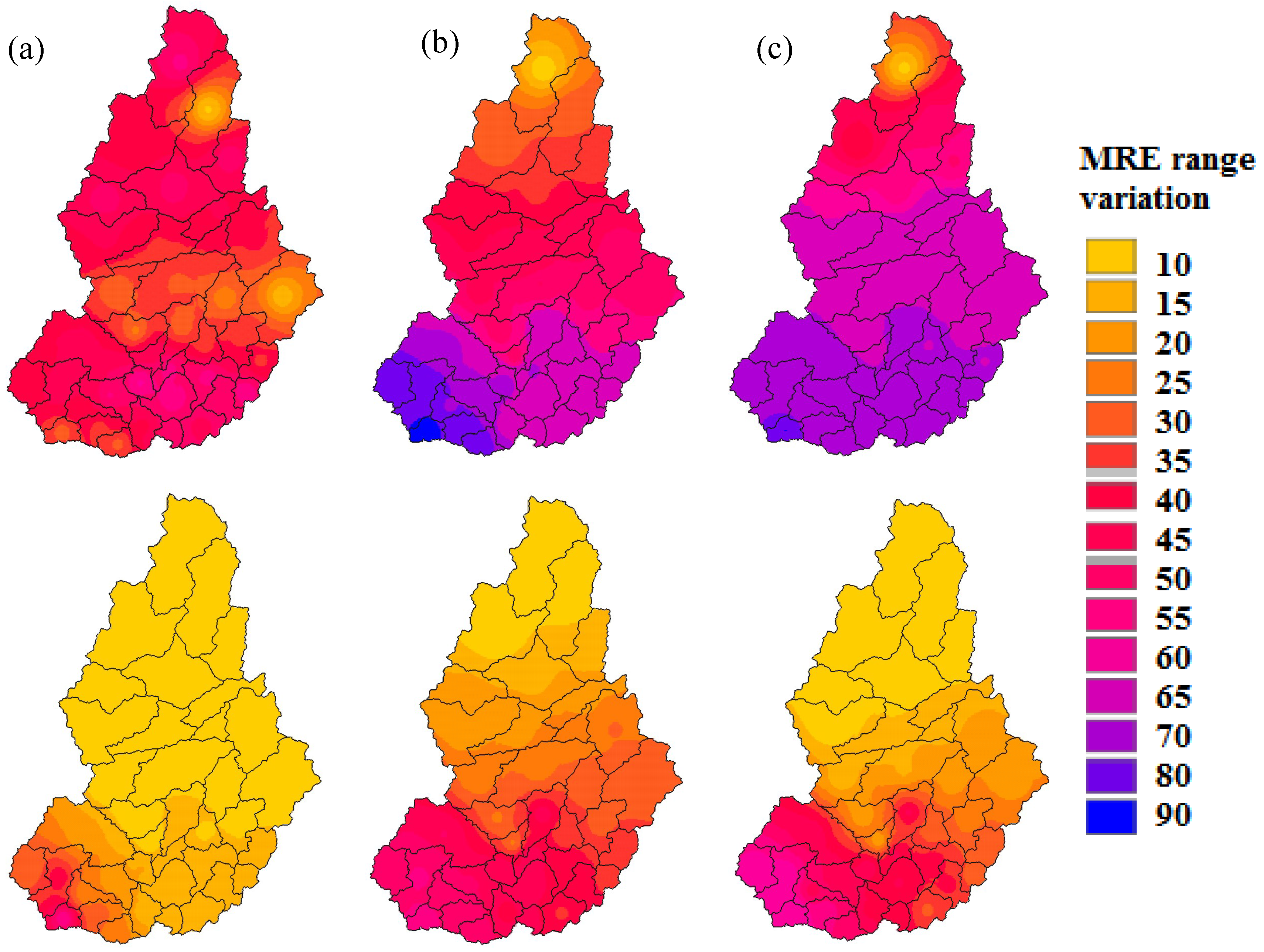
4.1. Real-Time Accuracy Improvement of the Precipitation
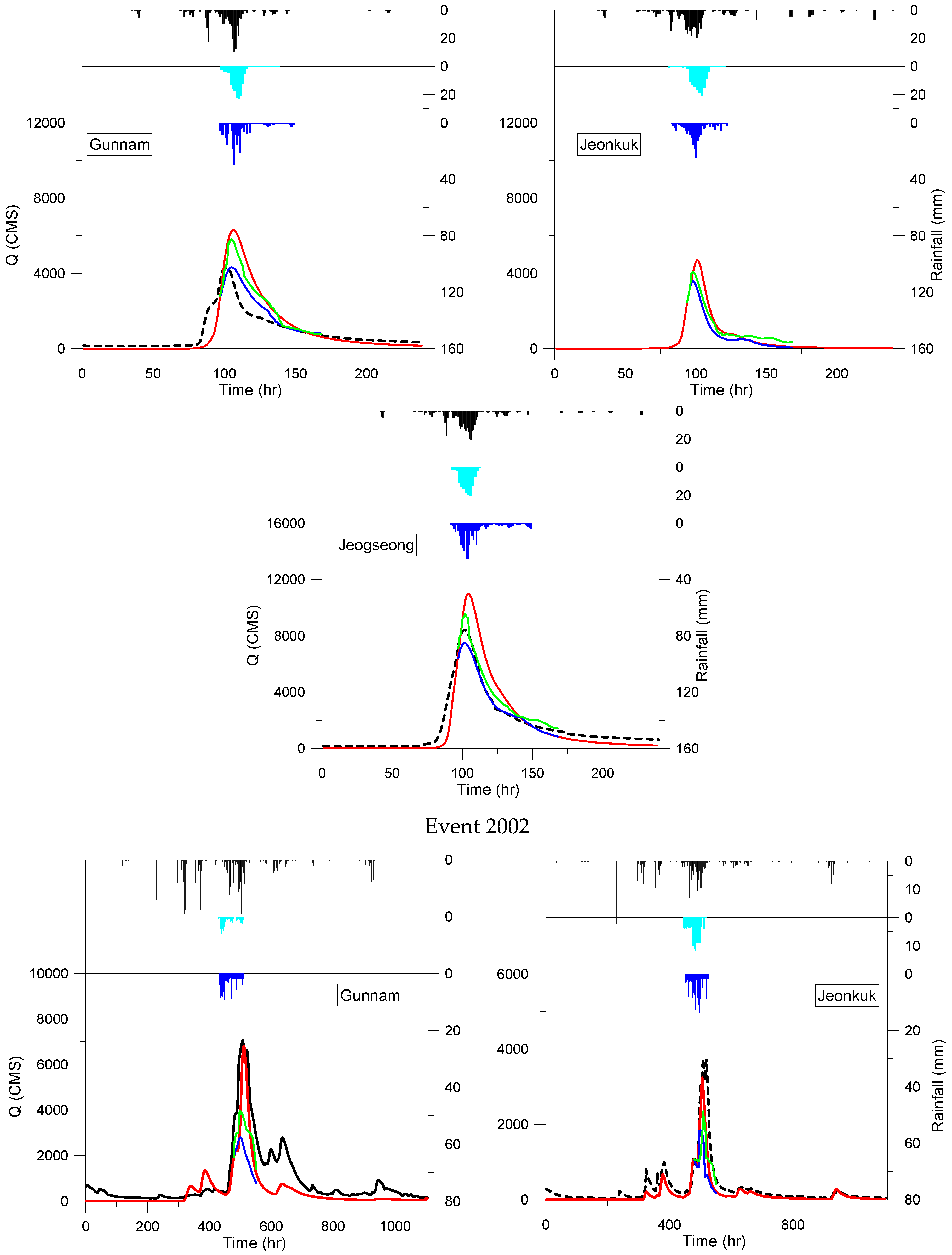
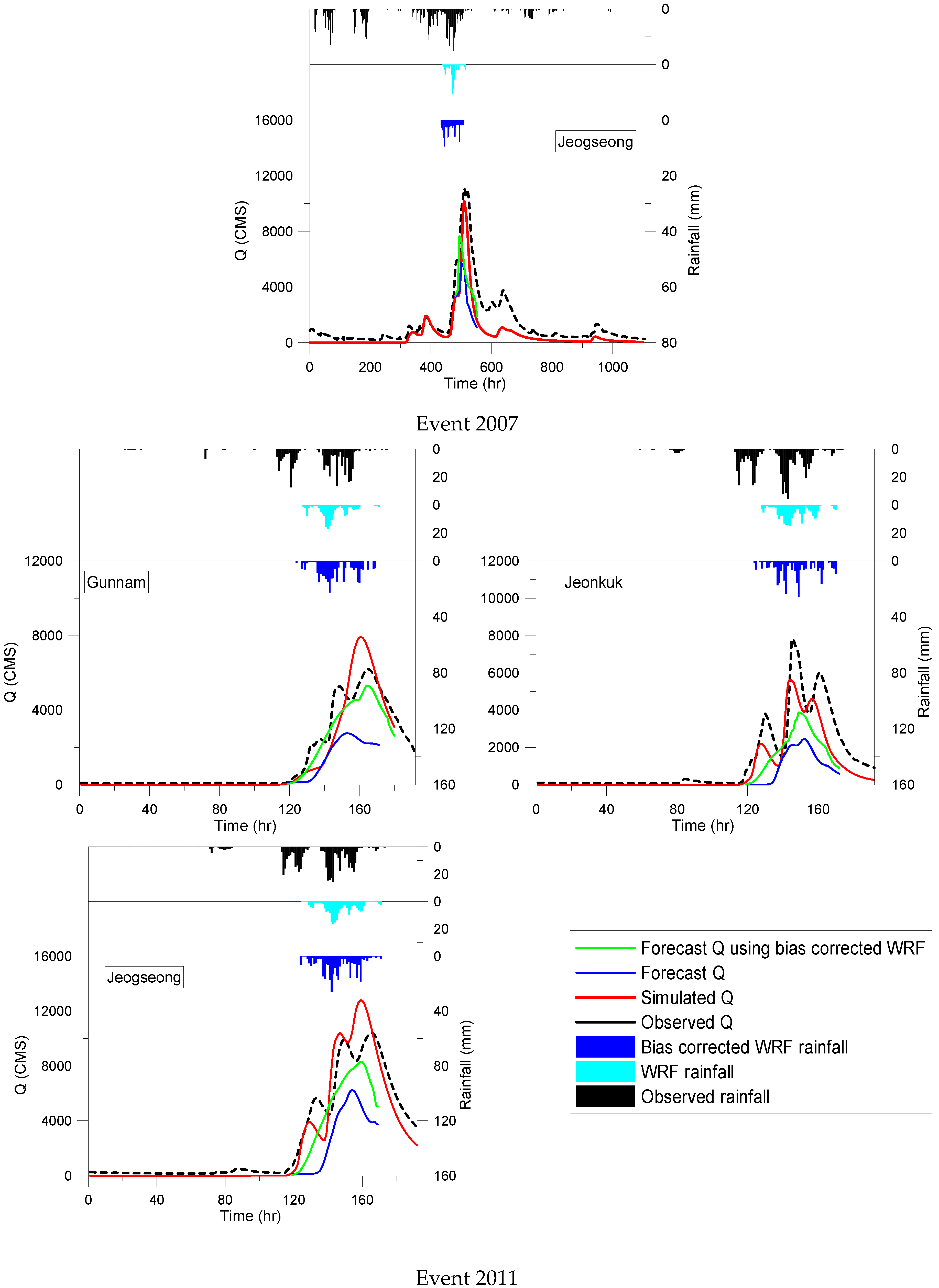
4.2. Real-Time Flood Forecasting Accuracy Improvement
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
- (1)
- Applying ANN for bias correction improved the forecast performance by reducing MRE, RB, REV and MAER by 69.71, 57.84, 80.05 and 72.77%, respectively, in the 2002 event; by 75.12, 88.62, 82.22 and 80.47%, respectively, in the 2007 event; and by 58.09, 83.98, 75.92 and 63.98%, respectively, in the 2011 event.
- (2)
- The sum, minimum, maximum and the underestimation of the WRF real-time forecast data were improved after applying the ANN bias correction to the real-time WRF data.
- (3)
- By applying the ANN bias correction, the underestimation of WRF data improved 65.79, 23.69 and 73.68% in the 2002, 2007 and 2011 events, respectively. The error was also reduced by 75.28, 89.53 and 88.74% over the Imjin catchment in terms of the accumulated MAP in the 2002, 2007 and 2011 events, respectively.
- (4)
- The error comparison in each sub-basin indicated that the average percentage of MRE reduction in the catchment was 69.71, 61.24 and 53.90% for the 2002, 2007 and 2011 events, respectively.
- (5)
- By applying the ANN bias correction, the performance of the SURR-WRF coupled models in real-time flood forecasts increased by increasing the NSE and KGE and reducing the MRE and REV for Gunnam, Jeonkuk and Jeogseong stations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Pan, S.; Tang, K.; Li, C.; Han, D. A real-time flood forecasting system with dual updating of the NWP rainfall and the river flow. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 1161–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincendon, B.; Ducrocq, V.; Nuissier, O.; Vie’, B. Perturbation of convection-permitting NWP forecasts for flash-flood ensemble forecasting. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 1529–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.A.; Wen, L.; Lu, G.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Tong, L. Real-time forecast of the 2005 and 2007 summer severe floods in the Huaihe River Basin of China. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davolio, S.; Miglietta, M.M.; Diomede, T.; Marsigli, C.; Montani, A. A flood episode in northern Italy: Multi-model and single-model mesoscale meteorological ensembles for hydrological predictions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2107–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghim, S.; Bras, R.L. Bias Correction of Climate Modeled Temperature and Precipitation Using Artificial Neural Networks. J. Hydrometeor. 2017, 18, 1867–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S.; Xu, X.; Braithwaite, D.; Verbist, K.M.J. Bias Adjustment of Satellite-based Precipitation Estimation using Gauge Observations-A Case Study in Chile. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2016, 121, 3790–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crochemore, L.; Ramos, M.H.; Pappenberger, F. Bias correcting precipitation forecasts to improve the skill of seasonal streamflow forecasts. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3601–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogelis, M.C.; Werner, M. Streamflow forecasts from WRF precipitation for flood early warning in mountain tropical areas. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 22, 853–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applequist, S.; Garhs, G.; Pfeffer, R. Comparisons of methodologies for probabilistic quantitative precipitation forecasting. Weather Forecast. 2002, 17, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charba, J.; Samplatsky, F. High-resolution GFS-based MOS quantitative precipitation forecasts on a 4-km grid. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 39–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cane, D.; Ghigo, S.; Rabuffetti, D.; Milelli, D. Real-time flood forecasting coupling different post processing techniques of precipitation forecast ensembles with a distributed hydrological model. The case study of May 2008 flood in western Piemonte, Italy. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Brissette, F.P.; Chaumont, D.; Braun, M. Finding appropriate bias correction methods in downscaling precipitation for hydrologic impact studies over North America. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 4187–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiador, F.J.; Kidd, C.; Hsu, K.-L.; Marzano, F.S. Neural networks in satellite rainfall estimation. Meteorol. Appl. 2004, 11, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.; Gao, H.; Soroshian, S.; Gupta, H. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1997, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivolta, G.; Marzano, F.S.; Coppola, E.; Verdecchia, M. Artificial neural-network technique for precipitation nowcasting from satellite imagery. Adv. Geosci. 2006, 7, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichouri, I.; Hani, A.; Bougherira, N.; Djabri, L.; Chaffai, H.; Lallahem, S. River flow model using artificial neural networks. Energy Proced. 2015, 74, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Chau, K.W. Rainfall–runoff modeling using artificial neural network coupled with singular spectrum analysis. J. Hydrol. 2011, 399, 394–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, C.; Fu, W. Streamflow forecasting using empirical wavelet transform and artificial neural networks. Water 2017, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Min, J.; Chen, Y.; Xiang-Yu, H.; Zeng, M.; Li, X. Improving precipitation forecast with hybrid 3DVar and time-lagged ensembles in a heavy rainfall event. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.M.; Chang, F.J. Integrating hydrometeorological information for rainfall–runoff modelling by artificial neural networks. Hydrol Process. 2009, 23, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Simonovic, S.P. An artificial neural network model for generating hydrograph from hydro-meteorological parameters. J. Hydrol. 2005, 315, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.J.; Tsai, M.J. A nonlinear spatio-temporal lumping of radar rainfall for modeling multi-step-ahead inflow forecasts by data-driven techniques. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayfur, G.; Singh, V.P.; Moramarco, T.; Barbetta, S. Flood Hydrograph Prediction Using Machine Learning Methods. Water 2018, 10, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Peng, T.; Zhang, C.; Sun, N. Data Pre-Analysis and Ensemble of Various Artificial Neural Networks for Monthly Streamflow Forecasting. Water 2018, 10, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.-C.; Amin, M.Z.M.; Yang, S.-N.; Chang, F.-J. Building ANN-Based Regional Multi-Step-Ahead Flood Inundation Forecast Models. Water 2018, 10, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Shen, H.Y.; Chang, F.J. Regional flood inundation nowcast using hybrid SOM and dynamic neural networks. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien Bui, D.; Khosravi, K.; Li, S.; Shahabi, H.; Panahi, M.; Singh, V.P.; Chapi, K.; Shirzadi, A.; Panahi, S.; Chen, W.; et al. New Hybrids of ANFIS with Several Optimization Algorithms for Flood Susceptibility Modeling. Water 2018, 10, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.R.; Dandy, G.C. Neural networks for the prediction and forecasting of water resources variables: A review of modelling issues and applications. Environ. Model. Softw. 2000, 15, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.R.; Jain, A.; Dandy, G.C.; Sudheer, K.P. Methods used for the development of neural networks for the prediction of water resource variables in river systems: Current status and future directions. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 891–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Borah, B. Indian summer monsoon rainfall prediction using artificial neural network. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess 2013, 27, 1585–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.R.; Kapelan, Z.; Kasprzyk, J.; Kollat, J.; Matott, L.S.; Cunha, M.C.; Dandy, G.C.; Gibbs, M.S.; Keedwell, E.; Marchi, A.; et al. Evolutionary algorithms and other metaheuristics in water resources: Current status, research challenges and future directions. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 62, 271–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Bae, D.H.; Cho, C.H. Changes in future precipitation over South Korea using a global high-resolution climate model. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 49, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, J.; Lee, O.; Yoon, J.; Kim, S. Estimation of Probable Maximum Precipitation in Korea using a Regional Climate Model. Water 2017, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.W.; Won, Y.S.; Chung, I.M. The scale of typhoon RUSA. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 3, 3147–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.H.; Lee, D.I.; Jang, S.M.; Jang, M.; Uyeda, U.; Shinoda, Y.; Kobayashi, F. Characteristics of rainfall systems accompanied with Changma front at Chujado in Korea. ASIA-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 46, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Ra, I.; Rhee, K.H.; Kim, C.S. Estimation of real-time flood risk on roads based on rainfall calculated by the revised method of missing rainfall. Sustainability 2014, 6, 6418–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, J.-B.; Kim, S. Sensitivity Study on High-Resolution WRF Precipitation Forecast for a Heavy Rainfall Event. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, I.; Onen, A.; Yilmaz, K.; Gochis, D. Calibration and evaluation of a flood forecasting system: Utility of numerical weather prediction model, data assimilation and satellite-based rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K.; Eom, D.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, J.B. High-resolution summer rainfall prediction in the JHWC real-time WRF system. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 46, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Han, D.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; O’Neill, P.; Islam, T.; Gupta, M.; Dai, Q. Performance evaluation of WRF-Noah Land surface model estimated soil moisture for hydrological application: Synergistic evaluation using SMOS retrieved soil moisture. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.M.; Duda, G.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 3; Tech. Note, NCAR/TN-475+STR; National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, D.H.; Lee, B.J. Development of Continuous Rainfall Runoff Model for Flood Forecasting on the Large Scale Basin. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2011, 44, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T. The Flood Runoff Analysis Method by the Storage Function Model; The Public Works Research Institute Ministry of Construction: Tsukuba, Japan, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through. Part, I. A conceptual model discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the mean squared error and nse performance criteria: Implications for improving hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.C.; Quintero, F.; Krajewski, F.W. High-Resolution QPF Uncertainty and Its Implications for Flood Prediction: A Case Study for the Eastern Iowa Flood of 2016. J. Hydrometeor. 2016, 19, 1289–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.; Boyle, D.P.; Bäse, F. Comparison of different efficiency criteria for hydrological model assessment. Adv. Geosci. 2005, 5, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, H.L.; Pappenberger, F. Ensemble flood forecasting: A review. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadgar, S.; Moradkhani, H.; Garen, D. Towards improved post-processing of hydrologic forecast ensembles. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 28, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobold, M.; Suselj, K. Precipitation forecasts and their uncertainty as input into hydrological models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.; McBride, J. Verification of precipitation in weather systems: Determination of systematic errors. J. Hydrol. 2000, 239, 179–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Steinle, P.; Seed, A.; Xiao, Y. The Sensitivity of Heavy Precipitation to Horizontal Resolution, Domain Size, and Rain Rate Assimilation: Case Studies with a Convection-Permitting Model. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 7943845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankov, I.; Gallus, W.A.; Segal, M.; Koch, S.E. Influence of Initial Conditions on the WRF–ARW Model QPF Response to Physical Parameterization Changes. Weather Forecast. 2007, 22, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Metric | Calibration Period 23 July–4 September 2007 | Calibration Period 1 July–22 August 2008 | Verification Period 21 June–4 August 2009 | ||||||
| Gunnam | Jeonkuk | Jeogseong | Gunnam | Jeonkuk | Jeogseong | Gunnam | Jeonkuk | Jeogseong | |
| NSE | 0.69 | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.83 | 0.79 | 0.57 | 0.85 | 0.79 |
| REV | −0.48 | −0.12 | −0.52 | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.16 | −0.22 | 0.03 |
| KGE | 0.53 | 0.62 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 0.75 | 0.68 | 0.80 |
| Metric | Verification Period 9 July–20 August 2010 | Verification Period 16 June–2 August 2011 | Verification Period 31 July–13 September 2012 | ||||||
| Gunnam | Jeonkuk | Jeogseong | Gunnam | Jeonkuk | Jeogseong | Gunnam | Jeonkuk | Jeogseong | |
| NSE | 0.62 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.71 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.59 | 0.78 | 0.66 |
| REV | 0.23 | −0.34 | −0.07 | −0.09 | −0.19 | −0.11 | −0.28 | −0.20 | −0.05 |
| KGE | 0.42 | 0.61 | 0.65 | 0.87 | 0.76 | 0.88 | 0.47 | 0.79 | 0.71 |
| Index | Formula |
|---|---|
| Relative Bias (RB) | |
| Mean Relative Error (MRE) | |
| Mean Absolute Error (MAER) |
| Event | Forecast data | MRE | RB | REV | MAER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | WRF | 38.45 | 67.73 | 38.78 | 114.47 |
| Bias-adjusted WRF | 11.64 | 42.91 | 7.74 | 31.17 | |
| Improvement (%) | 69.71 | 57.84 | 80.05 | 72.77 | |
| 2007 | WRF | 42.40 | 35.42 | 23.20 | 105.84 |
| Bias-adjusted WRF | 10.55 | 4.03 | 4.13 | 20.67 | |
| Improvement (%) | 75.12 | 88.62 | 82.22 | 80.47 | |
| 2011 | WRF | 65.61 | 85.81 | 61.54 | 59.83 |
| Bias-adjusted WRF | 27.24 | 13.75 | 14.82 | 21.55 | |
| Improvement (%) | 58.09 | 83.98 | 75.92 | 63.98 |
| Event | Data | ∑ (mm) | Min (mm) | Max (mm) | Underestimation (%) | Error Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | Observation | 11100.52 | 196.19 | 351.40 | - | - |
| WRF | 6795.70 | 132.64 | 246.12 | 97.37 | - | |
| WRF-revised | 11959.45 | 288.62 | 362.03 | 31.58 | 75.28 | |
| 2007 | Observation | 1904.96 | 299.06 | 641.59 | - | - |
| WRF | 14622.80 | 158.51 | 450.84 | 78.95 | - | |
| WRF-revised | 18255.56 | 356.49 | 596.11 | 55.26 | 89.53 | |
| 2011 | Observation | 17445.92 | 293.18 | 743.25 | - | - |
| WRF | 6709.83 | 52.56 | 218.64 | 100 | - | |
| WRF-revised | 18021.18 | 306.21 | 593.00 | 34.21 | 88.74 |
| Index | Station | SURR | SURR-WRF | SURR-Revised WRF | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event 2002 | |||||
| NSE | Gunnam | 0.26 | −18.27 | −7.24 | 60.21 |
| MRE | −0.09 | −0.95 | −0.24 | 74.74 | |
| REV | 0.16 | 0.70 | 0.43 | 38.57 | |
| KGE | 0.41 | −1.20 | −0.52 | 56.67 | |
| NSE | Jeogseong | 0.68 | −19.85 | −8.68 | 56.27 |
| MRE | −0.25 | 0.80 | 0.26 | 67.50 | |
| REV | 0.03 | 0.53 | 0.27 | 49.06 | |
| KGE | 0.60 | −1.14 | −0.68 | 40.35 | |
| Event 2007 | |||||
| NSE | Gunnam | 0.69 | −4.57 | −2.01 | 56.02 |
| MRE | −0.58 | −0.60 | −0.56 | 6.67 | |
| REV | −0.48 | −0.57 | −0.52 | 8.77 | |
| KGE | 0.53 | −5.03 | −3.98 | 20.87 | |
| NSE | Jeonkuk | 0.78 | −6.63 | −0.82 | 87.63 |
| MRE | −0.60 | −0.77 | −0.37 | 51.95 | |
| REV | −0.12 | −0.22 | −0.18 | 18.18 | |
| KGE | 0.62 | −2.77 | −1.65 | 40.43 | |
| NSE | Jeogseong | 0.71 | −10.30 | −5.71 | 44.56 |
| MRE | −0.69 | −0.78 | −0.65 | 16.67 | |
| REV | −0.52 | −0.54 | −0.59 | 9.26 | |
| KGE | 0.51 | −3.30 | −2.24 | 32.12 | |
| Event 2011 | |||||
| NSE | Gunnam | 0.80 | −0.47 | 0.07 | 85.11 |
| MRE | −0.49 | −0.79 | −0.51 | 35.44 | |
| REV | −0.08 | −0.59 | −0.37 | 37.29 | |
| KGE | 0.81 | −0.26 | −0.09 | 65.38 | |
| NSE | Jeonkuk | 0.81 | −0.87 | −0.06 | 93.10 |
| MRE | −0.63 | −0.67 | −0.58 | 13.43 | |
| REV | −0.34 | −0.73 | −0.42 | 42.47 | |
| KGE | 0.60 | −0.79 | −0.21 | 73.42 | |
| NSE | Jeogseong | 0.90 | −1.06 | −0.23 | 78.30 |
| MRE | −0.06 | −0.56 | −0.07 | 87.50 | |
| REV | −0.45 | −0.60 | −0.32 | 46.67 | |
| KGE | 0.81 | −1.22 | −0.46 | 62.29 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jabbari, A.; Bae, D.-H. Application of Artificial Neural Networks for Accuracy Enhancements of Real-Time Flood Forecasting in the Imjin Basin. Water 2018, 10, 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111626
Jabbari A, Bae D-H. Application of Artificial Neural Networks for Accuracy Enhancements of Real-Time Flood Forecasting in the Imjin Basin. Water. 2018; 10(11):1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111626
Chicago/Turabian StyleJabbari, Aida, and Deg-Hyo Bae. 2018. "Application of Artificial Neural Networks for Accuracy Enhancements of Real-Time Flood Forecasting in the Imjin Basin" Water 10, no. 11: 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111626
APA StyleJabbari, A., & Bae, D.-H. (2018). Application of Artificial Neural Networks for Accuracy Enhancements of Real-Time Flood Forecasting in the Imjin Basin. Water, 10(11), 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111626




