Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Reveals Dysregulation of Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation in Eating Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gene Expression Data
2.2. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis
2.3. Gene Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.4. Hub Gene Analysis
3. Results
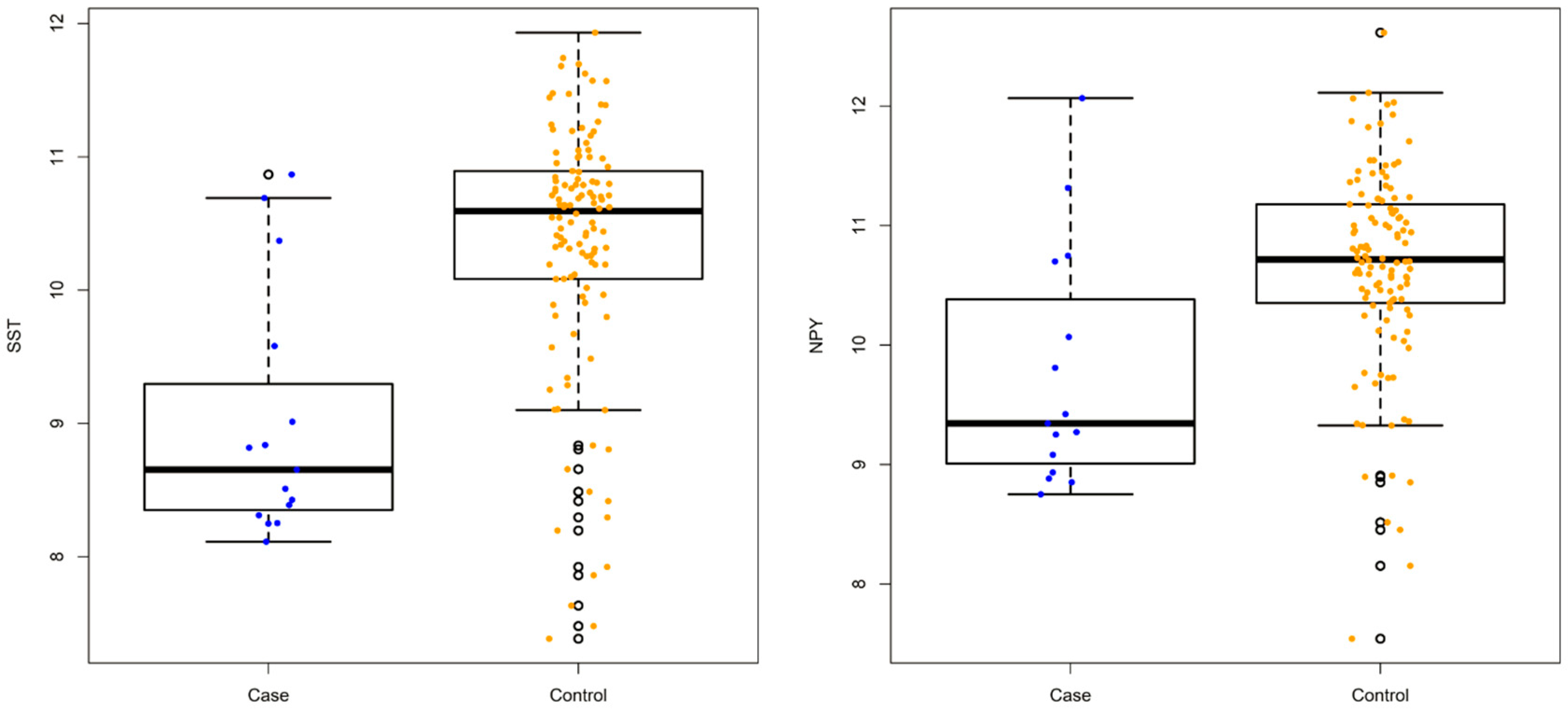
3.1. Differentially Expressed Genes
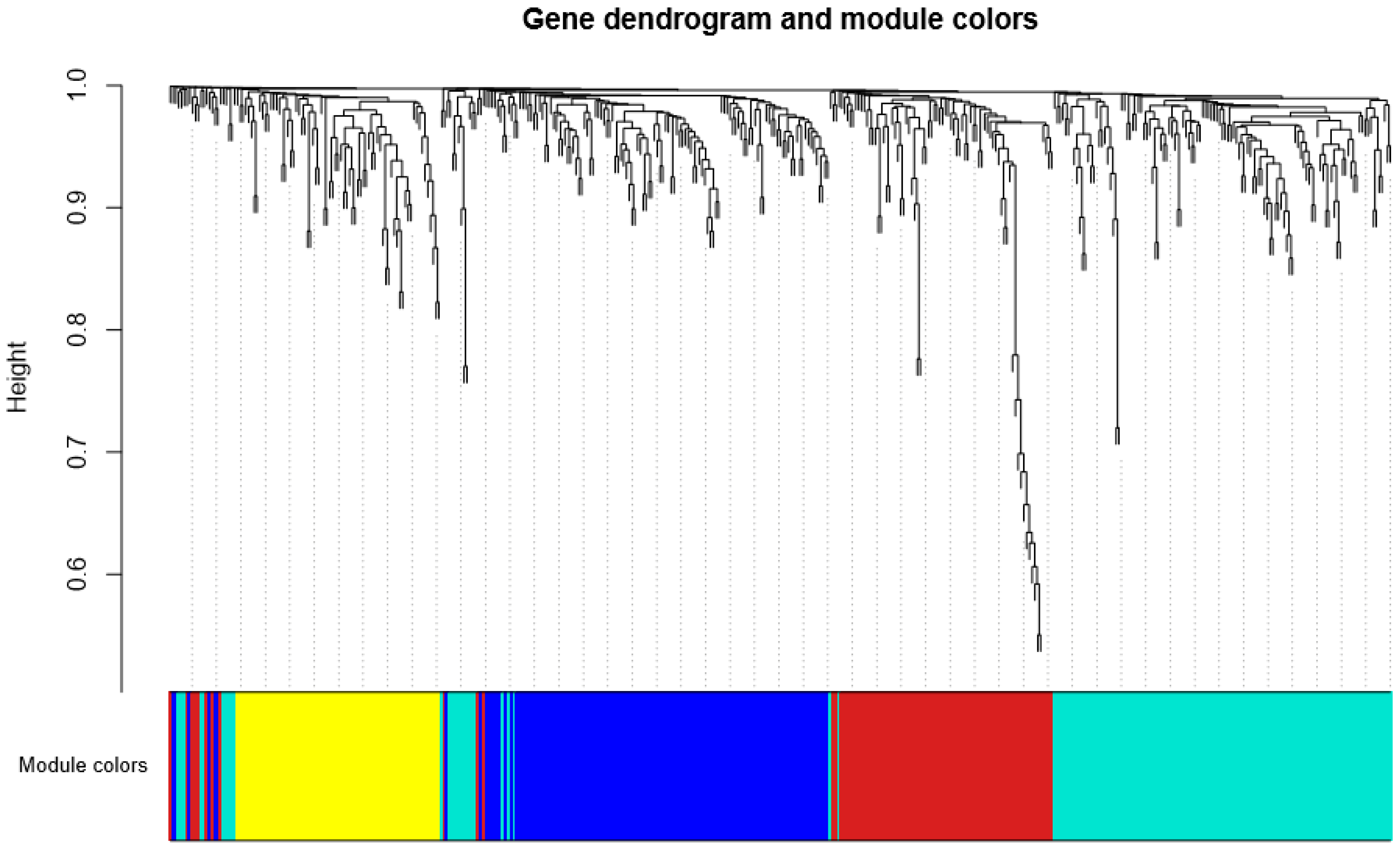
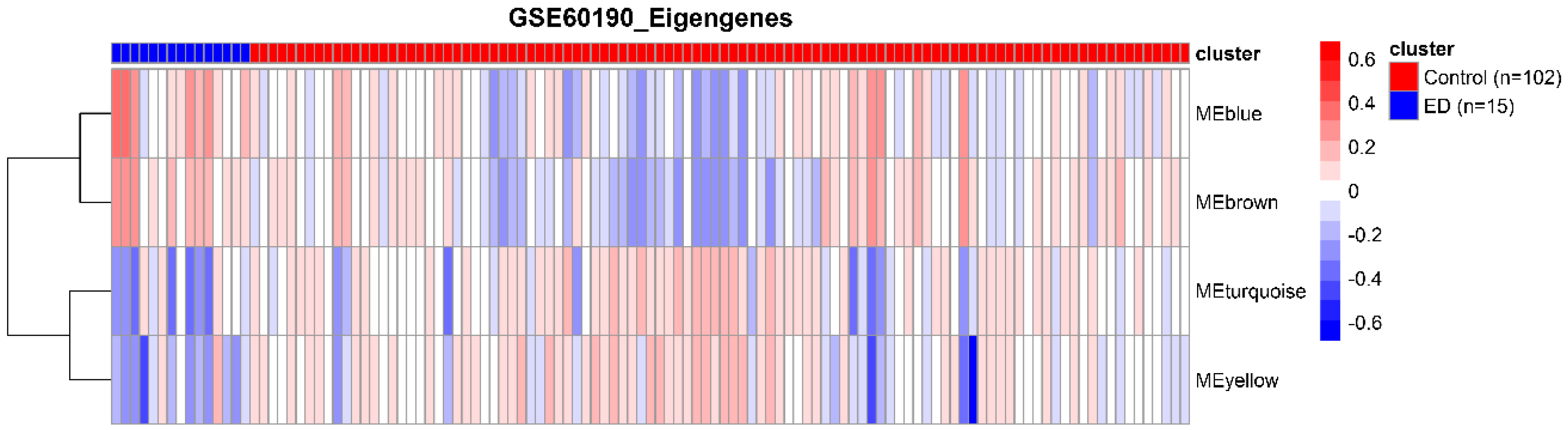
3.2. Detection of Functional Modules in Gene Co-Expression Networks
3.3. Identification of Hub Genes
3.4. Protein-Protein Interaction Network Analysis of Detected Modules
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ben-Dor, D.H.; Laufer, N.; Apter, A.; Frisch, A.; Weizman, A. Heritability, genetics and association findings in anorexia nervosa. Isr. J. Psychiatry Relat. Sci. 2002, 39, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Krom, M.; Bauer, F.; Collier, D.; Adan, R.A.; la Fleur, S.E. Genetic variation and effects on human eating behavior. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2009, 29, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulik, C.M.; Sullivan, P.F.; Wade, T.D.; Kendler, K.S. Twin studies of eating disorders: A review. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2000, 27, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M.; Prasuna, J.G. Twin studies: A unique epidemiological tool. Indian J. Community Med. 2016, 41, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capusan, A.J.; Yao, S.; Kuja-Halkola, R.; Bulik, C.M.; Thornton, L.M.; Bendtsen, P.; Marteinsdottir, I.; Thorsell, A.; Larsson, H. Genetic and environmental aspects in the association between attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder symptoms and binge-eating behavior in adults: A twin study. Psychol. Med. 2017, 47, 2866–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairweather-Schmidt, A.K.; Wade, T.D. Changes in genetic and environmental influences on disordered eating between early and late adolescence: A longitudinal twin study. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 3249–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munn-Chernoff, M.A.; Keel, P.K.; Klump, K.L.; Grant, J.D.; Bucholz, K.K.; Madden, P.A.; Heath, A.C.; Duncan, A.E. Prevalence of and familial influences on purging disorder in a community sample of female twins. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 48, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boraska, V.; Franklin, C.S.; Floyd, J.A.; Thornton, L.M.; Huckins, L.M.; Southam, L.; Rayner, N.W.; Tachmazidou, I.; Klump, K.L.; Treasure, J.; et al. A genome-wide association study of anorexia nervosa. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Bloss, C.S.; Duvvuri, V.; Kaye, W.; Schork, N.J.; Berrettini, W.; Hakonarson, H. Price Foundation Collaborative Group. A genome-wide association study on common SNPs and rare CNVs in anorexia nervosa. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akula, N.; Wendland, J.R.; Choi, K.H.; McMahon, F.J. An integrative genomic study implicates the postsynaptic density in the pathogenesis of bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, S.; Boks, M.P.; Fuller, T.F.; Strengman, E.; Janson, E.; de Kovel, C.G.; Ori, A.P.; Vi, N.; Mulder, F.; Blom, J.D.; et al. A gene co-expression network in whole blood of schizophrenia patients is independent of antipsychotic-use and enriched for brain-expressed genes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Ellis, S.E.; Ashar, F.N.; Moes, A.; Bader, J.S.; Zhan, J.; West, A.B.; Arking, D.E. Transcriptome analysis reveals dysregulation of innate immune response genes and neuronal activity-dependent genes in autism. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.; Kim, J.; Shin, J.Y.; Kim, J.I.; Seo, J.S.; Webster, M.J.; Lee, D.; Kim, S. Gene expression profiling by mRNA sequencing reveals increased expression of immune/inflammation-related genes in the hippocampus of individuals with schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2013, 3, e321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, A.E.; Deep-Soboslay, A.; Tao, R.; Hauptman, D.T.; Kaye, W.H.; Arango, V.; Weinberger, D.R.; Hyde, T.M.; Kleinman, J.E. Genetic neuropathology of obsessive psychiatric syndromes. Transl. Psychiatry 2014, 4, e432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Kibbe, W.A.; Lin, S.M. Lumi: A pipeline for processing Illumina microarray. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1547–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Horvath, S. A general framework for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2005, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Xu, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, K. Dynamic modular architecture of protein-protein interaction networks beyond the dichotomy of ‘date’ and ‘party’ hubs. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravasz, E.; Somera, A.L.; Mongru, D.A.; Oltvai, Z.N.; Barabasi, A.L. Hierarchical organization of modularity in metabolic networks. Science 2002, 297, 1551–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaimo, S.; Marceca, G.P.; Ferro, A.; Pulvirenti, A. detecting disease specific pathway substructures through an integrated systems biology approach. Noncod. RNA 2017, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaimo, S.; Giugno, R.; Acunzo, M.; Veneziano, D.; Ferro, A.; Pulvirenti, A. Post-transcriptional knowledge in pathway analysis increases the accuracy of phenotypes classification. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 54572–54582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şenbabaoğlu, Y.; Sümer, S.O.; Sánchez-Vega, F.; Bemis, D.; Ciriello, G.; Schultz, N.; Sander, C. A multi-method approach for proteomic network inference in 11 human cancers. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.H.; Elashoff, M.; Higgs, B.W.; Song, J.; Kim, S.; Sabunciyan, S.; Diglisic, S.; Yolken, R.H.; Knable, M.B.; Torrey, E.F.; et al. Putative psychosis genes in the prefrontal cortex: Combined analysis of gene expression microarrays. BMC Psychiatry 2008, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, A.; Grayson, D.R.; Caruncho, H.J. Epigenetic RELN dysfunction in schizophrenia and related neuropsychiatric disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoftman, G.D.; Volk, D.W.; Bazmi, H.H.; Li, S.; Sampson, A.R.; Lewis, D.A. Altered cortical expression of GABA-related genes in schizophrenia: Illness progression vs. developmental disturbance. Schizophr. Bull. 2015, 41, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, S.; Mirnics, K. Immune system disturbances in schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadarajulu, J.; Schmitt, A.; Falkai, P.; Alsaif, M.; Turck, C.W.; Martins-de-Souza, D. Differential expression of HINT1 in schizophrenia brain tissue. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 262, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafavi, S.; Ray, D.; Wardefarley, D.; Grouios, C.; Morris, Q. GeneMANIA: A real-time multiple association network integration algorithm for predicting gene function. Genome Biol. 2008, 9 (Suppl. 1), 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasan, R.O.; Verma, D.; Wood, J.; Lach, G.; Hörmer, B.; de Lima, T.C.; Herzog, H.; Sperk, G. The role of Neuropeptide Y in fear conditioning and extinction. Neuropeptides 2016, 55, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, B. Neuropeptide Y in normal eating and in genetic and dietary-induced obesity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1159–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbett, K.; Ebert, P.J.; Mitchell, A.; Lintas, C.; Manzi, B.; Mirnics, K.; Persico, A.M. Immune transcriptome alterations in the temporal cortex of subjects with autism. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 30, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victor, V.M.; Rovira-Llopis, S.; Saiz-Alarcon, V.; Sanguesa, M.C.; Rojo-Bofill, L.; Banuls, C.; Falcon, R.; Castello, R.; Rojo, L.; Rocha, M.; et al. Altered mitochondrial function and oxidative stress in leukocytes of anorexia nervosa patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindfors, C.; Nilsson, I.A.; Garcia-Roves, P.M.; Zuberi, A.R.; Karimi, M.; Donahue, L.R.; Roopenian, D.C.; Mulder, J.; Uhlen, M.; Ekstrom, T.J.; et al. Hypothalamic mitochondrial dysfunction associated with anorexia in the anx/anx mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18108–18113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulik, C.M.; Thornton, L.M.; Root, T.L.; Pisetsky, E.M.; Lichtenstein, P.; Pedersen, N.L. Understanding the relation between anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa in a Swedish national twin sample. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trace, S.E.; Baker, J.H.; Peñas-Lledó, E.; Bulik, C.M. The genetics of eating disorders. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2013, 9, 589–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blinder, B.J.; Cumella, E.J.; Sanathara, V.A. Psychiatric comorbidities of female inpatients with eating disorders. Psychosom. Med. 2006, 68, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, G.Y.; Tam, W.W.; Lu, Y.; Ho, C.S.; Zhang, M.W.; Ho, R.C. Prevalence of depression in the community from 30 countries between 1994 and 2014. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smink, F.R.; van Hoeken, D.; Hoek, H.W. Epidemiology of eating disorders: Incidence, prevalence and mortality rates. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2012, 14, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, M.; Walker, J.; Holm Hansen, C.; Martin, P.; Symeonides, S.; Gourley, C.; Wall, L.; Weller, D.; Murray, G. SMaRT (Symptom Management Research Trials) Oncology-2 Team. Integrated collaborative care for comorbid major depression in patients with cancer (SMaRT Oncology-2): A multicentre randomised controlled effectiveness trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.J.; Freedland, K.E.; Clouse, R.E.; Lustman, P.J. The prevalence of comorbid depression in adults with diabetes: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Turki, T.; Tan, H.; Wei, Z.; Chang, X. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Reveals Dysregulation of Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation in Eating Disorders. Genes 2018, 9, 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9070325
Yang L, Li Y, Turki T, Tan H, Wei Z, Chang X. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Reveals Dysregulation of Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation in Eating Disorders. Genes. 2018; 9(7):325. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9070325
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Liulin, Yun Li, Turki Turki, Huizi Tan, Zhi Wei, and Xiao Chang. 2018. "Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Reveals Dysregulation of Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation in Eating Disorders" Genes 9, no. 7: 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9070325
APA StyleYang, L., Li, Y., Turki, T., Tan, H., Wei, Z., & Chang, X. (2018). Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Reveals Dysregulation of Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation in Eating Disorders. Genes, 9(7), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9070325




